Urticaria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a kind of skin rash with red, raised, itchy bumps. Hives may burn or sting. The patches of rash may appear on different body parts, with variable duration from minutes to days, and does not leave any long-lasting skin change. Fewer than 5% of cases last for more than six weeks. The condition frequently recurs.
Hives frequently occur following an infection or as a result of an


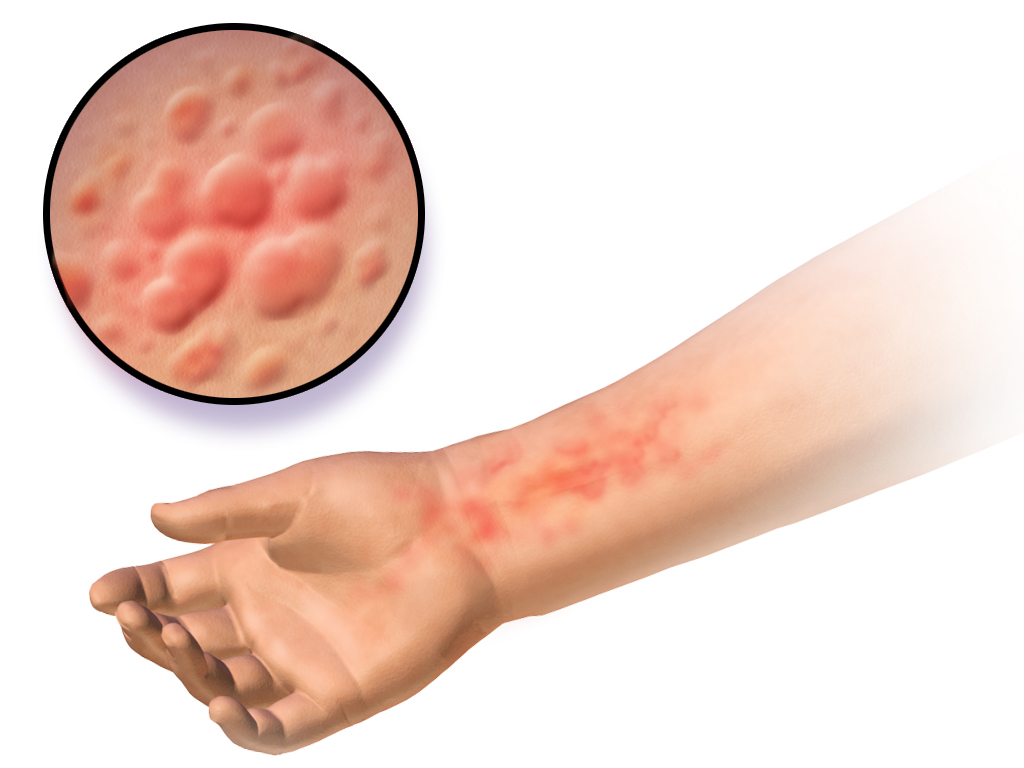 Hives, or urticaria, is a form of skin rash with red, raised, itchy bumps. They may also burn or sting. Welts (raised areas surrounded by a red base) from hives can appear anywhere on the surface of the skin. Whether the trigger is allergic or not, a complex release of inflammatory mediators, including
Hives, or urticaria, is a form of skin rash with red, raised, itchy bumps. They may also burn or sting. Welts (raised areas surrounded by a red base) from hives can appear anywhere on the surface of the skin. Whether the trigger is allergic or not, a complex release of inflammatory mediators, including
 Diagnosis is typically based on the appearance. The cause of chronic hives can rarely be determined. Patch testing may be useful to determine the allergy. In some cases regular extensive allergy testing over a long period of time is requested in hopes of getting new insight. No evidence shows regular allergy testing results in identification of a problem or relief for people with chronic hives. Regular allergy testing for people with chronic hives is not recommended.
Diagnosis is typically based on the appearance. The cause of chronic hives can rarely be determined. Patch testing may be useful to determine the allergy. In some cases regular extensive allergy testing over a long period of time is requested in hopes of getting new insight. No evidence shows regular allergy testing results in identification of a problem or relief for people with chronic hives. Regular allergy testing for people with chronic hives is not recommended.
