sugar beet on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A sugar beet is a plant whose root contains a high concentration of

 The species beet consists of several cultivar groups. The 16th-century French scientist
The species beet consists of several cultivar groups. The 16th-century French scientist
sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
and that is grown commercially for sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
production. In plant breeding, it is known as the Altissima cultivar group
A Group (previously cultivar-groupInternational Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants, 4th edition (1969), 5th edition (1980) and 6th edition (1995)) is a formal category in the ''International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants'' ('' ...
of the common beet (''Beta vulgaris
''Beta vulgaris'' (beet) is a species of flowering plant in the subfamily Betoideae of the family Amaranthaceae. Economically, it is the most important crop of the large order Caryophyllales. It has several cultivar groups: the sugar beet, of gre ...
''). Together with other beet cultivars, such as beetroot
The beetroot is the taproot portion of a beet plant, usually known in North America as beets while the vegetable is referred to as beetroot in British English, and also known as the table beet, garden beet, red beet, dinner beet or golden beet ...
and chard
Chard or Swiss chard (; ''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris'', Cicla Group and Flavescens Group) is a green leafy vegetable. In the cultivars of the Flavescens Group, the leaf stalks are large and often prepared separately from the leaf blade; ...
, it belongs to the subspecies ''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris'' but classified as ''var. saccharifera ''. Its closest wild relative is the sea beet (''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''maritima'').
Sugar beets are grown in climates that are too cold for sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with ...
. In 2020, Russia, the United States, Germany, France and Turkey were the world's five largest sugar beet producers. In 2010–2011, Europe, and North America except Arctic territories failed to supply the overall domestic demand for sugar and were all net importers of sugar. The US harvested of sugar beets in 2008. In 2009, sugar beets accounted for 20% of the world's sugar production and nearly 30% by 2013. Sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with ...
accounts for most of the rest of sugar produced globally. In February 2015, a USDA factsheet reported that sugar beets generally account for about 55 percent of domestically produced sugar, and sugar cane for about 45 percent.
Description
The sugar beet has a conical, white, fleshy root (a taproot) with a flat crown. The plant consists of the root and a rosette of leaves. Sugar is formed by photosynthesis in the leaves and is then stored in the root. The root of the beet contains 75% water, about 20% sugar, and 5% pulp. The exact sugar content can vary between 12% and 21%, depending on the cultivar and growing conditions. Sugar is the primary value of sugar beet as acash crop
A cash crop or profit crop is an Agriculture, agricultural crop which is grown to sell for profit. It is typically purchased by parties separate from a farm. The term is used to differentiate marketed crops from staple crop (or "subsistence crop") ...
. The pulp, insoluble in water and mainly composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity ...
, and pectin
Pectin ( grc, πηκτικός ': "congealed" and "curdled") is a heteropolysaccharide, a structural acid contained in the primary lamella, in the middle lamella, and in the cell walls of terrestrial plants. The principal, chemical component of ...
, is used in animal feed. The byproducts of the sugar beet crop, such as pulp and molasses
Molasses () is a viscous substance resulting from refining sugarcane or sugar beets into sugar. Molasses varies in the amount of sugar, method of extraction and age of the plant. Sugarcane molasses is primarily used to sweeten and flavour foods ...
, add another 10% to the value of the harvest.
Sugar beets grow exclusively in the temperate zone, in contrast to sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with ...
, which grows exclusively in the tropical and subtropical zones. The average weight of a sugar beet ranges between . Sugar beet foliage has a rich, brilliant green color and grows to a height of about . The leaves are numerous and broad and grow in a tuft from the crown of the beet, which is usually level with or just above the ground surface.
History of the sugar beet
Discovery of beet sugar

 The species beet consists of several cultivar groups. The 16th-century French scientist
The species beet consists of several cultivar groups. The 16th-century French scientist Olivier de Serres
Olivier de Serres (; 1539–1619) was a French author and soil scientist whose '' Théâtre d'Agriculture'' (1600) was the accepted textbook of French agriculture in the 17th century.
Biography
Serres was born in 1539 at Villeneuve-de-Berg, A ...
discovered a process for preparing sugar syrup from (red) beetroot
The beetroot is the taproot portion of a beet plant, usually known in North America as beets while the vegetable is referred to as beetroot in British English, and also known as the table beet, garden beet, red beet, dinner beet or golden beet ...
. He wrote: "The beet-root, when being boiled, yields a juice similar to syrup of sugar, which is beautiful to look at on account of its vermilion colour" (1575). Because crystallized cane sugar was already available and had a better taste, this process did not become popular.
Modern sugar beets date to the mid-18th century Silesia where Frederick the Great, king of Prussia, subsidized experiments to develop processes for sugar extraction. In 1747, Andreas Sigismund Marggraf, professor of physics in the Academy of Science of Berlin, isolated sugar from beetroots and found them at concentrations of 1.3–1.6%. He also demonstrated that the sugar that could be extracted from beets was identical to that produced from cane. He found the best of these vegetable sources for sugar was the white beet. Despite Marggraf's success in isolating sugar from beets, it did not lead to commercial sugar production.
