The Guianas on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Guianas, sometimes called by the
The Guianas, sometimes called by the

Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
loan-word ''Guayanas'' (''Las Guayanas''), is a region in north-eastern South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sout ...
which includes the following three territories:
* French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label=French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic coast of South America in the Guianas. ...
, an overseas department and region of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
* Guyana, formerly known as British Guiana from 1831 until 1966, after the colonies of Berbice, Essequibo, and Demerara
Demerara ( nl, Demerary, ) is a historical region in the Guianas, on the north coast of South America, now part of the country of Guyana. It was a colony of the Dutch West India Company between 1745 and 1792 and a colony of the Dutch state ...
, taken from the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
in 1814, were merged into a single colony
* Suriname, formerly Dutch Guiana, until 1814 together with Berbice, Essequibo and Demerara
In the wider context, the Guianas also includes the following two territories:
* Guayana Region
The Guayana Region is an administrative region of eastern Venezuela.
History
In the 1970s, after the process of forming the Political-Administrative Regions through CORDIPLAN in the government of Rafael Caldera, the Region of Guyana was f ...
in eastern Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
( Amazonas, Bolívar, and Delta Amacuro
Delta Amacuro State ( es, Estado Delta Amacuro, ) is one of the 23 states of Venezuela, and is the location of the Orinoco Delta. The Paria Gulf and the Atlantic Ocean are found to the north, Bolívar State is found to the south, the Atlantic ...
states), formerly the Guayana Province
Guayana Province (1585−1864) was a former province of Spanish Colonial Venezuela and independent Venezuela, located in the Guyana region of northeastern South America.
The province was part of the Spanish colonial New Andalusia Province and ...
, alternatively known as Spanish Guayana
* State of Amapá in northern Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, known as Portuguese Guiana (or Brazilian Guiana)
History


Pre-colonial period
Before the arrival of European colonials, the Guianas were populated by scattered bands of nativeArawak
The Arawak are a group of indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. Specifically, the term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to the Lokono of South America and the Taíno, who historically lived in the Great ...
people. The native tribe
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to confli ...
s of the Northern Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek mythology
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technolog ...
are most closely related to the natives of the Caribbean; most evidence suggests that the Arawaks immigrated from the Orinoco and Essequibo River Basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, t ...
s in Venezuela and Guiana into the northern islands, and were then supplanted by more warlike tribes of Carib Indians, who departed from these same river valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams ...
s a few centuries later.
Over the centuries of the pre-colonial period, the ebb and flow of power between Arawak and Carib interests throughout the Caribbean resulted in a great deal of intermingling (some forced through capture, some accidental through contact). This ethnic mixing, particularly in the Caribbean margins like the Guianas, produced a hybridized culture. Despite their political rivalry, the ethnic and cultural blending between the two groups had reached such a level that, by the time of the Europeans' arrival, the Carib/Arawak complex in Guiana was so homogeneous that the two groups were almost indistinguishable to outsiders. Through the contact period following Columbus's arrival, the term "Guiana" was used to refer to all areas between the Orinoco, the Rio Negro, and the Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek mythology
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technolog ...
, and was seen so much as a unified, isolated entity that it was often referred to as the “Island of Guiana.”
European colonization
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
first spotted the coast of the Guianas in 1498, but real interest in the exploration and colonization of the Guianas, which came to be known as the "Wild Coast," did not begin until the end of the sixteenth century. Walter Raleigh
Sir Walter Raleigh (; – 29 October 1618) was an English statesman, soldier, writer and explorer. One of the most notable figures of the Elizabethan era, he played a leading part in English colonisation of North America, suppressed rebelli ...
began the exploration of the Guianas in earnest in 1594. He was in search of a great golden city at the headwaters of the Caroní River
The Caroní River is the second most important river of Venezuela, the second in flow, and one of the longest, from the Kukenan tepui through to its confluence with the Orinoco River. The name "Caroní" is applied starting from the confluence ...
