sodium-iodide symporter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The sodium/iodide cotransporter, also known as the sodium/iodide symporter (NIS), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLC5A5'' gene. It is a transmembrane glycoprotein with a molecular weight of 87 k Da and 13 transmembrane domains, which transports two sodium cations (Na+) for each iodide anion (I−) into the cell. NIS mediated uptake of iodide into follicular cells of the thyroid gland is the first step in the synthesis of
 Apart from thyroid cells NIS can also be found, although less expressed, in other tissues such as the
Apart from thyroid cells NIS can also be found, although less expressed, in other tissues such as the
thyroid hormone
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4
rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone
rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone
rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus
rect 66 216 386 25 ...
.
Iodine uptake
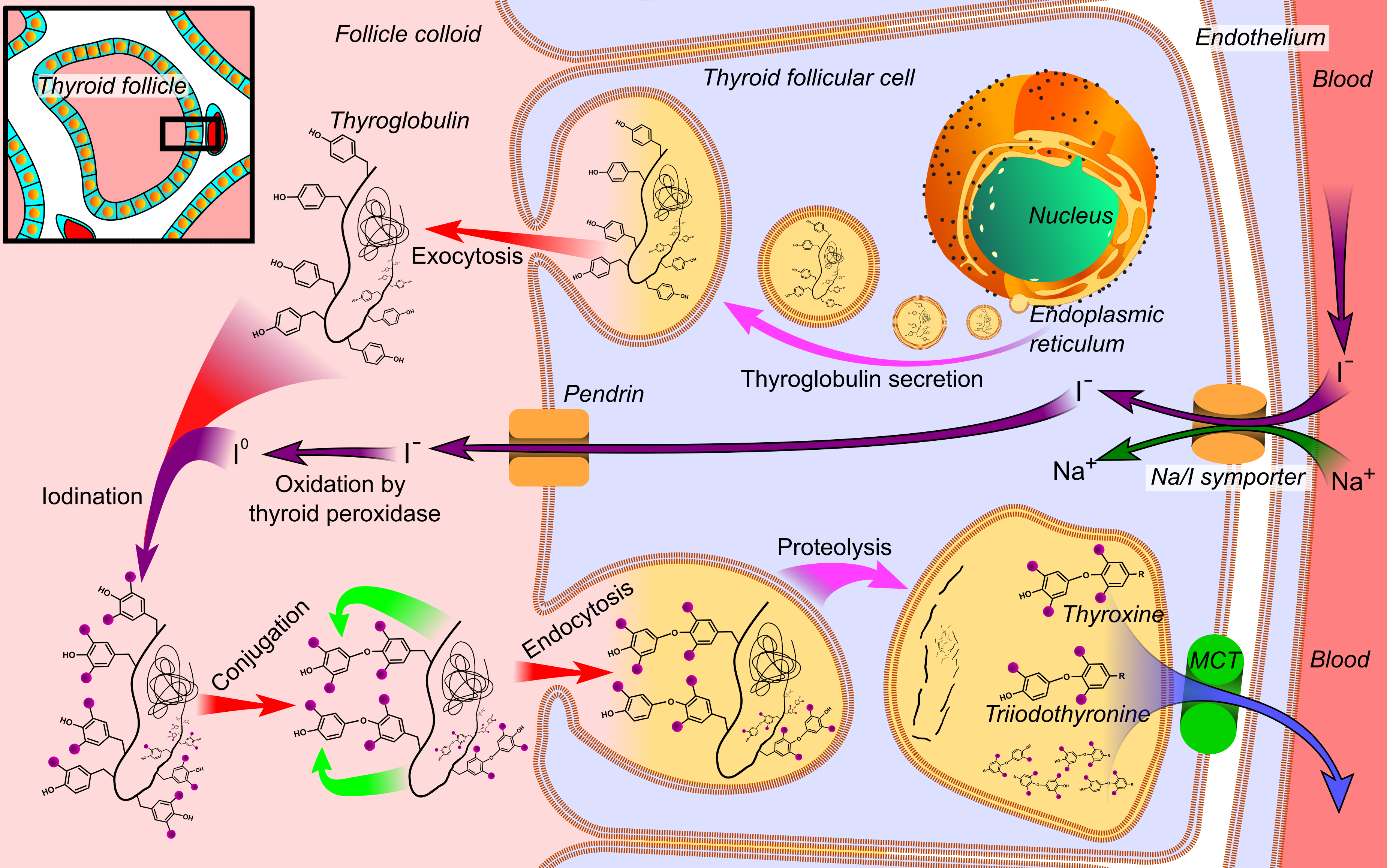
Iodine uptake mediated by thyroid follicular cells from the blood plasma is the first step for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. This ingested iodine is bound to serum proteins, especially toalbumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All the proteins of the albumin family are water-soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Albumins ...
s. The rest of the iodine which remains unlinked and free in bloodstream, is removed from the body through urine (the kidney is essential in the removal of iodine from extracellular space).
