Zócalo on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Zócalo () is the common name of the main square in central
 Prior to the conquest, the area that the occupies was open space, in the center of the Aztec capital . It was bordered to the east by 's "New Houses" or Palace (which would become the National Palace) and to the west by the "Old Houses", the palace of (1469–1481) where the Emperor , 's uncle and immediate predecessor also lived. A European-style plaza was not part of the conquered
Prior to the conquest, the area that the occupies was open space, in the center of the Aztec capital . It was bordered to the east by 's "New Houses" or Palace (which would become the National Palace) and to the west by the "Old Houses", the palace of (1469–1481) where the Emperor , 's uncle and immediate predecessor also lived. A European-style plaza was not part of the conquered
 Again the plaza was cleared (with exception of the Parian) by proclamation of
Again the plaza was cleared (with exception of the Parian) by proclamation of
 A symbolic move upon Independence was the dismantling and removal of the equestrian monument to Charles IV from Plaza. The statue itself can still be seen in front of the National Art Museum where its current, and much smaller, base states that it is preserved solely for its artistic value. The statue's former oval base was moved to what was then the university building and the balustrade was moved to the
A symbolic move upon Independence was the dismantling and removal of the equestrian monument to Charles IV from Plaza. The statue itself can still be seen in front of the National Art Museum where its current, and much smaller, base states that it is preserved solely for its artistic value. The statue's former oval base was moved to what was then the university building and the balustrade was moved to the
 In 1878, Antonio Escandon donated a kiosk to the city which was set over and on top of Santa Anna's base. It was lit with four large iron
In 1878, Antonio Escandon donated a kiosk to the city which was set over and on top of Santa Anna's base. It was lit with four large iron
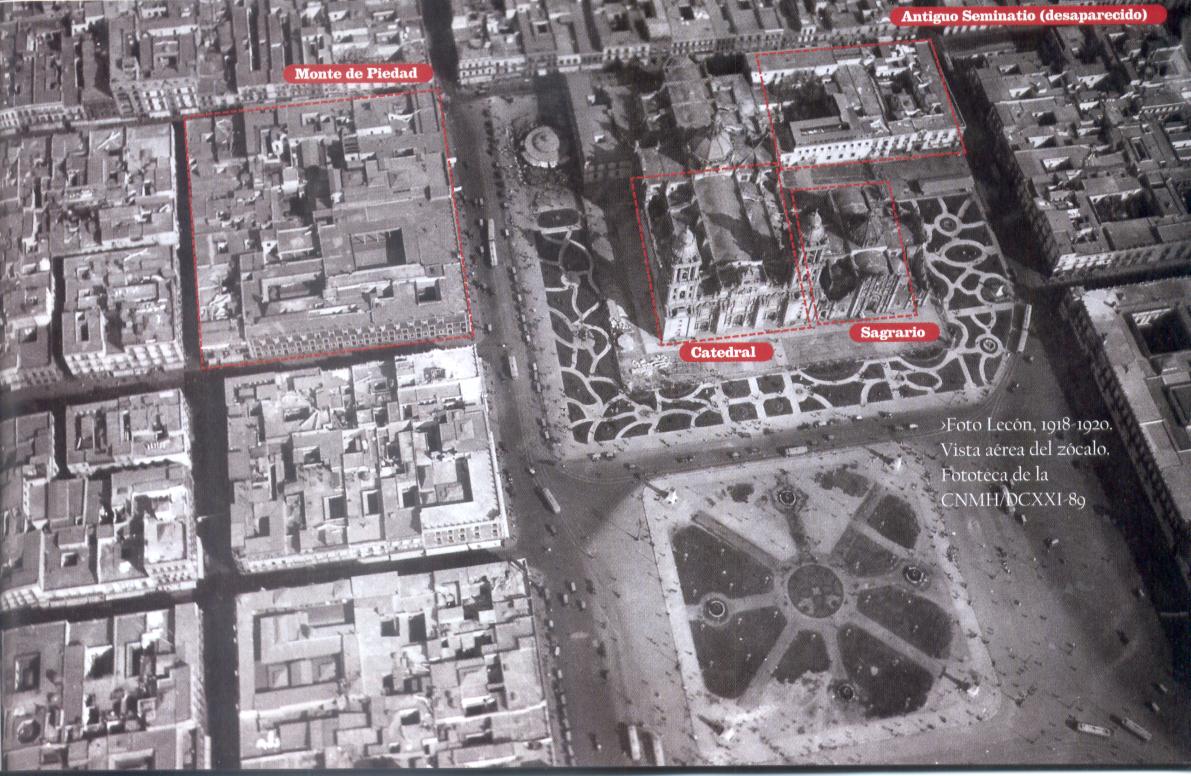 During the ''Decena Trágica'' (the ten days from 9 to 19 February 1913), the National Palace was bombarded from the nearby military fort, incidentally damaging the Zócalo. In 1914, the ash trees planted in the previous century (which meanwhile had grown considerably) were taken out; new footpaths, grassy areas, and garden space were created; and palm trees were planted in each corner of the plaza.
