أ“engus I on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
أ“engus son of Fergus ( xpi, *Onuist map Vurguist; sga, أ“engus mac Fergusso, "Angus son of Fergus"), was
 The
The
 An early medieval Irish genealogy tract claims أ“engus to be a descendant of Cairpre Cruithnechأ،in or " Cairbre the little Pict", of the
An early medieval Irish genealogy tract claims أ“engus to be a descendant of Cairpre Cruithnechأ،in or " Cairbre the little Pict", of the
 In the 730s, أ“engus fought against Dأ،l Riata whose traditional overlords and protectors in Ireland, the
In the 730s, أ“engus fought against Dأ،l Riata whose traditional overlords and protectors in Ireland, the
king of the Picts
The list of kings of the Picts is based on the Pictish Chronicle king lists. These are late documents and do not record the dates when the kings reigned. The various surviving lists disagree in places as to the names of kings, and the lengths o ...
, of possible Gaelic origin, from 732 until his death in 761. His reign can be reconstructed in some detail from a variety of sources. The unprecedented territorial gains he made from coast to coast, and the legacy he left, mean أ“engus can be considered the first king of what would become Scotland.
Wresting power from his rivals, أ“engus became the chief king in Pictland
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from ear ...
following a period of civil war in the late 720s.
The most powerful ruler in Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
over more than two decades, kings from أ“engus's family dominated Pictland for a century, until defeat at the hands of Vikings
Vikings ; non, vأkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
in 839 began a new period of instability, ending with the coming to power of a Gaelic line, that of Cinأ،ed mac Ailpأn.
Sources and background
Surviving Pictish sources for the period are few, limited to king lists, the original of which was prepared in the early 720s, and a number of accounts relating to the foundation ofSt Andrews
St Andrews ( la, S. Andrea(s); sco, Saunt Aundraes; gd, Cill Rأ¬mhinn) is a town on the east coast of Fife in Scotland, southeast of Dundee and northeast of Edinburgh. St Andrews had a recorded population of 16,800 , making it Fife's fou ...
, then called Cennrأgmonaid. Beyond Pictland, the principal sources are the Irish annals
A number of Irish annals, of which the earliest was the Chronicle of Ireland, were compiled up to and shortly after the end of the 17th century. Annals were originally a means by which monks determined the yearly chronology of feast days. Over t ...
, of which the ''Annals of Ulster
The ''Annals of Ulster'' ( ga, Annأ،la Uladh) are annals of medieval Ireland. The entries span the years from 431 AD to 1540 AD. The entries up to 1489 AD were compiled in the late 15th century by the scribe Ruaidhrأ أ“ Luinأn, ...
'' and the ''Annals of Tigernach
The ''Annals of Tigernach'' (abbr. AT, ga, Annأ،la Tiarnaigh) are chronicles probably originating in Clonmacnoise, Ireland. The language is a mixture of Latin and Old and Middle Irish.
Many of the pre-historic entries come from the 12th-centur ...
'' are the most reliable. These include materials from an annal kept at the monastery of Iona
Iona (; gd, أŒ Chaluim Chille (IPA: ˆiثگثˆxaة«جھة¯imثˆأ§iتژة™, sometimes simply ''أŒ''; sco, Iona) is a small island in the Inner Hebrides, off the Ross of Mull on the western coast of Scotland. It is mainly known for Iona Abbey, though there ...
in Scotland. أ“engus and the Picts appear occasionally in Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
sources, such as the ''Annales Cambriae
The (Latin for ''Annals of Wales'') is the title given to a complex of Latin chronicles compiled or derived from diverse sources at St David's in Dyfed, Wales. The earliest is a 12th-century presumed copy of a mid-10th-century original; later ed ...
'', and more frequently in Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
n sources, of which the Continuation of Bede
Bede ( ; ang, Bا£da , ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, The Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable ( la, Beda Venerabilis), was an English monk at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom o ...
's chronicle and the ''Historia Regum Anglorum'' attributed to Symeon of Durham
__NOTOC__
Symeon (or Simeon) of Durham (died after 1129) was an English chronicler and a monk of Durham Priory.
Biography
Symeon entered the Benedictine monastery at Jarrow as a youth. It moved to Durham in 1074, and he was professed in 1085 or ...
are the most important.
