Video quality on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Video quality is a characteristic of a
 Objective models can be classified by the amount of information available about the original signal, the received signal, or whether there is a signal present at all:
* Full Reference Methods (FR): FR models compute the quality difference by comparing the original video signal against the received
Objective models can be classified by the amount of information available about the original signal, the received signal, or whether there is a signal present at all:
* Full Reference Methods (FR): FR models compute the quality difference by comparing the original video signal against the received
VQM
or the MOVIE Index, may be able to produce more accurate predictions of human-perceived quality.
NORM
.
P.1201
2012 * ITU-T Rec
P.1202
2012 * ITU-T Rec
P.1203.1
2016 *ITU-T Rec
P.1204.3
2020
Laboratory for Image and Video Engineering (LIVE)
as well th
A collection of databases can be found in th
QUALINET Databases
repository. Th
Consumer Digital Video Library
(CDVL) hosts freely available video test sequences for model development. In theory, a model can be trained on a set of data in such a way that it produces perfectly matching scores on that dataset. However, such a model will be over-trained and will therefore not perform well on new datasets. It is therefore advised to validate models against new data and use the resulting performance as a real indicator of the model's prediction accuracy. To measure the performance of a model, some frequently used metrics are the linear correlation coefficient,
P.1401
gives an overview of statistical procedures to evaluate and compare objective models.
BT.500
and ITU-T recommendatio
P.910
In such tests, video sequences are shown to a group of viewers. The viewers' opinion is recorded and averaged into the
Interpretation of objective video quality metrics
ITU-R recommendations on subjective video quality
ITU-T recommendations on objective and subjective video quality
Noise (graphics) Film and video technology Digital television Video codecs Codecs
video
Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) syst ...
passed through a video transmission or processing system that describes perceived video degradation (typically, compared to the original video). Video processing systems may introduce some amount of distortion or artifacts in the video signal that negatively impacts the user's perception of a system. For many stakeholders in video production
Video production is the process of producing video content for video. It is the equivalent of filmmaking, but with video recorded either as analog signals on videotape, digitally in video tape or as computer files stored on optical discs, hard dri ...
and distribution, assurance of video quality is an important task.
Video quality evaluation is performed to describe the quality of a set of video sequences under study. Video quality can be evaluated objectively (by mathematical models) or subjectively (by asking users for their rating). Also, the quality of a system can be determined offline (i.e., in a laboratory setting for developing new codecs or services), or in-service (to monitor and ensure a certain level of quality).
From analog to digital video
Since the world's first video sequence was recorded and transmitted, many video processing systems have been designed. Such systems encode video streams and transmit them over various kinds of networks or channels. In the ages ofanalog video
Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying
Copying is the duplication of information or an artifact based on an instance of that information or artifact, and not using the process that originally generated it. With analog f ...
systems, it was possible to evaluate the quality aspects of a video processing system by calculating the system's frequency response
In signal processing and electronics, the frequency response of a system is the quantitative measure of the magnitude and phase of the output as a function of input frequency. The frequency response is widely used in the design and analysis of s ...
using test signals (for example, a collection of color bars and circles).
Digital video systems have almost fully replaced analog ones, and quality evaluation methods have changed. The performance of a digital video processing and transmission system can vary significantly and depends on many factors including the characteristics of the input video signal (e.g. amount of motion or spatial details), the settings used for encoding and transmission, and the channel fidelity or network performance
Network performance refers to measures of service quality of a network as seen by the customer.
There are many different ways to measure the performance of a network, as each network is different in nature and design. Performance can also be model ...
.
Objective video quality
Objective video quality models are mathematical models that approximate results from subjective quality assessment, in which human observers are asked to rate the quality of a video. In this context, the term ''model'' may refer to a simple statistical model in which several independent variables (e.g. the packet loss rate on a network and the video coding parameters) are fit against results obtained in a subjective quality evaluation test using regression techniques. A model may also be a more complicated algorithm implemented insoftware
Software is a set of computer programs and associated software documentation, documentation and data (computing), data. This is in contrast to Computer hardware, hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
...
or hardware.
Terminology
The terms ''model'' and ''metric'' are often used interchangeably in the field to mean a descriptive statistic which provides anindicator
Indicator may refer to:
Biology
* Environmental indicator of environmental health (pressures, conditions and responses)
* Ecological indicator of ecosystem health (ecological processes)
* Health indicator, which is used to describe the health ...
of quality. The term “objective” relates to the fact that, in general, quality models are based on criteria that can be ''measured'' objectively – that is, free from human interpretation. They can be automatically evaluated by a computer program
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. Computer programs are one component of software, which also includes documentation and other intangible components.