Urticaria photo library at Dermnet
{{Authority control Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate Skin conditions resulting from errors in metabolism Type I hypersensitivity Urticaria and angioedema
allergic reaction
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, refer a number of conditions caused by the hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic derm ...
such as to medication, insect bites, or food. Psychological stress
In psychology, stress is a feeling of emotional strain and pressure. Stress is a type of psychological pain. Small amounts of stress may be beneficial, as it can improve athletic performance, motivation and reaction to the environment. Excess ...
, cold temperature, or vibration may also be a trigger. In half of cases the cause remains unknown. Risk factors include having conditions such as hay fever
Allergic rhinitis, of which the seasonal type is called hay fever, is a type of inflammation in the nose that occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens in the air. Signs and symptoms include a runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, red, i ...
or asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, co ...
. Diagnosis is typically based on the appearance. Patch testing may be useful to determine the allergy.
Prevention is by avoiding whatever it is that causes the condition. Treatment is typically with antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provide ...
s such as diphenhydramine
Diphenhydramine (DPH) is an antihistamine and sedative mainly used to treat allergies, insomnia, and symptoms of the common cold. It is also less commonly used for tremor in parkinsonism, and nausea. It is taken by mouth, injected into ...
and cetirizine. In severe cases, corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are inv ...
s or leukotriene inhibitors
An antileukotriene, also known as leukotriene modifier and leukotriene receptor antagonist, is a medication which functions as a leukotriene-related enzyme inhibitor (arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase) or leukotriene receptor antagonist ( cysteinyl leuko ...
may also be used. Keeping the environmental temperature cool is also useful. For cases that last more than six weeks immunosuppressant
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified in ...
s such as ciclosporin may be used.
About 20% of people are affected. Cases of short duration occur equally in males and females while cases of long duration are more common in females. Cases of short duration are more common among children while cases of long duration are more common among those who are middle aged. Hives have been described at least since the time of Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history o ...
. The term urticaria is from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
''urtica'' meaning " nettle".
Signs and symptoms

 Hives, or urticaria, is a form of skin rash with red, raised, itchy bumps. They may also burn or sting. Welts (raised areas surrounded by a red base) from hives can appear anywhere on the surface of the skin. Whether the trigger is allergic or not, a complex release of inflammatory mediators, including
Hives, or urticaria, is a form of skin rash with red, raised, itchy bumps. They may also burn or sting. Welts (raised areas surrounded by a red base) from hives can appear anywhere on the surface of the skin. Whether the trigger is allergic or not, a complex release of inflammatory mediators, including histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Since histamine was discover ...
from cutaneous mast cells
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a p ...
, results in fluid leakage from superficial blood vessels. Welts may be pinpoint in size or several inches in diameter. Often the patches of rash move around.
About 20% of people are affected. Cases of short duration occur equally in males and females, lasting a few days and without leaving any long-lasting skin changes. Cases of long duration are more common in females. Cases of short duration are more common among children while cases of long duration are more common among those who are middle aged. Fewer than 5% of cases last for more than six weeks. The condition frequently recurs. In half of cases of hives, the cause remains unknown.
Angioedema
Angioedema is an area of swelling (edema) of the lower layer of skin and tissue just under the skin or mucous membranes. The swelling may occur in the face, tongue, larynx, abdomen, or arms and legs. Often it is associated with hives, which are ...
is a related condition (also from allergic and nonallergic causes), though fluid leakage is from much deeper blood vessels in the subcutaneous or submucosal layers. Individual hives that are painful, last more than 24 hours, or leave a bruise as they heal are more likely to be a more serious condition called urticarial vasculitis. Hives caused by stroking the skin (often linear in appearance) are due to a benign condition called dermatographic urticaria
Dermatographic urticaria is a skin disorder and one of the most common types of urticaria, affecting 2–5% of the population.
