Solar maximum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
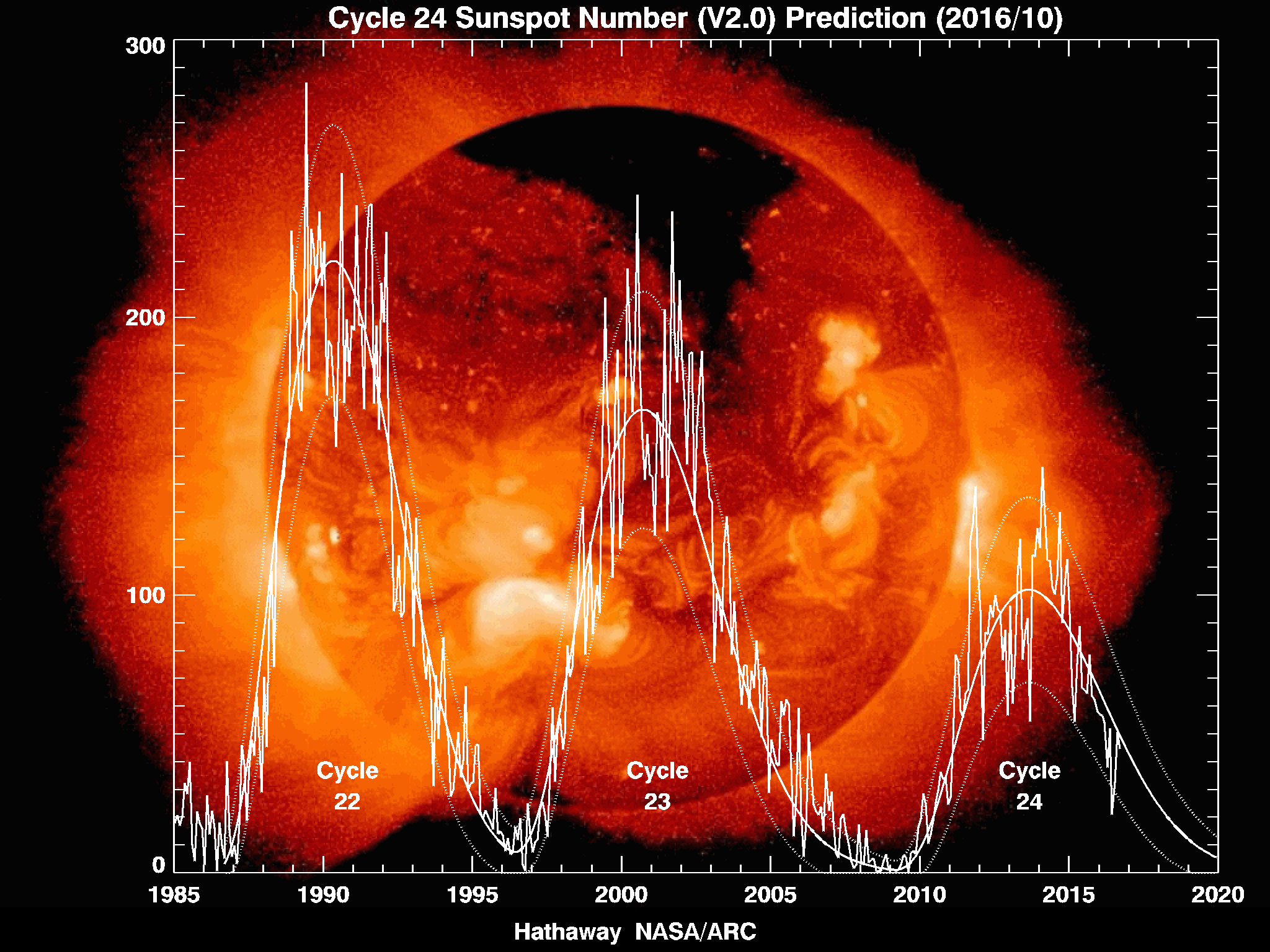 Solar maximum is the regular period of greatest solar activity during the Sun's 11-year
Solar maximum is the regular period of greatest solar activity during the Sun's 11-year  Large solar storms often occur during solar maximum. For example, the
Large solar storms often occur during solar maximum. For example, the
"Solar Storm Warning"
Science@NASA'', 10 March 2006, Accessed 26 Mar. 2010 However, the solar maximum was not declared to have occurred until 2014, and even then was ranked among the weakest on record.
