|
Advanced Technology Vehicle
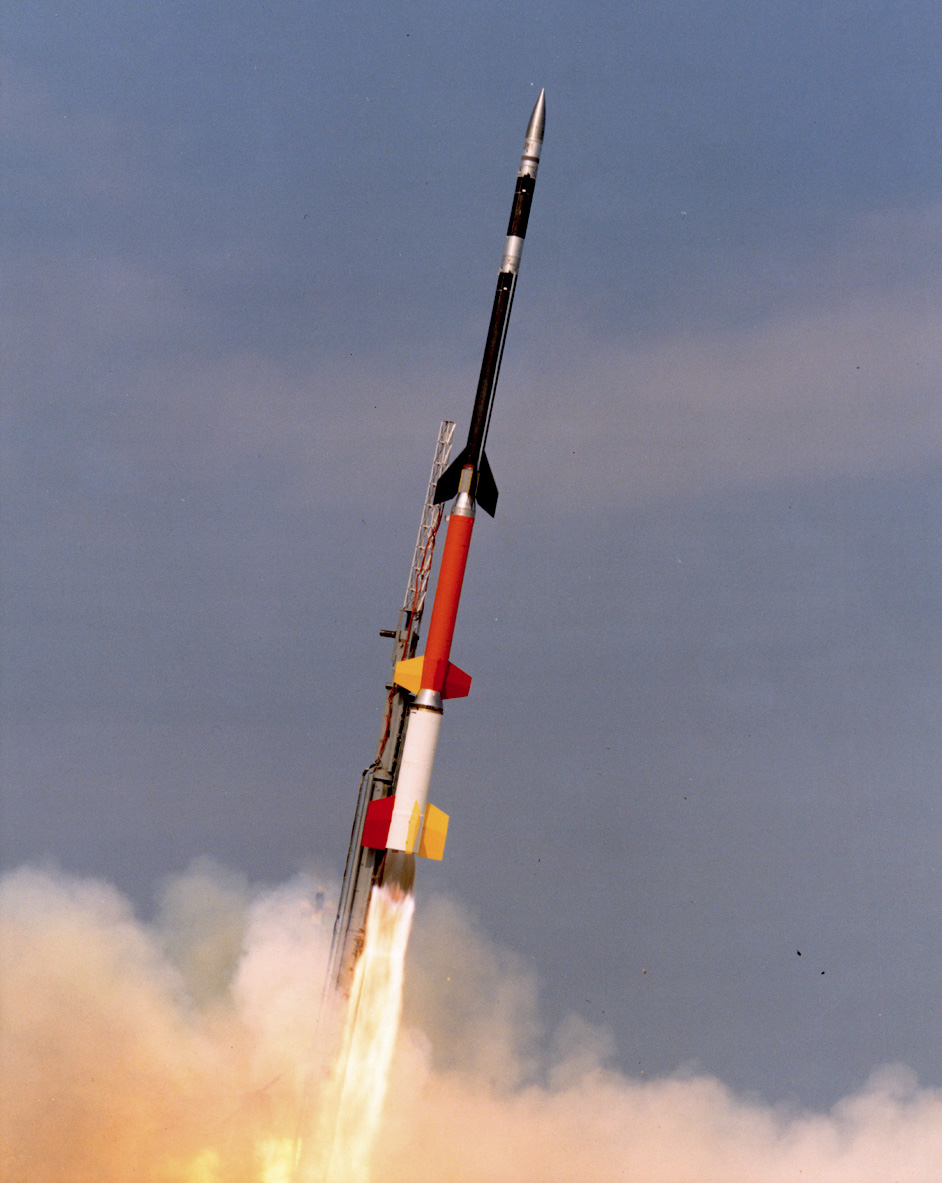
The Advanced Technology Vehicle is a modified Indian sounding rocket developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It is based on the Rohini-560 rocket. The ATV program was created to test the development of a native dual-mode air-breathing scramjet A scramjet (supersonic combustion ramjet) is a variant of a ramjet airbreathing jet engine in which combustion takes place in supersonic airflow. As in ramjets, a scramjet relies on high vehicle speed to compress the incoming air forcefully ... engine. , ISRO has flown two test missions. ATV-01 On 3 March 2010 at 03:00 UTC, ISRO conducted the first test flight of the Advanced Technology vehicle, designated ATV-D01. It weighed at lift-off, and measured long with a diameter of . It carried a passive scramjet engine combustor module as a demonstration of the air-breathing propulsion technology. The ATV successfully reached Mach 6 for seven seconds and maintained a dynamic pressure of . ATV-02 On 28 Augus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scramjet Programs
Scramjet programs refers to research and testing programs for the development of supersonic combustion ramjets, known as scramjets. This list provides a short overview of national and international collaborations, and civilian and military programs. The USA, Russia, India, and China (2014), have succeeded at developing scramjet technologies. USA X-15 When the second X-15 aircraft (piloted by John B. McKay) crashed on flight 74, it was damaged but survived well enough to be rebuilt. North American Aviation rebuilt it as the X-15-A2. Among other things, one of the changes was provisions for a dummy scramjet to test if wind tunnel testing was correct. Unfortunately, on the final flight of the X-15-A2 ( flight 188), the shock waves sent out by the scramjet at Mach 6.7 caused extremely intense heating of over . This then drilled into the ventral fin and melted large holes. The plane survived but never flew again. Test data were limited due to the limited flights of the scramjet befor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISRO
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO; ) is the national space agency of India, headquartered in Bengaluru. It operates under the Department of Space (DOS) which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India, while the Chairman of ISRO acts as the executive of DOS as well. ISRO is India's primary agency for performing tasks related to space-based applications, space exploration and the development of related technologies. It is one of six government space agencies in the world which possess full launch capabilities, deploy cryogenic engines, launch extraterrestrial missions and operate large fleets of artificial satellites. The Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) was established by Jawaharlal Nehru under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) in 1962, on the urging of scientist Vikram Sarabhai, recognising the need in space research. INCOSPAR grew and became ISRO in 1969, within DAE. In 1972, the government of India set up a Space Commissi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