 The
The Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from ea ...
were one of four political groups in north Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
in the early 8th century. Pictland ran from the River Forth
The River Forth is a major river in central Scotland, long, which drains into the North Sea on the east coast of the country. Its drainage basin covers much of Stirlingshire in Scotland's Central Belt. The Gaelic name for the upper reach of th ...
northwards, including Orkney
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknأ¸jar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north ...
, Shetland
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the no ...
and the Western Isles
The Outer Hebrides () or Western Isles ( gd, Na h-Eileanan Siar or or ("islands of the strangers"); sco, Waster Isles), sometimes known as the Long Isle/Long Island ( gd, An t-Eilean Fada, links=no), is an island chain off the west coas ...
. Prior to the Viking Age
The Viking Age () was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonizing, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. It followed the Migration Period and the Ger ...
, the main power in Pictland appears to have been the kingdom of Fortriu
Fortriu ( la, Verturiones; sga, *Foirtrinn; ang, Wأ¦rteras; xpi, *Uerteru) was a Pictish kingdom that existed between the 4th and 10th centuries. It was traditionally believed to be located in and around Strathearn in central Scotland, but is ...
. Known high-status sites in Fortriu include Burghead
Burghead ( sco, Burgheid or ''The Broch'', gd, Am Broch) is a small town in Moray, Scotland, about north-west of Elgin. The town is mainly built on a peninsula that projects north-westward into the Moray Firth, surrounding it by water on t ...
and Craig Phأ،draig by Inverness
Inverness (; from the gd, Inbhir Nis , meaning "Mouth of the River Ness"; sco, Innerness) is a city in the Scottish Highlands. It is the administrative centre for The Highland Council and is regarded as the capital of the Highlands. Histori ...
. Pictland appears to have had only one bishop with his seat at Rosemarkie
Rosemarkie ( sco, Rossmartnie, from gd, Ros Mhaircnidh meaning "promontory of the horse stream") is a village on the south coast of the Black Isle peninsula in Ross-shire (Ross and Cromarty), northern Scotland.
Geography
Rosemarkie lies a quart ...
.
From the Forth south to the River Humber
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal rivers Ouse and Trent. From there to the North Sea, it forms part of the boundary between the ...
lay the kingdom of Northumbria. Once the dominant force in Britain, it remained a powerful kingdom, but the end of the old dynasty of kings with the death of Osric Osric is an Anglo-Saxon name and may refer to:
__NOTOC__ People Anglo-Saxon kings
* Osric of Deira, king of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Deira in the 630s
* Osric of Northumbria, king of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Northumbria in the 720s
* Osric of ...
in 729 led to conflict between rival families for the throne. The growing power of the Mercia
la, Merciorum regnum
, conventional_long_name=Kingdom of Mercia
, common_name=Mercia
, status=Kingdom
, status_text=Independent kingdom (527–879)Client state of Wessex ()
, life_span=527–918
, era=Heptarchy
, event_start=
, date_start=
, ye ...
n kingdom to the south added to the problems faced by Northumbrian kings. For most of أ“engus's reign Northumbria was ruled by King Eadberht Eating.
To the south-west of Pictland were the Gaels
The Gaels ( ; ga, Na Gaeil ; gd, Na Gأ idheil ; gv, Ny Gaeil ) are an ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man in the British Isles. They are associated with the Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic langu ...
of Dأ،l Riata
Dأ،l Riata or Dأ،l Riada (also Dalriada) () was a Gaelic kingdom that encompassed the western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel. At its height in the 6th and 7th centuries, it covered what is now ...
where the kingship was disputed between the Cenأ©l Loairn
The Cenأ©l Loairn, the descendants of Loarn mac Eirc, controlled parts of northern Argyll around the Firth of Lorne, most probably centred in Lorne but perhaps including the islands of Mull and Colonsay, Morvern and Ardnamurchan. The boundary to ...
of northern Argyll
Argyll (; archaically Argyle, in modern Gaelic, ), sometimes called Argyllshire, is a historic county and registration county of western Scotland.
Argyll is of ancient origin, and corresponds to most of the part of the ancient kingdom of ...
and the Cenأ©l nGabrأ،in
The Cenأ©l nGabrأ،in was a kingroup, presumed to descend from Gabrأ،n mac Domangairt, which dominated the kingship of Dأ،l Riata until the late 7th century and continued to provide kings thereafter. Kings of Alba and of Scotland traced their desc ...
of Kintyre
Kintyre ( gd, Cinn Tأ¬re, ) is a peninsula in western Scotland, in the southwest of Argyll and Bute. The peninsula stretches about , from the Mull of Kintyre in the south to East and West Loch Tarbert in the north. The region immediately north ...