Signs and symptoms
The condition manifests as an allergic-like reaction, causing a warm red wheal to appear on the sk ...
.
Cause
Hives can also be classified by the purported causative agent. Many different substances in the environment may cause hives, including medications, food and physical agents. In perhaps more than 50% of people with chronic hives of unknown cause, it is due to an autoimmune reaction. Risk factors include having conditions such ashay fever
Allergic rhinitis, of which the seasonal type is called hay fever, is a type of inflammation in the nose that occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens in the air. Signs and symptoms include a runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, red, i ...
or asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, co ...
.
Medications
Drugs that have caused allergic reactions evidenced as hives includecodeine
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, ''Papaver somniferum''. It is typically ...
, sulphate of morphia
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. T ...
, dextroamphetamine, aspirin
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and/or inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat inc ...
, ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used for treating pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It may also be used to close a patent ductus ar ...
, penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from '' Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum usin ...
, clotrimazole
Clotrimazole, sold under the brand name Lotrimin, among others, is an antifungal medication. It is used to treat vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, diaper rash, tinea versicolor, and types of ringworm including athlete's foot and jock ...
, trichazole, sulfonamide
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. ...
s, anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of ...
s, cefaclor
Cefaclor, sold under the trade name Ceclor among others, is a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used to treat certain bacterial infections such as pneumonia and infections of the ear, lung, skin, throat, and urinary tract. It is also avail ...
, piracetam
Piracetam is a drug marketed as a treatment for myoclonus. It is also used as a cognitive enhancer to improve memory, attention, and learning. Evidence to support its use is unclear, with some studies showing modest benefits in specific popula ...
, vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified.
s, and antidiabetic drug
Drugs used in diabetes treat diabetes mellitus by altering the glucose level in the blood. With the exceptions of insulin, most GLP receptor agonists ( liraglutide, exenatide, and others), and pramlintide, all are administered orally and are ...
s. The antidiabetic sulphonylurea glimepiride
Glimepiride, is an anti-diabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is less preferred than metformin. Use is recommended together with diet and exercise. It is taken by mouth. Glimepiride takes up to three hours for maximum effect and l ...
, in particular, has been documented to induce allergic reactions manifesting as hives.
Food
The most common food allergies in adults areshellfish
Shellfish is a colloquial and fisheries term for exoskeleton-bearing aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish are harvested from saltwater environ ...
and nuts. The most common food allergies in children are shellfish
Shellfish is a colloquial and fisheries term for exoskeleton-bearing aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish are harvested from saltwater environ ...
, nuts, eggs, wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, and soy. One study showed Balsam of Peru, which is in many processed foods, to be the most common cause of immediate contact urticaria. Another food allergy that can cause hives is alpha-gal allergy
Alpha-gal allergy — or mammalian meat allergy (MMA) — is a type of meat allergy characterized by a delayed onset of symptoms (3–8 hours) after ingesting mammalian meat and resulting from past exposure to tick bites. It was first reported in ...
, which may cause sensitivity to milk and red meat. A less common cause is exposure to certain bacteria, such as '' Streptococcus'' species or possibly '' Helicobacter pylori''.
Infection or environmental agent
Hives including chronic spontaneous hives can be a complication and symptom of a parasitic infection, such as blastocystosis and strongyloidiasis among others. The rash that develops from poison ivy,poison oak Poison oak refers to two plant species in the genus ''Toxicodendron,'' both of which can cause skin irritation:
*''Toxicodendron diversilobum'' or Western poison oak, found in western North America
*''Toxicodendron pubescens
''Toxicodendron pub ...
, and poison sumac contact is commonly mistaken for urticaria. This rash is caused by contact with urushiol
Urushiol is an oily mixture of organic compounds with allergenic properties found in plants of the family Anacardiaceae, especially '' Toxicodendron'' ''spp.'' (e.g., poison oak, Chinese lacquer tree, poison ivy, poison sumac), ''Comoclad ...
and results in a form of contact dermatitis called urushiol-induced contact dermatitis. Urushiol is spread by contact but can be washed off with a strong grease- or oil-dissolving detergent and cool water and rubbing ointments.