The Zócalo was a meeting place for protests for 1 May. In 1968, students protested against the authoritarian measures taken by then-president
During the ''Decena Trágica'' (the ten days from 9 to 19 February 1913), the National Palace was bombarded from the nearby military fort, incidentally damaging the Zócalo. In 1914, the ash trees planted in the previous century (which meanwhile had grown considerably) were taken out; new footpaths, grassy areas, and garden space were created; and palm trees were planted in each corner of the plaza.
The Zócalo was a meeting place for protests for 1 May. In 1968, students protested against the authoritarian measures taken by then-president
 In 2009, former mayor
In 2009, former mayor
 The plaza is also home to regularly occurring political events. Just before 11 pm on each 15 September, the
The plaza is also home to regularly occurring political events. Just before 11 pm on each 15 September, the
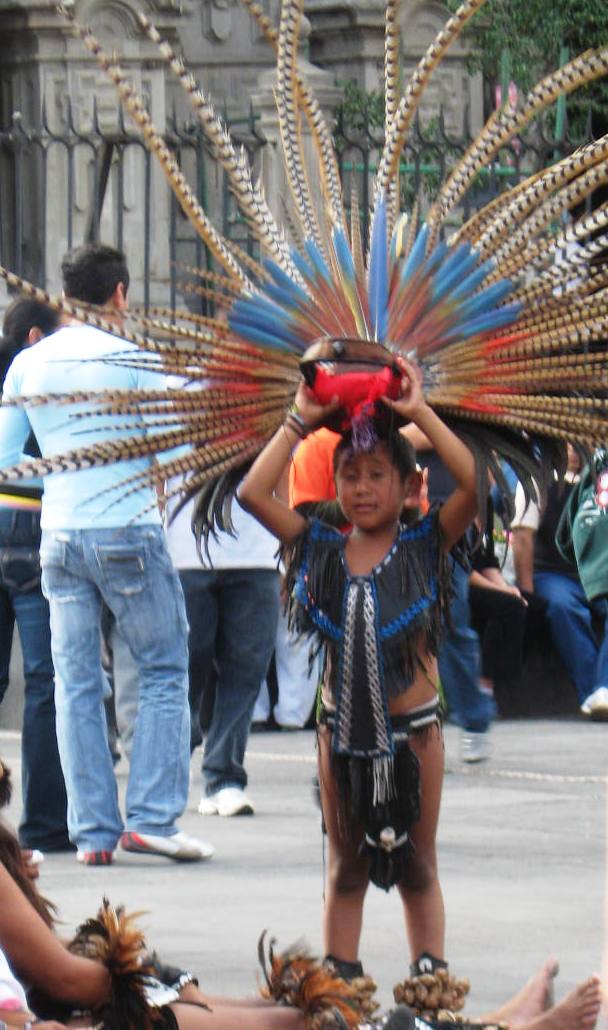 Since 1982, due to efforts to revitalize the city center, the Zócalo has become the scene of a number of artistic and cultural events. There are daily impromptu shows of Aztec dancers dancing to drums, wearing feathered headdresses and anklets made of concha shells. On a grander scale, some examples of events held here recently are
Since 1982, due to efforts to revitalize the city center, the Zócalo has become the scene of a number of artistic and cultural events. There are daily impromptu shows of Aztec dancers dancing to drums, wearing feathered headdresses and anklets made of concha shells. On a grander scale, some examples of events held here recently are
Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital and largest city of Mexico, and the most populous city in North America. One of the world's alpha cities, it is located in the Valley o ...
. Prior to the colonial period, it was the main ceremonial center in the Aztec city of Tenochtitlan
, ; es, Tenochtitlan also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, ; es, México-Tenochtitlan was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear. The date 13 March 1325 was ...
. The plaza used to be known simply as the "Main Square" or "Arms Square", and today its formal name is Plaza de la Constitución (''Constitution Square''). This name does not come from any of the Mexican constitution
The Constitution of Mexico, formally the Political Constitution of the United Mexican States ( es, Constitución Política de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos), is the current constitution of Mexico. It was drafted in Santiago de Querétaro, in ...
s that have governed the country but rather from the Cádiz Constitution, which was signed in Spain in the year 1812. Even so, it is almost always called the ''Zócalo'' today. Plans were made to erect a column as a monument to Independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the stat ...
, but only the base, or ''zócalo'' (meaning "plinth
A pedestal (from French ''piédestal'', Italian ''piedistallo'' 'foot of a stall') or plinth is a support at the bottom of a statue, vase, column, or certain altars. Smaller pedestals, especially if round in shape, may be called socles. In ...
"), was built. The plinth was buried long ago, but the name has lived on. Many other Mexican towns and cities, such as Oaxaca
Oaxaca ( , also , , from nci, Huāxyacac ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca), is one of the 32 states that compose the Federative Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 570 municipaliti ...
, Mérida, and Guadalajara
Guadalajara ( , ) is a metropolis in western Mexico and the capital of the state of Jalisco. According to the 2020 census, the city has a population of 1,385,629 people, making it the 7th largest city by population in Mexico, while the Guadalaj ...
, have adopted the word ''zócalo'' to refer to their main plazas, but not all.
