Thermoplastic elastomer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), sometimes referred to as thermoplastic rubbers, are a class of
 There are six generic classes of commercial TPEs (designations acc. to ISO 18064):
*Styrenic block copolymers, TPS (TPE-s)
* Thermoplastic polyolefinelastomers, TPO (TPE-o)
*Thermoplastic Vulcanizates, TPV (TPE-v or TPV)
*
There are six generic classes of commercial TPEs (designations acc. to ISO 18064):
*Styrenic block copolymers, TPS (TPE-s)
* Thermoplastic polyolefinelastomers, TPO (TPE-o)
*Thermoplastic Vulcanizates, TPV (TPE-v or TPV)
*
 TPE became a commercial reality when thermoplastic polyurethane polymers became available in the 1950s. During the 1960s styrene block copolymer became available, and in the 1970s a wide range of TPEs came on the scene. The worldwide usage of TPEs (680,000 tons/year in 1990) is growing at about nine percent per year. The styrene-butadiene materials possess a two-phase microstructure due to incompatibility between the
TPE became a commercial reality when thermoplastic polyurethane polymers became available in the 1950s. During the 1960s styrene block copolymer became available, and in the 1970s a wide range of TPEs came on the scene. The worldwide usage of TPEs (680,000 tons/year in 1990) is growing at about nine percent per year. The styrene-butadiene materials possess a two-phase microstructure due to incompatibility between the 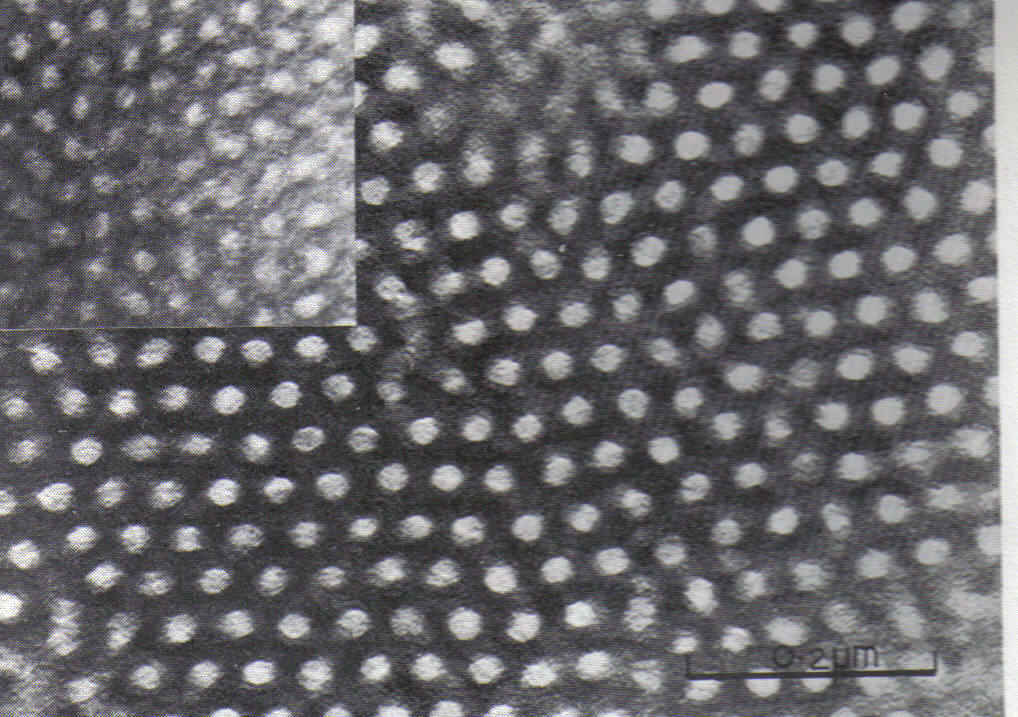 Block copolymers are interesting because they can "microphase separate" to form periodic nanostructures, as in the styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) block copolymer shown at right. The polymer is known as Kraton and is used for shoe soles and
Block copolymers are interesting because they can "microphase separate" to form periodic nanostructures, as in the styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) block copolymer shown at right. The polymer is known as Kraton and is used for shoe soles and  Other TPEs have crystalline domains where one kind of block co-crystallizes with other block in adjacent chains, such as in copolyester rubbers, achieving the same effect as in the SBS block polymers. Depending on the block length, the domains are generally more stable than the latter owing to the higher crystal
Other TPEs have crystalline domains where one kind of block co-crystallizes with other block in adjacent chains, such as in copolyester rubbers, achieving the same effect as in the SBS block polymers. Depending on the block length, the domains are generally more stable than the latter owing to the higher crystal
 TPEs are used where conventional elastomers cannot provide the range of physical properties needed in the product. These materials find large application in the automotive sector and in household appliances sector. In 2014, the world market for TPEs reached a volume of ca. 16.7 billion US dollars. About 40% of all TPE products are used in the manufacturing of vehicles. For instance, copolyester TPEs are used in
TPEs are used where conventional elastomers cannot provide the range of physical properties needed in the product. These materials find large application in the automotive sector and in household appliances sector. In 2014, the world market for TPEs reached a volume of ca. 16.7 billion US dollars. About 40% of all TPE products are used in the manufacturing of vehicles. For instance, copolyester TPEs are used in 
Latest Material and Technological Developments for Activewear
(Joanne Yip, 2020, ''page 66-67)'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Thermoplastic Elastomer Biomaterials Polymers
copolymer
In polymer chemistry, a copolymer is a polymer derived from more than one species of monomer. The polymerization of monomers into copolymers is called copolymerization. Copolymers obtained from the copolymerization of two monomer species are some ...
