yeast infection on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Candidiasis is a


 Signs and symptoms of candidiasis vary depending on the area affected. Most candidal infections result in minimal complications such as redness, itching, and discomfort, though complications may be severe or even fatal if left untreated in certain populations. In healthy ( immunocompetent) persons, candidiasis is usually a localized infection of the skin, fingernails or toenails (onychomycosis), or mucosal membranes, including the
Signs and symptoms of candidiasis vary depending on the area affected. Most candidal infections result in minimal complications such as redness, itching, and discomfort, though complications may be severe or even fatal if left untreated in certain populations. In healthy ( immunocompetent) persons, candidiasis is usually a localized infection of the skin, fingernails or toenails (onychomycosis), or mucosal membranes, including the



 In oral candidiasis, simply inspecting the person's mouth for white patches and irritation may make the diagnosis. A sample of the infected area may also be taken to determine what organism is causing the infection.
Symptoms of vaginal candidiasis are also present in the more common
In oral candidiasis, simply inspecting the person's mouth for white patches and irritation may make the diagnosis. A sample of the infected area may also be taken to determine what organism is causing the infection.
Symptoms of vaginal candidiasis are also present in the more common
fungal infection
Fungal infection, also known as mycosis, is disease caused by fungi. Different types are traditionally divided according to the part of the body affected; superficial, subcutaneous, and systemic. Superficial fungal infections include common ti ...
due to any type of '' Candida'' (a type of yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constit ...
). When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth and throat. Other symptoms may include soreness and problems swallowing. When it affects the vagina, it may be referred to as a yeast infection or thrush. Signs and symptoms include genital itching, burning, and sometimes a white "cottage cheese-like" discharge from the vagina. Yeast infections of the penis are less common and typically present with an itchy rash. Very rarely, yeast infections may become invasive, spreading to other parts of the body. This may result in fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
s along with other symptoms depending on the parts involved.
More than 20 types of ''Candida'' can cause infection with ''Candida albicans
''Candida albicans'' is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usu ...
'' being the most common. Infections of the mouth are most common among children less than one month old, the elderly, and those with weak immune systems. Conditions that result in a weak immune system include HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ...
, the medications used after organ transplantation
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transpor ...
, diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
, and the use of corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are inv ...
s. Other risks include dentures, following antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
therapy, and breastfeeding. Vaginal infections occur more commonly during pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
, in those with weak immune systems, and following antibiotic use. Individuals at risk for invasive candidiasis
Invasive candidiasis is an infection (candidiasis) that can be caused by various species of ''Candida'' yeast. Unlike ''Candida'' infections of the mouth and throat ( oral candidiasis) or vagina ( ''Candidal'' vulvovaginitis), invasive candidia ...
include low birth weight babies, people recovering from surgery, people admitted to intensive care unit
220px, Intensive care unit
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensi ...
s, and those with an otherwise compromised immune system.
Efforts to prevent infections of the mouth include the use of chlorhexidine
Chlorhexidine (CHX) (commonly known by the salt forms chlorhexidine gluconate and chlorhexidine digluconate (CHG) or chlorhexidine acetate) is a disinfectant and antiseptic that is used for skin disinfection before surgery and to sterilize surgi ...
mouthwash in those with poor immune function and washing out the mouth following the use of inhaled steroids. Little evidence supports probiotic
Probiotics are live microorganisms promoted with claims that they provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the gut microbiota. Probiotics are considered generally safe to consume, but may cause bacteria-host i ...
s for either prevention or treatment, even among those with frequent vaginal infections. For infections of the mouth, treatment with topical
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ...
clotrimazole
Clotrimazole, sold under the brand name Lotrimin, among others, is an antifungal medication. It is used to treat vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, diaper rash, tinea versicolor, and types of ringworm including athlete's foot and jock ...
or nystatin is usually effective. Oral or intravenous fluconazole
Fluconazole is an antifungal medication used for a number of fungal infections. This includes candidiasis, blastomycosis, coccidiodomycosis, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, dermatophytosis, and pityriasis versicolor. It is also used to prev ...