It has been a gathering place for Mexicans since Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl ...
times, having been the site of Mexican
Mexican may refer to:
Mexico and its culture
*Being related to, from, or connected to the country of Mexico, in North America
** People
*** Mexicans, inhabitants of the country Mexico and their descendants
*** Mexica, ancient indigenous people ...
ceremonies, the swearing-in of viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning " ...
s, royal proclamations, military parades, Independence ceremonies, and modern religious events such as the festivals of Holy Week
Holy Week ( la, Hebdomada Sancta or , ; grc, Ἁγία καὶ Μεγάλη Ἑβδομάς, translit=Hagia kai Megale Hebdomas, lit=Holy and Great Week) is the most sacred week in the liturgical year in Christianity. In Eastern Churches, w ...
and Corpus Christi. It has received foreign heads of state and is the main venue for both national celebrations and national protests. The Zócalo and surrounding blocks have played a central role in the city's planning and geography for almost 700 years. The site is just one block southwest of the Templo Mayor, which, according to Aztec legend and mythology, was considered the center of the universe.
Description
The modern Zócalo in Mexico City is 57,600 m2 (240 m × 240 m). It is bordered by theMexico City Metropolitan Cathedral
The Metropolitan Cathedral of the Assumption of the Most Blessed Virgin Mary into Heaven ( es, Catedral Metropolitana de la Asunción de la Bienaventurada Virgen María a los cielos) is the cathedral church of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Me ...
to the north, the National Palace Buildings called National Palace include:
* National Palace (Dominican Republic), in Santo Domingo
*National Palace (El Salvador), in San Salvador
*National Palace (Ethiopia), in Addis Ababa; also known as the Jubilee Palace
*National Palace (Guatem ...
to the east, the Federal District buildings to the south and the Old Portal de Mercaderes to the west, the Nacional Monte de Piedad building at the north-west corner, with the Templo Mayor
The (Spanish: Main Temple) was the main temple of the Mexica people in their capital city of Tenochtitlan, which is now Mexico City. Its architectural style belongs to the late Postclassic period of Mesoamerica. The temple was called ' in ...
site to the northeast, just outside view. In the centre is a flagpole with an enormous Mexican flag ceremoniously raised and lowered each day and carried into the National Palace. There is an entrance to the Metro station "Zócalo/Tenochtitlan" located at the north-east corner of the square but no sign above ground indicates its presence.
History
Pre-conquest
 Prior to the conquest, the area that the occupies was open space, in the center of the Aztec capital . It was bordered to the east by 's "New Houses" or Palace (which would become the National Palace) and to the west by the "Old Houses", the palace of (1469–1481) where the Emperor , 's uncle and immediate predecessor also lived. A European-style plaza was not part of the conquered
Prior to the conquest, the area that the occupies was open space, in the center of the Aztec capital . It was bordered to the east by 's "New Houses" or Palace (which would become the National Palace) and to the west by the "Old Houses", the palace of (1469–1481) where the Emperor , 's uncle and immediate predecessor also lived. A European-style plaza was not part of the conquered Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl ...
; the old city had a sacred precinct or which was the absolute center of the city (and the universe, according to Aztec belief), but it was located to the immediate north and northeast of the modern-day .
The current occupies a space south-southwest of the intersection of roads that oriented . The north–south road was called (for the locations north and south it led to). The road led west and stretched east a little before leading into the lake that surrounded the city at the time. These roads were the width of three jousting
Jousting is a martial game or hastilude between two horse riders wielding lances with blunted tips, often as part of a tournament. The primary aim was to replicate a clash of heavy cavalry, with each participant trying to strike the opponen ...
lance
A lance is a spear designed to be used by a mounted warrior or cavalry soldier (lancer). In ancient and medieval warfare, it evolved into the leading weapon in cavalry charges, and was unsuited for throwing or for repeated thrusting, unlike s ...
s according to . This intersection divided the city into four neighborhoods. The sacred precinct, containing the , was located to the northeast of this intersection and walled off from the open area for commoners. As to this area's relationship to the proper, some historians say that it was part of it, but others say no.
Viceroyalty of New Spain (1521–1821)
The modern plaza of Mexico City was placed by Alonso Garcia Bravo shortly after theinvasion
An invasion is a military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitical entity aggressively enter territory owned by another such entity, generally with the objective of either: conquering; liberating or re-establishing ...
when he laid out what is now the historic center. After the destruction of Tenochtitlan, Cortés had the city redesigned for symbolic purposes. He kept the four major neighborhoods or "capullis" but he had a church, now the Cathedral of Mexico City, built at the place the four adjoined. He had the Temo become the cathedral. The southern half was called the "Plaza Mayor" (Main Square) and the northern one was called the "Plaza Chica" (Small Square). Fairly early in the colonial period, the Plaza Chica would be swallowed up by the growing city.
During early colonial times, the plaza was bordered to the north by the new church, and to the east by Cortés's new palace, built over and with the ruins of Moctezuma's palace. On the west side of the plaza, the Portales de Mercaderes (Merchants' Portals) were built, south of Cortés' other palace, the Palace of the Marquis of the Valley of Oaxaca. On the south side, was the Portal of the Flowers (Flores), named so after its owner, Maria Gutierrez Flores de Caballerias. Next to this portal was the House of the Ayuntamiento
''Ayuntamiento'' ()In other languages of Spain:
* ca, ajuntament ().
* gl, concello ().
* eu, udaletxea (). is the general term for the town council, or ''cabildo'', of a municipality or, sometimes, as is often the case in Spain and Latin Amer ...