Development of the sugar beet
Marggraf's student and successorFranz Karl Achard
Franz Karl Achard (28 April 1753 – 20 April 1821) was a German (Prussian) chemist, geoscientist, physicist, and biologist. His principal discovery was the production of sugar from sugar beets.
Life and work
Achard was born in Berlin, the so ...
began plant breeding
Plant breeding is the science of changing the traits of plants in order to produce desired characteristics. It has been used to improve the quality of nutrition in products for humans and animals. The goals of plant breeding are to produce cro ...
sugar beet in Kaulsdorf near Berlin in 1786. Achard started his plant breeding by evaluating 23 varieties of beet for sugar content. In the end he selected a local strain from Halberstadt in modern-day Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Moritz Baron von Koppy and his son further selected white, conical tubers from this strain. The selection was named ''weiße schlesische Zuckerrübe'', meaning white Silesian sugar beet. In about 1800, this cultivar boasted about 5–6% sucrose by (dry) weight. It would go on to be the progenitor of all modern sugar beets. The plant breeding process has continued since then, leading to a sucrose content of around 18% in modern varieties.
History of the beet sugar industry
Franz Karl Achard opened the world's first beet sugar factory in 1801, atKunern
Konary Castle or Knight's Castle Kunern is a castle in the village Konary (german: Kunern), Lower Silesia, Poland, located 55 km south of the city of Wrocław.Silesia (now Konary, Poland). The idea to produce sugar from beet was soon introduced to France, whence the European sugar beet industry rapidly expanded. By 1840, about 5% of the world's sugar was derived from sugar beets, and by 1880, this number had risen more than tenfold to over 50%. In North America, the first commercial production started in 1879 at a farm in Alvarado, California. The sugar beet was introduced to Chile by German settlers around 1850.


 The sugar beet, like
The sugar beet, like
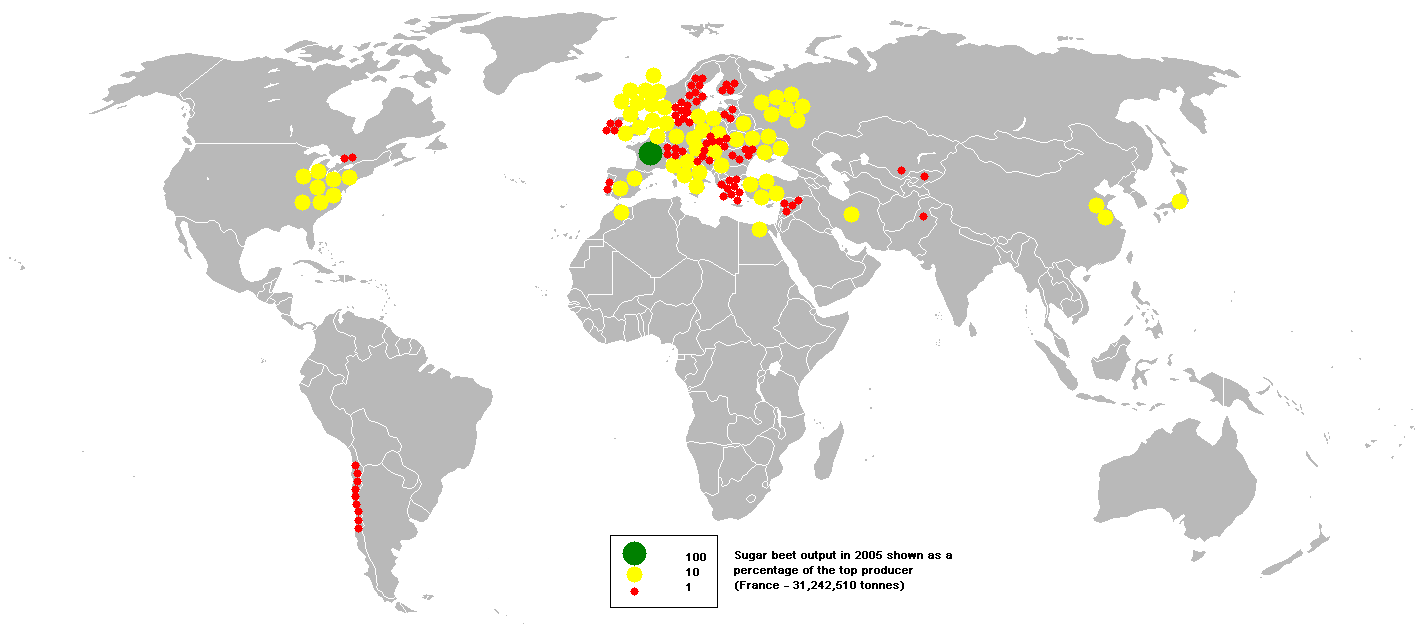 The world harvested of sugar beets in 2022. The world's largest producer was Russia, with a harvest. The average yield of sugar beet crops worldwide was 60.8 tonnes per hectare.
The most productive sugar beet farms in the world, in 2022, were in Chile, with a nationwide average yield of 106.2 tonnes per hectare.
Imperial Valley (California) farmers have achieved yields of about 160 tonnes per hectare and over 26 tonnes sugar per hectare. Imperial Valley farms benefit from high intensities of incident sunlight and intensive use of irrigation and fertilizers.