, itraconazole, or amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcosis ...
may be used if these do not work. A number of topical antifungal medications may be used for vaginal infections, including clotrimazole. In those with widespread disease, an echinocandin such as caspofungin
Caspofungin (INN) (brand name Cancidas) is a lipopeptide antifungal drug from Merck & Co., Inc. discovered by James Balkovec, Regina Black and Frances A. Bouffard. It is a member of a new class of antifungals termed the echinocandins. It work ...
or micafungin is used. A number of weeks of intravenous amphotericin B may be used as an alternative. In certain groups at very high risk, antifungal medications may be used preventatively.
Infections of the mouth occur in about 6% of babies less than a month old. About 20% of those receiving chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemother ...
for cancer and 20% of those with AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ma ...
also develop the disease. About three-quarters of women have at least one yeast infection at some time during their lives. Widespread disease is rare except in those who have risk factors.
Signs and symptoms


 Signs and symptoms of candidiasis vary depending on the area affected. Most candidal infections result in minimal complications such as redness, itching, and discomfort, though complications may be severe or even fatal if left untreated in certain populations. In healthy ( immunocompetent) persons, candidiasis is usually a localized infection of the skin, fingernails or toenails (onychomycosis), or mucosal membranes, including the
Signs and symptoms of candidiasis vary depending on the area affected. Most candidal infections result in minimal complications such as redness, itching, and discomfort, though complications may be severe or even fatal if left untreated in certain populations. In healthy ( immunocompetent) persons, candidiasis is usually a localized infection of the skin, fingernails or toenails (onychomycosis), or mucosal membranes, including the oral cavity
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on t ...
and pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its st ...
(thrush
''The Man from U.N.C.L.E.'' is an American spy fiction television series produced by Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Television and first broadcast on NBC. The series follows secret agents, played by Robert Vaughn and David McCallum, who work for a secret ...
), esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to t ...
, and the genitalia (vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen ...
, penis
A penis (plural ''penises'' or ''penes'' () is the primary sexual organ that male animals use to inseminate females (or hermaphrodites) during copulation. Such organs occur in many animals, both vertebrate and invertebrate, but males d ...
, etc.); less commonly in healthy individuals, the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and ...
, urinary tract
The urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, c ...
, and respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to ...
are sites of candida infection.
In immunocompromised individuals, ''Candida'' infections in the esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to t ...
occur more frequently than in healthy individuals and have a higher potential of becoming systemic
Systemic fundamental to a predominant social, economic, or political practice. This refers to:
In medicine
In medicine, ''systemic'' means affecting the whole body, or at least multiple organ systems. It is in contrast with ''topical'' or ''loc ...
, causing a much more serious condition, a fungemia
Fungemia is the presence of fungi or yeasts in the blood. The most common type, also known as candidemia, candedemia, or systemic candidiasis, is caused by '' Candida'' species; candidemia is also among the most common bloodstream infections of ...
called candidemia. Symptoms of esophageal candidiasis include difficulty swallowing, painful swallowing, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
Mouth
Infection in the mouth is characterized by white discolorations in the tongue, around the mouth, and throat. Irritation may also occur, causing discomfort when swallowing. Thrush is commonly seen in infants. It is not considered abnormal in infants unless it lasts longer than a few weeks.Genitals
Infection of the vagina orvulva
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, vulv ...
may cause severe itching, burning, soreness, irritation, and a whitish or whitish-gray cottage cheese
Cottage cheese is a curdled milk product with a mild flavor and a creamy, non-homogeneous, soupy texture. It is made from skimmed milk by draining the cheese, as opposed to pressing it to make cheese curd—retaining some of the whey and keep ...
-like discharge. Symptoms of infection of the male genitalia (balanitis thrush) include red skin around the head of the penis, swelling, irritation, itchiness and soreness of the head of the penis, thick, lumpy discharge under the foreskin, unpleasant odour, difficulty retracting the foreskin ( phimosis), and pain when passing urine or during sex.