Dermatographic urticaria
Dermatographic urticaria
Dermatographic urticaria is a skin disorder and one of the most common types of urticaria, affecting 2–5% of the population.
Signs and symptoms
The condition manifests as an allergic-like reaction, causing a warm red wheal to appear on the sk ...
(also known as dermatographism or "skin writing") is marked by the appearance of weals or welts on the skin as a result of scratching or firm stroking of the skin. Seen in 4–5% of the population, it is one of the most common types of urticaria, in which the skin becomes raised and inflamed when stroked, scratched, rubbed, and sometimes even slapped.
The skin reaction usually becomes evident soon after the scratching and disappears within 30 minutes. Dermatographism is the most common form of a subset of chronic hives, acknowledged as "physical hives".
It stands in contrast to the linear reddening that does not itch seen in healthy people who are scratched. In most cases, the cause is unknown, although it may be preceded by a viral infection, antibiotic therapy, or emotional upset. Dermatographism is diagnosed by applying pressure by stroking or scratching the skin. The hives should develop within a few minutes. Unless the skin is highly sensitive and reacts continually, treatment is not needed. Taking antihistamines can reduce the response in cases that are annoying to the person.
Pressure or delayed pressure
This type of hives can occur right away, precisely after a pressure stimulus or as a deferred response to sustained pressure being enforced to the skin. In the deferred form, the hives only appear after about six hours from the initial application of pressure to the skin. Under normal circumstances, these hives are not the same as those witnessed with most urticariae. Instead, the protrusion in the affected areas is typically more spread out. The hives may last from eight hours to three days. The source of the pressure on the skin can happen from tight fitted clothing, belts, clothing with tough straps, walking, leaning against an object, standing, sitting on a hard surface, etc. The areas of the body most commonly affected are the hands, feet, trunk, abdomen, buttocks, legs and face. Although this appears to be very similar to dermatographism, the cardinal difference is that the swelled skin areas do not become visible quickly and tend to last much longer. This form of the skin disease is, however, rare.Cholinergic or stress
Cholinergic urticaria
Cholinergic urticaria (CU) presents with tiny very itchy wheals and small bumps on a reddish background.
It is a type of physical urticaria (or ''hives'') that appears when a person is sweating or their core body temperature increases.
Sympt ...
(CU) is one of the physical urticaria which is provoked during sweating events such as exercise, bathing, staying in a heated environment, or emotional stress. The hives produced are typically smaller than classic hives and are generally shorter-lasting.
Multiple subtypes have been elucidated, each of which require distinct treatment.
Cold-induced
The cold type of urticaria is caused by exposure of the skin to extreme cold, damp and windy conditions; it occurs in two forms. The rare form is hereditary and becomes evident as hives all over the body 9 to 18 hours after cold exposure. The common form of cold urticaria demonstrates itself with the rapid onset of hives on the face, neck, or hands after exposure to cold. Cold urticaria is common and lasts for an average of five to six years. The population most affected is young adults, between 18 and 25 years old. Many people with the condition also have dermographism and cholinergic hives. Severe reactions can be seen with exposure to cold water; swimming in cold water is the most common cause of a severe reaction. This can cause a massive discharge of histamine, resulting in low blood pressure, fainting, shock and even loss of life. Cold urticaria is diagnosed by dabbing an ice cube against the skin of the forearm for 1 to 5 minutes. A distinct hive should develop if a person has cold urticaria. This is different from the normal redness that can be seen in people without cold urticaria. People with cold urticaria need to learn to protect themselves from a hasty drop in body temperature. Regular antihistamines are not generally efficacious. One particular antihistamine, cyproheptadine (Periactin), has been found to be useful. The tricyclic antidepressantdoxepin
Doxepin is a medication falling in the tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) class used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic hives, and insomnia. For label updates seFDA index page for NDA 022036/ref> For hives it is a less ...
has been found to be effective blocking agents of histamine. Finally, a medication named ketotifen, which keeps mast cells from discharging histamine, has also been employed with widespread success.