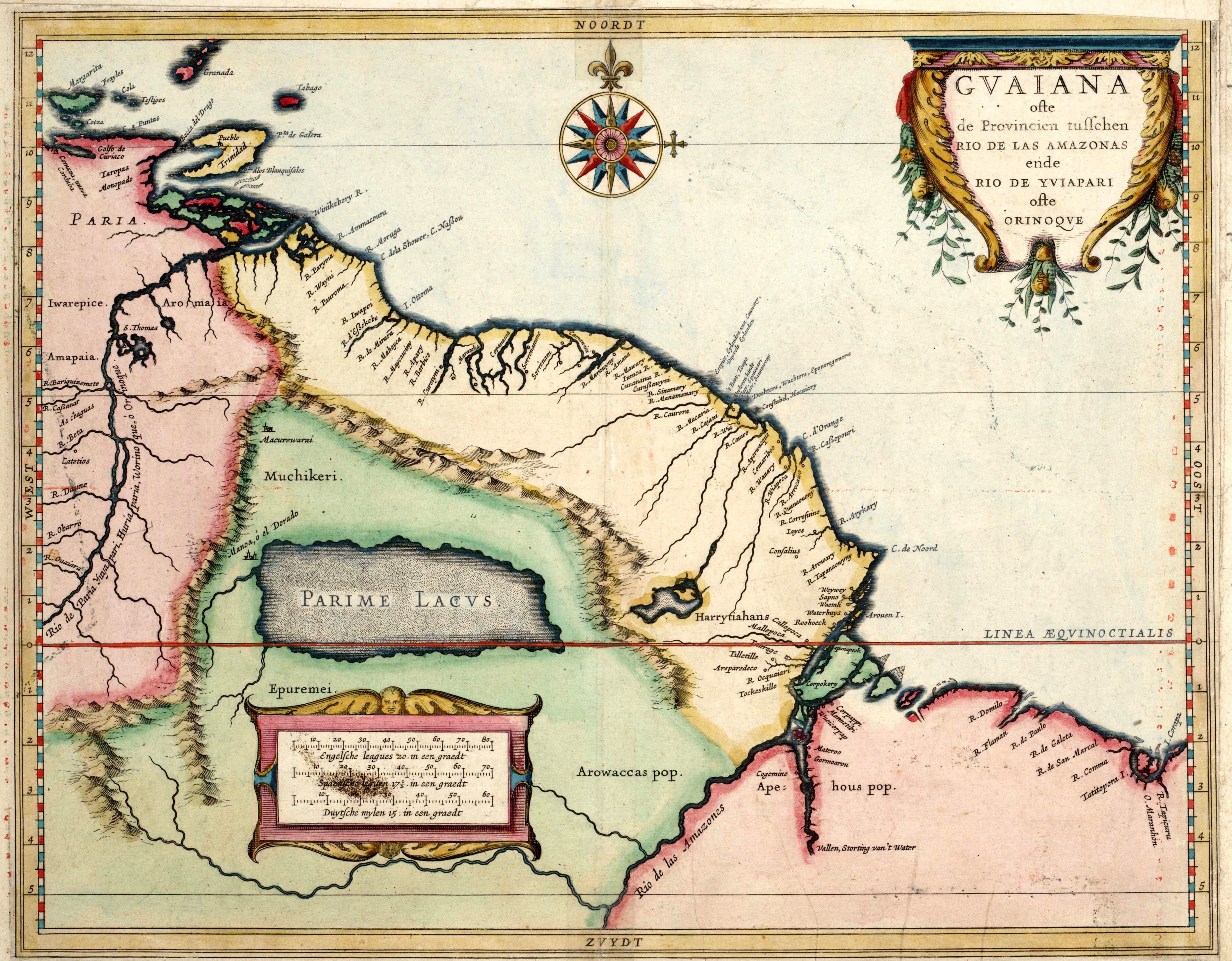
. A year later he explored what is now Guyana and eastern Venezuela in search of "Manoa", the legendary city of the king known as El Dorado. Raleigh described the city of El Dorado as being located on Lake Parime
Lake Parime or Lake Parima is a legendary lake located in South America. It was reputedly the location of the fabled city of El Dorado, also known as Manoa, much sought-after by European explorers. Repeated attempts to find the lake failed to con ...
far up the Orinoco River
The Orinoco () is one of the longest rivers in South America at . Its drainage basin, sometimes known as the Orinoquia, covers , with 76.3 percent of it in Venezuela and the remainder in Colombia. It is the fourth largest river in the wor ...
in Guyana. Much of his exploration is documented in his books ''The Discoverie of the Large, Rich, and Bewtiful Empyre of Guiana'', published first in 1596, and ''The Discovery of Guiana, and the Journal of the Second Voyage Thereto'', published in 1606.