Skin
Signs and symptoms of candidiasis in the skin include itching, irritation, and chafing or broken skin.Invasive infection
Common symptoms of gastrointestinal candidiasis in healthy individuals are anal itching, belching, bloating, indigestion, nausea, diarrhea, gas, intestinal cramps, vomiting, andgastric ulcer
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines i ...
s. Perianal candidiasis can cause anal itching; the lesion can be red, papular, or ulcerative in appearance, and it is not considered to be a sexually transmissible disease. Abnormal proliferation of the candida in the gut may lead to dysbiosis
Dysbiosis (also called dysbacteriosis) is characterized by a disruption to the microbiome resulting in an imbalance in the microbiota, changes in their functional composition and metabolic activities, or a shift in their local distribution. For e ...
. While it is not yet clear, this alteration may be the source of symptoms generally described as the irritable bowel syndrome, and other gastrointestinal diseases.
Causes
''Candida'' yeasts are generally present in healthy humans, frequently part of the human body's normal oral and intestinal flora, and particularly on the skin; however, their growth is normally limited by the humanimmune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
and by competition of other microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in old ...
s, such as bacteria occupying the same locations in the human body.
''Candida'' requires moisture for growth, notably on the skin. For example, wearing wet swimwear for long periods of time is believed to be a risk factor. Candida can also cause diaper rashes in babies. In extreme cases, superficial infections of the skin or mucous membranes may enter the bloodstream and cause systemic ''Candida'' infections.
Factors that increase the risk of candidiasis include HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ma ...
, mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis (IM, mono), also known as glandular fever, is an infection usually caused by the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV). Most people are infected by the virus as children, when the disease produces few or no symptoms. In young adult ...
, cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
treatments, steroids
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and ...
, stress
Stress may refer to:
Science and medicine
* Stress (biology), an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition
* Stress (linguistics), relative emphasis or prominence given to a syllable in a word, or to a word in a phrase ...
, antibiotic usage, diabetes, and nutrient deficiency. Hormone replacement therapy and infertility treatments may also be predisposing factors. Use of inhaled corticosteroids increases risk of candidiasis of the mouth. Inhaled corticosteroids with other risk factors such as antibiotics, oral glucocorticoids, not rinsing mouth after use of inhaled corticosteroids or high dose of inhaled corticosteroids put people at even higher risk. Treatment with antibiotics can lead to eliminating the yeast's natural competitors for resources in the oral and intestinal flora, thereby increasing the severity of the condition. A weakened or undeveloped immune system or metabolic illnesses are significant predisposing factors of candidiasis. Almost 15% of people with weakened immune systems develop a systemic illness caused by ''Candida'' species. Diets high in simple carbohydrates
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or m ...
have been found to affect rates of oral candidiases.
''C. albicans'' was isolated from the vaginas of 19% of apparently healthy people, i.e., those who experienced few or no symptoms of infection. External use of detergents or douches or internal disturbances (hormonal or physiological) can perturb the normal vaginal flora
Vaginal flora, vaginal microbiota or vaginal microbiome are the microorganisms that colonize the vagina. They were discovered by the German gynecologist Albert Döderlein in 1892 and are part of the overall human flora.
The amount and type of ...
, consisting of lactic acid bacteria, such as lactobacilli
The ''Lactobacillaceae'' are a family of lactic acid bacteria. It is the only family in the lactic acid bacteria which includes homofermentative and heterofermentative organisms; in the ''Lactobacillaceae,'' the pathway used for hexose fermentati ...
, and result in an overgrowth of ''Candida'' cells, causing symptoms of infection, such as local inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
. Pregnancy and the use of oral contraceptives have been reported as risk factors. Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
and the use of antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and preventio ...
are also linked to increased rates of yeast infections.
In penile candidiasis, the causes include sexual intercourse with an infected individual, low immunity, antibiotics, and diabetes. Male genital yeast infections are less common, but a yeast infection on the penis caused from direct contact via sexual intercourse with an infected partner is not uncommon.