. In 723 Selbach mac Ferchair
Selbach mac Ferchair (died 730) was king of the Cenأ©l Loairn and of Dأ،l Riata. Selbach's existence is well-attested as he is mentioned repeatedly in Irish annals.
Life
Selbach mac Ferchair was a son of Ferchar Fota. He ruled as king of the Cenأ ...
abdicated as head of the Cenأ©l Loairn and king of Dأ،l Riata in favour of his son Dأ؛ngal, who was driven out as king of Dأ،l Riata by Eochaid mac Echdach of the Cenأ©l nGabrأ،in in 726. Dأ؛ngal and Eochaid were still in conflict as late as 731, when Dأ؛ngal burnt Tarbert
Tarbert ( gd, An Tairbeart) is a place name in Scotland and Ireland. Places named Tarbert are characterised by a narrow strip of land, or isthmus. This can be where two lochs nearly meet, or a causeway out to an island.
Etymology
All placenames ...
.
The history of the fourth group, the Britons
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs mod ...
of Alt Clut
Dumbarton Castle ( gd, Dأ¹n Breatainn, ; ) has the longest recorded history of any stronghold in Scotland. It sits on a volcanic plug of basalt known as Dumbarton Rock which is high and overlooks the Scottish town of Dumbarton.
History
Dumba ...
, later the kingdom of Strathclyde, leaves little trace in the record. King Teudebur map Beli had ruled from Dumbarton Rock
Dumbarton (; also sco, Dumbairton; ) is a town in West Dunbartonshire, Scotland, on the north bank of the River Clyde where the River Leven flows into the Clyde estuary. In 2006, it had an estimated population of 19,990.
Dumbarton was the ca ...
since 722, and continued to do so until his death in 752 when his son Dumnagual succeeded him.
Rise to power
 An early medieval Irish genealogy tract claims أ“engus to be a descendant of Cairpre Cruithnechأ،in or " Cairbre the little Pict", of the
An early medieval Irish genealogy tract claims أ“engus to be a descendant of Cairpre Cruithnechأ،in or " Cairbre the little Pict", of the Eأ³ganachta
The Eأ³ganachta or Eoghanachta () were an Irish dynasty centred on Cashel which dominated southern Ireland (namely the Kingdom of Munster) from the 6/7th to the 10th centuries, and following that, in a restricted form, the Kingdom of Desmond, an ...
of Munster
Munster ( gle, an Mhumhain or ) is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the south of Ireland. In early Ireland, the Kingdom of Munster was one of the kingdoms of Gaelic Ireland ruled by a "king of over-kings" ( ga, rأ ruirech). Following the ...
. The branch of the kindred from which it is claimed he came, known in the annals as the أ‰oganachta of Mag Gergind, are generally accepted as having been located in modern Angus
Angus may refer to:
Media
* ''Angus'' (film), a 1995 film
* ''Angus Og'' (comics), in the ''Daily Record''
Places Australia
* Angus, New South Wales
Canada
* Angus, Ontario, a community in Essa, Ontario
* East Angus, Quebec
Scotland
* An ...
and the Mearns. أ“engus—also called Unust, Unuist or Onuist in Pictish and Old Gaelic
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic ( sga, Goأdelc, Ogham script: لڑŒلڑ‘لڑ”لڑ‡لڑ“لڑ‚لڑ‰; ga, Sean-Ghaeilge; gd, Seann-Ghأ idhlig; gv, Shenn Yernish or ), is the oldest form of the Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive writte ...
, was the son of Fergusso (alternatively Forgosso), in modern English, Fergus.
أ“engus thus appears to have been a native of the Mearns, possibly born into an established Verturian kindred there. It is relatively nearby, at the hill of Moncrieffe, near Perth, that he first appears in the records, defeating his rival, Alpin (or Pictish Elphin), in battle. That the Irish annals envision his kin as 'أ‰oganachta' suggests he was the descendant of an obscure 'Vuen' (or Wen), the Pictish British cognate of Gaelic أ‰ogan.
Much of أ“engus' early life is unknown; he was middle-aged by the time he entered into history. His close kin included at least two sons, Bridei (died 736) and Talorgan (died 782), and two brothers, Talorgan (died 750) and Bridei (died 763).
