Southern Appalachia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Appalachia () is a
 Since Appalachia lacks definite physiographical or topographical boundaries, there has been some disagreement over what exactly the region encompasses. The most commonly used modern definition of Appalachia is the one initially defined by the
Since Appalachia lacks definite physiographical or topographical boundaries, there has been some disagreement over what exactly the region encompasses. The most commonly used modern definition of Appalachia is the one initially defined by the
 While exploring inland along the northern coast of
While exploring inland along the northern coast of
 European migration into Appalachia began in the 18th century. As lands in eastern Pennsylvania, the
European migration into Appalachia began in the 18th century. As lands in eastern Pennsylvania, the
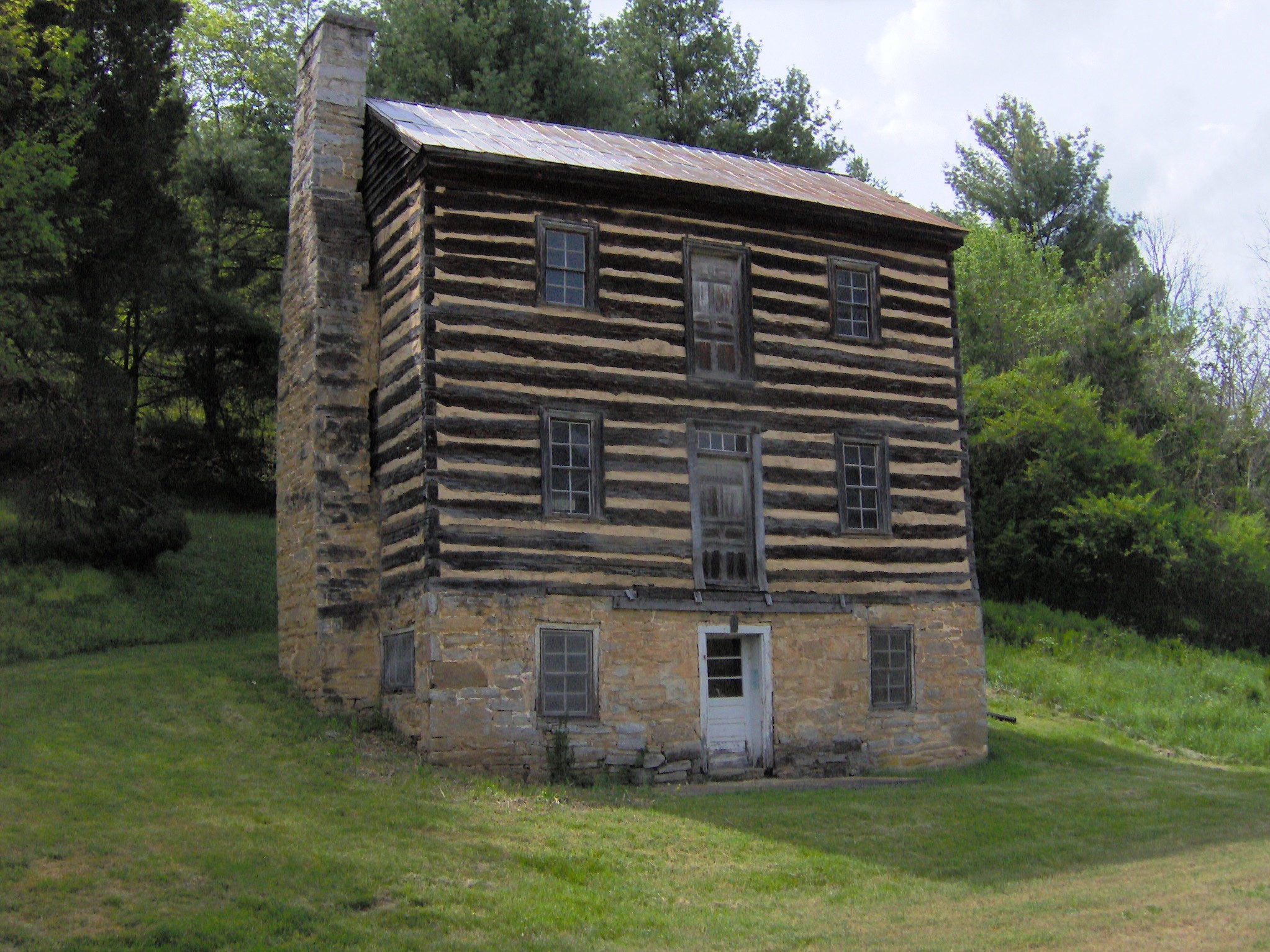 Appalachian frontiersmen have long been romanticized for their ruggedness and self-sufficiency. A typical depiction of an Appalachian pioneer involves a hunter wearing a
Appalachian frontiersmen have long been romanticized for their ruggedness and self-sufficiency. A typical depiction of an Appalachian pioneer involves a hunter wearing a
 By 1860, the Whig Party had disintegrated. Sentiments in northern Appalachia had shifted to the pro-
By 1860, the Whig Party had disintegrated. Sentiments in northern Appalachia had shifted to the pro-
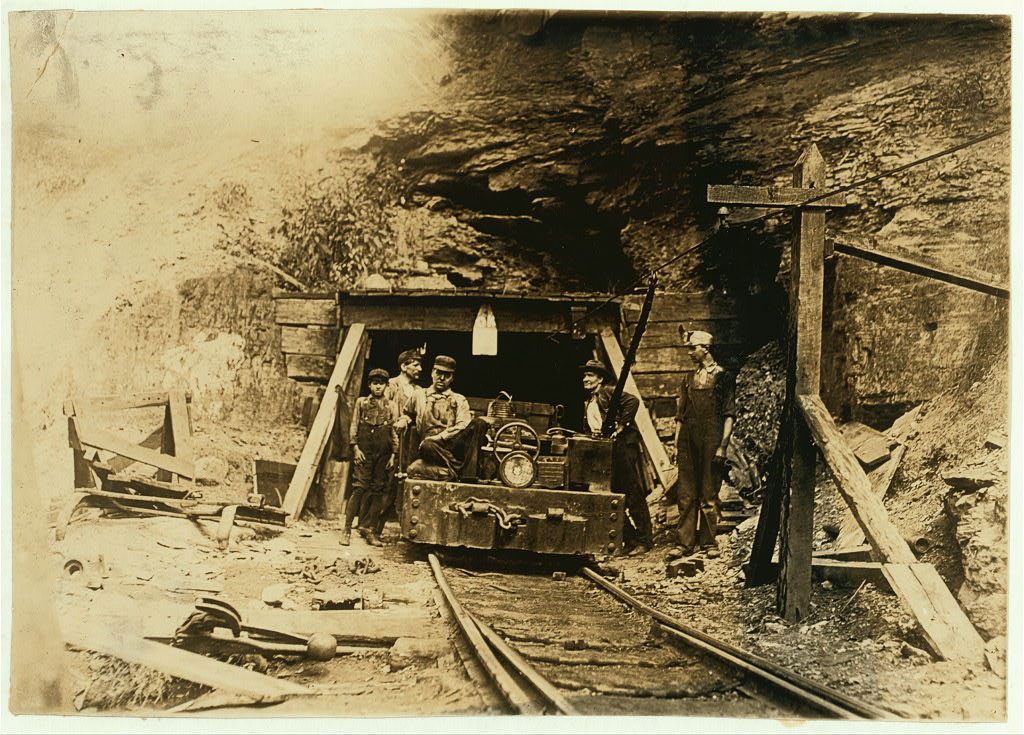 After the war, northern parts of Appalachia experienced an economic boom, while economies in the southern parts of the region stagnated, especially as Southern Democrats regained control of their respective state legislatures at the end of
After the war, northern parts of Appalachia experienced an economic boom, while economies in the southern parts of the region stagnated, especially as Southern Democrats regained control of their respective state legislatures at the end of
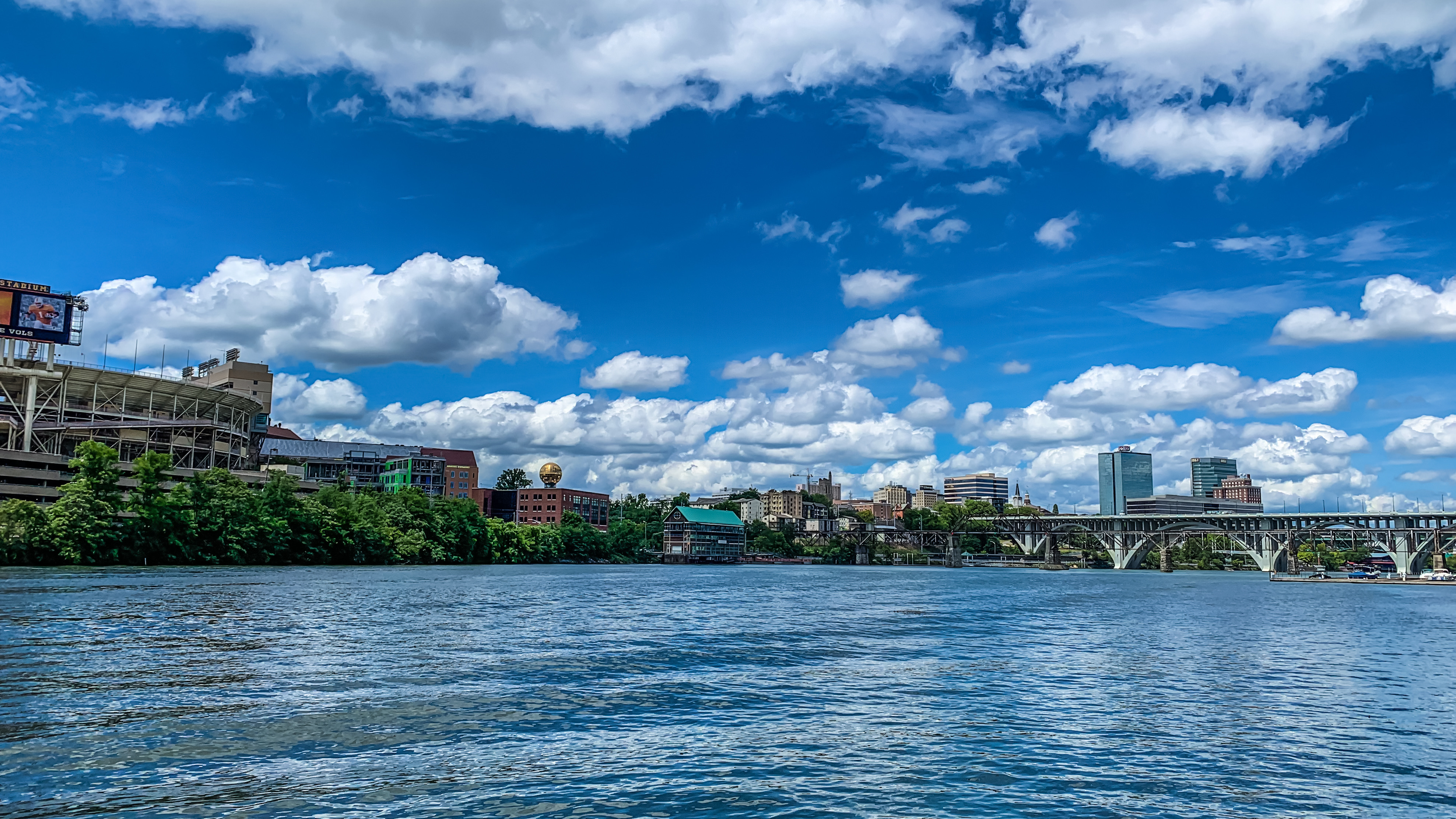
 Due to topographic considerations, several cities which are themselves or are in metropolitan areas that are near or part of the Appalachian region are not included in most definitions of Appalachia. These include Cleveland, Ohio,
Due to topographic considerations, several cities which are themselves or are in metropolitan areas that are near or part of the Appalachian region are not included in most definitions of Appalachia. These include Cleveland, Ohio,

 For much of the region's history, education in Appalachia has lagged behind the rest of the nation due in part to struggles with funding from respective state governments and an agrarian-oriented population that often did not see a practical need for formal education. Early education in the region evolved from teaching Christian morality and learning to read the
For much of the region's history, education in Appalachia has lagged behind the rest of the nation due in part to struggles with funding from respective state governments and an agrarian-oriented population that often did not see a practical need for formal education. Early education in the region evolved from teaching Christian morality and learning to read the
 Appalachian music is one of the best-known manifestations of Appalachian culture. Traditional Appalachian music is derived primarily from the English and Scottish
Appalachian music is one of the best-known manifestations of Appalachian culture. Traditional Appalachian music is derived primarily from the English and Scottish
 Early Appalachian literature typically centered on the observations of people from outside the region, such as Henry Timberlake's ''Memoirs'' (1765) and
Early Appalachian literature typically centered on the observations of people from outside the region, such as Henry Timberlake's ''Memoirs'' (1765) and
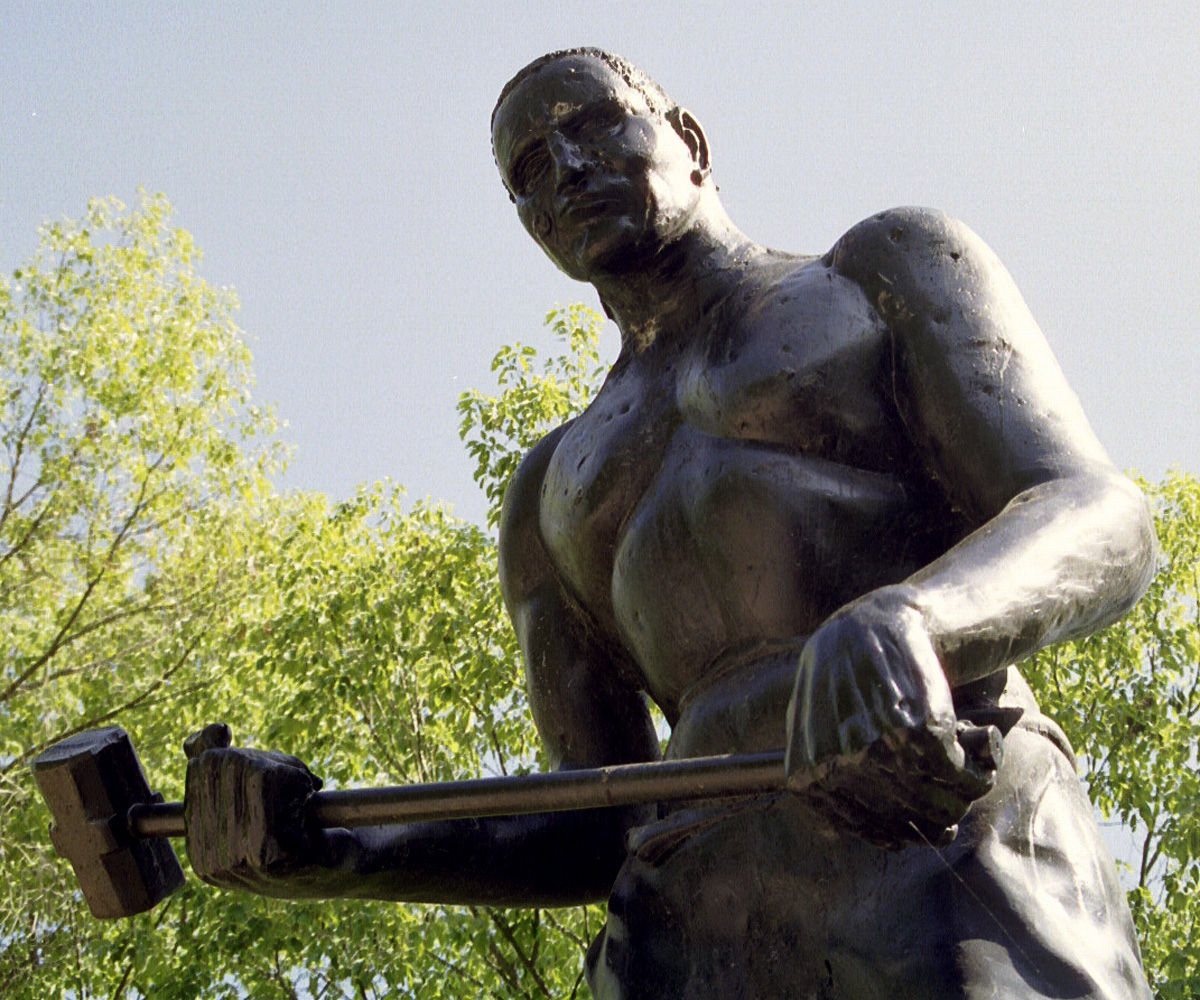 Appalachian folklore has a strong mixture of European, Native American (especially
Appalachian folklore has a strong mixture of European, Native American (especially
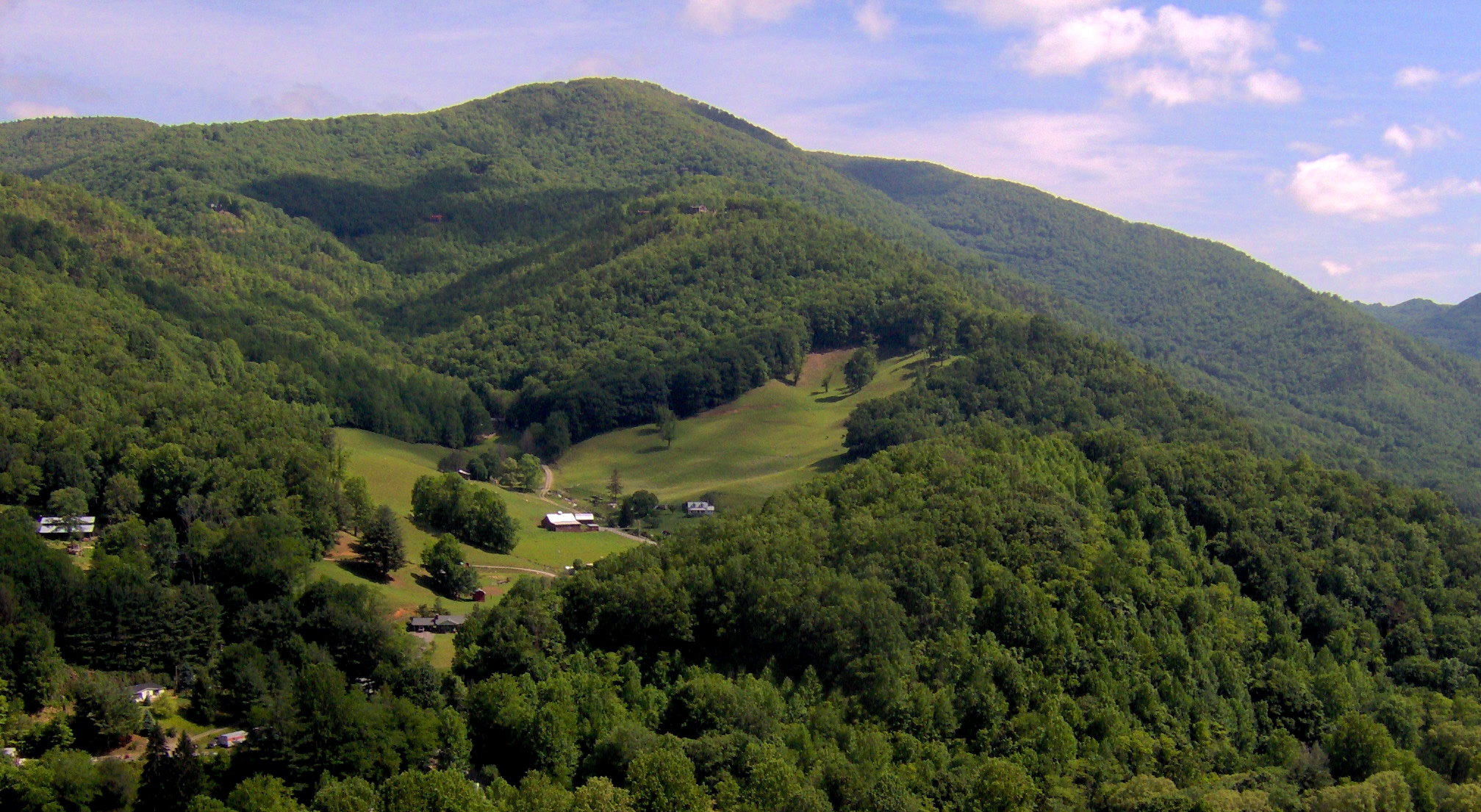 While the climate of the Appalachian region is suitable for agriculture, the region's hilly terrain greatly limits the size of the average farm, a problem exacerbated by population growth in the latter half of the 19th century.