Iodine uptake is a result of an active transport
In cellular biology, ''active transport'' is the movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration—against the concentration gradient. Active transport requires cellul ...
mechanism mediated by the NIS protein, which is found in the basolateral membrane Epithelial polarity is one example of the cell polarity that is a fundamental feature of many types of cells. Epithelial cells feature distinct 'apical', 'lateral' and 'basal' plasma membrane domains. Epithelial cells connect to one another via th ...
of thyroid follicular cells. As a result of this active transport, iodide concentration inside follicular cells of thyroid tissue is 20 to 50 times higher than in the plasma. The transport of iodide across the cell membrane is driven by the electrochemical gradient
An electrochemical gradient is a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane. The gradient consists of two parts, the chemical gradient, or difference in solute concentration across a membrane, and ...
of sodium (the intracellular concentration of sodium is approximately 12 mM and extracellular concentration 140 mM). Once inside the follicular cells, the iodide diffuses to the apical membrane, where it is metabolically oxidized through the action of thyroid peroxidase to iodinium (I+) which in turn iodinates tyrosine residues of the thyroglobulin proteins in the follicle colloid. Thus, NIS is essential for the synthesis of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4).
 Apart from thyroid cells NIS can also be found, although less expressed, in other tissues such as the
Apart from thyroid cells NIS can also be found, although less expressed, in other tissues such as the salivary glands
The salivary glands in mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands (parotid, submandibular, and sublingual), as well as hundreds of minor salivary glands. Salivary glan ...
, the gastric mucosa, the kidney, the placenta, the ovaries
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. T ...
and the mammary glands during pregnancy and lactation. NIS expression in the mammary glands is quite a relevant fact since the regulation of iodide absorption and its presence in the breast milk is the main source of iodine for a newborn. Note that the regulation of NIS expression in thyroid is done by the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), whereas in breast is done by a combination of three molecules: prolactin
Prolactin (PRL), also known as lactotropin, is a protein best known for its role in enabling mammals to produce milk. It is influential in over 300 separate processes in various vertebrates, including humans. Prolactin is secreted from the p ...
, oxytocin
Oxytocin (Oxt or OT) is a peptide hormone and neuropeptide normally produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary. It plays a role in social bonding, reproduction, childbirth, and the period after childbirth. Oxytocin ...
and β-estradiol.
Inhibition by Environmental Chemicals
Some anions like perchlorate,pertechnetate
The pertechnetate ion () is an oxyanion with the chemical formula . It is often used as a convenient water-soluble source of isotopes of the radioactive element technetium (Tc). In particular it is used to carry the 99mTc isotope (half-life 6 hou ...
and thiocyanate, can affect iodide capture by competitive inhibition
Competitive inhibition is interruption of a chemical pathway owing to one chemical substance inhibiting the effect of another by competing with it for binding or bonding. Any metabolic or chemical messenger system can potentially be affected ...
because they can use the symporter when their concentration in plasma is high, even though they have less affinity for NIS than iodide has. Many plant cyanogenic glycosides
In chemistry, a glycoside is a molecule in which a sugar is bound to another functional group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides play numerous important roles in living organisms. Many plants store chemicals in the form of inactive glycosides. ...
, which are important pesticides, also act via inhibition of NIS in a large part of animal cells of herbivores and parasites and not in plant cells. Some evidence suggests that fluoride, such as that present in drinking water, may decrease cellular expression of the sodium/iodide symporter.
Using a validated ''in vitro'' radioactive iodide uptake (RAIU) assay, the Besides the traditionally known anions such as perchlorate, organic chemicals may also pose inhibition of iodide uptake via NIS.
Regulation in iodine uptake
The iodine transport mechanisms are closely submitted to the regulation of NIS expression. There are two kinds of regulation on NIS expression: positive and negative regulation. Positive regulation depends on TSH, which acts by transcriptional and posttranslational mechanisms. On the other hand, negative regulation depends on the plasmatic concentrations of iodide.Transcriptional regulation
At a transcriptional level, TSH regulates the thyroid's function throughcAMP
Camp may refer to:
Outdoor accommodation and recreation
* Campsite or campground, a recreational outdoor sleeping and eating site
* a temporary settlement for nomads
* Camp, a term used in New England, Northern Ontario and New Brunswick to descri ...