Breast-feeding mothers may also develop candidiasis on and around the nipple as a result of moisture created by excessive milk-production.
Vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen ...
l candidiasis can cause congenital candidiasis in newborns
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used t ...
.
Diagnosis



 In oral candidiasis, simply inspecting the person's mouth for white patches and irritation may make the diagnosis. A sample of the infected area may also be taken to determine what organism is causing the infection.
Symptoms of vaginal candidiasis are also present in the more common
In oral candidiasis, simply inspecting the person's mouth for white patches and irritation may make the diagnosis. A sample of the infected area may also be taken to determine what organism is causing the infection.
Symptoms of vaginal candidiasis are also present in the more common bacterial vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a disease of the vagina caused by excessive growth of bacteria. Common symptoms include increased vaginal discharge that often smells like fish. The discharge is usually white or gray in color. Burning with urinati ...
; aerobic vaginitis is distinct and should be excluded in the differential diagnosis. In a 2002 study, only 33% of women who were self-treating for a yeast infection actually had such an infection, while most had either bacterial vaginosis or a mixed-type infection.
Diagnosis of a yeast infection is done either via microscopic examination or culturing. For identification by light microscopy, a scraping or swab of the affected area is placed on a microscope slide. A single drop of 10% potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which exp ...
(KOH) solution is then added to the specimen. The KOH dissolves the skin cells, but leaves the ''Candida'' cells intact, permitting visualization of pseudohyphae
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium.
Structure
A hypha consists of one o ...
and budding yeast cell
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitu ...
s typical of many ''Candida'' species.
For the culturing method, a sterile swab is rubbed on the infected skin surface. The swab is then streaked on a culture medium. The culture is incubated at 37 °C (98.6 °F) for several days, to allow development of yeast or bacterial colonies. The characteristics (such as morphology and colour) of the colonies may allow initial diagnosis of the organism causing disease symptoms.
Respiratory, gastrointestinal, and esophageal candidiasis require an endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are inse ...
to diagnose. For gastrointestinal candidiasis, it is necessary to obtain a 3–5 milliliter sample of fluid from the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine m ...
for fungal culture. The diagnosis of gastrointestinal candidiasis is based upon the culture containing in excess of 1,000 colony-forming units
In microbiology, colony-forming unit (CFU, cfu or Cfu) is a unit which estimates the number of microbial cells ( bacteria, fungi, viruses etc.) in a sample that are viable, able to multiply via binary fission under the controlled conditions. Coun ...
per milliliter.
Classification
Candidiasis may be divided into these types: * Mucosal candidiasis **Oral candidiasis
Oral candidiasis, also known as oral thrush among other names, is candidiasis that occurs in the mouth. That is, oral candidiasis is a mycosis (yeast/fungal infection) of ''Candida'' species on the mucous membranes of the mouth.
''Candida albic ...
(thrush, oropharyngeal candidiasis)
*** Pseudomembranous candidiasis
*** Erythematous candidiasis
*** Hyperplastic candidiasis
*** Denture-related stomatitis — ''Candida'' organisms are involved in about 90% of cases
*** Angular cheilitis
Angular cheilitis (AC) is inflammation of one or both corners of the mouth. Often the corners are red with skin breakdown and crusting. It can also be itchy or painful. The condition can last for days to years. Angular cheilitis is a type of ch ...
— ''Candida'' species are responsible for about 20% of cases, mixed infection of ''C. albicans'' and ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posit ...
'' for about 60% of cases.
*** Median rhomboid glossitis
** Candidal vulvovaginitis (vaginal yeast infection)
** Candidal balanitis — infection of the glans penis, almost exclusively occurring in uncircumcised males
** Esophageal candidiasis (candidal esophagitis)
** Gastrointestinal candidiasis
** Respiratory candidiasis
* Cutaneous candidiasis
** Candidal folliculitis
Folliculitis is the infection and inflammation of one or more hair follicles. The condition may occur anywhere on hair-covered skin. The rash may appear as pimples that come to white tips on the face, chest, back, arms, legs, buttocks, or head.