While the climate of the Appalachian region is suitable for agriculture, the region's hilly terrain greatly limits the size of the average farm, a problem exacerbated by population growth in the latter half of the 19th century.
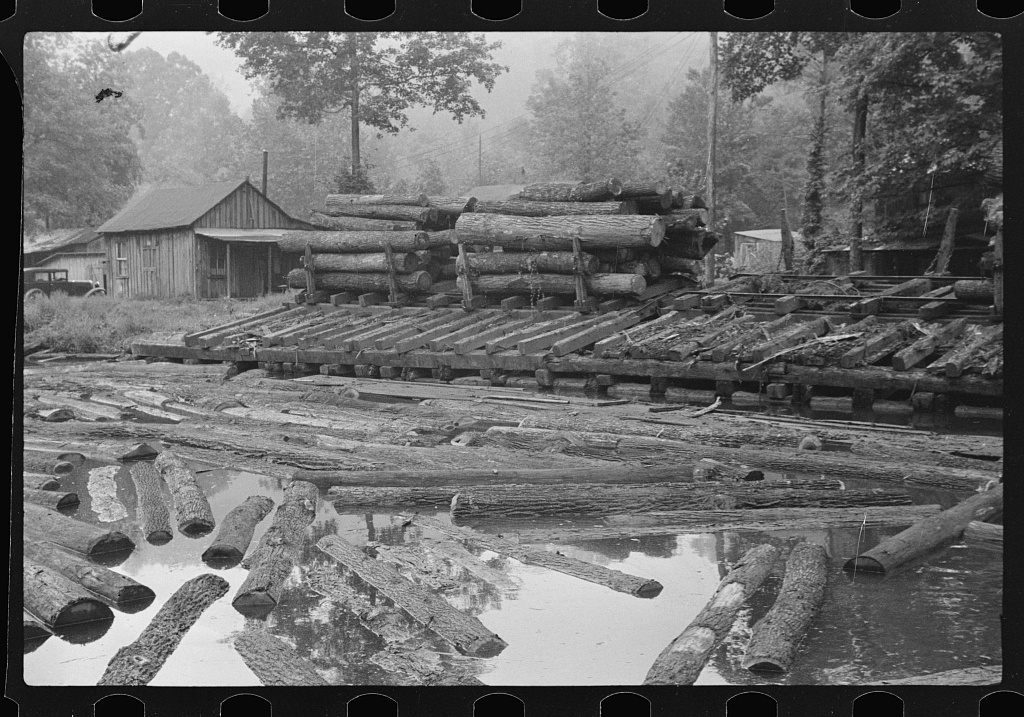 The mountains and valleys of Appalachia once contained what seemed to be an inexhaustible supply of timber. The poor roads, lack of railroads, and general inaccessibility of the region, however, prevented large-scale logging in most of the region throughout much of the 19th century. While logging firms were established in the Carolinas and the Kentucky River valley before the Civil War, most major firms preferred to harvest the more accessible timber stands in the Midwestern and Northeastern parts of the country. By the 1880s, these stands had been exhausted, and a spike in the demand for lumber forced logging firms to seek out the virgin forests of Appalachia.Paulson, Linda Daily, "Lumber Industry". ''Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2006), pp. 501–04. The first major logging ventures in Appalachia transported logs using mule teams or rivers, the latter method sometimes employing
The mountains and valleys of Appalachia once contained what seemed to be an inexhaustible supply of timber. The poor roads, lack of railroads, and general inaccessibility of the region, however, prevented large-scale logging in most of the region throughout much of the 19th century. While logging firms were established in the Carolinas and the Kentucky River valley before the Civil War, most major firms preferred to harvest the more accessible timber stands in the Midwestern and Northeastern parts of the country. By the 1880s, these stands had been exhausted, and a spike in the demand for lumber forced logging firms to seek out the virgin forests of Appalachia.Paulson, Linda Daily, "Lumber Industry". ''Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2006), pp. 501–04. The first major logging ventures in Appalachia transported logs using mule teams or rivers, the latter method sometimes employing
 Coal mining is the industry most frequently associated with the region in outsiders' minds, due in part to the fact that the region once produced two-thirds of the nation's coal. At present, however, the mining industry employs just 2% of the Appalachian workforce. The region's vast coalfield covers between northern Pennsylvania and central Alabama, mostly along the Cumberland Plateau and
Coal mining is the industry most frequently associated with the region in outsiders' minds, due in part to the fact that the region once produced two-thirds of the nation's coal. At present, however, the mining industry employs just 2% of the Appalachian workforce. The region's vast coalfield covers between northern Pennsylvania and central Alabama, mostly along the Cumberland Plateau and
 The manufacturing industry in Appalachia is rooted primarily in the ironworks and steelworks of early
The manufacturing industry in Appalachia is rooted primarily in the ironworks and steelworks of early
 One of the region's oldest industries, tourism became a more important part of the Appalachian economy in the latter half of the 20th century as mining and manufacturing steadily declined.Howell, Benita, "Tourism". ''Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2006), pp. 611–16. In 2000–2001, tourism in Appalachia accounted for nearly $30 billion and over 600,000 jobs. The mountain terrain—with its accompanying scenery and outdoor recreational opportunities—provide the region's primary attractions. The region is home to one of the world's most well-known hiking trails (the
One of the region's oldest industries, tourism became a more important part of the Appalachian economy in the latter half of the 20th century as mining and manufacturing steadily declined.Howell, Benita, "Tourism". ''Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2006), pp. 611–16. In 2000–2001, tourism in Appalachia accounted for nearly $30 billion and over 600,000 jobs. The mountain terrain—with its accompanying scenery and outdoor recreational opportunities—provide the region's primary attractions. The region is home to one of the world's most well-known hiking trails (the
 Poverty had plagued Appalachia for many years but was not brought to the attention of the rest of the United States until 1940, when James Agee and
Poverty had plagued Appalachia for many years but was not brought to the attention of the rest of the United States until 1940, when James Agee and
Arc.gov
 In its summary the report stated that "over 55,000 parcels of property in 80 counties were studied, representing some 20,000,000 acres of land and mineral rights..." It found that "41% of the 20 million acres of land and minerals...are held by only 50 private owners and 10 government agencies. The federal government is the single largest owner in Appalachia, holding over 2,000,000 acres." The study found that the extractive industries, i.e., timber, coal, etc., were "greatly underassessed for property tax purposes. Over 75% of the mineral owners in this survey pay under 25 cents per acre in property taxes." In the major coal counties surveyed the average tax per ton of known coal reserves is only $.0002 (1/50th of a cent).
The government-held lands are tax exempt, but the government makes a
In its summary the report stated that "over 55,000 parcels of property in 80 counties were studied, representing some 20,000,000 acres of land and mineral rights..." It found that "41% of the 20 million acres of land and minerals...are held by only 50 private owners and 10 government agencies. The federal government is the single largest owner in Appalachia, holding over 2,000,000 acres." The study found that the extractive industries, i.e., timber, coal, etc., were "greatly underassessed for property tax purposes. Over 75% of the mineral owners in this survey pay under 25 cents per acre in property taxes." In the major coal counties surveyed the average tax per ton of known coal reserves is only $.0002 (1/50th of a cent).
The government-held lands are tax exempt, but the government makes a
 Transportation has been the most challenging and expensive issue in Appalachia since the arrival of the first European settlers in the 18th century. With the exception of the October 1, 1940, opening of the
Transportation has been the most challenging and expensive issue in Appalachia since the arrival of the first European settlers in the 18th century. With the exception of the October 1, 1940, opening of the
 Depictions of Appalachia and its inhabitants in popular media are typically negative, making the region an object of humor, derision, and social concern. Ledford writes, "Always part of the mythical South, Appalachia continues to languish backstage in the American drama, still dressed, in the popular mind at least, in the garments of backwardness, violence, poverty, and hopelessness." Otto argues that comic strips ''
Depictions of Appalachia and its inhabitants in popular media are typically negative, making the region an object of humor, derision, and social concern. Ledford writes, "Always part of the mythical South, Appalachia continues to languish backstage in the American drama, still dressed, in the popular mind at least, in the garments of backwardness, violence, poverty, and hopelessness." Otto argues that comic strips ''
cultural region
In anthropology and geography, a cultural region, cultural sphere, cultural area or culture area refers to a geography with one relatively homogeneous human activity or complex of activities (culture). Such activities are often associated ...
in the Eastern United States
The Eastern United States, commonly referred to as the American East, Eastern America, or simply the East, is the region of the United States to the east of the Mississippi River. In some cases the term may refer to a smaller area or the East C ...
that stretches from the Southern Tier of New York State
New York, officially the State of New York, is a state in the Northeastern United States. It is often called New York State to distinguish it from its largest city, New York City. With a total area of , New York is the 27th-largest U.S. stat ...
to northern Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
and Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
. While the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
stretch from Belle Isle in Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic Canada, Atlantic region. The province comprises t ...
, Canada, to Cheaha Mountain in Alabama, ''Appalachia'' typically refers only to the cultural region of the central and southern portions of the range, from the Catskill Mountains of New York southwest to the Blue Ridge Mountains
The Blue Ridge Mountains are a Physiographic regions of the world, physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Mountains range. The mountain range is located in the Eastern United States, and extends 550 miles southwest from southern Pennsy ...
which run southwest from southern Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
to northern Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, and the Great Smoky Mountains
The Great Smoky Mountains (, ''Equa Dutsusdu Dodalv'') are a mountain range rising along the Tennessee–North Carolina border in the southeastern United States. They are a subrange of the Appalachian Mountains, and form part of the Blue Ridge ...
of Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
and North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and ...
. In 2020, the region was home to an estimated 26.1 million people, of which roughly 80% are white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White o ...
.
Since its recognition as a distinctive region in the late 19th century, Appalachia has been a source of enduring myths and distortions regarding the isolation, temperament, and behavior of its inhabitants. Early 20th century writers often engaged in yellow journalism
Yellow journalism and yellow press are American terms for journalism and associated newspapers that present little or no legitimate, well-researched news while instead using eye-catching headlines for increased sales. Techniques may include ...
focused on sensationalistic aspects of the region's culture, such as moonshining
Moonshine is high-proof liquor that is usually produced illegally. The name was derived from a tradition of creating the alcohol during the nighttime, thereby avoiding detection. In the first decades of the 21st century, commercial dist ...
and clan feuding, and often portrayed the region's inhabitants as uneducated and prone to impulsive acts of violence. Sociological studies in the 1960s and 1970s helped to re-examine and dispel these stereotypes.Abramson, Rudy. Introduction to ''Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2006), pp. xix–xxv. Stereotypes about Appalachian people being ignorant, anti-progress, and racist are still grappled in the region by portrayals in media and press publications.
While endowed with abundant natural resources, Appalachia has long struggled economically and been associated with poverty. In the early 20th century, large-scale logging and coal mining firms brought wage-paying jobs and modern amenities to Appalachia, but by the 1960s the region had failed to capitalize on any long-term benefits from these two industries. Beginning in the 1930s, the federal government sought to alleviate poverty in the Appalachian region with a series of New Deal initiatives, specifically the Tennessee Valley Authority
The Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) is a federally owned electric utility corporation in the United States. TVA's service area covers all of Tennessee, portions of Alabama, Mississippi, and Kentucky, and small areas of Georgia, North Carolin ...
. This was responsible for the construction of hydroelectric dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use ...
s that provide a vast amount of electricity and that support programs for better farming practices, regional planning, and economic development. On March 9, 1965, the Appalachian Regional Commission
The Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC) is a United States federal–state partnership that works with the people of Appalachia to create opportunities for self-sustaining economic development and improved quality of life. Congress established A ...
was created to further alleviate poverty in the region, mainly by diversifying the region's economy and helping to provide better health care and educational opportunities to the region's inhabitants. By 1990, Appalachia had largely joined the economic mainstream but still lagged behind the rest of the nation in most economic indicators.
Defining the Appalachian region
 Since Appalachia lacks definite physiographical or topographical boundaries, there has been some disagreement over what exactly the region encompasses. The most commonly used modern definition of Appalachia is the one initially defined by the
Since Appalachia lacks definite physiographical or topographical boundaries, there has been some disagreement over what exactly the region encompasses. The most commonly used modern definition of Appalachia is the one initially defined by the Appalachian Regional Commission
The Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC) is a United States federal–state partnership that works with the people of Appalachia to create opportunities for self-sustaining economic development and improved quality of life. Congress established A ...
in 1965 and expanded over subsequent decades. The region defined by the Commission currently includes 420 counties and eight independent cities in 13 states, including all 55 counties in West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the B ...
, 14 counties in New York, 52 in Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, 32 in Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, 3 in Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, 54 in Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia ...
, 25 counties and 8 cities
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
, 29 in North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and ...
, 52 in Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
, 6 in South Carolina
)'' Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
, 37 in Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, 37 in Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
, and 24 in Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
. When the Commission was established, counties were added based on economic need, however, rather than any cultural parameters.
The first major attempt to map Appalachia as a distinctive cultural region came in the 1890s with the efforts of Berea College
Berea College is a private liberal arts work college in Berea, Kentucky. Founded in 1855, Berea College was the first college in the Southern United States to be coeducational and racially integrated. Berea College charges no tuition; every a ...
president William Goodell Frost, whose "Appalachian America" included 194 counties in 8 states.John Alexander Williams, ''Appalachia: A History'' (Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 2002) In 1921, John C. Campbell published ''The Southern Highlander and His Homeland'' in which he modified Frost's map to include 254 counties in 9 states. A landmark survey of the region in the following decade by the United States Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of com ...
defined the region as consisting of 206 counties in 6 states. In 1984, Karl Raitz and Richard Ulack expanded the ARC's definition to include 445 counties in 13 states, although they removed all counties in Mississippi and added two in New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware ...
. Historian John Alexander Williams, in his 2002 book ''Appalachia: A History'', distinguished between a "core" Appalachian region consisting of 164 counties in West Virginia, Kentucky, Virginia, Tennessee, North Carolina, and Georgia, and a greater region defined by the ARC.
In the ''Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (2006), Appalachian State University historian Howard Dorgan suggested the term "Old Appalachia" for the region's cultural boundaries, noting an academic tendency to ignore the southwestern and northeastern extremes of the ARC's pragmatic definition. Sean Trende, senior elections analyst at '' RealClearPolitics'', defines "Greater Appalachia" in his 2012 book ''The Lost Majority'' as including both the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
region ( western Virginia and North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and ...
, the Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
region in western South Carolina, West Virginia, southern Ohio
Appalachian Ohio is a bioregion and political unit in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Ohio, characterized by the western foothills of the Appalachian Mountains and the Appalachian Plateau. The Appalachian Regional Commission defines ...
, the Cumberland Plateau in eastern Kentucky, East Tennessee, northern Georgia, Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
, and Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
) and the Upland South
The Upland South and Upper South are two overlapping cultural and geographic subregions in the inland part of the Southern and lower Midwestern United States. They differ from the Deep South and Atlantic coastal plain by terrain, history, econom ...
(southern Indiana
Southern Indiana is a region consisting of the southern third of the state of Indiana.
The region's history and geography has led to a blend of Northern and Southern culture distinct from the remainder of Indiana. It is often considered to be par ...
and Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockf ...
, the Bluegrass, Mississippi Plateau, Western Coal Field, and Jackson Purchase
The Jackson Purchase, also known as the Purchase Region or simply the Purchase, is a region in the U.S. state of Kentucky bounded by the Mississippi River to the west, the Ohio River to the north, and the Tennessee River to the east.
Jackson's ...
regions in central and western Kentucky, Middle and West Tennessee
West Tennessee is one of the three Grand Divisions of the U.S. state of Tennessee that roughly comprises the western quarter of the state. The region includes 21 counties between the Tennessee and Mississippi rivers, delineated by state law. Its ...
, Missouri
Missouri is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee to the east, Arkansas t ...
, the Ozarks
The Ozarks, also known as the Ozark Mountains, Ozark Highlands or Ozark Plateau, is a physiographic region in the U.S. states of Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma and the extreme southeastern corner of Kansas. The Ozarks cover a significant port ...
in Arkansas, Little Dixie and Southwestern Oklahoma
Southwest Oklahoma is a geographical name for the southwest portion of the state of Oklahoma, typically considered to be south of the Canadian River, extending eastward from the Texas border to a line roughly from Weatherford, to Anadarko, to ...
, North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
and East Texas
East Texas is a broadly defined cultural, geographic, and ecological region in the eastern part of the U.S. state of Texas that comprises most of 41 counties. It is primarily divided into Northeast and Southeast Texas. Most of the region cons ...
, and the Texas Hill Country) following Ulster Protestant
Ulster Protestants ( ga, Protastúnaigh Ultach) are an ethnoreligious group in the Irish province of Ulster, where they make up about 43.5% of the population. Most Ulster Protestants are descendants of settlers who arrived from Britain in the ...
migrations to the Southern and Midwestern United States
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. I ...
in the 18th and 19th centuries.
Toponymy and pronunciation
 While exploring inland along the northern coast of
While exploring inland along the northern coast of Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
in 1528, the members of the Narváez expedition
The Narváez expedition was a Spanish journey of exploration and colonization started in 1527 that intended to establish colonial settlements and garrisons in Florida. The expedition was initially led by Pánfilo de Narváez, who died in 1528. M ...
, including Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca
Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca (; 1488/90/92"Cabeza de Vaca, Alvar Núñez (1492?-1559?)." American Eras. Vol. 1: Early American Civilizations and Exploration to 1600. Detroit: Gale, 1997. 50-51. Gale Virtual Reference Library. Web. 10 Decembe ...
, found a village of indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
near present-day Tallahassee, Florida
Tallahassee ( ) is the capital city of the U.S. state of Florida. It is the county seat and only incorporated municipality in Leon County. Tallahassee became the capital of Florida, then the Florida Territory, in 1824. In 2020, the populatio ...
, whose name they transcribed as ''Apalchen'' or ''Apalachen'' (). The name was soon altered by the Spanish to ''Apalache'' (Apalachee
The Apalachee were an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, specifically an Indigenous people of Florida, who lived in the Florida Panhandle until the early 18th century. They lived between the Aucilla River and Ochlockonee River,B ...
) and used as a name for the tribe and region spreading well inland to the north. Pánfilo de Narváez
Pánfilo de Narváez (; 147?–1528) was a Spanish '' conquistador'' and soldier in the Americas. Born in Spain, he first embarked to Jamaica in 1510 as a soldier. He came to participate in the conquest of Cuba and led an expedition to Camagü ...
's expedition first entered Apalachee territory on June 15, 1528, and applied the name. Now spelled "Appalachian", it is the fourth oldest surviving European place-name in the U.S. After the de Soto expedition
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1500 – 21 May, 1542) was a Spanish explorer and ''conquistador'' who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire i ...
in 1540, Spanish cartographers began to apply the name of the tribe to the mountains themselves. The first cartographic appearance of ''Apalchen'' is on Diego Gutiérrez's map of 1562; the first use for the mountain range is the map of Jacques le Moyne de Morgues
Jacques le Moyne de Morgues ( 1533–1588) was a French artist and member of Jean Ribault's expedition to the New World. His depictions of Native American life and culture, colonial life, and plants are of extraordinary historical importa ...
in 1565. Le Moyne was also the first European to apply "Apalachen" specifically to a mountain range as opposed to a village, native tribe, or a southeastern region of North America.
