three-domain system on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The three-domain system is a taxonomic classification system that groups all cellular
The three-domain system is a taxonomic classification system that groups all cellular
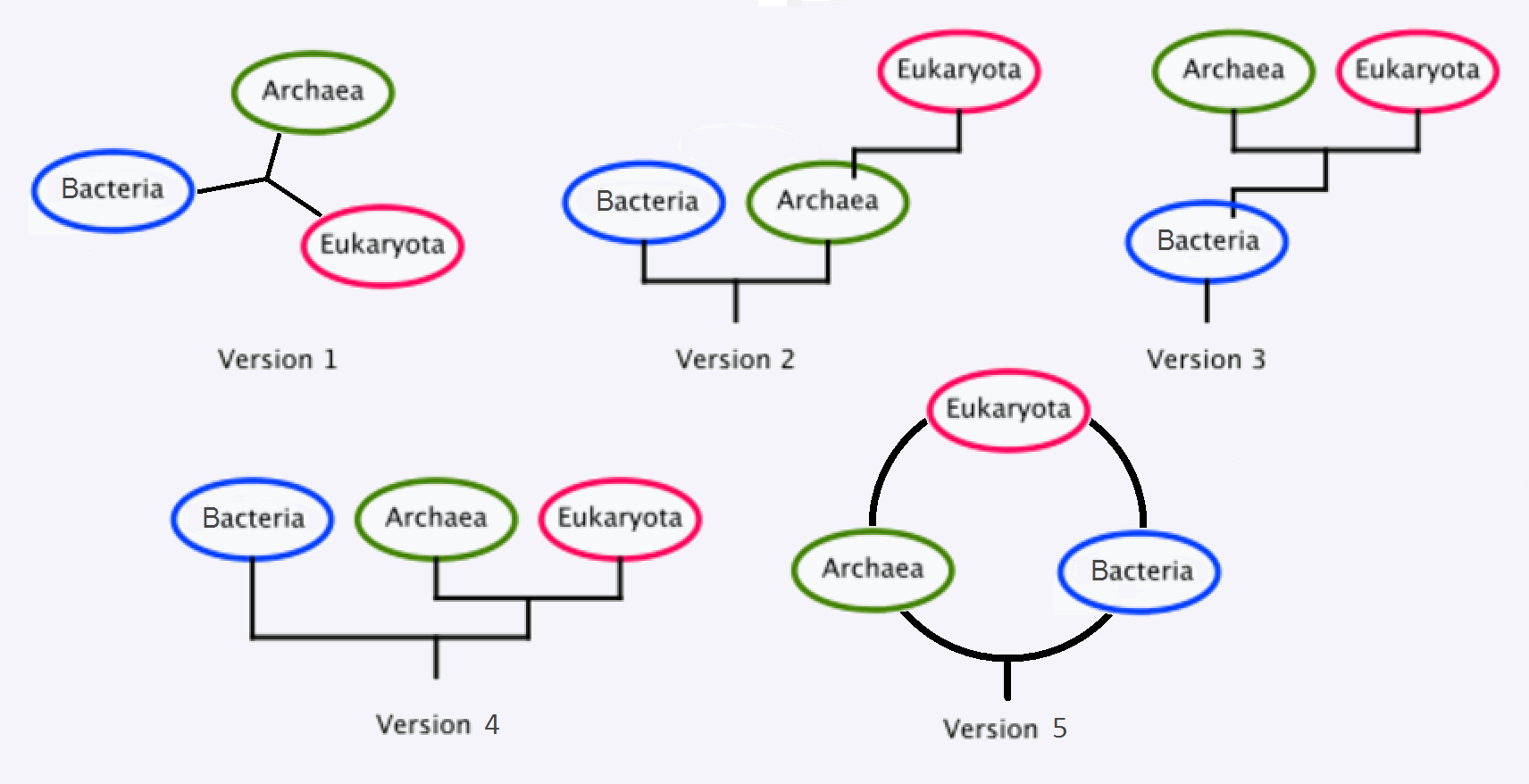 Parts of the three-domain theory have been challenged by scientists including
Parts of the three-domain theory have been challenged by scientists including
life
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, Structure#Biological, organisation, met ...
into three domains, namely Archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
, Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
and Eukarya
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose cells have a membrane-bound nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of l ...
, introduced by Carl Woese, Otto Kandler and Mark Wheelis in 1990. The key difference from earlier classifications such as the two-empire system and the five-kingdom classification is the splitting of Archaea (previously named "archaebacteria") from Bacteria as completely different organisms.
