Stele (biology) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In a
 The earliest
The earliest
 Siphonosteles have a central region of ground tissue called the
Siphonosteles have a central region of ground tissue called the
vascular plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They ...
, the stele is the central part of the root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the su ...
or stem
Stem or STEM may refer to:
Plant structures
* Plant stem, a plant's aboveground axis, made of vascular tissue, off which leaves and flowers hang
* Stipe (botany), a stalk to support some other structure
* Stipe (mycology), the stem of a mushro ...
containing the tissues derived from the procambium. These include vascular tissue
Vascular tissue is a complex conducting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. The primary components of vascular tissue are the xylem and phloem. These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients internally. The ...
, in some cases ground tissue (pith
Pith, or medulla, is a tissue in the stems of vascular plants. Pith is composed of soft, spongy parenchyma cells, which in some cases can store starch. In eudicotyledons, pith is located in the center of the stem. In monocotyledons, it ext ...
) and a pericycle
The pericycle is a cylinder of parenchyma or sclerenchyma cells that lies just inside the endodermis and is the outer most part of the stele of plants.
Although it is composed of non-vascular parenchyma cells, it's still considered part of the va ...
, which, if present, defines the outermost boundary of the stele. Outside the stele lies the endodermis
The endodermis is the central, innermost layer of cortex in land plants. It is a cylinder of compact living cells, the radial walls of which are impregnated with hydrophobic substances (Casparian strip) to restrict apoplastic flow of water to th ...
, which is the innermost cell layer of the cortex.
The concept of the stele was developed in the late 19th century by French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
botanists
This is a list of botanists who have Wikipedia articles, in alphabetical order by surname. The List of botanists by author abbreviation is mostly a list of plant taxonomists because an author receives a standard abbreviation only when that auth ...
P. E. L. van Tieghem and H. Doultion as a model for understanding the relationship between the shoot
In botany, a plant shoot consists of any plant stem together with its appendages, leaves and lateral buds, flowering stems, and flower buds. The new growth from seed germination that grows upward is a shoot where leaves will develop. In the sp ...
and root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the su ...
, and for discussing the evolution of vascular plant morphology
Phytomorphology is the study of the physical form and external structure of plants.Raven, P. H., R. F. Evert, & S. E. Eichhorn. ''Biology of Plants'', 7th ed., page 9. (New York: W. H. Freeman, 2005). . This is usually considered distinct from ...
. Now, at the beginning of the 21st century, plant molecular biologists are coming to understand the genetics and developmental pathways that govern tissue patterns in the stele. Moreover, physiologists are examining how the anatomy (sizes and shapes) of different steles affect the function of organs.
Protostele
 The earliest
The earliest vascular plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They ...
s had stems with a central core of vascular tissue. This consisted of a cylindrical strand of xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants, the other being phloem. The basic function of xylem is to transport water from roots to stems and leaves, but it also transports nutrients. The word ''xylem'' is derived from ...
, surrounded by a region of phloem
Phloem (, ) is the living tissue in vascular plants that transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis and known as ''photosynthates'', in particular the sugar sucrose, to the rest of the plant. This transport process is c ...
. Around the vascular tissue there might have been an endodermis
The endodermis is the central, innermost layer of cortex in land plants. It is a cylinder of compact living cells, the radial walls of which are impregnated with hydrophobic substances (Casparian strip) to restrict apoplastic flow of water to th ...
that regulated the flow of water into and out of the vascular system. Such an arrangement is termed a protostele.
There are usually three basic types of protostele:
* haplostele – consisting of a cylindrical core of xylem surrounded by a ring of phloem. An endodermis generally surrounds the stele. A centrarch (protoxylem in the center of a metaxylem cylinder) haplostele is prevalent in members of the rhyniophyte grade, such as '' Rhynia''.
* actinostele – a variation of the protostele in which the core is lobed or fluted. This stele is found in many species of club moss ('' Lycopodium'' and related genera). Actinosteles are typically exarch
An exarch (;
from Ancient Greek ἔξαρχος ''exarchos'', meaning “leader”) was the holder of any of various historical offices, some of them being political or military and others being ecclesiastical.
In the late Roman Empire and ea ...
(protoxylem external to the metaxylem) and consist of several to many patches of protoxylem at the tips of the lobes of the metaxylem. Exarch protosteles are a defining characteristic of the lycophyte lineage.
* plectostele – a protostele in which plate-like regions of xylem appear in transverse section surrounded by phloem tissue, thus appearing to form alternating bands. These discrete plates are interconnected in longitudinal section. Some modern club mosses have plectosteles in their stems. The plectostele may be derived from the actinostele.
Siphonostele
 Siphonosteles have a central region of ground tissue called the
Siphonosteles have a central region of ground tissue called the pith
Pith, or medulla, is a tissue in the stems of vascular plants. Pith is composed of soft, spongy parenchyma cells, which in some cases can store starch. In eudicotyledons, pith is located in the center of the stem. In monocotyledons, it ext ...
, with the vascular strand comprising a hollow cylinder surrounding the pith. Siphonosteles often have interruptions in the vascular strand where leaves (typically megaphylls) originate (called leaf gaps).
Siphonosteles can be called ''ectophloic'' (phloem present only external to the xylem) or they can be ''amphiphloic'' (with phloem both external and internal to the xylem). Among living plants, many ferns and some Asterid
In the APG IV system (2016) for the classification of flowering plants, the name asterids denotes a clade (a monophyletic group). Asterids is the largest group of flowering plants, with more than 80,000 species, about a third of the total flo ...
flowering plants have an amphiphloic stele.
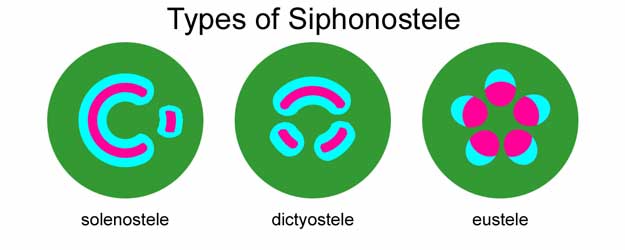
An amphiphloic siphonostele can be called a ''solenostele'', or this term may be used to refer to cases where the cylinder of vascular tissue contains no more than one leaf gap in any transverse section (i.e. has non-overlapping leaf gaps). This type of stele is primarily found in fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes exce ...
stems today. Where there are large overlapping leaf gaps (so that multiple gaps in the vascular cylinder exist in any one transverse section), the term ''dictyostele'' may be used. The numerous leaf gaps and leaf traces give a dictyostele the appearance of many isolated islands of xylem surrounded by phloem. Each of the apparently isolated units of a dictyostele that serve a single leaf can be called a ''meristele''. Among living plants, this type of stele is found only in the stems of ferns.
Most seed plant stems possess a vascular arrangement which has been interpreted as a derived siphonostele, and is called a ''eustele'' – in this arrangement, the primary vascular tissue consists of vascular bundles
A vascular bundle is a part of the transport system in vascular plants. The transport itself happens in the stem, which exists in two forms: xylem and phloem. Both these tissues are present in a vascular bundle, which in addition will includ ...
, usually in one or two rings around the pith
Pith, or medulla, is a tissue in the stems of vascular plants. Pith is composed of soft, spongy parenchyma cells, which in some cases can store starch. In eudicotyledons, pith is located in the center of the stem. In monocotyledons, it ext ...
. In addition to being found in stems, the eustele appears in the root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the su ...
s of monocot
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae '' sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one ...
flowering plants. The vascular bundles in a eustele can be collateral (with the phloem on only one side of the xylem) or bicollateral (with phloem on both sides of the xylem, as in some Solanaceae).
There is also a variant of the eustele found in monocots like maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American English, North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous ...
and rye. The variation has numerous scattered bundles in the stem and is called an ''atactostele'' (characteristic of monocot stems). However, it is really just a variant of the eustele.
See also
*Vascular tissue
Vascular tissue is a complex conducting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. The primary components of vascular tissue are the xylem and phloem. These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients internally. The ...
* Vascular bundle
A vascular bundle is a part of the transport system in vascular plants. The transport itself happens in the stem, which exists in two forms: xylem and phloem. Both these tissues are present in a vascular bundle, which in addition will inc ...
Citations
References
* * * * * * {{Authority control Plant anatomy Plant morphology