King Nechtan son of Der-Ilei abdicated to enter a monastery in 724 and was imprisoned by his successor Drest in 726. In 728 and 729, four kings competed for power in Pictland: Drest; Nechtan; Alpأn, of whom little is known; and أ“engus, who was a partisan of Nechtan, and perhaps his acknowledged heir.
Four battles large enough to be recorded in Ireland were fought in 728 and 729. Alpأn was defeated twice by أ“engus, after which Nechtan was restored to power. In 729 a battle between supporters of أ“engus and Nechtan's enemies was fought at Monith Carno (traditionally Cairn o' Mount, near Fettercairn
Fettercairn (, gd, Fothair Chأ rdain) is a small village in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, northwest of Laurencekirk in Aberdeenshire on the B966 from Edzell. Fettercairn is also reached via the Cairn O' Mount road (B974) from Deeside.
The name ...
) where the supporters of أ“engus were victorious. Nechtan was restored to the kingship, probably until his death in 732. On 12 August 729 أ“engus defeated and killed Drest in battle at Druimm Derg Blathuug, a place which has not been identified.
Piercing of Dal Riata
 In the 730s, أ“engus fought against Dأ،l Riata whose traditional overlords and protectors in Ireland, the
In the 730s, أ“engus fought against Dأ،l Riata whose traditional overlords and protectors in Ireland, the Cenأ©l Conaill
Cenأ©l is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*Cenأ©l Conaill, the name of the "kindred" or descendants of Conall Gulban, son of Niall Noأgiallach defined by oral and recorded history
*Cenأ©l nEأ³gain (in English, Cenel Eogan) is ...
, were much weakened at this time. A fleet from Dأ،l Riata fought for Flaithbertach mac Loingsig
Flaithbertach mac Loingsig (died 765) was a High King of Ireland. He was a member of the Cenأ©l Conaill, a branch of the northern Uأ Nأ©ill. He was the son of Loingsech mac أ“engusso (died 703), a previous high king. He ruled from 728 to 734.
He ...
, chief of the Cenأ©l Conaill, in his war with أپed Allأ،n
أپed Allأ،n (or أپed mac Fergaile) (died 743) was an 8th-century Irish king of Ailech and High King of Ireland. أپed Allأ،n was the son of Fergal mac Mأ،ele Dأ؛in and a member of the Cenأ©l nEأ³gain, a branch of the Northern Uأ Nأ©ill.
Ferga ...
of the Cenأ©l nEأ³gan
Cenأ©l is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*Cenأ©l Conaill, the name of the "kindred" or descendants of Conall Gulban, son of Niall Noأgiallach defined by oral and recorded history
*Cenأ©l nEأ³gain (in English, Cenel Eogan) is ...
, and suffered heavy losses in 733. Dأ،l Riata was ruled by Eochaid mac Echdach, possibly of the Cenأ©l nGabrأ،in who died in 733, and the king lists are unclear as to who, if anyone, succeeded him as overking. The Cenأ©l Loairn of north Argyll were ruled by Dأ؛ngal mac Selbaig whom Eochaid had deposed as overking of Dأ،l Riata in 726.