Solar urticaria
This form of the disease occurs on areas of the skin exposed to the sun; the condition becomes evident within minutes of exposure.Water-induced
This type of urticaria is also termed rare and occurs upon contact with water. The response is not temperature-dependent and the skin appears similar to the cholinergic form of the disease. The appearance of hives is within one to 15 minutes of contact with the water and can last from 10 minutes to two hours. This kind of hives does not seem to be stimulated by histamine discharge like the other physical hives. Most researchers believe this condition is actually skin sensitivity to additives in the water, such as chlorine. Water urticaria is diagnosed by dabbing tap water and distilled water to the skin and observing the gradual response. Aquagenic urticaria is treated with capsaicin (Zostrix) administered to the chafed skin. This is the same treatment used for shingles. Antihistamines are of questionable benefit in this instance since histamine is not the causative factor.Exercise
The condition was first distinguished in 1980. People with exercise urticaria (EU) experience hives, itchiness, shortness of breath and low blood pressure five to 30 minutes after beginning exercise. These symptoms can progress to shock and even sudden death. Jogging is the most common exercise to cause EU, but it is not induced by a hot shower, fever, or with fretfulness. This differentiates EU from cholinergic urticaria. EU sometimes occurs only when someone exercises within 30 minutes of eating particular foods, such as wheat or shellfish. For these individuals, exercising alone or eating the injuring food without exercising produces no symptoms. EU can be diagnosed by having the person exercise and then observing the symptoms. This method must be used with caution and only with the appropriate resuscitative measures at hand. EU can be differentiated from cholinergic urticaria by the hot water immersion test. In this test, the person is immersed in water at 43 °C (109.4 °F). Someone with EU will not develop hives, while a person with cholinergic urticaria will develop the characteristic small hives, especially on the neck and chest. The immediate symptoms of this type are treated with antihistamines,epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and ...
and airway support. Taking antihistamines prior to exercise may be effective. Ketotifen is acknowledged to stabilise mast cells and prevent histamine release, and has been effective in treating this hives disorder. Avoiding exercise or foods that cause the mentioned symptoms is very important. In particular circumstances, tolerance can be brought on by regular exercise, but this must be under medical supervision.
Pathophysiology
The skin lesions of urticarial disease are caused by an inflammatory reaction in the skin, causing leakage of capillaries in thedermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided ...
, and resulting in an edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area ma ...
which persists until the interstitial fluid is absorbed into the surrounding cells.
Hives are caused by the release of histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Since histamine was discover ...
and other mediators of inflammation (cytokines
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
) from cells in the skin. This process can be the result of an allergic or nonallergic reaction, differing in the eliciting mechanism of histamine release.
Allergic hives
Histamine and other proinflammatory substances are released frommast cells
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a p ...
in the skin and tissues in response to the binding of allergen
An allergen is a type of antigen that produces an abnormally vigorous immune response in which the immune system fights off a perceived threat that would otherwise be harmless to the body. Such reactions are called allergies.
In technical t ...
-bound IgE antibodies to high-affinity cell surface receptors. Basophils and other inflammatory cells are also seen to release histamine and other mediators, and are thought to play an important role, especially in chronic urticarial diseases.
Autoimmune hives
Over half of all cases of chronic idiopathic hives are the result of an autoimmune trigger. Roughly 50% of people with chronic urticaria spontaneously develop autoantibodies directed at the receptor FcεRI located on skin mast cells. Chronic stimulation of this receptor leads to chronic hives. People with hives often have other autoimmune conditions, such asautoimmune thyroiditis
Autoimmune thyroiditis, is a chronic disease in which the body interprets the thyroid glands and its hormone products T3, T4 and TSH as threats, therefore producing special antibodies that target the thyroid's cells, thereby destroying it. It ma ...
, celiac disease, type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that originates when cells that make insulin (beta cells) are destroyed by the immune system. Insulin is a hormone required for the cells to use blood sugar f ...
, rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are inv ...
, Sjögren's syndrome or systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Commo ...
.
Infections
Hive-like rashes commonly accompany viral illnesses, such as the common cold. They usually appear three to five days after the cold has started, and may even appear a few days after the cold has resolved.Nonallergic hives
Mechanisms other than allergen-antibody interactions are known to cause histamine release from mast cells. Many drugs, for examplemorphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. T ...
, can induce direct histamine release not involving any immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of th ...
molecule. Also, a diverse group of signaling substances called neuropeptides, have been found to be involved in emotionally induced hives. Dominantly inherited cutaneous and neurocutaneous porphyrias
Porphyria is a group of liver disorders in which substances called porphyrins build up in the body, negatively affecting the skin or nervous system. The types that affect the nervous system are also known as acute porphyria, as symptoms are ...
( porphyria cutanea tarda, hereditary coproporphyria, variegate porphyria
Variegate porphyria, also known by several other names, is an autosomal dominant porphyria that can have acute (severe but usually not long-lasting) symptoms along with symptoms that affect the skin. The disorder results from low levels of the en ...
and erythropoietic protoporphyria) have been associated with solar urticaria
Solar urticaria (SU) is a rare condition in which exposure to ultraviolet or UV radiation, or sometimes even visible light, induces a case of urticaria or hives that can appear in both covered and uncovered areas of the skin. It is classified as ...
. The occurrence of drug-induced solar urticaria may be associated with porphyrias. This may be caused by IgG binding, not IgE.
Dietary histamine poisoning
This is termed scombroid food poisoning. Ingestion of free histamine released by bacterial decay in fish flesh may result in a rapid-onset, allergic-type symptom complex which includes hives. However, the hives produced by scombroid is reported not to include wheals.Stress and chronic idiopathic hives
Chronic idiopathic hives has been anecdotally linked to stress since the 1940s. A large body of evidence demonstrates an association between this condition and both poor emotional well-being and reduced health-relatedquality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
. A link between stress and this condition has also been shown. A recent study has demonstrated an association between stressful life events (e.g. bereavement, divorce, etc.) and chronic idiopathic urticaria and also an association between post-traumatic stress and chronic idiopathic hives.
Diagnosis
 Diagnosis is typically based on the appearance. The cause of chronic hives can rarely be determined. Patch testing may be useful to determine the allergy. In some cases regular extensive allergy testing over a long period of time is requested in hopes of getting new insight. No evidence shows regular allergy testing results in identification of a problem or relief for people with chronic hives. Regular allergy testing for people with chronic hives is not recommended.
Diagnosis is typically based on the appearance. The cause of chronic hives can rarely be determined. Patch testing may be useful to determine the allergy. In some cases regular extensive allergy testing over a long period of time is requested in hopes of getting new insight. No evidence shows regular allergy testing results in identification of a problem or relief for people with chronic hives. Regular allergy testing for people with chronic hives is not recommended.
Acute versus chronic
* urticaria is defined as the presence ofevanescent
Evanescent may refer to:
* Evanescent (dermatology)
Evanescent skin lesions, like wheals, are those that last for less than 24 hours before resolving.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical ...
wheals which completely resolve within six weeks. Acute urticaria becomes evident a few minutes after the person has been exposed to an allergen. The outbreak may last several weeks, but usually the hives are gone in six weeks. Typically, the hives are a reaction to food, but in about half the cases, the trigger is unknown. Common foods may be the cause, as well as bee or wasp stings, or skin contact with certain fragrances. Acute viral infection is another common cause of acute urticaria (viral exanthem
An exanthem is a widespread rash occurring on the outside of the body and usually occurring in children. An exanthem can be caused by toxins, drugs, or microorganisms, or can result from autoimmune disease.
The term exanthem is from the Greek el ...
). Less common causes of hives include friction, pressure, temperature extremes, exercise, and sunlight.
* urticaria (ordinary urticaria) is defined as the presence of evanescent wheals which persist for greater than six weeks. Some of the more severe chronic cases have lasted more than 20 years. A survey indicated chronic urticaria lasted a year or more in more than 50% of those affected and 20 years or more in 20% of them.
