The British Empire was composed of the
dominion
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire.
"Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 1926 ...
s,
colonies,
protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its inter ...
s,
mandates, and other
territories
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or an ...
ruled or administered by the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Nor ...
and its predecessor states. It began with the
overseas possessions and
trading post
A trading post, trading station, or trading house, also known as a factory, is an establishment or settlement where goods and services could be traded.
Typically the location of the trading post would allow people from one geographic area to tr ...
s established by
England between the late 16th and early 18th centuries.
At its height it was the
largest empire in history and, for over a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, its
constitutional,
legal
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been vari ...
,
linguistic
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguis ...
, and
cultural legacy is widespread. At the peak of its power, it was described as "
the empire on which the sun never sets
The phrase "the empire on which the sun never sets" ( es, el imperio donde nunca se pone el sol) was used to describe certain global empires that were so extensive that it seemed as though it was always daytime in at least one part of its territ ...
", as the Sun was always shining on at least one of its territories.
During the
Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafaring ...
in the 15th and 16th centuries,
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a Sovereign state, country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southern Europe, Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes ...
and
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
pioneered European exploration of the globe, and in the process established large overseas empires. Envious of the great wealth these empires generated, England,
France, and the
Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Neth ...
began to establish colonies and trade networks of their own in the
Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with t ...
and
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
. A series of wars in the 17th and 18th centuries with the Netherlands and France left England (
Britain, following the
1707 Act of Union with Scotland) the dominant
colonial power
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colony, colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose the ...
in
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the C ...
. Britain became the dominant power in the
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India ...
after the
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sout ...
's
conquest of
Mughal Bengal
The Bengal Subah ( bn, সুবাহ বাংলা; fa, ), also referred to as Mughal Bengal ( bn, মোগল বাংলা), was the largest subdivision of the Mughal Empire (and later an independent state under the Nawabs of Be ...
at the
Battle of Plassey
The Battle of Plassey was a decisive victory of the British East India Company over the Nawab of Bengal and his French allies on 23 June 1757, under the leadership of Robert Clive. The victory was made possible by the defection of Mir Jafar, w ...
in 1757.
The
American War of Independence
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
resulted in Britain losing some of its oldest and most populous colonies in North America by 1783. British attention then turned towards Asia,
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, and the
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
. After the defeat of France in the
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
(1803–1815), Britain emerged as the principal naval and imperial power of the 19th century and expanded its imperial holdings. The period of relative peace (1815–1914) during which the British Empire became the global
hegemon
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one state over other states. In Ancient Greece (8th BC – AD 6th ), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of the ''hegemon'' city-state over other city-states. ...
was later described as ("British Peace"). Alongside the formal control that Britain exerted over its colonies, its dominance of much of world trade meant that it effectively
controlled the economies of many regions, such as Asia and
Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived f ...
.
[ Porter, p. 8.]Marshall
Marshall may refer to:
Places
Australia
* Marshall, Victoria, a suburb of Geelong, Victoria
Canada
* Marshall, Saskatchewan
* The Marshall, a mountain in British Columbia
Liberia
* Marshall, Liberia
Marshall Islands
* Marshall Islands, a ...
, pp. 156–57. Increasing degrees of autonomy were granted to its white
settler colonies, some of which were reclassified as
Dominion
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire.
"Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 1926 ...
s.
By the start of the 20th century,
Germany and the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territo ...
had begun to challenge Britain's economic lead. Military and economic tensions between Britain and Germany were major causes of the
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighti ...
, during which Britain relied heavily on its empire. The conflict placed enormous strain on its military, financial, and manpower resources. Although the empire achieved its largest territorial extent immediately after the First World War, Britain was no longer the world's preeminent industrial or military power. In the
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, Britain's colonies in
East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea and ...
and
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
were occupied by the
Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent for ...
. Despite the final victory of Britain and
its allies, the damage to British prestige helped accelerate the decline of the empire.
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, Britain's most valuable and populous possession, achieved
independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the st ...
in 1947 as part of a larger
decolonisation
Decolonization or decolonisation is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. Some scholars of decolonization focus especially on independence ...
movement, in which Britain granted independence to most territories of the empire. The
Suez Crisis
The Suez Crisis, or the Second Arab–Israeli war, also called the Tripartite Aggression ( ar, العدوان الثلاثي, Al-ʿUdwān aṯ-Ṯulāṯiyy) in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel,Also known as the Suez War or 1956 Wa ...
of 1956 confirmed Britain's decline as a global power, and the
transfer of Hong Kong to China on 1 July 1997 marked for many the end of the British Empire.
Fourteen
overseas territories
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, particularly belonging or connected to a country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually either the total area from which a state may extract power resources or an ...
remain under British sovereignty. After independence, many former British colonies, along with most of the dominions, joined the
Commonwealth of Nations, a free association of independent states. Fifteen of these, including the United Kingdom,
retain a common monarch, currently
King Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms. He was the longest-serving heir apparent and Prince of Wales and, at age 73, became the oldest person to a ...
.
Origins (1497–1583)

The foundations of the British Empire were laid when
England and
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to th ...
were separate kingdoms. In 1496, King
Henry VII of England
Henry VII (28 January 1457 – 21 April 1509) was King of England and Lord of Ireland from his seizure of the crown on 22 August 1485 until his death in 1509. He was the first monarch of the House of Tudor.
Henry's mother, Margaret Beaufort, ...
, following the successes of
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
and
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a Sovereign state, country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southern Europe, Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes ...
in overseas exploration, commissioned
John Cabot
John Cabot ( it, Giovanni Caboto ; 1450 – 1500) was an Italian navigator and explorer. His 1497 voyage to the coast of North America under the commission of Henry VII of England is the earliest-known European exploration of coastal No ...
to lead an expedition to discover a
northwest passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea route between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The eastern route along the Arct ...
to Asia via the North Atlantic. Cabot sailed in 1497, five years after the
first voyage of Christopher Columbus, and made landfall on the coast of
Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
. He believed he had reached Asia, and there was no attempt to found a colony. Cabot led another voyage to the Americas the following year but he did not return from this voyage and it is unknown what happened to his ships.
No further attempts to establish English colonies in the Americas were made until well into the
reign of Queen Elizabeth I, during the last decades of the 16th century. In the meantime,
Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disagr ...
's 1533
Statute in Restraint of Appeals
The Ecclesiastical Appeals Act 1532 (24 Hen 8 c 12), also called the Statute in Restraint of Appeals, the Act of Appeals and The Act of Restraints in Appeals, was an Act of the Parliament of England.
It was passed in the first week of April 1533 ...
had declared "that this realm of England is an Empire". The
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
turned
England and
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
Spain into implacable enemies. In 1562, Elizabeth I encouraged the
privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
s
John Hawkins and
Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake ( – 28 January 1596) was an English explorer, sea captain, privateer, slave trader, naval officer, and politician. Drake is best known for his circumnavigation of the world in a single expedition, from 1577 to 1580 (t ...
to engage in
slave-raiding attacks against Spanish and Portuguese ships off the coast of
West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, ...
with the aim of establishing an
Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in the Americas, enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the tria ...
. This effort was rebuffed and later, as the
Anglo-Spanish Wars intensified,
Elizabeth I gave her blessing to further privateering raids against Spanish ports in the Americas and shipping that was returning across the Atlantic,
laden with treasure from the
New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 3 ...
. At the same time, influential writers such as
Richard Hakluyt
Richard Hakluyt (; 1553 – 23 November 1616) was an English writer. He is known for promoting the English colonization of North America through his works, notably ''Divers Voyages Touching the Discoverie of America'' (1582) and ''The Pri ...
and
John Dee
John Dee (13 July 1527 – 1608 or 1609) was an English mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, teacher, occultist, and alchemist. He was the court astronomer for, and advisor to, Elizabeth I, and spent much of his time on alchemy, divinatio ...
(who was the first to use the term "British Empire") were beginning to press for the establishment of England's own empire. By this time, Spain had become the dominant power in the Americas and was exploring the Pacific Ocean, Portugal had established trading posts and forts from the coasts of
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and
Brazil to
China, and France had begun to settle the
Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting t ...
area, later to become
New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to King ...
.
Although England tended to trail behind Portugal, Spain, and France in establishing overseas colonies, it carried out its first modern colonisation, referred to as the
Ulster Plantation
The Plantation of Ulster ( gle, Plandáil Uladh; Ulster-Scots: ''Plantin o Ulstèr'') was the organised colonisation ('' plantation'') of Ulstera province of Irelandby people from Great Britain during the reign of King James I. Most of the s ...
, in 16th century
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
by settling
English Protestants
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
in
Ulster
Ulster (; ga, Ulaidh or ''Cúige Uladh'' ; sco, label=Ulster Scots dialects, Ulster Scots, Ulstèr or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: si ...
. England had already colonised part of the country following the
Norman invasion of Ireland
The Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland took place during the late 12th century, when Anglo-Normans gradually conquered and acquired large swathes of land from the Irish, over which the kings of England then claimed sovereignty, all allegedly san ...
in 1169. Several people who helped establish the Ulster Plantations later played a part in the early colonisation of North America, particularly a group known as the
West Country Men
The West Country Men were a group of individuals in Elizabethan England who advocated the
English colonisation of Ireland, attacks on the Spanish Empire and other overseas colonial expansion. The group included Humphrey Gilbert, Walter Raleigh, ...
.
English overseas possessions (1583–1707)
In 1578, Elizabeth I granted a patent to
Humphrey Gilbert
Sir Humphrey Gilbert (c. 1539 – 9 September 1583) was an English adventurer, explorer, member of parliament and soldier who served during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I and was a pioneer of the English colonial empire in North America ...
for discovery and overseas exploration. That year, Gilbert sailed for the
Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean S ...
with the intention of engaging in
piracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
and establishing a colony in North America, but the expedition was aborted before it had crossed the Atlantic. In 1583, he embarked on a second attempt. On this occasion, he formally claimed the harbour of the island of Newfoundland, although no settlers were left behind. Gilbert did not survive the return journey to England and was succeeded by his half-brother,
Walter Raleigh
Sir Walter Raleigh (; – 29 October 1618) was an English statesman, soldier, writer and explorer. One of the most notable figures of the Elizabethan era, he played a leading part in English colonisation of North America, suppressed rebellion ...
, who was granted his own patent by Elizabeth in 1584. Later that year, Raleigh founded the
Roanoke Colony
The establishment of the Roanoke Colony ( ) was an attempt by Sir Walter Raleigh to found the first permanent English settlement in North America. The English, led by Sir Humphrey Gilbert, had briefly claimed St. John's, Newfoundland, in 15 ...
on the coast of present-day
North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and S ...
, but lack of supplies caused the colony to fail.
In 1603,
James VI of Scotland
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until hi ...
ascended (as James I) to the English throne and in 1604 negotiated the
Treaty of London, ending hostilities with Spain. Now at peace with its main rival, English attention shifted from preying on other nations' colonial infrastructures to the business of establishing its own overseas colonies. The British Empire began to take shape during the early 17th century, with the
English settlement
''English Settlement'' is the fifth studio album and first double album by the English rock band XTC, released 12 February 1982 on Virgin Records. It marked a turn towards the more pastoral pop songs that would dominate later XTC releases, w ...
of North America and the smaller islands of the Caribbean, and the establishment of
joint-stock companies
A joint-stock company is a business entity in which shares of the company's stock can be bought and sold by shareholders. Each shareholder owns company stock in proportion, evidenced by their shares (certificates of ownership). Shareholders are ...
, most notably the
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Sout ...
, to administer colonies and overseas trade. This period, until the loss of the
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies, also known as the Thirteen British Colonies, the Thirteen American Colonies, or later as the United Colonies, were a group of British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America. Founded in the 17th and 18th centuri ...
after the
American War of Independence
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
towards the end of the 18th century, has been referred to by some historians as the "First British Empire".
Americas, Africa and the slave trade
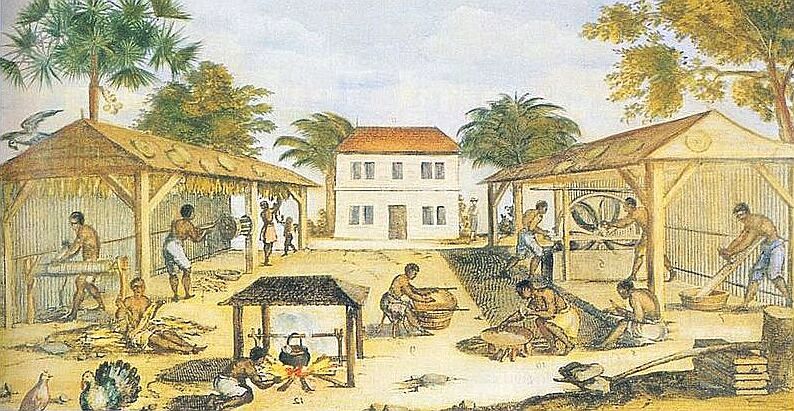

