Traction Battery on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
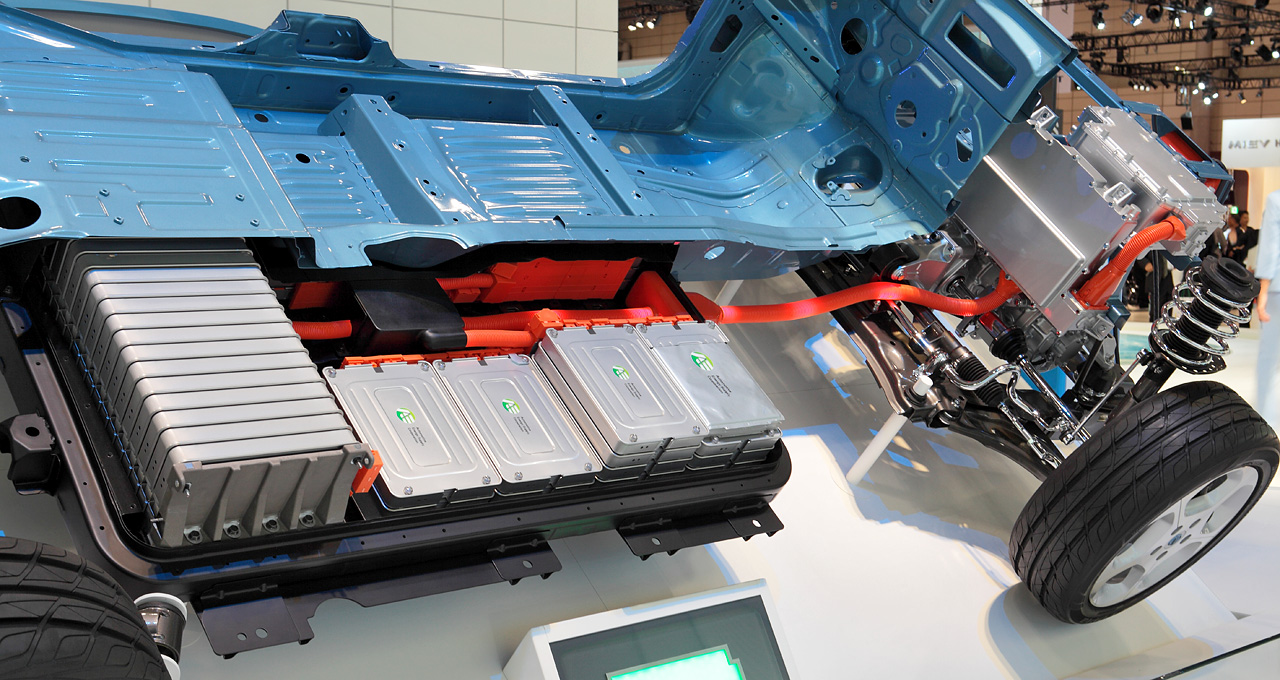 An electric vehicle battery (EVB, also known as a traction battery) is a
An electric vehicle battery (EVB, also known as a traction battery) is a
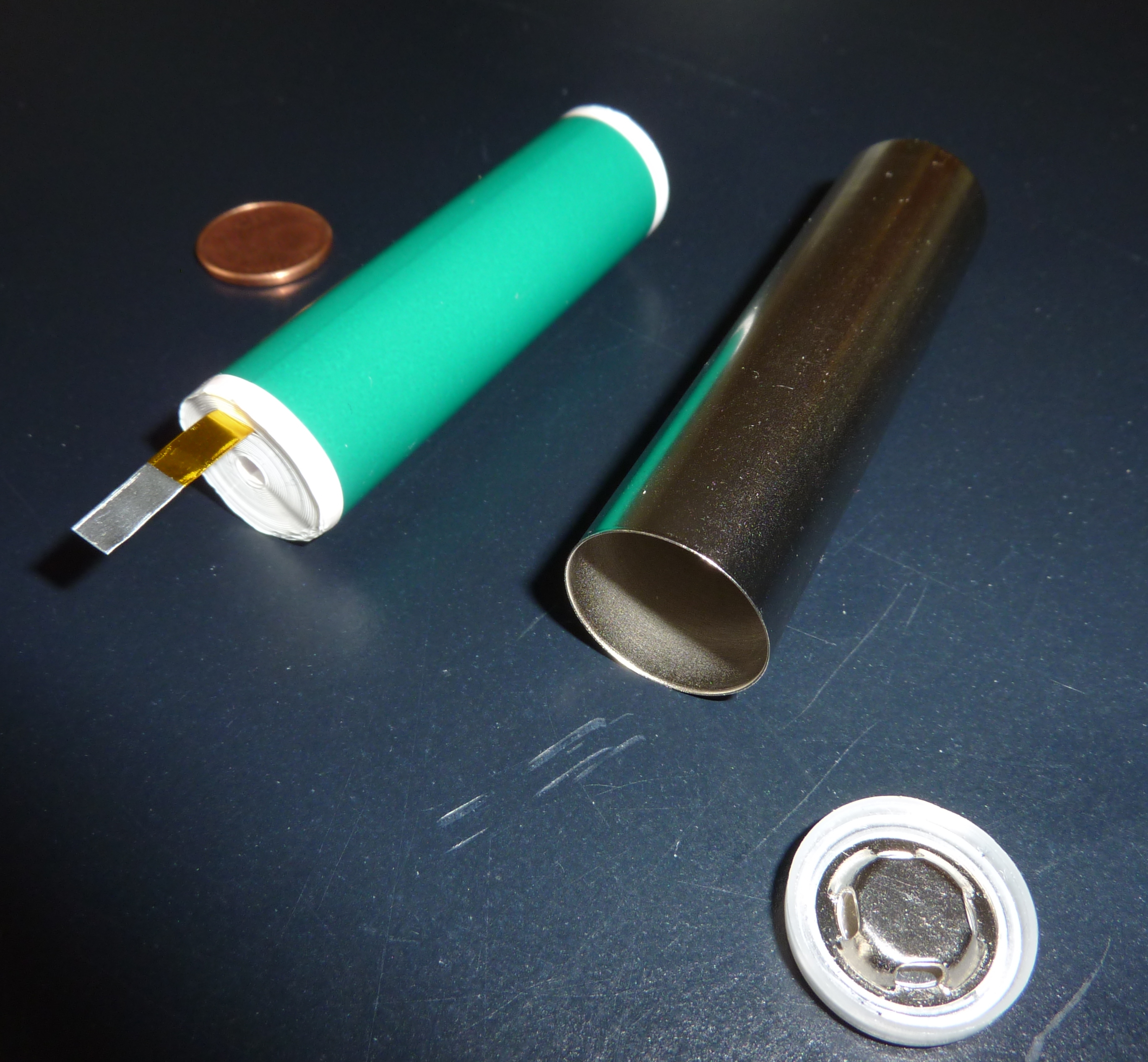



 Nickel-metal hydride batteries are now considered a relatively
Nickel-metal hydride batteries are now considered a relatively
 In 2010, scientists at the
In 2010, scientists at the
rechargeable battery
A rechargeable battery, storage battery, or secondary cell (formally a type of energy accumulator), is a type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or prima ...
used to power the electric motor
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate f ...
s of a battery electric vehicle
A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of electric vehicle (EV) that exclusively uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs, wi ...
(BEV) or hybrid electric vehicle
A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) is a type of hybrid vehicle that combines a conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) system with an Electric motor, electric propulsion system (hybrid vehicle drivetrain). The presence of the electric powertr ...
(HEV). Typically lithium-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also se ...
, they are specifically designed for high electric charge
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes charged matter to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative'' (commonly carried by protons and electrons res ...
(or energy) capacity.
Electric vehicle batteries differ from starting, lighting, and ignition (SLI) batteries as they are designed to give power over sustained periods of time and are deep-cycle batteries. Batteries for electric vehicles are characterized by their relatively high power-to-weight ratio
Power-to-weight ratio (PWR, also called specific power, or power-to-mass ratio) is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measuremen ...
, specific energy and energy density
In physics, energy density is the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. It is sometimes confused with energy per unit mass which is properly called specific energy or .
Often only the ''useful'' or extrac ...
; smaller, lighter batteries are desirable because they reduce the weight of the vehicle and therefore improve its performance. Compared to liquid fuels, most current battery technologies have much lower specific energy, and this often impacts the maximum all-electric range of the vehicles.
The most common battery type in modern electric vehicles
An electric vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that uses one or more electric motors for propulsion. It can be powered by a collector system, with electricity from extravehicular sources, or it can be powered autonomously by a battery (sometimes ch ...
are lithium-ion and lithium polymer
A lithium polymer battery, or more correctly lithium-ion polymer battery (abbreviated as LiPo, LIP, Li-poly, lithium-poly and others), is a rechargeable battery of lithium-ion technology using a polymer electrolyte instead of a liquid electro ...
, because of their high energy density compared to their weight. Other types of rechargeable batteries used in electric vehicles include lead–acid ("flooded", deep-cycle, and valve regulated lead acid), nickel-cadmium, nickel–metal hydride, and, less commonly, zinc–air, and sodium nickel chloride ("zebra") batteries. The amount of electricity (i.e. electric charge) stored in batteries is measured in ampere hour
An ampere hour or amp hour (symbol: A⋅h or A h; often simplified as Ah) is a unit of electric charge, having dimensions of electric current multiplied by time, equal to the charge transferred by a steady current of one ampere flowing for ...
s or in coulomb
The coulomb (symbol: C) is the unit of electric charge in the International System of Units (SI).
In the present version of the SI it is equal to the electric charge delivered by a 1 ampere constant current in 1 second and to elementary char ...
s, with the total energy often measured in kilowatt-hour
A kilowatt-hour ( unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common b ...
s (kWh).
Since the late 1990s, advances in lithium-ion battery technology have been driven by demands from portable electronics, laptop computers, mobile phones, and power tools. The BEV and HEV marketplace has reaped the benefits of these advances both in performance and energy density. Unlike earlier battery chemistries, notably nickel-cadmium, lithium-ion batteries can be discharged and recharged daily and at any state of charge.
The battery pack makes up a significant cost of a BEV or a HEV. , the cost of electric vehicle batteries has fallen 87% since 2010 on a per kilowatt-hour basis. As of 2018, vehicles with over of all-electric range, such as the Tesla Model S
The Tesla Model S is a battery-powered liftback car serving as the flagship model of Tesla, Inc. The Model S features a dual-motor, all-wheel drive layout, although earlier versions of the Model S featured a rear-motor and rear-wheel drive ...
, have been commercialized and are now available in numerous vehicle segments.
In terms of operating costs, the price of electricity to run a BEV is a small fraction of the cost of fuel for equivalent internal combustion engines, reflecting higher energy efficiency.
Electric vehicle battery types


Lead-acid
Flooded lead-acid batteries are the oldest, cheapest, and, in the past, most common vehicle batteries available. There are two main types of lead-acid batteries: automobile engine starter batteries, and deep cycle batteries. Automobile engine starter batteries are designed to use a small percentage of their capacity to provide high charge rates to start the engine, while deep cycle batteries are used to provide continuous electricity to run electric vehicles like forklifts or golf carts. Deep cycle batteries are also used as the auxiliary batteries in recreational vehicles, but they require different, multi-stage charging.(discussing damage caused by sulfation due to discharge below 50%) No lead acid battery should be discharged below 50% of its capacity, as it shortens the battery's life. Flooded batteries require inspection of electrolyte levels and occasional replacement of water, which gases away during the normal charging cycle. Previously, most electric vehicles used lead-acid batteries due to their mature technology, high availability, and low cost, with the notable exception of some early BEVs, such as the Detroit Electric which used anickel–iron battery
The nickel–iron battery (NiFe battery) is a rechargeable battery having nickel(III) oxide-hydroxide positive plates and iron negative plates, with an electrolyte of potassium hydroxide. The active materials are held in nickel-plated steel tub ...
