snowbelt on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
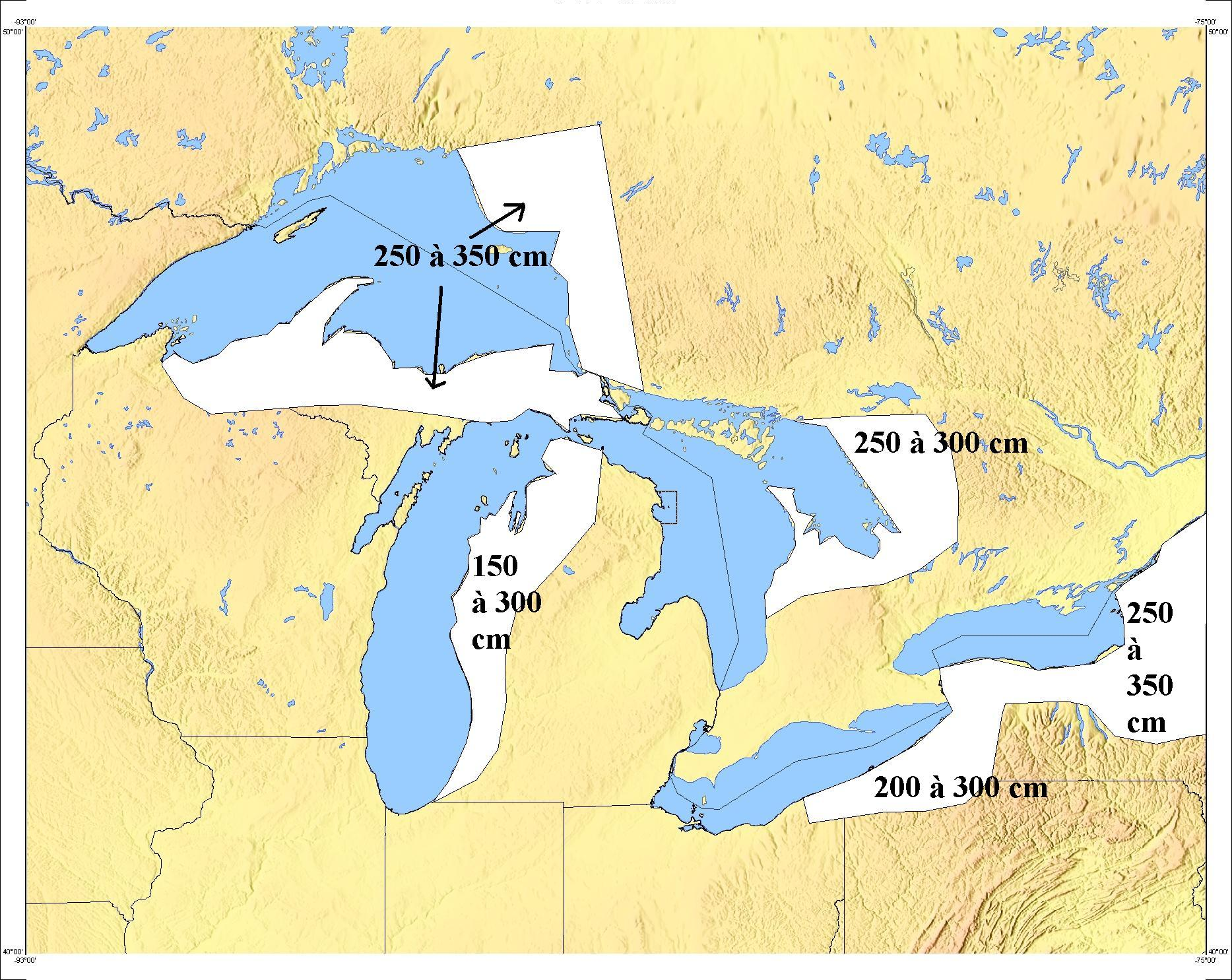 The Snowbelt is the region near the
The Snowbelt is the region near the

 In the
In the "Lake has great impacts on storm, weather"
''
 The Snowbelt is the region near the
The Snowbelt is the region near the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
where heavy snow
Snow comprises individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water throughout ...
fall in the form of lake-effect snow
Lake-effect snow is produced during cooler atmospheric conditions when a cold air mass moves across long expanses of warmer lake water. The lower layer of air, heated up by the lake water, picks up water vapor from the lake and rises up through ...
is particularly common. Snowbelts are typically found downwind of the lakes, principally off the eastern and southern shores.