The world harvested of sugar beets in 2022. The world's largest producer was Russia, with a harvest. The average yield of sugar beet crops worldwide was 60.8 tonnes per hectare.
The most productive sugar beet farms in the world, in 2022, were in Chile, with a nationwide average yield of 106.2 tonnes per hectare.
Imperial Valley (California) farmers have achieved yields of about 160 tonnes per hectare and over 26 tonnes sugar per hectare. Imperial Valley farms benefit from high intensities of incident sunlight and intensive use of irrigation and fertilizers.
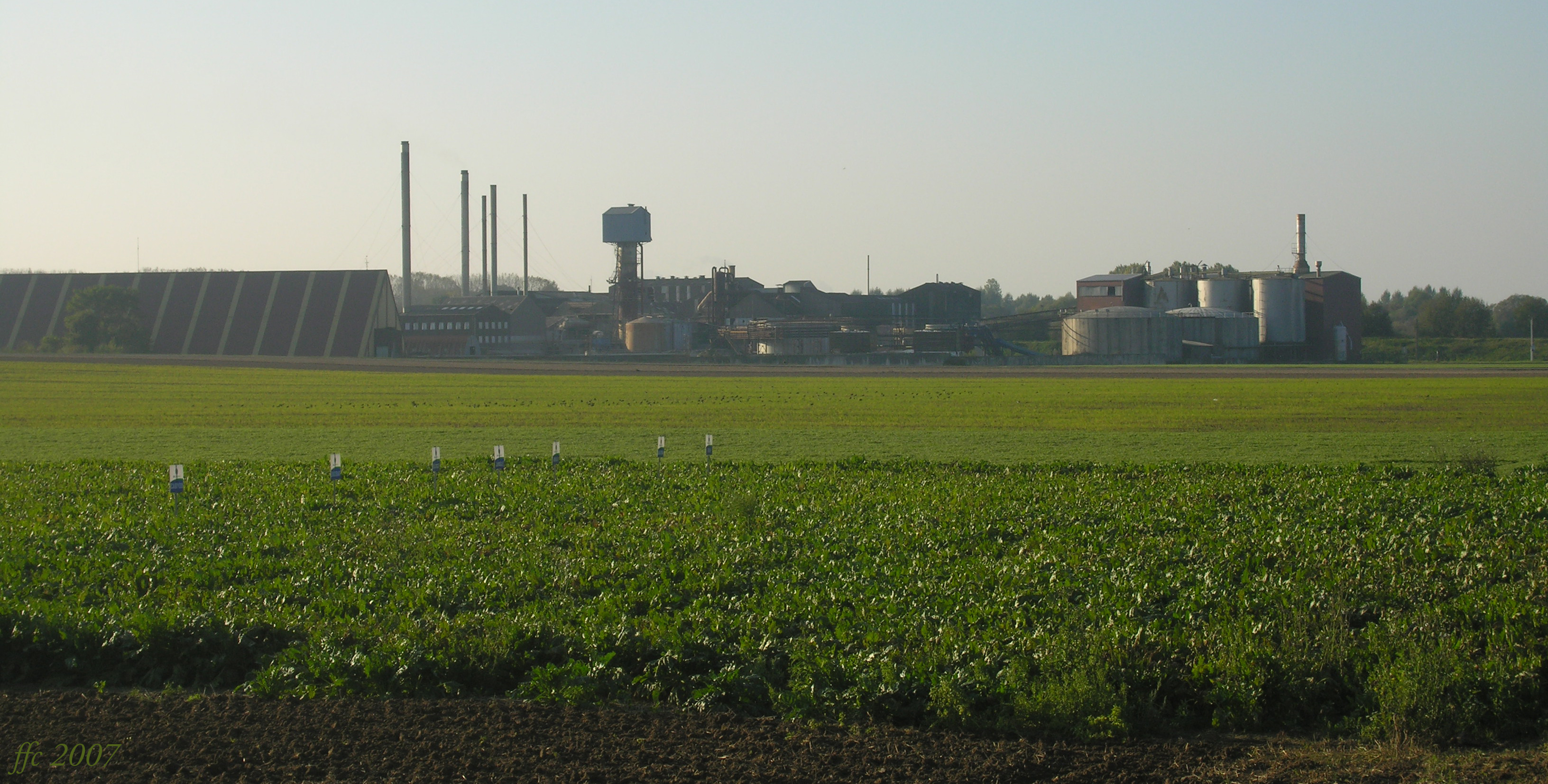 Most sugar beet are used to create white sugar. This is done in a beet sugar factory, often abbreviated to sugar factory. Nowadays these most of the time also act as a sugar refinery, but historically the beet sugar factory produced raw sugar and the sugar refinery refined raw sugar to create white sugar.
Most sugar beet are used to create white sugar. This is done in a beet sugar factory, often abbreviated to sugar factory. Nowadays these most of the time also act as a sugar refinery, but historically the beet sugar factory produced raw sugar and the sugar refinery refined raw sugar to create white sugar.
 The next steps to produce white sugar are not specific for producing sugar from sugar beet. They also apply to producing white sugar from sugar cane. As such, they belong to the sugar refining process, not to the beet sugar production process per se.
* Purification, the raw juice undergoes a chemical process to remove impurities and create thin juice.