, a government building for the city. Both of these were behind a small drainage canal that ran east–west.
Flooding was always an issue for the plaza and the city in general. The plaza was flooded in 1629 with water two meters deep, ruining many of the merchants located there and requiring many of the portals to be rebuilt. The drainage project to control flooding, known as the '' desagüe'', drafted Indian men over nearly the whole colonial period, to work on this major infrastructure project. Controlling flooding meant health benefits for Mexico City residents by preventing human waste from polluting the city during floods and controlling mosquitoes, which spread disease. It also changed the ecological system that supported birds and fish populations and allowed for Indian cultivation of crops.
After the cathedral was constructed in the latter half of the 16th century, the look of the plaza changed. The old church faced east and not to the plaza itself. The new cathedral's three portals towered south over the plaza and giving the area a north–south orientation, which exists to this day.
Over much of the 17th century, the plaza became overrun with market stalls. After a mob burned the Viceregal Palace in 1692, depicted in the famous 1696 painting by Cristóbal de Villalpando, authorities attempted to completely clear the plaza to make way for the "Parian", a set of shops set in the southwest corner of the plaza used to warehouse and sell products brought by galleon
Galleons were large, multi-decked sailing ships first used as armed cargo carriers by European states from the 16th to 18th centuries during the age of sail and were the principal vessels drafted for use as warships until the Anglo-Dutch ...
s from Europe and Asia. This was opened in 1703. The Parián is shown at the bottom of Villalpando's painting; it was later destroyed in an 1828 riot.
This, however, did not keep the rest of the plaza from becoming filled again with makeshift stalls such as the group known as "San José" located next to the Parian itself. This prompted historian Francisco Sedano to comment that it was ugly and unsightly. He claimed it was very difficult to walk around here at the time because of its uneven pavement, mud in the rainy season, aggressive street dogs, mounds of trash and human excrement tossed among the corn husks and other discarded wrappings.
Charles IV of Spain
, house = Bourbon-Anjou
, father = Charles III of Spain
, mother = Maria Amalia of Saxony
, birth_date =11 November 1748
, birth_place =Palace of Portici, Portici, Naples
, death_date =
, death_place ...
in December 1789. Then-viceroy Juan Vicente Güemes Pacheco had the plaza repaved and the open gutters covered with stone blocks. He also had a fountain installed in each corner. During this work, the Aztec Calendar was unearthed, as well as a statue of the goddess Coatlicue. The Calendar was put on display on the west side of the cathedral, where it remained until about 1890 when it was moved to the old "Centro Museum". It now resides in the Museum of Anthropology. The statue eventually made its way to this museum, but not until it was practically buried in one of the back patios of the Royal and Pontifical University until after Independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the stat ...
. The former merchants of the plaza were moved primarily to a new building called the ''Mercado de Volador'' (Market of the Flyer), located southeast of the plaza where the Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
building stands today.
The plaza was converted into a public space with 64 lamps. The cathedral was separated from the plaza by iron grating; 124 stone benches were placed and the plaza was marked off by low iron poles connected by an iron chain. The main feature of the redesigned plaza was an equestrian statue of Charles IV by Manuel Tolsá
Manuel Vicente Tolsá Sarrión ( Enguera, Valencia, Spain, May 4, 1757 – Mexico City, December 24, 1816) was a prolific Neoclassical architect and sculptor in Spain and Mexico. He served as the first director of the Academy of San Carlos.
B ...
. It was first placed in the southeastern corner of the plaza, first on a gilded wood base to inaugurate it in December 1803. When the monument was finished, the wooden base was replaced by an oval one of stone measuring 113 meters by 95.5 meters, with its own balustrade
A baluster is an upright support, often a vertical moulded shaft, square, or lathe-turned form found in stairways, parapets, and other architectural features. In furniture construction it is known as a spindle. Common materials used in its c ...
and fountains at the corners created by José del Mazo.
This was the backdrop when Viceroy Don Felix Maria Calleja
Felix may refer to:
* Felix (name), people and fictional characters with the name
Places
* Arabia Felix is the ancient Latin name of Yemen
* Felix, Spain, a municipality of the province Almería, in the autonomous community of Andalusia, ...
, other authorities and assembled people swore allegiance to the Constitution of Cadiz, and fealty to the Spanish Crown on 22 May 1813 as the Mexican War of Independence
The Mexican War of Independence ( es, Guerra de Independencia de México, links=no, 16 September 1810 – 27 September 1821) was an armed conflict and political process resulting in Mexico's independence from Spain. It was not a single, co ...
raged. This event also resulted in renaming the square as the "Plaza of the Constitution." The last changes to the plaza before Independence in 1821 were done by Manuel Tolsá
Manuel Vicente Tolsá Sarrión ( Enguera, Valencia, Spain, May 4, 1757 – Mexico City, December 24, 1816) was a prolific Neoclassical architect and sculptor in Spain and Mexico. He served as the first director of the Academy of San Carlos.
B ...
placing the Cross of Mañozca at the southeast corner and placing another, similar cross to the northwest. Both of these were set on stone Neoclassical pedestals.