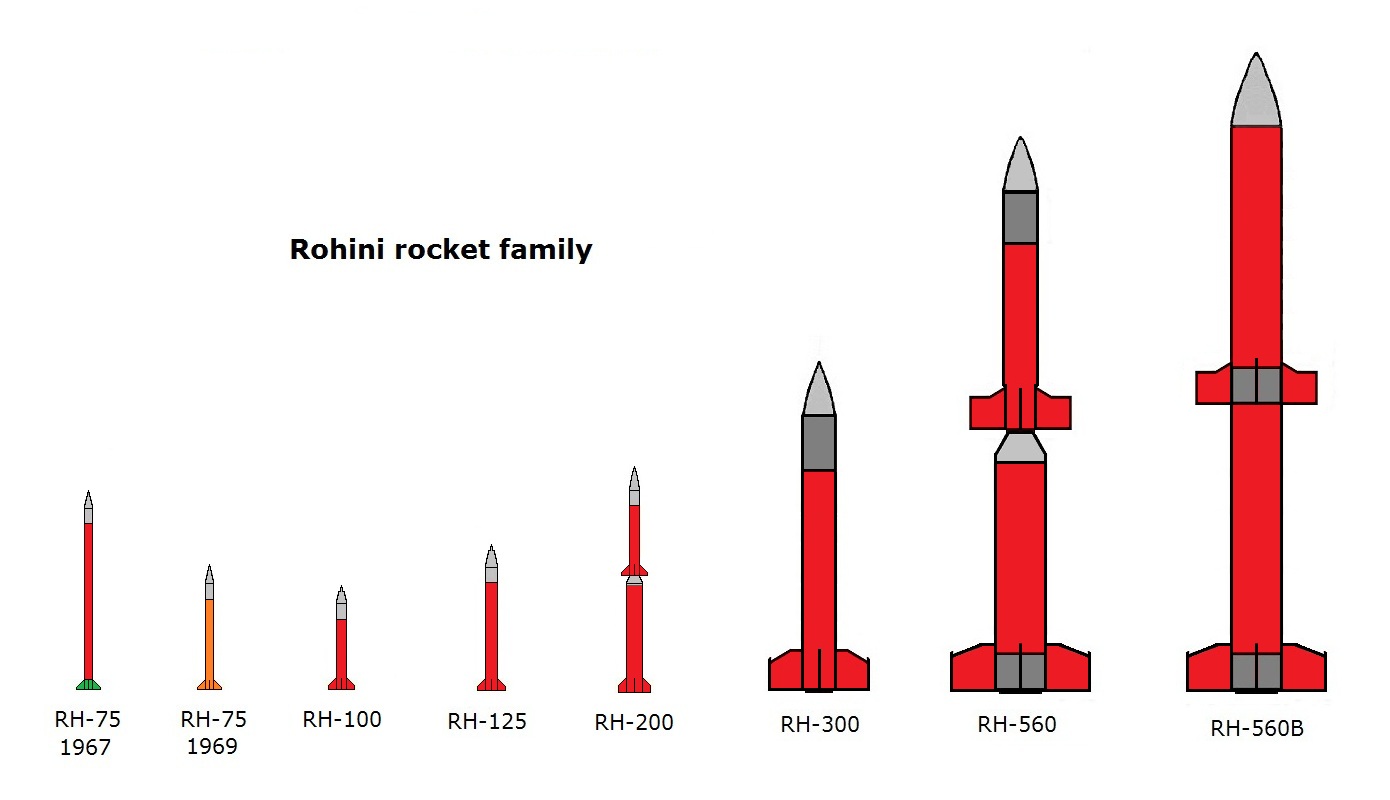
Rohini (rocket Family)
Rohini is a series of sounding rockets developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) for meteorological and atmospheric study. These sounding rockets are capable of carrying payloads of between altitudes of . The ISRO currently uses RH-200, RH-300, RH-300 Mk-II, RH-560 Mk-II and RH-560 Mk-III rockets, which are launched from the Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching (TERLS) in Thumba and the Satish Dhawan Space Center in Sriharikota. Various programs such as Equatorial ElectroJet (EEJ), Leonid Meteor Shower (LMS), Indian Middle Atmosphere Programme (IMAP), Monsoon Experiment (MONEX), Middle Atmosphere Dynamics (MIDAS), and Sooryagrahan-2010 have been conducted using the Rohini sounding rocket series. It has been the forerunners for ISRO's heavier and more complex launch vehicles, with continued usage even today for atmospheric and meteorological Nomenclature The rockets in the series are designated with the letters RH (for "Rohini"), followed by a number corresponding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satish Dhawan Space Centre
Satish Dhawan Space Centre - SDSC (formerly Sriharikota Range - SHAR) is a rocket launch centre ( spaceport) operated by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It is located in Sriharikota, Tirupati district of Andhra Pradesh. Sriharikota Range was renamed in 2002 after ISRO's former chairman Satish Dhawan. History Sriharikota island was chosen in 1969 for a satellite launching station. The centre became operational in 1971 when an RH-125 sounding rocket was launched. The first attempted launch of an orbital satellite, Rohini 1A aboard a Satellite Launch Vehicle, took place on 10 August 1979, but due to a failure in thrust vectoring of the rocket's second stage, the satellite's orbit decayed on 19 August 1979. SHAR was named as 'Satish Dhawan Space Centre SHAR' (SDSC), on 5 September 2002, in memory of Satish Dhawan, former chairman of the ISRO. The SHAR facility now consists of two launch pads, with the second built in 2005. The second launch pad was used for launche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sounding Rocket
A sounding rocket or rocketsonde, sometimes called a research rocket or a suborbital rocket, is an instrument-carrying rocket designed to take measurements and perform scientific experiments during its sub-orbital flight. The rockets are used to launch instruments from 48 to 145 km (30 to 90 miles) above the surface of the Earth, the altitude generally between weather balloons and satellites; the maximum altitude for balloons is about 40 km (25 miles) and the minimum for satellites