The name was not commonly used for the whole mountain range until the late 19th century. A competing and often more popular name was the "Allegheny Mountains
The Allegheny Mountain Range (; also spelled Alleghany or Allegany), informally the Alleghenies, is part of the vast Appalachian Mountain Range of the Eastern United States and Canada and posed a significant barrier to land travel in less devel ...
", "Alleghenies", and even "Alleghania".
In northern U.S. dialects, the mountains are pronounced or . The cultural region of Appalachia is pronounced , also , all with a third syllable like "lay". In southern U.S. dialects, the mountains are called the , and the cultural region of Appalachia is pronounced , both with a third syllable like the "la" in "latch". This pronunciation is favored in the "core" region in central and southern parts of the Appalachian range. The occasional use of the "sh" sound for the "ch" in the last syllable in northern dialects was popularized by Appalachian Trail
The Appalachian Trail (also called the A.T.), is a hiking trail in the Eastern United States, extending almost between Springer Mountain in Georgia and Mount Katahdin in Maine, and passing through 14 states.Gailey, Chris (2006)"Appalachian ...
organizations in New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
in the early 20th century.
History
Early history
Native American hunter-gatherers first arrived in what is now Appalachia over 16,000 years ago. The earliest discovered site is theMeadowcroft Rockshelter
Meadowcroft Rockshelter is an archaeological site located near Avella in Jefferson Township, Pennsylvania. The site is a rock shelter in a bluff overlooking Cross Creek (a tributary of the Ohio River), and contains evidence that the area may have ...
in Washington County, Pennsylvania, which some scientists claim is pre-Clovis culture
The Clovis culture is a prehistoric Paleoamerican culture, named for distinct stone and bone tools found in close association with Pleistocene fauna, particularly two mammoths, at Blackwater Locality No. 1 near Clovis, New Mexico, in 1936 a ...
. Several other Archaic period (8000–1000 BC) archaeological sites have been identified in the region, such as the St. Albans site in West Virginia and the Icehouse Bottom site in Tennessee. The presence of Africans in the Appalachian Mountains dates back to the sixteenth century with the arrival of European colonists. Enslaved Africans were first brought to America during the 16th century Spanish expeditions to the mountainous regions of the South. In 1526 enslaved Africans were brought to the Pedee River region of western North Carolina by Spanish explorer, Lucas Vazquez de Ayllõn. Enslaved Africans also accompanied the expeditions of Fernando de Soto in 1540 and Juan Pardo, in 1566 who both traveled through Appalachia.
In the 16th century, the de Soto and Juan Pardo expeditions explored the mountains of South Carolina, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Georgia, and encountered complex agrarian societies consisting of Muskogean-speaking inhabitants. De Soto indicated that much of the region west of the mountains was part of the domain of Coosa, a paramount chief
A paramount chief is the English-language designation for the highest-level political leader in a regional or local polity or country administered politically with a chief-based system. This term is used occasionally in anthropological and ar ...
dom centered around a village complex in northern Georgia. By the time English explorers arrived in Appalachia in the late 17th century, the central part of the region was controlled by Algonquian tribes (namely the Shawnee
The Shawnee are an Algonquian-speaking indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands. In the 17th century they lived in Pennsylvania, and in the 18th century they were in Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana and Illinois, with some bands in Kentucky a ...
) and the southern part of the region was controlled by the Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
. The French based in modern-day Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
also made inroads into the northern areas of the region in modern-day New York state and Pennsylvania. By the mid 18th century the French had outposts such as Fort Duquesne
Fort Duquesne (, ; originally called ''Fort Du Quesne'') was a fort French colonization of the Americas, established by the French in 1754, at the confluence of the Allegheny River, Allegheny and Monongahela River, Monongahela rivers. It was lat ...
and Fort Le Boeuf
Fort Le Bœuf (often referred to as Fort de la Rivière au Bœuf) was a fort established by the French during 1753 on a fork of French Creek (in the drainage area of the River Ohio), in present-day Waterford, in northwest Pennsylvania. The fort ...
controlling the access points of the Allegheny River valley and upper Ohio valley
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illino ...
after exploration by Celeron de Bienville
Celeron is Intel's brand name for low-end IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor models targeted at low-cost personal computers.
Celeron processors are compatible with IA-32 software. They typically offer less performance per clock speed ...
. European migration into Appalachia began in the 18th century. As lands in eastern Pennsylvania, the
European migration into Appalachia began in the 18th century. As lands in eastern Pennsylvania, the Tidewater region of Virginia
Tidewater refers to the north Atlantic coastal plain region of the United States of America.
Definition
Culturally, the Tidewater region usually includes the low-lying plains of southeast Virginia, northeastern North Carolina, southern Maryl ...
and the Carolinas
The Carolinas are the U.S. states of North Carolina and South Carolina, considered collectively. They are bordered by Virginia to the north, Tennessee to the west, and Georgia to the southwest. The Atlantic Ocean is to the east.
Combining Nor ...
filled up, immigrants began pushing further and further westward into the Appalachian Mountains. A relatively large proportion of the early backcountry
In the United States, a backcountry or backwater is a geographical area that is remote, undeveloped, isolated, or difficult to access.
Terminology Backcountry and wilderness within United States national parks
The National Park Service (NPS) ...
immigrants were Ulster Scots—later known as " Scotch-Irish", a group mostly originating from southern Scotland and northern England, many of whom had settled in Ulster Ireland prior to migrating to America — who were seeking cheaper land and freedom from Quaker leaders, many of whom considered the Scotch-Irish "savages". Others included Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
from the Palatinate region and English settlers from the Anglo-Scottish border
The Anglo-Scottish border () is a border separating Scotland and England which runs for between Marshall Meadows Bay on the east coast and the Solway Firth in the west. The surrounding area is sometimes referred to as "the Borderlands".
The ...
country. Between 1730 and 1763, immigrants trickled into western Pennsylvania
Western Pennsylvania is a region in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, covering the western third of the state. Pittsburgh is the region's principal city, with a metropolitan area population of about 2.4 million people, and serves as its economic ...
, the Shenandoah Valley area of Virginia, and western Maryland
upright=1.2, An enlargeable map of Maryland's 23 counties and one independent city
Western Maryland, also known as the Maryland Panhandle, is the portion of the U.S. state of Maryland that typically consists of Washington, Allegany, and Garre ...
. Thomas Walker's discovery of the Cumberland Gap
The Cumberland Gap is a pass through the long ridge of the Cumberland Mountains, within the Appalachian Mountains, near the junction of the U.S. states of Kentucky, Virginia, and Tennessee. It is famous in American colonial history for its r ...
in 1750 and the end of the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
in 1763 lured settlers deeper into the mountains, namely to upper east Tennessee, northwestern North Carolina, upstate South Carolina
The Upstate is the region in the westernmost part of South Carolina, United States, also known as the Upcountry, which is the historical term. Although loosely defined among locals, the general definition includes the 10 counties of the commerc ...
, and central Kentucky.
During the 18th century, enslaved Africans were brought to Appalachia by European settlers of trans-Appalachia Kentucky and the upper Blue Ridge Valley. According to the first census of 1790, more than 3,000 enslaved Africans were transported across the mountains into East Tennessee and more than 12,000 into the Kentucky mountains. Between 1790 and 1840, a series of treaties with the Cherokee and other Native American tribes opened up lands in north Georgia
North Georgia is the northern hilly/mountainous region in the U.S. state of Georgia. At the time of the arrival of settlers from Europe, it was inhabited largely by the Cherokee. The counties of north Georgia were often scenes of important eve ...
, north Alabama
North Alabama is a region of the U.S. state of Alabama. Several geographic definitions for the area exist, with all descriptions including the nine counties of Alabama's Tennessee Valley region. The North Alabama Industrial Development Associ ...
, the Tennessee Valley
The Tennessee Valley is the drainage basin of the Tennessee River and is largely within the U.S. state of Tennessee. It stretches from southwest Kentucky to north Alabama and from northeast Mississippi to the mountains of Virginia and North Car ...
, the Cumberland Plateau regions, and the Great Smoky Mountains
The Great Smoky Mountains (, ''Equa Dutsusdu Dodalv'') are a mountain range rising along the Tennessee–North Carolina border in the southeastern United States. They are a subrange of the Appalachian Mountains, and form part of the Blue Ridge ...
along what is now the Tennessee-North Carolina border. The last of these treaties culminated in the removal of the bulk of the Cherokee population (as well as Choctaw, Chickasaw
The Chickasaw ( ) are an indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands. Their traditional territory was in the Southeastern United States of Mississippi, Alabama, and Tennessee as well in southwestern Kentucky. Their language is classif ...
and others) from the region via the Trail of Tears
The Trail of Tears was an ethnic cleansing and forced displacement of approximately 60,000 people of the " Five Civilized Tribes" between 1830 and 1850 by the United States government. As part of the Indian removal, members of the Cherokee, ...
from 1831 until 1838.
Appalachian frontier
 Appalachian frontiersmen have long been romanticized for their ruggedness and self-sufficiency. A typical depiction of an Appalachian pioneer involves a hunter wearing a
Appalachian frontiersmen have long been romanticized for their ruggedness and self-sufficiency. A typical depiction of an Appalachian pioneer involves a hunter wearing a coonskin cap
A coonskin cap is a hat fashioned from the skin and fur of a raccoon. The original coonskin cap consisted of the entire skin of the raccoon including its head and tail. Beginning as traditional Native American headgear, coonskin caps became assoc ...
and buckskin clothing, and sporting a long rifle and shoulder-strapped powder horn
A powder horn is a container for gunpowder, and was generally created from cow, ox or buffalo horn (anatomy), horn. The term may also be used for any personal container for gunpowder, although powder flask is the strictly correct term.
Featur ...
. Perhaps no single figure symbolizes the Appalachian pioneer more than Daniel Boone
Daniel Boone (September 26, 1820) was an American pioneer and frontiersman whose exploits made him one of the first folk heroes of the United States. He became famous for his exploration and settlement of Kentucky, which was then beyond the we ...
(1734–1820), a long hunter and surveyor instrumental in the early settlement of Kentucky and Tennessee. Like Boone, Appalachian pioneers moved into areas largely separated from "civilization" by high mountain ridges, and had to fend for themselves against the elements. As many of these early settlers were living on Native American lands, attacks from Native American tribes were a continuous threat until the 19th century.Caudill, Harry. ''Night Comes to the Cumberlands''
As early as the 18th century, Appalachia (then known simply as the "backcountry") began to distinguish itself from its wealthier lowland and coastal neighbors to the east. Frontiersmen often bickered with lowland and tidewater "elites" over taxes, sometimes to the point of armed revolts such as the Regulator Movement (1767–1771) in North Carolina.Drake, Richard. ''A History of Appalachia'' (Lexington: University Press of Kentucky, 2001) In 1778, at the height of the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
, backwoodsmen from Pennsylvania, Virginia, and what is now Kentucky took part in George Rogers Clark's Illinois campaign
The Illinois campaign, also known as Clark's Northwestern campaign (1778–1779), was a series of events during the American Revolutionary War in which a small force of Virginia militiamen, led by George Rogers Clark, seized control of several B ...
. Two years later, a group of Appalachian frontiersmen known as the Overmountain Men
The Overmountain Men were American frontiersmen from west of the Blue Ridge Mountains which are the leading edge of the Appalachian Mountains, who took part in the American Revolutionary War. While they were present at multiple engagements in t ...
routed British forces at the Battle of Kings Mountain
The Battle of Kings Mountain was a military engagement between Patriot and Loyalist militias in South Carolina during the Southern Campaign of the American Revolutionary War, resulting in a decisive victory for the Patriots. The battle took pla ...
after rejecting a call by the British to disarm. After the war, residents throughout the Appalachian backcountry—especially the Monongahela region in western Pennsylvania, and antebellum
Antebellum, Latin for "before war", may refer to:
United States history
* Antebellum South, the pre-American Civil War period in the Southern United States
** Antebellum Georgia
** Antebellum South Carolina
** Antebellum Virginia
* Antebellum ...
northwestern Virginia (now the north-central part of West Virginia) — refused to pay a tax placed on whiskey by the new American government, leading to what became known as the Whiskey Rebellion
The Whiskey Rebellion (also known as the Whiskey Insurrection) was a violent tax protest in the United States beginning in 1791 and ending in 1794 during the presidency of George Washington. The so-called "whiskey tax" was the first tax impo ...
. The resulting tighter Federal controls in the Monongahela valley resulted in many whiskey/bourbon makers migrating via the Ohio River to Kentucky and Tennessee where the industry could flourish.
Early 19th century
In the early 19th century, the rift between theyeoman
Yeoman is a noun originally referring either to one who owns and cultivates land or to the middle ranks of servants in an English royal or noble household. The term was first documented in mid-14th-century England. The 14th century also witn ...
farmers of Appalachia and their wealthier lowland counterparts continued to grow, especially as the latter dominated most state legislatures. People in Appalachia began to feel slighted over what they considered unfair taxation methods and lack of state funding for improvements (especially for roads). In the northern half of the region, the lowland "elites" consisted largely of industrial and business interests, whereas in the parts of the region south of the Mason–Dixon line
The Mason–Dixon line, also called the Mason and Dixon line or Mason's and Dixon's line, is a demarcation line separating four U.S. states, forming part of the borders of Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware, and West Virginia (part of Virginia ...
, the lowland elites consisted of large-scale land-owning planters. The Whig Party, formed in the 1830s, drew widespread support from disaffected Appalachians.
Tensions between the mountain counties and state governments sometimes reached the point of mountain counties threatening to break off and form separate states. In 1832, bickering between western Virginia and eastern Virginia over the state's constitution led to calls on both sides for the state's separation into two states. In 1841, Tennessee state senator (and later U.S. president) Andrew Johnson introduced legislation in the Tennessee Senate
The Tennessee Senate is the upper house of the U.S. state of Tennessee's state legislature, which is known formally as the Tennessee General Assembly.
The Tennessee Senate has the power to pass resolutions concerning essentially any issue rega ...
calling for the creation of a separate state in East Tennessee. The proposed state would have been known as " Frankland" and would have invited like-minded mountain counties in Virginia, North Carolina, Georgia, and Alabama to join it.
Proposal to rename the United States
In 1839Washington Irving
Washington Irving (April 3, 1783 – November 28, 1859) was an American short-story writer, essayist, biographer, historian, and diplomat of the early 19th century. He is best known for his short stories "Rip Van Winkle" (1819) and " The Legen ...
proposed to rename the United States "Alleghania" or "Appalachia" in place of "America", since the latter name belonged to Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived f ...
too. Edgar Allan Poe
Edgar Allan Poe (; Edgar Poe; January 19, 1809 – October 7, 1849) was an American writer, poet, editor, and literary critic. Poe is best known for his poetry and short stories, particularly his tales of mystery and the macabre. He is wid ...
later took up the idea, and considered Appalachia a much better name than America or Alleghania; he thought it better defined the United States as a distinct geographical entity, separate from the rest of the Americas, and he also thought it did honor to both Irving and the natives who the Appalachian Mountains had been named after. At the time, however, the United States had already reached far beyond the greater Appalachian region, but the "magnificence" of Appalachia Poe considered enough to rechristen the nation with a name that would be unique to its own character. However, Poe's popular influence only grew decades after his death, and so the name was never seriously considered.
U.S. Civil War
 By 1860, the Whig Party had disintegrated. Sentiments in northern Appalachia had shifted to the pro-
By 1860, the Whig Party had disintegrated. Sentiments in northern Appalachia had shifted to the pro-abolitionist
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
Republican Party. In southern Appalachia, abolitionists still constituted a radical minority, although several smaller opposition parties (most of which were both pro-Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
and pro-slavery) were formed to oppose the planter-dominated Southern Democrats
Southern Democrats, historically sometimes known colloquially as Dixiecrats, are members of the U.S. Democratic Party who reside in the Southern United States. Southern Democrats were generally much more conservative than Northern Democrats wi ...
. As states in the southern United States moved toward secession
Secession is the withdrawal of a group from a larger entity, especially a political entity, but also from any organization, union or military alliance. Some of the most famous and significant secessions have been: the former Soviet republics le ...
, a majority of Southern Appalachians still supported the Union.Gordon McKinney, "The Civil War". ''Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2006), pp. 1579–81. In 1861, a Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
newspaper identified 161 counties in Southern Appalachia—which the paper called "Alleghenia"—where Union support remained strong, and which might provide crucial support for the defeat of the Confederacy. However, many of these Unionists—especially in the mountain areas of North Carolina, Georgia, and Alabama—were "conditional" Unionists in that they opposed secession, but also opposed violence to prevent secession, and thus when their respective state legislatures voted to secede, their support shifted to the Confederacy. Kentucky sought to remain neutral at the outset of the conflict, opting not to supply troops to either side. After Virginia voted to secede, several mountain counties in northwestern Virginia rejected the ordinance and with the help of the Union Army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union of the collective states. It proved essential to th ...
established a separate state, admitted to the Union as West Virginia in 1863. However, half the counties included in the new state, comprising two-thirds of its territory, were secessionist and pro-Confederate.
This caused great difficulty for the new Unionist state government in Wheeling, both during and after the war. A similar effort occurred in East Tennessee, but the initiative failed after Tennessee's governor ordered the Confederate Army to occupy the region, forcing East Tennessee's Unionists to flee to the north or go into hiding. The one exception was the so-called Free and Independent State of Scott.
Both central and southern Appalachia suffered tremendous violence and turmoil during the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
. While there were two major theaters of operation in the region—namely the Shenandoah Valley of Virginia (and present-day West Virginia) and the Chattanooga area along the Tennessee-Georgia border—much of the violence was caused by bushwhacker
Bushwhacking was a form of guerrilla warfare common during the American Revolutionary War, War of 1812, American Civil War and other conflicts in which there were large areas of contested land and few governmental resources to control these tra ...
s and guerrilla war
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, raids, petty warfare, hit-and-run tactics ...
. The northernmost battles of the entire war were fought in Appalachia with the Battle of Buffington Island
The Battle of Buffington Island, also known as the St. Georges Creek Skirmish, was an American Civil War engagement in Meigs County, Ohio, and Jackson County, West Virginia, on July 19, 1863, during Morgan's Raid. The largest battle in Ohio d ...
and the Battle of Salineville resulting from Morgan's Raid
Morgan's Raid was a diversionary incursion by Confederate cavalry into the Union states of Indiana, Kentucky, Ohio and West Virginia during the American Civil War. The raid took place from June 11 to July 26, 1863, and is named for the command ...
. Large numbers of livestock were killed (grazing was an important part of Appalachia's economy), and numerous farms were destroyed, pillaged, or neglected. The actions of both Union and Confederate armies left many inhabitants in the region resentful of government authority and suspicious of outsiders for decades after the war.
Late 19th and early 20th centuries
Economic boom
 After the war, northern parts of Appalachia experienced an economic boom, while economies in the southern parts of the region stagnated, especially as Southern Democrats regained control of their respective state legislatures at the end of
After the war, northern parts of Appalachia experienced an economic boom, while economies in the southern parts of the region stagnated, especially as Southern Democrats regained control of their respective state legislatures at the end of Reconstruction
Reconstruction may refer to:
Politics, history, and sociology
*Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company
*'' Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Unio ...
. Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Western Pennsylvania, the second-most populous city in Pennsylva ...
as well as Knoxville
Knoxville is a city in and the county seat of Knox County in the U.S. state of Tennessee. As of the 2020 United States census, Knoxville's population was 190,740, making it the largest city in the East Tennessee Grand Division and the state' ...
grew into major industrial centers, especially regarding iron and steel production. By 1900, the Chattanooga area and north Georgia and northern Alabama had experienced similar changes due to manufacturing booms in Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia, but its territory falls in both Fulton and DeKalb counties. With a population of 498,715 ...
and Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1. ...
at the edge of the Appalachian region. Railroad construction between the 1880s and early 20th century gave the greater nation access to the vast coalfields in central Appalachia, making the economy
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the ...
in that part of the region practically synonymous with coal mining. As the nationwide demand for lumber skyrocketed, lumber firms turned to the virgin forests of southern Appalachia, using sawmill and logging railroad innovations to reach remote timber stands. The Tri-Cities area of Tennessee and Virginia and the Kanawha Valley
The Kanawha River ( ) is a tributary of the Ohio River, approximately 97 mi (156 km) long, in the U.S. state of West Virginia. The largest inland waterway in West Virginia, its valley has been a significant industrial region of the sta ...
of West Virginia became major petrochemical
Petrochemicals (sometimes abbreviated as petchems) are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable so ...
production centers.