Independence and the 1828 Parián Riot
 A symbolic move upon Independence was the dismantling and removal of the equestrian monument to Charles IV from Plaza. The statue itself can still be seen in front of the National Art Museum where its current, and much smaller, base states that it is preserved solely for its artistic value. The statue's former oval base was moved to what was then the university building and the balustrade was moved to the
A symbolic move upon Independence was the dismantling and removal of the equestrian monument to Charles IV from Plaza. The statue itself can still be seen in front of the National Art Museum where its current, and much smaller, base states that it is preserved solely for its artistic value. The statue's former oval base was moved to what was then the university building and the balustrade was moved to the Alameda Central
Alameda Central is a public urban park in downtown Mexico City. Created in 1592, the Alameda Central is the oldest public park in the Americas. It is located in Cuauhtémoc borough, adjacent to the Palacio de Bellas Artes, between Juárez Aven ...
. This left the plaza bare except for the Parian.
On 4 and 5 December 1828, the Parián market, the most active of Mexico City's markets, was looted and damaged by a popular uprising. Several merchants died and most were ruined. President Santa Anna Santa Anna may refer to:
* Santa Anna, Texas, a town in Coleman County in Central Texas, United States
* Santa Anna, Starr County, Texas
* Santa Anna Township, DeWitt County, Illinois, one of townships in DeWitt County, Illinois, United States. ...
finally had the Parián demolished in 1843. This left the plaza bare again, except for some ash tree
''Fraxinus'' (), commonly called ash, is a genus of flowering plants in the olive and lilac family, Oleaceae. It contains 45–65 species of usually medium to large trees, mostly deciduous, though a number of subtropical species are evergr ...
s and flower gardens that were planted and protected by stone borders. Santa Anna wanted to build a monument to Mexican Independence in the center of the plaza but his project got only as far as the base (zócalo), which stayed there for decades and gave the plaza its current popular name. It stayed this way until 1866 when the Paseo (path) del Zócalo was created in response to the numbers of people who were using the plaza to take walks. A garden with footpaths was created; fountains were placed at each corner; 72 iron benches were installed and the area was lighted by hydrogen gas lamps. Santa Anna's base, however, was not removed.
Era of the Porfiriato
candelabra
A candelabra (plural candelabras) or candelabrum (plural candelabra or candelabrums) is a candle holder with multiple arms.
Although electricity has relegated candleholders to decorative use, interior designers continue to model light fixtures ...
s and designed to be similar to one in the Bois de Boulogne
The Bois de Boulogne (, "Boulogne woodland") is a large public park located along the western edge of the 16th arrondissement of Paris, near the suburb of Boulogne-Billancourt and Neuilly-sur-Seine. The land was ceded to the city of Paris by t ...
in Paris. Soon afterward, the company ''Ferrocarriles del Distrito Federal'' ("Trains of the Federal District") converted part of the Zócalo into a streetcar station with ticket kiosk and stand. The streetcars and lighting were converted to electric power in 1894, and the Zócalo's paths were paved with asphalt
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term ...
in 1891.
From the latter half of the nineteenth century to the beginning of the twentieth, the Zócalo again filled with market stalls, including the "Centro Mercantil" which sold fabric, clothing, and Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau (; ) is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. The style is known by different names in different languages: in German, in Italian, in Catalan, and also known as the Modern ...
stonework. The other stalls concentrated on more mundane merchandise. This caused pedestrians to take their walks on Alameda Central or on San Francisco and Madero streets, to the west of the Zócalo.
20th century
 During the ''Decena Trágica'' (the ten days from 9 to 19 February 1913), the National Palace was bombarded from the nearby military fort, incidentally damaging the Zócalo. In 1914, the ash trees planted in the previous century (which meanwhile had grown considerably) were taken out; new footpaths, grassy areas, and garden space were created; and palm trees were planted in each corner of the plaza.
The Zócalo was a meeting place for protests for 1 May. In 1968, students protested against the authoritarian measures taken by then-president
During the ''Decena Trágica'' (the ten days from 9 to 19 February 1913), the National Palace was bombarded from the nearby military fort, incidentally damaging the Zócalo. In 1914, the ash trees planted in the previous century (which meanwhile had grown considerably) were taken out; new footpaths, grassy areas, and garden space were created; and palm trees were planted in each corner of the plaza.
The Zócalo was a meeting place for protests for 1 May. In 1968, students protested against the authoritarian measures taken by then-president Gustavo Díaz Ordaz
Gustavo Díaz Ordaz Bolaños (; 12 March 1911 – 15 July 1979) was a Mexican politician and member of the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI). He served as the President of Mexico from 1964 to 1970.
Díaz Ordaz was born in San Andrés ...
. It was also the starting point of the marathon
The marathon is a long-distance foot race with a distance of , usually run as a road race, but the distance can be covered on trail routes. The marathon can be completed by running or with a run/walk strategy. There are also wheelchair div ...
run in the 1968 Summer Olympics
The 1968 Summer Olympics ( es, Juegos Olímpicos de Verano de 1968), officially known as the Games of the XIX Olympiad ( es, Juegos de la XIX Olimpiada) and commonly known as Mexico 1968 ( es, México 1968), were an international multi-sport ev ...