. Deep-cycle lead batteries are expensive and have a shorter life than the vehicle itself, typically needing replacement every 3 years.
Lead-acid batteries in EV applications end up being a significant (25–50%) portion of the final vehicle mass. Like all batteries, they have significantly lower specific energy than petroleum fuels—in this case, 30–50 W⋅h/kg. While the difference isn't as extreme as it first appears due to the lighter drive-train in an EV, even the best batteries tend to lead to higher masses when applied to vehicles with a normal range. The efficiency (70–75%) and storage capacity of the current generation of common deep cycle lead acid batteries decreases with lower temperatures, and diverting power to run a heating coil reduces efficiency and range by up to 40%.
Charging and operation of batteries typically results in the emission of hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
and sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formul ...
, which are naturally occurring and normally harmless if properly vented. Early Citicar
The CitiCar is an electric car produced from 1974 to 1977 by Sebring, Florida–based Sebring-Vanguard, Inc. After being bought out by Commuter Vehicles, Inc, Sebring-Vanguard produced the similar Comuta-Car and Comuta-Van from 1979 to 1982. Si ...
owners discovered that, if not vented properly, unpleasant sulfur smells would leak into the cabin immediately after charging.
Lead-acid batteries powered such early modern EVs as the original versions of the EV1
The General Motors EV1 was an electric car produced and leased by General Motors from 1996 to 1999. It was the first mass-produced and purpose-designed electric vehicle of the modern era from a major automaker and the first GM car designed to be ...
.
Nickel-metal hydride
 Nickel-metal hydride batteries are now considered a relatively
Nickel-metal hydride batteries are now considered a relatively mature technology
A mature technology is a technology that has been in use for long enough that most of its initial faults and inherent problems have been removed or reduced by further development. In some contexts, it may also refer to technology that has not se ...
. While less efficient (60–70%) in charging and discharging than even lead-acid, they have a specific energy of 30–80 W⋅h/kg, far higher than lead-acid. When used properly, nickel-metal hydride batteries can have exceptionally long lives, as has been demonstrated in their use in hybrid car
A hybrid vehicle is one that uses two or more distinct types of power, such as submarines that use diesel when surfaced and batteries when submerged. Other means to store energy include pressurized fluid in hydraulic hybrids.
The basic princi ...
s and in the surviving first-generation NiMH Toyota RAV4 EVs that still operate well after and over a decade of service. Downsides include the poor efficiency, high self-discharge, very finicky charge cycles, and poor performance in cold weather.
GM Ovonic produced the NiMH battery used in the second generation EV-1, and Cobasys makes a nearly identical battery (ten 1.2 V 85 A⋅h NiMH cells in series in contrast with eleven cells for Ovonic battery). This worked very well in the EV-1. Patent encumbrance has limited the use of these batteries in recent years.
Zebra
The sodium nickel chloride or "Zebra" battery uses a molten sodium chloroaluminate (NaAlCl4) salt as the electrolyte. A relatively mature technology, the Zebra battery has a specific energy of 120 W⋅h/kg. Since the battery must be heated for use, cold weather does not strongly affect its operation except for increasing heating costs. They have been used in several EVs such as theModec
Modec was an electric vehicle manufacturer in Coventry, in the United Kingdom, specialising in Commercial vehicles in the N2 category. It unveiled its first model in April 2006 and announced its intention to commence series production in Ma ...
commercial vehicle
A commercial vehicle is any type of motor vehicle used for transporting goods or paying passengers.
The United States defines a "commercial motor vehicle" as any self-propelled or towed vehicle used on a public highway in interstate commerce to t ...
. Zebra batteries can last for a few thousand charge cycles and are nontoxic. The downsides to the Zebra battery include poor specific power (<300 W/kg) and the requirement of having to heat the electrolyte to about , which wastes some energy, presents difficulties in long-term storage of charge, and is potentially a hazard.
Lithium-ion
lithium-ion (and the mechanistically similar lithium polymer) batteries, were initially developed and commercialized for use in laptops and consumer electronics. With their high energy density and long cycle life they have become the leading battery type for use in EVs. The first commercialized lithium-ion chemistry was a lithium cobalt oxidecathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. A conventional current describes the direction in whi ...
and a graphite anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ...
first demonstrated by N. Godshall in 1979, and by John Goodenough, and Akira Yoshino shortly thereafter. The downside of traditional lithium-ion batteries include sensitivity to temperature, low temperature power performance, and performance degradation with age. Due to the volatility of organic electrolytes, the presence of highly oxidized metal oxides, and the thermal instability of the anode SEI layer, traditional lithium-ion batteries pose a fire safety risk if punctured or charged improperly. These early cells did not accept or supply charge when extremely cold, and so heaters can be necessary in some climates to warm them. The maturity of this technology is moderate. The Tesla Roadster (2008)
The Tesla Roadster is a battery electric vehicle (BEV) sports car, based on the Lotus Elise chassis, that was produced by the electric car firm Tesla Motors (now Tesla, Inc.) in California from 2008 to 2012. The Roadster was the first highway ...
and other cars produced by the company used a modified form of traditional lithium-ion "laptop battery" cells.
Recent EVs are using new variations on lithium-ion chemistry that sacrifice specific energy and specific power to provide fire resistance, environmental friendliness, rapid charging (as quickly as a few minutes), and longer lifespans. These variants (phosphates, titanates, spinels, etc.) have been shown to have a much longer lifetime, with A123 types using lithium iron phosphate
Lithium iron phosphate or lithium ferro-phosphate (LFP) is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a gray, red-grey, brown or black solid that is insoluble in water. The material has attracted attention as a component of lithium iron phosp ...
lasting at least more than 10 years and more than 7000 charge/discharge cycles, and LG Chem expecting their lithium-manganese spinel batteries to last up to 40 years.
Much work is being done on lithium-ion batteries in the lab. Lithium vanadium oxide has already made its way into the Subaru
( or ; ) is the automobile manufacturing division of Japanese transportation conglomerate Subaru Corporation (formerly known as Fuji Heavy Industries), the twenty-first largest automaker by production worldwide in 2017.
Subaru cars are ...
prototype G4e, doubling energy density. Silicon nanowires, silicon nanoparticles, and tin nanoparticles promise several times the energy density in the anode, while composite and superlattice cathodes also promise significant density improvements.
New data has shown that exposure to heat and the use of fast charging promote the degradation of Li-ion batteries more than age and actual use, and that the average electric vehicle battery will retain 90% of its initial capacity after six years and six months of service. For example, the battery in a Nissan Leaf
The , stylized as LEAF, is a compact five-door hatchback battery electric vehicle (BEV) manufactured by Nissan. It was introduced in Japan and the United States in December 2010, and its second generation was introduced in October 2017. The Lea ...
will degrade twice as fast as the battery in a Tesla, because the Leaf does not have an active cooling system for its battery.
Battery capacity
Non–plug-in hybrid cars have battery capacities between 0.65 kW⋅h (2012Honda Civic Hybrid
The is a series of automobiles manufactured by Honda since 1972. Since 2000, the Civic has been categorized as a compact car, while previously it occupied the subcompact class. , the Civic is positioned between the Honda Fit/City and Honda Ac ...
) and 1.8 kW⋅h (2001 Toyota Prius
The is a car built by Toyota which has a hybrid drivetrain, combining an internal combustion engine with an electric motor. Initially offered as a four-door sedan, it has been produced only as a five-door liftback since 2003.
In 2007, ...
).
Plug-in hybrid cars have battery capacities between 4.4 kW⋅h (2012 Toyota Prius Plug-in Hybrid) and 40.6 kW⋅h (Li Auto One
The Li Auto One (, literal translation: dream or ideal ONE) is a luxury mid-size crossover SUV by Li Xiang, and it is also the first vehicle from the Chinese automobile manufacturer.
As of 2021 it has the second-longest electric range of any ...
).
All-electric cars have battery capacities between 6.0 kW⋅h (2012 Renault Twizy
The Renault Twizy is a two-seat Electric vehicle, electric microcar designed and marketed by Renault. It is classified in Europe as either a Motorised quadricycle#Light quadricycles (L6e), light or Motorised quadricycle#Heavy quadricycles (L7e), h ...
) and 212.7 kW⋅h (2022 GMC Hummer EV
The GMC Hummer EV (also known as Hummer EV and badged as HEV) is a line of battery electric full-size vehicles produced by General Motors under the GMC marque, and its own sub-brand. The Hummer EV line was introduced in October 2020 with t ...
).
Battery cost
 In 2010, scientists at the
In 2010, scientists at the Technical University of Denmark
The Technical University of Denmark ( da, Danmarks Tekniske Universitet), often simply referred to as DTU, is a polytechnic university and school of engineering. It was founded in 1829 at the initiative of Hans Christian Ørsted as Denmark's fir ...
paid US$10,000 for a certified EV battery with 25 kWh capacity (i.e. US$400/kWh), with no rebates or surcharges. Two out of 15 battery producers could supply the necessary technical documents about quality and fire safety. In 2010 it was estimated that at most 10 years would pass before the battery price would come down to one-third.
According to a 2010 study, by the United States National Research Council
The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (also known as NASEM or the National Academies) are the collective scientific national academy of the United States. The name is used interchangeably in two senses: (1) as an umbrell ...
, the cost of a lithium-ion battery pack was about /kWh
A kilowatt-hour (unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common bill ...
of usable energy, and considering that a PHEV
A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) is a hybrid electric vehicle whose battery pack can be recharged by plugging a charging cable into an external electric power source, in addition to internally by its on-board internal combustion engi ...
-10 requires about 2.0 kWh and a PHEV-40 about 8 kWh, the manufacturer cost of the battery pack for a PHEV-10 is around and it goes up to for a PHEV-40. The MIT Technology Review
''MIT Technology Review'' is a bimonthly magazine wholly owned by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and editorially independent of the university. It was founded in 1899 as ''The Technology Review'', and was re-launched without "The" in ...