 Solar maximum is the regular period of greatest solar activity during the Sun's 11-year
Solar maximum is the regular period of greatest solar activity during the Sun's 11-year solar cycle
The solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a nearly periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun's surf ...
. During solar maximum, large numbers of sunspot
Sunspots are phenomena on the Sun's photosphere that appear as temporary spots that are darker than the surrounding areas. They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic flux that inhibit convection. S ...
s appear, and the solar irradiance
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area ( surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument.
Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre ...
output grows by about 0.07%. On average, the solar cycle
The solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a nearly periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun's surf ...
takes about 11 years to go from one solar maximum to the next, with duration observed varying from 9 to 14 years.
 Large solar storms often occur during solar maximum. For example, the
Large solar storms often occur during solar maximum. For example, the Carrington Event
The Carrington Event was the most intense geomagnetic storm in recorded history, peaking from 1 to 2 September 1859 during solar cycle 10. It created strong auroral displays that were reported globally and caused sparking and even fires in mul ...
, which took place a few months before the solar maximum of solar cycle 10, was the most intense geomagnetic storm in recorded history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world his ...
and widely considered to have been caused by an equally large solar storm.
Predictions
Predictions of a future maximum's timing and strength are very difficult; predictions vary widely. There was a solar maximum in 2000. In 2006,NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeedin ...
initially expected a solar maximum in 2010 or 2011, and thought that it could be the strongest since 1958
Events
January
* January 1 – The European Economic Community (EEC) comes into being.
* January 3 – The West Indies Federation is formed.
* January 4
** Edmund Hillary's Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition completes the third ...
.Science@NASA'', 10 March 2006, Accessed 26 Mar. 2010 However, the solar maximum was not declared to have occurred until 2014, and even then was ranked among the weakest on record.
Grand solar minima and maxima
In addition to the ~11 year solar cycle, the intensity of the solar maxima can vary from cycle to cycle. When several solar cycles exhibit greater than average activity for decades or centuries, this period is labelled "Grand solar maximum". Solar cycles still occur during these grand solar maximum periods, but the intensity of those cycles is greater. Likewise, extended periods in which the solar maximum is lower than average are labeled "grand solar minima". Some researchers suggest that grand solar maxima have shown some correlation with global and regional climate changes, although others dispute this hypothesis (''e.g.'', seeMedieval Warm Period
The Medieval Warm Period (MWP), also known as the Medieval Climate Optimum or the Medieval Climatic Anomaly, was a time of warm climate in the North Atlantic region that lasted from to . Climate proxy records show peak warmth occurred at differe ...
).
Following the advent of telescopic solar observation with Galileo's 1611 observations, the intensity of solar maxima is typically measured by counting numbers and size of sunspots; for periods previous to this, isotope ratios in ice core
An ice core is a core sample that is typically removed from an ice sheet or a high mountain glacier. Since the ice forms from the incremental buildup of annual layers of snow, lower layers are older than upper ones, and an ice core contains ...
s can be used to estimate solar activity. The table below shows the approximate dates of some of the proposed solar minima in historical times.
The idea of a Modern Maximum has now been thrown into question with the release of a paper at the International Astronomical Union General Assembly in August 2015.
A proposed list of historical Grand minima of solar activity includes also Grand minima ca. 690 AD, 360 BC, 770 BC, 1390 BC, 2860 BC, 3340 BC, 3500 BC, 3630 BC, 3940 BC, 4230 BC, 4330 BC, 5260 BC, 5460 BC, 5620 BC, 5710 BC, 5990 BC, 6220 BC, 6400 BC, 7040 BC, 7310 BC, 7520 BC, 8220 BC, 9170 BC.
See also
*Solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the sol ...
* Solar variation
The solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a nearly periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun's surfa ...
* Solar minimum
* List of solar cycles Solar cycles are nearly periodic 11-year changes in the Sun's activity that are based on the number of sunspots present on the Sun's surface. The first solar cycle conventionally is said to start in 1755 when Rudolf Wolf began extensive reporting ...
– table of solar cycles
References
{{The Sun Solar phenomena