Stereotypes
The late 19th and early 20th centuries also saw the development of various regional stereotypes. Attempts by PresidentRutherford B. Hayes
Rutherford Birchard Hayes (; October 4, 1822 – January 17, 1893) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 19th president of the United States from 1877 to 1881, after serving in the U.S. House of Representatives and as governo ...
to enforce the whiskey tax in the late 1870s led to an explosion in violence between Appalachian " moonshiners" and federal "revenuers" that lasted through the Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcohol ...
period in the 1920s. The breakdown of authority and law enforcement during the Civil War may have contributed to an increase in clan feuding, which by the 1880s was reported to be a problem across most of Kentucky's Cumberland region as well as Carter County in Tennessee, Carroll County in Virginia, and Mingo and Logan counties in West Virginia. Regional writers from this period such as Mary Noailles Murfree and Horace Kephart
Horace Sowers Kephart (September 8, 1862 – April 2, 1931) was an American travel writer and librarian, best known as the author of '' Our Southern Highlanders'' (a memoir about his life in the Great Smoky Mountains of western North Carolina) ...
liked to focus on such sensational aspects of mountain culture, leading readers outside the region to believe they were more widespread than in reality. In an 1899 article in ''The Atlantic
''The Atlantic'' is an American magazine and multi-platform publisher. It features articles in the fields of politics, foreign affairs, business and the economy, culture and the arts, technology, and science.
It was founded in 1857 in Boston, ...
'', Berea College
Berea College is a private liberal arts work college in Berea, Kentucky. Founded in 1855, Berea College was the first college in the Southern United States to be coeducational and racially integrated. Berea College charges no tuition; every a ...
president William G. Frost attempted to redefine the inhabitants of Appalachia as "noble mountaineers"—relics of the nation's pioneer period whose isolation had left them unaffected by modern times.
Today, residents of Appalachia are viewed by many Americans as uneducated and unrefined, resulting in culture-based stereotyping and discrimination in many areas, including employment and housing. Such discrimination has prompted some to seek redress under prevailing federal and state civil rights
Civil and political rights are a class of rights that protect individuals' freedom from infringement by governments, social organizations, and private individuals. They ensure one's entitlement to participate in the civil and political life o ...
laws.
Feuds
Appalachia, and especially Kentucky, became nationally known for its violent feuds, especially in the remote mountain districts. They pitted the men in extended clans against each other for decades, often using assassination and arson as weapons, along withambush
An ambush is a long-established military tactic in which a combatant uses an advantage of concealment or the element of surprise to attack unsuspecting enemy combatants from concealed positions, such as among dense underbrush or behind mo ...
es, gunfight
A shootout, also called a firefight or gunfight, is a fight between armed combatants using firearms. The term can be used to describe any such fight, though it is typically used to describe those that do not involve military forces or only in ...
s, and pre-arranged shootout
A shootout, also called a firefight or gunfight, is a fight between armed combatants using firearms. The term can be used to describe any such fight, though it is typically used to describe those that do not involve military forces or only invo ...
s. The infamous Hatfield-McCoy Feud of the 19th century was the best known of these family feuds. Some of the feuds were continuations of violent local Civil War episodes. Journalists often wrote about the violence, using stereotypes that "city folks" had developed about Appalachia; they interpreted the feuds as the natural products of profound ignorance, poverty, and isolation, and perhaps even inbreeding
Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the mating or breeding of individuals or organisms that are closely related genetically. By analogy, the term is used in human reproduction, but more commonly refers to the genetic disorders and o ...
. In reality, the leading participants were typically well-to-do local elites with networks of clients who, like the Northeast and Chicago political machines, fought for their own power over local and regional politics.
Modern Appalachia
Logging firms' rapid devastation of the forests of the Appalachians sparked a movement among conservationists to preserve what remained and allow the land to "heal". In 1911, Congress passed theWeeks Act
The Weeks Act is a federal law (36 Stat. 961) enacted by the United States Congress on March 1, 1911. Introduced by Massachusetts Congressman John W. Weeks and signed into law by President William Howard Taft, the law authorized the United States ...
, giving the federal government authority to create national forests east of the Mississippi River and control timber harvesting. Regional writers and business interests led a movement to create national parks in the eastern United States similar to Yosemite and Yellowstone
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowston ...
in the west, culminating in the creation of the Great Smoky Mountains National Park
Great Smoky Mountains National Park is an American national park in the southeastern United States, with parts in North Carolina and Tennessee. The park straddles the ridgeline of the Great Smoky Mountains, part of the Blue Ridge Mountains, w ...
in Tennessee and North Carolina, Shenandoah National Park
Shenandoah National Park (often ) is an American national park that encompasses part of the Blue Ridge Mountains in the Commonwealth of Virginia. The park is long and narrow, with the Shenandoah River and its broad valley to the west, and the ...
in Virginia, Cumberland Gap National Historical Park
The Cumberland Gap National Historical Park is a United States National Historical Park located at the border between Kentucky, Tennessee, and Virginia, centered on the Cumberland Gap, a natural break in the Appalachian Mountains.
The park lies ...
in Kentucky, Virginia and Tennessee, and the Blue Ridge Parkway
The Blue Ridge Parkway is a National Parkway and All-American Road in the United States, noted for its scenic beauty. The parkway, which is America's longest linear park, runs for through 29 Virginia and North Carolina counties, linking Shenan ...
(connecting the two) in the 1930s. During the same period, New England forester Benton MacKaye
Benton MacKaye ( ; March 6, 1879 – December 11, 1975) was an American forester, planner and conservationist. He was born in Stamford, Connecticut; his father was actor and dramatist Steele MacKaye. After studying forestry at Harvard Unive ...
led the movement to build the Appalachian Trail
The Appalachian Trail (also called the A.T.), is a hiking trail in the Eastern United States, extending almost between Springer Mountain in Georgia and Mount Katahdin in Maine, and passing through 14 states.Gailey, Chris (2006)"Appalachian ...
, stretching from Georgia to Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ...
.
Several significant moments of investment by the United States government into areas of science and technology were established in the mid-20th century, notably with NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, crucial with the design of Apollo program launch vehicles and propulsion of the Space Shuttle program
The Space Shuttle program was the fourth human spaceflight program carried out by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), which accomplished routine transportation for Earth-to-orbit crew and cargo from 1981 to 2011. I ...
, and at adjacent facilities Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) is a U.S. multiprogram science and technology national laboratory sponsored by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and administered, managed, and operated by UT–Battelle as a federally funded research an ...
and the Y-12 National Security Complex
The Y-12 National Security Complex is a United States Department of Energy National Nuclear Security Administration facility located in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, near the Oak Ridge National Laboratory. It was built as part of the Manhattan Proje ...
in Oak Ridge, Tennessee with the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
and advancements in supercomputing and nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced ...
.
By the 1950s, poor farming techniques and the loss of jobs to mechanization
Mechanization is the process of changing from working largely or exclusively by hand or with animals to doing that work with machinery. In an early engineering text a machine is defined as follows:
In some fields, mechanization includes the ...
in the mining industry had left much of central and southern Appalachia poverty-stricken. The lack of jobs also led to widespread difficulties with outmigration. Beginning in the 1930s, federal agencies such as the Tennessee Valley Authority
The Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) is a federally owned electric utility corporation in the United States. TVA's service area covers all of Tennessee, portions of Alabama, Mississippi, and Kentucky, and small areas of Georgia, North Carolin ...
began investing in the Appalachian region. Sociologists such as James Brown and Cratis Williams and authors such as Harry Caudill and Michael Harrington
Edward Michael Harrington Jr. (February 24, 1928 – July 31, 1989) was an American democratic socialist. As a writer, he was perhaps best known as the author of '' The Other America''. Harrington was also a political activist, theorist, profess ...
brought attention to the region's plight in the 1960s, prompting Congress to create the Appalachian Regional Commission
The Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC) is a United States federal–state partnership that works with the people of Appalachia to create opportunities for self-sustaining economic development and improved quality of life. Congress established A ...
in 1965. The commission's efforts helped to stem the tide of outmigration and diversify the region's economies. Although there have been drastic improvements in the region's economic conditions since the commission's founding, the ARC still listed 80 counties as "distressed" in 2020, with nearly half of them (38) in Kentucky.
Since the 1980s, population growth in the Southern Appalachian section of the region has brought about concerns of farmland loss and hazards to the local environment. Regarding housing development, exurban development, characterized by its low-density housing, has violated the habitats of native species and contributed significantly to the decline in agricultural land-use in larger Appalachia.
There are growing IT sectors in many parts of the region. Summit, the fastest supercomputer in the world as of 2019, is currently housed at Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) is a U.S. multiprogram science and technology national laboratory sponsored by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and administered, managed, and operated by UT–Battelle as a federally funded research an ...
near Knoxville, Tennessee
Knoxville is a city in and the county seat of Knox County in the U.S. state of Tennessee. As of the 2020 United States census, Knoxville's population was 190,740, making it the largest city in the East Tennessee Grand Division and the state' ...
.
Cities

 Due to topographic considerations, several cities which are themselves or are in metropolitan areas that are near or part of the Appalachian region are not included in most definitions of Appalachia. These include Cleveland, Ohio,
Due to topographic considerations, several cities which are themselves or are in metropolitan areas that are near or part of the Appalachian region are not included in most definitions of Appalachia. These include Cleveland, Ohio, Nashville, Tennessee
Nashville is the capital city of the U.S. state of Tennessee and the seat of Davidson County. With a population of 689,447 at the 2020 U.S. census, Nashville is the most populous city in the state, 21st most-populous city in the U.S., and ...
, and Atlanta, Georgia
Atlanta ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia, but its territory falls in both Fulton and DeKalb counties. With a population of 498,7 ...
. Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Western Pennsylvania, the second-most populous city in Pennsylva ...
is the largest city by population to be wholly within the Appalachian region.
Notable cities with at least 40,000 residents within Appalachia include:
* Altoona, Pennsylvania
Altoona is a city in Blair County, Pennsylvania. It is the principal city of the Altoona Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA). The population was 43,963 at the time of the 2020 Census, making it the eighteenth most populous city in Pennsylvania. T ...
* Asheville, North Carolina
* Binghamton, New York
* Birmingham, Alabama
Birmingham ( ) is a city in the north central region of the U.S. state of Alabama. Birmingham is the seat of Jefferson County, Alabama's most populous county. As of the 2021 census estimates, Birmingham had a population of 197,575, down 1% fr ...
* Charleston, West Virginia
* Chattanooga, Tennessee
Chattanooga ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Hamilton County, Tennessee, United States. Located along the Tennessee River bordering Georgia, it also extends into Marion County on its western end. With a population of 181,099 in 2020 ...
* Cleveland, Tennessee
* Erie, Pennsylvania
Erie (; ) is a city on the south shore of Lake Erie and the county seat of Erie County, Pennsylvania, United States. Erie is the fifth largest city in Pennsylvania and the largest city in Northwestern Pennsylvania with a population of 94,831 ...
* Greenville, South Carolina
* Hagerstown, Maryland
* Huntington, West Virginia
* Huntsville, Alabama
Huntsville is a city in Madison County, Limestone County, and Morgan County, Alabama, United States. It is the county seat of Madison County. Located in the Appalachian region of northern Alabama, Huntsville is the most populous city in ...
* Johnson City, Tennessee
Johnson City is a city in Washington, Carter, and Sullivan counties in the U.S. state of Tennessee, mostly in Washington County. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 71,046, making it the eighth largest city in Tennessee. Joh ...
* Knoxville, Tennessee
Knoxville is a city in and the county seat of Knox County in the U.S. state of Tennessee. As of the 2020 United States census, Knoxville's population was 190,740, making it the largest city in the East Tennessee Grand Division and the state' ...
* Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Western Pennsylvania, the second-most populous city in Pennsylva ...
* Roanoke, Virginia
Roanoke ( ) is an independent city in the U.S. state of Virginia. At the 2020 census, the population was 100,011, making it the 8th most populous city in the Commonwealth of Virginia and the largest city in Virginia west of Richmond. It is ...
* Scranton, Pennsylvania
Scranton is a city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Lackawanna County. With a population of 76,328 as of the 2020 U.S. census, Scranton is the largest city in Northeastern Pennsylvania, the Wyoming V ...
* State College, Pennsylvania
State College is a home rule municipality in Centre County in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. It is a college town, dominated economically, culturally and demographically by the presence of the University Park campus of the Pennsylvania Sta ...
* Winston-Salem, North Carolina
Winston-Salem is a city and the county seat of Forsyth County, North Carolina, United States. In the 2020 census, the population was 249,545, making it the second-largest municipality in the Piedmont Triad region, the 5th most populous city in ...
Culture
Ethnic groups
An estimated 90% of Appalachia's earliest European settlers originated from the Anglo-Scottish border country—namely theEnglish counties
The counties of England are areas used for different purposes, which include administrative, geographical, cultural and political demarcation. The term "county" is defined in several ways and can apply to similar or the same areas used by each ...
of Cumberland, Westmorland
Westmorland (, formerly also spelt ''Westmoreland'';R. Wilkinson The British Isles, Sheet The British IslesVision of Britain/ref> is a historic county in North West England spanning the southern Lake District and the northern Dales. It had an ...
, Northumberland
Northumberland () is a county in Northern England, one of two counties in England which border with Scotland. Notable landmarks in the county include Alnwick Castle, Bamburgh Castle, Hadrian's Wall and Hexham Abbey.
It is bordered by land ...
, County Durham, Lancashire
Lancashire ( , ; abbreviated Lancs) is the name of a historic county, ceremonial county, and non-metropolitan county in North West England. The boundaries of these three areas differ significantly.
The non-metropolitan county of Lancash ...
and Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other English counties, functions have ...
, and the Lowland Scottish counties
The shires of Scotland ( gd, Siorrachdan na h-Alba), or counties of Scotland, are historic subdivisions of Scotland established in the Middle Ages and used as administrative divisions until 1975. Originally established for judicial purposes (bei ...
of Ayrshire, Dumfriesshire
Dumfriesshire or the County of Dumfries or Shire of Dumfries (''Siorrachd Dhùn Phris'' in Gaelic) is a historic county and registration county in southern Scotland. The Dumfries lieutenancy area covers a similar area to the historic county.
I ...
, Roxburghshire, Berwickshire
Berwickshire ( gd, Siorrachd Bhearaig) is a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area in south-eastern Scotland, on the English border. Berwickshire County Council existed from 1890 until 1975, when the area became part of t ...
and Wigtownshire
Wigtownshire or the County of Wigtown (, ) is one of the historic counties of Scotland, covering an area in the south-west of the country. Until 1975, Wigtownshire was an administrative county used for local government. Since 1975 the area has f ...
. Most of these were from families who had been resettled in the Ulster Plantation
The Plantation of Ulster ( gle, Plandáil Uladh; Ulster-Scots: ''Plantin o Ulstèr'') was the organised colonisation (''plantation'') of Ulstera province of Irelandby people from Great Britain during the reign of King James I. Most of the set ...
in northern Ireland in the 17th century, but some came directly from the Anglo-Scottish border region. Fischer, David Hackett, '' Albion's Seed: Four British Folkways in America'' (New York: Oxford University Press, 1989), pp. 620–30. In America, these people are often grouped under the single name " Scotch-Irish" or "Scots-Irish". While various 20th century writers tried to associate Appalachia with Scottish highlanders
The Highlands ( sco, the Hielands; gd, a’ Ghàidhealtachd , 'the place of the Gaels') is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland Sc ...
, Highland Scots were a relatively insignificant percentage of the region's early European immigrants.
Although Swedes and Finns formed only a tiny portion of the Appalachian settlers it was Swedish and Finnish settlers of New Sweden
New Sweden ( sv, Nya Sverige) was a Swedish colony along the lower reaches of the Delaware River in what is now the United States from 1638 to 1655, established during the Thirty Years' War when Sweden was a great military power. New Sweden f ...
who brought the northern European woodsman skills such as log cabin construction which formed the basis of backwoods Appalachian material culture."DANIEL BOONE’S CULTURAL ANCESTORS, if not actually his genetic ones,..." Stoll, Steven. Ramp Hollow: The Ordeal of Appalachia (p. 86-88). Farrar, Straus and Giroux. Kindle Edition.
Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
were a major pioneer group to migrate to Appalachia, settling mainly in western Pennsylvania and southwest Virginia
Southwest Virginia, often abbreviated as SWVA, is a mountainous region of Virginia in the westernmost part of the commonwealth. Located within the broader region of western Virginia, Southwest Virginia has been defined alternatively as all Virg ...
. Smaller numbers of Germans were also among the initial wave of migrants to the southern mountains. In the 19th century, Welsh immigrants were brought into the region for their mining and metallurgical expertise, and by 1900 over 100,000 Welsh immigrants were living in western Pennsylvania alone. Thousands of German-speaking Swiss
The Swiss people (german: die Schweizer, french: les Suisses, it, gli Svizzeri, rm, ils Svizzers) are the citizens of Switzerland or people of Swiss ancestry.
The number of Swiss nationals has grown from 1.7 million in 1815 to 8.7 millio ...
migrated to Appalachia in the second half of the 19th century, and their descendants remain in places such as East Bernstadt, Kentucky
East Bernstadt is a census-designated place (CDP) and coal town in Laurel County, Kentucky, United States. The population was 716 at the 2010 census, down from 774 at the 2000 census.
Geography
East Bernstadt is located in northern Laurel Coun ...
, and Gruetli-Laager, Tennessee. The coal mining and manufacturing boom in the late 19th and early 20th centuries brought large numbers of Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whic ...
ans to Appalachia, although most of these families left the region when the Great Depression shattered the economy in the 1930s. African Americans have been present in the region since the 18th century, and currently make up 8% of the ARC-designated region, mostly concentrated in urban areas and former mining and manufacturing towns; the African-American component of Appalachia is sometimes termed Affrilachia.
Native Americans, the region's original inhabitants, are now only a small percentage of the region's present population, their most notable concentration being the reservation of the Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians
The Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians (EBCI), (Cherokee: ᏣᎳᎩᏱ ᏕᏣᏓᏂᎸᎩ, ''Tsalagiyi Detsadanilvgi'') is a federally recognized Indian Tribe based in Western North Carolina in the United States. They are descended from the smal ...
in North Carolina. The Melungeon
Melungeons ( ) are an ethnicity from the Southeastern United States who descend from Europeans, Native American, and sub-Saharan Africans brought to America as indentured servants and later as slaves. Historically, the Melungeons were associated ...
s, a group of mixed African, European, and Native American ancestry, are scattered across northeastern Tennessee, eastern Kentucky, and southwestern Virginia.
According to the American Factfinder
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
's 2013 data, the Southern Appalachia has a white majority, comprising 84% of the population. African Americans are 7% and Hispanics or Latinos are 6% of the population. Asians and Pacific Islanders are 1.5% of the population. Although the counties have great differences among themselves, in terms of racial and ethnic diversity.
Religion

Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
has long been the main religion in Appalachia. Religion in Appalachia is characterized by a sense of independence and a distrust of religious hierarchies
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important ...
, both rooted in the evangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being " born again", in which an individual expe ...
tendencies of the region's pioneers, many of whom had been influenced by the "New Light
The terms Old Lights and New Lights (among others) are used in Protestant Christian circles to distinguish between two groups who were initially the same, but have come to a disagreement. These terms originated in the early 18th century from a spl ...
" movement in England. Many of the denominations brought from Europe underwent modifications or factioning during the Second Great Awakening
The Second Great Awakening was a Protestant religious revival during the early 19th century in the United States. The Second Great Awakening, which spread religion through revivals and emotional preaching, sparked a number of reform movements. R ...