England's early efforts at colonisation in the Americas met with mixed success. An attempt to establish a colony in
Guiana
The Guianas, sometimes called by the Spanish loan-word ''Guayanas'' (''Las Guayanas''), is a region in north-eastern South America which includes the following three territories:
* French Guiana, an overseas department and region of France
* ...
in 1604 lasted only two years and failed in its main objective to find gold deposits. Colonies on the Caribbean islands of
St Lucia
Saint Lucia ( acf, Sent Lisi, french: Sainte-Lucie) is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. The island was previously called Iouanalao and later Hewanorra, names given by the native Arawaks and Caribs, two Amerind ...
(1605) and
Grenada
Grenada ( ; Grenadian Creole French: ) is an island country in the West Indies in the Caribbean Sea at the southern end of the Grenadines island chain. Grenada consists of the island of Grenada itself, two smaller islands, Carriacou and ...
(1609) rapidly folded.
[ Canny, p. 221.] The first permanent English settlement in the Americas was founded in 1607 in
Jamestown by Captain
John Smith, and managed by the
Virginia Company
The Virginia Company was an English trading company chartered by King James I on 10 April 1606 with the object of colonizing the eastern coast of America. The coast was named Virginia, after Elizabeth I, and it stretched from present-day Main ...
; the Crown took direct control of the venture in 1624, thereby founding the
Colony of Virginia.
Bermuda
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = National song
, song = " Hail to Bermuda"
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, mapsize2 =
, map_caption2 =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name =
, e ...
was settled and claimed by England as a result of the 1609 shipwreck of the Virginia Company's
flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the ...
, while
attempts to settle Newfoundland were largely unsuccessful. In 1620,
Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymou ...
was founded as a haven by
Puritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become more Protestant. ...
religious separatists, later known as the
Pilgrims. Fleeing from
religious persecution
Religious persecution is the systematic mistreatment of an individual or a group of individuals as a response to their religious beliefs or affiliations or their lack thereof. The tendency of societies or groups within societies to alienate o ...
would become the motive for many English would-be colonists to risk the arduous
trans-Atlantic voyage:
Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to it ...
was established by
English Roman Catholics
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national i ...
(1634),
Rhode Island (1636) as a colony
tolerant of all religions and Connecticut (1639) for
Congregationalists. England's North American holdings were further expanded by the annexation of the Dutch colony of
New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva P ...
in 1664, following the capture of
New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam ( nl, Nieuw Amsterdam, or ) was a 17th-century Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''factory'' gave rise ...
, which was renamed
New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* ...
. Although less financially successful than colonies in the Caribbean, these territories had large areas of good agricultural land and attracted far greater numbers of English emigrants, who preferred their temperate climates.
The
British West Indies
The British West Indies (BWI) were colonized British territories in the West Indies: Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada ...
initially provided England's most important and lucrative colonies. Settlements were successfully established in
St. Kitts
Saint Kitts, officially the Saint Christopher Island, is an island in the West Indies. The west side of the island borders the Caribbean Sea, and the eastern coast faces the Atlantic Ocean. Saint Kitts and the neighbouring island of Nevis cons ...
(1624),
Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate). ...
(1627) and
Nevis
Nevis is a small island in the Caribbean Sea that forms part of the inner arc of the Leeward Islands chain of the West Indies. Nevis and the neighbouring island of Saint Kitts constitute one country: the Federation of Saint Kitts and N ...
(1628),
but struggled until the "Sugar Revolution" transformed the Caribbean economy in the mid-17th century.
Large
sugarcane plantations were first established in the 1640s on Barbados, with assistance from Dutch merchants and
Sephardic Jews
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefa ...
fleeing
Portuguese Brazil
Colonial Brazil ( pt, Brasil Colonial) comprises the period from 1500, with the arrival of the Portuguese, until 1815, when Brazil was elevated to a kingdom in union with Portugal as the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves. Duri ...
. At first, sugar was grown primarily using white
indentured labour
Indentured servitude is a form of labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract, called an "indenture", may be entered "voluntarily" for purported eventual compensation or debt repayment, ...
, but rising costs soon led English traders to embrace the use of imported African slaves. The enormous wealth generated by slave-produced sugar made Barbados the most successful colony in the Americas, and one of the most densely populated places in the world.
This boom led to the spread of sugar cultivation across the Caribbean, financed the development of non-plantation colonies in North America, and accelerated the growth of the
Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade, or Euro-American slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in the Americas, enslaved African people, mainly to the Americas. The slave trade regularly used the tria ...
, particularly the
triangular trade
Triangular trade or triangle trade is trade between three ports or regions. Triangular trade usually evolves when a region has export commodities that are not required in the region from which its major imports come. It has been used to offset ...
of slaves, sugar and provisions between Africa, the West Indies and Europe.
To ensure that the increasingly healthy profits of colonial trade remained in English hands, Parliament
decreed
A decree is a legal proclamation, usually issued by a head of state (such as the president of a republic or a monarch), according to certain procedures (usually established in a constitution). It has the force of law. The particular term used for ...
in 1651 that only English ships would be able to ply their trade in English colonies. This led to hostilities with the
United Dutch Provinces—a series of
Anglo-Dutch Wars—which would eventually strengthen England's position in the Americas at the expense of the Dutch. In 1655, England annexed the island of
Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of Hispanio ...
from the Spanish, and in 1666 succeeded in colonising the
Bahamas.
In 1670,
Charles II incorporated by royal charter the
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trade, fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake b ...
(HBC), granting it a monopoly on the
fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the mo ...
in the area known as
Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land (french: Terre de Rupert), or Prince Rupert's Land (french: Terre du Prince Rupert, link=no), was a territory in British North America which comprised the Hudson Bay drainage basin; this was further extended from Rupert's Land ...
, which would later form a large proportion of the
Dominion of Canada
While a variety of theories have been postulated for the name of Canada, its origin is now accepted as coming from the St. Lawrence Iroquoian word , meaning 'village' or 'settlement'. In 1535, indigenous inhabitants of the present-day Quebec C ...
. Forts and trading posts established by the HBC were frequently the subject of attacks by the French, who had established their own fur trading colony in adjacent
New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to King ...
.
[ Buckner, p. 25.]
Two years later, the
Royal African Company
The Royal African Company (RAC) was an English mercantile (trading) company set up in 1660 by the royal Stuart family and City of London merchants to trade along the west coast of Africa. It was led by the Duke of York, who was the brother of ...
was granted a monopoly on the supply of slaves to the British colonies in the Caribbean. The company would transport more slaves across the Atlantic than any other, and significantly grew England's share of the trade, from 33 per cent in 1673 to 74 per cent in 1683. The removal of this monopoly between 1688 and 1712 allowed independent British slave traders to thrive, leading to a rapid escalation in the number of slaves transported. British ships carried a third of all slaves shipped across the Atlantic—approximately 3.5 million Africans—and dominated global slave trading in the 25 years preceding its abolition by Parliament in 1807 (see ). To facilitate the shipment of slaves, forts were established on the coast of West Africa, such as
James Island,
Accra
Accra (; tw, Nkran; dag, Ankara; gaa, Ga or ''Gaga'') is the capital and largest city of Ghana, located on the southern coast at the Gulf of Guinea, which is part of the Atlantic Ocean. As of 2021 census, the Accra Metropolitan District, , ...
and
Bunce Island
Bunce Island (also spelled "Bence," "Bense," or "Bance" at different periods) is an island in the Sierra Leone River. It is situated in Freetown Harbour, the estuary of the Rokel River and Port Loko Creek, about upriver from Sierra Leone's cap ...
. In the British Caribbean, the percentage of the population of African descent rose from 25 per cent in 1650 to around 80 per cent in 1780, and in the Thirteen Colonies from 10 per cent to 40 per cent over the same period (the majority in the southern colonies). The transatlantic slave trade played a pervasive role in British economic life, and became a major economic mainstay for western port cities. Ships registered in
Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in ...
,
Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a populat ...
and
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major s ...
were responsible for the bulk of British slave trading. For the transported, harsh and unhygienic conditions on the slaving ships and poor diets meant that the average
mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of de ...
during the
Middle Passage
The Middle Passage was the stage of the Atlantic slave trade in which millions of enslaved Africans were transported to the Americas as part of the triangular slave trade. Ships departed Europe for African markets with manufactured goods (first ...
was one in seven.
Rivalry with other European empires

At the end of the 16th century, England and the
Dutch Empire began to challenge the
Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire ( pt, Império Português), also known as the Portuguese Overseas (''Ultramar Português'') or the Portuguese Colonial Empire (''Império Colonial Português''), was composed of the overseas colonies, factories, and the ...
's monopoly of trade with Asia, forming private joint-stock companies to finance the voyages—the English, later British, East India Company and the
Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock co ...
, chartered in 1600 and 1602 respectively. The primary aim of these companies was to tap into the lucrative
spice trade, an effort focused mainly on two regions: the
East Indies archipelago, and an important hub in the trade network, India. There, they competed for trade supremacy with Portugal and with each other. Although England eclipsed the Netherlands as a colonial power, in the short term the Netherlands' more advanced financial system and the three
Anglo-Dutch Wars of the 17th century left it with a stronger position in Asia. Hostilities ceased after the
Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and ...
of 1688 when the Dutch
William of Orange ascended the English throne, bringing peace between the
Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
and England. A deal between the two nations left the
spice trade of the
East Indies
The East Indies (or simply the Indies), is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Discovery. The Indies refers to various lands in the East or the Eastern hemisphere, particularly the islands and mainlands found in and around t ...
archipelago to the Netherlands and the
textiles industry of India to England, but textiles soon overtook spices in terms of profitability.
Peace between England and the Netherlands in 1688 meant the two countries entered the
Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by the Habsburg monarch ...
as allies, but the conflict—waged in Europe and overseas between France, Spain and the Anglo-Dutch alliance—left the English a stronger colonial power than the Dutch, who were forced to devote a larger proportion of their
military budget
A military budget (or military expenditure), also known as a defense budget, is the amount of financial resources dedicated by a state to raising and maintaining an armed forces or other methods essential for defense purposes.
Financing milita ...
to the costly land war in Europe. The death of
Charles II of Spain
Charles II of Spain (''Spanish: Carlos II,'' 6 November 1661 – 1 November 1700), known as the Bewitched (''Spanish: El Hechizado''), was the last Habsburg ruler of the Spanish Empire. Best remembered for his physical disabilities and the War o ...
in 1700 and his bequeathal of Spain and its colonial empire to
Philip V of Spain
Philip V ( es, Felipe; 19 December 1683 – 9 July 1746) was King of Spain from 1 November 1700 to 14 January 1724, and again from 6 September 1724 to his death in 1746. His total reign of 45 years is the longest in the history of the Spanish mona ...
, a grandson of the
King of France
France was ruled by monarchs from the establishment of the Kingdom of West Francia in 843 until the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, with several interruptions.
Classical French historiography usually regards Clovis I () as the fir ...
, raised the prospect of the unification of France, Spain and their respective colonies, an unacceptable state of affairs for England and the other powers of Europe.
In 1701, England, Portugal and the Netherlands sided with the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 un ...
against Spain and France in the
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phi ...
, which lasted for thirteen years.
Scottish attempt to expand overseas
In 1695, the
Parliament of Scotland
The Parliament of Scotland ( sco, Pairlament o Scotland; gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba) was the legislature of the Kingdom of Scotland from the 13th century until 1707. The parliament evolved during the early 13th century from the king's council of ...
granted a charter to the
Company of Scotland, which established a settlement in 1698 on the
Isthmus of Panama
The Isthmus of Panama ( es, Istmo de Panamá), also historically known as the Isthmus of Darien (), is the narrow strip of land that lies between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, linking North and South America. It contains the countr ...
. Besieged by neighbouring
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
colonists of
New Granada, and affected by
malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or deat ...
, the colony was abandoned two years later. The
Darien scheme
The Darien scheme was an unsuccessful attempt, backed largely by investors of the Kingdom of Scotland, to gain wealth and influence by establishing ''New Caledonia'', a colony on the Isthmus of Panama, in the late 1690s. The plan was for the co ...
was a financial disaster for Scotland: a quarter of Scottish capital was lost in the enterprise. The episode had major political consequences, helping to persuade the government of the
Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland (; , ) was a sovereign state in northwest Europe traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a l ...
of the merits of turning the
personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
with
England into a political and economic one under the
Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, whi ...
established by the
Acts of Union 1707.
"First" British Empire (1707–1783)

The 18th century saw the
newly united Great Britain rise to be the world's dominant colonial power, with France becoming its main rival on the imperial stage. Great Britain, Portugal, the Netherlands, and the Holy Roman Empire continued the War of the Spanish Succession, which lasted until 1714 and was concluded by the
Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vacant throne of ...
.
Philip V of Spain
Philip V ( es, Felipe; 19 December 1683 – 9 July 1746) was King of Spain from 1 November 1700 to 14 January 1724, and again from 6 September 1724 to his death in 1746. His total reign of 45 years is the longest in the history of the Spanish mona ...
renounced his and his descendants' claim to the French throne, and Spain lost its empire in Europe.
[ Shennan, pp. 11–17.] The British Empire was territorially enlarged: from France, Britain gained
Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
and
Acadia
Acadia (french: link=no, Acadie) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. During much of the 17th and early 18t ...
, and from Spain
Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = "Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gibr ...
and
Menorca
Menorca or Minorca (from la, Insula Minor, , smaller island, later ''Minorica'') is one of the Balearic Islands located in the Mediterranean Sea belonging to Spain. Its name derives from its size, contrasting it with nearby Majorca. Its capi ...
. Gibraltar became a
critical naval base and allowed Britain to control the
Atlantic entry and exit point to the
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
. Spain ceded the rights to the lucrative ''
asiento'' (permission to sell African slaves in
Spanish America
Spanish America refers to the Spanish territories in the Americas during the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The term "Spanish America" was specifically used during the territories' imperial era between 15th and 19th centuries. To the ...
) to Britain. With the outbreak of the Anglo-Spanish
War of Jenkins' Ear
The War of Jenkins' Ear, or , was a conflict lasting from 1739 to 1748 between Britain and the Spanish Empire. The majority of the fighting took place in New Granada and the Caribbean Sea, with major operations largely ended by 1742. It is co ...
in 1739, Spanish privateers attacked British merchant shipping along the
Triangle Trade
Triangular trade or triangle trade is trade between three ports or regions. Triangular trade usually evolves when a region has export commodities that are not required in the region from which its major imports come. It has been used to offset ...
routes. In 1746, the Spanish and British began peace talks, with the King of Spain agreeing to stop all attacks on British shipping; however, in the
Treaty of Madrid Britain lost its slave-trading rights in
Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived f ...
.
In the East Indies, British and Dutch merchants continued to compete in spices and textiles. With textiles becoming the larger trade, by 1720, in terms of sales, the British company had overtaken the Dutch. During the middle decades of the 18th century, there were
several outbreaks of military conflict on the
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India ...
, as the English East India Company and its
French counterpart, struggled alongside local rulers to fill the vacuum that had been left by the decline of the
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
. The
Battle of Plassey
The Battle of Plassey was a decisive victory of the British East India Company over the Nawab of Bengal and his French allies on 23 June 1757, under the leadership of Robert Clive. The victory was made possible by the defection of Mir Jafar, w ...
in 1757, in which the British defeated the
Nawab of Bengal
The Nawab of Bengal ( bn, বাংলার নবাব) was the hereditary ruler of Bengal Subah in Mughal India. In the early 18th-century, the Nawab of Bengal was the ''de facto'' independent ruler of the three regions of Bengal, Bihar, a ...
and his French allies, left the British East India Company in control of
Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predo ...
and as the major military and political power in India. France was left control of its
enclaves
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
but with military restrictions and an obligation to support British
client state
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite state, ...
s, ending French hopes of controlling India. In the following decades the British East India Company gradually increased the size of the territories under its control, either ruling directly or via local rulers under the threat of force from the
Presidency Armies
The presidency armies were the armies of the three presidencies of the East India Company's rule in India, later the forces of the British Crown in India, composed primarily of Indian sepoys. The presidency armies were named after the presiden ...
, the vast majority of which was composed of Indian
sepoy
''Sepoy'' () was the Persian-derived designation originally given to a professional Indian infantryman, traditionally armed with a musket, in the armies of the Mughal Empire.
In the 18th century, the French East India Company and its ot ...
s, led by British officers. The British and French struggles in India became but one theatre of the global
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754– ...
(1756–1763) involving France, Britain, and the other major European powers.
The signing of the
Treaty of Paris of 1763
The Treaty of Paris, also known as the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763 by the kingdoms of Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement, after Great Britain and Prussia's victory over France and Spain during th ...
had important consequences for the future of the British Empire. In North America, France's future as a colonial power effectively ended with the recognition of British claims to Rupert's Land,
and the
ceding of New France to Britain (leaving a sizeable
French-speaking population under British control) and
Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
to Spain. Spain ceded Florida to Britain. Along with its victory over France in India, the Seven Years' War therefore left Britain as the world's most powerful
maritime power
A maritime power is a nation with a very strong navy, which often is also a great power, or at least a regional power. A maritime power is able to easily control their coast, and exert influence upon both nearby and far countries. A nation that d ...
.
[ Pagden, p. 91.]
Loss of the Thirteen American Colonies