Fighting between the Picts, led by أ“engus's son Bridei, and the Dأ،l Riata, led by Talorgan mac Congussa, is recorded in 731. In 733, Dأ؛ngal mac Selbaig "profaned he sanctuary
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana مپ¸
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
of Tory Island
Tory Island, or simply Tory (officially known by its Irish name ''Toraigh''),Toraigh/Tory Island
 Battles between the Picts and the Britons of Alt Clut, or
Battles between the Picts and the Britons of Alt Clut, or
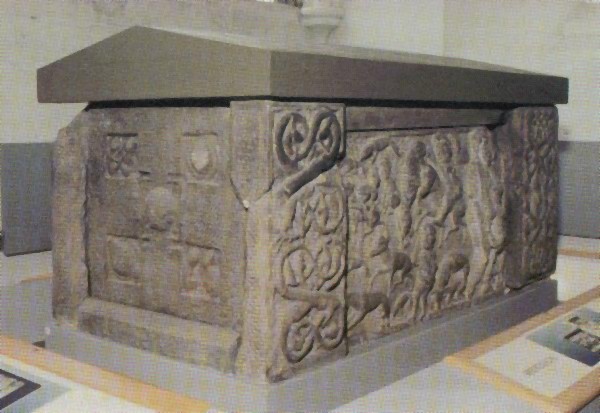 The story of the foundation of St Andrews, originally ''Cennrأgmonaid'', is not contemporary and may contain legend. The Irish annals report the death of "Tuathalأ،n, abbot of Cinrigh Mأ³na", in 747, making it certain that St Andrews had been founded before that date, probably by أ“engus or by Nechtan son of Der-Ilei. It is generally presumed that the St Andrews Sarcophagus was executed at the command of أ“engus. Later generations may have conflated this king أ“engus with the 9th century king of the same name. The choice of
The story of the foundation of St Andrews, originally ''Cennrأgmonaid'', is not contemporary and may contain legend. The Irish annals report the death of "Tuathalأ،n, abbot of Cinrigh Mأ³na", in 747, making it certain that St Andrews had been founded before that date, probably by أ“engus or by Nechtan son of Der-Ilei. It is generally presumed that the St Andrews Sarcophagus was executed at the command of أ“engus. Later generations may have conflated this king أ“engus with the 9th century king of the same name. The choice of
CELT: Corpus of Electronic Texts
at
Annals of Clonmacnoise
at
p. 113ff
Bede's Ecclesiastical History and the Continuation of Bede (pdf)
a
CCEL
tr. A.M. Sellar
at th
The Rolls edition of the Brut y Tywyssogion
(PDF) a
Stanford University Library
{{DEFAULTSORT:Oengus 01 Of The Picts 7th-century births 761 deaths Pictish monarchs 8th-century Scottish monarchs
Muiredach mac Ainbcellaig
Muiredach mac Ainbcellaig was king of the Cenأ©l Loairn, and of Dأ،l Riata (modern western Scotland), from about 733 until 736.
He was the son of Ainbcellach mac Ferchair. His coming to power is reported in 733, and is not obviously associated wit ...
.
In 734 Talorgan mac Congussa was handed over to the Picts by his brother and drowned by them. Talorgan son of Drostan was captured near Dأ؛n Ollaigh. He appears to have been the King of Atholl
Atholl or Athole ( gd, Athall; Old Gaelic ''Athfhotla'') is a large historical division in the Scottish Highlands, bordering (in anti-clockwise order, from Northeast) Marr, Badenoch, Lochaber, Breadalbane, Strathearn, Perth, and Gowrie. H ...
, and was drowned on أ“engus's order in 739. Dأ؛ngal too was a target in this year. He was wounded, the unidentified fortress of Dأ؛n Leithfinn was destroyed, and he "fled into Ireland, to be out of the power of أ“engus".
The annals report a second campaign by أ“engus against the Dأ،l Riata in 736. Dأ؛ngal, who had returned from Ireland, and his brother Feradach, were captured and bound in chains. The fortresses of Creic and Dunadd
Dunadd (Scottish Gaelic ''Dأ؛n Ad'', "fort on the iverAdd") is a hillfort in Argyll and Bute, Scotland, dating from the Iron Age and early medieval period and is believed to be the capital of the ancient kingdom of Dأ،l Riata. Dal Riata was a ki ...
were taken and burnt. Muiredach of the Cenأ©l Loairn was no more successful, defeated with heavy loss by أ“engus's brother Talorgan mac Fergusa, perhaps by Loch Awe
Loch Awe (Scottish Gaelic: ''Loch Obha'') is a large body of freshwater in Argyll and Bute, Scottish Highlands. It has also given its name to a village on its banks, variously known as Loch Awe or Lochawe. There are islands within the loch such ...
. A final campaign—known as the "smiting"—in 741 saw the Dأ،l Riata again defeated. With this Dأ،l Riata disappears from the record for a generation.
It may be that أ“engus was involved in wars in Ireland, perhaps fighting with أپed Allأ،n, or against him as an ally of Cathal mac Finguine
Cathal mac Finguine (died 742) was an Irish King of Munster or Cashel, and effectively High King of Ireland as well. He belonged to the Eأ³ganacht Glendamnach sept of the dominant Eأ³ganachta kin-group whose members dominated Munster from the 7 ...
. The full extent of his involvement, though, is unknown. There is the presence of أ“engus's son Bridei at Tory Island, on the north-west coast of Donegal in 733, close to the lands of أپed Allأ،n's enemy Flaithbertach mac Loingsig. Less certainly, the ''Fragmentary Annals of Ireland
The ''Fragmentary Annals of Ireland'' or ''Three Fragments'' are a Middle Irish combination of chronicles from various Irish annals and narrative history. They were compiled in the kingdom of Osraige, probably in the lifetime of Donnchad mac Gil ...
