top dead centre on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
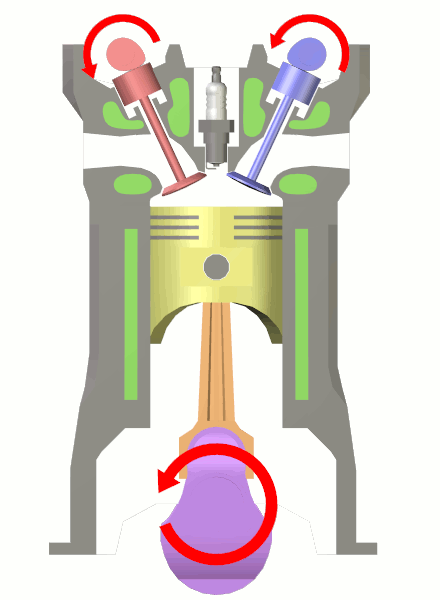 In a
In a  More generally, the dead centre is any position of a crank where the applied force is straight along its axis, meaning no turning force can be applied. Many sorts of machines are crank driven, including
More generally, the dead centre is any position of a crank where the applied force is straight along its axis, meaning no turning force can be applied. Many sorts of machines are crank driven, including
 In a
In a reciprocating engine
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common featu ...
, the dead centre is the position of a piston in which it is either farthest from, or nearest to, the crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecting ...
. The former is known as Top Dead Centre (TDC) while the latter is known as Bottom Dead Centre (BDC).
 More generally, the dead centre is any position of a crank where the applied force is straight along its axis, meaning no turning force can be applied. Many sorts of machines are crank driven, including
More generally, the dead centre is any position of a crank where the applied force is straight along its axis, meaning no turning force can be applied. Many sorts of machines are crank driven, including unicycle
A unicycle is a vehicle that touches the ground with only one wheel. The most common variation has a bicycle frame, frame with a bicycle saddle, saddle, and has a human-powered vehicle, pedal-driven direct-drive mechanism, direct-drive. A two spee ...
s, bicycle
A bicycle, also called a pedal cycle, bike or cycle, is a human-powered or motor-powered assisted, pedal-driven, single-track vehicle, having two wheels attached to a frame, one behind the other. A is called a cyclist, or bicyclist.
Bic ...
s, tricycle
A tricycle, sometimes abbreviated to trike, is a human-powered (or gasoline or electric motor powered or assisted, or gravity powered) three-wheeled vehicle.
Some tricycles, such as cycle rickshaws (for passenger transport) and freight trikes, ...
s, various types of machine press
A forming press, commonly shortened to press, is a machine tool that changes the shape of a work-piece by the application of pressure. The operator of a forming press is known as a press-tool setter, often shortened to tool-setter.
Presses ...
es, gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic co ...
engines
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power g ...
, diesel engines, steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomot ...
s, and other steam engines. Crank-driven machines rely on the energy stored in a flywheel
A flywheel is a mechanical device which uses the conservation of angular momentum to store rotational energy; a form of kinetic energy proportional to the product of its moment of inertia and the square of its rotational speed. In particular, ass ...
to overcome the dead centre, or are designed, in the case of multi-cylinder engines, so that dead centres can never exist on all cranks at the same time. A steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomot ...
is an example of the latter, the connecting rods being arranged such that the dead centre for each cylinder occurs out of phase with the other one (or more) cylinders.
Bicycles
Bicycle
A bicycle, also called a pedal cycle, bike or cycle, is a human-powered or motor-powered assisted, pedal-driven, single-track vehicle, having two wheels attached to a frame, one behind the other. A is called a cyclist, or bicyclist.
Bic ...
cranks have dead centres at approximately 12 o'clock and 6 o'clock where simple pushing down of the pedal will not turn the chainwheel
The crankset (in the US) or chainset (in the UK), is the component of a bicycle drivetrain that converts the reciprocating motion of the rider's legs into rotational motion used to drive the chain or belt, which in turn drives the rear wheel. ...
, but the rider's leg is able to apply tangential force at the pedal to overcome it. Fixed-gear bicycles (without a freehub
A freehub is a type of bicycle hub that incorporates a ratcheting mechanism.