. The plaza deteriorated until, by the 1970s, all that was left were light poles and a large flagpole in the center. Then the ground was leveled again, the train tracks taken out, and the whole plaza cemented over. Automobile parking was prohibited and the plaza's shape was squared to 200 meters on each side. Later in the 1970s, the Zócalo was repaved with pink cobblestones; small trees protected by metal grates were planted; and small areas of grass were seeded around the flagpole.
As the end of the twentieth century neared, the Zócalo, along with most of the city center (called the ''Colonia Centro'') was in massive disrepair. This caused ''The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Eco ...
'' magazine to remark that the Zócalo and the area surrounding it "... should be one of the most compelling architectural destinations in the Americas. Instead, much of it is a slum of gutted buildings, dark and dirty streets blocked by milling vendors, and garbage-strewn vacant lots."
In the late 1990s, Cuauhtémoc Cárdenas
Cuauhtémoc Cárdenas Solórzano (; born 1 May 1934) is a Mexican prominent politician. The son of 51st President of Mexico Lázaro Cárdenas, he is a former Head of Government of Mexico City and a founder of the Party of the Democratic Revol ...
, then mayor of Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital and largest city of Mexico, and the most populous city in North America. One of the world's alpha cities, it is located in the Valley o ...
, and Dr. Rene Coulomb, general director of the Historic Center Trust, launched a $300,000,000 renovation of the Zócalo and the surrounding city center, with the aim of attracting businesses and residents back to the area. There were plans to remove the iron grating separating the cathedral from the Zócalo, but there was so much public opposition to the idea that it was eventually scrapped.
21st century
 In 2009, former mayor
In 2009, former mayor Marcelo Ebrard
Marcelo Luis Ebrard Casaubón (; born 10 October 1959) is a Mexican politician who is serving as the Secretary of Foreign Affairs of Mexico. Affiliated with the National Regeneration Movement (MORENA) since 2018, he was appointed to lead the f ...
launched a campaign to perform maintenance works in the Historic Center (which, because of Congressional reduction of the annual budget of the local government, was largely supported with the money collected in the streets for that purpose by government officials). The campaign had satisfactory results.
In 2010, a replica of the Angel de la Independencia
The Angel of Independence, most commonly known by the shortened name ''El Ángel'' and officially known as ''Monumento a la Independencia'' ("Monument to Independence"), is a victory column on a roundabout on the major thoroughfare of Paseo de ...
was brought to Zócalo as a way of spreading out the protesters from the original Angel site. This is because the original site of the Angel is located in a financial area, with a high traffic flow, making policing more difficult than the Zócalo.
A Day of the Dead parade has been held at the square since 2016 after the James Bond film ''Spectre
Spectre, specter or the spectre may refer to:
Religion and spirituality
* Vision (spirituality)
* Apparitional experience
* Ghost
Arts and entertainment Film and television
* ''Spectre'' (1977 film), a made-for-television film produced and wri ...
'' featured a parade there.
As political hub
The Zócalo is the center of government of both the nation and of the capital, where the powers-that-be are. This makes it a popular place for protests, and it is often dotted with protesters in makeshift camps and banners. As the plaza can hold more than 100,000 people, it is also the scene of major political rallies. Thousands rallied here in protest when Cuauhtémoc Cárdenas lost against Carlos Salinas in a presidential election widely believed to have been rigged in 1988. In 2001, followers of Zapatista leaderSubcomandante Marcos
Rafael Sebastián Guillén Vicente (born 19 June 1957) is a Mexican insurgent, the former military leader and spokesman for the Zapatista Army of National Liberation (EZLN) in the ongoing Chiapas conflict,Pasztor, S. B. (2004). Marcos, Subcoman ...
, mostly poor Chiapan indigenous people, marched into the Zócalo to support a bill that would give them greater political autonomy. Following Cárdenas' lead, Andrés Manuel López Obrador
Andrés Manuel López Obrador (; born 13 November 1953), also known by his initials AMLO, is a Mexican politician who has been serving as the 65th president of Mexico since 1 December 2018. He previously served as Head of Government of Mex ...
staged major protests here after the 2006 Mexican presidential elections as well as a rally with thousands of participants against President Calderón
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
's initiative to allow private and foreign investment in Mexico's state-owned energy company, PEMEX
Pemex (a portmanteau of Petróleos Mexicanos, which translates to ''Mexican Petroleum'' in English; ) is the Mexican state-owned petroleum company managed and operated by the Mexican government. It was formed in 1938 by nationalization and expr ...
. On 30 August 2008, a peaceful protest against crime and violence filled the Zócalo to capacity.
 The plaza is also home to regularly occurring political events. Just before 11 pm on each 15 September, the
The plaza is also home to regularly occurring political events. Just before 11 pm on each 15 September, the president of Mexico
The president of Mexico ( es, link=no, Presidente de México), officially the president of the United Mexican States ( es, link=no, Presidente de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos), is the head of state and head of government of Mexico. Under the ...
comes out onto the central balcony of the National Palace to perform the Grito de Dolores
A ''grito'' or ''grito mexicano'' (, Spanish for "shout") is a common Mexican interjection, used as an expression.