After the publication of Raleigh's accounts, several other Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
an powers developed interest in the Guianas. The Dutch joined in the exploration of the Guianas before the end of the century. In the 80 years between the start of the Dutch Revolt in 1568 and 1648, when the Treaty of Münster was signed with the Spanish, the Dutch had been practising the delicate art of cobbling together different ethnicities and religious faiths into a viable economic entity. When beginning an empire, the Dutch concerned themselves more with trade and establishing viable networks and outposts than with claiming tracts of land to act as a buffer against neighbouring states. With this goal in mind, the Dutch dispatched explorer Jacob Cornelisz
Jacob Cornelisz van Oostsanen (before 1470 – 1533) was a Northern Netherlandish designer of woodcuts and painter. He was one of the first important artists working in Amsterdam, at a time when it was a flourishing and beautiful provincial ...
to survey the area in 1597. His clerk, Adriaen Cabeliau, related the voyage of Cornelisz and his survey of Indian groups and areas of potential trade partnerships in his diary. Throughout the seventeenth century, the Dutch made gains by establishing trading colonies and outposts in the region and in the neighboring Caribbean islands under the banner of the Dutch West India Company. The company, established in 1621 for such purposes, benefited from a larger investment of capital than the English, primarily through foreign investors like Isaac de Pinto, a Portuguese Jew. The area was also cursorily explored by Amerigo Vespucci and Vasco Núñez de Balboa
Vasco Núñez de Balboa (; c. 1475around January 12–21, 1519) was a Spanish explorer, governor, and conquistador. He is best known for having crossed the Isthmus of Panama to the Pacific Ocean in 1513, becoming the first European to lead an ...
, and in 1608 the Grand Duchy of Tuscany also organized an expedition to the Guianas, but this was cut short by the untimely death of the Grand Duke.
English and Dutch settlers were regularly harassed by the Spanish and Portuguese, who viewed settlement of the area as a violation of the Treaty of Tordesillas. In 1613, Dutch trading posts on the Essequibo and Corantijn Rivers were completely destroyed by Spanish troops. The troops had been sent into the Guianas from neighboring Venezuela under the premise of stamping out privateering
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
and with the support of a cédula passed by the Spanish Council of the Indies
The Council of the Indies ( es, Consejo de las Indias), officially the Royal and Supreme Council of the Indies ( es, Real y Supremo Consejo de las Indias, link=no, ), was the most important administrative organ of the Spanish Empire for the Amer ...
and King Philip III. Nonetheless, the Dutch returned in 1615, founding a new settlement at present-day Cayenne (later abandoned in favor of Suriname), one on the Wiapoco River (now more commonly known as the Oyapock) and one on the upper Amazon. By 1621, a charter was granted by the Dutch States-General, but even a few years prior to the official chartering a fort and trading post had been built at Kijkoveral, under the supervision of Aert Groenewegen, at the confluence of the Essequibo, Cuyuni, and Mazaruni Rivers. British settlers also succeeded in establishing a small settlement in 1606 and a much larger one in modern-day Suriname in 1650, under the leadership of former Barbadian governor Francis Willoughby, Lord Parham.
The French had also made less significant attempts at colonization, first in 1604 along the Sinnamary River. The settlement collapsed within a summer, and initial attempts at settlement near modern-day Cayenne, beginning in 1613, were met with similar setbacks. French priorities — land acquisition and Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
conversion — were not easily reconciled with the difficulties of initial settlement-building on the Wild Coast. Even as late as 1635, the King of France granted permission to the whole of Guiana to a joint-stock company of Norman merchants. When these merchants made a settlement near the modern city of Cayenne, failure ensued. Eight years later, a reinforcement contingent led by Charles Poncet de Brétigny found only a few of the original colonists left alive, living among the aborigines. Later that year, among the combined total of the original surviving settlers, the reinforcement contingent led by de Brétigny, and a subsequent reinforcement later in the year, only two individuals remained alive long enough to reach the Dutch settlement on the Pomeroon River
The Pomeroon River (also ''Río Pomerón'' ''or Pomaron'') is located in Guyana, South America, situated between the Orinoco and the Essequibo rivers. The area has long been inhabited by Lokono people. The Pomeroon River is also one of the deepes ...
in 1645, begging for refuge. Though some trading outposts that could be considered permanent settlements were founded as early as 1624, French “possession” of the land now known as French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label=French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic coast of South America in the Guianas. ...
is not recognized as having taken place until at least 1637. Cayenne itself, the first permanent settlement of comparable size to the Dutch colonies, experienced instability until 1643.