* Evaporation, the thin juice is concentrated by evaporation to make a "thick juice", roughly 60% sucrose by weight.
* Crystallization, by boiling under reduced pressure the sugar liquor is turned into crystals and remaining liquor.
* Centrifugation, in a centrifuge the white sugar crystals are separated from the remaining sugar liquor.
* The remaining liquor is then boiled and centrifuged, producing a lower grade of crystallised sugar (which is redissolved to feed the white sugar pans) and molasses.
* Further sugar can be recovered from the molasses eg by the Steffen Process.
The next steps to produce white sugar are not specific for producing sugar from sugar beet. They also apply to producing white sugar from sugar cane. As such, they belong to the sugar refining process, not to the beet sugar production process per se.
* Purification, the raw juice undergoes a chemical process to remove impurities and create thin juice.
* Evaporation, the thin juice is concentrated by evaporation to make a "thick juice", roughly 60% sucrose by weight.
* Crystallization, by boiling under reduced pressure the sugar liquor is turned into crystals and remaining liquor.
* Centrifugation, in a centrifuge the white sugar crystals are separated from the remaining sugar liquor.
* The remaining liquor is then boiled and centrifuged, producing a lower grade of crystallised sugar (which is redissolved to feed the white sugar pans) and molasses.
* Further sugar can be recovered from the molasses eg by the Steffen Process.
 An unrefined sugary syrup can be produced directly from sugar beet. This thick, dark syrup is produced by cooking shredded sugar beet for several hours, then pressing the resulting mash and concentrating the juice produced until it has a consistency similar to that of
An unrefined sugary syrup can be produced directly from sugar beet. This thick, dark syrup is produced by cooking shredded sugar beet for several hours, then pressing the resulting mash and concentrating the juice produced until it has a consistency similar to that of
 Sugar beets are an important part of a crop rotation cycle.
Sugar beet plants are susceptible to '' Rhizomania'' ("root madness"), which turns the bulbous tap root into many small roots, making the crop economically unprocessable. Strict controls are enforced in European countries to prevent the spread, but it is already present in some areas. It is also susceptible to both the
Sugar beets are an important part of a crop rotation cycle.
Sugar beet plants are susceptible to '' Rhizomania'' ("root madness"), which turns the bulbous tap root into many small roots, making the crop economically unprocessable. Strict controls are enforced in European countries to prevent the spread, but it is already present in some areas. It is also susceptible to both the
How Beet Sugar is Made
* ttps://digital.library.unt.edu/permalink/meta-dc-1503:1 ''Sugar beet culture in the northern Great Plains area''hosted by th
University of North Texas Government Documents Department
* ttps://books.google.com/books?id=IikDAAAAMBAJ&dq=Popular+Science+1932+plane&pg=PA38 "Sugar From Beets"''Popular Science Monthly'', March 1935 * {{Taxonbar, from=Q151964
Culture


 The sugar beet, like
The sugar beet, like sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with ...
, needs a particular soil and a proper climate for its successful cultivation. The most important requirements are that the soil must contain a large supply of nutrients, be rich in humus
In classical soil science, humus is the dark organic matter in soil that is formed by the decomposition of plant and animal matter. It is a kind of soil organic matter. It is rich in nutrients and retains moisture in the soil. Humus is the Lati ...
, and be able to contain a great deal of moisture. A certain amount of alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a ...
is not necessarily detrimental, as sugar beets are not especially susceptible to injury by some alkali. The ground should be fairly level and well-drained, especially where irrigation is practiced.
Generous crops can be grown in both sandy soil and heavy loam
Loam (in geology and soil science) is soil composed mostly of sand (particle size > ), silt (particle size > ), and a smaller amount of clay (particle size < ). By weight, its mineral composition is about 40–40–20% concentration of sand–sil ...
s, but the ideal soil is a sandy loam, i.e., a mixture of organic matter, clay and sand. A subsoil of gravel, or the presence of hardpan, is not desirable, as cultivation to a depth of from is necessary to produce the best results.
Climatic conditions, temperature, sunshine, rainfall and winds have an important bearing upon the success of sugar beet agriculture. A temperature ranging from during the growing months is most favorable. In the absence of adequate irrigation, of rainfall are necessary to raise an average crop. High winds are harmful, as they generally crust the land and prevent the young beets from coming through the ground. The best results are obtained along the coast of southern California, where warm, sunny days succeeded by cool, foggy nights seem to meet sugar beet's favored growth conditions. Sunshine of long duration but not of great intensity is the most important factor in the successful cultivation of sugar beets. Near the equator, the shorter days and the greater heat of the sun sharply reduce the sugar content in the beet.
In high elevation regions such as those of Idaho, Colorado and Utah, where the temperature is high during the daytime, but where the nights are cool, the quality of the sugar beet is excellent. In Michigan, the long summer days from the relatively high latitude (the Lower Peninsula, where production is concentrated, lies between the 41st and 46th parallels North) and the influence of the Great Lakes result in satisfactory climatic conditions for sugar beet culture. Sebewaing, Michigan
Sebewaing is a village in Huron County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 1,759 at the 2010 census. The village is within Sebewaing Township. This community is known as the Sugar Beet Capital, due to the Michigan Sugar slicing m ...