The three domain hypothesis is considered obsolete by some since it is thought that eukaryotes do not form a separate domain of life; instead, they arose from a fusion between two different species, one from within Archaea and one from within Bacteria. (see Two-domain system)
Background
Woese argued, on the basis of differences in16S rRNA
16S ribosomal RNA (or 16Svedberg, S rRNA) is the RNA component of the 30S subunit of a prokaryotic ribosome (SSU rRNA). It binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and provides most of the SSU structure.
The genes coding for it are referred to as ...
gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s, that bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes each arose separately from an ancestor with poorly developed genetic machinery, often called a progenote. To reflect these primary lines of descent, he treated each as a domain, divided into several different kingdoms
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchic state or realm ruled by a king or queen.
** A monarchic chiefdom, represented or governed by a king or queen.
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and me ...
. Originally his split of the prokaryotes was into ''Eubacteria'' (now ''Bacteria'') and ''Archaebacteria'' (now ''Archaea''). Woese initially used the term "kingdom" to refer to the three primary phylogenic groupings, and this nomenclature was widely used until the term "domain" was adopted in 1990.
Acceptance of the validity of Woese's phylogenetically valid classification was a slow process. Prominent biologists including Salvador Luria
Salvador Edward Luria (; ; born Salvatore Luria; August 13, 1912 – February 6, 1991) was an Italian microbiologist, later a Naturalized citizen of the United States#Naturalization, naturalized U.S. citizen. He won the Nobel Prize in Physiology ...
and Ernst Mayr
Ernst Walter Mayr ( ; ; 5 July 1904 – 3 February 2005) was a German-American evolutionary biologist. He was also a renowned Taxonomy (biology), taxonomist, tropical explorer, ornithologist, Philosophy of biology, philosopher of biology, and ...
objected to his division of the prokaryotes. Not all criticism of him was restricted to the scientific level. A decade of labor-intensive oligonucleotide
Oligonucleotides are short DNA or RNA molecules, oligomers, that have a wide range of applications in genetic testing, Recombinant DNA, research, and Forensic DNA, forensics. Commonly made in the laboratory by Oligonucleotide synthesis, solid-phase ...
cataloging left him with a reputation as "a crank", and Woese would go on to be dubbed "Microbiology's Scarred Revolutionary" by a news article printed in the journal ''Science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
'' in 1997. The growing amount of supporting data led the scientific community
The scientific community is a diverse network of interacting scientists. It includes many "working group, sub-communities" working on particular scientific fields, and within particular institutions; interdisciplinary and cross-institutional acti ...
to accept the Archaea by the mid-1980s. Today, very few scientists still accept the concept of a unified Prokarya.
Classification
The three-domain system adds a level of classification (the domains) "above" the kingdoms present in the previously used five- or six-kingdom systems. This classification system recognizes the fundamental divide between the two prokaryotic groups, insofar as Archaea appear to be more closely related to eukaryotes than they are to otherprokaryotes
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a single-celled organism whose cell lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'before', and (), meaning 'nut' ...
– bacteria-like organisms with no cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (; : nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have #Anucleated_cells, ...
. The three-domain system sorts the previously known kingdoms into these three domains: Archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
, Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
, and Eukarya
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose cells have a membrane-bound nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of l ...
.
Domain Archaea
TheArchaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
are prokaryotic, with no nuclear membrane, but with biochemistry and RNA markers that are distinct from bacteria. The archaeans possess unique, ancient evolutionary history for which they are considered some of the oldest species of organisms on Earth, most notably their diverse, exotic metabolisms.
Some examples of archaeal organisms are:
* methanogen
Methanogens are anaerobic archaea that produce methane as a byproduct of their energy metabolism, i.e., catabolism. Methane production, or methanogenesis, is the only biochemical pathway for Adenosine triphosphate, ATP generation in methanogens. A ...
s – which produce the gas methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
* halophile
A halophile (from the Greek word for 'salt-loving') is an extremophile that thrives in high salt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more ...
s – which live in very salty water
* thermoacidophiles – which thrive in acidic high-temperature water
Domain Bacteria
TheBacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
are also prokaryotic; their domain consists of cells with bacterial rRNA, no nuclear membrane, and whose membranes possess primarily ''diacyl glycerol diester lipids''. Traditionally classified as bacteria, many thrive in the same environments favored by humans, and were the first prokaryotes discovered; they were briefly called the Eubacteria or "true" bacteria when the Archaea were first recognized as a distinct clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
.