(especially the Holiness movement) in the early 19th century. A number of 18th and 19th-century religious traditions are still practiced in parts of Appalachia, including natural water (or "creek") baptism
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost ...
, rhythmically chanted preaching, congregational shouting, snake handling, and foot washing. While most church-goers in Appalachia attend fairly well organized churches affiliated with regional or national bodies, small unaffiliated congregations are not uncommon in rural mountain areas.
Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
is the most dominant denomination in Appalachia, although there is a significant Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
presence in the northern half of the region and in urban areas, like Pittsburgh and Scranton. The region's early Lowland and Ulster Scot immigrants brought Presbyterianism
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their nam ...
to Appalachia, eventually organizing into bodies such as the Cumberland Presbyterian Church. English Baptists—most of whom had been influenced by the Separate Baptist and Regular Baptist movements—were also common on the Appalachian frontier, and today are represented in the region by groups such as the Free Will Baptist
Free Will Baptists are a group of General Baptist denominations of Christianity that teach free grace, free salvation and free will. The movement can be traced back to the 1600s with the development of General Baptism in England. Its formal est ...
s, the Southern Baptists
The Southern Baptist Convention (SBC) is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is the world's largest Baptist denomination, and the largest Protestant and second-largest Christian denomination in the United States. The wo ...
, Missionary Baptists, and "old-time" groups such as the United Baptists and Primitive Baptists
Primitive Baptists – also known as Hard Shell Baptists, Foot Washing Baptists or Old School Baptists – are conservative Baptists adhering to a degree of Calvinist beliefs who coalesced out of the controversy among Baptists in the early 19th c ...
.Grammich, Clifford, "Baptists, the Old-Time Groups". ''Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2006), pp. 1298–300. Circuit riders such as Francis Asbury
Francis Asbury (August 20 or 21, 1745 – March 31, 1816) was one of the first two bishops of the Methodist Episcopal Church in the United States. During his 45 years in the colonies and the newly independent United States, he devoted his life to ...
helped spread Methodism
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's br ...
to Appalachia in the early 19th century, and today 9.2% of the region's population is Methodist, represented by such bodies as the United Methodist Church
The United Methodist Church (UMC) is a worldwide mainline Protestant denomination based in the United States, and a major part of Methodism. In the 19th century, its main predecessor, the Methodist Episcopal Church, was a leader in evangelic ...
, the Free Methodist Church
The Free Methodist Church (FMC) is a Methodist Christian denomination within the holiness movement, based in the United States. It is evangelical in nature and is Wesleyan–Arminian in theology.
The Free Methodist Church has members in over 100 ...
, and the African Methodist Episcopal Zion Church. Pentecostal
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a Protestant Charismatic Christian movement
movements within the region include the Church of God (based in Cleveland, Tennessee) and the Assemblies of God. Scattered Mennonite
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the Radi ...
colonies exist throughout the region.
Dialect
The Appalachian dialect is a dialect ofMidland American English
Midland American English is a regional dialect or super-dialect of American English, geographically lying between the traditionally-defined Northern and Southern United States. The boundaries of Midland American English are not entirely clear, b ...
known as the Southern Midland dialect, and is spoken primarily in central and southern Appalachia. The Northern Midland dialect is spoken in the northern parts of the region, while Pittsburgh English
Western Pennsylvania English, known more narrowly as Pittsburgh English or popularly as Pittsburghese, is a dialect of American English native primarily to the western half of Pennsylvania, centered on the city of Pittsburgh, but potentially a ...
(more commonly known as "Pittsburghese") is strongly influenced by Appalachian dialect. The Southern Appalachian dialect is considered part of the Southern American dialect, although the two are distinguished by the rhotic nature of the Appalachian dialect. Early 20th century writers believed the Appalachian dialect to be a surviving relic of Old World Scottish or Elizabethan dialects. Recent research suggests, however, that while the dialect has a stronger Scottish influence than other American dialects, most of its distinguishing characteristics have developed in the United States.
Education
Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts ...
in small, one-room school
One-room schools, or schoolhouses, were commonplace throughout rural portions of various countries, including Prussia, Norway, Sweden, the United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, Ireland, and Spain. In most rural and s ...
houses that convened in months when children were not needed to help with farm work. After the Civil War, mandatory education laws and state assistance helped larger communities begin to establish grade schools and high schools. During the same period, many of the region's institutions of higher education were established or greatly expanded.DeYoung, Alan, Introduction to Education section, ''Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2006), pp. 1517–21. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, service organizations such as Pi Beta Phi
Pi Beta Phi (), often known simply as Pi Phi, is an international women's fraternity founded at Monmouth College, in Monmouth, Illinois on April 28, 1867 as I. C. Sorosis, the first national secret college society of women to be modeled after ...
and various religious organizations established settlement school
Settlement schools are social reform institutions established in rural Appalachia in the early 20th century with the purpose of educating mountain children and improving their isolated rural communities.
Settlement schools have played an import ...
s and mission schools in the region's more rural areas.
In the 20th century, national trends began to have more of an effect on education in Appalachia, sometimes clashing with the region's traditional values. The Scopes Trial—the nation's most publicized debate over the teaching of the theory of evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
—took place in Dayton, Tennessee
Dayton is a city and county seat in Rhea County, Tennessee, Rhea County, Tennessee, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the city population was 7,065. The Dayton Urban Cluster, which includes developed areas adjacent ...
, in southern Appalachia in 1925. In spite of consolidation and centralization, schools in Appalachia struggled to keep up with federal and state demands into the 21st century. Since 2001, a number of the region's public schools were threatened with loss of funding due to difficulties fulfilling the demands of No Child Left Behind
The No Child Left Behind Act of 2001 (NCLB) was a U.S. Act of Congress that reauthorized the Elementary and Secondary Education Act; it included Title I provisions applying to disadvantaged students. It supported standards-based education ...
.
Music
 Appalachian music is one of the best-known manifestations of Appalachian culture. Traditional Appalachian music is derived primarily from the English and Scottish
Appalachian music is one of the best-known manifestations of Appalachian culture. Traditional Appalachian music is derived primarily from the English and Scottish ballad
A ballad is a form of verse, often a narrative set to music. Ballads derive from the medieval French ''chanson balladée'' or ''ballade'', which were originally "dance songs". Ballads were particularly characteristic of the popular poetry and ...
tradition and Irish and Scottish fiddle music. African-American blues musicians played a significant role in developing the instrumental aspects of Appalachian music, most notably with the introduction of the five-stringed banjo—one of the region's iconic symbols—in the late 18th century. Another instrument known in Appalachian culture was the Appalachian dulcimer
The Appalachian dulcimer (many variant names; see below) is a fretted string instrument of the zither family, typically with three or four strings, originally played in the Appalachian region of the United States. The body extends the length of ...
which, in a practical way, is a guitar-shaped instrument laid on its side with a flat bottom and the strings plucked in a manner to make alternating notes.
In the years following World War I, British folklorist Cecil Sharp
Cecil James Sharp (22 November 1859 – 23 June 1924) was an English-born collector of folk songs, folk dances and instrumental music, as well as a lecturer, teacher, composer and musician. He was the pre-eminent activist in the development of t ...
brought attention to Southern Appalachia when he noted that its inhabitants still sang hundreds of English and Scottish ballads that had been passed down to them from their ancestors. Commercial recordings of Appalachian musicians in the 1920s would have a significant impact on the development of country music
Country (also called country and western) is a genre of popular music that originated in the Southern and Southwestern United States in the early 1920s. It primarily derives from blues, church music such as Southern gospel and spirituals, ...
, bluegrass, and old-time music
Old-time music is a genre of North American folk music. It developed along with various North American folk dances, such as square dancing, clogging, and buck dancing. It is played on acoustic instruments, generally centering on a combinati ...
. Appalachian music saw a resurgence in popularity during the American folk music revival of the 1960s, when musicologists such as Mike Seeger
Mike Seeger (August 15, 1933August 7, 2009) was an American folk musician and folklorist. He was a distinctive singer and an accomplished musician who played autoharp, banjo, fiddle, dulcimer, guitar, mouth harp, mandolin, dobro, jaw harp, a ...
, John Cohen, and Ralph Rinzler traveled to remote parts of the region in search of musicians unaffected by modern music. Today, dozens of annual music festivals held throughout the region preserve the Appalachian music tradition.
Literature
 Early Appalachian literature typically centered on the observations of people from outside the region, such as Henry Timberlake's ''Memoirs'' (1765) and
Early Appalachian literature typically centered on the observations of people from outside the region, such as Henry Timberlake's ''Memoirs'' (1765) and Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was previously the natio ...
's ''Notes on the State of Virginia
''Notes on the State of Virginia'' (1785) is a book written by the American statesman, philosopher, and planter Thomas Jefferson. He completed the first version in 1781 and updated and enlarged the book in 1782 and 1783. It originated in Jeffers ...
'' (1784), although there are notable exceptions, including Davy Crockett's ''A Narrative of the Life of Davy Crockett'' (1834). Travellers' accounts published in 19th-century magazines gave rise to Appalachian local color, which reached its height with George Washington Harris's Sut Lovingood character of the 1860s and native novelists such as Mary Noailles Murfree. Works such as Rebecca Harding Davis's ''Life in the Iron Mills'' (1861), Emma Bell Miles' ''The Spirit of the Mountains'' (1905), Catherine Marshall's '' Christy'' (1912), Horace Kephart
Horace Sowers Kephart (September 8, 1862 – April 2, 1931) was an American travel writer and librarian, best known as the author of '' Our Southern Highlanders'' (a memoir about his life in the Great Smoky Mountains of western North Carolina) ...
's ''Our Southern Highlanders
''Our Southern Highlanders: A Narrative of Adventure in the Southern Appalachians and a Study of Life Among the Mountaineers'' is a book written by American author Horace Kephart (1862–1931), first published in 1913 and revised in 1922. Insp ...
'' (1913) marked a shift in the region's literature from local color to realism. The transition from an agrarian society to an industrial society and its effects on Appalachia are captured in works such as Olive Tilford Dargan's ''Call Home to the Heart'' (1932), Agnes Sligh Turnbull
Agnes Sligh Turnbull (October 14, 1888, New Alexandria, Pennsylvania – January 31, 1982, Livingston, New Jersey) was a bestselling United States, American writer, most noted for her works of historical fiction based in her native Western Penn ...
's '' The Rolling Years'' (1936), James Still's ''The River of Earth'' (1940), Harriette Simpson Arnow
Harriette Simpson Arnow (July 7, 1908 – March 22, 1986) was an American novelist and historian, who lived in Kentucky and Michigan. Arnow has been called an expert on the people of the Southern Appalachian Mountains, but she herself loved citie ...
's ''The Dollmaker'' (1954), and Harry Caudill's '' Night Comes to the Cumberlands'' (1962). In the 1970s and 1980s, the rise of authors like Breece D'J Pancake, Dorothy Allison, and Lisa Alther brought greater literary diversity to the region.Edwards, Grace Toney, "Literature – Introduction", ''Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2006), pp. 1035–39.
Along with the above-mentioned, some of Appalachia's best known writers include James Agee ('' A Death in the Family''), Anne W. Armstrong
Anne Wetzell Armstrong (September 20, 1872 – March 17, 1958) was an American novelist and businesswoman, active primarily in the first half of the 20th century. She is best known for her novel, ''This Day and Time'', an account of life in a ...
(''This Day and Time''), Wendell Berry
Wendell Erdman Berry (born August 5, 1934) is an American novelist, poet, essayist, environmental activist, cultural critic, and farmer. Closely identified with rural Kentucky, Berry developed many of his agrarian themes in the early essays of ...
(''Hannah Coulter'', ''The Unforeseen Wilderness: An Essay on Kentucky's Red River Gorge'', ''Selected Poems of Wendell Berry''), Jesse Stuart
Jesse may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Jesse (biblical figure), father of David in the Bible.
* Jesse (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters
* Jesse (surname), a list of people
Music
* ''Jesse'' ( ...
(''Taps for Private Tussie'', ''The Thread That Runs So True''), Denise Giardina
Denise Giardina is an American novelist. Her book '' Storming Heaven'' was a Discovery Selection of the Book-of-the-Month Club and received the 1987 W. D. Weatherford Award for the best published work about the Appalachian South. '' The Unquiet Ea ...
(''The Unquiet Earth'', ''Storming Heaven''), Lee Smith Lee Smith is the name of:
Arts, entertainment and media
*Lee Smith (fiction author) (born 1944), American author of fiction
* Lee Smith (film editor) (born 1960), Australian film editor
* Lee Smith (musician) (born 1983), American drummer
* Lee Sm ...
(''Fair and Tender Ladies'', ''On Agate Hill''), Silas House
Silas Dwane House (born August 7, 1971) is an American writer best known for his novels. He is also a music journalist, environmental activist, and columnist. House's fiction is known for its attention to the natural world, working class characte ...
(''Clay's Quilt'', ''A Parchment of Leaves''), Wilma Dykeman (''The Far Family'', ''The Tall Woman''), Keith Maillard (''Alex Driving South'', ''Light in the Company of Women'', ''Hazard Zones'', ''Gloria'', ''Running'', ''Morgantown'', ''Lyndon Johnson and the Majorettes'', ''Looking Good'') Maurice Manning (''Bucolics'', ''A Companion for Owls''), Anne Shelby (''Appalachian Studies'', ''We Keep a Store''), George Ella Lyon (''Borrowed Children'', ''Don't You Remember?''), Pamela Duncan (''Moon Women'', ''The Big Beautiful''), David Joy (''Where All Light Tends to Go'', ''The Weight of This World''), Chris Offutt (''No Heroes'', ''The Good Brother''), Charles Frazier
Charles Frazier (born November 4, 1950) is an American novelist. He won the 1997 National Book Award for Fiction for '' Cold Mountain''.
Biography
Early life
Frazier was born in Asheville, North Carolina, grew up in Andrews and Franklin, North ...
('' Cold Mountain'', ''Thirteen Moons''), Sharyn McCrumb
Sharyn McCrumb (born February 26, 1948) is an American writer whose books celebrate the history and folklore of Appalachia. McCrumb is the winner of numerous literary awards, and the author of the Elizabeth McPherson mystery series, the Ballad ...
(''The Hangman's Beautiful Daughter''), Robert Morgan (''Gap Creek''), Jim Wayne Miller
Jim Wayne Miller (October 21, 1936 – August 18, 1996) was an American poet and educator who had a major influence on literature in the Appalachian region.
Biography
Early years
Jim Wayne Miller was born on October 21, 1936, in Leicester, N ...
(''The Brier Poems''), Gurney Norman
Gurney Norman (born 1937) is an American writer, documentarian, and professor.
Biography
Gurney Norman was born in Grundy, Virginia, in 1937. He grew up in the southern Appalachian Mountains and was raised alternately by his maternal grandparen ...
(''Divine Right's Trip'', ''Kinfolks''), Ron Rash (''Serena''), Elizabeth Madox Roberts (''The Great Meadow'', ''The Time of Man''), Thomas Wolfe
Thomas Clayton Wolfe (October 3, 1900 – September 15, 1938) was an American novelist of the early 20th century.
Wolfe wrote four lengthy novels as well as many short stories, dramatic works, and novellas. He is known for mixing highly origin ...
(''Look Homeward Angel'', ''You Can't Go Home Again''), Rachel Carson
Rachel Louise Carson (May 27, 1907 – April 14, 1964) was an American marine biologist, writer, and conservationist whose influential book '' Silent Spring'' (1962) and other writings are credited with advancing the global environmental ...
('' The Sea Around Us'', ''Silent Spring
''Silent Spring'' is an environmental science book by Rachel Carson. Published on September 27, 1962, the book documented the environmental harm caused by the indiscriminate use of pesticides. Carson accused the chemical industry of spreading d ...
''; Presidential Medal of Freedom
The Presidential Medal of Freedom is the highest civilian award of the United States, along with the Congressional Gold Medal. It is an award bestowed by the president of the United States to recognize people who have made "an especially merit ...
), and Jeannette Walls
Jeannette Walls (born April 21, 1960) is an American author and journalist widely known as former gossip columnist for MSNBC.com and author of '' The Glass Castle'', a memoir of the nomadic family life of her childhood. Published in 2005, it had ...
(''The Glass Castle
''The Glass Castle'' is a 2005 memoir by American author Jeannette Walls. Walls recounts her dysfunctional and nomadic yet vibrant upbringing, emphasizing her resilience and her father's attempts toward redemption. Despite her family's flaws, t ...
'').
Appalachian literature crosses with the larger genre of Southern literature. Internationally renowned writers such as William Faulkner
William Cuthbert Faulkner (; September 25, 1897 – July 6, 1962) was an American writer known for his novels and short stories set in the fictional Yoknapatawpha County, based on Lafayette County, Mississippi, where Faulkner spent most o ...
and Cormac McCarthy
Cormac McCarthy (born Charles Joseph McCarthy Jr., July 20, 1933) is an American writer who has written twelve novels, two plays, five screenplays and three short stories, spanning the Western and post-apocalyptic genres. He is known for his gr ...
have made notable contributions to the American canon with tales set within Appalachia. McCarthy's '' Suttree'' (1979) is an intense vision of the squalidness and brutality of life along the Tennessee River
The Tennessee River is the largest tributary of the Ohio River. It is approximately long and is located in the southeastern United States in the Tennessee Valley. The river was once popularly known as the Cherokee River, among other name ...
, in the heart of Appalachia. Other McCarthy novels set in Appalachia include ''The Orchard Keeper
''The Orchard Keeper'' is the first novel by the American novelist Cormac McCarthy. It won the 1966 William Faulkner Foundation Award for notable first novel.
Plot
''The Orchard Keeper'' is set during the inter-war period in the hamlet of Red Br ...
'' (1968) and ''Child of God
''Child of God'' (1973) is the third novel by American author Cormac McCarthy. It depicts the life of a violent young outcast and serial killer in 1960s Appalachian Tennessee.
Though the novel received critical praise, it was not a financial ...
'' (1973). Appalachia also serves as the origin point for the kid, the protagonist of McCarthy's Western masterpiece ''Blood Meridian
''Blood Meridian or the Evening Redness in the West'' is a 1985 in literature, 1985 Epic (genre), epic novel by American author Cormac McCarthy, classified under the Western (genre), Western, or sometimes the Revisionist Western, anti-Western, g ...
''. Faulkner's hometown of Oxford, Mississippi
Oxford is a city and college town in the U.S. state of Mississippi. Oxford lies 75 miles (121 km) south-southeast of Memphis, Tennessee, and is the county seat of Lafayette County. Founded in 1837, it was named after the British city of Ox ...
, is on the borderlands of what is considered Appalachia, but his fictional Yoknapatawpha should be considered part of the region. Almost all of the fiction which earned him the Nobel Prize is set there, including '' Light in August'' and '' Absalom, Absalom''.
Folklore and legends
 Appalachian folklore has a strong mixture of European, Native American (especially
Appalachian folklore has a strong mixture of European, Native American (especially Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
), and Biblical influences. The Cherokee taught the region's early European pioneers how to plant and cultivate crops such as corn and squash
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
and how to find edible plants such as ramps
An inclined plane, also known as a ramp, is a flat supporting surface tilted at an angle from the vertical direction, with one end higher than the other, used as an aid for raising or lowering a load. The inclined plane is one of the six clas ...
. The Cherokee also passed along their knowledge of the medicinal properties of hundreds of native herbs and roots, and how to prepare tonics from such plants. Before the introduction of modern agricultural techniques in the region in the 1930s and 1940s, many Appalachian farmers followed the Biblical tradition of planting by "the signs", such as the phases of the moon
Concerning the lunar month of ~29.53 days as viewed from Earth, the lunar phase or Moon phase is the shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion, which can be expressed quantitatively using areas or angles, or described qualitatively using the t ...
, or when certain weather conditions occurred.