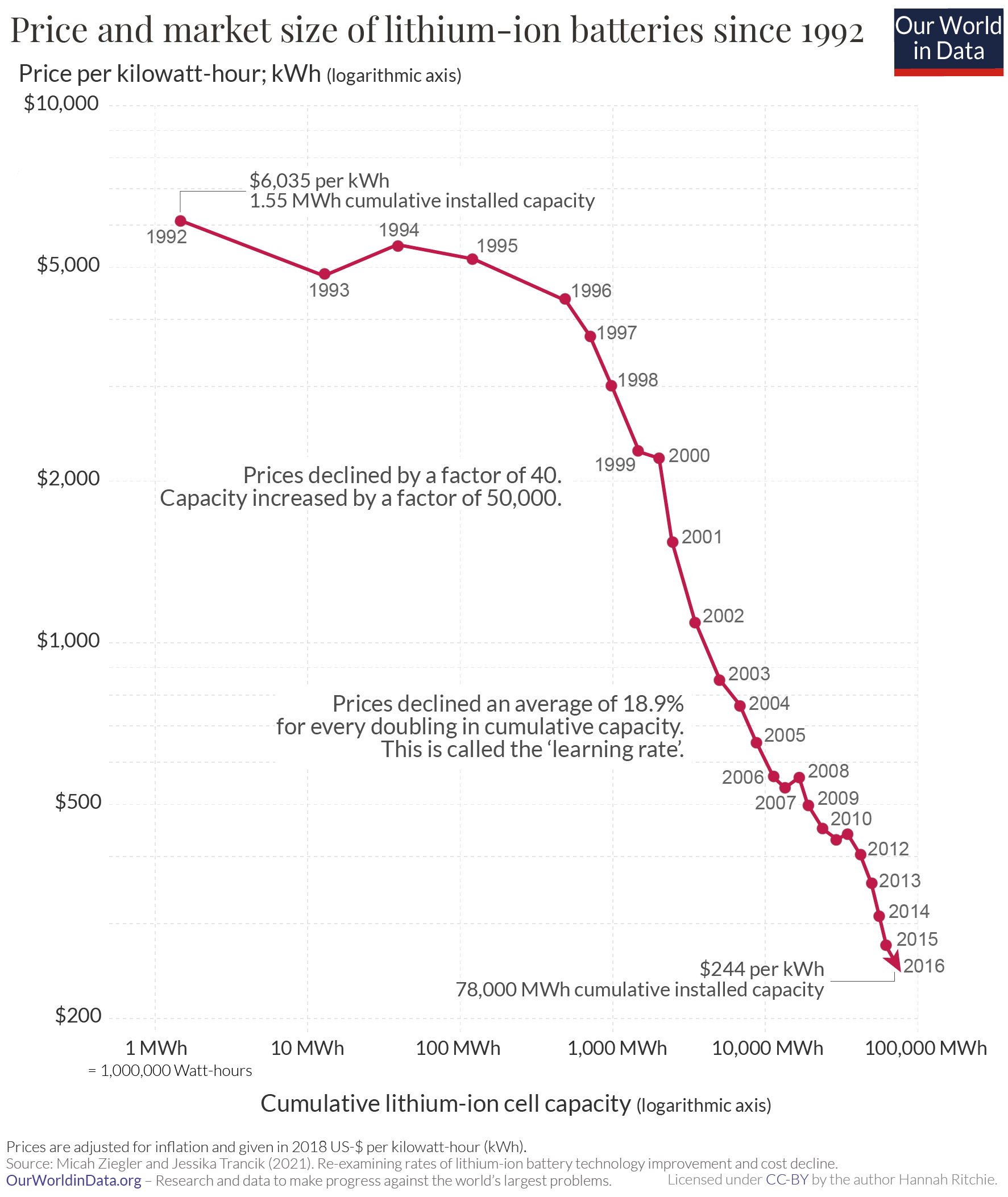
estimated the cost of automotive battery packs to be between to per kilowatt hour by 2020. A 2013 study by the American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy reported that battery costs came down from /kWh in 2007 to /kWh in 2012. The U.S. Department of Energy has set cost targets for its sponsored battery research of /kWh in 2015 and /kWh by 2022. Cost reductions through advances in battery technology and higher production volumes will allow plug-in electric vehicles to be more competitive with conventional internal combustion engine vehicles. In 2016, the world had a Li-ion production capacity of 41.57 GW⋅h.
The actual costs for cells are subject to much debate and speculation as most EV manufacturers refuse to discuss this topic in detail. However, in October 2015, car maker GM revealed at their annual Global Business Conference that they expected a price of /kWh for Li-ion cells entering 2016, substantially lower than other analysts' cost estimates. GM also expects a cost of /kWh by the end of 2021.
According to a study published in February 2016 by Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF), battery prices fell 65% since 2010, and 35% just in 2015, reaching /kWh. The study concludes that battery costs are on a trajectory to make electric vehicles without government subsidies
A subsidy or government incentive is a form of financial aid or support extended to an economic sector (business, or individual) generally with the aim of promoting economic and social policy. Although commonly extended from the government, the ter ...
as affordable as internal combustion engine cars in most countries by 2022. BNEF projects that by 2040, long-range electric cars will cost less than expressed in 2016 dollars. BNEF expects electric car battery costs to be well below /kWh by 2030, and to fall further thereafter as new chemistries become available. ''See embedded video.''
;Battery cost estimate comparison
EV parity
In 2010, battery professor Poul Norby stated that he believed that lithium batteries will need to double their specific energy and bring down the price from US$500 (2010) to US$100 perkWh
A kilowatt-hour (unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common bill ...
capacity in order to make an impact on petrol cars. Citigroup
Citigroup Inc. or Citi ( stylized as citi) is an American multinational investment bank and financial services corporation headquartered in New York City. The company was formed by the merger of banking giant Citicorp and financial conglomera ...
indicates US$230/kWh.
Toyota Prius 2012 plug-in's official page declare of range and a battery capacity of 5.2 kWh with a ratio of /kWh, while the Addax (2015 model) utility vehicle already reaches 110 kilometres (68.5 mi) or a ratio of 7.5 kilometers (4.6 mi)/kWh.
Battery electric cars have an energy consumption
Energy consumption is the amount of energy used.
Biology
In the body, energy consumption is part of energy homeostasis. It derived from food energy. Energy consumption in the body is a product of the basal metabolic rate and the physical activit ...
between /kWh (85 MPGe) and /kWh (135 MPGe).
United States Secretary of Energy Steven Chu
Steven Chu lithium-ion, Li-poly, Aluminium-air batteries and zinc-air batteries have demonstrated specific energies high enough to deliver range and recharge times comparable to conventional fossil fueled vehicles.

 Battery pack designs for electric vehicles (EVs) are complex and vary widely by manufacturer and specific application. However, they all incorporate a combination of several simple mechanical and electrical component systems which perform the basic required functions of the pack.
The actual battery cells can have different chemistry, physical shapes, and sizes as preferred by various pack manufacturers. Battery packs will always incorporate many discrete cells connected in series and parallel to achieve the total voltage and current requirements of the pack. Battery packs for all electric drive EVs can contain several hundred individual cells. Each cell has a nominal voltage of 3-4
Battery pack designs for electric vehicles (EVs) are complex and vary widely by manufacturer and specific application. However, they all incorporate a combination of several simple mechanical and electrical component systems which perform the basic required functions of the pack.
The actual battery cells can have different chemistry, physical shapes, and sizes as preferred by various pack manufacturers. Battery packs will always incorporate many discrete cells connected in series and parallel to achieve the total voltage and current requirements of the pack. Battery packs for all electric drive EVs can contain several hundred individual cells. Each cell has a nominal voltage of 3-4
"0.5''C''"
, thereby taking two or more hours for a full charge, but faster charging is available even for large capacity batteries. Charging time at home is limited by the capacity of the household
(Website). ''The Auto Channel'', 1998-11-24. Retrieved on 2007-08-21. An inductive charging advocate from Toyota contended in 1998, that overall cost differences were minimal, while a conductive charging advocate from Ford contended that conductive charging was more cost efficient.
 There are mainly four stages during the lifecycle of lithium-based EV batteries: the raw materials phase, the battery manufacturing, operation phase and the end-of-life management phase. As shown in the schematic of life cycle of EV batteries, during the first stage, the rare earth materials are extracted in different parts of the world. After they are refined by pre-processing factories, the battery manufacturing companies take over these materials and start to produce batteries and assemble them into packs. These battery packs are then sent to car manufacturing companies for EV integration. In the last stage, if no management is in place, valuable materials in the batteries could be potentially wasted. A good end-of-life management phase will try to close the loop. The used battery packs will either be reused as stationary storage or recycled depending on the battery state of health (SOH).
The battery lifecycle is rather long and requires close cooperation between companies and countries. Currently, the raw materials phase and the battery manufacturing and operation phase are well established. The end-of-life management phase is struggled to grow, especially the recycling process mainly because of economics. For example, only 6% of lithium-ion batteries were collected for recycling in 2017–2018 in Australia. However, closing the loop is extremely important. Not only because of a predicted tightened supply of nickel, cobalt and lithium in the future, also recycling EV batteries has the potential to maximize the environmental benefit. Xu et al. predicted that in the sustainable development scenario, lithium, cobalt and nickel will reach or surpass the amount of known reserves in the future if no recycling is in place. Ciez and Whitacre found that by deploying battery recycling some green house gas (GHG) emission from mining could be avoided.
There are mainly four stages during the lifecycle of lithium-based EV batteries: the raw materials phase, the battery manufacturing, operation phase and the end-of-life management phase. As shown in the schematic of life cycle of EV batteries, during the first stage, the rare earth materials are extracted in different parts of the world. After they are refined by pre-processing factories, the battery manufacturing companies take over these materials and start to produce batteries and assemble them into packs. These battery packs are then sent to car manufacturing companies for EV integration. In the last stage, if no management is in place, valuable materials in the batteries could be potentially wasted. A good end-of-life management phase will try to close the loop. The used battery packs will either be reused as stationary storage or recycled depending on the battery state of health (SOH).
The battery lifecycle is rather long and requires close cooperation between companies and countries. Currently, the raw materials phase and the battery manufacturing and operation phase are well established. The end-of-life management phase is struggled to grow, especially the recycling process mainly because of economics. For example, only 6% of lithium-ion batteries were collected for recycling in 2017–2018 in Australia. However, closing the loop is extremely important. Not only because of a predicted tightened supply of nickel, cobalt and lithium in the future, also recycling EV batteries has the potential to maximize the environmental benefit. Xu et al. predicted that in the sustainable development scenario, lithium, cobalt and nickel will reach or surpass the amount of known reserves in the future if no recycling is in place. Ciez and Whitacre found that by deploying battery recycling some green house gas (GHG) emission from mining could be avoided.

 To develop a deeper understanding of the lifecycle of EV batteries, it is important to analyze the emission associated with different phases. Using NMC cylindrical cells as an example, Ciez and Whitacre found that around 9 kg CO2e kg battery''−''1 is emitted during raw materials pre-processing and battery manufacturing under the US average electricity grid. The biggest part of the emission came from materials preparation accounting for more than 50% of the emissions. If NMC pouch cell is used, the total emission increases to almost 10 kg CO2e kg battery''−''1 while materials manufacturing still contributes to more than 50% of the emission. During the end-of-life management phase, the refurbishing process adds little emission to the lifecycle emission. The recycling process, on the other hand, as suggested by Ciez and Whitacre emits a significant amount of GHG. As shown in the battery recycling emission plot a and c, the emission of the recycling process varies with the different recycling processes, different chemistry and different form factor. Thus, the net emission avoided compared to not recycling also varies with these factors. At a glance, as shown in the plot b and d, the direct recycling process is the most ideal process for recycling pouch cell batteries, while the hydrometallurgical process is most suitable for cylindrical type battery. However, with the error bars shown, the best approach cannot be picked with confidence. It is worth noting that for the lithium iron phosphates (LFP) chemistry, the net benefit is negative. Because LFP cells lacks cobalt and nickel which are expensive and energy intensive to produce, it is more energetically efficient to mine. In general, in addition to promoting the growth of a single sector, a more integrated effort should be in place to reduce the lifecycle emission of EV batteries. A finite total supply of rare earth material can apparently justify the need for recycling. But the environmental benefit of recycling needs closer scrutiny. Based on current recycling technology, the net benefit of recycling depends on the form factors, the chemistry and the recycling process chosen.
To develop a deeper understanding of the lifecycle of EV batteries, it is important to analyze the emission associated with different phases. Using NMC cylindrical cells as an example, Ciez and Whitacre found that around 9 kg CO2e kg battery''−''1 is emitted during raw materials pre-processing and battery manufacturing under the US average electricity grid. The biggest part of the emission came from materials preparation accounting for more than 50% of the emissions. If NMC pouch cell is used, the total emission increases to almost 10 kg CO2e kg battery''−''1 while materials manufacturing still contributes to more than 50% of the emission. During the end-of-life management phase, the refurbishing process adds little emission to the lifecycle emission. The recycling process, on the other hand, as suggested by Ciez and Whitacre emits a significant amount of GHG. As shown in the battery recycling emission plot a and c, the emission of the recycling process varies with the different recycling processes, different chemistry and different form factor. Thus, the net emission avoided compared to not recycling also varies with these factors. At a glance, as shown in the plot b and d, the direct recycling process is the most ideal process for recycling pouch cell batteries, while the hydrometallurgical process is most suitable for cylindrical type battery. However, with the error bars shown, the best approach cannot be picked with confidence. It is worth noting that for the lithium iron phosphates (LFP) chemistry, the net benefit is negative. Because LFP cells lacks cobalt and nickel which are expensive and energy intensive to produce, it is more energetically efficient to mine. In general, in addition to promoting the growth of a single sector, a more integrated effort should be in place to reduce the lifecycle emission of EV batteries. A finite total supply of rare earth material can apparently justify the need for recycling. But the environmental benefit of recycling needs closer scrutiny. Based on current recycling technology, the net benefit of recycling depends on the form factors, the chemistry and the recycling process chosen.