, lies in the Thumb region of Michigan; both the region and state are major sugar beet producers. Sebewaing is home to one of four Michigan Sugar Company factories. The town sponsors an annual Michigan Sugar Festival.
To cultivate beets successfully, the land must be properly prepared. Deep ploughing is the first principle of beet culture. It allows the roots to penetrate the subsoil without much obstruction, thereby preventing the beet from growing out of the ground, besides enabling it to extract considerable nourishment and moisture from the lower soil. If the latter is too hard, the roots will not penetrate it readily and, as a result, the plant will be pushed up and out of the earth during the process of growth. A hard subsoil is impervious to water and prevents proper drainage. It should not be too loose, however, as this allows the water to pass through more freely than is desirable. Ideally, the soil should be deep, fairly fine and easily penetrable by the roots. It should also be capable of retaining moisture and at the same time admit of a free circulation of air and good drainage. Sugar beet crops exhaust the soil rapidly. Crop rotation is recommended and necessary. Normally, beets are grown in the same ground every third year, peas, beans or grain being raised the other two years.
In most temperate climates, beets are planted in the spring and harvested in the autumn. At the northern end of its range, growing seasons as short as 100 days can produce commercially viable sugar beet crops. In warmer climates, such as in California's Imperial Valley, sugar beets are a winter crop, planted in the autumn and harvested in the spring. In recent years, Syngenta
Syngenta AG is a provider of agricultural science and technology, in particular seeds and pesticides with its management headquarters in Basel, Switzerland. It is owned by ChemChina, a Chinese state-owned enterprise.
Syngenta was founded in 2 ...
has developed the so-called tropical sugar beet. It allows the plant to grow in tropical and subtropical regions. Beets are planted from a small seed; of beet seed comprises 100,000 seeds and will plant over of ground ( will plant about .
Until the latter half of the 20th century, sugar beet production was highly labor-intensive, as weed control was managed by densely planting the crop, which then had to be manually thinned two or three times with a hoe
Hoe or HOE may refer to:
* Hoe (food), a Korean dish of raw fish
* Hoe (letter), a Georgian letter
* Hoe (tool), a hand tool used in gardening and farming
** Hoe-farming, a term for primitive forms of agriculture
* Backhoe, a piece of excavati ...
during the growing season. Harvesting also required many workers. Although the roots could be lifted by a plough
A plough or plow ( US; both ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses, but in modern farms are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden, iron or ...
-like device that could be pulled by a horse team, the rest of the preparation was by hand. One laborer grabbed the beets by their leaves, knocked them together to shake free loose soil, and then laid them in a row, root to one side, greens to the other. A second worker equipped with a beet hook (a short-handled tool between a billhook and a sickle) followed behind, and would lift the beet and swiftly chop the crown and leaves from the root with a single action. Working this way, he would leave a row of beets that could be forked into the back of a cart
A cart or dray (Australia and New Zealand) is a vehicle designed for transport, using two wheels and normally pulled by one or a pair of draught animals. A handcart is pulled or pushed by one or more people.
It is different from the flatbed tr ...
.
Today, mechanical sowing, herbicide
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weedkillers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page fo ...
application for weed control, and mechanical harvesting have displaced this reliance on manual farm work. A root beater uses a series of blades to chop the leaf and crown (which is high in nonsugar impurities) from the root. The beet harvester
A Sugarbeet harvester is an agricultural machine for harvesting sugar beet. It was invented by German farmer and agricultural engineer Otto Wilke in 1927. From 1936, series production then started first at Krupp, then later at Lanz (today John D ...
lifts the root, and removes excess soil from the root in a single pass over the field. A modern harvester is typically able to cover six rows at the same time. The beets are dumped into trucks as the harvester rolls down the field, and then delivered to the factory. The conveyor then removes more soil.
If the beets are to be left for later delivery, they are formed into clamps. Straw bales are used to shield the beets from the weather. Provided the clamp is well built with the right amount of ventilation, the beets do not significantly deteriorate. Beets that freeze and then defrost, produce complex carbohydrates that cause severe production problems in the factory. In the UK, loads may be hand examined at the factory gate before being accepted.
In the US, the fall harvest begins with the first hard frost, which arrests photosynthesis and the further growth of the root. Depending on the local climate, it may be carried out over the course of a few weeks or be prolonged throughout the winter months. The harvest and processing of the beet is referred to as "the campaign", reflecting the organization required to deliver the crop at a steady rate to processing factories that run 24 hours a day for the duration of the harvest and processing (for the UK, the campaign lasts about five months). In the Netherlands, this period is known as , a time to be careful when driving on local roads in the area while the beets are being grown, because the naturally high clay content of the soil tends to cause slippery roads when soil falls from the trailers during transport.
Production statistics
From sugar beet to white sugar
 Most sugar beet are used to create white sugar. This is done in a beet sugar factory, often abbreviated to sugar factory. Nowadays these most of the time also act as a sugar refinery, but historically the beet sugar factory produced raw sugar and the sugar refinery refined raw sugar to create white sugar.