A ...
** Candidal intertrigo
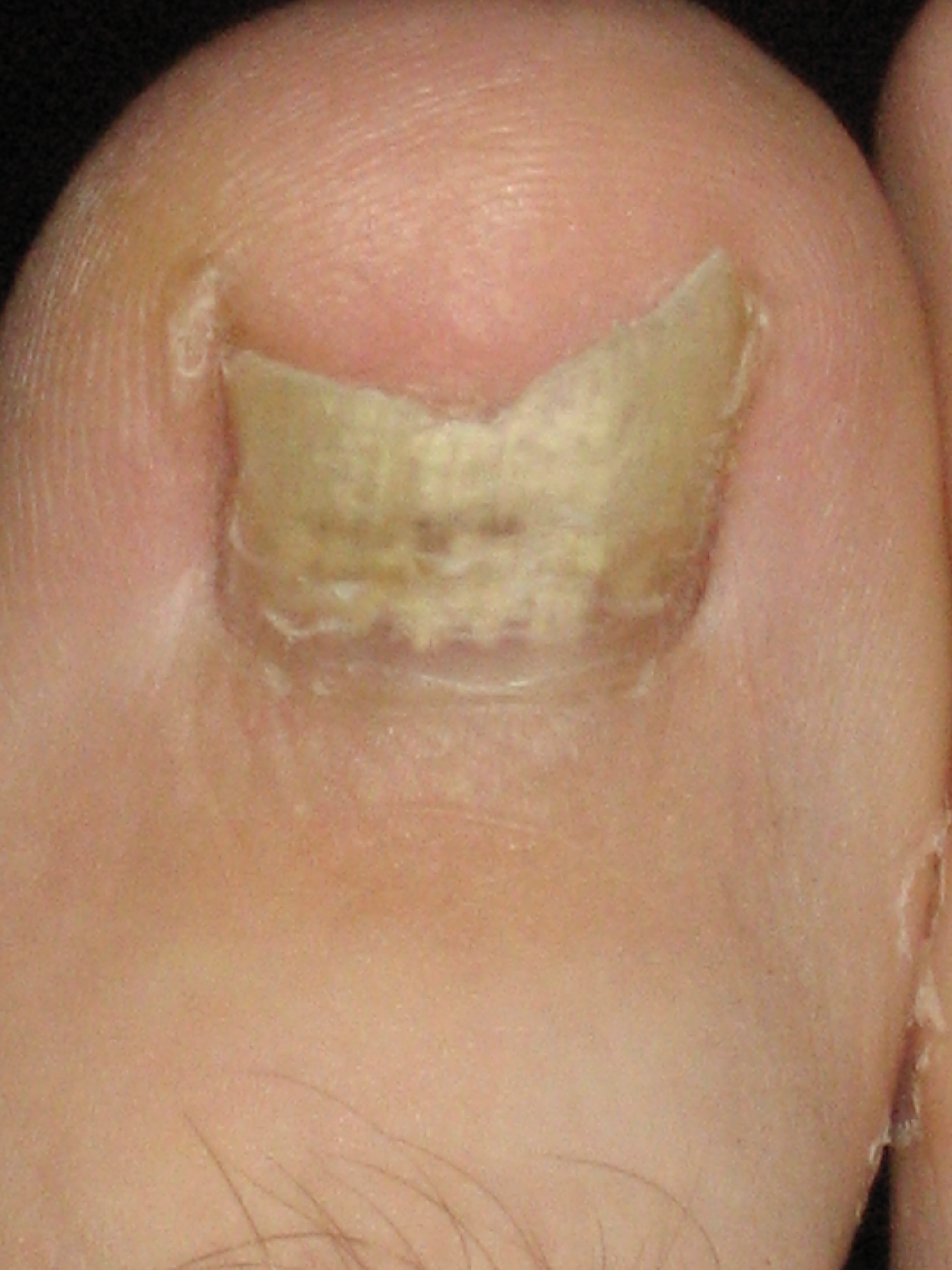
** Candidal paronychia
** Perianal candidiasis, may present as pruritus ani
Pruritus ani is the irritation of the skin at the exit of the rectum, known as the anus, causing the desire to scratch. The intensity of anal itching increases from moisture, pressure, and rubbing caused by clothing and sitting. At worst, anal i ...