Sila NanotechPrologium
and Li metal anod
CubergSolid Power
. In general, for active materials production, there are three steps: materials preparation, materials processing and refinement. Schmuch et al. discussed materials manufacturing in greater details. In the cell manufacturing stage, the prepared electrode will be processed to the desired shape for packaging in a cylindrical, rectangular or pouch format. Then after filling the electrolytes and sealing the cells, the battery cells are cycled carefully to form SEI protecting the anode. Then, these batteries are assembled into packs ready for vehicle integration. Kwade et al. discuss the overall battery manufacturing process in greater detail.
 Second, it is costly and time-intensive to disassemble modules and cells. Following the last point, the first step is testing to determine the remaining SOH of the battery modules. This operation could vary for each retired system. Next, the module must be fully discharged. Then, the pack must be disassembled and reconfigured to meet the power and energy requirement of the second life application. It is important to note that qualified workers and specialized tools are required to dismantle the high weight and high voltage EV batteries. Besides the solutions discussed in the previous section, a refurbishing company can sell or reuse the discharged energy from the module to reduce the cost of this process. To accelerate the disassembly process, there have been several attempts to incorporate robots in this process. In this case, robots can handle more dangerous task increasing the safety of the dismantling process.
Third, battery technology is non-transparent and lacks standards. Because battery development is the core part of EV, it is difficult for the manufacturer to label the exact chemistry of cathode, anode and electrolytes on the pack. In addition, the capacity and the design of the cells and packs changes on a yearly basis. The refurbishing company needs to closely work with the manufacture to have a timely update on this information. On the other hand, government can set up labeling standard.
Lastly, the refurbishing process adds cost to the used batteries. Since 2010, the battery costs have decreased by over 85% which is significantly faster than the prediction. Because of the added cost of refurbishing, the refurbished unit may be less attractive than the new batteries to the market.
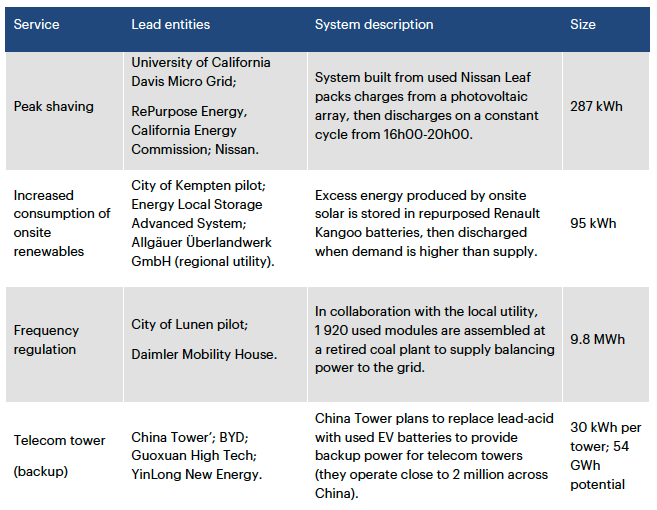
Nonetheless, there have been several successes on the second-life application as shown in the examples of storage projects using second-life EV batteries. They are used in less demanding stationary storage application as peak shaving or additional storage for renewable-based generating sources.
Second, it is costly and time-intensive to disassemble modules and cells. Following the last point, the first step is testing to determine the remaining SOH of the battery modules. This operation could vary for each retired system. Next, the module must be fully discharged. Then, the pack must be disassembled and reconfigured to meet the power and energy requirement of the second life application. It is important to note that qualified workers and specialized tools are required to dismantle the high weight and high voltage EV batteries. Besides the solutions discussed in the previous section, a refurbishing company can sell or reuse the discharged energy from the module to reduce the cost of this process. To accelerate the disassembly process, there have been several attempts to incorporate robots in this process. In this case, robots can handle more dangerous task increasing the safety of the dismantling process.
Third, battery technology is non-transparent and lacks standards. Because battery development is the core part of EV, it is difficult for the manufacturer to label the exact chemistry of cathode, anode and electrolytes on the pack. In addition, the capacity and the design of the cells and packs changes on a yearly basis. The refurbishing company needs to closely work with the manufacture to have a timely update on this information. On the other hand, government can set up labeling standard.
Lastly, the refurbishing process adds cost to the used batteries. Since 2010, the battery costs have decreased by over 85% which is significantly faster than the prediction. Because of the added cost of refurbishing, the refurbished unit may be less attractive than the new batteries to the market.
Nonetheless, there have been several successes on the second-life application as shown in the examples of storage projects using second-life EV batteries. They are used in less demanding stationary storage application as peak shaving or additional storage for renewable-based generating sources.
 Although battery life span can be extended by enabling a second-life application, ultimately EV batteries need to be recycled. Recyclability is not currently an important design consideration for battery manufacturers, and in 2019 only 5% of electric vehicle batteries were recycled. BEV technologies lack an established recycling framework in many countries, making the usage of BEV and other battery-operated electrical equipment a large energy expenditure, ultimately increasing emissions - especially in countries lacking renewable energy resources. Currently, there are five types of recycling processes: Pyrometallurgical recovery, Physical materials separation, Hydrometallurgical metal reclamation, Direct recycling method and Biological metals reclamation. The most widely used processes are the first three processes listed, as shown in the examples of current lithium-ion battery recycling facilities. The last two methods are still on lab or pilot scale, however, they can potentially avoid the largest amount of emission from mining.
The pyrometallurgical process involves burning the battery materials with slag, limestone, sand and coke to produce a metal alloy using a high-temperature furnace. The resulted materials are a metallic alloy, slag and gases. The gases comprise molecules that are evaporated from the electrolyte and binder components. The metal alloy can be separated through hydrometallurgical processes into constituent materials. The slag which is a mixture of metals aluminum, manganese and lithium can either be reclaimed by hydrometallurgical processes or used in the cement industry. This process is very versatile and relatively safe. Because there is no pre-sorting needed, it can work with a wide variety of batteries. In addition, because the whole cell is burnt, the metal from the current collectors could help the smelting process and because of the exothermic reaction of burning electrolyte sand plastics the energy consumption can also be reduced. However, this process still requires relatively higher energy consumption and only a limited number of materials can be reclaimed. Physical materials separation recovered materials by mechanical crushing and exploiting physical properties of different components such as particle size, density, ferromagnetism and hydrophobicity. Copper, aluminum and steel casing can be recovered by sorting. The remaining materials, called "black mass", which is composed of nickel, cobalt, lithium and manganese, need a secondary treatment to recover. For the hydrometallurgical process, the cathode materials need to be crushed to remove the current collector. Then, the cathode materials are leached by aqueous solutions to extract the desired metals from cathode materials. Direct cathode recycling as the name suggested extracts the materials directly, yielding a cathode power that is ready to be used as new cathode pristine material. This process involves extracting the electrolyte using liquid or supercritical CO2. After the size of the recovered components is reduced, the cathode materials can be separated out. For the biological metals reclamation or bio-leaching, the process uses microorganisms to digest metal oxides selectively. Then, recyclers can reduce these oxides to produce metal nanoparticles. Although bio-leaching has been used successfully in the mining industry, this process is still nascent to the recycling industry and plenty of opportunities exists for further investigation.
There have been many efforts around the world to promote recycling technologies development and deployment. In the US, the Department of Energy Vehicle Technologies Offices (VTO) set up two efforts targeting at innovation and practicability of recycling processes. ReCell Lithium Recycling RD center brings in three universities and three national labs together to develop innovative, efficient recycling technologies. Most notably, the direct cathode recycling method was developed by the ReCell center. On the other hand, VTO also set up the battery recycling prize to incentivize American entrepreneurs to find innovative solutions to solve current challenges.
Although battery life span can be extended by enabling a second-life application, ultimately EV batteries need to be recycled. Recyclability is not currently an important design consideration for battery manufacturers, and in 2019 only 5% of electric vehicle batteries were recycled. BEV technologies lack an established recycling framework in many countries, making the usage of BEV and other battery-operated electrical equipment a large energy expenditure, ultimately increasing emissions - especially in countries lacking renewable energy resources. Currently, there are five types of recycling processes: Pyrometallurgical recovery, Physical materials separation, Hydrometallurgical metal reclamation, Direct recycling method and Biological metals reclamation. The most widely used processes are the first three processes listed, as shown in the examples of current lithium-ion battery recycling facilities. The last two methods are still on lab or pilot scale, however, they can potentially avoid the largest amount of emission from mining.
The pyrometallurgical process involves burning the battery materials with slag, limestone, sand and coke to produce a metal alloy using a high-temperature furnace. The resulted materials are a metallic alloy, slag and gases. The gases comprise molecules that are evaporated from the electrolyte and binder components. The metal alloy can be separated through hydrometallurgical processes into constituent materials. The slag which is a mixture of metals aluminum, manganese and lithium can either be reclaimed by hydrometallurgical processes or used in the cement industry. This process is very versatile and relatively safe. Because there is no pre-sorting needed, it can work with a wide variety of batteries. In addition, because the whole cell is burnt, the metal from the current collectors could help the smelting process and because of the exothermic reaction of burning electrolyte sand plastics the energy consumption can also be reduced. However, this process still requires relatively higher energy consumption and only a limited number of materials can be reclaimed. Physical materials separation recovered materials by mechanical crushing and exploiting physical properties of different components such as particle size, density, ferromagnetism and hydrophobicity. Copper, aluminum and steel casing can be recovered by sorting. The remaining materials, called "black mass", which is composed of nickel, cobalt, lithium and manganese, need a secondary treatment to recover. For the hydrometallurgical process, the cathode materials need to be crushed to remove the current collector. Then, the cathode materials are leached by aqueous solutions to extract the desired metals from cathode materials. Direct cathode recycling as the name suggested extracts the materials directly, yielding a cathode power that is ready to be used as new cathode pristine material. This process involves extracting the electrolyte using liquid or supercritical CO2. After the size of the recovered components is reduced, the cathode materials can be separated out. For the biological metals reclamation or bio-leaching, the process uses microorganisms to digest metal oxides selectively. Then, recyclers can reduce these oxides to produce metal nanoparticles. Although bio-leaching has been used successfully in the mining industry, this process is still nascent to the recycling industry and plenty of opportunities exists for further investigation.
There have been many efforts around the world to promote recycling technologies development and deployment. In the US, the Department of Energy Vehicle Technologies Offices (VTO) set up two efforts targeting at innovation and practicability of recycling processes. ReCell Lithium Recycling RD center brings in three universities and three national labs together to develop innovative, efficient recycling technologies. Most notably, the direct cathode recycling method was developed by the ReCell center. On the other hand, VTO also set up the battery recycling prize to incentivize American entrepreneurs to find innovative solutions to solve current challenges.
This standard is divided into three parts: * On-board electrical energy storage, i.e. the battery * Functional safety means and protection against failures * Protection of persons against electrical hazards.
Cost parity
Different costs are important. One issue is purchase price, the other issue is total cost of ownership. As of 2015, electric cars are more expensive to initially purchase, but cheaper to run, and in at least some cases, total cost of ownership may be lower. According to ''Kammen et al., 2008'', new PEVs would become cost efficient to consumers if battery prices would decrease from US$1300/kWh to about US$500/kWh (so that the battery may pay for itself). In 2010, theNissan Leaf
The , stylized as LEAF, is a compact five-door hatchback battery electric vehicle (BEV) manufactured by Nissan. It was introduced in Japan and the United States in December 2010, and its second generation was introduced in October 2017. The Lea ...
battery pack was reportedly produced at a cost of US$18,000. Nissan's initial production costs at the launch of the Leaf were therefore about US$750 per kilowatt hour (for the 24 kWh battery).