A computer program ...
. Unlike a panel of human observers, an objective model should always deterministically output the same quality score for a given set of input parameters.
Objective quality models are sometimes also referred to as ''instrumental (quality) models'', in order to emphasize their application as measurement instruments. Some authors suggest that the term “objective” is misleading, as it “implies that instrumental measurements bear objectivity, which they only do in case that they can be generalized.”
Classification of objective video quality models

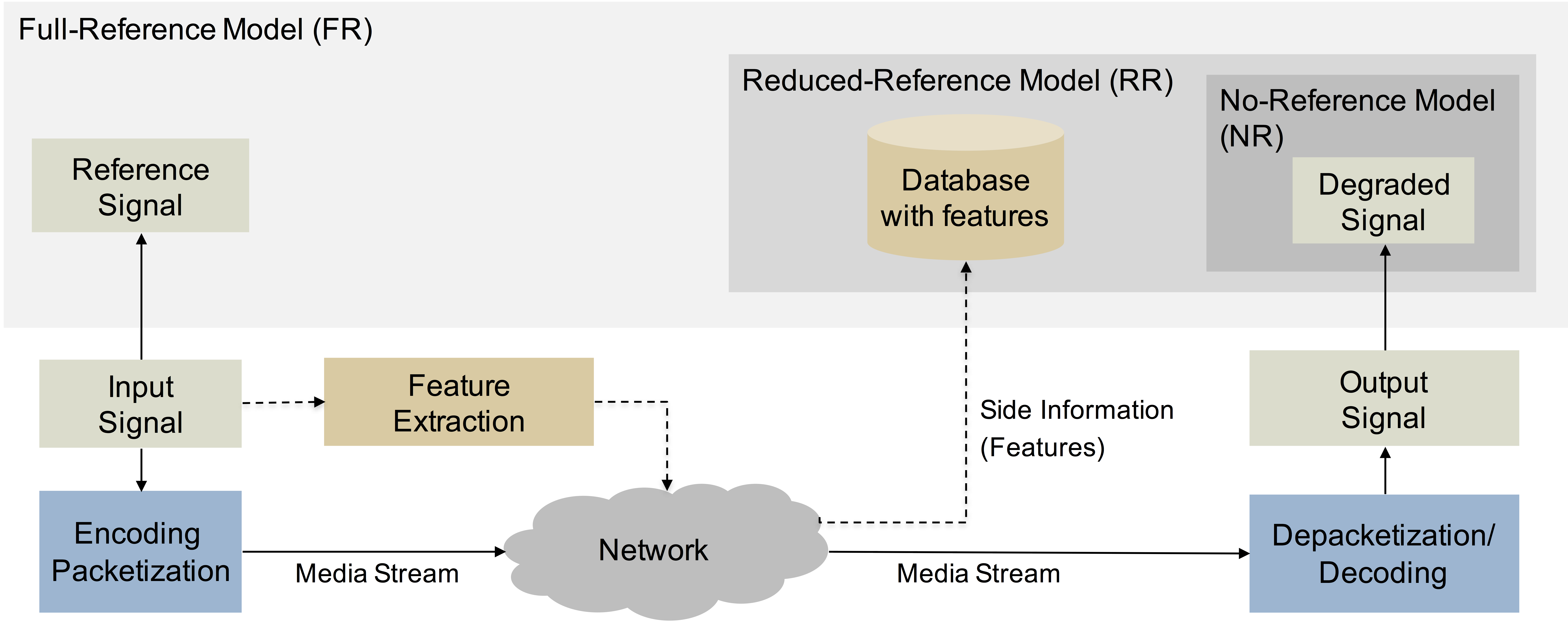
 Objective models can be classified by the amount of information available about the original signal, the received signal, or whether there is a signal present at all:
* Full Reference Methods (FR): FR models compute the quality difference by comparing the original video signal against the received
Objective models can be classified by the amount of information available about the original signal, the received signal, or whether there is a signal present at all:
* Full Reference Methods (FR): FR models compute the quality difference by comparing the original video signal against the received video signal
Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) sy ...
. Typically, every pixel from the source is compared against the corresponding pixel at the received video, with no knowledge about the encoding or transmission process in between. More elaborate algorithms may choose to combine the pixel-based estimation with other approaches such as described below. FR models are usually the most accurate at the expense of higher computational effort. As they require availability of the original video before transmission or coding, they cannot be used in all situations (e.g., where the quality is measured from a client device).