** Candidid
Candidid is a skin condition, an id reaction, similar to dermatophytids.
See also
* Candidiasis
* List of cutaneous conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the ...
** Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis
** Congenital cutaneous candidiasis
** Diaper candidiasis: an infection of a child's diaper
A diaper /ˈdaɪpə(r)/ (American and Canadian English) or a nappy (Australian English, British English, and Hiberno-English) is a type of underwear that allows the wearer to urinate or defecate without using a toilet, by absorbing or cont ...
area
** Erosio interdigitalis blastomycetica
** Candidal onychomycosis (nail infection) caused by ''Candida''
* Systemic candidiasis
** Candidemia, a form of fungemia
Fungemia is the presence of fungi or yeasts in the blood. The most common type, also known as candidemia, candedemia, or systemic candidiasis, is caused by '' Candida'' species; candidemia is also among the most common bloodstream infections of ...
which may lead to sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
** Invasive candidiasis
Invasive candidiasis is an infection (candidiasis) that can be caused by various species of ''Candida'' yeast. Unlike ''Candida'' infections of the mouth and throat ( oral candidiasis) or vagina ( ''Candidal'' vulvovaginitis), invasive candidia ...
(disseminated candidiasis) — organ infection by ''Candida''
** Chronic systemic candidiasis (hepatosplenic candidiasis) — sometimes arises during recovery from neutropenia
Neutropenia is an abnormally low concentration of neutrophils (a type of white blood cell) in the blood. Neutrophils make up the majority of circulating white blood cells and serve as the primary defense against infections by destroying bacteri ...
* Antibiotic candidiasis (iatrogenic candidiasis)
Prevention
A diet that supports the immune system and is not high in simple carbohydrates contributes to a healthy balance of the oral and intestinal flora. While yeast infections are associated with diabetes, the level of blood sugar control may not affect the risk. Wearing cotton underwear may help to reduce the risk of developing skin and vaginal yeast infections, along with not wearing wet clothes for long periods of time. For women who experience recurrent yeast infections, there is limited evidence that oral or intravaginal probiotics help to prevent future infections. This includes either as pills or as yogurt. Oral hygiene can help prevent oral candidiasis when people have a weakened immune system. For people undergoing cancer treatment, chlorhexidine mouthwash can prevent or reduce thrush. People who use inhaled corticosteroids can reduce the risk of developing oral candidiasis by rinsing the mouth with water or mouthwash after using the inhaler. People with dentures should also disinfect their dentures regularly to prevent oral candidiasis.Treatment
Candidiasis is treated withantifungal medication
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryp ...
s; these include clotrimazole
Clotrimazole, sold under the brand name Lotrimin, among others, is an antifungal medication. It is used to treat vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, diaper rash, tinea versicolor, and types of ringworm including athlete's foot and jock ...
, nystatin, fluconazole
Fluconazole is an antifungal medication used for a number of fungal infections. This includes candidiasis, blastomycosis, coccidiodomycosis, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, dermatophytosis, and pityriasis versicolor. It is also used to prev ...
, voriconazole
Voriconazole, sold under the brand name Vfend among others, is an antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. This includes aspergillosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, penicilliosis, and infections by ' ...
, amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcosis ...
, and echinocandins. Intravenous fluconazole or an intravenous echinocandin such as caspofungin
Caspofungin (INN) (brand name Cancidas) is a lipopeptide antifungal drug from Merck & Co., Inc. discovered by James Balkovec, Regina Black and Frances A. Bouffard. It is a member of a new class of antifungals termed the echinocandins. It work ...
are commonly used to treat immunocompromised or critically ill individuals.