During the 1760s and early 1770s, relations between the Thirteen Colonies and Britain became increasingly strained, primarily because of resentment of the British Parliament's attempts to govern and tax American colonists without their consent. This was summarised at the time by the slogan "
No taxation without representation
"No taxation without representation" is a political slogan that originated in the American Revolution, and which expressed one of the primary grievances of the American colonists for Great Britain. In short, many colonists believed that as the ...
", a perceived violation of the guaranteed
Rights of Englishmen
The "rights of Englishmen" are the traditional rights of English subjects and later English-speaking subjects of the British Crown. In the 18th century, some of the colonists who objected to British rule in the thirteen British North American ...
. The
American Revolution began with a rejection of Parliamentary authority and moves towards self-government. In response, Britain sent troops to reimpose direct rule, leading to the outbreak of war in 1775. The following year, in 1776, the
Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a late-18th-century meeting of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolutionary War. The Congress was creating a new country it first named " United Colonies" and in ...
issued the
Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence or declaration of statehood or proclamation of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the ...
proclaiming the colonies' sovereignty from the British Empire as the new United States of America. The entry of France in the American Revolutionary War, French and Spain and the American Revolutionary War, Spanish forces into the war tipped the military balance in the Americans' favour and after a decisive defeat at Siege of Yorktown, Yorktown in 1781, Britain began negotiating peace terms. American independence was acknowledged at the Peace of Paris (1783), Peace of Paris in 1783.
The loss of such a large portion of British America, at the time Britain's most populous overseas possession, is seen by some historians as the event defining the transition between the "first" and "second" empires, in which Britain shifted its attention away from the Americas to Asia, the Pacific and later Africa. Adam Smith's ''The Wealth of Nations, Wealth of Nations'', published in 1776, had argued that colonies were redundant, and that free trade should replace the old Mercantilism, mercantilist policies that had characterised the first period of colonial expansion, dating back to the protectionism of Spain and Portugal.
The growth of trade between the newly independent
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territo ...
and Britain after 1783 seemed to confirm Smith's view that political control was not necessary for economic success.
The war to the south influenced British policy in Canada, where between 40,000 and 100,000 defeated Loyalist (American Revolution), Loyalists had migrated from the new United States following independence. The 14,000 Loyalists who went to the Saint John River (New Brunswick), Saint John and Saint Croix River (Maine – New Brunswick), Saint Croix river valleys, then part of Nova Scotia, felt too far removed from the provincial government in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Halifax, so London split off New Brunswick as a separate colony in 1784. The Constitutional Act of 1791 created the provinces of Upper Canada (mainly English Canada, English speaking) and Lower Canada (mainly French Canadians, French-speaking) to defuse tensions between the French and British communities, and implemented governmental systems similar to those employed in Britain, with the intention of asserting imperial authority and not allowing the sort of popular control of government that was perceived to have led to the American Revolution.
Tensions between Britain and the United States escalated again during the
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, as Britain tried to cut off American trade with France and boarded American ships to Impressment, impress men into the Royal Navy. The United States Congress declared war, the War of 1812, and invaded Canadian territory. In response, Britain invaded the US, but the pre-war boundaries were reaffirmed by the 1814 Treaty of Ghent, ensuring Canada's future would be separate from that of the United States.
Rise of the "Second" British Empire (1783–1815)
Exploration of the Pacific

Since 1718, penal transportation, transportation to the American colonies had been a penalty for various offences in Britain, with approximately one thousand convicts transported per year. Forced to find an alternative location after the loss of the Thirteen Colonies in 1783, the British government turned to Australia. The New Holland (Australia), coast of Australia had been discovered for Europeans by the Dutch Janszoon voyage of 1605–06, in 1606,
[#refMulligan2001, Mulligan & Hill, pp. 20–23.] but there was no attempt to colonise it. In 1770 James Cook charted the eastern coast while on a scientific First voyage of James Cook, voyage, claimed the continent for Britain, and named it Colony of New South Wales, New South Wales. In 1778, Joseph Banks, Cook's botanist on the voyage, presented evidence to the government on the suitability of Botany Bay for the establishment of a Penal colony, penal settlement, and in 1787 the first shipment of Convicts in Australia, convicts set sail, arriving in 1788. Unusually, Australia was claimed through proclamation. Indigenous Australians were considered too uncivilised to require treaties, and colonisation brought disease and violence that together with the deliberate dispossession of land and culture were devastating to these peoples. Britain continued to transport convicts to New South Wales until 1840, to Colony of Tasmania, Tasmania until 1853 and to Colony of Western Australia, Western Australia until 1868. The Australian colonies became profitable exporters of wool and gold, mainly because of the Victorian gold rush, making its capital Melbourne for a time the richest city in the world.
During his voyage, Cook visited New Zealand, known to Europeans due to the 1642 voyage of the Dutch explorer, Abel Tasman. Cook claimed both the North Island, North and the South Island, South islands for the British crown in 1769 and 1770 respectively. Initially, interaction between the indigenous Māori people, Maori population and Pākehā settlers, European settlers was limited to the trading of goods. European settlement increased through the early decades of the 19th century, with many trading stations being established, especially in the North. In 1839, the New Zealand Company announced plans to buy large tracts of land and establish colonies in New Zealand. On 6 February 1840, Captain William Hobson and around 40 Maori chiefs signed the Treaty of Waitangi which is considered to be New Zealand's founding document despite differing interpretations of the Māori language, Maori and English language, English versions of the text being the cause of ongoing dispute.
The British also expanded their mercantile interests in the North Pacific. Spain and Britain had become rivals in the area, culminating in the Nootka Crisis in 1789. Both sides mobilised for war, but when France refused to support Spain it was forced to back down, leading to the Nootka Convention. The outcome was a humiliation for Spain, which practically renounced all sovereignty on the North Pacific coast. This opened the way to British expansion in the area, and a number of expeditions took place; firstly a Vancouver Expedition, naval expedition led by George Vancouver which explored the inlets around the Pacific North West, particularly around Vancouver Island.
On land, expeditions sought to discover a river route to the Pacific for the extension of the North American fur trade. Alexander Mackenzie (explorer), Alexander Mackenzie of the North West Company led the first, starting out in 1792, and a year a later he became the first European to reach the Pacific overland north of the Rio Grande, reaching the ocean near present-day Bella Coola, British Columbia, Bella Coola. This preceded the Lewis and Clark Expedition by twelve years. Shortly thereafter, Mackenzie's companion, John Finlay (fur trader), John Finlay, founded the first permanent European settlement in British Columbia, Fort St. John, British Columbia, Fort St. John. The North West Company sought further exploration and backed expeditions by David Thompson (explorer), David Thompson, starting in 1797, and later by Simon Fraser (explorer), Simon Fraser. These pushed into the wilderness territories of the Rocky Mountains and Interior Plateau to the Strait of Georgia on the Pacific Coast, expanding British North America westward.
Wars with France

Britain was challenged again by France under Napoleon, in a struggle that, unlike previous wars, represented a contest of ideologies between the two nations. It was not only Britain's position on the world stage that was at risk: Napoleon threatened to invade Britain itself, just as his armies had overrun many countries of continental Europe.
The Napoleonic Wars were therefore ones in which Britain invested large amounts of capital and resources to win. French ports were blockaded by the Royal Navy, which won a decisive victory over a French Imperial Navy-Spanish Navy fleet at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805. Overseas colonies were attacked and occupied, including those of the Netherlands, which was annexed by Napoleon in 1810. France was finally defeated by a coalition of European armies in 1815. Britain was again the beneficiary of peace treaties: France ceded the United States of the Ionian Islands, Ionian Islands, Malta Protectorate, Malta (which it had occupied in 1798), British Mauritius, Mauritius, St Lucia, the Seychelles, and Tobago; Spain ceded Trinidad; the Netherlands ceded Guyana, British Ceylon, Ceylon and the Cape Colony, while the Danish ceded British Administration of Heligoland, Heligoland. Britain returned Guadeloupe, Martinique, French Guiana, and Réunion to France;
Menorca
Menorca or Minorca (from la, Insula Minor, , smaller island, later ''Minorica'') is one of the Balearic Islands located in the Mediterranean Sea belonging to Spain. Its name derives from its size, contrasting it with nearby Majorca. Its capi ...
to Spain; Danish West Indies to Denmark and Java and Suriname to the Netherlands.
[#refJames2001, James, p. 165.]
Abolition of slavery
With the advent of the Industrial Revolution, goods produced by slavery became less important to the British economy. Added to this was the cost of suppressing regular slave rebellions. With support from the British Abolitionism in the United Kingdom, abolitionist movement, Parliament of the United Kingdom, Parliament enacted the Slave Trade Act 1807, Slave Trade Act in 1807, which abolished the slave trade in the empire. In 1808, Sierra Leone Colony was designated an official British colony for freed slaves. Parliamentary reform in 1832 saw the influence of the West India Committee decline. The Slavery Abolition Act 1833, Slavery Abolition Act, passed the following year, abolished slavery in the British Empire on 1 August 1834, finally bringing the Empire into line with the law in the UK (with the exception of the territories administered by the East India Company and Ceylon, where slavery was ended in 1844). Under the Act, slaves were granted full emancipation after a period of four to six years of "apprenticeship". Facing further opposition from abolitionists, the apprenticeship system was abolished in 1838. The British government compensated slave-owners.
Britain's imperial century (1815–1914)
Between 1815 and 1914, a period referred to as Britain's "imperial century" by some historians, around of territory and roughly 400 million people were added to the British Empire. Victory over Napoleon left Britain without any serious international rival, other than The Great Game, Russia in Central Asia.
[ Porter, p. 401.] Unchallenged at sea, Britain adopted the role of global policeman, a state of affairs later known as the ''Pax Britannica'',
[ Porter, p. 332.] and a foreign policy of "splendid isolation". Alongside the formal control it exerted over its own colonies, Britain's dominant position in world trade meant that it effectively controlled the economies of many countries, such as China, Argentina and Thailand, Siam, which has been described by some historians as an "Informal Empire".

British imperial strength was underpinned by the steamship and the telegraph, new technologies invented in the second half of the 19th century, allowing it to control and defend the empire. By 1902, the British Empire was linked together by a network of telegraph cables, called the All Red Line.
East India Company rule and the British Raj in India
The East India Company drove the expansion of the British Empire in Asia. The Company's army had first joined forces with the Royal Navy during the Seven Years' War, and the two continued to co-operate in arenas outside India: the eviction of the French from Egypt (1799), the Invasion of Java (1811), capture of Java from the Netherlands (1811), the Penang Island#History, acquisition of Penang Island (1786), Founding of modern Singapore, Singapore (1819) and Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824, Malacca (1824), and the First Anglo-Burmese War, defeat of Burma (1826).
From its base in India, the Company had been engaged in an increasingly profitable opium export trade to Qing dynasty, Qing China since the 1730s. This trade, illegal since it was outlawed by China in 1729, helped reverse the trade imbalances resulting from the British imports of tea, which saw large outflows of silver from Britain to China. In 1839, the confiscation by the Chinese authorities at Guangzhou, Canton of 20,000 chests of opium led Britain to attack China in the First Opium War, and resulted in the seizure by Britain of British Hong Kong, Hong Kong Island, at that time a minor settlement, and other Concessions in China, Treaty Ports including Shanghai International Settlement, Shanghai.
During the late 18th and early 19th centuries, the British Crown began to assume an increasingly large role in the affairs of the Company. A series of Acts of Parliament were passed, including the Regulating Act of 1773, Pitt's India Act of 1784 and the Charter Act of 1813 which regulated the Company's affairs and established the sovereignty of the Crown over the territories that it had acquired. The Company's eventual end was precipitated by the Indian Rebellion of 1857, Indian Rebellion in 1857, a conflict that had begun with the mutiny of sepoys, Indian troops under British officers and discipline. The rebellion took six months to suppress, with heavy loss of life on both sides. The following year the British government dissolved the company and assumed direct control over India through the Government of India Act 1858, establishing the British Raj, where an appointed Governor-General of India, governor-general administered India and Queen Victoria was crowned the Empress of India. India became the empire's most valuable possession, "the Jewel in the Crown", and was the most important source of Britain's strength.
[#refOHBEv4, Brown, p. 5.]
A series of serious crop failures in the late 19th century led to Famine in India, widespread famines on the subcontinent in which it is estimated that over 15 million people died. The East India Company had failed to implement any coordinated policy to deal with the famines during its period of rule. Later, under direct British rule, commissions were set up after each famine to investigate the causes and implement new policies, which took until the early 1900s to have an effect.
Rivalry with Russia
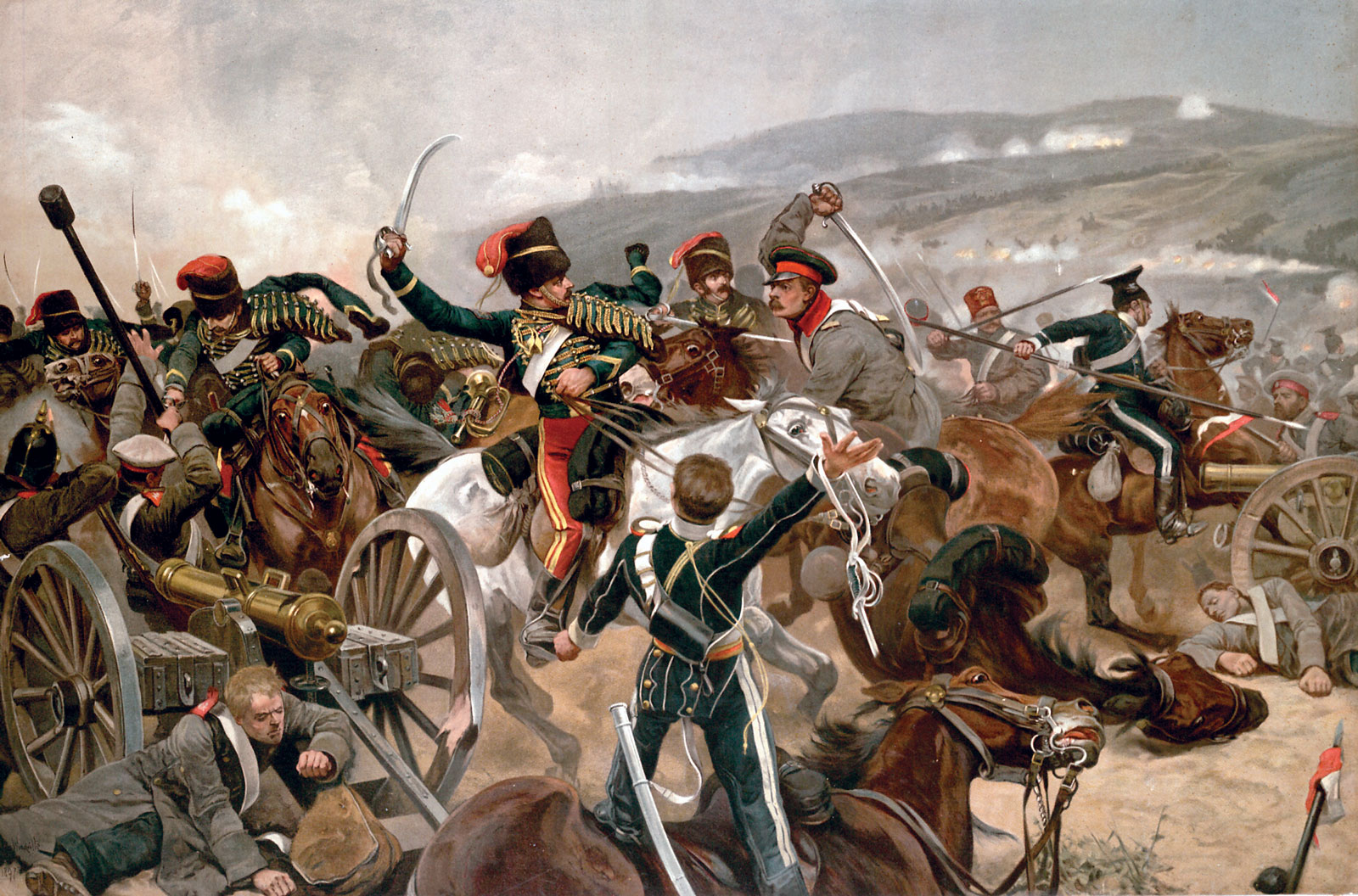

During the 19th century, Britain and the Russian Empire vied to fill the power vacuums that had been left by the declining Ottoman Empire, Qajar dynasty and Qing dynasty. This rivalry in Central Asia came to be known as the "Great Game". As far as Britain was concerned, defeats inflicted by Russia on Russo-Persian War (1826–1828), Persia and Russo-Turkish War (1828–1829), Turkey demonstrated its imperial ambitions and capabilities and stoked fears in Britain of an overland invasion of India. In 1839, Britain moved to pre-empt this by invading Afghanistan, but the First Anglo-Afghan War was a disaster for Britain.
[#refJames2001, James, p. 182.]
When Russia invaded the Rumelia, Ottoman Balkans in 1853, fears of Russian dominance in the Mediterranean and the Middle East led Britain and France to enter the war in support of the Ottoman Empire and invade the Crimean Peninsula to destroy Russian naval capabilities.
The ensuing Crimean War (1854–1856), which involved new techniques of modern warfare, was the only global war fought between Britain and another Imperialism, imperial power during the ''Pax Britannica'' and was a resounding defeat for Russia.
The situation remained unresolved in Central Asia for two more decades, with Britain annexing Baluchistan (Chief Commissioner's Province), Baluchistan in 1876 and Russia annexing Kirghizia, Kazakhstan, and Turkmenistan. For a while, it appeared that another war would be inevitable, but the two countries reached an agreement on their respective Sphere of influence, spheres of influence in the region in 1878 and on all outstanding matters in 1907 with the signing of the Anglo-Russian Entente. The destruction of the Imperial Russian Navy by the Imperial Japanese Navy at the Battle of Tsushima during the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905 limited its threat to the British.
[#refhodge47, Hodge, p. 47.]
Cape to Cairo