* Reduced Reference Methods (RR): RR models extract some features of both videos and compare them to give a quality score. They are used when all the original video is not available, or when it would be practically impossible to do so, e.g. in a transmission with a limited bandwidth. This makes them more efficient than FR models at the expense of lower accuracy.
* No-Reference Methods (NR): NR models try to assess the quality of a distorted video without any reference to the original signal. Due to the absence of an original signal, they may be less accurate than FR or RR approaches, but are more efficient to compute.
** Pixel-Based Methods (NR-P): Pixel-based models use a decoded representation of the signal and analyze the quality based on the pixel information. Some of these evaluate specific degradation types only, such as blurring or other coding artifacts.
** Parametric/Bitstream Methods (NR-B): These models make use of features extracted from the transmission container and/or video bitstream, e.g. MPEG-TS
MPEG transport stream (MPEG-TS, MTS) or simply transport stream (TS) is a standard digital container format for transmission and storage of audio, video, and Program and System Information Protocol (PSIP) data. It is used in broadcast syste ...
packet headers, motion vectors and quantization parameters. They do not have access to the original signal and require no decoding of the video, which makes them more efficient. In contrast to NR-P models, they have no access to the final decoded signal. However, the picture quality predictions they deliver are not very accurate.
** Hybrid Methods (Hybrid NR-P-B): Hybrid models combine parameters extracted from the bitstream with a decoded video signal. They are therefore a mix between NR-P and NR-B models.
Use of picture quality models for video quality estimation
Some models that are used for video quality assessment (such asPSNR
Peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) is an engineering term for the ratio between the maximum possible power of a Signal (information theory), signal and the power of corrupting noise that affects the fidelity of its representation. Because many sign ...
or SSIM) are simply image quality models, whose output is calculated for every frame of a video sequence. This quality measure of every frame can then be recorded and pooled over time to assess the quality of an entire video sequence. While this method is easy to implement, it does not factor in certain kinds of degradations that develop over time, such as the moving artifacts caused by packet loss
Packet loss occurs when one or more packets of data travelling across a computer network fail to reach their destination. Packet loss is either caused by errors in data transmission, typically across wireless networks, or network congestion.Kur ...
and its concealment. A video quality model that considers the temporal aspects of quality degradations, likVQM
or the MOVIE Index, may be able to produce more accurate predictions of human-perceived quality.
Examples
In Addition
An overview of recent no-referenceimage quality Image quality can refer to the level of accuracy with which different imaging systems capture, process, store, compress, transmit and display the signals that form an image. Another definition refers to image quality as "the weighted combination of ...
models has been given in a journal paper by Shahid et al. As mentioned above, these can be used for video applications as well. The Video Quality Experts Group has a dedicated working group on developing no-reference metrics (calleNORM
.
Bitstream-based metrics
Full or reduced-reference metrics still require access to the original video bitstream before transmission or at least part of it. In practice, an original stream may not always be available for comparison, for example when measuring the quality from the user side. In other situations, a network operator may want to measure the quality of video streams passing through their network, without fully decoding them. For a more efficient estimation of video quality in such cases, parametric/bitstream-based metrics have also been standardized: * ITU-T RecP.1201
2012 * ITU-T Rec
P.1202
2012 * ITU-T Rec
P.1203.1
2016 *ITU-T Rec
P.1204.3
2020
Benchmarks
Training and performance evaluation
Since objective video quality models are expected to predict results given by human observers, they are developed with the aid of subjective test results. During the development of an objective model, its parameters should be trained so as to achieve the best correlation between the objectively predicted values and the subjective scores, often available asmean opinion score Mean opinion score (MOS) is a measure used in the domain of Quality of Experience and telecommunications engineering, representing overall quality of a stimulus or system. It is the arithmetic mean over all individual "values on a predefined scale t ...
s (MOS).
The most widely used subjective test materials are in the public domain and include still pictures, motion pictures, streaming video, high definition, 3-D (stereoscopic), and special-purposes picture quality-related datasets. These so-called databases are created by various research laboratories around the world. Some of them have become de facto standards, including several public-domain subjective picture quality databases created and maintained by thLaboratory for Image and Video Engineering (LIVE)
as well th
A collection of databases can be found in th
QUALINET Databases
repository. Th
Consumer Digital Video Library
(CDVL) hosts freely available video test sequences for model development. In theory, a model can be trained on a set of data in such a way that it produces perfectly matching scores on that dataset. However, such a model will be over-trained and will therefore not perform well on new datasets. It is therefore advised to validate models against new data and use the resulting performance as a real indicator of the model's prediction accuracy. To measure the performance of a model, some frequently used metrics are the linear correlation coefficient,
Spearman's rank correlation coefficient
In statistics, Spearman's rank correlation coefficient or Spearman's ''ρ'', named after Charles Spearman and often denoted by the Greek letter \rho (rho) or as r_s, is a nonparametric measure of rank correlation ( statistical dependence betwee ...