Acute and chronic hives are visually indistinguishable.
Related conditions
Angioedema
Angioedema
Angioedema is an area of swelling (edema) of the lower layer of skin and tissue just under the skin or mucous membranes. The swelling may occur in the face, tongue, larynx, abdomen, or arms and legs. Often it is associated with hives, which are ...
is similar to hives, but in angioedema, the swelling occurs in a lower layer of the dermis than in hives, as well as in the subcutis. This swelling can occur around the mouth, eyes, in the throat, in the abdomen, or in other locations. Hives and angioedema sometimes occur together in response to an allergen
An allergen is a type of antigen that produces an abnormally vigorous immune response in which the immune system fights off a perceived threat that would otherwise be harmless to the body. Such reactions are called allergies.
In technical t ...
, and is a concern in severe cases, as angioedema of the throat can be fatal.
Vibratory angioedema
This very rare form of angioedema develops in response to contact with vibration. In vibratory angioedema, symptoms develop within two to five minutes after contact with a vibrating object and abate after about an hour. People with this disorder do not experience dermographism or pressure urticaria. Vibratory angioedema is diagnosed by holding a vibrating device such as a laboratory vortex machine against the forearm for four minutes. Speedy swelling of the whole forearm extending into the upper arm is also noted later. The principal treatment is avoidance of vibratory stimulants. Antihistamines have also been proven helpful.Management
The mainstay of therapy for both acute and chronic hives is education, avoiding triggers and using antihistamines. Chronic hives can be difficult to treat and lead to significant disability. Unlike the acute form, 50–80% of people with chronic hives have no identifiable triggers. But 50% of people with chronic hives will experience remission within 1 year. Overall, treatment is geared towards symptomatic management. Individuals with chronic hives may need other medications in addition to antihistamines to control symptoms. People who experience hives with angioedema require emergency treatment as this is a life-threatening condition. Treatment guidelines for the management of chronic hives have been published. According to the 2014 American practice parameters, treatment involves a stepwise approach. Step 1 consists of second generation, H1 receptor blocking antihistamines. Systemic glucocorticoids can also be used for episodes of severe disease but should not be used for long term due to their long list of side effects. Step 2 consists of increasing the dose of the current antihistamine, adding other antihistamines, or adding a leukotriene receptor antagonist such as montelukast. Step 3 consists of adding or replacing the current treatment with hydroxyzine or doxepin. If the individual doesn't respond to steps 1–3 then they are considered to have refractory symptoms. At this point, anti-inflammatory medications (dapsone, sulfasalazine), immunosuppressants (cyclosporin, sirolimus) or other medications like omalizumab can be used. These options are explained in more detail below.Antihistamines
Non-sedating antihistamines that block histamine H1 receptors are the first line of therapy. First-generation antihistamines, such asdiphenhydramine
Diphenhydramine (DPH) is an antihistamine and sedative mainly used to treat allergies, insomnia, and symptoms of the common cold. It is also less commonly used for tremor in parkinsonism, and nausea. It is taken by mouth, injected into ...
or hydroxyzine, block both brain and peripheral H1 receptors, and cause sedation. Second-generation antihistamines, such as loratadine, cetirizine or desloratadine
Desloratadine (trade names Clarinex and Aerius) is a tricyclic H1 inverse agonist that is used to treat allergies. It is an active metabolite of loratadine.
It was patented in 1984 and came into medical use in 2001.
Medical uses
Deslora ...
, selectively antagonize peripheral H1 receptors, and are less sedating, less anticholinergic, and generally preferred over the first-generation antihistamines. Fexofenadine, a new-generation antihistamine that blocks histamine H1 receptors, may be less sedating than some second-generation antihistamines.
People who do not respond to the maximum dose of H1 antihistamines may benefit from increasing the dose, then to switching to another non-sedating antihistamine, then to adding a leukotriene antagonist, then to using an older antihistamine, then to using systemic steroids and finally to using ciclosporin or omalizumab.
