virtuous cycle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
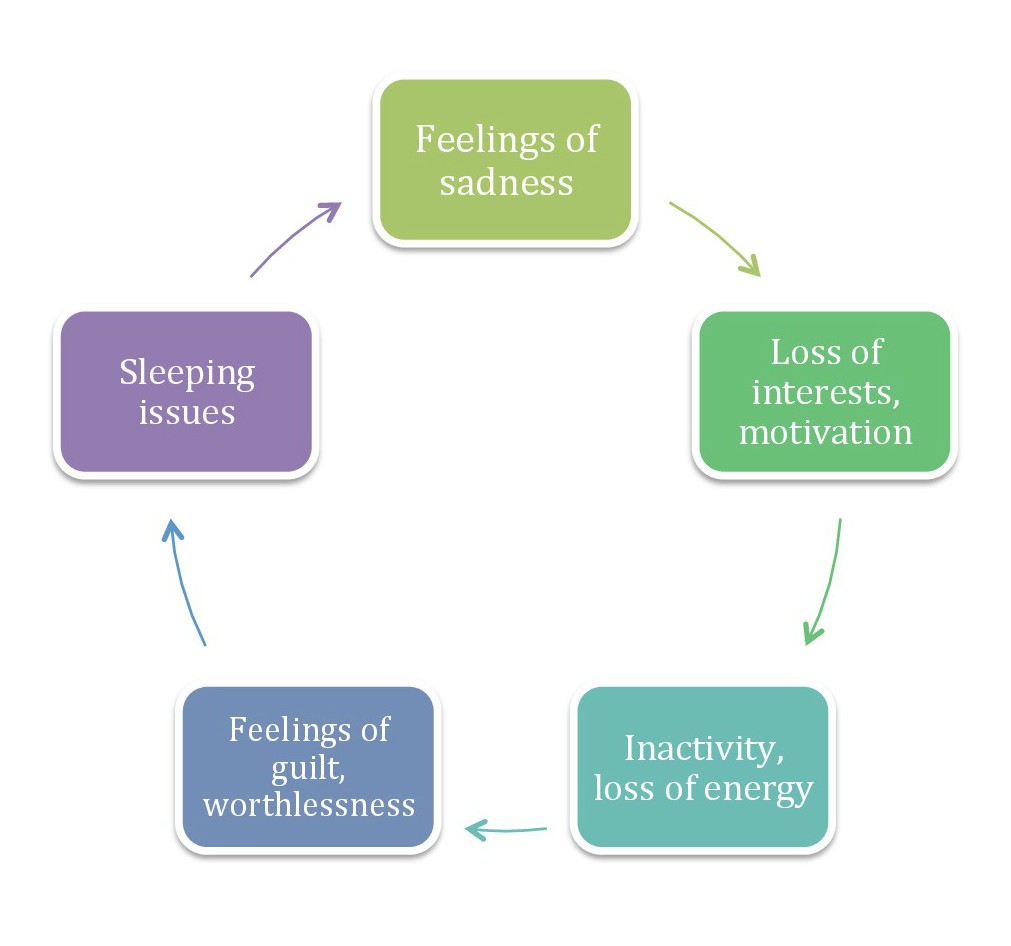 A vicious circle (or cycle) is a complex
A vicious circle (or cycle) is a complex
Rational Choice with Passion:Virtue in a Model of Rational Addiction
– In this link the author uses Aristotelian virtue as a mediator between passion and reason in the construction of utility/consumption functions in an esoteric part of consumer behaviour theory related to decision making in addictive situations.
China: A Stabilizing or Deflationary Influence in East Asia? The Problem of Conflicted Virtue
– In this paper the author is using virtue in the sense of a positive outcome (balance of payments surplus) that conflicts with long term regional growth and stability.
 A vicious circle (or cycle) is a complex
A vicious circle (or cycle) is a complex chain of events
A chain of events is a number of actions and their effects that are contiguous and linked together that results in a particular outcome. In the physical sciences, chain reactions are a primary example.
Determinism
''Determinism'' is the philo ...
that reinforces itself through a feedback loop
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause-and-effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handled c ...
, with detrimental results. It is a system with no tendency toward equilibrium (social
Social organisms, including human(s), live collectively in interacting populations. This interaction is considered social whether they are aware of it or not, and whether the exchange is voluntary or not.
Etymology
The word "social" derives from ...
, economic
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the ...
, ecological
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps wi ...
, etc.), at least in the short run. Each iteration of the cycle reinforces the previous one, in an example of positive feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in th ...
. A vicious circle will continue in the direction of its momentum until an external factor intervenes to break the cycle.
A well-known example of a vicious circle in economics is hyperinflation
In economics, hyperinflation is a very high and typically accelerating inflation. It quickly erodes the real value of the local currency, as the prices of all goods increase. This causes people to minimize their holdings in that currency as t ...