In 2012, McKinsey Quarterly linked battery prices to gasoline prices on a basis of 5-year total cost of ownership
Total cost of ownership (TCO) is a financial estimate intended to help buyers and owners determine the direct and indirect costs of a product or service. It is a management accounting concept that can be used in full cost accounting or even ecolog ...
for a car, estimating that US$3.50/gallon equates to US$250/kWh. In 2017 McKinsey
McKinsey & Company is a global management consulting firm founded in 1926 by University of Chicago professor James O. McKinsey, that offers professional services to corporations, governments, and other organizations. McKinsey is the oldest a ...
estimated that electric cars will be competitive at a battery pack cost of US$100/kWh (expected around 2030), and expects pack costs to be US$190/kWh by 2020.
In October 2015, car maker GM revealed at their annual Global Business Conference that they expected a price of US$145 per kilowatt hour for Li-ion cells entering 2016.
Range parity
Driving range parity means that the electric vehicle has the same range as an average all-combustion vehicle (), with batteries of specific energy greater than 1 kWh/kg. Higher range means that the electric vehicles would run more kilometers without recharge. Currently, electric vehicle sales are lower than expected due range anxiety - even with the same range as an average all-combustion vehicle, buyers must be assured that there are widely available and compatible charging stations for their vehicles, which are currently not as common as gas stations. Japanese and European Union officials are in talks to jointly develop advanced rechargeable batteries for electric cars to help nations reduce greenhouse-gas emissions. Developing a battery that can power an electric vehicle on a single charging is feasible, said Japanese battery makerGS Yuasa
is a Kyoto-based Japanese company specializing in the development and production of lead acid and lithium-ion batteries, used in automobiles, motorcycles and other areas including aerospace and defense applications.
History
Yuasa
In 1909 ...
Corp. Sharp Corp
is a Japanese multinational corporation that designs and manufactures electronic products, headquartered in Sakai-ku, Sakai, Osaka Prefecture. Since 2016 it has been majority owned by the Taiwan-based Foxconn Group. Sharp employs more than 5 ...
and GS Yuasa are among Japanese solar-power cell and battery makers that may benefit from cooperation.
* The lithium-ion battery in the AC Propulsion tzero provides of range per charge (single charge range). The list price of this vehicle when it was released in 2003 was US$220,000.
* Driving in a Daihatsu Mira equipped with 74 kWh
A kilowatt-hour (unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a unit of energy: one kilowatt of power for one hour. In terms of SI derived units with special names, it equals 3.6 megajoules (MJ). Kilowatt-hours are a common bill ...
lithium ion batteries, the Japan EV Club has achieved a world record for an electric car: without recharging.
* Zonda Bus, in Jiangsu
Jiangsu (; ; pinyin: Jiāngsū, alternatively romanized as Kiangsu or Chiangsu) is an eastern coastal province of the People's Republic of China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with it ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
offers the Zonda Bus New Energy with a only-electric range.
* The supercar Rimac Concept One with 82 kWh battery has a range of 500 km. The car has been in production since 2013. Only 8 have been made and it costs over $1 million.
* The pure electric car BYD e6 with 60 kWh battery has a range of 300 km.
Specifics
Internal components

 Battery pack designs for electric vehicles (EVs) are complex and vary widely by manufacturer and specific application. However, they all incorporate a combination of several simple mechanical and electrical component systems which perform the basic required functions of the pack.
The actual battery cells can have different chemistry, physical shapes, and sizes as preferred by various pack manufacturers. Battery packs will always incorporate many discrete cells connected in series and parallel to achieve the total voltage and current requirements of the pack. Battery packs for all electric drive EVs can contain several hundred individual cells. Each cell has a nominal voltage of 3-4
Battery pack designs for electric vehicles (EVs) are complex and vary widely by manufacturer and specific application. However, they all incorporate a combination of several simple mechanical and electrical component systems which perform the basic required functions of the pack.
The actual battery cells can have different chemistry, physical shapes, and sizes as preferred by various pack manufacturers. Battery packs will always incorporate many discrete cells connected in series and parallel to achieve the total voltage and current requirements of the pack. Battery packs for all electric drive EVs can contain several hundred individual cells. Each cell has a nominal voltage of 3-4 volt
The volt (symbol: V) is the unit of electric potential, electric potential difference (voltage), and electromotive force in the International System of Units (SI). It is named after the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745–1827).
Defin ...
s, depending on its chemical composition.
To assist in manufacturing and assembly, the large stack of cells is typically grouped into smaller stacks called modules. Several of these modules are placed into a single pack. Within each module the cells are welded together to complete the electrical path for current flow. Modules can also incorporate cooling mechanisms, temperature monitors, and other devices. Modules must remain within a specific temperature range for optimal performance. In most cases, modules also allow for monitoring the voltage produced by each battery cell in the stack by using a battery management system (BMS).
The battery cell stack has a main fuse which limits the current of the pack under a short circuit. A "service plug" or "service disconnect" can be removed to split the battery stack into two electrically isolated halves. With the service plug removed, the exposed main terminals of the battery present no high potential electrical danger to service technicians.
The battery pack also contains relays, or contactors, which control the distribution of the battery pack's electrical power to the output terminals. In most cases there will be a minimum of two main relays which connect the battery cell stack to the main positive and negative output terminals of the pack, which then supply high current to the electrical drive motor. Some pack designs include alternate current paths for pre-charging the drive system through a pre-charge resistor or for powering an auxiliary bus which will also have their own associated control relays. For safety reasons these relays are all normally open.
The battery pack also contains a variety of temperature, voltage, and current sensors. Collection of data from the pack sensors and activation of the pack relays are accomplished by the pack's battery monitoring unit (BMU) or BMS. The BMS is also responsible for communications with the vehicle outside the battery pack.
Recharging
Batteries in BEVs must be periodically recharged. BEVs most commonly charge from thepower grid
An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. It consists of:Kaplan, S. M. (2009). Smart Grid. Electrical Power ...
(at home or using a street or shop recharging point
A charging station, also known as a charge point or electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE), is a piece of equipment that supplies electrical power for charging plug-in electric vehicles (including electric cars, electric trucks, electric b ...
), which is in turn generated from a variety of domestic resources, such as coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
, hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined an ...
, nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
, natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon d ...
, and others. Home or grid power, such as photovoltaic
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially ...
solar cell panels, wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few ...
, or microhydro
Micro hydro is a type of hydroelectric power that typically produces from 5 kW to 100 kW of electricity using the natural flow of water. Installations below 5 kW are called pico hydro. These installations can provide power to an ...
may also be used and are promoted because of concerns regarding global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
.
With suitable power supplies, good battery lifespan is usually achieved at charging rates not exceeding half of the capacity of the battery per hour"0.5''C''"
, thereby taking two or more hours for a full charge, but faster charging is available even for large capacity batteries. Charging time at home is limited by the capacity of the household
electrical outlet
AC power plugs and sockets connect electric equipment to the alternating current (AC) mains electricity power supply in buildings and at other sites. Electrical plugs and sockets differ from one another in voltage and current rating, shape, ...
, unless specialized electrical wiring work is done. In the US, Canada, Japan, and other countries with 120V electricity, a normal household outlet delivers 1.5 kilowatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named after James ...
s. In other countries with 230V electricity between 7 and 14 kilowatts can be delivered (230V single phase and 400V three-phase, respectively). In Europe, a 400V (three-phase 230V) grid connection is increasingly popular since newer houses don't have natural gas connection due to the European Union's safety regulations.
Recharging time
Electric cars likeTesla Model S
The Tesla Model S is a battery-powered liftback car serving as the flagship model of Tesla, Inc. The Model S features a dual-motor, all-wheel drive layout, although earlier versions of the Model S featured a rear-motor and rear-wheel drive ...
, Renault Zoe
The Renault Zoe (stylized as ZOE and pronounced as "Zoey"), known as Renault Zoe E-Tech Electric since 2021, is a five-door supermini electric car produced by the French manufacturer Renault. Renault originally unveiled, under the Zoe name, a ...
, BMW i3
The BMW i3 is a B-segment, high-roof hatchback manufactured and marketed by BMW with an electric powertrain using rear-wheel drive via a single-speed transmission and an underfloor lithium-ion battery pack and an optional range-extending pe ...
, etc., can recharge their batteries to 80 percent at quick charging stations within 30 minutes. For example, a Tesla Model 3 Long Range charging on a 250 kW Tesla Version 3 Supercharger went from 2% state of charge with of range to 80% state of charge with of range in 27 minutes, which equates to per hour.
Connectors
The charging power can be connected to the car in two ways. The first is a direct electrical connection known as conductive coupling. This might be as simple as a mains lead into a weatherproofsocket
Socket may refer to:
Mechanics
* Socket wrench, a type of wrench that uses separate, removable sockets to fit different sizes of nuts and bolts
* Socket head screw, a screw (or bolt) with a cylindrical head containing a socket into which the hexag ...
through special high capacity cables with connectors to protect the user from high voltage
High voltage electricity refers to electrical potential large enough to cause injury or damage. In certain industries, ''high voltage'' refers to voltage above a certain threshold. Equipment and conductors that carry high voltage warrant sp ...
s. The modern standard for plug-in vehicle charging is the SAE1772 conductive connector (IEC62196 Type1) in the US. The ACEA has chosen the VDE-AR-E 2623-2-2
IEC 62196 ''Plugs, socket-outlets, vehicle connectors and vehicle inlets – Conductive charging of electric vehicles'' is a series of international standards that define requirements and tests for plugs, socket-outlets, vehicle connectors and veh ...
(IEC62196 Type2) for deployment in Europe, which, without a latch, means unnecessary extra power requirements for the locking mechanism.
The second approach is known as inductive charging
Inductive charging (also known as wireless charging or cordless charging) is a type of wireless power transfer. It uses electromagnetic induction to provide electricity to portable devices. Inductive charging is also used in vehicles, power too ...
. A special 'paddle' is inserted into a slot on the car. The paddle is one winding of a transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer' ...
, while the other is built into the car. When the paddle is inserted it completes a magnetic circuit which provides power to the battery pack. In one inductive charging system, one winding is attached to the underside of the car, and the other stays on the floor of the garage. The advantage of the inductive approach is that there is no possibility of electrocution
Electrocution is death or severe injury caused by electric shock from electric current passing through the body. The word is derived from "electro" and "execution", but it is also used for accidental death.
The term "electrocution" was coin ...
as there are no exposed conductors, although interlocks, special connectors and ground fault detectors can make conductive coupling nearly as safe. Inductive charging can also reduce vehicle weight, by moving more charging componentry offboard."Car Companies' Head-on Competition In Electric Vehicle Charging."(Website). ''The Auto Channel'', 1998-11-24. Retrieved on 2007-08-21. An inductive charging advocate from Toyota contended in 1998, that overall cost differences were minimal, while a conductive charging advocate from Ford contended that conductive charging was more cost efficient.
Recharging spots
, there are 93,439 locations and 178,381 EV charging stations worldwide. Though there are a lot of charging stations worldwide, and the number is only growing, an issue with this is that an EV driver may find themselves at a remote charging station with another vehicle plugged in to the only charger or they may find another vehicle parked in the only EV spot. Currently, no laws prohibit unplugging another person's vehicle, it is simply ruled by etiquette.Travel range before recharging
The range of a BEV depends on the number and type of batteries used. The weight and type of vehicle as well as terrain, weather, and the performance of the driver also have an impact, just as they do on the mileage of traditional vehicles. Electric vehicle conversion performance depends on a number of factors including the battery chemistry: * Lead-acid batteries are the most available and inexpensive. Such conversions generally have a range of . Production EVs with lead-acid batteries are capable of up to per charge. *NiMH NIMH may refer to:
*Nickel–metal hydride battery (NiMH), a type of electrical battery
*National Institute of Mental Health, an agency of the United States government
*National Institute of Medical Herbalists, a professional organisation in the Un ...
batteries have higher specific energy than lead-acid; prototype EVs deliver up to of range.
* New lithium-ion battery-equipped EVs provide of range per charge. Lithium is also less expensive than nickel.