H2-receptor antagonists are sometimes used in addition to H1-antagonists to treat urticaria, but there is limited evidence for their efficacy.
Systemic steroids
Oral glucocorticoids are effective in controlling symptoms of chronic hives however they have an extensive list of adverse effects such as adrenal suppression, weight gain, osteoporosis, hyperglycemia, etc. Therefore, their use should be limited to a couple of weeks. In addition, one study found that systemic glucocorticoids combined with antihistamines did not hasten the time to symptom control compared with antihistamines alone.Leukotriene-receptor antagonists
Leukotrienes are released from mast cells along with histamine. The medications, montelukast and zafirlukast block leukotriene receptors and can be used as add on treatment or in isolation for people with CU. It is important to note that these medications may be more beneficial for people with NSAID induced CU.Other
Other options for refractory symptoms of chronic hives include anti-inflammatory medications, omalizumab, and immunosuppressants. Potential anti-inflammatory agents include dapsone, sulfasalazine, and hydroxychloroquine. Dapsone is a sulfone antimicrobial agent and is thought to suppress prostaglandin and leukotriene activity. It is helpful in therapy-refractory cases and is contraindicated in people with G6PD deficiency. Sulfasalazine, a 5-ASA derivative, is thought to alter adenosine release and inhibit IgE mediated mast cell degranulation, Sulfasalazine is a good option for people with anemia who cannot take dapsone. Hydroxychloroquine is an antimalarial agent that suppresses T lymphocytes. It has a low cost however it takes longer than dapsone or sulfasalazine to work. Omalizumab was approved by the FDA in 2014 for people with hives 12 years old and above with chronic hives. It is a monoclonal antibody directed against IgE. Significant improvement in pruritus and quality of life was observed in a phase III, multicenter, randomized control trial. Immunosuppressants used for CU include cyclosporine, tacrolimus, sirolimus, and mycophenolate. Calcineurin inhibitors, such as cyclosporine and tacrolimus, inhibit cell responsiveness to mast cell products and inhibit T cell activity. They are preferred by some experts to treat severe symptoms. Sirolimus and mycophenolate have less evidence for their use in the treatment of chronic hives but reports have shown them to be efficacious. Immunosuppressants are generally reserved as the last line of therapy for severe cases due to their potential for serious adverse effects.Research
Afamelanotide is being studied as a hives treatment. Opioid antagonists such as naltrexone have tentative evidence to support their use.History
The term ''urticaria'' was first used by the Scottish physicianWilliam Cullen
William Cullen FRS FRSE FRCPE FPSG (; 15 April 17105 February 1790) was a Scottish physician, chemist and agriculturalist, and professor at the Edinburgh Medical School. Cullen was a central figure in the Scottish Enlightenment: He was ...
in 1769. It originates from the Latin word ''urtica'', meaning stinging hair or nettle, as the classical presentation follows the contact with a perennial flowering plant '' Urtica dioica''. The history of urticaria dates back to 1000–2000 BC with its reference as a wind-type concealed rash in the book ''The Yellow Emperor's Inner Classic'' from '' Huangdi Neijing''. Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history o ...
in the 4th century first described urticaria as "knidosis" after the Greek word ''knido'' for nettle. The discovery of mast cells by Paul Ehrlich
Paul Ehrlich (; 14 March 1854 – 20 August 1915) was a Nobel Prize-winning German physician and scientist who worked in the fields of hematology, immunology, and antimicrobial chemotherapy. Among his foremost achievements were finding a cure ...
in 1879 brought urticaria and similar conditions under a comprehensive idea of allergic conditions.Juhlin L. (2000) ''The History of Urticaria and Angioedema''. Department of Dermatology, University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden. ESHDV Special Annual Lecture.
See also
* Urticarial vasculitis *Dermatitis
Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved c ...
References
External links
Urticaria photo library at Dermnet
{{Authority control Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate Skin conditions resulting from errors in metabolism Type I hypersensitivity Urticaria and angioedema