is approximately 121 km (75 miles). Certain sounding rockets have an apogee between 1,000 and 1,500 km (620 and 930 miles), such as the Black Brant X and XII, which is the maximum apogee of their class. Sounding rockets often use military surplus rocket motors. NASA routinely flies the Terrier Mk 70 boosted Improved Orion, lifting 270–450-kg (600–1,000-pound) payloads into the exoatmospheric region between 97 and 201 km (60 and 125 miles). Etymology The origin of the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Space Research Organisation
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO; ) is the national space agency of India, headquartered in Bengaluru. It operates under the Department of Space (DOS) which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India, while the Chairman of ISRO acts as the executive of DOS as well. ISRO is India's primary agency for performing tasks related to space-based applications, space exploration and the development of related technologies. It is one of six government space agencies in the world which possess full launch capabilities, deploy cryogenic engines, launch extraterrestrial missions and operate large fleets of artificial satellites. The Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) was established by Jawaharlal Nehru under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) in 1962, on the urging of scientist Vikram Sarabhai, recognising the need in space research. INCOSPAR grew and became ISRO in 1969, within DAE. In 1972, the government of India set up a Space Commissi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scramjet
A scramjet (supersonic combustion ramjet) is a variant of a ramjet airbreathing jet engine in which combustion takes place in supersonic airflow. As in ramjets, a scramjet relies on high vehicle speed to compress the incoming air forcefully before combustion (hence ''ram''jet), but whereas a ramjet decelerates the air to subsonic velocities before combustion using shock cones, a scramjet has no shock cone and slows the airflow using shockwaves produced by its ignition source in place of a shock cone. This allows the scramjet to operate efficiently at extremely high speeds. History Before 2000 The Bell X-1 attained supersonic flight in 1947 and, by the early 1960s, rapid progress toward faster aircraft suggested that operational aircraft would be flying at "hypersonic" speeds within a few years. Except for specialized rocket research vehicles like the North American X-15 and other rocket-powered spacecraft, aircraft top speeds have remained level, generally in the range of M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RLV Technology Demonstration Programme