s or a physical mix of polymers (usually a plastic and a rubber) that consist of materials with both thermoplastic
A thermoplastic, or thermosoft plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.
Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate ...
and elastomer
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of ''elastic ...
ic properties. While most elastomers are thermoset
In materials science, a thermosetting polymer, often called a thermoset, is a polymer that is obtained by irreversibly hardening (" curing") a soft solid or viscous liquid prepolymer (resin). Curing is induced by heat or suitable radiation and ...
s, thermoplastics are in contrast relatively easy to use in manufacturing, for example, by injection moulding
Injection moulding (U.S. spelling: injection molding) is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for ...
. Thermoplastic elastomers show advantages typical of both rubbery materials and plastic materials. The benefit of using thermoplastic elastomers is the ability to stretch to moderate elongations and return to its near original shape creating a longer life and better physical range than other materials. The principal difference between thermoset elastomers and thermoplastic elastomers is the type of cross-linking bond in their structures. In fact, crosslinking is a critical structural factor which imparts high elastic properties.
Types
 There are six generic classes of commercial TPEs (designations acc. to ISO 18064):
*Styrenic block copolymers, TPS (TPE-s)
* Thermoplastic polyolefinelastomers, TPO (TPE-o)
*Thermoplastic Vulcanizates, TPV (TPE-v or TPV)
*
There are six generic classes of commercial TPEs (designations acc. to ISO 18064):
*Styrenic block copolymers, TPS (TPE-s)
* Thermoplastic polyolefinelastomers, TPO (TPE-o)
*Thermoplastic Vulcanizates, TPV (TPE-v or TPV)
*Thermoplastic polyurethane
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is any of a class of polyurethane plastics with many properties, including elasticity, transparency, and resistance to oil, grease, and abrasion. Technically, they are thermoplastic elastomers consisting of linea ...
s, TPU (TPU)
*Thermoplastic copolyester, TPC (TPE-E)
*Thermoplastic polyamides, TPA (TPE-A)
*Not classified thermoplastic elastomers, TPZ
Examples of TPE materials that come from block copolymers group are amongst others CAWITON, THERMOLAST K, THERMOLAST M, Arnitel, Hytrel, Dryflex, Mediprene, Kraton, Pibiflex, Sofprene, and Laprene. Out of these styrenic block copolymers (TPE-s) are CAWITON, THERMOLAST K, THERMOLAST M, Sofprene, Dryflex, Laprene and Tuftec. Laripur, Desmopan or Elastollan are examples of thermoplastic polyurethane
Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is any of a class of polyurethane plastics with many properties, including elasticity, transparency, and resistance to oil, grease, and abrasion. Technically, they are thermoplastic elastomers consisting of linea ...
s (TPU). Sarlink, Santoprene, Termoton, Solprene, THERMOLAST V, Vegaprene, or Forprene are examples of TPV materials. Examples of thermoplastic olefin elastomers (TPO) compound are For-Tec E or Engage. Ninjaflex used for 3D printing
3D printing or additive manufacturing is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer ...
.