, and the root mean square error (RMSE). Other metrics are the kappa coefficient and the outliers ratio. ITU-T RecP.1401
gives an overview of statistical procedures to evaluate and compare objective models.
Uses and application of objective models
Objective video quality models can be used in various application areas. Invideo codec
A video codec is software or hardware that compresses and decompresses digital video. In the context of video compression, ''codec'' is a portmanteau of ''encoder'' and ''decoder'', while a device that only compresses is typically called an '' ...
development, the performance of a codec is often evaluated in terms of PSNR or SSIM. For service providers, objective models can be used for monitoring a system. For example, an IPTV
Internet Protocol television (IPTV) is the delivery of television content over Internet Protocol (IP) networks. This is in contrast to delivery through traditional terrestrial, satellite, and cable television formats. Unlike downloaded med ...
provider may choose to monitor their service quality by means of objective models, rather than asking users for their opinion, or waiting for customer complaints about bad video quality. Few of these standards have found commercial applications, including PEVQ and VQuad-HD. SSIM is also part of a commercially available video quality toolset (SSIMWAVE). VMAF is used by Netflix
Netflix, Inc. is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service and production company based in Los Gatos, California. Founded in 1997 by Reed Hastings and Marc Randolph in Scotts Valley, California, it offers a fi ...
to tune their encoding and streaming algorithms, and to quality-control all streamed content. It is also being used by other technology companies like Bitmovin and has been integrated into software such as FFmpeg
FFmpeg is a free and open-source software project consisting of a suite of libraries and programs for handling video, audio, and other multimedia files and streams. At its core is the command-line ffmpeg tool itself, designed for processing of vid ...
.
An objective model should only be used in the context that it was developed for. For example, a model that was developed using a particular video codec is not guaranteed to be accurate for another video codec. Similarly, a model trained on tests performed on a large TV screen should not be used for evaluating the quality of a video watched on a mobile phone.
Other approaches
When estimating quality of a video codec, all the mentioned objective methods may require repeating post-encoding tests in order to determine the encoding parameters that satisfy a required level of visual quality, making them time consuming, complex and impractical for implementation in real commercial applications. There is ongoing research into developing novel objective evaluation methods which enable prediction of the perceived quality level of the encoded video before the actual encoding is performed.Video quality artifacts
All the visual artifacts are still valuable for video quality. Unique not mentioned attributes include Spatial * Blurring — a result of loss of high spatial frequency image detail, usually at sharp edges. * Blocking — is caused by multiple algorithms because of the internal representation of an image with blocks size 8, 16, or 32. With specific parameters, they can average pixels inside a block making blocks distinct * Ringing, echoing or ghosting - takes the form of a “halo,” band, or “ghost” near sharp edges. * Color bleeding — occurs when the edges of one colour in the image unintentionally bleeds or overlaps into another colour * Staircase noise — is a special case of blocking along a diagonal or curved edge. Rather than rendering as smooth, it takes on the appearance of stair steps Temporal * Flickering — is usually frequent brightness or colour changes along the time dimension. It is often broken out as fine-grain flickering and coarse-grain flickering. * Mosquito noise — a variant of flickering, it’s typified as haziness and/or shimmering around high-frequency content (sharp transitions between foreground entities and the background or hard edges). * Floating — refers to illusory motion in certain regions while the surrounding areas remain static. Visually, these regions appear as if they were floating on top of the surrounding background * Jerkiness or judder — is the perceived uneven or wobbly motion due to frame sampling. It’s often caused by the conversion of 24 fps movies to a 30 or 60 fps video format. The majority of them can be grouped into compression artifactsSubjective video quality
The main goal of many-objective video quality metrics is to automatically estimate the average user's (viewer's) opinion on the quality of a video processed by a system. Procedures forsubjective video quality
Subjective video quality is video quality as experienced by humans. It is concerned with how video is perceived by a viewer (also called "observer" or "subject") and designates their opinion on a particular video sequence. It is related to the fiel ...
measurements are described in ITU-R
The ITU Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) is one of the three sectors (divisions or units) of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and is responsible for radio communications.