The Dutch East India Company had founded the Dutch Cape Colony on the Cape of Good Hope, southern tip of Africa in 1652 as a way station for its ships travelling to and from its colonies in the Indies, East Indies. Britain formally acquired the colony, and its large Afrikaner (or Boer) population in 1806, having occupied it in 1795 to prevent its falling into French hands during the Flanders Campaign. British immigration to the Cape Colony began to rise after 1820, and pushed thousands of Boers, resentful of British rule, northwards to found their own—mostly short-lived—Boer republics, independent republics, during the Great Trek of the late 1830s and early 1840s. In the process the Voortrekkers clashed repeatedly with the British, who had their own agenda with regard to colonial expansion in South Africa and to the various native African polities, including those of the Sotho people and the Zulu Kingdom. Eventually, the Boers established two republics that had a longer lifespan: the South African Republic or Transvaal Republic (1852–1877; 1881–1902) and the Orange Free State (1854–1902). In 1902 Britain occupied both republics, concluding a treaty with the two Boer Republics following the Second Boer War (1899–1902).
In 1869 the Suez Canal opened under Napoleon III of France, Napoleon III, linking the Mediterranean Sea with the Indian Ocean. Initially the Canal was opposed by the British; but once opened, its strategic value was quickly recognised and became the "jugular vein of the Empire". In 1875, the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative government of Benjamin Disraeli bought the indebted Egyptian ruler Isma'il Pasha's 44 per cent shareholding in the Suez Canal for £4 million (equivalent to £ in ). Although this did not grant outright control of the strategic waterway, it did give Britain leverage. Joint Anglo-French financial control over Egypt ended in outright British occupation in 1882. Although Britain controlled the Khedivate of Egypt into the 20th century, it was officially a Vassal and tributary states of the Ottoman Empire, vassal state of the Ottoman Empire and not part of the British Empire. The French were still majority shareholders and attempted to weaken the British position, but a compromise was reached with the 1888 Convention of Constantinople, which made the Canal officially neutral territory.
With competitive French, Belgian colonial empire, Belgian and Portuguese activity in the lower Congo River region undermining orderly colonisation of tropical Africa, the Berlin Conference of 1884–85 was held to regulate the competition between the European powers in what was called the "Scramble for Africa" by defining "effective occupation" as the criterion for international recognition of territorial claims. The scramble continued into the 1890s, and caused Britain to reconsider its decision in 1885 to withdraw from Sudan. A joint force of British and Egyptian troops defeated the Mahdist War, Mahdist Army in 1896 and rebuffed an attempted French invasion Fashoda Incident, at Fashoda in 1898. Sudan was nominally made an Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, Anglo-Egyptian condominium, but a British colony in reality.
British gains in Southern and East Africa prompted Cecil Rhodes, pioneer of British expansion in Southern Africa, to urge a "Cape to Cairo Railway, Cape to Cairo" railway linking the strategically important Suez Canal to the mineral-rich south of the continent. During the 1880s and 1890s, Rhodes, with his privately owned British South Africa Company, company rule in Rhodesia, occupied and annexed territories named after him, Rhodesia (name), Rhodesia.
Changing status of the white colonies
The path to independence for the white colonies of the British Empire began with the 1839 Report on the Affairs of British North America, Durham Report, which proposed unification and self-government for Upper and Lower Canada, as a solution to political unrest which had erupted in Rebellions of 1837, armed rebellions in 1837. This began with the passing of the Act of Union 1840, Act of Union in 1840, which created the Province of Canada. Responsible government was first granted to Nova Scotia in 1848, and was soon extended to the other British North American colonies. With the passage of the British North America Act, 1867 by the British Parliament, the Province of Canada, New Brunswick and Nova Scotia were formed into Canada, a confederation enjoying full self-government with the exception of international relations. Australia and New Zealand achieved similar levels of self-government after 1900, with the Australian colonies federation of Australia, federating in 1901. The term "dominion status" was officially introduced at the 1907 Imperial Conference.
The last decades of the 19th century saw concerted political campaigns for Irish home rule. Ireland had been united with Britain into the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland with the Act of Union 1800 after the Irish Rebellion of 1798, and had suffered a severe Great Famine (Ireland), famine between 1845 and 1852. Home rule was supported by the British Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Prime minister, William Ewart Gladstone, William Gladstone, who hoped that Ireland might follow in Canada's footsteps as a Dominion within the empire, but his 1886 Government of Ireland Bill 1886, Home Rule bill was defeated in Parliament. Although the bill, if passed, would have granted Ireland less autonomy within the UK than the Canadian provinces had within their own federation, many MPs feared that a partially independent Ireland might pose a security threat to Great Britain or mark the beginning of the break-up of the empire.
[#refJames2001, James, p. 315.] A Irish Government Bill 1893, second Home Rule bill was defeated for similar reasons.
A Home Rule Act 1914, third bill was passed by Parliament in 1914, but not implemented because of the outbreak of the
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighti ...
leading to the 1916 Easter Rising.
World wars (1914–1945)

By the turn of the 20th century, fears had begun to grow in Britain that it would no longer be able to defend the metropole and the entirety of the empire while at the same time maintaining the policy of "splendid isolation".
Germany was rapidly rising as a military and industrial power and was now seen as the most likely opponent in any future war. Recognising that it was overstretched in the Pacific and threatened at home by the Imperial German Navy, Britain Anglo-Japanese Alliance, formed an alliance with Japan in 1902 and with its old enemies Entente cordiale, France and Russia in 1904 and 1907, respectively.
First World War
Britain's fears of war with Germany were realised in 1914 with the outbreak of the First World War. Britain quickly invaded and occupied most of Germany's overseas colonies in Africa. In the Pacific, Australia and New Zealand occupied German New Guinea and German Samoa respectively. Plans for a post-war division of the Ottoman Empire, which had joined the war on Germany's side, were secretly drawn up by Britain and France under the 1916 Sykes–Picot Agreement. This agreement was not divulged to the Hussein bin Ali, Sharif of Mecca, Sharif of Mecca, who the British had been encouraging to launch an Arab revolt against their Ottoman rulers, giving the impression that Britain was supporting the creation of an independent Arab state.
[#refOHBEv4, Brown, pp. 494–95.]
The British declaration of war on Germany and its allies committed the colonies and Dominions, which provided invaluable military, financial and material support. Over 2.5 million men served in the armies of the
Dominion
The term ''Dominion'' is used to refer to one of several self-governing nations of the British Empire.
"Dominion status" was first accorded to Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland, South Africa, and the Irish Free State at the 1926 ...
s, as well as many thousands of volunteers from the Crown colonies. The contributions of Australian and New Zealand troops during the 1915 Gallipoli Campaign against the Ottoman Empire had a great impact on the national consciousness at home and marked a watershed in the transition of Australia and New Zealand from colonies to nations in their own right. The countries continue to commemorate this occasion on Anzac Day. Canadians viewed the Battle of Vimy Ridge in a similar light. The important contribution of the Dominions to the war effort was recognised in 1917 by the British Prime Minister David Lloyd George when he invited each of the Dominion Prime Ministers to join an Imperial War Cabinet to co-ordinate imperial policy.
Under the terms of the concluding Treaty of Versailles signed in 1919, the empire reached its greatest extent with the addition of and 13 million new subjects. The colonies of Germany and the Ottoman Empire were distributed to the Allied powers as League of Nations mandates. Britain gained control of Mandatory Palestine, Palestine, Emirate of Transjordan, Transjordan, Kingdom of Iraq (Mandate administration), Iraq, parts of British Cameroons, Cameroon and British Togoland, Togoland, and Tanganyika (territory), Tanganyika. The Dominions themselves acquired mandates of their own: the Union of South Africa gained South West Africa (modern-day Namibia), Australia gained Territory of New Guinea, New Guinea, and New Zealand Western Samoa Trust Territory, Western Samoa. History of Nauru#World War I to World War II, Nauru was made a combined mandate of Britain and the two Pacific Dominions.
Inter-war period

The changing world order that the war had brought about, in particular the growth of the United States and Japan as naval powers, and the rise of independence movements in India and Ireland, caused a major reassessment of British imperial policy. Forced to choose between alignment with the United States or Japan, Britain opted not to renew its Anglo-Japanese Alliance and instead signed the 1922 Washington Naval Treaty, where Britain accepted naval parity with the United States.
[#refLouis2006, Louis, p. 302.] This decision was the source of much debate in Britain during the 1930s as militaristic governments took hold in Germany and Japan helped in part by the Great Depression, for it was feared that the empire could not survive a simultaneous attack by both nations. The issue of the empire's security was a serious concern in Britain, as it was vital to the Economy of the United Kingdom, British economy.
In 1919, the frustrations caused by delays to Irish Home Rule movement, Irish home rule led the MPs of Sinn Féin, a pro-independence party that had won a majority of the Irish seats in the 1918 Irish general election, 1918 British general election, to establish an Dáil Éireann (Irish Republic), independent parliament in Dublin, at which Irish Declaration of Independence, Irish independence was declared. The Irish Republican Army simultaneously began a guerrilla warfare, guerrilla war against the British administration. The Irish War of Independence ended in 1921 with a stalemate and the signing of the Anglo-Irish Treaty, creating the Irish Free State, a Dominion within the British Empire, with effective internal independence but still constitutionally linked with the British Crown. Northern Ireland, consisting of six of the 32 Counties of Ireland, Irish counties which had been established as a devolved region under the 1920 Government of Ireland Act 1920, Government of Ireland Act, immediately exercised its option under the treaty to retain its existing status within the United Kingdom.

A similar struggle began in India when the Government of India Act 1919 failed to satisfy the demand for independence. Concerns over communist and foreign plots following the Ghadar conspiracy ensured that war-time strictures were renewed by the Rowlatt Acts. This led to tension,
[#refJames2001, James, p. 416.] particularly in the Punjab region, where repressive measures culminated in the Jallianwala Bagh massacre, Amritsar Massacre. In Britain, public opinion was divided over the morality of the massacre, between those who saw it as having saved India from anarchy, and those who viewed it with revulsion.
The non-cooperation movement was called off in March 1922 following the Chauri Chaura incident, and discontent continued to simmer for the next 25 years.
In 1922, Egypt, which had been declared a British
protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its inter ...
at the outbreak of the First World War, was Unilateral Declaration of Egyptian Independence, granted formal independence, though it continued to be a British client state until 1954. British Army, British troops remained stationed in Egypt until the signing of the Anglo-Egyptian treaty of 1936, Anglo-Egyptian Treaty in 1936, under which it was agreed that the troops would withdraw but continue to occupy and defend the Suez Canal zone. In return, Egypt was assisted in joining the League of Nations. Iraq, a British mandate since 1920, gained membership of the League in its own right after achieving independence from Britain in 1932. In Palestine, Britain was presented with the problem of mediating between the Arabs and increasing numbers of Jews. The Balfour Declaration, which had been incorporated into the terms of the mandate, stated that a national home for the Jewish people would be established in Palestine, and Jewish immigration allowed up to a limit that would be determined by the mandatory power. This led to increasing conflict with the Arab population, who openly 1936–39 Arab revolt in Palestine, revolted in 1936. As the threat of war with Germany increased during the 1930s, Britain judged the support of Arabs as more important than the establishment of a Jewish homeland, and shifted to a pro-Arab stance, limiting Jewish immigration and in turn triggering a Jewish insurgency in Palestine, Jewish insurgency.
The right of the Dominions to set their own foreign policy, independent of Britain, was recognised at the 1923 Imperial Conference. Britain's request for military assistance from the Dominions at the outbreak of the Chanak Crisis the previous year had been turned down by Canada and South Africa, and Canada had refused to be bound by the Treaty of Lausanne (1923), 1923 Treaty of Lausanne. After pressure from the Irish Free State and South Africa, the 1926 Imperial Conference issued the Balfour Declaration of 1926, declaring the Dominions to be "autonomous Communities within the British Empire, equal in status, in no way subordinate one to another" within a "British Commonwealth of Nations". This declaration was given legal substance under the 1931 Statute of Westminster 1931, Statute of Westminster.
[#refRhodes2009, Rhodes, Wanna & Weller, pp. 5–15.] The parliaments of Canada, Australia, New Zealand, the Union of South Africa, the Irish Free State and Dominion of Newfoundland, Newfoundland were now independent of British legislative control, they could nullify Law of the United Kingdom, British laws and Britain could no longer pass laws for them without their consent. Newfoundland reverted to colonial status in 1933, suffering from financial difficulties during the Great Depression. In 1937 the Irish Free State introduced a Constitution of Ireland, republican constitution renaming itself ''Ireland''.
Second World War

Britain's declaration of war against Nazi Germany in September 1939 included the Crown colonies and India but did not automatically commit the Dominions of Australia, Canada, New Zealand, Newfoundland and South Africa. All soon declared war on Germany. While Britain continued to regard Ireland as still within the British Commonwealth, Ireland chose to remain Irish neutrality during World War II, legally neutral throughout The Emergency (Ireland), the war.
After the Fall of France in June 1940, Britain and the empire stood alone against Germany, until the German invasion of Greece on 7 April 1941. British Prime Minister Winston Churchill successfully lobbied President Franklin D. Roosevelt for military aid from the United States, but Roosevelt was not yet ready to ask United States Congress, Congress to commit the country to war. In August 1941, Churchill and Roosevelt met and signed the Atlantic Charter, which included the statement that "the rights of all peoples to choose the form of government under which they live" should be respected. This wording was ambiguous as to whether it referred to European countries invaded by Germany and Italy, or the peoples colonised by European nations, and would later be interpreted differently by the British, Americans, and nationalist movements.
[#refLloyd1996, Lloyd, p. 316.]
For Churchill, the entry of the United States into the war was the "greatest joy". He felt that Britain was now assured of victory, but failed to recognise that the "many disasters, immeasurable costs and tribulations [which he knew] lay ahead" in December 1941 would have permanent consequences for the future of the empire. The manner in which British forces were rapidly defeated in the Far East irreversibly harmed Britain's standing and prestige as an imperial power, including, particularly, the Battle of Singapore, Fall of Singapore, which had previously been hailed as an impregnable fortress and the eastern equivalent of Gibraltar. The realisation that Britain could not defend its entire empire pushed Australia and New Zealand, which now appeared threatened by Japanese forces, into closer ties with the United States and, ultimately, the 1951 ANZUS, ANZUS Pact.
The war weakened the empire in other ways: undermining Britain's control of politics in India, inflicting long-term economic damage, and irrevocably changing geopolitics by pushing the Soviet Union and the United States to the centre of the global stage.
Decolonisation and decline (1945–1997)
Though Britain and the empire emerged victorious from the Second World War, the effects of the conflict were profound, both at home and abroad. Much of Europe, a continent that had dominated the world for several centuries, was in ruins, and host to the armies of the United States and the Soviet Union, who now held the balance of global power. Britain was left essentially bankrupt, with insolvency only averted in 1946 after the negotiation of Anglo-American loan, a US$4.33 billion loan from the United States, the last installment of which was repaid in 2006.
At the same time, anti-colonial movements were on the rise in the colonies of European nations. The situation was complicated further by the increasing Cold War rivalry of the United States and the Soviet Union. In principle, both nations were opposed to European colonialism. In practice, American anti-communism prevailed over anti-imperialism, and therefore the United States supported the continued existence of the British Empire to keep Communist expansion in check. At first British politicians believed it would be possible to maintain Britain's role as a world power at the head of a re-imagined Commonwealth, but by 1960 they were forced to recognise that there was an irresistible "Wind of Change (speech), wind of change" blowing. Their priorities changed to maintaining an extensive zone of British influence and ensuring that stable, non-Communist governments were established in former colonies. In this context, while other European powers such as France and Portugal waged costly and unsuccessful wars to keep their empires intact, Britain generally adopted a policy of peaceful disengagement from its colonies, although violence occurred in Malaya, Kenya and Palestine. Between 1945 and 1965, the number of people under British rule outside the UK itself fell from 700 million to 5 million, 3 million of whom were in Hong Kong.
Initial disengagement