Characteristics
This interjection is similar to the ''yahoo'' or '' yeehaw'' of the American cowboy during a hoedown, with added ...
to the crowd gathered in the plaza. Even this is sometimes subject to the political winds of the country. For the 2006 Grito, the crowd in the Zócalo was addressed not by then-President Vicente Fox
Vicente Fox Quesada (; born 2 July 1942) is a Mexican businessman and politician who served as the 62nd president of Mexico from 1 December 2000 to 30 November 2006. After campaigning as a right-wing populist, Fox was elected president on the ...
, who had gone to Dolores Hidalgo, Guanajuato
Guanajuato (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guanajuato ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Guanajuato), is one of the 32 states that make up the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 46 municipalities and its capital city i ...
to deliver the Grito, but by Alejandro Encinas
Alejandro is the Spanish form of the name Alexander.
Alejandro has multiple variations in different languages, including Aleksander (Czech, Polish), Alexandre ( French), Alexandros (Greek), Alsander ( Irish), Alessandro (Italian), Aleksandr (R ...
, then-mayor of Mexico City. This was done to avoid mass protests in the Zócalo following the disputed presidential election between Felipe Calderón and López Obrador. Under the unpopular rule of Enrique Peña Nieto
Enrique Peña Nieto (; born 20 July 1966), commonly referred to by his initials EPN, is a Mexican politician who served as the 64th president of Mexico from 1 December 2012 to 30 November 2018. A member of the Institutional Revolutionary Party ...
, the ceremony has been subjected to widespread criticism —mostly from left-leaning sources— for the government's notorious use of ''acarreados'' (people who are literally carried into the square by bus and paid for with food or other minor goods) in order to boost attendance numbers and simulate popular enthusiasm.
An alternative expression of Mexican pride is the celebration of the spring equinox on the Zócalo. This is done by groups looking to reassert the superiority of indigenous ethnic bloodlines (La Raza
The Spanish expression ('the people' or 'the community'; literal translation: 'the race') has historically been used to refer to the Hispanophone populations (primarily though not always exclusively in the Western Hemisphere), considered a ...
) and pre-Hispanic culture. They choose to do the ceremony here not only because it is close to where such rites used to be performed before the Spaniards came, but also because they are right next to the symbols of "Spanish" ecclesiastical and secular power (the cathedral and National Palace, respectively), which they oppose.
The Zócalo area has been, since 2014, where large rallies have been held in the aftermath of the 2014 Iguala mass kidnapping
On September 26, 2014, forty-three male students disappeared from the Ayotzinapa Rural Teachers' College after being forcibly abducted in Iguala, Guerrero, Mexico. They were allegedly taken into custody by local police officers from Iguala an ...
, an event that has become symbolic for the climate of widespread criminality, impunity and governmental corruption that many feel the country faces.
As artistic venue
Spencer Tunick
Spencer Tunick (born January 1, 1967) is an American photographer best known for organizing large-scale nude shoots. Since 1994, he has photographed over 75 human installations around the world.
Life and career
Spencer Tunick was born in Middle ...
's photo shoot where nearly 18,000 Mexicans bared all for the artist, surpassing the record set earlier in Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
and artist Gregory Colbert
Gregory Colbert (born 1960) is a Canadian filmmaker and photographer best known as the creator of ''Ashes and Snow'', an exhibition of photographic artworks and films housed in the Nomadic Museum. Colbert sees himself as an apprentice to nature. H ...
's Ashes and Snow
''Ashes and Snow'' by Canadian artist Gregory Colbert is an installation of photographic artworks, films, and a novel in letters that travels in the Nomadic Museum, a temporary structure built exclusively to house the exhibition. The work explores ...
Nomadic Museum
''Ashes and Snow'' by Canadian artist Gregory Colbert is an installation of photographic artworks, films, and a novel in letters that travels in the Nomadic Museum, a temporary structure built exclusively to house the exhibition. The work explores ...
. One curious event was the building of a temporary ice-skating rink of about 3,200 m2 in the middle of the Zócalo, for use by the city's residents for free in the winter of 2007. Since then, the rink has been repeatedly built up for several winter seasons.
The Festival de México is an annual event with programs dedicated to art (popular and fine) and academia held in the Zócalo and some other venues in the historic center. In 2008, the 24th Festival had 254 performances and shows from over 20 countries in 65 plazas and other locations near the plaza.
The Zocalo is often the site of major parades in the city including the Mexico City Alebrije Parade.
Concerts by popular singers and groups have also been held here. Café Tacuba
Café Tacvba (Pronounced ''kaˈfe taˈkuβa'') is a band from Ciudad Satélite, Mexico. The group gained popularity in the early 1990s. They were founded in 1989, before they had the current lineup of Rubén Isaac Albarrán Ortega (lead vocals, ...
drew almost 100,000 people to the plaza in 2005 and Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the ...
n superstar Shakira
Shakira Isabel Mebarak Ripoll ( , ; born 2 February 1977), professionally known by the mononym Shakira, is a Colombian singer and songwriter. Born and raised in Barranquilla, she has been referred to as the "Honorific nicknames in popular ...
drew a crowd of about 210,000 according to Mexico's Civil Protection. In August 2008, a skateboarding
Skateboarding is an action sport originating in the United States that involves riding and performing tricks using a skateboard, as well as a recreational activity, an art form, an entertainment industry job, and a method of transportation ...