Reusable Launch Vehicle–Technology Demonstration Programme is a series of technology demonstration missions that has been conceived by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) as a first step towards realising a Two Stage To Orbit (TSTO) re-usable launch vehicle. For this purpose, a winged reusable launch vehicle technology demonstrator (RLV-TD) has been configured. The RLV-TD acted as a flying test bed to evaluate various technologies like powered cruise flight, hypersonic flight, and autonomous landing using air-breathing propulsion. Application of these technologies would bring down the launch cost by a factor of 10. This project has no connection with the Avatar spaceplane concept by India's Defence Research and Development Organisation. Development In 2006 the Indian Space Research Organisation performed a series of ground tests to demonstrate stable supersonic combustion for nearly 7 seconds with an inlet Mach number of 6. In March 2010, ISRO conducted the flight t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sounding Rockets Of India
Sounding or soundings may refer to: *Sounding (archaeology), a test dig in archaeology * "Sounding" (''Justified''), an episode of the TV series ''Justified'' * ''Soundings'' (journal), an academic journal of leftist political thinking * ''Soundings'' (radio drama), science fiction radio drama series produced from 1985 to 1989 in Ottawa * ''Soundings'' (Williams), 2003 orchestral composition by John Williams * ''Soundings'' (Carter), 2005 orchestral composition by Elliott Carter *Sound (medical instrument), instruments for probing and dilating passages within the body **Urethral sounding, using sounds to increase the inner diameter of the urethra * Depth sounding, a measurement of depth within a body of water *Whale sounding, the act of diving by whales See also *Sound (other) *Sonde (other) * * *Sonar, use of sound propagation to navigate, communicate with or detect objects on or under water *Remote sensing, acquisition of information about an object or phenome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2010s In India
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2010 In Spaceflight
The year 2010 saw a number of notable events in worldwide spaceflight activities. These included the first test flight of the SpaceX Dragon commercial resupply spacecraft, which is intended to resupply the International Space Station (ISS), and the maiden flights of the Falcon 9 and Minotaur IV rockets. In June 2010, South Korea conducted a second Naro-1 launch, after the failure of the rocket's maiden flight in 2009; however, the second attempt also failed. The Kosmos-3M was retired from service, making its final flight in April. The Molniya-M was also retired from service, making its final flight in September. Overview The first suborbital launch of 2010 was conducted at 23:00 GMT on 10 January, when a Black Brant IX sounding rocket was launched as a target for the Boeing YAL-1 airborne-laser platform. On 11 January, China conducted an ABM test, involving two missiles. The first orbital launch occurred at 16:12 UTC on 16 January, when a Long March 3C launched the Compass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |