tetragonal disphenoid on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In geometry, a disphenoid () is a tetrahedron whose four Face (geometry), faces are Congruence (geometry), congruent acute-angled triangles. It can also be described as a tetrahedron in which every two Edge (geometry), edges that are opposite each other have equal lengths. Other names for the same shape are isotetrahedron,.
sphenoid,. bisphenoid, isosceles tetrahedron,. equifacial tetrahedron, almost regular tetrahedron, and tetramonohedron.
All the solid angles and vertex figures of a disphenoid are the same, and the sum of the face angles at each vertex is equal to two right angles. However, a disphenoid is not a regular polyhedron, because, in general, its faces are not regular polygons, and its edges have three different lengths.
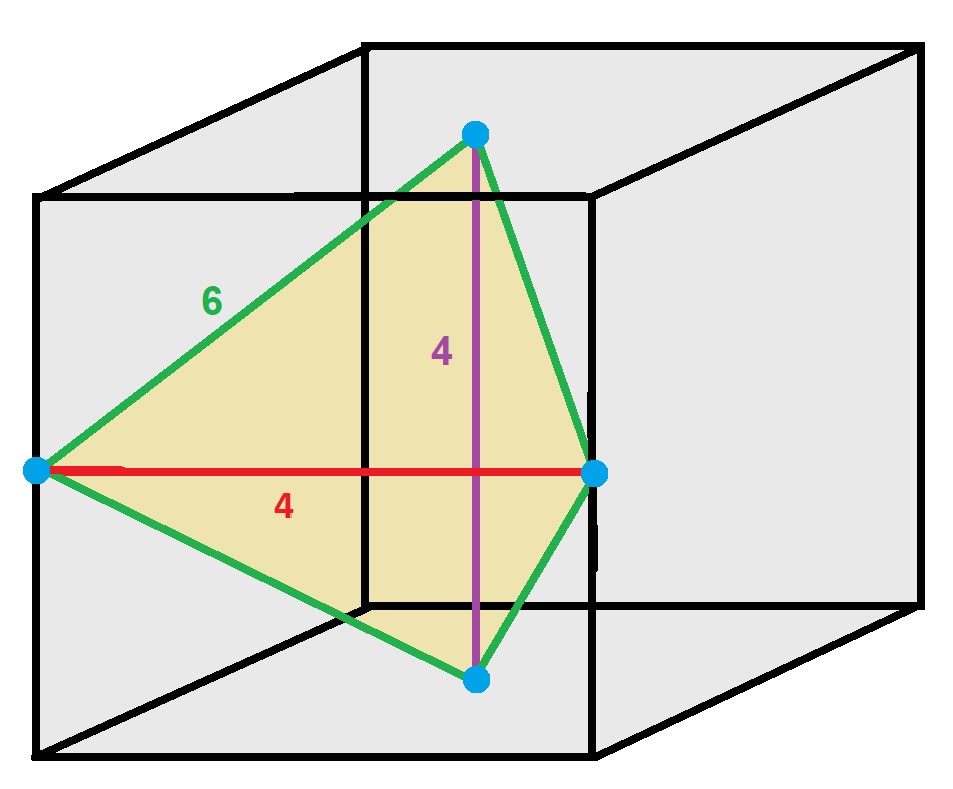 Some tetragonal disphenoids will form honeycomb (geometry), honeycombs. The disphenoid whose four vertices are (-1, 0, 0), (1, 0, 0), (0, 1, 1), and (0, 1, -1) is such a disphenoid. Each of its four faces is an isosceles triangle with edges of lengths , , and 2. It can Tessellation, tessellate space to form the disphenoid tetrahedral honeycomb. As describes, it can be folded without cutting or overlaps from a single sheet of a4 paper. Reprinted in
"Disphenoid" is also used to describe two forms of Crystal system, crystal:
* A wedge-shaped crystal form of the Tetragonal crystal system, tetragonal or Orthorhombic crystal system, orthorhombic system. It has four triangular faces that are alike and that correspond in position to alternate faces of the tetragonal or orthorhombic Bipyramid, dipyramid. It is symmetrical about each of three mutually perpendicular diad axes of symmetry in all classes except the tetragonal-disphenoidal, in which the form is generated by an inverse tetrad axis of symmetry.
*A crystal form bounded by eight scalene triangles arranged in pairs, constituting a tetragonal scalenohedron.
Some tetragonal disphenoids will form honeycomb (geometry), honeycombs. The disphenoid whose four vertices are (-1, 0, 0), (1, 0, 0), (0, 1, 1), and (0, 1, -1) is such a disphenoid. Each of its four faces is an isosceles triangle with edges of lengths , , and 2. It can Tessellation, tessellate space to form the disphenoid tetrahedral honeycomb. As describes, it can be folded without cutting or overlaps from a single sheet of a4 paper. Reprinted in
"Disphenoid" is also used to describe two forms of Crystal system, crystal:
* A wedge-shaped crystal form of the Tetragonal crystal system, tetragonal or Orthorhombic crystal system, orthorhombic system. It has four triangular faces that are alike and that correspond in position to alternate faces of the tetragonal or orthorhombic Bipyramid, dipyramid. It is symmetrical about each of three mutually perpendicular diad axes of symmetry in all classes except the tetragonal-disphenoidal, in which the form is generated by an inverse tetrad axis of symmetry.
*A crystal form bounded by eight scalene triangles arranged in pairs, constituting a tetragonal scalenohedron.
Mathematical Analysis of Disphenoid by H C Rajpoot
from Academia.edu * *{{Mathworld , urlname=IsoscelesTetrahedron , title=Isosceles tetrahedron Polyhedra
Special cases and generalizations
If the faces of a disphenoid are equilateral triangles, it is a regular tetrahedron with Td tetrahedral symmetry, although this is not normally called a disphenoid. When the faces of a disphenoid are isosceles triangles, it is called a tetragonal disphenoid. In this case it has D2d dihedral symmetry. A sphenoid with scalene triangles as its faces is called a rhombic disphenoid and it has D2 dihedral symmetry. Unlike the tetragonal disphenoid, the rhombic disphenoid has no reflection symmetry, so it is chirality, chiral. Both tetragonal disphenoids and rhombic disphenoids are isohedral figure, isohedra: as well as being congruent to each other, all of their faces are symmetric to each other. It is not possible to construct a disphenoid with right triangle or obtuse triangle faces. When right triangles are glued together in the pattern of a disphenoid, they form a flat figure (a doubly-covered rectangle) that does not enclose any volume.. When obtuse triangles are glued in this way, the resulting surface can be folded to form a disphenoid (by Alexandrov's uniqueness theorem) but one with acute triangle faces and with edges that in general do not lie along the edges of the given obtuse triangles. Two more types of tetrahedron generalize the disphenoid and have similar names. The digonal disphenoid has faces with two different shapes, both isosceles triangles, with two faces of each shape. The phyllic disphenoid similarly has faces with two shapes of scalene triangles. Disphenoids can also be seen as digonal antiprisms or as Alternation (geometry), alternated quadrilateral Prism (geometry), prisms.Characterizations
A tetrahedron is a disphenoid if and only if its circumscribed parallelepiped is right-angled. We also have that a tetrahedron is a disphenoid if and only if the Center (geometry), center in the circumscribed sphere and the inscribed sphere coincide.. Another characterization states that if ''d1'', ''d2'' and ''d3'' are the common perpendiculars of ''AB'' and ''CD''; ''AC'' and ''BD''; and ''AD'' and ''BC'' respectively in a tetrahedron ''ABCD'', then the tetrahedron is a disphenoid if and only if ''d1'', ''d2'' and ''d3'' are pairwise perpendicular.. The disphenoids are the only polyhedra having infinitely many non-self-intersecting closed geodesics. On a disphenoid, all closed geodesics are non-self-intersecting. The disphenoids are the tetrahedra in which all four faces have the same perimeter, the tetrahedra in which all four faces have the same area, and the tetrahedra in which the angular defects of all four vertices equal . They are the polyhedra having a Net (polyhedron), net in the shape of an acute triangle, divided into four similar triangles by segments connecting the edge midpoints..Metric formulas