Cherokee folklore continues to influence storytelling in the Appalachians, including depictions and characteristics of regional animals. As told by Eastern Band Cherokee
The Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians (EBCI), (Cherokee: ᏣᎳᎩᏱ ᏕᏣᏓᏂᎸᎩ, ''Tsalagiyi Detsadanilvgi'') is a federally recognized Indian Tribe based in Western North Carolina in the United States. They are descended from the smal ...
and western North Carolina
Western North Carolina (often abbreviated as WNC) is the region of North Carolina which includes the Appalachian Mountains; it is often known geographically as the state's Mountain Region. It contains the highest mountains in the Eastern United ...
storyteller Jerry Wolfe, these creatures include the chipmunk
Chipmunks are small, striped rodents of the family Sciuridae. Chipmunks are found in North America, with the exception of the Siberian chipmunk which is found primarily in Asia.
Taxonomy and systematics
Chipmunks may be classified either as ...
, also known as "seven stripes" from an angry bear scratching him down the back—four claw marks and the spaces in between making seven—and the copperhead who sneaks and thieves his way into becoming venomous.
Appalachian folk tales are rooted in English, Scottish, and Irish fairy tales, as well as regional heroic figures and events. Jack tales
__NOTOC__
Jack is an English hero and archetypal stock character appearing in multiple legends, fairy tales, and nursery rhymes.
Examples of Jack tales
Some of the most famous Jack Tales are "Jack and the Beanstalk", "Jack Frost", " Jack the ...
, which tend to revolve around the exploits of a simple-but-dedicated figure named "Jack
Jack may refer to:
Places
* Jack, Alabama, US, an unincorporated community
* Jack, Missouri, US, an unincorporated community
* Jack County, Texas, a county in Texas, USA
People and fictional characters
* Jack (given name), a male given name, ...
", are popular at story-telling festivals. Other stories involve wild animals, such as hunting tales. In the industrial areas of western Pennsylvania and northern West Virginia the composite Joe Magarac steelworker story has been handed down. Regional folk heroes such as the railroad worker John Henry and frontiersmen Davy Crockett, Mike Fink
Mike Fink (also spelled Miche Phinck)O'Neil, Paul. ''The Old West: The Rivermen''. Time-Life Books, New York. 1975 p. 71 (c. 1770/1780 – c. 1823), called "king of the keelboaters", was a semi-legendary brawler and river boatman who exempli ...
and Johnny Appleseed
John Chapman (September 26, 1774March 18, 1845), better known as Johnny Appleseed, was an American pioneer nurseryman who introduced apple trees to large parts of Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, and Ontario, as well as the northern cou ...
are examples of real-life figures that evolved into popular folk tale subjects. Murder stories, such as Omie Wise and John Hardy, are popular subjects for Appalachian ballads. Ghost stories, or " haint tales" in regional English, are a common feature of southern oral and literary tradition. Ghost stories native to the region include the story of the Greenbrier Ghost, which is rooted in a Greenbrier County, West Virginia
Greenbrier County () is a county in the U.S. state of West Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 32,977. Its county seat is Lewisburg. The county was formed in 1778 from Botetourt and Montgomery counties in Virginia.
History
...
, murder.Deborah Thompson and Irene Moser, "Appalachian Folklife". ''A Handbook to Appalachia: An Introduction to the Region'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2006), pp. 143–56.
Several urban legends and horror stories have been rooted in the Appalachia region. Since the 1960s the Point Pleasant, West Virginia
Point Pleasant is a city in and the county seat of Mason County, West Virginia, United States, at the confluence of the Ohio and Kanawha Rivers. The population was 4,101 at the 2020 census. It is the principal city of the Point Pleasant, ...
, legend of Mothman
In West Virginia folklore, the Mothman is a humanoid creature reportedly seen in the Point Pleasant area from November 15, 1966, to December 15, 1967. The first newspaper report was published in the ''Point Pleasant Register'', dated ...
has originated and been explored in popular culture including the 2002 film '' The Mothman Prophecies'' loosely retelling the original tale. Since the 1910s, reports of glowing orbs around the Brown Mountain ridgeline in North Carolina have been the subject of paranormal theories including the ghost of slaves or Cherokee tribal warriors. Known as the Brown Mountain lights, the story has been adapted in popular culture, including an episode of the 1990s sci-fi drama ''The X-Files
''The X-Files'' is an American science fiction drama television series created by Chris Carter. The series revolves around Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) Special Agents Fox Mulder (David Duchovny) and Dana Scully (Gillian Anderson), who ...
''. The infamous story of the Bell Witch haunting in Tennessee has influenced several major films of the horror genre, including '' Poltergeist'', ''The Blair Witch Project
''The Blair Witch Project'' is a 1999 American supernatural horror film written, directed and edited by Daniel Myrick and Eduardo Sánchez. It is a fictional story of three student filmmakers—Heather Donahue, Michael C. Williams, and Josh ...
'', and the ''Paranormal Activity
Paranormal events are purported phenomena described in popular culture, folk, and other non-scientific bodies of knowledge, whose existence within these contexts is described as being beyond the scope of normal scientific understanding. Not ...
'' series.
Urban Appalachians
Urban Appalachians are people from Appalachia who are living in metropolitan areas outside the Appalachian region. In the decades following the Great Depression and World War II, many Appalachian residents moved to industrial cities in the north and west in a migration that became known as the "Hillbilly Highway In the United States, the Hillbilly Highway is the out-migration of Appalachians from the Appalachian Highlands region to industrial cities in northern, midwestern, and western states, primarily in the years following World War II in search of bette ...
". Mechanization of coal mining during the 1950s and 1960s was the major source of unemployment in central Appalachia. Many migration streams covered relatively short distances, with West Virginians moving to Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along the southern shore of Lake Erie, across the U.S. ...
and other cities in eastern and central Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, and eastern Kentuckians moving to Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Hamilton County. Settled in 1788, the city is located at the northern side of the confluence of the Licking and Ohio rivers, the latter of which marks the state line wit ...
and southwest Ohio in search of jobs. More distant cities like Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at t ...
and Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
attracted migrants from many states. Enclaves of Appalachian culture can still be found in some of these communities.
Communications
In the 1940s through the 1960s,Wheeling, West Virginia
Wheeling is a city in the U.S. state of West Virginia. Located almost entirely in Ohio County, of which it is the county seat, it lies along the Ohio River in the foothills of the Appalachian Mountains and also contains a tiny portion extending ...
, became a cultural center of the region because it had a clear-channel
A clear-channel station is an AM radio station in North America that has the highest protection from interference from other stations, particularly concerning night-time skywave propagation. The system exists to ensure the viability of cross-cou ...
AM radio station, WWVA, which could be heard throughout the entirety of the eastern United States at night. Although Pittsburgh's KDKA was a 50 kilowatt clear channel station that dated back to the early 1920s (as well as spanning all the East Coast in signal strength), WWVA prided itself on rural and farm programming that appealed to a wider audience in the rural region. Cincinnati's WLW
WLW (700 AM) is a commercial news/talk radio station licensed to Cincinnati, Ohio. Owned by iHeartMedia, WLW is a clear-channel station, often identifying itself as The Big One.
WLW operates with around the clock. Its daytime signal provides ...
also was relied on by many in the central and northern areas of Appalachia.
In the southern part of the region, WSB-AM
WSB (750 kHz) is a commercial AM radio station in Atlanta, Georgia. It airs a news/talk radio format, simulcast on Doraville-licensed WSBB-FM. WSB is the flagship station for Cox Media Group; in addition to WSB and WSBB-FM, it owns three o ...
Atlanta and WSM-AM
WSM (650 kHz) is a 50,000-watt clear channel AM radio station located in Nashville, Tennessee. It broadcasts a full-time country music format (with classic country and Americana leanings, the latter of which is branded as "Route 650") at 650& ...
Nashville, flagship of the '' Grand Ole Opry'', were major stations for the region's population during the 20th century, and remain strong in the sub-region.
Appalachian studies
Appalachia as an academic interest was the product of a critical scholarship that emerged across the disciplines in the 1960s and 1970s. With a renewed interest in issues of power, scholars could not dismiss the social inequity, class conflict, and environmental destruction encountered by America's so-called "hillbillies
Hillbilly is a term (often derogatory) for people who dwell in rural, mountainous areas in the United States, primarily in southern Appalachia and the Ozarks. The term was later used to refer to people from other rural and mountainous areas west ...
". Appalachia's emergence in academia is a result of the intersection between social conditions and critical academic interests, and has resulted in the development of many Appalachian studies programs in colleges and universities across the region, as well as in the Appalachian Studies Association.
Economy
The economy of Appalachia traditionally rested on agriculture, mining, timber, and in the cities, manufacturing. Since the late 20th century,tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mor ...
and second-home developments have assumed an increasingly major role.
Agriculture
 While the climate of the Appalachian region is suitable for agriculture, the region's hilly terrain greatly limits the size of the average farm, a problem exacerbated by population growth in the latter half of the 19th century.
While the climate of the Appalachian region is suitable for agriculture, the region's hilly terrain greatly limits the size of the average farm, a problem exacerbated by population growth in the latter half of the 19th century. Subsistence farming
Subsistence agriculture occurs when farmers grow food crops to meet the needs of themselves and their families on smallholdings. Subsistence agriculturalists target farm output for survival and for mostly local requirements, with little or no su ...
was the backbone of the Appalachian economy throughout much of the 19th century, and while economies in places such as western Pennsylvania, the Great Valley of Virginia, and the upper Tennessee Valley in east Tennessee, transitioned to a large-scale farming or manufacturing base around the time of the Civil War, subsistence farming remained an important part of the region's economy until the 1950s. In the early 20th century, Appalachian farmers were struggling to mechanize, and abusive farming practices had over the years left much of the already-limited farmland badly eroded. Various federal entities intervened in the 1930s to restore damaged areas and introduce less-harmful farming techniques. In recent decades, the concept of sustainable agriculture
Sustainable agriculture is farming in sustainable ways meeting society's present food and textile needs, without compromising the ability for current or future generations to meet their needs. It can be based on an understanding of ecosystem ser ...
has been applied to the region's small farms, with some success. Nevertheless, the number of farms in the Appalachian region continues to dwindle, plunging from 354,748 farms on in 1969 to 230,050 farms on in 1997.Best, Michael, and Curtis Wood, Introduction to the Agriculture section in the '' Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2006), pp. 395–402.
Early Appalachian farmers grew both crops introduced from their native Europe as well as crops native to North America (such as corn and squash
Squash may refer to:
Sports
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extremely one-sided match in professional wrestling
* Squash tennis, a game similar to squash but pla ...
). Tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
has long been an important cash crop in Southern Appalachia, especially since the land is ill-suited for cash crops such as cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor pe ...
. Apples have been grown in the region since the late 18th century, their cultivation being aided by the presence of thermal belts in the region's mountain valleys. Hogs, which could free range
Free range denotes a method of farming husbandry where the animals, for at least part of the day, can roam freely outdoors, rather than being confined in an enclosure for 24 hours each day.
On many farms, the outdoors ranging area is fenced, ...
in the region's abundant forests, often on chestnuts, were the most popular livestock among early Appalachian farmers. The American chestnut was also an important human food source until the chestnut blight struck in the 20th century. The early settlers also brought cattle and sheep to the region, which they would typically graze in highland meadows known as balds during the growing season when bottomlands were needed for crops. Cattle, mainly the Hereford, Angus, and Charolais breeds, are now the region's chief livestock.
Logging
 The mountains and valleys of Appalachia once contained what seemed to be an inexhaustible supply of timber. The poor roads, lack of railroads, and general inaccessibility of the region, however, prevented large-scale logging in most of the region throughout much of the 19th century. While logging firms were established in the Carolinas and the Kentucky River valley before the Civil War, most major firms preferred to harvest the more accessible timber stands in the Midwestern and Northeastern parts of the country. By the 1880s, these stands had been exhausted, and a spike in the demand for lumber forced logging firms to seek out the virgin forests of Appalachia.Paulson, Linda Daily, "Lumber Industry". ''Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2006), pp. 501–04. The first major logging ventures in Appalachia transported logs using mule teams or rivers, the latter method sometimes employing
The mountains and valleys of Appalachia once contained what seemed to be an inexhaustible supply of timber. The poor roads, lack of railroads, and general inaccessibility of the region, however, prevented large-scale logging in most of the region throughout much of the 19th century. While logging firms were established in the Carolinas and the Kentucky River valley before the Civil War, most major firms preferred to harvest the more accessible timber stands in the Midwestern and Northeastern parts of the country. By the 1880s, these stands had been exhausted, and a spike in the demand for lumber forced logging firms to seek out the virgin forests of Appalachia.Paulson, Linda Daily, "Lumber Industry". ''Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2006), pp. 501–04. The first major logging ventures in Appalachia transported logs using mule teams or rivers, the latter method sometimes employing splash dam
A splash dam was a temporary wooden dam used to raise the water level in streams to float logs downstream to sawmills. By impounding water and allowing it to be released on the log drive's schedule, these dams allowed many more logs to be brought ...
s. In the 1890s, innovations such as the Shay locomotive, the steam-powered loader, and the steam-powered skidder allowed massive harvesting of the most remote forest sections.
Logging in Appalachia reached its peak in the early 20th century, when firms such as the Ritter Lumber Company cut the virgin forests on an alarming scale, leading to the creation of national forests in 1911 and similar state entities to better manage the region's timber resources. Arguably the most successful logging firm in Appalachia was the Georgia Hardwood Lumber Company, established in 1927 and renamed Georgia-Pacific in 1948 when it expanded nationally. Although logging in Appalachia declined as the industry shifted focus to the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Tho ...
in the 1950s, rising overseas demand in the 1980s brought a resurgence in Appalachian logging. In 1987, there were 4,810 lumber firms operating in the region. In the late 1990s, the Appalachian lumber industry was a multibillion-dollar industry, employing 50,000 people in Tennessee, 26,000 in Kentucky, and 12,000 in West Virginia alone. By 1999, 1.4 million acres were extinguished as a result of deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated ...
by natural resource industries. Pollution from mining processes and disruption of the land ensued numerous environmental issues. Removal of vegetation and other alterations in the land increased erosion and flooding of surrounding areas. Water quality and aquatic life were also affected.
Coal mining
 Coal mining is the industry most frequently associated with the region in outsiders' minds, due in part to the fact that the region once produced two-thirds of the nation's coal. At present, however, the mining industry employs just 2% of the Appalachian workforce. The region's vast coalfield covers between northern Pennsylvania and central Alabama, mostly along the Cumberland Plateau and
Coal mining is the industry most frequently associated with the region in outsiders' minds, due in part to the fact that the region once produced two-thirds of the nation's coal. At present, however, the mining industry employs just 2% of the Appalachian workforce. The region's vast coalfield covers between northern Pennsylvania and central Alabama, mostly along the Cumberland Plateau and Allegheny Plateau
The Allegheny Plateau , in the United States, is a large dissected plateau area of the Appalachian Mountains in western and central New York (state), New York, northern and western Pennsylvania, northern and western West Virginia, and eastern Oh ...
regions. Most mining activity has been concentrated in eastern Kentucky, southwestern Virginia, West Virginia, and western Pennsylvania, with smaller operations in western Maryland
upright=1.2, An enlargeable map of Maryland's 23 counties and one independent city
Western Maryland, also known as the Maryland Panhandle, is the portion of the U.S. state of Maryland that typically consists of Washington, Allegany, and Garre ...
, Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
and Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
. The Pittsburgh coal seam
The Pittsburgh Coal Seam is the thickest and most extensive coal bed in the Appalachian Basin; hence, it is the most economically important coal bed in the eastern United States. The Upper Pennsylvanian Pittsburgh coal bed of the Monongahela Gro ...
, which has produced 13 billion tons of coal since the early 19th century, has been called the world's most valuable mineral deposit. There are over 60 major coal seams in West Virginia, and over 80 in eastern Kentucky. Most of the coal mined is bituminous
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term ...
, although significant anthracite deposits exist on the fringe of the region in central Pennsylvania.Abramson, Rudy, "Bituminous Coal Industry". ''Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2006), pp. 457–60. About two-thirds of Appalachia's coal is produced by underground mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic vi ...
, the rest by surface mining. Mountaintop removal
Mountaintop removal mining (MTR), also known as mountaintop mining (MTM), is a form of surface mining at the summit or summit ridge of a mountain. Coal seams are extracted from a mountain by removing the land, or overburden, above the seams. Thi ...
, a form of surface mining, is a highly controversial mining practice in central Appalachia due to its negative impacts on the environment and health of local residents.
In the late 19th century, the post-Civil War Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
and the expansion of the nation's railroads brought a soaring demand for coal, and mining operations expanded rapidly across Appalachia. Hundreds of thousands of workers poured into the region from across the United States and from overseas, essentially overhauling the cultural makeup of eastern Kentucky, West Virginia, and western Pennsylvania. Mining corporations gained considerable influence in state and municipal governments, especially as they often owned the entire towns in which the miners lived. The mining industry was vulnerable to economic downturns, however, and booms and busts were frequent, with major booms occurring during World War I and II, and the worst bust occurring during the Great Depression. The Appalachian mining industry also saw some of the nation's bloodiest labor strife between the 1890s and the 1930s. Mining-related injuries and deaths were not uncommon, and ailments such as black lung disease
Coal workers' pneumoconiosis (CWP), also known as black lung disease or black lung, is an occupational type of pneumoconiosis caused by long-term exposure to coal dust. It is common in coal miners and others who work with coal. It is similar to ...
afflicted miners throughout the 20th century. After World War II, innovations in mechanization (such as longwall mining) and competition from oil and natural gas led to a decline in the region's mining operations. Environmental restrictions, such as those placed on high- sulfur coal in the 1980s, brought further mine closures. While with annual earnings of $55,000, Appalachian miners make more than most other local workers, Appalachian coal mining employed just under 50,000 in 2004.
Coal mining has made a comeback in some regions in the early 21st century because of the increased prominence of Consol Energy
Consol Energy Inc. is an American energy company with interests in coal headquartered in the suburb of Cecil Township, in the Southpointe complex, just outside Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. In 2017, Consol formed two separate entities: CNX Resour ...
, based in Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Western Pennsylvania, the second-most populous city in Pennsylva ...
. The Quecreek Mine rescue in 2002 and continuing mine subsidence
Subsidence is a general term for downward vertical movement of the Earth's surface, which can be caused by both natural processes and human activities. Subsidence involves little or no horizontal movement, which distinguishes it from slope move ...
problems in abandoned coal mines in western Pennsylvania
Western Pennsylvania is a region in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, covering the western third of the state. Pittsburgh is the region's principal city, with a metropolitan area population of about 2.4 million people, and serves as its economic ...
as well as the Sago Mine disaster
The Sago Mine disaster was a coal mine explosion on January 2, 2006, at the Sago Mine in Sago, West Virginia, United States, near the Upshur County seat of Buckhannon. The blast and collapse trapped 13 miners for nearly two days; only one su ...
and Upper Big Branch Mine disaster in West Virginia and other regions have also been highlighted in recent times.
Manufacturing
 The manufacturing industry in Appalachia is rooted primarily in the ironworks and steelworks of early
The manufacturing industry in Appalachia is rooted primarily in the ironworks and steelworks of early Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Western Pennsylvania, the second-most populous city in Pennsylva ...
and Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1. ...
, and in the textile mills that sprang up in North Carolina's Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
region in the mid-19th century. Factory construction increased greatly after the Civil War, and the region experienced a manufacturing boom between 1890 and 1930. This economic shift led to a mass migration from small farms and rural areas to large urban centers, causing the populations of cities such as Birmingham, Knoxville, Tennessee
Knoxville is a city in and the county seat of Knox County in the U.S. state of Tennessee. As of the 2020 United States census, Knoxville's population was 190,740, making it the largest city in the East Tennessee Grand Division and the state' ...
, and Asheville, North Carolina, to swell exponentially. Manufacturing in the region suffered a setback during the Great Depression, but recovered during World War II and peaked in the 1950s and 1960s. However, difficulties paying retiree benefits, environmental struggles, and the signing of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) in 1994 led to a decline in the region's manufacturing operations. Pittsburgh lost 44% of its factory jobs in the 1980s, and between 1970 and 2001, the number of apparel workers in the Appalachian region decreased from 250,000 to 83,000 and the number of textile workers decreased from 275,000 to 193,000.Hurst, Jack, Introduction to Business, Technology, and Industry section, ''Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee, 2006), pp. 441–47.