Most known pathogenic prokaryotic organisms belong to bacteria (see for exceptions). For that reason, and because the Archaea are typically difficult to grow in laboratories, Bacteria are currently studied more extensively than Archaea.
Some examples of bacteria include:
* "Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteri ...
" – photosynthesizing bacteria that are related to the chloroplasts of eukaryotic plants and algae
* Spirochaetota – Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists ...
bacteria that include those causing syphilis and Lyme disease
* Actinomycetota – Gram-positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
The Gram stain is ...
bacteria including '' Bifidobacterium animalis'' which is present in the human large intestine
Domain Eukarya
Eukaryota
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
are organisms whose cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus. They include many large single-celled organisms and all known non- microscopic organisms. The domain contains, for example:
* Holomycota
Holomycota or Nucletmycea are a basal Opisthokont clade as sister of the Holozoa. It consists of the Cristidiscoidea and the kingdom Fungi. The position of nucleariids, unicellular free-living phagotrophic amoebae, as the earliest lineage o ...
– mushrooms and allies
* Viridiplantae – green plants
* Holozoa – animals and allies
* Stramenopile
The stramenopiles, also called heterokonts, are protists distinguished by the presence of stiff tripartite external hairs. In most species, the hairs are attached to flagella, in some they are attached to other areas of the cellular surface, an ...
s – includes brown algae
* Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa is a major Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of Amoeba, amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, Pseudopod#Morphology, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In trad ...
– solitary and social amoebae
* Discoba
Excavata is an obsolete, extensive and diverse Paraphyly, paraphyletic group of unicellular Eukaryote, Eukaryota. The group was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and the name latinized and assigned a rank by Thomas Cavalier-Smit ...
– includes euglenoids
Niches
Each of the three cell types tends to fit into recurring specialities or roles. Bacteria tend to be the most prolific reproducers, at least in moderate environments. Archaeans tend to adapt quickly to extreme environments, such as high temperatures, high acids, high sulfur, etc. This includes adapting to use a wide variety of food sources. Eukaryotes are the most flexible with regard to forming cooperative colonies, such as in multi-cellular organisms, including humans. In fact, the structure of a eukaryote is likely to have derived from a joining of different cell types, formingorganelle
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell (biology), cell, that has a specific function. The name ''organelle'' comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as Organ (anatomy), organs are to th ...
s.
''Parakaryon myojinensis
''Parakaryon myojinensis'', also known as the Myojin parakaryote, is a highly unusual species of single-celled organism known only from a single specimen, described in 2012. It has features of both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but is apparently ...
'' (''incertae sedis
or is a term used for a taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group where its broader relationships are unknown or undefined. Alternatively, such groups are frequently referred to as "enigmatic taxa". In the system of open nomenclature, uncertainty ...
'') is a single-celled organism known to be a unique example. "This organism appears to be a life form distinct from prokaryotes
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a single-celled organism whose cell lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'before', and (), meaning 'nut' ...
and eukaryotes
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose cells have a membrane-bound nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of ...
", with features of both.
Alternatives
 Parts of the three-domain theory have been challenged by scientists including
Parts of the three-domain theory have been challenged by scientists including Ernst Mayr
Ernst Walter Mayr ( ; ; 5 July 1904 – 3 February 2005) was a German-American evolutionary biologist. He was also a renowned Taxonomy (biology), taxonomist, tropical explorer, ornithologist, Philosophy of biology, philosopher of biology, and ...
, Thomas Cavalier-Smith, and Radhey S. Gupta.
Recent work has proposed that Eukaryota may have actually branched off from the domain Archaea. According to Spang ''et al.'', Lokiarchaeota forms a monophyletic group with eukaryotes in phylogenomic analyses. The associated genomes also encode an expanded repertoire of eukaryotic signature proteins that are suggestive of sophisticated membrane remodelling capabilities. This work suggests a two-domain system as opposed to the three-domain system. Exactly how and when Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya developed and how they are related continues to be debated.
See also
* Two-domain system * Neomura *Bacterial phyla
Bacterial phyla constitute the major lineages of the domain Bacteria. While the exact definition of a bacterial phylum is debated, a popular definition is that a bacterial phylum is a monophyletic lineage of bacteria whose 16S rRNA genes share ...
* Eocyte hypothesis
* Taxonomy
image:Hierarchical clustering diagram.png, 280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy
Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme o ...
* Two-empire system
References
{{Reflist, 30em Biological classification High-level systems of taxonomy Biology controversies de:Domäne (Biologie) fr:Domaine (biologie)