The pro-decolonisation Labour Party (UK), Labour government, elected at the 1945 United Kingdom general election, 1945 general election and led by Clement Attlee, moved quickly to tackle the most pressing issue facing the empire: Indian independence movement, Indian independence. India's two major political parties—the Indian National Congress (led by Mahatma Gandhi) and the All-India Muslim League, Muslim League (led by Muhammad Ali Jinnah)—had been campaigning for independence for decades, but disagreed as to how it should be implemented. Congress favoured a unified secular Indian state, whereas the League, fearing domination by the Hindu majority, desired a separate Islamic state for Muslim-majority regions. Increasing Civil disorder, civil unrest and the Royal Indian Navy mutiny, mutiny of the History of the Indian Navy, Royal Indian Navy during 1946 led Attlee to promise independence no later than 30 June 1948. When the urgency of the situation and risk of civil war became apparent, the newly appointed (and last) Viceroy, Louis Mountbatten, 1st Earl Mountbatten of Burma, Lord Mountbatten, hastily brought forward the date to 15 August 1947. The borders drawn by the British to broadly Partition of India, partition India into Hindu and Muslim areas left tens of millions as minorities in the newly independent states of India and Pakistan. Millions of Muslims crossed from India to Pakistan and Hindus vice versa, and violence between the two communities cost hundreds of thousands of lives. Burma, which had been administered as part of the British Raj, and Sri Lanka gained their independence the following year in 1948. India, Pakistan and Sri Lanka became members of the Commonwealth, while Burma chose not to join.
The British Mandate in Palestine, where an Arab majority lived alongside a Jewish minority, presented the British with a similar problem to that of India. The matter was complicated by large numbers of Jewish refugees seeking to be admitted to Palestine following the The Holocaust, Holocaust, while Arabs were opposed to the creation of a Jewish state. Frustrated by the intractability of the problem, attacks by Jewish paramilitary organisations and the increasing cost of maintaining its military presence, Britain announced in 1947 that it would withdraw in 1948 and leave the matter to the United Nations to solve. The United Nations General Assembly, UN General Assembly subsequently voted for a United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine, plan to partition Palestine into a Jewish and an Arab state. It was immediately followed by the outbreak of a 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war between the Arabs and Jews of Palestine, and British forces withdrew amid the fighting. The British Mandate for Palestine officially terminated at midnight on 15 May 1948 as the State of Israel declared independence and the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, 1948 Arab-Israeli War broke out, during which the territory of the former Mandate was partitioned between Israel and the surrounding Arab states. Amid the fighting, British forces continued to withdraw from Israel, with the last British troops departing from Haifa on 30 June 1948.
Following the surrender of Japan in the Second World War, anti-Japanese resistance movements in Malaya turned their attention towards the British, who had moved to quickly retake control of the colony, valuing it as a source of rubber and tin.
[#refLloyd1996, Lloyd, p. 335.] The fact that the guerrillas were primarily Malaysian Chinese Communists meant that the British attempt to quell the uprising was supported by the Islam in Malaysia, Muslim Malay majority, on the understanding that once the insurgency had been quelled, independence would be granted.
The Malayan Emergency, as it was called, began in 1948 and lasted until 1960, but by 1957, Britain felt confident enough to grant independence to the Federation of Malaya within the Commonwealth. In 1963, the 11 states of the federation together with Singapore, Sarawak and Crown Colony of North Borneo, North Borneo joined to form Malaysia, but in 1965 Chinese-majority Singapore was expelled from the union following tensions between the Malay and Chinese populations and became an independent city-state. Brunei, which had been a British protectorate since 1888, declined to join the union.
Suez and its aftermath

In the 1951 United Kingdom general election, 1951 general election, the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party returned to power in Britain under the leadership of Winston Churchill. Churchill and the Conservatives believed that Britain's position as a world power relied on the continued existence of the empire, with the base at the Suez Canal allowing Britain to maintain its pre-eminent position in the Middle East in spite of the loss of India. Churchill could not ignore Gamal Abdel Nasser, Gamal Abdul Nasser's new revolutionary Politics of Egypt, government of Egypt that had Egyptian Revolution of 1952, taken power in 1952, and the following year it was agreed that British troops would withdraw from the Suez Canal zone and that Sudan would be granted self-determination by 1955, with independence to follow. Sudan was History of Sudan (1956–69), granted independence on 1 January 1956.
In July 1956, Nasser unilaterally nationalised the Suez Canal. The response of Anthony Eden, who had succeeded Churchill as Prime Minister, was to collude with France to engineer an Israeli attack on Republic of Egypt (1953–58), Egypt that would give Britain and France an excuse to intervene militarily and retake the canal. Eden infuriated US President Dwight D. Eisenhower by his lack of consultation, and Eisenhower refused to back the invasion. Another of Eisenhower's concerns was the possibility of a wider war with the Soviet Union after it threatened to intervene on the Egyptian side. Eisenhower applied leverage (finance), financial leverage by threatening to sell US reserves of the Pound sterling, British pound and thereby precipitate a collapse of the British currency. Though the invasion force was militarily successful in its objectives, UN intervention and US pressure forced Britain into a humiliating withdrawal of its forces, and Eden resigned.
The
Suez Crisis
The Suez Crisis, or the Second Arab–Israeli war, also called the Tripartite Aggression ( ar, العدوان الثلاثي, Al-ʿUdwān aṯ-Ṯulāṯiyy) in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel,Also known as the Suez War or 1956 Wa ...
very publicly exposed Britain's limitations to the world and confirmed Britain's decline on the world stage and its end as a first-rate power, demonstrating that henceforth it could no longer act without at least the acquiescence, if not the full support, of the United States. The events at Suez wounded British Patriotism, national pride, leading one Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Member of Parliament (MP) to describe it as "Britain's Battle of Waterloo, Waterloo"
[#refOHBEv4, Brown, p. 343.] and another to suggest that the country had become an "American Satellite state, satellite". Margaret Thatcher later described the mindset she believed had befallen Britain's political leaders after Suez where they "went from believing that Britain could do anything to an almost neurotic belief that Britain could do nothing", from which Britain did not recover until the successful recapture of the Falkland Islands from Argentina in 1982.
While the Suez Crisis caused British power in the Middle East to weaken, it did not collapse. Britain again deployed its armed forces to the region, intervening in Muscat and Oman, Oman (Jebel Akhdar War, 1957), Jordan (United Nations Security Council Resolution 127, 1958) and Sheikhdom of Kuwait, Kuwait (Operation Vantage, 1961), though on these occasions with American approval, as the new Prime Minister Harold Macmillan's foreign policy was to remain firmly aligned with the United States.
Although Britain granted Kuwait independence in 1961, it continued to maintain a military presence in the Middle East for another decade. On 16 January 1968, a few weeks after the Pound sterling#Bretton Woods, devaluation of the pound, Prime Minister Harold Wilson and his Secretary of State for Defence, Defence Secretary Denis Healey announced that British Armed Forces troops would be withdrawn from major military bases East of Suez, which included the ones in the Middle East, and primarily from Malaysia and Singapore by the end of 1971, instead of 1975 as earlier planned. By that time over 50,000 British military personnel were still stationed in the Far East, including 30,000 in Singapore. The British granted independence to the Maldives in 1965 but continued to station a garrison there until 1976, withdrew from South Yemen, Aden in 1967, and granted independence to Bahrain, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates in 1971.
Wind of change
Macmillan gave a speech in Cape Town, South Africa in February 1960 where he spoke of "the wind of change blowing through this continent". Macmillan wished to avoid the same kind of Algerian War, colonial war that France was fighting in French Algeria, Algeria, and under his premiership decolonisation proceeded rapidly. To the three colonies that had been granted independence in the 1950s—Sudan, the Gold Coast (British colony), Gold Coast and Malaya—were added nearly ten times that number during the 1960s.
Britain's remaining colonies in Africa, except for self-governing colony, self-governing Southern Rhodesia, were all granted independence by 1968. British withdrawal from the southern and eastern parts of Africa was not a peaceful process. Kenyan independence was preceded by the eight-year Mau Mau uprising, in which tens of thousands of suspected rebels were interned by the colonial government in detention camps. In Rhodesia, the 1965 Rhodesia's Unilateral Declaration of Independence, Unilateral Declaration of Independence by the white minority resulted in a Rhodesian Bush War, civil war that lasted until the Lancaster House Agreement of 1979, which set the terms for recognised independence in 1980, as the new nation of Zimbabwe.
In Cyprus, a guerrilla war waged by the Greek Cypriots, Greek Cypriot organisation EOKA against British rule, was ended in 1959 by the London and Zürich Agreements, which resulted in Cyprus being granted independence in 1960. The UK retained the military bases of Akrotiri and Dhekelia as sovereign base areas. The List of islands in the Mediterranean, Mediterranean colony of Malta (island), Malta was amicably granted independence from the UK in 1964 and became the country of Malta, though the idea had been raised in 1955 of 1956 Maltese United Kingdom integration referendum, integration with Britain.
Most of the UK's Caribbean territories achieved independence after the departure in 1961 and 1962 of Jamaica and Trinidad from the West Indies Federation, established in 1958 in an attempt to unite the British Caribbean colonies under one government, but which collapsed following the loss of its two largest members.
[#refKnight1989, Knight & Palmer, pp. 14–15.] Jamaica attained independence in 1962, as did Trinidad and Tobago. Barbados achieved independence in 1966 and the remainder of the eastern Caribbean islands, including the Bahamas, in the 1970s and 1980s,
but Anguilla and the Turks and Caicos Islands opted to revert to British rule after they had already started on the path to independence. The British Virgin Islands, The Cayman Islands and Montserrat opted to retain ties with Britain, while Guyana achieved independence in 1966. Britain's last colony on the American mainland, British Honduras, became a self-governing colony in 1964 and was renamed Belize in 1973, achieving full independence in 1981. A Belizean-Guatemalan territorial dispute, dispute with Guatemala over claims to Belize was left unresolved.
British Overseas Territories in the Pacific acquired independence in the 1970s beginning with Fiji in 1970 and ending with Vanuatu in 1980. Vanuatu's independence was delayed because of political conflict between English and French-speaking communities, as the islands had been jointly administered as a Condominium (international law), condominium with France. Fiji, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands and Tuvalu became Commonwealth realms.
End of empire
By 1981, aside from a scattering of islands and outposts, the process of decolonisation that had begun after the Second World War was largely complete. In 1982, Britain's resolve in defending its remaining overseas territories was tested when 1982 invasion of the Falkland Islands, Argentina invaded the Falkland Islands, acting on a long-standing claim that dated back to the Spanish Empire. Britain's successful military response to retake the Falkland Islands during the ensuing Falklands War contributed to reversing the downward trend in Britain's status as a world power.
The 1980s saw Canada, Australia, and New Zealand sever their final constitutional links with Britain. Although granted legislative independence by the Statute of Westminster 1931, vestigial constitutional links had remained in place. The British Parliament retained the power to amend key Canadian constitutional statutes, meaning that effectively an act of the British Parliament was required to make certain changes to the Constitution of Canada, Canadian Constitution. The British Parliament had the power to pass laws extending to Canada at Canadian request. Although no longer able to pass any laws that would apply as Australian Commonwealth law, the British Parliament retained the power to legislate for the individual States and territories of Australia, Australian states. With regard to New Zealand, the British Parliament retained the power to pass legislation applying to New Zealand with the New Zealand Parliament's consent. In 1982, the last legal link between Canada and Britain was severed by the Canada Act 1982, which was passed by the British parliament, formally patriation, patriating the Canadian Constitution. The act ended the need for British involvement in changes to the Canadian constitution.
[#refOHBEv4, Brown, p. 594.] Similarly, the Australia Act 1986 (effective 3 March 1986) severed the constitutional link between Britain and the Australian states, while New Zealand's Constitution Act 1986 (effective 1 January 1987) reformed the constitution of New Zealand to sever its constitutional link with Britain.
On 1 January 1984, Brunei, Britain's last remaining Asian protectorate, was granted independence. Independence had been delayed due to the opposition of the List of sultans of Brunei, Sultan, who had preferred British protection.
In September 1982 the Prime Minister, Margaret Thatcher, travelled to Beijing to negotiate with the Chinese Communist government, on the future of Britain's last major and most populous overseas territory, Hong Kong. Under the terms of the 1842 Treaty of Nanking and 1860 Convention of Peking, Hong Kong Island and Kowloon Peninsula had been respectively ceded to Britain ''in perpetuity'', but the majority of the colony consisted of the New Territories, which had been acquired under a Convention for the Extension of Hong Kong Territory, 99-year lease in 1898, due to expire in 1997. Thatcher, seeing parallels with the Falkland Islands, initially wished to hold Hong Kong and proposed British administration with Chinese sovereignty, though this was rejected by China. A deal was reached in 1984—under the terms of the Sino-British Joint Declaration, Hong Kong would become a special administrative region of the People's Republic of China. The Hong Kong handover ceremony, handover ceremony in 1997 marked for many,
[#refBrendon, Brendon, p. 660.] including Charles III of the United Kingdom, Charles, Prince of Wales, who was in attendance, "the end of Empire".
Legacy