In order to qualify as a thermoplastic elastomer, a material must have these three essential characteristics:
*The ability to be stretched to moderate elongations and, upon the removal of stress, return to something close to its original shape
*Processable as a melt at elevated temperature
*Absence of significant creep
Background
polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a ...
and polybutadiene
Polybutadiene utadiene rubber BRis a synthetic rubber. Polybutadiene rubber is a polymer formed from the polymerization of the monomer 1,3-butadiene. Polybutadiene has a high resistance to wear and is used especially in the manufacture of tir ...
blocks, the former separating into spheres or rods depending on the exact composition. With low polystyrene content, the material is elastomeric with the properties of the polybutadiene predominating. Generally they offer a much wider range of properties than conventional cross-linked rubbers because the composition can vary to suit final construction goals.
 Block copolymers are interesting because they can "microphase separate" to form periodic nanostructures, as in the styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) block copolymer shown at right. The polymer is known as Kraton and is used for shoe soles and
Block copolymers are interesting because they can "microphase separate" to form periodic nanostructures, as in the styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) block copolymer shown at right. The polymer is known as Kraton and is used for shoe soles and adhesive
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
The use of adhesives offers certain advant ...
s. Owing to the microfine structure, a transmission electron microscope
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a gr ...
(TEM) was needed to examine the structure. The butadiene matrix was stained with osmium tetroxide
Osmium tetroxide (also osmium(VIII) oxide) is the chemical compound with the formula OsO4. The compound is noteworthy for its many uses, despite its toxicity and the rarity of osmium. It also has a number of unusual properties, one being that th ...
to provide contrast in the image. The material was made by living polymerization
In polymer chemistry, living polymerization is a form of chain growth polymerization where the ability of a growing polymer chain to terminate has been removed. This can be accomplished in a variety of ways. Chain termination and chain transfer r ...
so that the blocks are almost monodisperse, so helping to create a very regular microstructure. The molecular weight
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
of the polystyrene blocks in the main picture is 102,000; the inset picture has a molecular weight of 91,000, producing slightly smaller domains. The spacing between domains has been confirmed by small-angle X-ray scattering
Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) is a small-angle scattering technique by which nanoscale density differences in a sample can be quantified. This means that it can determine nanoparticle size distributions, resolve the size and shape of (monodis ...
, a technique which gives information about microstructure
Microstructure is the very small scale structure of a material, defined as the structure of a prepared surface of material as revealed by an optical microscope above 25× magnification. The microstructure of a material (such as metals, polymers ...
.
Since most polymers are incompatible with one another, forming a block polymer will usually result in phase separation, and the principle has been widely exploited since the introduction of the SBS block polymers, especially where one of the block is highly crystalline. One exception to the rule of incompatibility is the material Noryl
The NORYL family of modified resins consists of amorphous blends of polyphenylene oxides (PPO) or polyphenylene ether (PPE) resins with polystyrene. They combine the inherent benefits of PPE resin (affordable high heat resistance, good electric ...
, where polystyrene and polyphenylene oxide or PPO form a continuous blend with one another.
melting point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends ...
. That point determines the processing temperatures needed to shape the material, as well as the ultimate service use temperatures of the product. Such materials include Hytrel, a polyester-polyether copolymer and Pebax
Polyether block amide or PEBA is a thermoplastic elastomer (TPE). It is known under the tradename of PEBAX® (Arkema) and VESTAMID® E ( Evonik Industries). It is a block copolymer obtained by polycondensation of a carboxylic acid polyamide ( PA ...
, a nylon or polyamide-polyether copolymer.
Advantages
Depending on the environment, TPEs have outstanding thermal properties and material stability when exposed to a broad range of temperatures and non-polar materials. TPEs consume less energy to produce, can be colored easily by most dyes, and allow economical quality control. TPE requires little or no compounding, with no need to add reinforcing agents, stabilizers or cure systems. Hence, batch-to-batch variations in weighting and metering components are absent, leading to improved consistency in both raw materials and fabricated articles. TPE materials have the potential to berecyclable
Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new materials and objects. The recovery of energy from waste materials is often included in this concept. The recyclability of a material depends on its ability to reacquire the ...
since they can be molded, extruded and reused like plastics, but they have typical elastic properties of rubbers which are not recyclable owing to their thermosetting characteristics. They can also be ground up and turned into 3D printing filament with a recyclebot
A recyclebot (or RecycleBot) is an open-source hardware device for converting waste plastic into filament for open-source 3D printers like the RepRap. Making DIY 3D printer filament at home is both less costly and better for the environment than ...
.