. TSH first binds to its receptors which are joined to G proteins, and then induces the activation of the enzyme adenylate cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction:
:A ...
, which will raise the intracellular levels of cAMP. This can activate the CREB
CREB-TF (CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein) is a cellular transcription factor. It binds to certain DNA sequences called cAMP response elements (CRE), thereby increasing or decreasing the transcription of the genes. CREB was first des ...
transcription factor (cAMP Response Element-Binding) that will bind to the CRE (cAMP Responsive Element). However, this might not occur and, instead, the increase in cAMP can be followed by PKA
PKA may refer to:
* Professionally known as:
** Pen name
** Stage persona
* p''K''a, the symbol for the acid dissociation constant at logarithmic scale
* Protein kinase A, a class of cAMP-dependent enzymes
* Pi Kappa Alpha, the North-American so ...
(Protein kinase A) activation and, as a result, the activation of the transcription factor Pax8
Paired box gene 8, also known as PAX8, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''PAX8'' gene.
Function
This gene is a member of the paired box (PAX) family of transcription factors. Members of this gene family typically encode proteins w ...
after phosphorylation.
These two transcription factors influence the activity of NUE (NIS Upstream Enhancer), which is essential for initiating transcription of NIS. NUE's activity depends on 4 relevant sites which have been identified by mutational analysis. The transcriptional factor Pax8 binds in two of these sites. Pax8 mutations lead to a decrease in the transcriptional activity of NUE. Another binding-site is the CRE, where the CREB binds, taking part in NIS transcription.
In contrast, growth factors such as IGF-1
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also called somatomedin C, is a hormone similar in molecular structure to insulin which plays an important role in childhood growth, and has anabolic effects in adults.
IGF-1 is a protein that in humans is ...
and TGF-β
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is a multifunctional cytokine belonging to the transforming growth factor superfamily that includes three different mammalian isoforms (TGF-β 1 to 3, HGNC symbols TGFB1, TGFB2, TGFB3) and many other s ...
(which is induced by the BRAF-V600E oncogene) suppress NIS gene expression, not letting NIS localize in the membrane.
Posttranslational regulation
The TSH can also regulate the iodide uptake at a posttranslational level, since, if it's absent, the NIS can be resorted from the basolateral membrane of the cell in to the cytoplasm where it is no longer functional. Therefore, the iodide uptake is reduced.Thyroid diseases
The lack of iodide transport inside follicular cells tends to cause goitres. There are some mutations in the NIS DNA that causehypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as po ...
and thyroid dyshormonogenesis
Thyroid dyshormonogenesis is a rare condition due to genetic defects in the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
It is due to either deficiency of thyroid enzymes, inability to concentrate, or ineffective binding. Signs and symptoms
Patients develop hy ...
.
Moreover, antibodies anti-NIS have been found in thyroid autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly a ...
s. Using RT-PCR
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is a laboratory technique combining reverse transcription of RNA into DNA (in this context called complementary DNA or cDNA) and amplification of specific DNA targets using polymerase chai ...
tests, it has been proved that there is no expression of NIS in cancer cells (which forms a thyroid carcinoma). Nevertheless, thanks to immunohistochemical techniques it is known that NIS is not functional in these cells, since it is mainly localized in the cytosol, and not in the basolateral membrane.
There is also a connection between the V600E mutation of the BRAF oncogene and papillary thyroid cancer
Papillary thyroid cancer or papillary thyroid carcinoma is the most common type of thyroid cancer, representing 75 percent to 85 percent of all thyroid cancer cases.Chapter 20 in: 8th edition. It occurs more frequently in women and presents in th ...
that cannot concentrate iodine into its follicular cells.
Use with radioiodine (131I)
The main goal for the treatment of non-thyroid carcinoma is the research of less aggressive procedures that could also provide less toxicity. One of these therapies is based on transferring NIS in cancer cells of different origin (breast, colon, prostate...) using adenoviruses or retroviruses ( viral vectors). This genetic technique is calledgene targeting
Gene targeting (also, replacement strategy based on homologous recombination) is a genetic technique that uses homologous recombination to modify an endogenous gene. The method can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene and modify ...
. Once NIS is transferred in these cells, the patient is treated with radioiodine (131I), being the result a low cancer cell survival rate. Therefore, a lot is expected from these therapies.
See also
*Symporter
A symporter is an integral membrane protein that is involved in the transport of two (or more) different molecules across the cell membrane in the same direction. The symporter works in the plasma membrane and molecules are transported across the ...
* Solute carrier family
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* * {{Thyroid hormone receptor modulators Solute carrier family Thyroid