* Nickel-zinc battery are cheaper and lighter than Nickel-cadmium batteries. They are also cheaper than (but not as light as) lithium-ion batteries.
The internal resistance
A practical electrical power source which is a linear electric circuit may, according to Thévenin's theorem, be represented as an ideal voltage source in series with an impedance. This impedance is termed the internal resistance of the source. ...
of some batteries may be significantly increased at low temperature which can cause noticeable reduction in the range of the vehicle and on the lifetime of the battery.
Finding the economic balance of range versus performance, battery capacity versus weight, and battery type versus cost challenges every EV manufacturer.
With an AC system or advanced DC system, regenerative braking
Regenerative braking is an energy recovery mechanism that slows down a moving vehicle or object by converting its kinetic energy into a form that can be either used immediately or stored until needed. In this mechanism, the electric traction mo ...
can extend range by up to 50% under extreme traffic conditions without complete stopping. Otherwise, the range is extended by about 10 to 15% in city driving, and only negligibly in highway driving, depending upon terrain.
BEVs (including buses and trucks) can also use genset trailer
A genset trailer is a range extending device for use with battery electric vehicles consisting of an internal combustion engine and an electric generator (collectively called a genset). They run on traditional fuels such as gasoline or diesel an ...
s and pusher trailer A pusher trailer is a device attached to the rear of a vehicle or bike that provides force to assist the vehicle.
For bikes Electric
Electric pusher trailers use energy stored in a battery, typically of lithium ion or sealed lead acid chemistry, ...
s in order to extend their range when desired without the additional weight during normal short range use. Discharged basket trailers can be replaced by recharged ones en route. If rented then maintenance costs can be deferred to the agency.
Some BEVs can become Hybrid vehicle
A hybrid vehicle is one that uses two or more distinct types of power, such as submarines that use diesel when surfaced and batteries when submerged. Other means to store energy include pressurized fluid in hydraulic hybrids.
The basic princi ...
s depending on the trailer and car types of energy and powertrain.
Trailers
Auxiliary battery capacity carried in trailers can increase the overall vehicle range, but also increases the loss of power arising fromaerodynamic drag
In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) is a force acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding ...
, increases weight transfer
Weight transfer and load transfer are two expressions used somewhat confusingly to describe two distinct effects:
*the change in load borne by different wheels of even perfectly rigid vehicles during acceleration
*the change in center of mas ...
effects and reduces traction capacity.
Swapping and removing
An alternative to recharging is to exchange drained or nearly drained batteries (or battery range extender modules) with fully charged batteries. This is called battery swapping and is done in exchange stations. Features of swap stations include: # The consumer is no longer concerned with battery capital cost, life cycle, technology, maintenance, or warranty issues; # Swapping is far faster than charging: battery swap equipment built by the firm Better Place has demonstrated automated swaps in less than 60 seconds; # Swap stations increase the feasibility of distributed energy storage via the electric grid; Concerns about swap stations include: # Potential for fraud (battery quality can only be measured over a full discharge cycle; battery lifetime can only be measured over repeated discharge cycles; those in the swap transaction cannot know if they are getting a worn or reduced effectiveness battery; battery quality degrades slowly over time, so worn batteries will be gradually forced into the system) # Manufacturers' unwillingness to standardize battery access / implementation details # Safety concernsRe-filling
Zinc-bromine flow batteries can be re-filled using a liquid, instead of recharged by connectors, saving time.Lifecycle of lithium-based EV batteries
 There are mainly four stages during the lifecycle of lithium-based EV batteries: the raw materials phase, the battery manufacturing, operation phase and the end-of-life management phase. As shown in the schematic of life cycle of EV batteries, during the first stage, the rare earth materials are extracted in different parts of the world. After they are refined by pre-processing factories, the battery manufacturing companies take over these materials and start to produce batteries and assemble them into packs. These battery packs are then sent to car manufacturing companies for EV integration. In the last stage, if no management is in place, valuable materials in the batteries could be potentially wasted. A good end-of-life management phase will try to close the loop. The used battery packs will either be reused as stationary storage or recycled depending on the battery state of health (SOH).
The battery lifecycle is rather long and requires close cooperation between companies and countries. Currently, the raw materials phase and the battery manufacturing and operation phase are well established. The end-of-life management phase is struggled to grow, especially the recycling process mainly because of economics. For example, only 6% of lithium-ion batteries were collected for recycling in 2017–2018 in Australia. However, closing the loop is extremely important. Not only because of a predicted tightened supply of nickel, cobalt and lithium in the future, also recycling EV batteries has the potential to maximize the environmental benefit. Xu et al. predicted that in the sustainable development scenario, lithium, cobalt and nickel will reach or surpass the amount of known reserves in the future if no recycling is in place. Ciez and Whitacre found that by deploying battery recycling some green house gas (GHG) emission from mining could be avoided.
There are mainly four stages during the lifecycle of lithium-based EV batteries: the raw materials phase, the battery manufacturing, operation phase and the end-of-life management phase. As shown in the schematic of life cycle of EV batteries, during the first stage, the rare earth materials are extracted in different parts of the world. After they are refined by pre-processing factories, the battery manufacturing companies take over these materials and start to produce batteries and assemble them into packs. These battery packs are then sent to car manufacturing companies for EV integration. In the last stage, if no management is in place, valuable materials in the batteries could be potentially wasted. A good end-of-life management phase will try to close the loop. The used battery packs will either be reused as stationary storage or recycled depending on the battery state of health (SOH).
The battery lifecycle is rather long and requires close cooperation between companies and countries. Currently, the raw materials phase and the battery manufacturing and operation phase are well established. The end-of-life management phase is struggled to grow, especially the recycling process mainly because of economics. For example, only 6% of lithium-ion batteries were collected for recycling in 2017–2018 in Australia. However, closing the loop is extremely important. Not only because of a predicted tightened supply of nickel, cobalt and lithium in the future, also recycling EV batteries has the potential to maximize the environmental benefit. Xu et al. predicted that in the sustainable development scenario, lithium, cobalt and nickel will reach or surpass the amount of known reserves in the future if no recycling is in place. Ciez and Whitacre found that by deploying battery recycling some green house gas (GHG) emission from mining could be avoided.

 To develop a deeper understanding of the lifecycle of EV batteries, it is important to analyze the emission associated with different phases. Using NMC cylindrical cells as an example, Ciez and Whitacre found that around 9 kg CO2e kg battery''−''1 is emitted during raw materials pre-processing and battery manufacturing under the US average electricity grid. The biggest part of the emission came from materials preparation accounting for more than 50% of the emissions. If NMC pouch cell is used, the total emission increases to almost 10 kg CO2e kg battery''−''1 while materials manufacturing still contributes to more than 50% of the emission. During the end-of-life management phase, the refurbishing process adds little emission to the lifecycle emission. The recycling process, on the other hand, as suggested by Ciez and Whitacre emits a significant amount of GHG. As shown in the battery recycling emission plot a and c, the emission of the recycling process varies with the different recycling processes, different chemistry and different form factor. Thus, the net emission avoided compared to not recycling also varies with these factors. At a glance, as shown in the plot b and d, the direct recycling process is the most ideal process for recycling pouch cell batteries, while the hydrometallurgical process is most suitable for cylindrical type battery. However, with the error bars shown, the best approach cannot be picked with confidence. It is worth noting that for the lithium iron phosphates (LFP) chemistry, the net benefit is negative. Because LFP cells lacks cobalt and nickel which are expensive and energy intensive to produce, it is more energetically efficient to mine. In general, in addition to promoting the growth of a single sector, a more integrated effort should be in place to reduce the lifecycle emission of EV batteries. A finite total supply of rare earth material can apparently justify the need for recycling. But the environmental benefit of recycling needs closer scrutiny. Based on current recycling technology, the net benefit of recycling depends on the form factors, the chemistry and the recycling process chosen.
To develop a deeper understanding of the lifecycle of EV batteries, it is important to analyze the emission associated with different phases. Using NMC cylindrical cells as an example, Ciez and Whitacre found that around 9 kg CO2e kg battery''−''1 is emitted during raw materials pre-processing and battery manufacturing under the US average electricity grid. The biggest part of the emission came from materials preparation accounting for more than 50% of the emissions. If NMC pouch cell is used, the total emission increases to almost 10 kg CO2e kg battery''−''1 while materials manufacturing still contributes to more than 50% of the emission. During the end-of-life management phase, the refurbishing process adds little emission to the lifecycle emission. The recycling process, on the other hand, as suggested by Ciez and Whitacre emits a significant amount of GHG. As shown in the battery recycling emission plot a and c, the emission of the recycling process varies with the different recycling processes, different chemistry and different form factor. Thus, the net emission avoided compared to not recycling also varies with these factors. At a glance, as shown in the plot b and d, the direct recycling process is the most ideal process for recycling pouch cell batteries, while the hydrometallurgical process is most suitable for cylindrical type battery. However, with the error bars shown, the best approach cannot be picked with confidence. It is worth noting that for the lithium iron phosphates (LFP) chemistry, the net benefit is negative. Because LFP cells lacks cobalt and nickel which are expensive and energy intensive to produce, it is more energetically efficient to mine. In general, in addition to promoting the growth of a single sector, a more integrated effort should be in place to reduce the lifecycle emission of EV batteries. A finite total supply of rare earth material can apparently justify the need for recycling. But the environmental benefit of recycling needs closer scrutiny. Based on current recycling technology, the net benefit of recycling depends on the form factors, the chemistry and the recycling process chosen.
Manufacturing
There are mainly three stages during the manufacturing process of EV batteries: materials manufacturing, cell manufacturing and integration, as shown in Manufacturing process of EV batteries graph in grey, green and orange color respectively. This shown process does not include manufacturing of cell hardware, i.e. casings and current collectors. During the materials manufacturing process, the active material, conductivity additives, polymer binder and solvent are mixed first. After this, they are coated on the current collectors ready for the drying process. During this stage, the methods of making active materials depend on the electrode and the chemistry. For the cathode, two of the most popular chemistry are transition metal oxides, i.e. Lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxides (Li-NMC) and Lithium metal phosphates, i.e. Lithium iron phosphates (LFP). For the anode, the most popular chemistry now is graphite. However, recently there have been a lot of companies started to make Si mixed anodeSila Nanotech
and Li metal anod
Cuberg
. In general, for active materials production, there are three steps: materials preparation, materials processing and refinement. Schmuch et al. discussed materials manufacturing in greater details. In the cell manufacturing stage, the prepared electrode will be processed to the desired shape for packaging in a cylindrical, rectangular or pouch format. Then after filling the electrolytes and sealing the cells, the battery cells are cycled carefully to form SEI protecting the anode. Then, these batteries are assembled into packs ready for vehicle integration. Kwade et al. discuss the overall battery manufacturing process in greater detail.
= Reusing and repurposing
= When an EV battery pack degrades to 70% to 80% of its original capacity, it is defined to reach the end-of-life. One of the waste management methods is to reuse the pack. By repurposing the pack for stationary storage, more value can be extracted from the battery pack while reducing the per kWh lifecycle impact. However, enabling battery second-life is not easy. Several challenges are hindering the development of the battery refurbishing industry. First, uneven and undesired battery degradation happens during EV operation. Each battery cell could degrade differently during operation. Currently, the state of health (SOH) information from a battery management system (BMS) can be extracted on a pack level. Getting the cell state of health information requires next-generation BMS. In addition, because a lot of factors could contribute to the low SOH at the end of life, such as temperature during operation, charging/discharging pattern and calendar degradation, the degradation mechanism could be different. Thus, just knowing the SOH is not enough to ensure the quality of the refurbished pack. To solve this challenge, engineers can mitigate the degradation by engineering the next-generation thermal management system. To fully understand the degradation inside the battery, computational methods including the first-principle method, physics-based model and machine learning based method should work together to identify the different degradation modes and quantify the level of degradation after severe operations. Lastly, more efficient battery characteristics tools, for instance, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) should be used to ensure the quality of the battery pack. Second, it is costly and time-intensive to disassemble modules and cells. Following the last point, the first step is testing to determine the remaining SOH of the battery modules. This operation could vary for each retired system. Next, the module must be fully discharged. Then, the pack must be disassembled and reconfigured to meet the power and energy requirement of the second life application. It is important to note that qualified workers and specialized tools are required to dismantle the high weight and high voltage EV batteries. Besides the solutions discussed in the previous section, a refurbishing company can sell or reuse the discharged energy from the module to reduce the cost of this process. To accelerate the disassembly process, there have been several attempts to incorporate robots in this process. In this case, robots can handle more dangerous task increasing the safety of the dismantling process.