Processing
The two most important manufacturing methods with TPEs areextrusion
Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross-sectional profile by pushing material through a die of the desired cross-section. Its two main advantages over other manufacturing processes are its ability to create very complex ...
and injection molding. TPEs can now be 3D printed and have been shown to be economically advantageous to make products using distributed manufacturing
Distributed manufacturing also known as distributed production, cloud producing and local manufacturing is a form of decentralized manufacturing practiced by enterprises using a network of geographically dispersed manufacturing facilities that are ...
. Compression molding
Compression molding is a method of molding in which the molding material, generally preheated, is first placed in an open, heated mold cavity. The mold is closed with a top force or plug member, pressure is applied to force the material int ...
is seldom, if ever, used. Fabrication via injection molding is extremely rapid and highly economical. Both the equipment and methods normally used for the extrusion or injection molding of a conventional thermoplastic are generally suitable for TPEs. TPEs can also be processed by blow molding
Blow molding (or moulding) is a manufacturing process for forming hollow plastic parts. It is also used for forming glass bottles or other hollow shapes.
In general, there are three main types of blow molding: extrusion blow molding, injection ...
, melt calendaring, thermoforming
Thermoforming is a manufacturing process where a plastic sheet is heated to a pliable forming temperature, formed to a specific shape in a mold, and trimmed to create a usable product. The sheet, or "film" when referring to thinner gauges and cer ...
, and heat welding.
Applications
 TPEs are used where conventional elastomers cannot provide the range of physical properties needed in the product. These materials find large application in the automotive sector and in household appliances sector. In 2014, the world market for TPEs reached a volume of ca. 16.7 billion US dollars. About 40% of all TPE products are used in the manufacturing of vehicles. For instance, copolyester TPEs are used in
TPEs are used where conventional elastomers cannot provide the range of physical properties needed in the product. These materials find large application in the automotive sector and in household appliances sector. In 2014, the world market for TPEs reached a volume of ca. 16.7 billion US dollars. About 40% of all TPE products are used in the manufacturing of vehicles. For instance, copolyester TPEs are used in snowmobile
A snowmobile, also known as a Ski-Doo, snowmachine, sled, motor sled, motor sledge, skimobile, or snow scooter, is a motorized vehicle designed for winter travel and recreation on snow. It is designed to be operated on snow and ice and does not ...
tracks where stiffness and abrasion resistance are at a premium. Thermoplastic olefins (TPO) are increasingly used as a roofing material. TPEs are also widely used for catheter
In medicine, a catheter (/ˈkæθətər/) is a thin tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Cath ...
s where nylon block copolymers offer a range of softness ideal for patients. Thermoplastic silicone and olefin blends are used for extrusion of glass run and dynamic weatherstripping
Weatherstripping is the process of sealing openings such as doors, windows, and trunks from the waters above. The term can also refer to the materials used to carry out such sealing processes. The goal of weatherstripping is to prevent rain and w ...
car profiles. Styrene block copolymers are used in shoe soles for their ease of processing, and widely as adhesives.
Owing to their unrivaled abilities in two-component injection molding to various thermoplastic substrates, engineered TPS materials also cover a broad range of technical applications ranging from automotive market to consumer and medical products. Examples of those are soft grip surfaces, design elements, back-lit switches and surfaces, as well as sealings, gaskets, or damping elements. TPE is commonly used to make suspension bushings for automotive performance applications because of its greater resistance to deformation when compared to regular rubber bushings. Thermoplastics have experienced growth in the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. ...
) industry due to the function, cost effectiveness and adaptability to modify plastic resins into a variety of covers, fans and housings. TPE may also be used in medical devices, electrical cable jacket and inner insulation, sex toy
A sex toy is an object or device that is primarily used to facilitate human sexual pleasure, such as a dildo, artificial vagina or vibrator. Many popular sex toys are designed to resemble human genitals, and may be vibrating or non-vibrati ...
s, and some headphone
Headphones are a pair of small loudspeaker drivers worn on or around the head over a user's ears. They are electroacoustic transducers, which convert an electrical signal to a corresponding sound. Headphones let a single user listen to an au ...
cables.

References
Further reading
* PR Lewis and C Price, ''Polymer'', 13, 20 (1972) * Modern Plastic Mid-October Encyclopedia Issue, Introduction to TPEs, ''page:109-110''Latest Material and Technological Developments for Activewear
(Joanne Yip, 2020, ''page 66-67)'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Thermoplastic Elastomer Biomaterials Polymers