tosylate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 In
In
 The tosyl group is also useful as a protecting group for
The tosyl group is also useful as a protecting group for
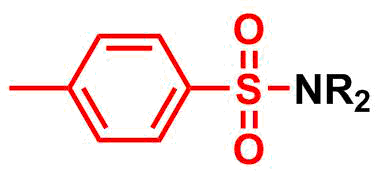 Tosyl (Ts) group is commonly used as a
Tosyl (Ts) group is commonly used as a
 * Refluxing with TMSCl,
* Refluxing with TMSCl,
organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J ...
, a toluenesulfonyl group (tosyl group, abbreviated Ts or Tos) is a univalent functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the r ...
with the chemical formula
In chemistry, a chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, ...
–. It consists of a tolyl group, –, joined to a sulfonyl
In organosulfur chemistry, a sulfonyl group can refer either to a functional group found primarily in sulfones, or to a substituent obtained from a sulfonic acid by the removal of the hydroxyl group, similarly to acyl groups. Sulfonyl groups c ...
group, ––, with the open valence on sulfur. This group is usually derived from the compound tosyl chloride, (abbreviated TsCl), which forms ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ...
s and amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it i ...
s of toluenesulfonic acid
''p''-Toluenesulfonic acid (PTSA or ''p''TsOH) or tosylic acid (TsOH) is an organic compound with the formula CH3 C6H4 SO3H. It is a white extremely hygroscopic solid that is soluble in water, alcohols, and other polar organic solvents. The CH3C ...
, (abbreviated TsOH). The para orientation illustrated (''p''-toluenesulfonyl) is most common, and by convention ''tosyl'' without a prefix refers to the ''p''-toluenesulfonyl group.
The toluenesulfonate (or tosylate) group refers to the – (TsO–) group, with an additional oxygen attached to sulfur and open valence on an oxygen. In a chemical name, the term ''tosylate'' may either refer to the salts containing the anion of ''p''-toluenesulfonic acid, (M = alkali metal
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names ...
, , , etc), or it may refer to ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ...
s of ''p''-toluenesulfonic acid, TsOR (R = organyl group).
Applications
For SN2 reactions, alkyl alcohols can also be converted to alkyl tosylates, often through addition of tosyl chloride. In this reaction, the lone pair of the alcohol oxygen attacks the sulfur of the tosyl chloride, displacing the chloride and forming the tosylate with retention of reactant stereochemistry. This is useful because alcohols are poor leaving groups in SN2 reactions, in contrast to the tosylate group. It is the transformation of alkyl alcohols to alkyl tosylates that allows an SN2 reaction to occur in the presence of a good nucleophile. A tosyl group can function as aprotecting group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis.
In man ...
in organic synthesis. Alcohols can be converted to tosylate groups so that they do not react. The tosylate group may later be converted back into an alcohol. The use of these functional groups is exemplified in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
of the drug tolterodine, wherein one of the steps a phenol
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it r ...
group is protected as its tosylate and the primary alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
as its nosylate. The latter is a leaving group for displacement by diisopropylamine
Diisopropylamine is a secondary amine with the chemical formula (Me2CH)2NH (Me = methyl). Diisopropylamine is a colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Its lithium derivative, lithium diisopropylamide, known as LDA is a widely used reagent. ...
:Reaction sequence: organic reduction
Organic reductions or organic oxidations or organic redox reactions are redox reactions that take place with organic compounds. In organic chemistry oxidations and reductions are different from ordinary redox reactions, because many reactions carr ...
of ''ethyl benzoylacetate'' by sodium borohydride
Sodium borohydride, also known as sodium tetrahydridoborate and sodium tetrahydroborate, is an inorganic compound with the formula Na BH4. This white solid, usually encountered as an aqueous basic solution, is a reducing agent that finds applica ...
to a diol, followed by Friedel-Crafts alkylation with p-cresol
''para''-Cresol, also 4-methylphenol, is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4(OH). It is a colourless solid that is widely used intermediate in the production of other chemicals. It is a derivative of phenol and is an isomer of ''o'' ...
and iron(III) chloride
Iron(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula . Also called ferric chloride, it is a common compound of iron in the +3 oxidation state. The anhydrous compound is a crystalline solid with a melting point of 307.6 °C. The col ...
to a phenol. The tosyl and nosyl groups are introduced as their respective chlorides with either sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly caustic base and al ...
or triethylamine
Triethylamine is the chemical compound with the formula N(CH2CH3)3, commonly abbreviated Et3N. It is also abbreviated TEA, yet this abbreviation must be used carefully to avoid confusion with triethanolamine or tetraethylammonium, for which TEA ...
as a base. The next step is nucleophilic displacement of the nosyl group by diisopropylamine
Diisopropylamine is a secondary amine with the chemical formula (Me2CH)2NH (Me = methyl). Diisopropylamine is a colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Its lithium derivative, lithium diisopropylamide, known as LDA is a widely used reagent. ...
, the remaining tosyl group is removed by another round of NaOH. Not shown: optical resolution
Optical resolution describes the ability of an imaging system to resolve detail, in the object that is being imaged.
An imaging system may have many individual components, including one or more lenses, and/or recording and display components. ...
by L-tartaric acid to optically pure (R)-isomer
: The tosyl group is also useful as a protecting group for
The tosyl group is also useful as a protecting group for amines
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such ...
. The resulting sulfonamide
In organic chemistry, the sulfonamide functional group (also spelled sulphonamide) is an organosulfur group with the structure . It consists of a sulfonyl group () connected to an amine group (). Relatively speaking this group is unreactive. ...
structure is extremely stable. It can be deprotected to reveal the amine using reductive or strongly acidic conditions.
Amine protection – tosyl (Ts)
 Tosyl (Ts) group is commonly used as a
Tosyl (Ts) group is commonly used as a protecting group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis.
In man ...
for amines
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such ...
in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
.
Most common amine protection methods
* Tosyl chloride andpyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid w ...
in dichloromethane
Dichloromethane (DCM or methylene chloride, methylene bichloride) is an organochlorine compound with the formula . This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like, sweet odour is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible wit ...
Most common amine deprotection methods
* HBr andacetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main componen ...
at 70 °C * Refluxing with TMSCl,
* Refluxing with TMSCl, sodium iodide
Sodium iodide (chemical formula NaI) is an ionic compound formed from the chemical reaction of sodium metal and iodine. Under standard conditions, it is a white, water-soluble solid comprising a 1:1 mix of sodium cations (Na+) and iodide anions (I ...
and acetonitrile
Acetonitrile, often abbreviated MeCN (methyl cyanide), is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile ( hydrogen cyanide is a simpler nitrile, but the cyanide anion is not clas ...
* Reduction with SmI2
* Reduction with Red-Al
Related compounds
Closely related to the tosylates are the nosylates andbrosylate
In organic chemistry, brosyl (or ''para''-bromophenylsulfonyl) group is a functional group with the chemical formula BrC6H4SO2. This group is usually introduced using the compound brosyl chloride, BrC6H4SO2Cl, which forms sulfonyl esters and amide ...
s, which are the abbreviated names for ''o''- or ''p-''nitrobenzenesulfonates and ''p''-bromobenzenesulfonates, respectively.
See also
* Tosylic acid * Sulfonyl groupNotes
References
{{Reflist Sulfonyl groups Leaving groups Sulfonate esters