A set of sprockets (called a " cassette") is mounted onto a splined shaft of the freehub to engage the chain. The ratcheting mechanism is a part of the hub, in contra ...
) use the momentum
In Newtonian mechanics, momentum (more specifically linear momentum or translational momentum) is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. If is an object's mass an ...
of the bicycle and rider to keep the chainwheel turning even if the rider makes no attempt to pedal in a circular motion.
Reciprocating engine
In areciprocating engine
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common featu ...
, top dead centre of piston #1 is the point from which ignition system
An ignition system generates a spark or heats an electrode to a high temperature to ignite a fuel-air mixture in spark ignition internal combustion engines, oil-fired and gas-fired boilers, rocket engines, etc. The widest application for spark i ...
measurements are made and the firing order
The firing order of an internal combustion engine is the sequence of ignition for the cylinders.
In a spark ignition (e.g. gasoline/petrol) engine, the firing order corresponds to the order in which the spark plugs are operated. In a diesel engi ...
is determined. For example, ignition timing
In a spark ignition internal combustion engine, ignition timing is the timing, relative to the current piston position and crankshaft angle, of the release of a spark in the combustion chamber near the end of the compression stroke.
The need for ...
is normally specified as degrees of crankshaft rotation before top dead centre (BTDC). A very few small and fast-burning engines require a spark just after top dead centre (ATDC), such as the Nissan MA engine
The MA is a straight-4 SOHC 0.9 L, 1.0 L, or 1.2 L engine introduced in 1982 by Nissan, intended primarily for the K10 series Micra/March model. It shares design similarities with the older E engine, with an 8-valve hemispherical cylinder head ...
with hemispherical combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combusti ...
s, or hydrogen engines.
Top dead centre for cylinder one is often marked on the crankshaft pulley, the flywheel
A flywheel is a mechanical device which uses the conservation of angular momentum to store rotational energy; a form of kinetic energy proportional to the product of its moment of inertia and the square of its rotational speed. In particular, ass ...
or harmonic balancer
A harmonic damper is a device fitted to the free (accessory drive) end of the crankshaft of an internal combustion engine to counter torsional and resonance vibrations from the crankshaft. This device must be interference fit to the crankshaft in ...
or both, with adjacent timing mark
A timing mark is an indicator used for setting the timing of the ignition system of an engine, typically found on the crankshaft pulley (as pictured) or the flywheel, being the largest radius rotating at crankshaft speed and therefore the place w ...
s showing the recommended ignition timing settings as decided during engine development. These timing marks can be used to set the ignition timing either statically by hand or dynamically using a timing light
A timing light is a stroboscope used to dynamically set the ignition timing of an Otto cycle or similar internal combustion engine equipped with a distributor. Modern electronically controlled passenger vehicle engines require use of a scan tool ...
, by rotating the distributor
A distributor is an enclosed rotating switch used in spark-ignition internal combustion engines that have mechanically timed ignition. The distributor's main function is to route high voltage current from the ignition coil to the spark plugs ...
in its seat.
In a multi-cylinder engine, pistons may reach top dead centre simultaneously or at different times depending on the engine configuration
The engine configuration describes the fundamental operating principles by which internal combustion engines are categorized.
Piston engines are often categorized by their cylinder layout, valves and camshafts. Wankel engines are often categorize ...
. For example:
* In the V-twin
A V-twin engine, also called a V2 engine, is a two-cylinder piston engine where the cylinders share a common crankshaft and are arranged in a V configuration.
Although widely associated with motorcycles (installed either transversely or longi ...
configuration, the two pistons reach TDC at different times, equal to the angular displacement
Angular displacement of a body is the angle (in radians, degrees or revolutions) through which a point revolves around a centre or a specified axis in a specified sense. When a body rotates about its axis, the motion cannot simply be analyzed ...
between the cylinders.
* In the flat twin
A flat-twin engine is a two-cylinder internal combustion engine with the cylinders on opposite sides of the crankshaft. The most common type of flat-twin engine is the boxer-twin engine, where both pistons move inwards and outwards at the same ti ...
configuration, two opposing pistons reach TDC simultaneously, which is also called 0° displacement - but one piston will be at TDC of the compression stroke, the other on TDC of the exhaust stroke.