U.S. Steel, founded in Pittsburgh in 1901, was the world's first corporation with more than a billion dollars in initial capitalization. Another Pittsburgh company, Alcoa, helped establish the nation's aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
industry in the early 20th century, and has had a significant impact on the economies of western Pennsylvania and east Tennessee. Union Carbide
Union Carbide Corporation is an American chemical corporation wholly owned subsidiary (since February 6, 2001) by Dow Chemical Company. Union Carbide produces chemicals and polymers that undergo one or more further conversions by customers befo ...
built the world's first petrochemical
Petrochemicals (sometimes abbreviated as petchems) are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable so ...
plant in Clendenin, West Virginia
Clendenin is a town in Kanawha County, West Virginia, United States, situated along the Elk River. The population was 850 at the 2020 census.
History
In the 1800s, Clendenin was a small settlement at the confluence of Big Sandy Creek and the Elk ...
, in 1920, and in subsequent years the Kanawha Valley
The Kanawha River ( ) is a tributary of the Ohio River, approximately 97 mi (156 km) long, in the U.S. state of West Virginia. The largest inland waterway in West Virginia, its valley has been a significant industrial region of the sta ...
became known as the "Chemical Capital of the World". Eastman Chemical, also established in 1920, is Tennessee's largest single employer. Companies such as Champion Fibre and Bowater
Bowater Inc. was a paper and pulp business headquartered in Greenville, South Carolina. It merged with Abitibi-Consolidated in 2007, and the combined company went on to become Resolute Forest Products.
History
The North American assets of Bow ...
established large pulp
Pulp may refer to:
* Pulp (fruit), the inner flesh of fruit
Engineering
* Dissolving pulp, highly purified cellulose used in fibre and film manufacture
* Pulp (paper), the fibrous material used to make paper
* Molded pulp, a packaging material
...
operations in Canton, North Carolina
Canton is the second largest town in Haywood County, North Carolina, United States. It is located about west of Asheville and is part of that city's metropolitan area. The town is named after the city of Canton, Ohio. The population was 4,227 a ...
, and Greenville, South Carolina, respectively, although the former was dogged by battles with environmentalists throughout the 20th century.
Tourism
 One of the region's oldest industries, tourism became a more important part of the Appalachian economy in the latter half of the 20th century as mining and manufacturing steadily declined.Howell, Benita, "Tourism". ''Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2006), pp. 611–16. In 2000–2001, tourism in Appalachia accounted for nearly $30 billion and over 600,000 jobs. The mountain terrain—with its accompanying scenery and outdoor recreational opportunities—provide the region's primary attractions. The region is home to one of the world's most well-known hiking trails (the
One of the region's oldest industries, tourism became a more important part of the Appalachian economy in the latter half of the 20th century as mining and manufacturing steadily declined.Howell, Benita, "Tourism". ''Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2006), pp. 611–16. In 2000–2001, tourism in Appalachia accounted for nearly $30 billion and over 600,000 jobs. The mountain terrain—with its accompanying scenery and outdoor recreational opportunities—provide the region's primary attractions. The region is home to one of the world's most well-known hiking trails (the Appalachian Trail
The Appalachian Trail (also called the A.T.), is a hiking trail in the Eastern United States, extending almost between Springer Mountain in Georgia and Mount Katahdin in Maine, and passing through 14 states.Gailey, Chris (2006)"Appalachian ...
), the nation's most-visited national park (the Great Smoky Mountains National Park
Great Smoky Mountains National Park is an American national park in the southeastern United States, with parts in North Carolina and Tennessee. The park straddles the ridgeline of the Great Smoky Mountains, part of the Blue Ridge Mountains, w ...
), and the nation's most visited national parkway (the Blue Ridge Parkway
The Blue Ridge Parkway is a National Parkway and All-American Road in the United States, noted for its scenic beauty. The parkway, which is America's longest linear park, runs for through 29 Virginia and North Carolina counties, linking Shenan ...
). The craft
A craft or trade is a pastime or an occupation that requires particular skills and knowledge of skilled work. In a historical sense, particularly the Middle Ages and earlier, the term is usually applied to people occupied in small scale pro ...
industry, including the teaching, selling, and display or demonstration of regional crafts, also accounts for an important part of the Appalachian economy, bringing (for example) over $100 million annually to the economy of western North Carolina and over $80 million to the economy of West Virginia. Important heritage tourism
Cultural heritage tourism (or just heritage tourism) is a branch of tourism oriented towards the cultural heritage of the location where tourism is occurring.
The National Trust for Historic Preservation in the United States defines heritage t ...
attractions in the region include the Biltmore Estate and the Eastern Band of the Cherokee
The Eastern Band of Cherokee Indians (EBCI), (Cherokee: ᏣᎳᎩᏱ ᏕᏣᏓᏂᎸᎩ, ''Tsalagiyi Detsadanilvgi'') is a federally recognized Indian Tribe based in Western North Carolina in the United States. They are descended from the smal ...
reservation in North Carolina, Cades Cove
Cades Cove is an isolated valley located in the Tennessee section of the Great Smoky Mountains National Park. The valley was home to numerous settlers before the formation of the national park. Today Cades Cove, the single most popular destinati ...
in Tennessee, and Harpers Ferry
Harpers Ferry is a historic town in Jefferson County, West Virginia. It is located in the lower Shenandoah Valley. The population was 285 at the 2020 census. Situated at the confluence of the Potomac and Shenandoah rivers, where the U.S. stat ...
in West Virginia. Important theme parks include Dollywood
Dollywood is a theme park jointly owned by entertainer Dolly Parton and Herschend Family Entertainment. It is located in the Knoxville metropolitan area in Pigeon Forge, Tennessee, near the gateway to The Great Smoky Mountains. Hosting nearly ...
and Ghost Town Village
Ghost Town Village (formerly "Ghost Town in the Sky at Ghost Mountain Park") is an abandoned Wild West-themed amusement park in Maggie Valley, North Carolina, United States that is currently, as of October 2019, under contract for possible sa ...
, both on the periphery of the Great Smoky Mountains
The Great Smoky Mountains (, ''Equa Dutsusdu Dodalv'') are a mountain range rising along the Tennessee–North Carolina border in the southeastern United States. They are a subrange of the Appalachian Mountains, and form part of the Blue Ridge ...
.
The mineral-rich mountain springs of the Appalachians—which for many years were thought to have health-restoring qualities—were drawing visitors to the region as early as the 18th century with the establishment of resorts at Hot Springs, Virginia
Hot Springs is a census-designated place (CDP) in Bath County, Virginia, United States. The population as of the 2010 Census was 738. It is located about southwest of Warm Springs on U.S. Route 220.
Hot Springs has several historic resorts, f ...
, White Sulphur Springs, West Virginia
White Sulphur Springs is a city in Greenbrier County in southeastern West Virginia, United States. The population was 2,231 at the 2020 census. The city emblem consists of five dandelion flowers and the citizens celebrate spring with an annual Da ...
, and what is now Hot Springs, North Carolina
Hot Springs is a town in Madison County, North Carolina, United States. The population was 560 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Asheville Metropolitan Statistical Area. It is a resort town, reliant on the tourist economy of its namesake spri ...
. Along with the mineral springs, the cool and clear air of the range's high elevations provided an escape for lowland elites, and elaborate hotels—such as The Greenbrier
The Greenbrier is a luxury resort located in the Allegheny Mountains near White Sulphur Springs in Greenbrier County, West Virginia, in the United States.
Since 1778, visitors have traveled to this part of the state to "take the waters" of th ...
in West Virginia and the Balsam Mountain Inn __NOTOC__
The Balsam Mountain Inn is an historic wooden Neoclassical architecture, Neo-Classical and Victorian architecture, Victorian hotel located at 68 Seven Springs Drive in Balsam, North Carolina, United States. In July, 1982, it was added to ...
in North Carolina—were built throughout the region's remote valleys and mountain slopes. The end of World War I (which opened up travel opportunities to Europe) and the arrival of the automobile (which changed the nation's vacation habits) led to the demise of all but a few of the region's spa resorts. The establishment of national parks in the 1930s brought an explosion of tourist traffic to the region, but created problems with urban sprawl
Urban sprawl (also known as suburban sprawl or urban encroachment) is defined as "the spreading of urban developments (such as houses and shopping centers) on undeveloped land near a city." Urban sprawl has been described as the unrestricted growt ...
in the various host communities. In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, states have placed greater focus on sustaining tourism while preserving host communities.
Poverty
 Poverty had plagued Appalachia for many years but was not brought to the attention of the rest of the United States until 1940, when James Agee and
Poverty had plagued Appalachia for many years but was not brought to the attention of the rest of the United States until 1940, when James Agee and Walker Evans
Walker Evans (November 3, 1903 – April 10, 1975) was an American photographer and photojournalist best known for his work for the Farm Security Administration (FSA) documenting the effects of the Great Depression. Much of Evans' work from ...
published '' Let Us Now Praise Famous Men'', a book that documented families in Appalachia during the Great Depression in words and photos. In 1963, John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination ...
established the President's Appalachian Regional Commission. His successor, Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
, crystallized Kennedy's efforts in the form of the Appalachian Regional Commission
The Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC) is a United States federal–state partnership that works with the people of Appalachia to create opportunities for self-sustaining economic development and improved quality of life. Congress established A ...
, which passed into law in 1965.
In Appalachia, severe poverty and desolation were paired with the necessity for careful cultural sensitivity. Many Appalachian people feared that the birth of a new modernized Appalachia would lead to the death of their traditional values and heritage. Because of the isolation of the region, Appalachian people had been unable to catch up to the modernization that lowlanders have achieved. In the 1960s, many people in Appalachia had a standard of living comparable to Third World
The term "Third World" arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact. The United States, Canada, Japan, South Korea, Western European nations and their allies represented the " First ...
countries'. Lyndon B. Johnson declared a "War on Poverty
The war on poverty is the unofficial name for legislation first introduced by United States President Lyndon B. Johnson during his State of the Union address on January 8, 1964. This legislation was proposed by Johnson in response to a national ...
" while standing on the front porch of an Inez, Kentucky
Inez ( ) is a home rule-class city in and the county seat of Martin County, Kentucky, United States. The population was 546 at the 2020 census.
Geography
Inez is located at (37.866431, -82.539058). According to the United States Census Burea ...
, home whose residents had been suffering from a long-ignored problem. The Appalachian Regional Development Act of 1965 stated:
Since the creation of the Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC) in 1965, the region has seen dramatic progress. New roads, schools, health care facilities, water and sewer systems, and other improvements have brought a better life to many Appalachian residents. In the 1960s, 219 counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
in the 13-state Appalachian Region were considered economically distressed. Now that list has been cut by more than half, to 82 counties, but these are "hard-core" pockets of poverty, seemingly impervious to all efforts at improving their lot.Appalachian Regional CommissioArc.gov
Martin County, Kentucky
Martin County is a county located in the U.S. state of Kentucky. As of the 2010 census, the population was 12,929. Its county seat is Inez. The county was founded in 1870 and is named for Congressman John Preston Martin. Warfield, Kentucky, ...
, the site of Johnson's 1964 speech, is one such county still ranked as "distressed" by the ARC. As of 2000, the per capita income
Per capita income (PCI) or total income measures the average income earned per person in a given area (city, region, country, etc.) in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area's total income by its total population.
Per capita i ...
in Martin County was $10,650, and 37% of its residents lived below the poverty line.
Like Johnson, President Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
brought attention to the remaining areas of poverty in Appalachia. On July 5, 1999, he made a public statement concerning the situation in Tyner, Kentucky. Clinton told the enthusiastic crowd:
The region's poverty has been documented often since the early 1960s. John Cohen documents rural lifestyle and culture in ''The High Lonesome Sound'', while photojournalist Earl Dotter has been visiting and documenting poverty, healthcare and mining in Appalachia for nearly forty years. Another photojournalist, Shelby Lee Adams, has been photographing Appalachian families and lifestyle for decades.
Poverty has caused health problems in the region. The diseases of despair
The diseases of despair are three classes of behavior-related medical conditions that increase in groups of people who experience despair due to a sense that their long-term social and economic prospects are bleak. The three disease types are dr ...
, including the opioid epidemic in the United States
In the United States, the opioid epidemic (also known as the opioid crisis) is an extensive ongoing overuse of opioid medications, both from medical prescriptions and from illegal sources. The epidemic began in the United States in the late ...
, and some diseases of poverty
Diseases of poverty (also known as poverty-related diseases) are diseases that are more prevalent in low-income populations. They include infectious diseases, as well as diseases related to malnutrition and poor health behaviour. Poverty is one o ...
are prevalent in Appalachia.
Tax revenue and absentee land ownership
In 1982 a seven-volume study conducted by the Appalachian Land Ownership Task Force was issued by the Appalachian Regional Commission which investigated the issue of absentee land ownership. The study covered 80 counties in six states approximating the area designated "Southern Appalachia" as defined by Thomas R. Ford's 1962 work. The states selected were Alabama (15 counties), Kentucky (12 counties), North Carolina (12 counties), Tennessee (14 counties), Virginia (12 counties), and West Virginia (15 counties). In its summary the report stated that "over 55,000 parcels of property in 80 counties were studied, representing some 20,000,000 acres of land and mineral rights..." It found that "41% of the 20 million acres of land and minerals...are held by only 50 private owners and 10 government agencies. The federal government is the single largest owner in Appalachia, holding over 2,000,000 acres." The study found that the extractive industries, i.e., timber, coal, etc., were "greatly underassessed for property tax purposes. Over 75% of the mineral owners in this survey pay under 25 cents per acre in property taxes." In the major coal counties surveyed the average tax per ton of known coal reserves is only $.0002 (1/50th of a cent).
The government-held lands are tax exempt, but the government makes a
In its summary the report stated that "over 55,000 parcels of property in 80 counties were studied, representing some 20,000,000 acres of land and mineral rights..." It found that "41% of the 20 million acres of land and minerals...are held by only 50 private owners and 10 government agencies. The federal government is the single largest owner in Appalachia, holding over 2,000,000 acres." The study found that the extractive industries, i.e., timber, coal, etc., were "greatly underassessed for property tax purposes. Over 75% of the mineral owners in this survey pay under 25 cents per acre in property taxes." In the major coal counties surveyed the average tax per ton of known coal reserves is only $.0002 (1/50th of a cent).
The government-held lands are tax exempt, but the government makes a payment in lieu of taxes A payment in lieu of taxes (usually abbreviated as PILOT, or sometimes as PILT) is a payment made to compensate a government for some or all of the property tax revenue lost due to tax exempt ownership or use of real property.
Canada
The federal g ...
, which is usually less than the normal tax rates.
"Taken together, the failure to tax minerals adequately, the underassessment of surface lands, and the revenue loss from concentrated federal holdings has a marked impact on local governments in Appalachia. The effect, essentially, is to produce a situation in which a) the small owners carry a disproportionate share of the tax burden; b) counties depend upon federal and state funds to provide revenues, while the large, corporate and absentee owners of the regions's resources go relatively tax-free; and c) citizens face a poverty of needed services despite the presence in their counties of taxable property wealth, especially in the form of coal and other natural resources."
In 2013, a similar study that concentrated solely on West Virginia found that 25 private owners hold 17.6% of the state's private land of 13 million acres. The federal government owns 1,133,587 acres in West Virginia, 7.4% of the total state acreage of 15,410,560 acres. In 11 counties the top ten absentee landowners own 41% to almost 72% of the private land in each county.
Appalachian Regional Commission
TheAppalachian Regional Commission
The Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC) is a United States federal–state partnership that works with the people of Appalachia to create opportunities for self-sustaining economic development and improved quality of life. Congress established A ...
(ARC) was created by the U.S. Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washin ...
in 1965 to bring poor areas of the 13 U.S. states of the main (southern) range of the Appalachians into the mainstream of the American economy. The commission is a partnership of federal, state, and local governments, and was created to promote economic growth and improve the quality of life in the region. The region as defined by the ARC includes 420 counties, including all of West Virginia; counties in 12 other states: Alabama, Georgia, Kentucky, Maryland, Mississippi, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Virginia; and also eight cities
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
in Virginia, where state law makes cities administratively separate from counties. The ARC is a planning, research, advocacy and funding organization; it does not have any governing powers.
The ARC's geographic range of coverage was defined broadly so as to cover as many economically underdeveloped areas as possible; it extends well beyond the area usually thought of as "Appalachia". For instance, parts of Alabama and Mississippi were included in the commission because of problems with unemployment and poverty similar to those in Appalachia proper, and the ARC region extends into the Northeastern states, which are not traditionally considered part of Appalachia culturally (though a "northern Appalachia" identity has emerged in recent times in parts of both NY and PA, particularly in rural areas). More recently, the Youngstown, Ohio
Youngstown is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio, and the largest city and county seat of Mahoning County. At the 2020 census, Youngstown had a city population of 60,068. It is a principal city of the Youngstown–Warren metropolitan area, whi ...
, region was declared part of Appalachia by the ARC due to the collapse of the steel industry in the region in the early 1980s and the continuing unemployment problems in the region since, though aside from Columbiana County, Ohio, the Youngstown DMA isn't traditionally or culturally considered part of the region. The ARC's wide scope also grew out of the " pork barrel" phenomenon, as politicians from outside the traditional Appalachia area saw a new way to bring home federal money to their areas. However, former Ohio governor Bob Taft
Robert Alphonso Taft III (born January 8, 1942) is an American politician and attorney, who served as the 67th governor of Ohio from 1999 to 2007 as a member of the Republican Party.
A member of the Taft political dynasty, Taft served first in ...
has stated, "What is good for Appalachia is good for all of Ohio."
Transportation
 Transportation has been the most challenging and expensive issue in Appalachia since the arrival of the first European settlers in the 18th century. With the exception of the October 1, 1940, opening of the
Transportation has been the most challenging and expensive issue in Appalachia since the arrival of the first European settlers in the 18th century. With the exception of the October 1, 1940, opening of the Pennsylvania Turnpike
The Pennsylvania Turnpike (Penna Turnpike or PA Turnpike) is a toll highway operated by the Pennsylvania Turnpike Commission (PTC) in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. A controlled-access highway, it runs for across the state. The turnpike's w ...
, the region's mountainous terrain continuously thwarted major federal intervention attempts at major road construction until the 1970s. This left large parts of the region virtually isolated and slowing economic growth. Before the Civil War, major cities in the region were connected via wagon roads to lowland areas, and flatboat
A flatboat (or broadhorn) was a rectangular flat-bottomed boat with square ends used to transport freight and passengers on inland waterways in the United States. The flatboat could be any size, but essentially it was a large, sturdy tub with a ...
s provided an important means for transporting goods out of the region. By 1900, railroads connected most of the region with the rest of the nation, although the poor roads made travel beyond railroad hubs difficult. When the Appalachian Regional Commission was created in 1965, road construction was considered its most important initiative, and in subsequent decades the commission spent more on road construction than all other projects combined.Burton, Mark, and Richard Hatcher, Introduction to Transportation section, ''Encyclopedia of Appalachia'' (Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2006), pp. 685–90.
The effort to connect Appalachia with the outside world has required numerous civil engineering feats. Millions of tons of rock were removed to build road segments such as Interstate 40
Interstate 40 (I-40) is a major east–west Interstate Highway running through the south-central portion of the United States. At a length of , it is the third-longest Interstate Highway in the country, after I-90 and I-80. From west to ea ...
through the Pigeon River Gorge at the Tennessee-North Carolina state line and U.S. Route 23 in Letcher County, Kentucky
Letcher County is a county located in the U.S. state of Kentucky. As of the 2020 census, the population was 21,548. Its county seat is Whitesburg. The county, founded in 1842, is named for Robert P. Letcher, Governor of Kentucky from 1840 t ...