/BMX
BMX, an abbreviation for bicycle motocross or bike motocross, is a cycle sport performed on BMX bikes, either in competitive BMX racing or freestyle BMX, or else in general street or off-road recreation.
History
BMX began during the earl ...
event drew 50,000 young people on a Sunday afternoon. Paul McCartney
Sir James Paul McCartney (born 18 June 1942) is an English singer, songwriter and musician who gained worldwide fame with the Beatles, for whom he played bass guitar and shared primary songwriting and lead vocal duties with John Lennon. One ...
drew an attendance of 250,000 people for a free concert played on the plaza on 10 May 2012 as a part of his On the Run Tour. Justin Bieber
Justin Drew Bieber ( ; born March 1, 1994) is a Canadian singer. Bieber is recognized for his genre-melding musicianship and has played an influential role in modern-day popular music. He was discovered by American record executive Scooter ...
also offered a free show on 11 July 2012, where he performed in front of 210,000 people as part of the tour for his 2012 album ''Believe
Believe may refer to:
*Belief, a psychological state in which an individual holds a proposition or premise to be true, with or without proof for such proposition
*Faith, a belief in something which has not been proven
Arts, entertainment, and me ...
''. On 1 October 2016, Roger Waters
George Roger Waters (born 6 September 1943) is an English musician, singer-songwriter and composer. In 1965, he co-founded the progressive rock band Pink Floyd. Waters initially served as the bassist, but following the departure of singer-s ...
performed in the square before 170,000 people, once again for free and with a strong political message against Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021.
Trump graduated from the Wharton School of the University of P ...
and Enrique Peña Nieto
Enrique Peña Nieto (; born 20 July 1966), commonly referred to by his initials EPN, is a Mexican politician who served as the 64th president of Mexico from 1 December 2012 to 30 November 2018. A member of the Institutional Revolutionary Party ...
included in sections of the show, which consisted of outtakes from his Pink Floyd
Pink Floyd are an English rock band formed in London in 1965. Gaining an early following as one of the first British psychedelic groups, they were distinguished by their extended compositions, sonic experimentation, philosophical lyrics an ...
years.
In popular culture
Thesci-fi
Science fiction (sometimes shortened to Sci-Fi or SF) is a genre of speculative fiction which typically deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts such as advanced science and technology, space exploration, time travel, parallel universe ...
series ''Babylon 5
''Babylon 5'' is an American space opera television series created by writer and producer J. Michael Straczynski, under the Babylonian Productions label, in association with Straczynski's Synthetic Worlds Ltd. and Warner Bros. Domestic Tele ...
'' uses the name "Zocalo" as the station's main gathering place.
Dutch trance music
Trance is a genre of electronic dance music that emerged from the British new-age music scene and the early 1990s German techno and hardcore scenes.
Trance music is characterized by a tempo generally lying between 135–150 beats per minut ...
producer Armin Van Buuren
Armin Jozef Jacobus Daniël van Buuren ( , ; born 25 December 1976) is a Dutch DJ and record producer from Leiden, South Holland. Since 2001, he has hosted '' A State of Trance'' (ASOT), a weekly radio show, which is broadcast to nearly 40&n ...
has a song called "Zocalo" on his 2005 album '' Shivers'', which, Josh Gabriel
Josh Gabriel is an American electronic dance music DJ and producer, most known for his collaborative partnership Gabriel & Dresden with Dave Dresden.
History Early years (1988–2000)
In 1988-89, a 20-year-old exchange student from Californi ...
, of Gabriel & Dresden, recounts is named after Zocalo Coffeehouse in San Leandro, California, which Armin visited while recording the song, and which is itself named after the Zocalo in Mexico City.
The pre-title sequence of the 2015 James Bond film ''Spectre
Spectre, specter or the spectre may refer to:
Religion and spirituality
* Vision (spirituality)
* Apparitional experience
* Ghost
Arts and entertainment Film and television
* ''Spectre'' (1977 film), a made-for-television film produced and wri ...
'' takes place largely above the Zocalo, as Bond takes command of a SPECTRE getaway helicopter. The scene is set against a Day of the Dead parade, which actually had never been held at the square before. However, after the film's release, the city officials decided to hold a Day of the Dead parade starting at the Angel of Independence
The Angel of Independence, most commonly known by the shortened name ''El Ángel'' and officially known as ''Monumento a la Independencia'' ("Monument to Independence"), is a victory column on a roundabout on the major thoroughfare of Paseo de ...
and finishing at the Zocalo square on 29 October 2016 using props and wardrobe from the film. The parade has been held every year since.
The release of the acoustic version of the ''Twenty One Pilots
Twenty One Pilots (stylized in all lowercase or as twenty øne piløts) are an American musical duo from Columbus, Ohio. Initially a band, the group was formed in 2009 by lead vocalist Tyler Joseph along with Nick Thomas and Chris Salih, who ...
'' song "Chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine i ...
" contains the coordinates to this location.
See also
* Statues of Pegasus, Mexico City, formerly installed in the plaza * Zócalo (Puebla)References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Zocalo Colonial Mexico Historic center of Mexico City History of Mexico City Independent Mexico Landmarks in Mexico City Mexican culture Modern Mexico National Monuments of Mexico National squares Olympic athletics venues Plazas in Mexico City Venues of the 1968 Summer Olympics