The Dutch appointed a new commandeur
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countries this naval rank is termed frigate captain.
...
of the Guiana settlements in 1742. In this year, Laurens Storm van 's Gravesande took over the region. He held the position for three decades, coordinating the development and expansion of the Dutch colonies from his plantation Soesdyke in Demerara
Demerara ( nl, Demerary, ) is a historical region in the Guianas, on the north coast of South America, now part of the country of Guyana. It was a colony of the Dutch West India Company between 1745 and 1792 and a colony of the Dutch state ...
. Gravesande’s tenure brought significant change to the colonies, though his policy was in many ways an extension of his predecessor, Hermanus Gelskerke. Commandeur Gelskerke had begun pressing for change from a trading focus to one of cultivation, especially of sugar. The area east of the existing Essequibo colony, known as Demerara
Demerara ( nl, Demerary, ) is a historical region in the Guianas, on the north coast of South America, now part of the country of Guyana. It was a colony of the Dutch West India Company between 1745 and 1792 and a colony of the Dutch state ...
, was relatively isolated and encompassed the trading areas of just a few indigenous tribes, thus it contained only two trading outposts during Gelskerke’s term of office. Demerara, though, showed great potential as a sugar-cultivating area, so the commandeur began shifting focus toward the development of the region, signifying his intentions by transferring the administrative center of the colony from Fort Kijkoveral to Flag Island, on the mouth of the Essequibo River, further east and closer to Demerara. These operations were carried out by Gravesande, acting as the Secretary of the Company under Gelskerke. Upon Gelskerke’s death, Gravesande continued the policy of Demerara expansion and the move to sugar cultivation.
Conflict among the British, Dutch, and French continued throughout the seventeenth century. The Treaty of Breda sealed peace between the English and the Dutch. The treaty allowed the Dutch to retain control over the valuable sugar plantations and factories on the coast of Suriname which had been secured by Abraham Crijnssen
Abraham Crijnssen (died 1 February 1669) was a Dutch naval commander, notable for capturing the English colony in Suriname in 1667 during the Second Anglo-Dutch War, resulting in the establishment of a long-term colony under Dutch control. The ...
earlier in 1667.
All the colonies along the Guiana coast were converted to profitable sugar plantations during the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. War continued off and on among the three principal powers in the Guianas (the Netherlands, France, and Britain) until a final peace was signed in 1814 (the Convention of London), heavily favouring the British. By this time France had sold off most of its North American territory in the Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase (french: Vente de la Louisiane, translation=Sale of Louisiana) was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. In return for fifteen million dollars, or app ...
and had lost all but Guadeloupe, Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago: or ) is an island and an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of the French Republic, Martinique is located in ...
, and French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label=French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic coast of South America in the Guianas. ...
in the Caribbean region. The Dutch lost Berbice, Essequibo, and Demerara; these colonies were consolidated under a central British administration and would be known after 1831 as British Guiana. The Dutch retained Suriname.
After 1814, the Guianas came to be recognized individually as British Guiana, French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label=French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic coast of South America in the Guianas. ...
, and Dutch Guiana.
See also
* Borders of Brazil *Borders of Venezuela
The borders of Venezuela are the international borders that Venezuela shares with neighboring countries. Venezuela borders with 14 countries totaling 5,161 kilometers which includes territories of France (Martinique and Guadeloupe), the Kingdom ...
* Guiana Shield
The Guiana Shield (french: Plateau des Guyanes, Bouclier guyanais; nl, Hoogland van Guyana, Guianaschild; pt, Planalto das Guianas, Escudo das Guianas; es, Escudo guayanés) is one of the three cratons of the South American Plate. It is a ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* Bahadur, Gaiutra. ''Coolie Woman
''Coolie Woman'' (full title: ''Coolie Woman: The Odyssey of Indenture'') is a book written by Gaiutra Bahadur and co-published in 2013 by Hurst and Company of London in Europe and the University of Chicago Press in the US. Editions from Hachette ...
: The Odyssey of Indenture''. The University of Chicago (2014)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Guianas, the
Regions of South America
Divided regions
History of French Guiana
History of Guyana
History of Suriname