. Large tunnels were built through mountain slopes at Cumberland Gap
The Cumberland Gap is a pass through the long ridge of the Cumberland Mountains, within the Appalachian Mountains, near the junction of the U.S. states of Kentucky, Virginia, and Tennessee. It is famous in American colonial history for its r ...
in 1996 to speed up travel along U.S. Route 25E, which acts as a regional arterial connecting Appalachia to the East Coast and the Great Lakes regions. The New River Gorge Bridge
The New River Gorge Bridge is a steel arch bridge long over the New River Gorge near Fayetteville, West Virginia, in the Appalachian Mountains of the eastern United States. With an arch long, the New River Gorge Bridge was the world's longest sin ...
in West Virginia, completed in 1977, was the longest and is now the fourth-longest single-arch bridge in the world. The Blue Ridge Parkway's Linn Cove Viaduct
The Linn Cove Viaduct is a long, concrete segmental bridge which snakes around Grandfather Mountain in western North Carolina. Completed in 1983 at a cost of $10 million, it was one of the last major construction projects on the Blue Ridge Parkw ...
, the construction of which required the assembly of 153 pre-cast segments up the slopes of Grandfather Mountain, has been designated a historic civil engineering landmark.
Physiographic provinces
The sixphysiographic province
physiographic province is a geographic region with a characteristic geomorphology, and often specific subsurface rock type or structural elements. The continents are subdivided into various physiographic provinces, each having a specific characte ...
s that in whole or in part are commonly treated as components of Appalachia are:
# Appalachian Plateau
The Appalachian Plateau is a series of rugged dissected plateaus located on the western side of the Appalachian Mountains. The Appalachian Mountains are a mountain range that run down the Eastern United States.
The Appalachian Plateau is the nor ...
# Allegheny Mountains
The Allegheny Mountain Range (; also spelled Alleghany or Allegany), informally the Alleghenies, is part of the vast Appalachian Mountain Range of the Eastern United States and Canada and posed a significant barrier to land travel in less devel ...
# Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians
The Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians, also called the Ridge and Valley Province or the Valley and Ridge Appalachians, are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian division and are also a belt within the Appalachian Mountains extending ...
# Great Appalachian Valley
The Great Appalachian Valley, also called The Great Valley or Great Valley Region, is one of the major landform features of eastern North America. It is a gigantic trough—a chain of valley lowlands—and the central feature of the Appalachian M ...
# Blue Ridge Mountains
The Blue Ridge Mountains are a Physiographic regions of the world, physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Mountains range. The mountain range is located in the Eastern United States, and extends 550 miles southwest from southern Pennsy ...
# Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
In popular culture
 Depictions of Appalachia and its inhabitants in popular media are typically negative, making the region an object of humor, derision, and social concern. Ledford writes, "Always part of the mythical South, Appalachia continues to languish backstage in the American drama, still dressed, in the popular mind at least, in the garments of backwardness, violence, poverty, and hopelessness." Otto argues that comic strips ''
Depictions of Appalachia and its inhabitants in popular media are typically negative, making the region an object of humor, derision, and social concern. Ledford writes, "Always part of the mythical South, Appalachia continues to languish backstage in the American drama, still dressed, in the popular mind at least, in the garments of backwardness, violence, poverty, and hopelessness." Otto argues that comic strips ''Li'l Abner
''Li'l Abner'' is a satirical American comic strip that appeared in many newspapers in the United States, Canada and Europe. It featured a fictional clan of hillbilly, hillbillies in the impoverished mountain village of Dogpatch, USA. Written a ...
'' by Al Capp and ''Barney Google
''Barney Google and Snuffy Smith'', originally ''Take Barney Google, F'rinstance'', is an American comic strip created by cartoonist Billy DeBeck. Since its debut on June 17, 1919, the strip has gained a large international readership, appearin ...
'' by Billy DeBeck, which both began in 1934, caricatured the laziness and weakness for "corn squeezin's" ( moonshine) of these "hillbillies". The popular 1960s '' Andy Griffith Show'' and ''The Beverly Hillbillies
''The Beverly Hillbillies'' is an American television sitcom that was broadcast on CBS from 1962 to 1971. It had an ensemble cast featuring Buddy Ebsen, Irene Ryan, Donna Douglas, and Max Baer Jr. as the Clampetts, a poor, backwoods family f ...
'' on television and James Dickey
James Lafayette Dickey (February 2, 1923 January 19, 1997) was an American poet and novelist. He was appointed the eighteenth United States Poet Laureate in 1966. He also received the Order of the South award.
Dickey is best known for his n ...
's 1970 novel ''Deliverance
''Deliverance'' is a 1972 American survival thriller film produced and directed by John Boorman, and starring Jon Voight, Burt Reynolds, Ned Beatty, and Ronny Cox, with the latter two making their feature film debuts. The screenplay was adapt ...
'' perpetuated the stereotype, although the region itself underwent so many changes after 1945 that it scarcely resembles the comic images.
* ''The Waltons
''The Waltons'' is an American historical drama television series about a family in rural Virginia during the Great Depression and World War II. It was created by Earl Hamner Jr., based on his 1961 book '' Spencer's Mountain'' and the 1963 fil ...
'' was a 1972-1981 television show which depicted a rural Virginia family during the Great Depression through World War 2
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
.
* '' The Trail of the Lonesome Pine'', '' The Little Shepherd of Kingdom Come'', and other early 20th-century novels of John Fox Jr., set in the Appalachian town of Big Stone Gap, Virginia
Big Stone Gap is a town in Wise County, Virginia, United States. The town was economically centered around the coal industry for much of its early development. The population was 5,643 at the 2010 census.
History
The community was formerly kno ...
, and surrounding areas, gave readers an image of frontier life in Appalachia and were made into popular films. Fox himself graduated from Harvard and was a bon vivant newspaperman in New York City. He returned home to the Cumberland Mountains
The Cumberland Mountains are a mountain range in the southeastern section of the Appalachian Mountains. They are located in western Virginia, southwestern West Virginia, the eastern edges of Kentucky, and eastern middle Tennessee, including the ...
of Tennessee to write his stories because of poor health.
* Big Stone Gap also is the setting for the early 21st-century ''Big Stone Gap'' series by Adriana Trigiani.
* The motion pictures '' Coal Miner's Daughter'' (based on the life of noted country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while ...
singer Loretta Lynn
Loretta Lynn (; April 14, 1932 – October 4, 2022) was an American country music singer and songwriter. In a career spanning six decades, Lynn released multiple gold albums. She had numerous hits such as "You Ain't Woman Enough (To Take My Ma ...
), ''Where the Lilies Bloom
''Where the Lilies Bloom'' is a 1974 American drama film adaptation of the novel by the same name, written by Bill and Vera Cleaver. The film was produced by Robert B. Radnitz and directed by William A. Graham in Watauga County (towns of Boon ...
'' and ''Songcatcher
''Songcatcher'' is a 2000 drama film directed by Maggie Greenwald. It is about a musicologist researching and collecting Appalachian folk music in the mountains of western North Carolina. Although ''Songcatcher'' is a fictional film, it is loosely ...
'' attempt an accurate portrayal of life in Appalachia which stresses the tensions between Appalachian traditions and the values of urbanized America.
* ''Songcatcher
''Songcatcher'' is a 2000 drama film directed by Maggie Greenwald. It is about a musicologist researching and collecting Appalachian folk music in the mountains of western North Carolina. Although ''Songcatcher'' is a fictional film, it is loosely ...
'' takes place in rural Appalachia in 1907 and features the "lost" ballads of the Scots-Irish brought over in the 19th century and a musicologist's quest to preserve them.
* '' Stranger With A Camera'' is a documentary film from Appalshop
Appalshop is a media, arts, and education center located in Whitesburg, Kentucky, in the heart of the southern Appalachian region of the United States.
History
Appalshop was founded in 1969 as the Appalachian Film Workshop, a project of the U ...
about the representation of Appalachian communities by outsiders in film and video.
* The 1972 film ''Deliverance
''Deliverance'' is a 1972 American survival thriller film produced and directed by John Boorman, and starring Jon Voight, Burt Reynolds, Ned Beatty, and Ronny Cox, with the latter two making their feature film debuts. The screenplay was adapt ...
'' takes place in southern Appalachia. The film perpetuated extremely negative stereotypes.
* Large-format
Large format refers to any imaging format of or larger. Large format is larger than "medium format", the or size of Hasselblad, Mamiya, Rollei, Kowa, and Pentax cameras (using 120- and 220-roll film), and much larger than the frame o ...
photographer Shelby Lee Adams, himself a son of Appalachian emigrants, has portrayed the Appalachian family life sympathetically in several books.
* '' Appalachian Spring'' is the name of a musical composition by Aaron Copland
Aaron Copland (, ; November 14, 1900December 2, 1990) was an American composer, composition teacher, writer, and later a conductor of his own and other American music. Copland was referred to by his peers and critics as "the Dean of American Com ...
and a ballet of the same name by Martha Graham. Copland did not intend for his music, which he composed for Graham and which incorporates Shaker melodies, to have an Appalachian theme. Graham gave the work its name; her ballet told the story of a young couple living on the frontier in western Pennsylvania.
* English composer Frederick Delius
Delius, photographed in 1907
Frederick Theodore Albert Delius ( 29 January 1862 – 10 June 1934), originally Fritz Delius, was an English composer. Born in Bradford in the north of England to a prosperous mercantile family, he resisted atte ...
wrote a theme and variations entitled ''Appalachia''; he first composed this music, subtitled "Variations on an Old Slave Song with final chorus", in 1896.
* Alan Hovhaness
Alan Hovhaness (; March 8, 1911 – June 21, 2000) was an American- Armenian composer. He was one of the most prolific 20th-century composers, with his official catalog comprising 67 numbered symphonies (surviving manuscripts indicate over 70) a ...
in 1985 composed a tone poem
A symphonic poem or tone poem is a piece of orchestral music, usually in a single continuous movement, which illustrates or evokes the content of a poem, short story, novel, painting, landscape, or other (non-musical) source. The German term ''T ...
named ''To the Appalachian Mountains'' (Symphony no. 60).
* Author Catherine Marshall wrote '' Christy'', loosely based on her mother's years as a teacher in the Appalachian region. The novel was highly popular and became the basis of a short-lived television series of the same name in 1994.
* The novel ''Prodigal Summer
''Prodigal Summer'' (2000) is the fifth novel by American author Barbara Kingsolver. Heavily emphasizing ecological themes and her trademark interweaving plots, this novel tells three stories of love, loss and connections in rural Virginia.
Pl ...
'' by Barbara Kingsolver explores the ecology of the region and how the removal of the predators, wolves and coyotes, affected the environment.
* Some comic strips often featured Appalachia, especially "Li'l Abner" by Al Capp (1909–1979). Inge notes that this comic strip, which ran 1934–77, largely ignored religion, politics, blacks and the Civil War, but instead focused its humor on the morality of Dogpatch, examining its memorable and often eccentric people who typically relied on violence to control the social order, and held deep to their faith in land, home, self-sufficiency, and antipathy to outsiders. Arnold finds that starting with World War II Capp increasingly emphasized sex and violence.
* "Face of Appalachia" is a song that appeared first on the album ''Tarzana Kid'' by John Sebastian
John Benson Sebastian (born March 17, 1944) is an American singer-songwriter, guitarist and harmonicist who founded the rock band The Lovin' Spoonful. He made an impromptu appearance at the Woodstock festival in 1969Lowell George, was described by Joel Canfield as follows: "Sebastian's lyrics weave a heart-rending picture of an old man's struggle to impart his childhood memories to his grandson; memories of places and people who no longer exist; of an era long gone." Cover versions of the song have been recorded by Valerie Carter (1977),
Coalfield Generations: Health, Mining and the Environment
''Southern Spaces'', July 16, 2008. * Drake, Richard B. ''A History of Appalachia'' (2001) * * Eller, Ronald D. ''Miners, Millhands, and Mountaineers: Industrialization of the Appalachian South, 1880–1930'' 1982. * Ford, Thomas R. ed. ''The Southern Appalachian Region: A Survey''. (1967), includes highly detailed statistics. *
text online
* Inscoe, John C. ''Movie-Made Appalachia: History, Hollywood, and the Highland South'' (U of North Carolina Press, 2020
online review
* Lee, Tom, "Southern Appalachia's Nineteenth-Century Bright Tobacco Boom: Industrialization, Urbanization, and the Culture of Tobacco", ''Agricultural History'' 88 (Spring 2014), 175–206
online
* Lewis, Ronald L. ''Transforming the Appalachian Countryside: Railroads, Deforestation, and Social Change in West Virginia, 1880–1920'' (1998
online edition
* Light, Melanie and Ken Light (2006). ''Coal Hollow''. Berkeley: University of California Press. * Noe, Kenneth W. and Shannon H. Wilson, ''Civil War in Appalachia'' (1997) * Obermiller, Phillip J., Thomas E. Wagner, and E. Bruce Tucker, editors (2000). ''Appalachian Odyssey: Historical Perspectives on the Great Migration.'' Westport, CT: Praeger. * Olson, Ted (1998). ''Blue Ridge Folklife''. University Press of Mississippi. * Pudup, Mary Beth, Dwight B. Billings, and Altina L. Waller, eds. ''Appalachia in the Making: The Mountain South in the Nineteenth Century''. (1995). * * Slap, Andrew L., (ed.) (2010). ''Reconstructing Appalachia: The Civil War's Aftermath'' Lexington, KY: University Press of Kentucky. * Stewart, Bruce E. (ed.) (2012). ''Blood in the Hills: A History of Violence in Appalachia.'' Lexington, KY: University Press of Kentucky. * Walls, David (1977)
"On the Naming of Appalachia"
''An Appalachian Symposium''. Edited by J. W. Williamson. Boone, NC: Appalachian State University Press. * Williams, John Alexander. ''Appalachia: A History'' (2002
online edition
* Woodard, Colin American Nations: A History of the Eleven Rival Regional Cultures of North America (2011)
Appalachian Journal
' Scholarly articles from 1972–present.
Space, Place, and Appalachia
A series about real and imagined spaces and places of Appalachia and their global connections in '' Southern Spaces''.
1965 Original Congressional definition
Appalachian Center for Civic Life
at
Appalachian Center for Craft
at
Appalachian Center for the Arts
Digital Library of Appalachia
Loyal Jones Appalachian Center
at
University of Kentucky Appalachian Center
* {{Authority control . . . Appalachian Mountains Eastern United States Hill people Regions of the Southern United States Regions of the United States Southeastern United States
Wendy Matthews
Wendy Joan Matthews (born 13 January 1960) is a Canadian-born Australian singer-songwriter who has been a member of Models and Absent Friends and is a solo artist. She released Top 20 hit singles in the 1990s including " Token Angels", " ...
(1992) and Julie Miller
Julie Anne Miller (born Julie Griffin, July 12, 1956) is a songwriter, singer, and recording artist living in Nashville, Tennessee. She married Buddy Miller in 1981. They sing and play on each other's solo projects and have recorded three duet ...
(1997).
* Much of the popular book series ''The Hunger Games
''The Hunger Games'' is a series of young adult dystopian novels written by American author Suzanne Collins. The first three novels are part of a trilogy following teenage protagonist Katniss Everdeen, and the fourth book is a prequel set 6 ...
'' is set in "an area that used to be called Appalachia" which is referred to in the book as District 12. Much of the surroundings and culture reflect present-day Appalachia, such as reliance on coal mining as an industry.
* The podcast "Old Gods of Appalachia" uses horror to examine Appalachian culture as well as the darker corners of its history.
See also
* Appalachian Center for Wilderness Medicine * Appalachian Ohio *Childbirth in rural Appalachia
Childbirth in rural Appalachia has long been a subject of concern amongst the population because infant mortality rates are higher in Appalachia than in other parts of the United States. Additionally, poor health in Uterus, utero, at birth, and in ...
* Environmental justice and coal mining in Appalachia
* Museum of Appalachia
The Museum of Appalachia, located in Norris, Tennessee, north of Knoxville, is a living history museum that interprets the pioneer and early 20th-century period of the Southern Appalachian region of the United States. Recently named an Affili ...
* Ozark culture
* Upland South
The Upland South and Upper South are two overlapping cultural and geographic subregions in the inland part of the Southern and lower Midwestern United States. They differ from the Deep South and Atlantic coastal plain by terrain, history, econom ...
References
Sources
* Abramson, Rudy, and Haskell, Jean, editors (2006). '' Encyclopedia of Appalachia'', University of Tennessee Press. * Becker, Jane S. ''Inventing Tradition: Appalachia and the Construction of an American Folk, 1930–1940'' (1998). * * * Davis, Donald Edward. ''Where There Are Mountains: An Environmental History of the Southern Appalachians'', 2000. * * Dotter, Earl.Coalfield Generations: Health, Mining and the Environment
''Southern Spaces'', July 16, 2008. * Drake, Richard B. ''A History of Appalachia'' (2001) * * Eller, Ronald D. ''Miners, Millhands, and Mountaineers: Industrialization of the Appalachian South, 1880–1930'' 1982. * Ford, Thomas R. ed. ''The Southern Appalachian Region: A Survey''. (1967), includes highly detailed statistics. *
text online
* Inscoe, John C. ''Movie-Made Appalachia: History, Hollywood, and the Highland South'' (U of North Carolina Press, 2020
online review
* Lee, Tom, "Southern Appalachia's Nineteenth-Century Bright Tobacco Boom: Industrialization, Urbanization, and the Culture of Tobacco", ''Agricultural History'' 88 (Spring 2014), 175–206
online
* Lewis, Ronald L. ''Transforming the Appalachian Countryside: Railroads, Deforestation, and Social Change in West Virginia, 1880–1920'' (1998
online edition
* Light, Melanie and Ken Light (2006). ''Coal Hollow''. Berkeley: University of California Press. * Noe, Kenneth W. and Shannon H. Wilson, ''Civil War in Appalachia'' (1997) * Obermiller, Phillip J., Thomas E. Wagner, and E. Bruce Tucker, editors (2000). ''Appalachian Odyssey: Historical Perspectives on the Great Migration.'' Westport, CT: Praeger. * Olson, Ted (1998). ''Blue Ridge Folklife''. University Press of Mississippi. * Pudup, Mary Beth, Dwight B. Billings, and Altina L. Waller, eds. ''Appalachia in the Making: The Mountain South in the Nineteenth Century''. (1995). * * Slap, Andrew L., (ed.) (2010). ''Reconstructing Appalachia: The Civil War's Aftermath'' Lexington, KY: University Press of Kentucky. * Stewart, Bruce E. (ed.) (2012). ''Blood in the Hills: A History of Violence in Appalachia.'' Lexington, KY: University Press of Kentucky. * Walls, David (1977)
"On the Naming of Appalachia"
''An Appalachian Symposium''. Edited by J. W. Williamson. Boone, NC: Appalachian State University Press. * Williams, John Alexander. ''Appalachia: A History'' (2002
online edition
* Woodard, Colin American Nations: A History of the Eleven Rival Regional Cultures of North America (2011)
Further reading
* A comprehensive series of articles on the region and the ARC. * * *Journals
*Appalachian Journal
' Scholarly articles from 1972–present.
Space, Place, and Appalachia
A series about real and imagined spaces and places of Appalachia and their global connections in '' Southern Spaces''.
External links
1965 Original Congressional definition
Appalachian Center for Civic Life
at
Emory and Henry College
Emory & Henry College (E&H or Emory) is a private liberal arts college in Emory, Virginia. The campus comprises of Washington County, which is part of the Appalachian highlands of Southwest Virginia. Founded in 1836, Emory & Henry College is ...
Appalachian Center for Craft
at
Tennessee Tech
Tennessee Technological University, commonly referred to as Tennessee Tech, is a public research university in Cookeville, Tennessee, United States. It was formerly known as Tennessee Polytechnic Institute, and before that as University of Dixie ...
Appalachian Center for the Arts
Digital Library of Appalachia
Loyal Jones Appalachian Center
at
Berea College
Berea College is a private liberal arts work college in Berea, Kentucky. Founded in 1855, Berea College was the first college in the Southern United States to be coeducational and racially integrated. Berea College charges no tuition; every a ...
University of Kentucky Appalachian Center
* {{Authority control . . . Appalachian Mountains Eastern United States Hill people Regions of the Southern United States Regions of the United States Southeastern United States