Britain retains sovereignty over 14 territories outside the British Isles. In 1983, the British Nationality Act 1981 renamed the existing Crown colony, Crown Colonies as "British Dependent Territories", and in 2002 they were renamed the British Overseas Territories.
[#refGapes2008, Gapes, pp. 145–47] Most former British colonies and protectorates are members of the
Commonwealth of Nations, a voluntary association of equal members, comprising a population of around 2.2 billion people. Fifteen Commonwealth realms voluntarily continue to share the British monarch, King Charles III, as their head of state. These fifteen nations are distinct and equal legal entities – the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, United Kingdom, Monarchy of Australia, Australia, Monarchy of Canada, Canada, Monarchy of New Zealand, New Zealand, Monarchy of Antigua and Barbuda, Antigua and Barbuda, Monarchy of the Bahamas, The Bahamas, Monarchy of Belize, Belize, Monarchy of Grenada, Grenada, Monarchy of Jamaica, Jamaica, Monarchy of Papua New Guinea, Papua New Guinea, Monarchy of Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Monarchy of Saint Lucia, Saint Lucia, Monarchy of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Monarchy of the Solomon Islands, Solomon Islands and Monarchy of Tuvalu, Tuvalu.
Decades, and in some cases centuries, of British rule and emigration have left their mark on the independent nations that arose from the British Empire. The empire established the use of the English language in regions around the world. Today it is the primary language of up to 460 million people and is spoken by about 1.5 billion as a first, second or foreign language. Individual and team sports developed in Britain, particularly association football, football, cricket, lawn tennis, and golf were exported. British missionary, missionaries who travelled around the globe often in advance of soldiers and civil servants spread Protestantism (including Anglicanism) to all continents. The British Empire provided refuge for religiously persecuted continental Europeans for hundreds of years.
Political boundaries drawn by the British did not always reflect homogeneous ethnicities or religions, contributing to conflicts in formerly colonised areas. The British Empire was responsible for large migrations of peoples. Millions left the British Isles, with the founding Settler colonialism, settler colonist populations of the United States, Canada, Australia and New Zealand coming mainly from Britain and Ireland. Tensions remain between the white settler populations of these countries and their indigenous minorities, and between white settler minorities and indigenous majorities in South Africa and Zimbabwe. Settlers in
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
from Great Britain have left their mark in the form of divided Irish nationalism, nationalist and Unionism in Ireland, unionist communities in Northern Ireland. Millions of people moved to and from British colonies, with large numbers of Non-resident Indian and Overseas Citizen of India, Overseas Indian people emigrating to other parts of the empire, such as Malaysia and Fiji, and Overseas Chinese people to Malaysia, Singapore and the Caribbean. The Demography of the United Kingdom, demographics of the United Kingdom itself were changed after the Second World War owing to Immigration to the United Kingdom since 1922#Post-war immigration (1945–1983), immigration to Britain from its former colonies.
In the 19th century, List of British innovations and discoveries, innovation in Britain led to revolutionary changes in manufacturing, the development of factory systems, and the growth of transportation by railway and steamship. British colonial architecture, such as in churches, railway stations and government buildings, can be seen in many cities that were once part of the British Empire. The British choice of system of measurement, the Imperial units, imperial system, continues to be used in some countries in various ways. The convention of Right- and left-hand traffic, driving on the left-hand side of the road has been retained in much of the former empire.
The Westminster system of Parliamentary system, parliamentary democracy has served as the template for the governments for many former colonies, and English law, English common law for legal systems. International commercial contracts are often based on English common law. The British Judicial Committee of the Privy Council still serves as the highest court of appeal for twelve former colonies.
Historians' historiography of the British Empire, approaches to understanding the British Empire are diverse and evolving.
Two key sites of debate over recent decades have been the impact of Postcolonialism, post-colonial studies, which seek to Critical theory, critically re-evaluate the history of imperialism, and the continued relevance of historians Ronald Robinson and Jack Gallagher (historian), John Gallagher, whose work greatly influenced imperial historiography during the 1950s and 1960s. In addition, differing assessments of the empire's legacy remain relevant to debates over recent history and politics, such as the Anglo-American 2003 invasion of Iraq, invasions of Iraq and United States invasion of Afghanistan, Afghanistan, as well as Britain's role and identity in the contemporary world.
Historians such as Caroline Elkins have argued against perceptions of the British Empire as a primarily liberalising and modernising enterprise, criticising its widespread use of violence and emergency laws to maintain power.
Common criticisms of the empire include the use of detention camps in its colonies, massacres of indigenous peoples,
and famine-response policies.
Some scholars, including Amartya Sen, assert that British policies worsened the famine in India, famines in India that killed millions during British rule.
[Sen, Amartya. Development as Freedom. ch 7] Conversely, historians such as Niall Ferguson say that the economic and institutional development the British Empire brought resulted in a net benefit to its colonies. Other historians treat its legacy as varied and ambiguous.
Public attitudes towards the empire within Britain remain somewhat positive.
Notes
See also
* List of British Empire-related topics
* Historiography of the British Empire
* Demographics of the British Empire
* Economy of the British Empire
* Territorial evolution of the British Empire
* History of the foreign relations of the United Kingdom
* Historical flags of the British Empire and the overseas territories
* List of countries that gained independence from the United Kingdom
References
Works cited
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Collection: "British Empire"from the University of Michigan Museum of Art
{{Authority control
British Empire,
Former empires
Imperialism
Victorian era
1583 establishments in the British Empire
States and territories established in 1583
States and territories disestablished in 1997
Overseas empires
History of the United Kingdom
Former countries in Ireland
Historical transcontinental empires
 The foundations of the British Empire were laid when England and
The foundations of the British Empire were laid when England and  England's early efforts at colonisation in the Americas met with mixed success. An attempt to establish a colony in
England's early efforts at colonisation in the Americas met with mixed success. An attempt to establish a colony in  At the end of the 16th century, England and the Dutch Empire began to challenge the
At the end of the 16th century, England and the Dutch Empire began to challenge the  The 18th century saw the newly united Great Britain rise to be the world's dominant colonial power, with France becoming its main rival on the imperial stage. Great Britain, Portugal, the Netherlands, and the Holy Roman Empire continued the War of the Spanish Succession, which lasted until 1714 and was concluded by the
The 18th century saw the newly united Great Britain rise to be the world's dominant colonial power, with France becoming its main rival on the imperial stage. Great Britain, Portugal, the Netherlands, and the Holy Roman Empire continued the War of the Spanish Succession, which lasted until 1714 and was concluded by the  During the 1760s and early 1770s, relations between the Thirteen Colonies and Britain became increasingly strained, primarily because of resentment of the British Parliament's attempts to govern and tax American colonists without their consent. This was summarised at the time by the slogan "
During the 1760s and early 1770s, relations between the Thirteen Colonies and Britain became increasingly strained, primarily because of resentment of the British Parliament's attempts to govern and tax American colonists without their consent. This was summarised at the time by the slogan " Since 1718, penal transportation, transportation to the American colonies had been a penalty for various offences in Britain, with approximately one thousand convicts transported per year. Forced to find an alternative location after the loss of the Thirteen Colonies in 1783, the British government turned to Australia. The New Holland (Australia), coast of Australia had been discovered for Europeans by the Dutch Janszoon voyage of 1605–06, in 1606,#refMulligan2001, Mulligan & Hill, pp. 20–23. but there was no attempt to colonise it. In 1770 James Cook charted the eastern coast while on a scientific First voyage of James Cook, voyage, claimed the continent for Britain, and named it Colony of New South Wales, New South Wales. In 1778, Joseph Banks, Cook's botanist on the voyage, presented evidence to the government on the suitability of Botany Bay for the establishment of a Penal colony, penal settlement, and in 1787 the first shipment of Convicts in Australia, convicts set sail, arriving in 1788. Unusually, Australia was claimed through proclamation. Indigenous Australians were considered too uncivilised to require treaties, and colonisation brought disease and violence that together with the deliberate dispossession of land and culture were devastating to these peoples. Britain continued to transport convicts to New South Wales until 1840, to Colony of Tasmania, Tasmania until 1853 and to Colony of Western Australia, Western Australia until 1868. The Australian colonies became profitable exporters of wool and gold, mainly because of the Victorian gold rush, making its capital Melbourne for a time the richest city in the world.
During his voyage, Cook visited New Zealand, known to Europeans due to the 1642 voyage of the Dutch explorer, Abel Tasman. Cook claimed both the North Island, North and the South Island, South islands for the British crown in 1769 and 1770 respectively. Initially, interaction between the indigenous Māori people, Maori population and Pākehā settlers, European settlers was limited to the trading of goods. European settlement increased through the early decades of the 19th century, with many trading stations being established, especially in the North. In 1839, the New Zealand Company announced plans to buy large tracts of land and establish colonies in New Zealand. On 6 February 1840, Captain William Hobson and around 40 Maori chiefs signed the Treaty of Waitangi which is considered to be New Zealand's founding document despite differing interpretations of the Māori language, Maori and English language, English versions of the text being the cause of ongoing dispute.
The British also expanded their mercantile interests in the North Pacific. Spain and Britain had become rivals in the area, culminating in the Nootka Crisis in 1789. Both sides mobilised for war, but when France refused to support Spain it was forced to back down, leading to the Nootka Convention. The outcome was a humiliation for Spain, which practically renounced all sovereignty on the North Pacific coast. This opened the way to British expansion in the area, and a number of expeditions took place; firstly a Vancouver Expedition, naval expedition led by George Vancouver which explored the inlets around the Pacific North West, particularly around Vancouver Island. On land, expeditions sought to discover a river route to the Pacific for the extension of the North American fur trade. Alexander Mackenzie (explorer), Alexander Mackenzie of the North West Company led the first, starting out in 1792, and a year a later he became the first European to reach the Pacific overland north of the Rio Grande, reaching the ocean near present-day Bella Coola, British Columbia, Bella Coola. This preceded the Lewis and Clark Expedition by twelve years. Shortly thereafter, Mackenzie's companion, John Finlay (fur trader), John Finlay, founded the first permanent European settlement in British Columbia, Fort St. John, British Columbia, Fort St. John. The North West Company sought further exploration and backed expeditions by David Thompson (explorer), David Thompson, starting in 1797, and later by Simon Fraser (explorer), Simon Fraser. These pushed into the wilderness territories of the Rocky Mountains and Interior Plateau to the Strait of Georgia on the Pacific Coast, expanding British North America westward.
Since 1718, penal transportation, transportation to the American colonies had been a penalty for various offences in Britain, with approximately one thousand convicts transported per year. Forced to find an alternative location after the loss of the Thirteen Colonies in 1783, the British government turned to Australia. The New Holland (Australia), coast of Australia had been discovered for Europeans by the Dutch Janszoon voyage of 1605–06, in 1606,#refMulligan2001, Mulligan & Hill, pp. 20–23. but there was no attempt to colonise it. In 1770 James Cook charted the eastern coast while on a scientific First voyage of James Cook, voyage, claimed the continent for Britain, and named it Colony of New South Wales, New South Wales. In 1778, Joseph Banks, Cook's botanist on the voyage, presented evidence to the government on the suitability of Botany Bay for the establishment of a Penal colony, penal settlement, and in 1787 the first shipment of Convicts in Australia, convicts set sail, arriving in 1788. Unusually, Australia was claimed through proclamation. Indigenous Australians were considered too uncivilised to require treaties, and colonisation brought disease and violence that together with the deliberate dispossession of land and culture were devastating to these peoples. Britain continued to transport convicts to New South Wales until 1840, to Colony of Tasmania, Tasmania until 1853 and to Colony of Western Australia, Western Australia until 1868. The Australian colonies became profitable exporters of wool and gold, mainly because of the Victorian gold rush, making its capital Melbourne for a time the richest city in the world.
During his voyage, Cook visited New Zealand, known to Europeans due to the 1642 voyage of the Dutch explorer, Abel Tasman. Cook claimed both the North Island, North and the South Island, South islands for the British crown in 1769 and 1770 respectively. Initially, interaction between the indigenous Māori people, Maori population and Pākehā settlers, European settlers was limited to the trading of goods. European settlement increased through the early decades of the 19th century, with many trading stations being established, especially in the North. In 1839, the New Zealand Company announced plans to buy large tracts of land and establish colonies in New Zealand. On 6 February 1840, Captain William Hobson and around 40 Maori chiefs signed the Treaty of Waitangi which is considered to be New Zealand's founding document despite differing interpretations of the Māori language, Maori and English language, English versions of the text being the cause of ongoing dispute.
The British also expanded their mercantile interests in the North Pacific. Spain and Britain had become rivals in the area, culminating in the Nootka Crisis in 1789. Both sides mobilised for war, but when France refused to support Spain it was forced to back down, leading to the Nootka Convention. The outcome was a humiliation for Spain, which practically renounced all sovereignty on the North Pacific coast. This opened the way to British expansion in the area, and a number of expeditions took place; firstly a Vancouver Expedition, naval expedition led by George Vancouver which explored the inlets around the Pacific North West, particularly around Vancouver Island. On land, expeditions sought to discover a river route to the Pacific for the extension of the North American fur trade. Alexander Mackenzie (explorer), Alexander Mackenzie of the North West Company led the first, starting out in 1792, and a year a later he became the first European to reach the Pacific overland north of the Rio Grande, reaching the ocean near present-day Bella Coola, British Columbia, Bella Coola. This preceded the Lewis and Clark Expedition by twelve years. Shortly thereafter, Mackenzie's companion, John Finlay (fur trader), John Finlay, founded the first permanent European settlement in British Columbia, Fort St. John, British Columbia, Fort St. John. The North West Company sought further exploration and backed expeditions by David Thompson (explorer), David Thompson, starting in 1797, and later by Simon Fraser (explorer), Simon Fraser. These pushed into the wilderness territories of the Rocky Mountains and Interior Plateau to the Strait of Georgia on the Pacific Coast, expanding British North America westward.
 British imperial strength was underpinned by the steamship and the telegraph, new technologies invented in the second half of the 19th century, allowing it to control and defend the empire. By 1902, the British Empire was linked together by a network of telegraph cables, called the All Red Line.
British imperial strength was underpinned by the steamship and the telegraph, new technologies invented in the second half of the 19th century, allowing it to control and defend the empire. By 1902, the British Empire was linked together by a network of telegraph cables, called the All Red Line.
 During the 19th century, Britain and the Russian Empire vied to fill the power vacuums that had been left by the declining Ottoman Empire, Qajar dynasty and Qing dynasty. This rivalry in Central Asia came to be known as the "Great Game". As far as Britain was concerned, defeats inflicted by Russia on Russo-Persian War (1826–1828), Persia and Russo-Turkish War (1828–1829), Turkey demonstrated its imperial ambitions and capabilities and stoked fears in Britain of an overland invasion of India. In 1839, Britain moved to pre-empt this by invading Afghanistan, but the First Anglo-Afghan War was a disaster for Britain.#refJames2001, James, p. 182.
When Russia invaded the Rumelia, Ottoman Balkans in 1853, fears of Russian dominance in the Mediterranean and the Middle East led Britain and France to enter the war in support of the Ottoman Empire and invade the Crimean Peninsula to destroy Russian naval capabilities. The ensuing Crimean War (1854–1856), which involved new techniques of modern warfare, was the only global war fought between Britain and another Imperialism, imperial power during the ''Pax Britannica'' and was a resounding defeat for Russia. The situation remained unresolved in Central Asia for two more decades, with Britain annexing Baluchistan (Chief Commissioner's Province), Baluchistan in 1876 and Russia annexing Kirghizia, Kazakhstan, and Turkmenistan. For a while, it appeared that another war would be inevitable, but the two countries reached an agreement on their respective Sphere of influence, spheres of influence in the region in 1878 and on all outstanding matters in 1907 with the signing of the Anglo-Russian Entente. The destruction of the Imperial Russian Navy by the Imperial Japanese Navy at the Battle of Tsushima during the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905 limited its threat to the British.#refhodge47, Hodge, p. 47.