Most sugar beet are used to create white sugar. This is done in a beet sugar factory, often abbreviated to sugar factory. Nowadays these most of the time also act as a sugar refinery, but historically the beet sugar factory produced raw sugar and the sugar refinery refined raw sugar to create white sugar.
Sugar factory
In the 1960s, beet sugar processing was described as consisting of these steps. * Harvesting and storage in a way that preserves the beet while they wait to be processed * Washing and scrubbing to remove soil and debris * Slicing the beet in small pieces called cossettes or chips * Removing the sugar from the beet in an osmosis process, resulting in raw juice and beet pulp. Nowadays, most sugar factories then refine the raw juice themselves, without moving it to a sugar refinery. The beet pulp is processed on site to become cattle fodder.Sugar refinery
Ethanol and alcohol
From molasses
There are two obvious methods to produce alcohol ( ethanol) from sugar beet. The first method produces alcohol as a byproduct of manufacturing sugar. It is about fermenting the sugar beet molasses that are left after (the second) centrifugation. This strongly resembles the manufacture of rum from sugar cane molasses. In a number of countries, notably the Czech Republic and Slovakia, this analogy led to making a rum-like distilled spirit called '' Tuzemak''. On theÅland Islands
Åland ( fi, Ahvenanmaa: ; ; ) is an autonomous and demilitarised region of Finland since 1920 by a decision of the League of Nations. It is the smallest region of Finland by area and population, with a size of 1,580 km2, and a populati ...
, a similar drink is made under the brand name ''Kobba Libre''.
From sugar beet
The second method to produce alcohol from sugar beet is to ferment the sugar beet themselves. I.e. without attempting to produce sugar. The idea to distill sugar from the beet came up soon after the first beet sugar factory was established. Between 1852 and 1854 Champonnois devised a good system to distill alcohol from sugar beet. Within a few years a large sugar distilling industry was created in France. The current process to produce alcohol by fermenting and distilling sugar beet consists of these steps: * AddingStarch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets ...
milk
* Liquefaction
In materials science, liquefaction is a process that generates a liquid from a solid or a gas or that generates a non-liquid phase which behaves in accordance with fluid dynamics.
It occurs both naturally and artificially. As an example of the ...
and Saccharification
* Fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food ...
in fermentation vats
* Distillation
* Dehydration, this results in Bioethanol
* Rectification
Rectification has the following technical meanings:
Mathematics
* Rectification (geometry), truncating a polytope by marking the midpoints of all its edges, and cutting off its vertices at those points
* Rectifiable curve, in mathematics
* Recti ...
* Refining, the result is a highly pure alcohol
Large sugar beet distilleries remain limited to Europe. In 2023 Tereos had 8 beet sugar distilleries, located in France, Czechia and Romania.
In many European countries rectified spirit from sugar beet is used to make Liquor
Liquor (or a spirit) is an alcoholic drink produced by distillation of grains, fruits, vegetables, or sugar, that have already gone through alcoholic fermentation. Other terms for liquor include: spirit drink, distilled beverage or hard ...
, e.g. vodka, Gin
Gin () is a distilled alcoholic drink that derives its flavour from juniper berries (''Juniperus communis'').
Gin originated as a medicinal liquor made by monks and alchemists across Europe, particularly in southern Italy, Flanders and the Ne ...
etc..
Other uses
Sugary syrup
 An unrefined sugary syrup can be produced directly from sugar beet. This thick, dark syrup is produced by cooking shredded sugar beet for several hours, then pressing the resulting mash and concentrating the juice produced until it has a consistency similar to that of
An unrefined sugary syrup can be produced directly from sugar beet. This thick, dark syrup is produced by cooking shredded sugar beet for several hours, then pressing the resulting mash and concentrating the juice produced until it has a consistency similar to that of honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primar ...
. No other ingredients are used.
In Germany, particularly the Rhineland area, and in the Netherlands, this sugar beet syrup (called ''Zuckerrüben-Sirup'' or ''Zapp'' in German, or ''Suikerstroop'' in Dutch) is used as a spread for sandwiches, as well as for sweetening sauces, cakes and desserts. Dutch people generally top their pancake
A pancake (or hotcake, griddlecake, or flapjack) is a flat cake, often thin and round, prepared from a Starch, starch-based batter (cooking), batter that may contain eggs, milk and butter and cooked on a hot surface such as a griddle or fryi ...
s with stroop.
Suikerstroop made according to the Dutch tradition is a Traditional Speciality Guaranteed under EU and UK law. Commercially, if the syrup has a dextrose equivalency (DE) above 30, the product has to be hydrolyzed
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis ...
and converted to a high-fructose syrup, much like high-fructose corn syrup, or isoglucose syrup in the EU.
Uridine
Uridine can be isolated from sugar beet.Alternative fuel
BP andAssociated British Foods
Associated British Foods plc (ABF) is a British multinational food processing and retailing company headquartered in London, England. Its ingredients division is the world's second-largest producer of both sugar and baker's yeast and a major pr ...
plan to use agricultural surpluses of sugar beet to produce biobutanol
220px, Butanol, a C-4 hydrocarbon is a promising bio-derived fuel, which shares many properties with gasoline.
Butanol may be used as a fuel in an internal combustion engine. It is more similar to gasoline than it is to ethanol. A C4-hydrocarbon ...
in East Anglia
East Anglia is an area in the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire. The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, a people whose name originated in Anglia, in ...
in the United Kingdom.