Its role is to manage the international radio-frequency sp ...
recommendatioBT.500
and ITU-T recommendatio
P.910
In such tests, video sequences are shown to a group of viewers. The viewers' opinion is recorded and averaged into the
mean opinion score Mean opinion score (MOS) is a measure used in the domain of Quality of Experience and telecommunications engineering, representing overall quality of a stimulus or system. It is the arithmetic mean over all individual "values on a predefined scale t ...
to evaluate the quality of each video sequence. However, the testing procedure may vary depending on what kind of system is tested.
Tools for video quality assessment
* FFmpeg - FFmpeg is the leading multimedia framework, able to decode, encode, transcode, mux, demux, stream, filter and play pretty much anything that humans and machines have created. It supports the most obscure ancient formats up to the cutting edge. No matter if they were designed by some standards committee, the community or a corporation. It is also highly portable: FFmpeg compiles, runs, and passes our testing infrastructure FATE across Linux, Mac OS X, Microsoft Windows, the BSDs, Solaris, etc. under a wide variety of build environments, machine architectures, and configurations. * MSU VQMT - MSU Video Quality Measurement Tool (VQMT) is a program for objective video quality assessment. It provides functionality for both full-reference (two videos are examined) and single-reference (one video is analyzed) comparisons. * EPFL VQMT - This software provides fast implementations of the following objective metrics: PSNR, SSIM, MS-SSIM, VIFp, PSNR-HVS, PSNR-HVS-M. In this software, the above metrics are implemented in OpenCV (C++) based on the original Matlab implementations provided by their developers. * OpenVQ - OpenVQ is a video quality assessment toolkit. The goal of this project is to provide anyone interested in video quality assessment with a toolkit that a) provides ready-to-use video quality metric implementations, and b) makes it easy to implement other video quality metrics. * Elecard - Video Quality measurement tool designed to compare the quality of encoded streams based on objective metrics, such as PSNR, APSNR, SSIM, DELTA, MSE, MSAD, VQM, NQI, VMAF and VMAF phone, VIF. * AviSynth - AviSynth is a powerful tool for video post-production. It provides ways of editing and processing videos. AviSynth works as a frameserver, providing instant editing without the need for temporary files. AviSynth itself does not provide a graphical user interface (GUI) but instead relies on a script system that allows advanced non-linear editing. *VQ Probe - VQ Probe is a professional visual instrument for objective and subjective video quality comparison. The tool allows users to compare different codec standards, build RD curves and calculate BD rates. *Vmaf.dev - Vmaf.dev is a tool for video quality analysis that runs on web browsers. The tool works with most video container formats and provides per-frame VMAF score visualization.QoE prediction for video quality
QoE prediction in videos is a great challenge because of the multiple situations that may arise and the subjective character of QoE. For this reason, to predict the QoE in the most precise way, we have to make use of a good classifier that can detect the most types of errors or unexpected situations that affect video quality. Some studies have demonstrated that a Gaussian Process Classifier give good results for this type of classification.See also
*Glossary of video terms
This glossary defines terms that are used in the documen"Defining Video Quality Requirements: A Guide for Public Safety" developed by thVideo Quality in Public Safety (VQIPS) Working Group It contains terminology and explanations of concepts relev ...
* MDI
* Mean opinion score Mean opinion score (MOS) is a measure used in the domain of Quality of Experience and telecommunications engineering, representing overall quality of a stimulus or system. It is the arithmetic mean over all individual "values on a predefined scale t ...
* MOVIE Index
* PSNR
Peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) is an engineering term for the ratio between the maximum possible power of a Signal (information theory), signal and the power of corrupting noise that affects the fidelity of its representation. Because many sign ...
* SSIM
* Subjective video quality
Subjective video quality is video quality as experienced by humans. It is concerned with how video is perceived by a viewer (also called "observer" or "subject") and designates their opinion on a particular video sequence. It is related to the fiel ...
* Video codecs
The following is a list of compression formats and related codecs.
Audio compression formats
Non-compression
* Linear pulse-code modulation (LPCM, generally only described as PCM) is the format for uncompressed audio in media files and it is al ...
* VMAF
* Visual Information Fidelity
References
{{ReflistFurther reading
Interpretation of objective video quality metrics
ITU-R recommendations on subjective video quality
ITU-T recommendations on objective and subjective video quality
Noise (graphics) Film and video technology Digital television Video codecs Codecs