The 2016 revision of the clinical practice guideline for the management of candidiasis lists a large number of specific treatment regimens for ''Candida'' infections that involve different ''Candida'' species, forms of antifungal drug resistance, immune statuses, and infection localization and severity. Gastrointestinal candidiasis in immunocompetent individuals is treated with 100–200 mg fluconazole per day for 2–3 weeks.
Localized infection
Mouth and throat candidiasis are treated with antifungal medication. Oral candidiasis usually responds to topical treatments; otherwise, systemic antifungal medication may be needed for oral infections. Candidal skin infections in the skin folds (candidal intertrigo) typically respond well to topical antifungal treatments (e.g., nystatin or miconazole). For breastfeeding mothers topical miconazole is the most effective treatment for treating candidiasis on the breasts. Gentian violet can be used for thrush inbreastfeeding
Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be expressed by hand or pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that bre ...
babies. Systemic treatment with antifungals by mouth is reserved for severe cases or if treatment with topical therapy is unsuccessful. Candida esophagitis may be treated orally or intravenously; for severe or azole-resistant esophageal candidiasis, treatment with amphotericin B may be necessary.
Vaginal yeast infections are typically treated with topical antifungal agents. Penile yeast infections are also treated with antifungal agents, but while an internal treatment may be used (such as a pessary) for vaginal yeast infections, only external treatments – such as a cream – can be recommended for penile treatment. A one-time dose of fluconazole by mouth is 90% effective in treating a vaginal yeast infection. For severe nonrecurring cases, several doses of fluconazole is recommended. Local treatment may include vaginal suppositories or medicated douches. Other types of yeast infections require different dosing. ''C. albicans'' can develop resistance to fluconazole, this being more of an issue in those with HIV/AIDS who are often treated with multiple courses of fluconazole for recurrent oral infections.
For vaginal yeast infection in pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
, topical imidazole
Imidazole (ImH) is an organic compound with the formula C3N2H4. It is a white or colourless solid that is soluble in water, producing a mildly alkaline solution. In chemistry, it is an aromatic heterocycle, classified as a diazole, and has non ...
or triazole
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within ...
antifungals are considered the therapy of choice owing to available safety data. Systemic absorption of these topical formulations is minimal, posing little risk of transplacental transfer. In vaginal yeast infection in pregnancy, treatment with topical azole antifungals is recommended for seven days instead of a shorter duration.
For vaginal yeast infections, many complementary treatments are proposed, however a number have side effects. No benefit from probiotics has been found for active infections.
Blood infection
Treatment typically consists of oral orintravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrie ...
antifungal medications. In candidal infections of the blood, intravenous fluconazole or an echinocandin such as caspofungin
Caspofungin (INN) (brand name Cancidas) is a lipopeptide antifungal drug from Merck & Co., Inc. discovered by James Balkovec, Regina Black and Frances A. Bouffard. It is a member of a new class of antifungals termed the echinocandins. It work ...
may be used. Amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcosis ...
is another option.
Prognosis
Among individuals being treated inintensive care unit
220px, Intensive care unit
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensi ...
s, the mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of d ...
is about 30–50% when systemic candidiasis develops.
Epidemiology
Oral candidiasis is the most common fungal infection of the mouth, and it also represents the most common opportunistic oral infection in humans. Infections of the mouth occur in about 6% of babies less than a month old. About 20% of those receivingchemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemother ...
for cancer and 20% of those with AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ma ...
also develop the disease.
It is estimated that 20% of women may be asymptomatically colonized by vaginal yeast. In the United States there are approximately 1.4 million doctor office visits every year for candidiasis. About three-quarters of women have at least one yeast infection at some time during their lives.
Esophageal candidiasis is the most common esophageal infection in persons with AIDS and accounts for about 50% of all esophageal infections, often coexisting with other esophageal diseases. About two-thirds of people with AIDS and esophageal candidiasis also have oral candidiasis.