.
A virtuous circle is an equivalent system with a favorable outcome.
Examples
Vicious circles in the subprime mortgage crisis
The contemporary subprime mortgage crisis is a complex group of vicious circles, both in its genesis and in its manifold outcomes, most notably thelate 2000s recession
The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline, i.e. a recession, observed in national economies globally that occurred from late 2007 into 2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At t ...
. A specific example is the circle related to housing. As housing prices decline, more homeowners go " underwater", when the market value of a home drops below that of the mortgage on it. This provides an incentive to walk away from the home, increasing defaults and foreclosures. This, in turn, lowers housing values further from over-supply, reinforcing the cycle.
The foreclosures reduce the cash flowing into banks and the value of mortgage-backed securities (MBS) widely held by banks. Banks incur losses and require additional funds, also called “recapitalization”. If banks are not capitalized sufficiently to lend, economic activity slows and unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the refere ...
increases, which further increase the number of foreclosures.
Economist Nouriel Roubini
Nouriel Roubini (born March 9 1958) is a Turkish-born Iranian-American economist. He is Professor Emeritus (2021–present) and was Professor of Economics (1995–2021) at the Stern School of Business, New York University, and also chairman of Ro ...
described the vicious circles within and across the housing market and financial markets during interviews with Charlie Rose in September and October 2008.
Designing ecological virtuous circles
By involving all stakeholders in managing ecological areas, a virtuous circle can be created where improved ecology encourages the actions that maintain and improve the area.Other
Other examples include thepoverty cycle
In economics, a cycle of poverty or poverty trap is caused by self-reinforcing mechanisms that cause poverty, once it exists, to persist unless there is outside intervention. It can persist across generations, and when applied to developing count ...
, sharecropping
Sharecropping is a legal arrangement with regard to agricultural land in which a landowner allows a tenant to use the land in return for a share of the crops produced on that land.
Sharecropping has a long history and there are a wide range ...
, and the intensification of drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
. The recurring surges of the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
is a vicious circle on a global scale.
See also
*Catch-22 (logic)
A catch-22 is a paradoxical situation from which an individual cannot escape because of contradictory rules or limitations. The term was coined by Joseph Heller, who used it in his 1961 novel ''Catch-22''. An example is Brantley Foster in '' The S ...
* Causal loop diagram
A causal loop diagram (CLD) is a causal diagram that aids in visualizing how different variables in a system are causally interrelated. The diagram consists of a set of words and arrows. Causal loop diagrams are accompanied by a narrative which de ...
* Chain reaction
A chain reaction is a sequence of reactions where a reactive product or by-product causes additional reactions to take place. In a chain reaction, positive feedback leads to a self-amplifying chain of events.
Chain reactions are one way that sys ...
* Cycle of poverty
In economics, a cycle of poverty or poverty trap is caused by self-reinforcing mechanisms that cause poverty, once it exists, to persist unless there is outside intervention. It can persist across generations, and when applied to developing count ...
* Cycle of violence
* Closed timelike curve
In mathematical physics, a closed timelike curve (CTC) is a world line in a Lorentzian manifold, of a material particle in spacetime, that is "closed", returning to its starting point. This possibility was first discovered by Willem Jacob van St ...
* Endogeneity (econometrics)
* Positive feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in th ...
* Rational addiction In behavioral economics, rational addiction is the hypothesis that addictions can be usefully modeled as specific kinds of rational, forward-looking, optimal consumption plans. The canonical theory comes from work done by Kevin M. Murphy and Gary ...
* Reflexivity (sociology)
In epistemology, and more specifically, the sociology of knowledge, reflexivity refers to circular relationships between cause and effect, especially as embedded in human belief structures. A reflexive relationship is bidirectional with both the ...
* Self-fulfilling prophecy
* Spiral of silence
The spiral of silence theory is a political science and mass communication theory proposed by the German political scientist Elisabeth Noelle-Neumann. It states that an individual's perception of the distribution of public opinion influences that ...
* Unintended consequences
In the social sciences, unintended consequences (sometimes unanticipated consequences or unforeseen consequences) are outcomes of a purposeful action that are not intended or foreseen. The term was popularised in the twentieth century by Ameri ...
References
General and cited references
*Rational Choice with Passion:Virtue in a Model of Rational Addiction
– In this link the author uses Aristotelian virtue as a mediator between passion and reason in the construction of utility/consumption functions in an esoteric part of consumer behaviour theory related to decision making in addictive situations.
China: A Stabilizing or Deflationary Influence in East Asia? The Problem of Conflicted Virtue
– In this paper the author is using virtue in the sense of a positive outcome (balance of payments surplus) that conflicts with long term regional growth and stability.
External links
* * * * {{Wiktionary inline, virtuous circle Business cycle Economic crises Vicious circle