'' report the presence of a Pictish fleet from Fortriu fighting for Flaithbertach in 733 rather than against him.
Alt Clut, Northumbria, and Mercia
In 740, a war between the Picts and the Northumbrians is reported, during which أ†thelbald, King of Mercia, took advantage of the absence of Eadberht of Northumbria to ravage his lands, and perhaps burnYork
York is a cathedral city with Roman origins, sited at the confluence of the rivers Ouse and Foss in North Yorkshire, England. It is the historic county town of Yorkshire. The city has many historic buildings and other structures, such as a ...
. The reason for the war is unclear, but it has been suggested that it was related to the killing of Earnwine son of Eadwulf Eadwulf (sometimes Eadulf) is an Anglo-Saxon male name. Notable people with the name include:
* Eadwulf of Elmham, a 10th-century Bishop of Elmham
* Eadwulf of Hereford (died 830s), Bishop of Hereford
* Eadwulf I of Northumbria, king of Northumb ...
on Eadberht's orders. Earnwine's father had probably been an exile in the north after his defeat in the civil war of 705–706, and it may be that أ“engus, or أ†thelbald, or both, had tried to place him on the Northumbrian throne.  Battles between the Picts and the Britons of Alt Clut, or
Battles between the Picts and the Britons of Alt Clut, or Strathclyde
Strathclyde ( in Gaelic, meaning "strath (valley) of the River Clyde") was one of nine former local government regions of Scotland created in 1975 by the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973 and abolished in 1996 by the Local Government et ...
, are recorded in 744 and again in 750, when Kyle
Kyle or Kyles may refer to:
Places
Canada
* Kyle, Saskatchewan, Canada
Ireland
* Kyle, County Laois
* Kyle, County Wexford
Scotland
* Kyle, Ayrshire, area of Scotland which stretched across parts of modern-day East Ayrshire and South Ayrshir ...
was taken from Alt Clut by Eadberht of Northumbria. The 750 battle between the Britons and the Picts is reported at a place named Mocetauc (perhaps Mugdock near Milngavie
Milngavie ( ; gd, Muileann-Ghaidh) is a town in East Dunbartonshire, Scotland and a suburb of Glasgow. It is on the Allander Water, at the northwestern edge of Greater Glasgow, and about from Glasgow city centre. It neighbours Bearsden. Milngav ...
) in which Talorgan mac Fergusa, أ“engus's brother, was killed. Following the defeat in 750, the ''Annals of Ulster'' record "the ebbing of the sovereignty of أ“engus". This is thought to refer to the coming to power of أپed Find, son of Eochaid mac Echdach, in all or part of Dأ،l Riata, and his rejection of أ“engus's overlordship.
A number of interpretations have been offered of the relations between أ“engus, Eadberht and أ†thelbald in the period from 740 to 750, which due to the paucity of sources remain otherwise unclear. One suggestion is that أ“engus and أ†thelbald were allied against Eadberht, or even that they exercised a joint rulership of Britain, or , أ“engus collecting tribute north of the River Humber and أ†thelbald south of the Humber. This rests largely on a confused passage in Symeon of Durham's ''Historia Regum Anglorum'', and it has more recently been suggested that the interpretation offered by Frank Stenton
Sir Frank Merry Stenton, FBA (17 May 1880 – 15 September 1967) was an English historian of Anglo-Saxon England, and president of the Royal Historical Society (1937–1945).
The son of Henry Stenton of Southwell, Nottinghamshire, he was edu ...
—that it is based on a textual error and that أ“engus and أ†thelbald were not associated in any sort of joint overlordship—is the correct one.
In 756, أ“engus is found campaigning alongside Eadberht of Northumbria. The campaign is reported as follows: In the year of the Lord's incarnation 756, king Eadberht in the eighteenth year of his reign, and Unust, king of Picts led armies to the town ofThat Ouania isDumbarton Dumbarton (; also sco, Dumbairton; ) is a town in West Dunbartonshire, Scotland, on the north bank of the River Clyde where the River Leven flows into the Clyde estuary. In 2006, it had an estimated population of 19,990. Dumbarton was the ca .... And hence the Britons accepted terms there, on the first day of the month of August. But on the tenth day of the same month perished almost the whole army which he led from Ouania to Niwanbirig.
