Washout (aviation) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
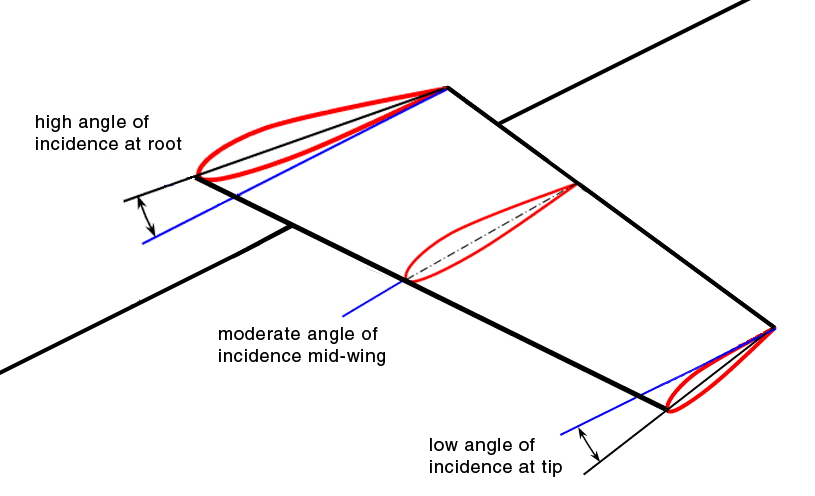
 Washout is a characteristic of
Washout is a characteristic of

 Washout is a characteristic of
Washout is a characteristic of aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or by using the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in ...
wing
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is e ...
design which deliberately reduces the lift distribution across the span of an aircraft’s wing. The wing is designed so that the angle of incidence is greater at the wing roots and decreases across the span, becoming lowest at the wing tip. This is usually to ensure that at stall speed the wing root stalls before the wing tips, providing the aircraft with continued aileron control and some resistance to spinning. Washout may also be used to modify the spanwise lift distribution to reduce lift-induced drag
In aerodynamics, lift-induced drag, induced drag, vortex drag, or sometimes drag due to lift, is an aerodynamic drag force that occurs whenever a moving object redirects the airflow coming at it. This drag force occurs in airplanes due to wings o ...
.
Design considerations
Washout is commonly achieved by designing thewing
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is e ...
with a slight twist
Twist may refer to:
In arts and entertainment Film, television, and stage
* ''Twist'' (2003 film), a 2003 independent film loosely based on Charles Dickens's novel ''Oliver Twist''
* ''Twist'' (2021 film), a 2021 modern rendition of ''Olive ...
, reducing the angle of incidence from root to tip, and therefore causing a lower angle of attack at the tips than at the roots. This feature is sometimes referred to as structural washout, to distinguish it from aerodynamic washout.
Wingtip stall is unlikely to occur symmetrically, especially if the aircraft is maneuvering. As an aircraft turns, the wing tip on the inside of the turn is moving more slowly and is most likely to stall. As an aircraft rolls, the descending wing tip is at higher angle of attack and is most likely to stall. When one wing tip stalls it leads to wing drop, a rapid rolling motion. Also, roll control may be reduced if the airflow over the ailerons is disrupted by the stall, reducing their effectiveness.
On aircraft with swept wing
A swept wing is a wing that angles either backward or occasionally forward from its root rather than in a straight sideways direction.
Swept wings have been flown since the pioneer days of aviation. Wing sweep at high speeds was first investiga ...
s, wing tip stall also produces an undesirable nose-up pitching moment which hampers recovery from the stall.
Washout may be accomplished by other means e.g. modified aerofoil section, vortex generators, leading edge wing fences, notches, or stall strips. This is referred to as aerodynamic washout. Its purpose is to tailor the spanwise lift distribution or reduce the probability of wing tip stall.
Winglets have the opposite effect to washout. Winglets allow a greater proportion of lift to be generated near the wing tips. (This can be described as aerodynamic wash-in.) Winglets also promote a greater bending moment at the wing root, possibly necessitating a heavier wing structure. Installation of winglets may necessitate greater aerodynamic washout in order to provide the required resistance to spinning, or to optimise the spanwise lift distribution.
The reverse twist (higher incidence at wingtip), wash-in, can also be found in some designs though less common. The Grumman X-29 had strong wash-in to compensate for the additional root-first stalling promoted by the forward sweep.
Washout near the tips can also be used to decrease lift-induced drag, since at a lower angle of incidence, the lift produced will be lower, and thus the component of that lift which acts against thrust is reduced, however, it has been theorised by Albion H. Bowers that certain washout characteristics in the tips, that lead to a bell-shaped span loading may in fact produce lift-induced thrust, and upwash. He thus suggests that birds do not utilise vertical stabilisers, since they do not need to counteract adverse yaw caused by lift-induced drag.
Washout is also found in glider
Glider may refer to:
Aircraft and transport Aircraft
* Glider (aircraft), heavier-than-air aircraft primarily intended for unpowered flight
** Glider (sailplane), a rigid-winged glider aircraft with an undercarriage, used in the sport of gliding
...
s and hang glider
Hang gliding is an air sport or recreational activity in which a pilot flies a light, non-motorised foot-launched heavier-than-air aircraft called a hang glider. Most modern hang gliders are made of an aluminium alloy or composite frame covered ...
s.
In helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attribu ...
s, blade twist is used to reduce lift towards the blade tip, thus reducing unequal rotor lift distribution.
See also
* Wing twist * Stall (flight) * Spin (flight) * Unequal rotor lift distributionReferences
{{ReflistExternal links
* http://www.allstar.fiu.edu/aero/Wing32.htm * http://www.fly-imaa.org/imaa/hfarticles/const/v1-4-10.html *http://www.propdesigner.co.uk/html/washout_and_washin.html Aerodynamics Aircraft wing design