The feedstock-to-yield ratio for sugarbeet is 56:9. Therefore, it takes 6.22 kg of sugar beet to produce 1 kg of ethanol (approximately 1.27 L at room temperature). In 2006 it was found that producing ethanol from sugar beet or cane became profitable when market prices for ethanol were close to $4 per gallon. According to Atlantic Biomass president Robert Kozak, a study at University of Maryland Eastern Shore indicates sugar beets appear capable of producing 860 to 900 gallons (3,256 to 3,407 liters) of ethanol per acre.
Cattle feed
In New Zealand, sugar beet is widely grown and harvested as feed for dairy cattle. It is regarded as superior tofodder beet
Mangelwurzel or mangold wurzel (from :de:Futterrübe, German ''Mangel/Mangold'', "chard" and ''Wurzel'', "root"), also called mangold,Wright, Clifford A. (2001) ''Mediterranean Vegetables: a cook's ABC of vegetables and their preparation in Spain ...
, because it has a lower water content (resulting in better storage properties). Both the beet bulb and the leaves (with 25% protein) are fed to cattle. Although long considered toxic to cattle, harvested beet bulbs can be fed to cattle if they are appropriately transitioned to their new diet. Dairy cattle in New Zealand can thrive on just pasture and beets, without silage or other supplementary feed. The crop is also now grown in some parts of Australia as cattle feed.
Monosodium glutamate
Molasses can serve to produce monosodium glutamate (MSG).Agriculture
beet leaf curl virus
Beet leaf curl virus (BLCV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Rhabdoviridae.
The host range for this virus includes species of '' Atriplex'', '' Beta'', ''Chenopodium'' and ''Spinacia'' and also ''Tetragonia tetragonioides''. The most im ...
, which causes crinkling and stunting of the leaves and beet yellows virus
Beet yellows virus (BYV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family '' Closteroviridae''. Beet yellows virus is transmitted by multiple species of aphid and causes a yellowing disease in ''Beta vulgaris'' and ''Spinacia oleracea
Spinach ('' ...
.
Continual research looks for varieties with resistance, as well as increased sugar yield. Sugar beet breeding research in the United States is most prominently conducted at various USDA Agricultural Research Stations, including one in Fort Collins, Colorado
Fort Collins is a home rule municipality that is the county seat and the most populous municipality of Larimer County, Colorado
Larimer County is a county located in the U.S. state of Colorado. As of the 2020 census, the population was 359 ...
, headed by Linda Hanson and Leonard Panella; one in Fargo, North Dakota
Fargo ( /ˈfɑɹɡoʊ/) is a city in and the county seat of Cass County, North Dakota, United States. According to the 2020 census, its population was 125,990, making it the most populous city in the state and the 219th-most populous city in ...
, headed by John Wieland; and one at Michigan State University
Michigan State University (Michigan State, MSU) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in East Lansing, Michigan. It was founded in 1855 as the Agricultural College of the State of Michigan, the fi ...
in East Lansing, Michigan, headed by Rachel Naegele.
Other economically important members of the subfamily Chenopodioideae
The Chenopodioideae are a subfamily of the flowering plant family Amaranthaceae in the APG III system, which is largely based on molecular phylogeny, but were included - together with other subfamilies - in family Chenopodiaceae in the Cronquist ...
:
* Beetroot
The beetroot is the taproot portion of a beet plant, usually known in North America as beets while the vegetable is referred to as beetroot in British English, and also known as the table beet, garden beet, red beet, dinner beet or golden beet ...
* Chard
Chard or Swiss chard (; ''Beta vulgaris'' subsp. ''vulgaris'', Cicla Group and Flavescens Group) is a green leafy vegetable. In the cultivars of the Flavescens Group, the leaf stalks are large and often prepared separately from the leaf blade; ...
* ''Mangelwurzel
Mangelwurzel or mangold wurzel (from :de:Futterrübe, German ''Mangel/Mangold'', "chard" and ''Wurzel'', "root"), also called mangold,Wright, Clifford A. (2001) ''Mediterranean Vegetables: a cook's ABC of vegetables and their preparation in Spain ...
'' or fodder beet
Genetic modification
In the United States, genetically modified sugar beets, engineered for resistance to glyphosate, aherbicide
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weedkillers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page fo ...
marketed as Roundup, were developed by Monsanto as a genetically modified crop
Genetically modified crops (GM crops) are plants used in agriculture, the DNA of which has been modified using genetic engineering methods. Plant genomes can be engineered by physical methods or by use of ''Agrobacterium'' for the delivery of s ...
. In 2005, the US Department of Agriculture-Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service ( USDA-APHIS
''Aphis'' is a genus of insects in the family Aphididae containing at least 600 species of aphids. It includes many notorious agricultural pests, such as the soybean aphid '' Aphis glycines''. Many species of ''Aphis'', such as '' A. coreopsidis ...