The volume of a disphenoid with opposite edges of length ''l'', ''m'' and ''n'' is given by. : The circumscribed sphere has radius (the circumradius) : and the inscribed sphere has radius : where ''V'' is the volume of the disphenoid and ''T'' is the area of any face, which is given by Heron's formula. There is also the following interesting relation connecting the volume and the circumradius: : The squares of the lengths of the Tetrahedron#Properties of a generalized tetrahedron, bimedians are :Other properties
If the four faces of a tetrahedron have the same perimeter, then the tetrahedron is a disphenoid. If the four faces of a tetrahedron have the same area, then it is a disphenoid. The centers in the circumscribed sphere, circumscribed and inscribed spheres coincide with the centroid of the disphenoid. The bimedians are perpendicular to the edges they connect and to each other.Honeycombs and crystals
 Some tetragonal disphenoids will form honeycomb (geometry), honeycombs. The disphenoid whose four vertices are (-1, 0, 0), (1, 0, 0), (0, 1, 1), and (0, 1, -1) is such a disphenoid. Each of its four faces is an isosceles triangle with edges of lengths , , and 2. It can Tessellation, tessellate space to form the disphenoid tetrahedral honeycomb. As describes, it can be folded without cutting or overlaps from a single sheet of a4 paper. Reprinted in
"Disphenoid" is also used to describe two forms of Crystal system, crystal:
* A wedge-shaped crystal form of the Tetragonal crystal system, tetragonal or Orthorhombic crystal system, orthorhombic system. It has four triangular faces that are alike and that correspond in position to alternate faces of the tetragonal or orthorhombic Bipyramid, dipyramid. It is symmetrical about each of three mutually perpendicular diad axes of symmetry in all classes except the tetragonal-disphenoidal, in which the form is generated by an inverse tetrad axis of symmetry.
*A crystal form bounded by eight scalene triangles arranged in pairs, constituting a tetragonal scalenohedron.
Some tetragonal disphenoids will form honeycomb (geometry), honeycombs. The disphenoid whose four vertices are (-1, 0, 0), (1, 0, 0), (0, 1, 1), and (0, 1, -1) is such a disphenoid. Each of its four faces is an isosceles triangle with edges of lengths , , and 2. It can Tessellation, tessellate space to form the disphenoid tetrahedral honeycomb. As describes, it can be folded without cutting or overlaps from a single sheet of a4 paper. Reprinted in
"Disphenoid" is also used to describe two forms of Crystal system, crystal:
* A wedge-shaped crystal form of the Tetragonal crystal system, tetragonal or Orthorhombic crystal system, orthorhombic system. It has four triangular faces that are alike and that correspond in position to alternate faces of the tetragonal or orthorhombic Bipyramid, dipyramid. It is symmetrical about each of three mutually perpendicular diad axes of symmetry in all classes except the tetragonal-disphenoidal, in which the form is generated by an inverse tetrad axis of symmetry.
*A crystal form bounded by eight scalene triangles arranged in pairs, constituting a tetragonal scalenohedron.
Other uses
Six tetragonal disphenoids attached end-to-end in a ring construct a kaleidocycle, a paper toy that can rotate on 4 sets of faces in a hexagon.See also
* Tetrahedron#Irregular tetrahedra, Irregular tetrahedra * Orthocentric tetrahedron * Snub disphenoid - A Johnson solid with 12 equilateral triangle faces and D2d symmetry. * Trirectangular tetrahedronReferences
External links
Mathematical Analysis of Disphenoid by H C Rajpoot
from Academia.edu * *{{Mathworld , urlname=IsoscelesTetrahedron , title=Isosceles tetrahedron Polyhedra