* In the straight-4
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the ...
configuration, the two end pistons (pistons 1 and 4) reach TDC simultaneously, as do the two centre pistons (pistons 2 and 3), but these two pairs reach TDC with an angular displacement of 180°. Similar patterns are found in almost all straight engine
The straight or inline engine is an internal combustion engine with all cylinders aligned in one row and having no offset. Usually found in four, six and eight cylinder configurations, they have been used in automobiles, locomotives and aircraft ...
s with even numbers of cylinders, with the two end pistons and two middle pistons moving together (not necessarily 180° out of phase however) and the intermediate pistons moving in pairs in mirror-image around the centre of the engine.
* In the flatplane V8 and many larger V engine
A V engine, sometimes called a Vee engine, is a common configuration for internal combustion engines. It consists of two cylinder banks—usually with the same number of cylinders in each bank—connected to a common crankshaft. These cylinder ...
s, the piston motion within each bank is similar to that of a straight engine, however in the crossplane V8 and all V10
A V10 engine is a ten-cylinder piston engine where two banks of five cylinders are arranged in a V configuration around a common crankshaft. V10 engines are much less common than V8 and V12 engines. Several V10 diesel engines have been pr ...
engines the motion is far more complex.
The concept of top dead centre is also extended to pistonless rotary engine
A pistonless rotary engine is an internal combustion engine that does not use pistons in the way a reciprocating engine does. Designs vary widely but typically involve one or more rotors, sometimes called rotary pistons. Although many differen ...
s, and means the point in the cycle in which the volume of a combustion chamber is smallest. This typically occurs several times per rotor revolution; In the Wankel engine
The Wankel engine (, ) is a type of internal combustion engine using an Eccentric (mechanism), eccentric rotary combustion engine, rotary design to convert pressure into rotating motion. It was invented by German engineer Felix Wankel, and desi ...
for example it occurs three times for every one revolution of the rotor (although only once per revolution of the engine output shaft, since the output rotates at three times the speed of the rotor).
Finding the volume of the cylinder using TDC and BDC and multiplying it by the number of cylinders will give the engine displacement
Engine displacement is the measure of the cylinder volume swept by all of the pistons of a piston engine, excluding the combustion chambers. It is commonly used as an expression of an engine's size, and by extension as a loose indicator of the ...
.
Steam engines
Assteam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be trans ...
s are commonly horizontal, the relevant terms are front dead centre and back dead centre rather than "top" and "bottom".
If a single-cylinder steam engine stops in either of the dead centre positions it must be moved off the dead centre before it will restart. In small engines this is done by turning the flywheel
A flywheel is a mechanical device which uses the conservation of angular momentum to store rotational energy; a form of kinetic energy proportional to the product of its moment of inertia and the square of its rotational speed. In particular, ass ...
by hand. In large engines the flywheel is moved with a lever or "turning bar". Both operations must be done with care to avoid the operator becoming entangled in the machinery. Even larger engines might require the use of a barring engine
A barring engine (also called barring motor) is a small engine that forms part of the installation of a large engine, and is used to turn the main engine to a favourable position from which it can be started. If the main engine has stopped close ...
.
Steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomot ...
s normally have at least two double acting cylinders, which enables the cranks to be set so that at least one piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tig ...
will always be off the dead centre and no starting assistance is required. In the common case of a two piston locomotive, the cranks are set at right angle
In geometry and trigonometry, a right angle is an angle of exactly 90 Degree (angle), degrees or radians corresponding to a quarter turn (geometry), turn. If a Line (mathematics)#Ray, ray is placed so that its endpoint is on a line and the ad ...
s, so that whenever one piston is at dead centre the other is in mid-stroke, and giving four equally spaced power strokes per revolution.
Other machines
This term is also used in the realm of production equipment. A mechanicalpunch press
A punch press is a type of machine press used to cut holes in material. It can be small and manually operated and hold one simple die set, or be very large, CNC operated, with a multi-station turret and hold a much larger and complex die set.
D ...
employs a crankshaft similar to that found in an engine. In the punch press the crankshaft drives a ram which when it is farthest away from the platen of the press is considered to be in the position of top dead centre.
See also
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Dead Centre Engine technology