During the 19th century, Britain and the Russian Empire vied to fill the power vacuums that had been left by the declining Ottoman Empire, Qajar dynasty and Qing dynasty. This rivalry in Central Asia came to be known as the "Great Game". As far as Britain was concerned, defeats inflicted by Russia on Russo-Persian War (1826–1828), Persia and Russo-Turkish War (1828–1829), Turkey demonstrated its imperial ambitions and capabilities and stoked fears in Britain of an overland invasion of India. In 1839, Britain moved to pre-empt this by invading Afghanistan, but the First Anglo-Afghan War was a disaster for Britain.#refJames2001, James, p. 182.
When Russia invaded the Rumelia, Ottoman Balkans in 1853, fears of Russian dominance in the Mediterranean and the Middle East led Britain and France to enter the war in support of the Ottoman Empire and invade the Crimean Peninsula to destroy Russian naval capabilities. The ensuing Crimean War (1854–1856), which involved new techniques of modern warfare, was the only global war fought between Britain and another Imperialism, imperial power during the ''Pax Britannica'' and was a resounding defeat for Russia. The situation remained unresolved in Central Asia for two more decades, with Britain annexing Baluchistan (Chief Commissioner's Province), Baluchistan in 1876 and Russia annexing Kirghizia, Kazakhstan, and Turkmenistan. For a while, it appeared that another war would be inevitable, but the two countries reached an agreement on their respective Sphere of influence, spheres of influence in the region in 1878 and on all outstanding matters in 1907 with the signing of the Anglo-Russian Entente. The destruction of the Imperial Russian Navy by the Imperial Japanese Navy at the Battle of Tsushima during the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905 limited its threat to the British.#refhodge47, Hodge, p. 47.
 The Dutch East India Company had founded the Dutch Cape Colony on the Cape of Good Hope, southern tip of Africa in 1652 as a way station for its ships travelling to and from its colonies in the Indies, East Indies. Britain formally acquired the colony, and its large Afrikaner (or Boer) population in 1806, having occupied it in 1795 to prevent its falling into French hands during the Flanders Campaign. British immigration to the Cape Colony began to rise after 1820, and pushed thousands of Boers, resentful of British rule, northwards to found their own—mostly short-lived—Boer republics, independent republics, during the Great Trek of the late 1830s and early 1840s. In the process the Voortrekkers clashed repeatedly with the British, who had their own agenda with regard to colonial expansion in South Africa and to the various native African polities, including those of the Sotho people and the Zulu Kingdom. Eventually, the Boers established two republics that had a longer lifespan: the South African Republic or Transvaal Republic (1852–1877; 1881–1902) and the Orange Free State (1854–1902). In 1902 Britain occupied both republics, concluding a treaty with the two Boer Republics following the Second Boer War (1899–1902).
In 1869 the Suez Canal opened under Napoleon III of France, Napoleon III, linking the Mediterranean Sea with the Indian Ocean. Initially the Canal was opposed by the British; but once opened, its strategic value was quickly recognised and became the "jugular vein of the Empire". In 1875, the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative government of Benjamin Disraeli bought the indebted Egyptian ruler Isma'il Pasha's 44 per cent shareholding in the Suez Canal for £4 million (equivalent to £ in ). Although this did not grant outright control of the strategic waterway, it did give Britain leverage. Joint Anglo-French financial control over Egypt ended in outright British occupation in 1882. Although Britain controlled the Khedivate of Egypt into the 20th century, it was officially a Vassal and tributary states of the Ottoman Empire, vassal state of the Ottoman Empire and not part of the British Empire. The French were still majority shareholders and attempted to weaken the British position, but a compromise was reached with the 1888 Convention of Constantinople, which made the Canal officially neutral territory.
With competitive French, Belgian colonial empire, Belgian and Portuguese activity in the lower Congo River region undermining orderly colonisation of tropical Africa, the Berlin Conference of 1884–85 was held to regulate the competition between the European powers in what was called the "Scramble for Africa" by defining "effective occupation" as the criterion for international recognition of territorial claims. The scramble continued into the 1890s, and caused Britain to reconsider its decision in 1885 to withdraw from Sudan. A joint force of British and Egyptian troops defeated the Mahdist War, Mahdist Army in 1896 and rebuffed an attempted French invasion Fashoda Incident, at Fashoda in 1898. Sudan was nominally made an Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, Anglo-Egyptian condominium, but a British colony in reality.
British gains in Southern and East Africa prompted Cecil Rhodes, pioneer of British expansion in Southern Africa, to urge a "Cape to Cairo Railway, Cape to Cairo" railway linking the strategically important Suez Canal to the mineral-rich south of the continent. During the 1880s and 1890s, Rhodes, with his privately owned British South Africa Company, company rule in Rhodesia, occupied and annexed territories named after him, Rhodesia (name), Rhodesia.
The Dutch East India Company had founded the Dutch Cape Colony on the Cape of Good Hope, southern tip of Africa in 1652 as a way station for its ships travelling to and from its colonies in the Indies, East Indies. Britain formally acquired the colony, and its large Afrikaner (or Boer) population in 1806, having occupied it in 1795 to prevent its falling into French hands during the Flanders Campaign. British immigration to the Cape Colony began to rise after 1820, and pushed thousands of Boers, resentful of British rule, northwards to found their own—mostly short-lived—Boer republics, independent republics, during the Great Trek of the late 1830s and early 1840s. In the process the Voortrekkers clashed repeatedly with the British, who had their own agenda with regard to colonial expansion in South Africa and to the various native African polities, including those of the Sotho people and the Zulu Kingdom. Eventually, the Boers established two republics that had a longer lifespan: the South African Republic or Transvaal Republic (1852–1877; 1881–1902) and the Orange Free State (1854–1902). In 1902 Britain occupied both republics, concluding a treaty with the two Boer Republics following the Second Boer War (1899–1902).
In 1869 the Suez Canal opened under Napoleon III of France, Napoleon III, linking the Mediterranean Sea with the Indian Ocean. Initially the Canal was opposed by the British; but once opened, its strategic value was quickly recognised and became the "jugular vein of the Empire". In 1875, the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative government of Benjamin Disraeli bought the indebted Egyptian ruler Isma'il Pasha's 44 per cent shareholding in the Suez Canal for £4 million (equivalent to £ in ). Although this did not grant outright control of the strategic waterway, it did give Britain leverage. Joint Anglo-French financial control over Egypt ended in outright British occupation in 1882. Although Britain controlled the Khedivate of Egypt into the 20th century, it was officially a Vassal and tributary states of the Ottoman Empire, vassal state of the Ottoman Empire and not part of the British Empire. The French were still majority shareholders and attempted to weaken the British position, but a compromise was reached with the 1888 Convention of Constantinople, which made the Canal officially neutral territory.
With competitive French, Belgian colonial empire, Belgian and Portuguese activity in the lower Congo River region undermining orderly colonisation of tropical Africa, the Berlin Conference of 1884–85 was held to regulate the competition between the European powers in what was called the "Scramble for Africa" by defining "effective occupation" as the criterion for international recognition of territorial claims. The scramble continued into the 1890s, and caused Britain to reconsider its decision in 1885 to withdraw from Sudan. A joint force of British and Egyptian troops defeated the Mahdist War, Mahdist Army in 1896 and rebuffed an attempted French invasion Fashoda Incident, at Fashoda in 1898. Sudan was nominally made an Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, Anglo-Egyptian condominium, but a British colony in reality.
British gains in Southern and East Africa prompted Cecil Rhodes, pioneer of British expansion in Southern Africa, to urge a "Cape to Cairo Railway, Cape to Cairo" railway linking the strategically important Suez Canal to the mineral-rich south of the continent. During the 1880s and 1890s, Rhodes, with his privately owned British South Africa Company, company rule in Rhodesia, occupied and annexed territories named after him, Rhodesia (name), Rhodesia.
 By the turn of the 20th century, fears had begun to grow in Britain that it would no longer be able to defend the metropole and the entirety of the empire while at the same time maintaining the policy of "splendid isolation". Germany was rapidly rising as a military and industrial power and was now seen as the most likely opponent in any future war. Recognising that it was overstretched in the Pacific and threatened at home by the Imperial German Navy, Britain Anglo-Japanese Alliance, formed an alliance with Japan in 1902 and with its old enemies Entente cordiale, France and Russia in 1904 and 1907, respectively.
By the turn of the 20th century, fears had begun to grow in Britain that it would no longer be able to defend the metropole and the entirety of the empire while at the same time maintaining the policy of "splendid isolation". Germany was rapidly rising as a military and industrial power and was now seen as the most likely opponent in any future war. Recognising that it was overstretched in the Pacific and threatened at home by the Imperial German Navy, Britain Anglo-Japanese Alliance, formed an alliance with Japan in 1902 and with its old enemies Entente cordiale, France and Russia in 1904 and 1907, respectively.
 The changing world order that the war had brought about, in particular the growth of the United States and Japan as naval powers, and the rise of independence movements in India and Ireland, caused a major reassessment of British imperial policy. Forced to choose between alignment with the United States or Japan, Britain opted not to renew its Anglo-Japanese Alliance and instead signed the 1922 Washington Naval Treaty, where Britain accepted naval parity with the United States.#refLouis2006, Louis, p. 302. This decision was the source of much debate in Britain during the 1930s as militaristic governments took hold in Germany and Japan helped in part by the Great Depression, for it was feared that the empire could not survive a simultaneous attack by both nations. The issue of the empire's security was a serious concern in Britain, as it was vital to the Economy of the United Kingdom, British economy.
In 1919, the frustrations caused by delays to Irish Home Rule movement, Irish home rule led the MPs of Sinn Féin, a pro-independence party that had won a majority of the Irish seats in the 1918 Irish general election, 1918 British general election, to establish an Dáil Éireann (Irish Republic), independent parliament in Dublin, at which Irish Declaration of Independence, Irish independence was declared. The Irish Republican Army simultaneously began a guerrilla warfare, guerrilla war against the British administration. The Irish War of Independence ended in 1921 with a stalemate and the signing of the Anglo-Irish Treaty, creating the Irish Free State, a Dominion within the British Empire, with effective internal independence but still constitutionally linked with the British Crown. Northern Ireland, consisting of six of the 32 Counties of Ireland, Irish counties which had been established as a devolved region under the 1920 Government of Ireland Act 1920, Government of Ireland Act, immediately exercised its option under the treaty to retain its existing status within the United Kingdom.
The changing world order that the war had brought about, in particular the growth of the United States and Japan as naval powers, and the rise of independence movements in India and Ireland, caused a major reassessment of British imperial policy. Forced to choose between alignment with the United States or Japan, Britain opted not to renew its Anglo-Japanese Alliance and instead signed the 1922 Washington Naval Treaty, where Britain accepted naval parity with the United States.#refLouis2006, Louis, p. 302. This decision was the source of much debate in Britain during the 1930s as militaristic governments took hold in Germany and Japan helped in part by the Great Depression, for it was feared that the empire could not survive a simultaneous attack by both nations. The issue of the empire's security was a serious concern in Britain, as it was vital to the Economy of the United Kingdom, British economy.
In 1919, the frustrations caused by delays to Irish Home Rule movement, Irish home rule led the MPs of Sinn Féin, a pro-independence party that had won a majority of the Irish seats in the 1918 Irish general election, 1918 British general election, to establish an Dáil Éireann (Irish Republic), independent parliament in Dublin, at which Irish Declaration of Independence, Irish independence was declared. The Irish Republican Army simultaneously began a guerrilla warfare, guerrilla war against the British administration. The Irish War of Independence ended in 1921 with a stalemate and the signing of the Anglo-Irish Treaty, creating the Irish Free State, a Dominion within the British Empire, with effective internal independence but still constitutionally linked with the British Crown. Northern Ireland, consisting of six of the 32 Counties of Ireland, Irish counties which had been established as a devolved region under the 1920 Government of Ireland Act 1920, Government of Ireland Act, immediately exercised its option under the treaty to retain its existing status within the United Kingdom.
 A similar struggle began in India when the Government of India Act 1919 failed to satisfy the demand for independence. Concerns over communist and foreign plots following the Ghadar conspiracy ensured that war-time strictures were renewed by the Rowlatt Acts. This led to tension,#refJames2001, James, p. 416. particularly in the Punjab region, where repressive measures culminated in the Jallianwala Bagh massacre, Amritsar Massacre. In Britain, public opinion was divided over the morality of the massacre, between those who saw it as having saved India from anarchy, and those who viewed it with revulsion. The non-cooperation movement was called off in March 1922 following the Chauri Chaura incident, and discontent continued to simmer for the next 25 years.
In 1922, Egypt, which had been declared a British
A similar struggle began in India when the Government of India Act 1919 failed to satisfy the demand for independence. Concerns over communist and foreign plots following the Ghadar conspiracy ensured that war-time strictures were renewed by the Rowlatt Acts. This led to tension,#refJames2001, James, p. 416. particularly in the Punjab region, where repressive measures culminated in the Jallianwala Bagh massacre, Amritsar Massacre. In Britain, public opinion was divided over the morality of the massacre, between those who saw it as having saved India from anarchy, and those who viewed it with revulsion. The non-cooperation movement was called off in March 1922 following the Chauri Chaura incident, and discontent continued to simmer for the next 25 years.
In 1922, Egypt, which had been declared a British  Britain's declaration of war against Nazi Germany in September 1939 included the Crown colonies and India but did not automatically commit the Dominions of Australia, Canada, New Zealand, Newfoundland and South Africa. All soon declared war on Germany. While Britain continued to regard Ireland as still within the British Commonwealth, Ireland chose to remain Irish neutrality during World War II, legally neutral throughout The Emergency (Ireland), the war.
After the Fall of France in June 1940, Britain and the empire stood alone against Germany, until the German invasion of Greece on 7 April 1941. British Prime Minister Winston Churchill successfully lobbied President Franklin D. Roosevelt for military aid from the United States, but Roosevelt was not yet ready to ask United States Congress, Congress to commit the country to war. In August 1941, Churchill and Roosevelt met and signed the Atlantic Charter, which included the statement that "the rights of all peoples to choose the form of government under which they live" should be respected. This wording was ambiguous as to whether it referred to European countries invaded by Germany and Italy, or the peoples colonised by European nations, and would later be interpreted differently by the British, Americans, and nationalist movements.#refLloyd1996, Lloyd, p. 316.
For Churchill, the entry of the United States into the war was the "greatest joy". He felt that Britain was now assured of victory, but failed to recognise that the "many disasters, immeasurable costs and tribulations [which he knew] lay ahead" in December 1941 would have permanent consequences for the future of the empire. The manner in which British forces were rapidly defeated in the Far East irreversibly harmed Britain's standing and prestige as an imperial power, including, particularly, the Battle of Singapore, Fall of Singapore, which had previously been hailed as an impregnable fortress and the eastern equivalent of Gibraltar. The realisation that Britain could not defend its entire empire pushed Australia and New Zealand, which now appeared threatened by Japanese forces, into closer ties with the United States and, ultimately, the 1951 ANZUS, ANZUS Pact. The war weakened the empire in other ways: undermining Britain's control of politics in India, inflicting long-term economic damage, and irrevocably changing geopolitics by pushing the Soviet Union and the United States to the centre of the global stage.
Britain's declaration of war against Nazi Germany in September 1939 included the Crown colonies and India but did not automatically commit the Dominions of Australia, Canada, New Zealand, Newfoundland and South Africa. All soon declared war on Germany. While Britain continued to regard Ireland as still within the British Commonwealth, Ireland chose to remain Irish neutrality during World War II, legally neutral throughout The Emergency (Ireland), the war.
After the Fall of France in June 1940, Britain and the empire stood alone against Germany, until the German invasion of Greece on 7 April 1941. British Prime Minister Winston Churchill successfully lobbied President Franklin D. Roosevelt for military aid from the United States, but Roosevelt was not yet ready to ask United States Congress, Congress to commit the country to war. In August 1941, Churchill and Roosevelt met and signed the Atlantic Charter, which included the statement that "the rights of all peoples to choose the form of government under which they live" should be respected. This wording was ambiguous as to whether it referred to European countries invaded by Germany and Italy, or the peoples colonised by European nations, and would later be interpreted differently by the British, Americans, and nationalist movements.#refLloyd1996, Lloyd, p. 316.