) deregulated glyphosate-resistant sugar beets after it conducted an environmental assessment and determined glyphosate-resistant sugar beets were highly unlikely to become a plant pest. Sugar from glyphosate-resistant sugar beets has been approved for human and animal consumption in multiple countries, but commercial production of biotech beets has been approved only in the United States and Canada. Studies have concluded the sugar from glyphosate-resistant sugar beets has the same nutritional value as sugar from conventional sugar beets. After deregulation in 2005, glyphosate-resistant sugar beets were extensively adopted in the United States. About 95% of sugar beet acres in the US were planted with glyphosate-resistant seed in 2011.
Weeds may be chemically controlled using glyphosate without harming the crop. After planting sugar beet seed, weeds emerge in fields and growers apply glyphosate to control them. Glyphosate is commonly used in field crops because it controls a broad spectrum of weed species and has a low toxicity. A study from the UK suggests yields of genetically modified beet were greater than conventional, while another from the North Dakota State University extension service found lower yields. The introduction of glyphosate-resistant sugar beets may contribute to the growing number of glyphosate-resistant weeds, so Monsanto has developed a program to encourage growers to use different herbicide modes of action to control their weeds.
In 2008, the Center for Food Safety
The Center for Food Safety (CFS) is a 501c3, U.S. non-profit advocacy organization, based in Washington, D.C. It maintains an office in San Francisco, California. The executive director is Andrew Kimbrell, an attorney. Its stated mission is to ...
, the Sierra Club
The Sierra Club is an environmental organization with chapters in all 50 United States, Washington D.C., and Puerto Rico. The club was founded on May 28, 1892, in San Francisco, California, by Scottish-American preservationist John Muir, who be ...
, the Organic Seed Alliance and High Mowing Seeds filed a lawsuit against USDA-APHIS regarding their decision to deregulate glyphosate-resistant sugar beets in 2005. The organizations expressed concerns regarding glyphosate-resistant sugar beets' ability to potentially cross-pollinate
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an Stamen, anther of a plant to the stigma (botany), stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds, most often by an animal or by Anemophily, wind. Pollinating agents can ...
with conventional sugar beets. U.S. District Judge Jeffrey S. White, US District Court for the Northern District of California
The United States District Court for the Northern District of California (in case citations, N.D. Cal.) is the federal United States district court whose jurisdiction comprises the following counties of California: Alameda, Contra Costa, Del ...
, revoked the deregulation of glyphosate-resistant sugar beets and declared it unlawful for growers to plant glyphosate-resistant sugar beets in the spring of 2011. Believing a sugar shortage would occur USDA-APHIS developed three options in the environmental assessment to address the concerns of environmentalists. In 2011, a federal appeals court for the Northern district of California in San Francisco overturned the ruling. In July 2012, after completing an environmental impact assessment and a plant pest risk assessment the USDA deregulated Monsanto's Roundup Ready sugar beets.
Genome and genetics
The sugar beet genome shares a triplication event somewhere super-Caryophyllales and at or sub-Eudicot
The eudicots, Eudicotidae, or eudicotyledons are a clade of flowering plants mainly characterized by having two seed leaves upon germination. The term derives from Dicotyledons.
Traditionally they were called tricolpates or non-magnoliid dicot ...
s. It has been sequenced and two reference genome sequences have already been generated. The genome size of the sugar beet is approximately 731 (714–758) Megabases, and sugar beet DNA is packaged in 18 metacentric chromosomes (2n=2x=18). All sugar beet centromeres are made up of a single satellite DNA family and centromere-specific LTR retrotransposons. More than 60% of sugar beet's DNA is repetitive, mostly distributed in a dispersed way along the chromosomes.
Crop wild beet populations (''B. vulgaris'' ssp. ''maritima'') have been sequenced as well, allowing for identification of the resistance gene ''Rz2'' in the wild progenitor. ''Rz2'' confers resistance to rhizomania, commonly known as the sugar beet root madness disease.
Breeding
Sugar beets have been bred for increased sugar content, from 8% to 18% in the 200 years , resistance toviral
Viral means "relating to viruses" (small infectious agents).
Viral may also refer to:
Viral behavior, or virality
Memetic behavior likened that of a virus, for example:
* Viral marketing, the use of existing social networks to spread a marke ...
and fungal diseases, increased taproot size, monogermy, and less bolting. Breeding has been eased by discovery of a cytoplasmic male sterility
Cytoplasmic male sterility is total or partial male sterility in plants as the result of specific nuclear and mitochondrial interactions. Male sterility is the failure of plants to produce functional anthers, pollen, or male gametes.
Background
Jo ...
line – this has especially been useful in yield breeding.
References
External links
How Beet Sugar is Made
* ttps://digital.library.unt.edu/permalink/meta-dc-1503:1 ''Sugar beet culture in the northern Great Plains area''hosted by th
University of North Texas Government Documents Department
* ttps://books.google.com/books?id=IikDAAAAMBAJ&dq=Popular+Science+1932+plane&pg=PA38 "Sugar From Beets"''Popular Science Monthly'', March 1935 * {{Taxonbar, from=Q151964
Beta vulgaris
''Beta vulgaris'' (beet) is a species of flowering plant in the subfamily Betoideae of the family Amaranthaceae. Economically, it is the most important crop of the large order Caryophyllales. It has several cultivar groups: the sugar beet, of gre ...
Crops
Phytoremediation plants
Root vegetables
Sugar