Third, battery technology is non-transparent and lacks standards. Because battery development is the core part of EV, it is difficult for the manufacturer to label the exact chemistry of cathode, anode and electrolytes on the pack. In addition, the capacity and the design of the cells and packs changes on a yearly basis. The refurbishing company needs to closely work with the manufacture to have a timely update on this information. On the other hand, government can set up labeling standard.
Lastly, the refurbishing process adds cost to the used batteries. Since 2010, the battery costs have decreased by over 85% which is significantly faster than the prediction. Because of the added cost of refurbishing, the refurbished unit may be less attractive than the new batteries to the market.
Nonetheless, there have been several successes on the second-life application as shown in the examples of storage projects using second-life EV batteries. They are used in less demanding stationary storage application as peak shaving or additional storage for renewable-based generating sources.
Second, it is costly and time-intensive to disassemble modules and cells. Following the last point, the first step is testing to determine the remaining SOH of the battery modules. This operation could vary for each retired system. Next, the module must be fully discharged. Then, the pack must be disassembled and reconfigured to meet the power and energy requirement of the second life application. It is important to note that qualified workers and specialized tools are required to dismantle the high weight and high voltage EV batteries. Besides the solutions discussed in the previous section, a refurbishing company can sell or reuse the discharged energy from the module to reduce the cost of this process. To accelerate the disassembly process, there have been several attempts to incorporate robots in this process. In this case, robots can handle more dangerous task increasing the safety of the dismantling process.
Third, battery technology is non-transparent and lacks standards. Because battery development is the core part of EV, it is difficult for the manufacturer to label the exact chemistry of cathode, anode and electrolytes on the pack. In addition, the capacity and the design of the cells and packs changes on a yearly basis. The refurbishing company needs to closely work with the manufacture to have a timely update on this information. On the other hand, government can set up labeling standard.
Lastly, the refurbishing process adds cost to the used batteries. Since 2010, the battery costs have decreased by over 85% which is significantly faster than the prediction. Because of the added cost of refurbishing, the refurbished unit may be less attractive than the new batteries to the market.
Nonetheless, there have been several successes on the second-life application as shown in the examples of storage projects using second-life EV batteries. They are used in less demanding stationary storage application as peak shaving or additional storage for renewable-based generating sources.
= Recycling
= Although battery life span can be extended by enabling a second-life application, ultimately EV batteries need to be recycled. Recyclability is not currently an important design consideration for battery manufacturers, and in 2019 only 5% of electric vehicle batteries were recycled. BEV technologies lack an established recycling framework in many countries, making the usage of BEV and other battery-operated electrical equipment a large energy expenditure, ultimately increasing emissions - especially in countries lacking renewable energy resources. Currently, there are five types of recycling processes: Pyrometallurgical recovery, Physical materials separation, Hydrometallurgical metal reclamation, Direct recycling method and Biological metals reclamation. The most widely used processes are the first three processes listed, as shown in the examples of current lithium-ion battery recycling facilities. The last two methods are still on lab or pilot scale, however, they can potentially avoid the largest amount of emission from mining.
The pyrometallurgical process involves burning the battery materials with slag, limestone, sand and coke to produce a metal alloy using a high-temperature furnace. The resulted materials are a metallic alloy, slag and gases. The gases comprise molecules that are evaporated from the electrolyte and binder components. The metal alloy can be separated through hydrometallurgical processes into constituent materials. The slag which is a mixture of metals aluminum, manganese and lithium can either be reclaimed by hydrometallurgical processes or used in the cement industry. This process is very versatile and relatively safe. Because there is no pre-sorting needed, it can work with a wide variety of batteries. In addition, because the whole cell is burnt, the metal from the current collectors could help the smelting process and because of the exothermic reaction of burning electrolyte sand plastics the energy consumption can also be reduced. However, this process still requires relatively higher energy consumption and only a limited number of materials can be reclaimed. Physical materials separation recovered materials by mechanical crushing and exploiting physical properties of different components such as particle size, density, ferromagnetism and hydrophobicity. Copper, aluminum and steel casing can be recovered by sorting. The remaining materials, called "black mass", which is composed of nickel, cobalt, lithium and manganese, need a secondary treatment to recover. For the hydrometallurgical process, the cathode materials need to be crushed to remove the current collector. Then, the cathode materials are leached by aqueous solutions to extract the desired metals from cathode materials. Direct cathode recycling as the name suggested extracts the materials directly, yielding a cathode power that is ready to be used as new cathode pristine material. This process involves extracting the electrolyte using liquid or supercritical CO2. After the size of the recovered components is reduced, the cathode materials can be separated out. For the biological metals reclamation or bio-leaching, the process uses microorganisms to digest metal oxides selectively. Then, recyclers can reduce these oxides to produce metal nanoparticles. Although bio-leaching has been used successfully in the mining industry, this process is still nascent to the recycling industry and plenty of opportunities exists for further investigation.
There have been many efforts around the world to promote recycling technologies development and deployment. In the US, the Department of Energy Vehicle Technologies Offices (VTO) set up two efforts targeting at innovation and practicability of recycling processes. ReCell Lithium Recycling RD center brings in three universities and three national labs together to develop innovative, efficient recycling technologies. Most notably, the direct cathode recycling method was developed by the ReCell center. On the other hand, VTO also set up the battery recycling prize to incentivize American entrepreneurs to find innovative solutions to solve current challenges.
Although battery life span can be extended by enabling a second-life application, ultimately EV batteries need to be recycled. Recyclability is not currently an important design consideration for battery manufacturers, and in 2019 only 5% of electric vehicle batteries were recycled. BEV technologies lack an established recycling framework in many countries, making the usage of BEV and other battery-operated electrical equipment a large energy expenditure, ultimately increasing emissions - especially in countries lacking renewable energy resources. Currently, there are five types of recycling processes: Pyrometallurgical recovery, Physical materials separation, Hydrometallurgical metal reclamation, Direct recycling method and Biological metals reclamation. The most widely used processes are the first three processes listed, as shown in the examples of current lithium-ion battery recycling facilities. The last two methods are still on lab or pilot scale, however, they can potentially avoid the largest amount of emission from mining.
The pyrometallurgical process involves burning the battery materials with slag, limestone, sand and coke to produce a metal alloy using a high-temperature furnace. The resulted materials are a metallic alloy, slag and gases. The gases comprise molecules that are evaporated from the electrolyte and binder components. The metal alloy can be separated through hydrometallurgical processes into constituent materials. The slag which is a mixture of metals aluminum, manganese and lithium can either be reclaimed by hydrometallurgical processes or used in the cement industry. This process is very versatile and relatively safe. Because there is no pre-sorting needed, it can work with a wide variety of batteries. In addition, because the whole cell is burnt, the metal from the current collectors could help the smelting process and because of the exothermic reaction of burning electrolyte sand plastics the energy consumption can also be reduced. However, this process still requires relatively higher energy consumption and only a limited number of materials can be reclaimed. Physical materials separation recovered materials by mechanical crushing and exploiting physical properties of different components such as particle size, density, ferromagnetism and hydrophobicity. Copper, aluminum and steel casing can be recovered by sorting. The remaining materials, called "black mass", which is composed of nickel, cobalt, lithium and manganese, need a secondary treatment to recover. For the hydrometallurgical process, the cathode materials need to be crushed to remove the current collector. Then, the cathode materials are leached by aqueous solutions to extract the desired metals from cathode materials. Direct cathode recycling as the name suggested extracts the materials directly, yielding a cathode power that is ready to be used as new cathode pristine material. This process involves extracting the electrolyte using liquid or supercritical CO2. After the size of the recovered components is reduced, the cathode materials can be separated out. For the biological metals reclamation or bio-leaching, the process uses microorganisms to digest metal oxides selectively. Then, recyclers can reduce these oxides to produce metal nanoparticles. Although bio-leaching has been used successfully in the mining industry, this process is still nascent to the recycling industry and plenty of opportunities exists for further investigation.
There have been many efforts around the world to promote recycling technologies development and deployment. In the US, the Department of Energy Vehicle Technologies Offices (VTO) set up two efforts targeting at innovation and practicability of recycling processes. ReCell Lithium Recycling RD center brings in three universities and three national labs together to develop innovative, efficient recycling technologies. Most notably, the direct cathode recycling method was developed by the ReCell center. On the other hand, VTO also set up the battery recycling prize to incentivize American entrepreneurs to find innovative solutions to solve current challenges.
Environmental impact
Transition to electric vehicles is estimated to require an 87,000% increase in supply of specific metals by 2060 that need to be mined initially, with recycling (see above) covering part of the demand in future. In the UK alone, it is estimated that switching 31.5 million petrol vehicles to electric would require "207,900 tonnes of cobalt, 264,600 tonnes of lithium carbonate, 7,200 tonnes of neodymium and dysprosium, and 2,362,500 tonnes of copper", and a worldwide switch would require 40 times these amounts. In 2022 the US government planned to give US states $5 billion over five years for electric vehicle chargers. According to IEA 2021 study, mineral supplies need to increase from 400 kilotonnes in 2020 to 11,800 kilotonnes in 2040 in order to cover the demand by EV. This increase creates a number of key challenges, from supply chain (as 60% of production is concentrated in China) to significant impact on climate and environment as result of such a large increase in mining operations.Vehicle-to-grid
Smart grid
A smart grid is an electrical grid which includes a variety of operation and energy measures including:
*Advanced metering infrastructure (of which smart meters are a generic name for any utility side device even if it is more capable e.g. a f ...
allows BEVs to provide power to the grid at any time, especially:
* During peak load
In electrical engineering, a load profile is a graph of the variation in the electrical load versus time. A load profile will vary according to customer type (typical examples include residential, commercial and industrial), temperature and hol ...
periods (When the selling price of electricity can be very high. Vehicles can then be recharged during off-peak
Peak demand on an electrical grid is simply the highest electrical power demand that has occurred over a specified time period (Gönen 2008). Peak demand is typically characterized as annual, daily or seasonal and has the unit of power.
Peak d ...
hours at cheaper rates which helps absorb excess night time generation. The vehicles serve as a distributed battery storage system to buffer power.)
* During blackouts, as backup power sources.
Safety
The safety issues of battery electric vehicles are largely dealt with by the international standard ISObr>6469This standard is divided into three parts: * On-board electrical energy storage, i.e. the battery * Functional safety means and protection against failures * Protection of persons against electrical hazards.
Firefighter
A firefighter is a first responder and rescuer extensively trained in firefighting, primarily to extinguish hazardous fires that threaten life, property, and the environment as well as to rescue people and in some cases or jurisdictions als ...
s and rescue personnel receive special training to deal with the higher voltages and chemicals encountered in electric and hybrid electric vehicle accidents. While BEV accidents may present unusual problems, such as fires and fumes resulting from rapid battery discharge, many experts agree that BEV batteries are safe in commercially available vehicles and in rear-end collisions, and are safer than gasoline-propelled cars with rear gasoline tanks.
Usually, battery performance testing includes the determination of:
* State Of Charge (SOC)
* State of Health (SOH)
* Energy Efficiency
Performance testing simulates the drive cycles for the drive trains of Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV), Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV) and Plug in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV) as per the required specifications of car manufacturers ( OEMs). During these drive cycles, controlled cooling of the battery can be performed, simulating the thermal conditions in the car.