Govan
Govan ( ; Cumbric?: ''Gwovan'?''; Scots: ''Gouan''; Scottish Gaelic: ''Baile a' Ghobhainn'') is a district, parish, and former burgh now part of south-west City of Glasgow, Scotland. It is situated west of Glasgow city centre, on the south ba ...
is now reasonably certain, but the location of Newanbirig is less so. Newburgh-on-Tyne near Hexham has been suggested. An alternative interpretation of the events of 756 has been advanced: it identifies Newanbirig with Newborough by Lichfield
Lichfield () is a cathedral city and civil parish in Staffordshire, England. Lichfield is situated roughly south-east of the county town of Stafford, south-east of Rugeley, north-east of Walsall, north-west of Tamworth and south-west o ...
in the kingdom of Mercia. A defeat here for Eadberht and أ“engus by أ†thelbald's Mercians would correspond with the claim in the Saint Andrews foundation legends that a king named أ“engus son of Fergus founded the church there as a thanksgiving to Saint Andrew
Andrew the Apostle ( grc-koi, ل¼ˆخ½خ´دپخل¾±د‚, Andrأ©ؤپs ; la, Andrؤ“ؤپs ; , syc, ـگـ°ـ¢ـ•فپـھـ¶ـگـکـ³ـ£, ت¾And’reت¾wؤپs), also called Saint Andrew, was an apostle of Jesus according to the New Testament. He is the brother of Simon Peter ...
for saving him after a defeat in Mercia. Marjorie Anderson supports this version of the St Andrews foundation legend.
Cult of Saint Andrew
 The story of the foundation of St Andrews, originally ''Cennrأgmonaid'', is not contemporary and may contain legend. The Irish annals report the death of "Tuathalأ،n, abbot of Cinrigh Mأ³na", in 747, making it certain that St Andrews had been founded before that date, probably by أ“engus or by Nechtan son of Der-Ilei. It is generally presumed that the St Andrews Sarcophagus was executed at the command of أ“engus. Later generations may have conflated this king أ“engus with the 9th century king of the same name. The choice of
The story of the foundation of St Andrews, originally ''Cennrأgmonaid'', is not contemporary and may contain legend. The Irish annals report the death of "Tuathalأ،n, abbot of Cinrigh Mأ³na", in 747, making it certain that St Andrews had been founded before that date, probably by أ“engus or by Nechtan son of Der-Ilei. It is generally presumed that the St Andrews Sarcophagus was executed at the command of أ“engus. Later generations may have conflated this king أ“engus with the 9th century king of the same name. The choice of David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dؤپwإ«d''; grc-koi, خ”خ±د…خگخ´, Dauأd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ل‹³ل‹ٹل‰µ, ''Dawit''; xcl, ش´ص،ض‚ص«ص©, ''Dawitت؟''; cu, ذ”ذ°ذ²أذ´رٹ, ''Davidإ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
as a model is, Alex Woolf suggests, an appropriate one, as David too was an usurper.
The cult of Saint Andrew may have come to Pictland from Northumbria, as had the cult of Saint Peter
Saint Peter; he, ש×עו×ں בר ×™×•× ×”, إ imت؟إچn bar Yإچnؤپh; ar, ط³ظگظ…ط¹ظژط§ظ† ط¨ظڈط·ط±ظڈط³, translit=Simت؟aج…n Buل¹rus; grc-gre, خ خد„دپخ؟د‚, Petros; cop, Ⲡⲉⲧⲣâ²ںâ²¥, Petros; lat, Petrus; ar, ط´ظ…ط¹ظˆظ† ط§ظ„طµظپظ€ط§, Sham'un ...
which had been favoured by Nechtan, and in particular from the monastery
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which ...
at Hexham which was dedicated to Saint Andrew. This apparent connection with the Northumbrian church may have left a written record. أ“engus, like his successors and possible kinsmen Caustantأn and Eأ³gan, is recorded prominently in the ''Liber Vitae Ecclesiae Dunelmensis'', a list of some 3000 benefactors for whom prayers were said in religious institutions connected with Durham Durham most commonly refers to:
*Durham, England, a cathedral city and the county town of County Durham
*County Durham, an English county
* Durham County, North Carolina, a county in North Carolina, United States
*Durham, North Carolina, a city in N ...