For Churchill, the entry of the United States into the war was the "greatest joy". He felt that Britain was now assured of victory, but failed to recognise that the "many disasters, immeasurable costs and tribulations [which he knew] lay ahead" in December 1941 would have permanent consequences for the future of the empire. The manner in which British forces were rapidly defeated in the Far East irreversibly harmed Britain's standing and prestige as an imperial power, including, particularly, the Battle of Singapore, Fall of Singapore, which had previously been hailed as an impregnable fortress and the eastern equivalent of Gibraltar. The realisation that Britain could not defend its entire empire pushed Australia and New Zealand, which now appeared threatened by Japanese forces, into closer ties with the United States and, ultimately, the 1951 ANZUS, ANZUS Pact. The war weakened the empire in other ways: undermining Britain's control of politics in India, inflicting long-term economic damage, and irrevocably changing geopolitics by pushing the Soviet Union and the United States to the centre of the global stage.
 The pro-decolonisation Labour Party (UK), Labour government, elected at the 1945 United Kingdom general election, 1945 general election and led by Clement Attlee, moved quickly to tackle the most pressing issue facing the empire: Indian independence movement, Indian independence. India's two major political parties—the Indian National Congress (led by Mahatma Gandhi) and the All-India Muslim League, Muslim League (led by Muhammad Ali Jinnah)—had been campaigning for independence for decades, but disagreed as to how it should be implemented. Congress favoured a unified secular Indian state, whereas the League, fearing domination by the Hindu majority, desired a separate Islamic state for Muslim-majority regions. Increasing Civil disorder, civil unrest and the Royal Indian Navy mutiny, mutiny of the History of the Indian Navy, Royal Indian Navy during 1946 led Attlee to promise independence no later than 30 June 1948. When the urgency of the situation and risk of civil war became apparent, the newly appointed (and last) Viceroy, Louis Mountbatten, 1st Earl Mountbatten of Burma, Lord Mountbatten, hastily brought forward the date to 15 August 1947. The borders drawn by the British to broadly Partition of India, partition India into Hindu and Muslim areas left tens of millions as minorities in the newly independent states of India and Pakistan. Millions of Muslims crossed from India to Pakistan and Hindus vice versa, and violence between the two communities cost hundreds of thousands of lives. Burma, which had been administered as part of the British Raj, and Sri Lanka gained their independence the following year in 1948. India, Pakistan and Sri Lanka became members of the Commonwealth, while Burma chose not to join.
The British Mandate in Palestine, where an Arab majority lived alongside a Jewish minority, presented the British with a similar problem to that of India. The matter was complicated by large numbers of Jewish refugees seeking to be admitted to Palestine following the The Holocaust, Holocaust, while Arabs were opposed to the creation of a Jewish state. Frustrated by the intractability of the problem, attacks by Jewish paramilitary organisations and the increasing cost of maintaining its military presence, Britain announced in 1947 that it would withdraw in 1948 and leave the matter to the United Nations to solve. The United Nations General Assembly, UN General Assembly subsequently voted for a United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine, plan to partition Palestine into a Jewish and an Arab state. It was immediately followed by the outbreak of a 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war between the Arabs and Jews of Palestine, and British forces withdrew amid the fighting. The British Mandate for Palestine officially terminated at midnight on 15 May 1948 as the State of Israel declared independence and the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, 1948 Arab-Israeli War broke out, during which the territory of the former Mandate was partitioned between Israel and the surrounding Arab states. Amid the fighting, British forces continued to withdraw from Israel, with the last British troops departing from Haifa on 30 June 1948.
Following the surrender of Japan in the Second World War, anti-Japanese resistance movements in Malaya turned their attention towards the British, who had moved to quickly retake control of the colony, valuing it as a source of rubber and tin.#refLloyd1996, Lloyd, p. 335. The fact that the guerrillas were primarily Malaysian Chinese Communists meant that the British attempt to quell the uprising was supported by the Islam in Malaysia, Muslim Malay majority, on the understanding that once the insurgency had been quelled, independence would be granted. The Malayan Emergency, as it was called, began in 1948 and lasted until 1960, but by 1957, Britain felt confident enough to grant independence to the Federation of Malaya within the Commonwealth. In 1963, the 11 states of the federation together with Singapore, Sarawak and Crown Colony of North Borneo, North Borneo joined to form Malaysia, but in 1965 Chinese-majority Singapore was expelled from the union following tensions between the Malay and Chinese populations and became an independent city-state. Brunei, which had been a British protectorate since 1888, declined to join the union.
The pro-decolonisation Labour Party (UK), Labour government, elected at the 1945 United Kingdom general election, 1945 general election and led by Clement Attlee, moved quickly to tackle the most pressing issue facing the empire: Indian independence movement, Indian independence. India's two major political parties—the Indian National Congress (led by Mahatma Gandhi) and the All-India Muslim League, Muslim League (led by Muhammad Ali Jinnah)—had been campaigning for independence for decades, but disagreed as to how it should be implemented. Congress favoured a unified secular Indian state, whereas the League, fearing domination by the Hindu majority, desired a separate Islamic state for Muslim-majority regions. Increasing Civil disorder, civil unrest and the Royal Indian Navy mutiny, mutiny of the History of the Indian Navy, Royal Indian Navy during 1946 led Attlee to promise independence no later than 30 June 1948. When the urgency of the situation and risk of civil war became apparent, the newly appointed (and last) Viceroy, Louis Mountbatten, 1st Earl Mountbatten of Burma, Lord Mountbatten, hastily brought forward the date to 15 August 1947. The borders drawn by the British to broadly Partition of India, partition India into Hindu and Muslim areas left tens of millions as minorities in the newly independent states of India and Pakistan. Millions of Muslims crossed from India to Pakistan and Hindus vice versa, and violence between the two communities cost hundreds of thousands of lives. Burma, which had been administered as part of the British Raj, and Sri Lanka gained their independence the following year in 1948. India, Pakistan and Sri Lanka became members of the Commonwealth, while Burma chose not to join.
The British Mandate in Palestine, where an Arab majority lived alongside a Jewish minority, presented the British with a similar problem to that of India. The matter was complicated by large numbers of Jewish refugees seeking to be admitted to Palestine following the The Holocaust, Holocaust, while Arabs were opposed to the creation of a Jewish state. Frustrated by the intractability of the problem, attacks by Jewish paramilitary organisations and the increasing cost of maintaining its military presence, Britain announced in 1947 that it would withdraw in 1948 and leave the matter to the United Nations to solve. The United Nations General Assembly, UN General Assembly subsequently voted for a United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine, plan to partition Palestine into a Jewish and an Arab state. It was immediately followed by the outbreak of a 1947–1948 civil war in Mandatory Palestine, civil war between the Arabs and Jews of Palestine, and British forces withdrew amid the fighting. The British Mandate for Palestine officially terminated at midnight on 15 May 1948 as the State of Israel declared independence and the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, 1948 Arab-Israeli War broke out, during which the territory of the former Mandate was partitioned between Israel and the surrounding Arab states. Amid the fighting, British forces continued to withdraw from Israel, with the last British troops departing from Haifa on 30 June 1948.
Following the surrender of Japan in the Second World War, anti-Japanese resistance movements in Malaya turned their attention towards the British, who had moved to quickly retake control of the colony, valuing it as a source of rubber and tin.#refLloyd1996, Lloyd, p. 335. The fact that the guerrillas were primarily Malaysian Chinese Communists meant that the British attempt to quell the uprising was supported by the Islam in Malaysia, Muslim Malay majority, on the understanding that once the insurgency had been quelled, independence would be granted. The Malayan Emergency, as it was called, began in 1948 and lasted until 1960, but by 1957, Britain felt confident enough to grant independence to the Federation of Malaya within the Commonwealth. In 1963, the 11 states of the federation together with Singapore, Sarawak and Crown Colony of North Borneo, North Borneo joined to form Malaysia, but in 1965 Chinese-majority Singapore was expelled from the union following tensions between the Malay and Chinese populations and became an independent city-state. Brunei, which had been a British protectorate since 1888, declined to join the union.
 In the 1951 United Kingdom general election, 1951 general election, the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party returned to power in Britain under the leadership of Winston Churchill. Churchill and the Conservatives believed that Britain's position as a world power relied on the continued existence of the empire, with the base at the Suez Canal allowing Britain to maintain its pre-eminent position in the Middle East in spite of the loss of India. Churchill could not ignore Gamal Abdel Nasser, Gamal Abdul Nasser's new revolutionary Politics of Egypt, government of Egypt that had Egyptian Revolution of 1952, taken power in 1952, and the following year it was agreed that British troops would withdraw from the Suez Canal zone and that Sudan would be granted self-determination by 1955, with independence to follow. Sudan was History of Sudan (1956–69), granted independence on 1 January 1956.
In July 1956, Nasser unilaterally nationalised the Suez Canal. The response of Anthony Eden, who had succeeded Churchill as Prime Minister, was to collude with France to engineer an Israeli attack on Republic of Egypt (1953–58), Egypt that would give Britain and France an excuse to intervene militarily and retake the canal. Eden infuriated US President Dwight D. Eisenhower by his lack of consultation, and Eisenhower refused to back the invasion. Another of Eisenhower's concerns was the possibility of a wider war with the Soviet Union after it threatened to intervene on the Egyptian side. Eisenhower applied leverage (finance), financial leverage by threatening to sell US reserves of the Pound sterling, British pound and thereby precipitate a collapse of the British currency. Though the invasion force was militarily successful in its objectives, UN intervention and US pressure forced Britain into a humiliating withdrawal of its forces, and Eden resigned.
The
In the 1951 United Kingdom general election, 1951 general election, the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party returned to power in Britain under the leadership of Winston Churchill. Churchill and the Conservatives believed that Britain's position as a world power relied on the continued existence of the empire, with the base at the Suez Canal allowing Britain to maintain its pre-eminent position in the Middle East in spite of the loss of India. Churchill could not ignore Gamal Abdel Nasser, Gamal Abdul Nasser's new revolutionary Politics of Egypt, government of Egypt that had Egyptian Revolution of 1952, taken power in 1952, and the following year it was agreed that British troops would withdraw from the Suez Canal zone and that Sudan would be granted self-determination by 1955, with independence to follow. Sudan was History of Sudan (1956–69), granted independence on 1 January 1956.
In July 1956, Nasser unilaterally nationalised the Suez Canal. The response of Anthony Eden, who had succeeded Churchill as Prime Minister, was to collude with France to engineer an Israeli attack on Republic of Egypt (1953–58), Egypt that would give Britain and France an excuse to intervene militarily and retake the canal. Eden infuriated US President Dwight D. Eisenhower by his lack of consultation, and Eisenhower refused to back the invasion. Another of Eisenhower's concerns was the possibility of a wider war with the Soviet Union after it threatened to intervene on the Egyptian side. Eisenhower applied leverage (finance), financial leverage by threatening to sell US reserves of the Pound sterling, British pound and thereby precipitate a collapse of the British currency. Though the invasion force was militarily successful in its objectives, UN intervention and US pressure forced Britain into a humiliating withdrawal of its forces, and Eden resigned.
The  Macmillan gave a speech in Cape Town, South Africa in February 1960 where he spoke of "the wind of change blowing through this continent". Macmillan wished to avoid the same kind of Algerian War, colonial war that France was fighting in French Algeria, Algeria, and under his premiership decolonisation proceeded rapidly. To the three colonies that had been granted independence in the 1950s—Sudan, the Gold Coast (British colony), Gold Coast and Malaya—were added nearly ten times that number during the 1960s.
Britain's remaining colonies in Africa, except for self-governing colony, self-governing Southern Rhodesia, were all granted independence by 1968. British withdrawal from the southern and eastern parts of Africa was not a peaceful process. Kenyan independence was preceded by the eight-year Mau Mau uprising, in which tens of thousands of suspected rebels were interned by the colonial government in detention camps. In Rhodesia, the 1965 Rhodesia's Unilateral Declaration of Independence, Unilateral Declaration of Independence by the white minority resulted in a Rhodesian Bush War, civil war that lasted until the Lancaster House Agreement of 1979, which set the terms for recognised independence in 1980, as the new nation of Zimbabwe.
In Cyprus, a guerrilla war waged by the Greek Cypriots, Greek Cypriot organisation EOKA against British rule, was ended in 1959 by the London and Zürich Agreements, which resulted in Cyprus being granted independence in 1960. The UK retained the military bases of Akrotiri and Dhekelia as sovereign base areas. The List of islands in the Mediterranean, Mediterranean colony of Malta (island), Malta was amicably granted independence from the UK in 1964 and became the country of Malta, though the idea had been raised in 1955 of 1956 Maltese United Kingdom integration referendum, integration with Britain.
Most of the UK's Caribbean territories achieved independence after the departure in 1961 and 1962 of Jamaica and Trinidad from the West Indies Federation, established in 1958 in an attempt to unite the British Caribbean colonies under one government, but which collapsed following the loss of its two largest members.#refKnight1989, Knight & Palmer, pp. 14–15. Jamaica attained independence in 1962, as did Trinidad and Tobago. Barbados achieved independence in 1966 and the remainder of the eastern Caribbean islands, including the Bahamas, in the 1970s and 1980s, but Anguilla and the Turks and Caicos Islands opted to revert to British rule after they had already started on the path to independence. The British Virgin Islands, The Cayman Islands and Montserrat opted to retain ties with Britain, while Guyana achieved independence in 1966. Britain's last colony on the American mainland, British Honduras, became a self-governing colony in 1964 and was renamed Belize in 1973, achieving full independence in 1981. A Belizean-Guatemalan territorial dispute, dispute with Guatemala over claims to Belize was left unresolved.
British Overseas Territories in the Pacific acquired independence in the 1970s beginning with Fiji in 1970 and ending with Vanuatu in 1980. Vanuatu's independence was delayed because of political conflict between English and French-speaking communities, as the islands had been jointly administered as a Condominium (international law), condominium with France. Fiji, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands and Tuvalu became Commonwealth realms.
Macmillan gave a speech in Cape Town, South Africa in February 1960 where he spoke of "the wind of change blowing through this continent". Macmillan wished to avoid the same kind of Algerian War, colonial war that France was fighting in French Algeria, Algeria, and under his premiership decolonisation proceeded rapidly. To the three colonies that had been granted independence in the 1950s—Sudan, the Gold Coast (British colony), Gold Coast and Malaya—were added nearly ten times that number during the 1960s.
Britain's remaining colonies in Africa, except for self-governing colony, self-governing Southern Rhodesia, were all granted independence by 1968. British withdrawal from the southern and eastern parts of Africa was not a peaceful process. Kenyan independence was preceded by the eight-year Mau Mau uprising, in which tens of thousands of suspected rebels were interned by the colonial government in detention camps. In Rhodesia, the 1965 Rhodesia's Unilateral Declaration of Independence, Unilateral Declaration of Independence by the white minority resulted in a Rhodesian Bush War, civil war that lasted until the Lancaster House Agreement of 1979, which set the terms for recognised independence in 1980, as the new nation of Zimbabwe.
In Cyprus, a guerrilla war waged by the Greek Cypriots, Greek Cypriot organisation EOKA against British rule, was ended in 1959 by the London and Zürich Agreements, which resulted in Cyprus being granted independence in 1960. The UK retained the military bases of Akrotiri and Dhekelia as sovereign base areas. The List of islands in the Mediterranean, Mediterranean colony of Malta (island), Malta was amicably granted independence from the UK in 1964 and became the country of Malta, though the idea had been raised in 1955 of 1956 Maltese United Kingdom integration referendum, integration with Britain.
Most of the UK's Caribbean territories achieved independence after the departure in 1961 and 1962 of Jamaica and Trinidad from the West Indies Federation, established in 1958 in an attempt to unite the British Caribbean colonies under one government, but which collapsed following the loss of its two largest members.#refKnight1989, Knight & Palmer, pp. 14–15. Jamaica attained independence in 1962, as did Trinidad and Tobago. Barbados achieved independence in 1966 and the remainder of the eastern Caribbean islands, including the Bahamas, in the 1970s and 1980s, but Anguilla and the Turks and Caicos Islands opted to revert to British rule after they had already started on the path to independence. The British Virgin Islands, The Cayman Islands and Montserrat opted to retain ties with Britain, while Guyana achieved independence in 1966. Britain's last colony on the American mainland, British Honduras, became a self-governing colony in 1964 and was renamed Belize in 1973, achieving full independence in 1981. A Belizean-Guatemalan territorial dispute, dispute with Guatemala over claims to Belize was left unresolved.
British Overseas Territories in the Pacific acquired independence in the 1970s beginning with Fiji in 1970 and ending with Vanuatu in 1980. Vanuatu's independence was delayed because of political conflict between English and French-speaking communities, as the islands had been jointly administered as a Condominium (international law), condominium with France. Fiji, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands and Tuvalu became Commonwealth realms.