In addition, climatic chambers control environmental conditions during testing and allow simulation of the full automotive temperature range and climatic conditions.
Patents
Patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A ...
s may be used to suppress development or deployment of battery technology. For example, patents relevant to the use of Nickel metal hydride cells in cars were held by an offshoot of Chevron Corporation
Chevron Corporation is an American multinational energy corporation. The second-largest direct descendant of Standard Oil, and originally known as the Standard Oil Company of California (shortened to Socal or CalSo), it is headquartered in S ...
, a petroleum company, who maintained veto power over any sale or licensing of NiMH technology.
Research, development and innovation
As of December 2019, billions of euro in research are planned to be invested around the world for improving batteries. Researchers have come up with some design considerations for contactless BEV chargers. Inductively coupled power transfer (ICPT) systems are made to transfer power efficiently from a primary source (charging station) to one or more secondary sources (BEVs) in a contactless way via magnetic coupling. Europe has plans for heavy investment in electric vehicle battery development and production, and Indonesia also aims to produce electric vehicle batteries in 2023, inviting Chinese battery firm GEM and Contemporary Amperex Technology Ltd to invest in Indonesia.Ultracapacitors
Electric double-layer capacitors (or "ultracapacitors") are used in some electric vehicles, such as AFS Trinity's concept prototype, to store rapidly available energy with their highspecific power
Power-to-weight ratio (PWR, also called specific power, or power-to-mass ratio) is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measuremen ...
, in order to keep batteries within safe resistive heating limits and extend battery life.
Since commercially available ultracapacitors have a low specific energy, no production electric cars use ultracapacitors exclusively.
In January 2020, Elon Musk
Elon Reeve Musk ( ; born June 28, 1971) is a business magnate and investor. He is the founder, CEO and chief engineer of SpaceX; angel investor, CEO and product architect of Tesla, Inc.; owner and CEO of Twitter, Inc.; founder of The B ...
, CEO of Tesla, stated that the advancements in Li-ion battery technology have made ultra-capacitors unnecessary for electric vehicles.
Promotion in the United States
There are several kinds of policy measures to make BEVs more desirable. Purchase-based incentives include a tax rebate or a subsidy when buying or registering a modern BEV. Use based policy measures include providing an exemption for congestion charging for BEV users, allowing BEV users to use bus lanes, or giving free parking to BEVs. These can be classified into local and global policy incentives. Local incentives including congestion charge exemptions or free BEV parking in a city only influence those located in this specific area. Global policy incentives including subsidies or national tax rebates apply to anyone in a country. In 2009, PresidentBarack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, Obama was the first Af ...
announced 48 new advanced battery and electric drive projects that would receive US$2.4 billion in funding under the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, p ...
. The government claimed that these projects would accelerate the development of U.S. manufacturing capacity for batteries and electric drive components as well as the deployment of electric drive vehicles, helping to establish American leadership in creating the next generation of advanced vehicles.
The announcement marked the single largest investment in advanced battery technology for hybrid and electric-drive vehicles ever made. Industry officials expected that this US$2.4 billion investment, coupled with another US$2.4 billion in cost share from the award winners, would result directly in the creation tens of thousands of manufacturing jobs in the U.S. battery and auto industries.
The awards cover US$1.5 billion in grant
Grant or Grants may refer to:
Places
*Grant County (disambiguation)
Australia
* Grant, Queensland, a locality in the Barcaldine Region, Queensland, Australia
United Kingdom
* Castle Grant
United States
* Grant, Alabama
* Grant, Inyo County, ...
s to United States-based manufacturers to produce batteries and their components and to expand battery recycling capacity.
* U.S. Vice President Joe Biden announced in Detroit over US$1 billion in grants to companies and universities based in Michigan. Reflecting the state's leadership in clean energy manufacturing, Michigan companies and institutions received the largest share of grant funding of any state. Two companies, A123 Systems
A123 Systems, LLC, a subsidiary of the Chinese Wanxiang Group Holdings, is a developer and manufacturer of lithium iron phosphate batteries and energy storage systems.
The company was founded in 2001 by Yet-Ming Chiang, Bart Riley, and Ric Fulo ...
and Johnson Controls
Johnson Controls International is an American
Irish-domiciled multinational conglomerate headquartered in Cork, Ireland, that produces fire, HVAC, and security equipment for buildings. As of mid-2019, it employed 105,000 people in around 2,00 ...
, would receive a total of approximately US$550 million to establish a manufacturing base in the state for advanced batteries, and two others, Compact Power and Dow Kokam, would receive a total of over US$300 million for manufacturing battery cells and materials. Large automakers based in Michigan, including GM, Chrysler, and Ford, would receive a total of more than US$400 million to manufacture batteries and electric drive components. Three educational institutions in Michigan — the University of Michigan
, mottoeng = "Arts, Knowledge, Truth"
, former_names = Catholepistemiad, or University of Michigania (1817–1821)
, budget = $10.3 billion (2021)
, endowment = $17 billion (2021)As o ...
, Wayne State University
Wayne State University (WSU) is a public research university in Detroit, Michigan. It is Michigan's third-largest university. Founded in 1868, Wayne State consists of 13 schools and colleges offering approximately 350 programs to nearly 25,000 ...
in Detroit, and Michigan Technological University
Michigan Technological University (Michigan Tech, MTU, or simply Tech) is a public research university in Houghton, Michigan, founded in 1885 as the Michigan Mining School, the first post-secondary institution in the Upper Peninsula of Michiga ...
in Houghton, in the Upper Peninsula — would receive a total of more than US$10 million for education and workforce training programs to train researchers, technicians, and service providers, and to conduct consumer research to accelerate the transition towards advanced vehicles and batteries.
* U.S. Energy Secretary Steven Chu visited Celgard, in Charlotte, North Carolina
Charlotte ( ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of North Carolina. Located in the Piedmont region, it is the county seat of Mecklenburg County. The population was 874,579 at the 2020 census, making Charlotte the 16th-most popu ...
, to announce a US$49 million grant for the company to expand its separator production capacity to serve the expected increased demand for lithium-ion batteries from manufacturing facilities in the United States. Celgard was planning to expand its manufacturing capacity in Charlotte, North Carolina, and nearby Concord, North Carolina
Concord is the county seat and largest city in Cabarrus County, in the U.S. state of North Carolina. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 105,186, with an estimated population in 2021 of 107,697. In terms of population, the c ...
, and the company expected the new separator production to come online in 2010. Celgard expected that approximately hundreds of jobs could be created, with the first of those jobs beginning as early as fall 2009.
* EPA Administrator Lisa Jackson was in St. Petersburg, Florida, to announce a US$95.5 million grant for Saft America, Inc. to construct a new plant in Jacksonville
Jacksonville is a city located on the Atlantic coast of northeast Florida, the most populous city proper in the state and is the List of United States cities by area, largest city by area in the contiguous United States as of 2020. It is the co ...
on the site of the former Cecil Field
Cecil Airport is a public airport and commercial spaceport located in Jacksonville, Florida, United States. It is owned by the Jacksonville Aviation Authority and services military aircraft, corporate aircraft, general aviation, and air cargo. ...
military base, to manufacture lithium-ion cells, modules and battery packs for military, industrial, and agricultural vehicles.
* Deputy Secretary of the Department of Transportation John Porcari
John Davis Porcari (born December 14, 1958) is an American government official who served as United States deputy secretary of transportation and is currently serving as the Port Envoy to the White House Supply Chain Disruptions Task Force. He was ...
visited East Penn Manufacturing Co, in Lyon Station, Pennsylvania
Lyons (also known as Lyon Station) is a borough in Berks County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 478 at the 2010 census.
History
Lyons was founded as Lyon Station in 1860 when the railroad was extended to that point. The commun ...
, to award the company a US$32.5 million grant to increase production capacity for their valve regulated lead-acid batteries and the UltraBattery, a lead-acid battery combined with a carbon supercapacitor, for micro and mild hybrid applications.
On 2 May 2022, President Biden announced the administration will begin a $3.16 billion plan to boost domestic manufacturing and recycling of batteries, in a larger effort to shift the country away from gas-powered cars to electric vehicles. The goal of the Biden administration is to have half of U.S. automobile production electric by 2030.
The Inflation Reduction Act
The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (IRA) is a landmark United States federal law which aims to curb inflation by reducing the deficit, lowering prescription drug prices, and investing into domestic energy production while promoting clean en ...
, passed August 16, 2022, aimed to incentivize clean energy manufacturing with a $7,500 consumer tax credit for EVs with US-built batteries, and subsidies for EV plants. By October 2022, billions of dollars of investment had been announced for over two dozen US battery plants, leading some commentators to nickname the Midwest as the "Battery Belt."
Promotion in Norway
Norway has become a leading example of BEV promotion. The BEV market share is highest in the world in Norway, the main reason being the strong incentives for promoting purchase and ownership of BEVs. Norway has an incentive package for BEVs that often equate or even make a BEV cheaper to purchase than an Internal Combustion Engine Vehicle (ICEV). In addition to the purchase price incentives, there are also incentives that make BEVs more cost-efficient and convenient in daily use. Incentive policies have a clear success for increasing BEV sales in Norway, making it a great case to learn from for other countries wanting to head in the same direction.See also
Examples
*List of hybrid vehicles
This is a list of hybrid vehicles, including both regular hybrid electric vehicles and plug-in hybrids in chronological order of first production:
Automobiles
Overview by decade
Early designs: 1899-1917
*1899: Carmaker Pieper of Belg ...
* List of production battery electric vehicles
* List of electric vehicle battery manufacturers
List
See also
*Electric vehicle battery
*List of production battery electric vehicles
This is a list of battery electric vehicles that are mass-produced, formerly produced, and planned. It includes only vehicles exclusively using chemi ...
Related
* Battery charging *Battery electric multiple unit
A battery electric multiple unit (BEMU), battery electric railcar or accumulator railcar is an electrically driven multiple unit or railcar whose energy is derived from rechargeable batteries driving the traction motors.
Prime advantages of these ...
* Battery locomotive
An electric locomotive is a locomotive powered by electricity from overhead lines, a third rail or on-board energy storage such as a battery or a supercapacitor. Locomotives with on-board fuelled prime movers, such as diesel engines or gas tu ...
* Charging station
A charging station, also known as a charge point or electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE), is a piece of equipment that supplies electrical power for charging plug-in electric vehicles (including electric cars, electric trucks, electric b ...
* Dual-mode vehicle
A dual-mode vehicle (DMV) is a vehicle that can operate on conventional road surfaces as well as a railway track or a dedicated track known as a " guideway". The development of these vehicles started together with personal rapid transport syst ...
* Electric car energy efficiency
* Flywheel energy storage
* List of battery types
This list is a summary of notable electric battery types composed of one or more electrochemical cells. Three lists are provided in the table. The primary (non-rechargeable) and secondary (rechargeable) cell lists are lists of battery chemistry. ...
* Rechargeable battery
A rechargeable battery, storage battery, or secondary cell (formally a type of energy accumulator), is a type of electrical battery which can be charged, discharged into a load, and recharged many times, as opposed to a disposable or prima ...
* Salt water battery
A saltwater battery is a type of battery that uses a mixture of water and salt as its electrolyte. Unlike traditional batteries, saltwater batteries are non-flammable and do not pollute as much. This makes them an eco-friendly energy storage solut ...
* Traction motor
A traction motor is an electric motor used for propulsion of a vehicle, such as locomotives, electric or hydrogen vehicles, elevators or electric multiple unit.
Traction motors are used in electrically powered rail vehicles ( electric multip ...
* Vehicle-to-grid
Vehicle-to-grid (V2G), also known as Vehicle-to-home (V2H) or Vehicle-to-load (V2L) describes a system in which plug-in electric vehicles (PEV) sell demand response services to the grid. Demand services are either delivering electricity or by red ...
(V2G)
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Electric Vehicle Battery Electric vehicle technologies Rechargeable batteries Battery applications