. However, argues Simon Taylor, there is "no absolute proof" that the cult existed before the 11th century.
Death and legacy
أ“engus died in 761, "aged probably more than seventy, ... the dominating figure in the politics of Northern Britain". His death is reported in the usual brief style by the annalists, except for the continuator of Bede in Northumbria, possibly relying upon a Dأ،l Riata source, who wrote, "أ“engus, king of the Picts, died. From the beginning of his reign right to the end he perpetrated bloody crimes, like a tyrannical slaughtered". ThePictish Chronicle
The Pictish Chronicle is a name used to refer to a pseudo-historical account of the kings of the Picts beginning many thousand years before history was recorded in Pictavia and ending after Pictavia had been enveloped by Scotland.
Version A
The ...
king lists have it that he was succeeded by his brother Bridei. His son Talorgan was also later king, reigning from around 780 until his death in 782. Talorgan is the first son of a Pictish king known to have become king, if not immediately upon his father's death.
The following 9th-century Irish praise poem from the Book of Leinster
The Book of Leinster ( mga, Lebor Laignech , LL) is a medieval Irish manuscript compiled c. 1160 and now kept in Trinity College, Dublin, under the shelfmark MS H 2.18 (cat. 1339). It was formerly known as the ''Lebor na Nuachongbأ،la'' "Book ...
is associated with أ“engus:
An assessment of أ“engus is problematic, not least because annalistic sources provide very little information on Scotland in the succeeding generations. His apparent Irish links add to the long list of arguments which challenge the idea that the "Gaelicisation" of eastern Scotland began in the time of Cinأ،ed mac Ailpأn; indeed there are good reasons for believing that process began before أ“engus's reign. Many of the Pictish kings until the death of Eأ³gan mac أ“engusa in 839 belong to the family of أ“engus, in particular the 9th-century sons of Fergus, Caustantأn and أ“engus.
Historians have noted أ“engus's decisive military victories—particularly as these ranged over a broad geographical area, his cultural patronage and religious foundation at St Andrews. The historian Keith Coleman describes أ“engus as an "exceptionally powerful" Pictish king, while Murray Pittock
Murray G. H. Pittock MAE FRSE (born 5 January 1962) is a Scottish historian, Bradley Professor of Literature at the University of Glasgow and Pro Vice Principal at the University, where he has served in senior roles including Dean and Vice Princip ...
has argued that not only was he more successful than any of his predecessors in uniting "all Scotia, Scotland north of the Forth, to his authority", but in doing so he "foreshadow da future united Scottish kingdom". Kings from his broader family continued to rule the Picts until they suffered a crushing defeat at the hands of Vikings in 839, when أ“engus's great-grandson—and men "almost without number"—was killed. This was followed by a period with numerous kings reigning briefly and in quick succession, most dying at the hands of rivals, until the accession of Kenneth I
Kenneth MacAlpin ( mga, Cinأ،ed mac Ailpin, label= Medieval Gaelic, gd, Coinneach mac Ailpein, label=Modern Scottish Gaelic; 810 – 13 February 858) or Kenneth I was King of Dأ،l Riada (841–850), King of the Picts (843–858), and the K ...
, or Cinأ،ed mac Alpin (Kenneth Macalpine) in 842. While أ“engus may have foreshadowed rulership over a united Scotland, Pittock argues that it is in Kenneth I that "by tradition" the first King of Scotland is found.
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * *External links
CELT: Corpus of Electronic Texts
at
University College Cork
University College Cork – National University of Ireland, Cork (UCC) ( ga, Colأ،iste na hOllscoile Corcaigh) is a constituent university of the National University of Ireland, and located in Cork.
The university was founded in 1845 as one of ...
including the Annals of Ulster, the Annals of Tigernach, the Chronicon Scotorum and genealogies from Rawlinson B 502Annals of Clonmacnoise
at
Cornell University
Cornell University is a private statutory land-grant research university based in Ithaca, New York. It is a member of the Ivy League. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, Cornell was founded with the intention to teach an ...
, sep. 113ff
Bede's Ecclesiastical History and the Continuation of Bede (pdf)
a
CCEL
tr. A.M. Sellar
at th
The Rolls edition of the Brut y Tywyssogion
(PDF) a
Stanford University Library
{{DEFAULTSORT:Oengus 01 Of The Picts 7th-century births 761 deaths Pictish monarchs 8th-century Scottish monarchs