Candidal sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
is rare. Candida is the fourth most common cause of bloodstream infections among hospital patients in the United States. The incidence of bloodstream candida in intensive care units varies widely between countries.
History
Descriptions of what sounds like oral thrush go back to the time ofHippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history o ...
''circa'' 460–370 BCE.
The first description of a fungus as the causative agent of an oropharyngeal and oesophageal candidosis was by Bernhard von Langenbeck in 1839.
Vulvovaginal candidiasis was first described in 1849 by Wilkinson. In 1875, Haussmann demonstrated the causative organism in both vulvovaginal and oral candidiasis is the same.
With the advent of antibiotics following World War II, the rates of candidiasis increased. The rates then decreased in the 1950s following the development of nystatin.
The colloquial term "thrush" refers to the resemblance of the white flecks present in some forms of candidiasis (e.g., pseudomembranous candidiasis) with the breast of the bird of the same name. The term candidosis is largely used in British English, and candidiasis in American English. ''Candida'' is also pronounced differently; in American English, the stress is on the "i", whereas in British English the stress is on the first syllable.
The genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ...
''Candida'' and species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriat ...
''C. albicans'' were described by botanist Christine Marie Berkhout in her doctoral thesis at the University of Utrecht in 1923. Over the years, the classification of the genera and species has evolved. Obsolete names for this genus include ''Mycotorula'' and ''Torulopsis''. The species has also been known in the past as ''Monilia albicans'' and ''Oidium albicans''. The current classification is ''nomen conservandum
Nomen may refer to:
* Nomen (Roman name), the middle part of Ancient Roman names
* Nomen (Ancient Egypt), the personal name of Ancient Egyptian pharaohs
* Jaume Nomen (born 1960), Catalan astronomer
*Nomen, Latin for a certain part of speech
*Nom ...
'', which means the name is authorized for use by the International Botanical Congress (IBC).
The genus ''Candida'' includes about 150 different species. However, only a few are known to cause human infections. ''C. albicans'' is the most significant pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a g ...
ic species. Other species pathogenic in humans include ''C. auris'', ''C. tropicalis'', ''C. glabrata'', ''C. krusei'', ''C. parapsilosis'', ''C. dubliniensis'', and ''C. lusitaniae''.
The name ''Candida'' was proposed by Berkhout. It is from the Latin word ''toga candida'', referring to the white toga
The toga (, ), a distinctive garment of ancient Rome, was a roughly semicircular cloth, between in length, draped over the shoulders and around the body. It was usually woven from white wool, and was worn over a tunic. In Roman historical tra ...
(robe) worn by candidates for the Senate of the ancient Roman republic. The specific epithet ''albicans'' also comes from Latin, ''albicare'' meaning "to whiten". These names refer to the generally white appearance of ''Candida'' species when cultured.
Alternative medicine
A 2005 publication noted that "a largepseudoscientific
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable claim ...
cult" has developed around the topic of ''Candida'', with claims stating that up to one in three people are affected by yeast-related illness, particularly a condition called "Candidiasis hypersensitivity". Some practitioners of alternative medicine have promoted these purported conditions and sold dietary supplements as supposed cures; a number of them have been prosecuted. In 1990, alternative health vendor Nature's Way signed an FTC consent agreement not to misrepresent in advertising any self-diagnostic test concerning yeast conditions or to make any unsubstantiated representation concerning any food or supplement's ability to control yeast conditions, with a fine of $30,000 payable to the National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the lat ...
for research in genuine candidiasis.
Research
High level ''Candida'' colonization is linked to several diseases of the gastrointestinal tract includingCrohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distensi ...
.
There has been an increase in resistance to antifungals worldwide over the past 30–40 years.
References
External links
* * {{Authority control Animal fungal diseases Bird diseases Bovine diseases Horse diseases Mycosis-related cutaneous conditions Sheep and goat diseases Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate Fungal diseases