Cause

Lake-effect snow
Lake-effect snow is produced during cooler atmospheric conditions when a cold air mass moves across long expanses of warmer lake water. The lower layer of air, heated up by the lake water, picks up water vapor from the lake and rises up through ...
occurs when cold air moves over warmer water, taking up moisture that later precipitates as snow when the air moves over land and cools. The lakes produce snowsquall
A snowsquall, or snow squall, is a sudden moderately heavy snowfall with blowing snow and strong, gusty surface winds. It is often referred to as a whiteout and is similar to a blizzard but is localized in time or in location and snow accumulat ...
s and persistently cloudy skies throughout the winter, as long as air temperatures are colder than water temperatures, or until a lake freezes over.
Location
 In the
In the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, snowbelts are located southeast of Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
from Cleveland, Ohio
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along the southern shore of Lake Erie, across the U.S. ...
, to Buffalo, New York
Buffalo is the second-largest city in the U.S. state of New York (behind only New York City) and the seat of Erie County. It is at the eastern end of Lake Erie, at the head of the Niagara River, and is across the Canadian border from South ...
, and south of Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border sp ...
stretching roughly from Rochester, New York
Rochester () is a City (New York), city in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, the county seat, seat of Monroe County, New York, Monroe County, and the fourth-most populous in the state after New York City, Buffalo, New York, Buffalo, ...
, over Syracuse, New York
Syracuse ( ) is a City (New York), city in and the county seat of Onondaga County, New York, Onondaga County, New York, United States. It is the fifth-most populous city in the state of New York following New York City, Buffalo, New York, Buffa ...
, to Utica, New York
Utica () is a Administrative divisions of New York, city in the Mohawk Valley and the county seat of Oneida County, New York, United States. The List of cities in New York, tenth-most-populous city in New York State, its population was 65,283 ...
, and northward to Watertown, New York
Watertown is a city in, and the county seat of, Jefferson County, New York, United States. It is approximately south of the Thousand Islands, along the Black River about east of where it flows into Lake Ontario. The city is bordered by the ...
. Other snowbelts are located on the eastern shore of Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume () and the third-largest by surface area (), after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that o ...
from Gary, Indiana
Gary is a city in Lake County, Indiana, United States. The city has been historically dominated by major industrial activity and is home to U.S. Steel's Gary Works, the largest steel mill complex in North America. Gary is located along the ...
, northward through Western Michigan
West Michigan and Western Michigan are terms for an arbitrary region in the U.S. state of Michigan's Lower Peninsula. Most narrowly it refers to the Grand Rapids-Muskegon-Holland, Michigan, Holland area, and more broadly to most of the region a ...
and Northern Michigan
Northern Michigan, also known as Northern Lower Michigan (known colloquially to residents of more southerly parts of the state and summer residents from cities such as Detroit as " Up North"), is a region of the U.S. state of Michigan. A popul ...
to the Straits of Mackinac
The Straits of Mackinac ( ; french: Détroit de Mackinac) are the short waterways between the U.S. state of Michigan's Upper and Lower Peninsulas, traversed by the Mackinac Bridge. The main strait is wide with a maximum depth of , and connects ...
, and on the eastern and southern shores of Lake Superior
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh wa ...
from northwest Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
through the northern half of the Upper Peninsula of Michigan
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Upper Michigan or colloquially the U.P. – is the northern and more elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; it is separated from the Lower Peninsula by t ...
.
Portions of the snowbelt are located in Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, which includes the eastern shore of Lake Superior from Sault Ste. Marie northward to Wawa, as well as the eastern and southern shores of Lake Huron
Lake Huron ( ) is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. Hydrology, Hydrologically, it comprises the easterly portion of Lake Michigan–Huron, having the same surface elevation as Lake Michigan, to which it is connected by the , Strait ...
and Georgian Bay
Georgian Bay (french: Baie Georgienne) is a large bay of Lake Huron, in the Laurentia bioregion. It is located entirely within the borders of Ontario, Canada. The main body of the bay lies east of the Bruce Peninsula and Manitoulin Island. To ...
from Parry Sound
Parry Sound is a sound or bay of Georgian Bay on Lake Huron, in Ontario, Canada. It is highly irregularly shaped with many deep bays and islands. Killbear Provincial Park is located on the large peninsula that separates the sound from Georgian B ...
to London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
. During the winter, north-westerly winds cause frequent road closures, with Highway 21 on the Lake Huron coast and Highway 26 south of Georgian Bay as far east as Barrie, Ontario
Barrie is a city in Southern Ontario, Canada, about north of Toronto. The city is within Simcoe County and located along the shores of Kempenfelt Bay, the western arm of Lake Simcoe. Although physically in Simcoe County, Barrie is politically i ...
, being strongly affected. The Niagara Peninsula
The Niagara Peninsula is an area of land lying between the southwestern shore of Lake Ontario and the northeastern shore of Lake Erie, in Ontario, Canada. Technically an isthmus rather than a peninsula, it stretches from the Niagara River in the ...
and the north-eastern shores of Lake Ontario are especially hard-hit by heavy snowfall when south-western winds are predominant.
Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
is the second smallest of the five Great Lakes and shallowest. It can completely freeze over during winter. Once frozen, lake-effect snow over land to the east and south of Lake Erie is temporarily alleviated. This does not end the possibility of a damaging winter storm. The Great Lakes Blizzard of 1977 that struck metropolitan Buffalo was a direct result of powder snow blown by high winds off Lake Erie, which had frozen earlier than normal. There was, for the region, no significant snowfall during the duration of the blizzard.
The southern and southeastern sides of the Great Salt Lake in Utah receive significant lake-effect snow. Since the Great Salt Lake never freezes, the lake effect can influence the weather along the Wasatch Front year-round. The lake effect largely contributes to the 55–80 inches (140–203 cm) annual snowfall amounts recorded south and east of the lake, and an average snowfall reaching 500 inches (13 m) in the Wasatch Range. The snow, which is often very light and dry because of the semiarid climate, is referred to as the "Greatest Snow on Earth" in the mountains. Lake-effect snow contributes to roughly six to eight snowfalls per year in Salt Lake City, with about 10% of the city's precipitation being contributed by the phenomenon.''
Deseret Morning News
The ''Deseret News'' () is the oldest continuously operating publication in the American west. Its multi-platform products feature journalism and commentary across the fields of politics, culture, family life, faith, sports, and entertainment. Th ...
'', August 5, 1999.
Skiing industries
Healthyskiing
Skiing is the use of skis to glide on snow. Variations of purpose include basic transport, a recreational activity, or a competitive winter sport. Many types of competitive skiing events are recognized by the International Olympic Committee (IO ...
industries have been established in snowbelt regions located near major cities such as Buffalo and Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the ancho ...
. The Erie/Ontario snowbelt, which extends to the northern slopes of the Allegheny Plateau
The Allegheny Plateau , in the United States, is a large dissected plateau area of the Appalachian Mountains in western and central New York, northern and western Pennsylvania, northern and western West Virginia, and eastern Ohio. It is divide ...
, has lent the region its nickname: ski country
Ski country is the hilly, snowy portions of the boundary between the Niagara Frontier and the Southern Tier of the western part of New York.
Weather
The area is a largely hilly terrain, mostly downwind from Lake Erie, Lake Ontario and the Fin ...
. To the south of Georgian Bay, ski resorts are found on the Niagara Escarpment
The Niagara Escarpment is a long escarpment, or cuesta, in Canada and the United States that runs predominantly east–west from New York through Ontario, Michigan, Wisconsin, and into Illinois. The escarpment is most famous as the cliff over ...
at Blue Mountain and on the Oro Moraine
The Oro Moraine is a glacial moraine in Simcoe County, Ontario, Canada.
The moraine covers north of Barrie, Ontario. The moraine drains into Georgian Bay on Lake Huron, and the smaller Lake Simcoe.
Water transporting layers within the mor ...
.
Outside North America
Ocean-effect snow
Lake-effect snow is produced during cooler atmospheric conditions when a cold air mass moves across long expanses of warmer lake water. The lower layer of air, heated up by the lake water, picks up water vapor from the lake and rises up through ...
conditions are found on the West side of the Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
ese island of Hokkaido
is Japan's second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost prefecture, making up its own region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; the two islands are connected by the undersea railway Seikan Tunnel.
The la ...
and the west side of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
's Kamchatka Peninsula
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: полуостров Камчатка, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and we ...
. There, cold winds blowing outward from the Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
n winter high pressure system
A high-pressure area, high, or anticyclone, is an area near the surface of a planet where the atmospheric pressure is greater than the pressure in the surrounding regions. Highs are middle-scale meteorological features that result from interpl ...
pick up moisture while crossing the Sea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it h ...
and the Sea of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk ( rus, Охо́тское мо́ре, Ohótskoye móre ; ja, オホーツク海, Ohōtsuku-kai) is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is located between Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands ...
and release it as heavy snowfall in Japan's snow country.
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
's east coast can be affected by similar conditions, particularly in the early winter when there is little ice on the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
.
See also
*Snow country (Japan)
refers to areas in Japan characterized by heavy, long-lasting snowfalls.
The rather poetic can refer to any place with heavy or deep snows and is generally understood as a reference to the Sea of Japan side of Honshū (Japan's main island) an ...
* Banana Belt
* Lake-effect snow
Lake-effect snow is produced during cooler atmospheric conditions when a cold air mass moves across long expanses of warmer lake water. The lower layer of air, heated up by the lake water, picks up water vapor from the lake and rises up through ...
* Great Salt Lake effect The Great Salt Lake effect is a small but detectable influence on the local climate and weather around the Great Salt Lake in Utah, United States. In particular, snowstorms are a common occurrence over the region and have major socio-economic impac ...
References
{{coord, 43, N, 78, W, scale:3000000, display=title Belt regions of the United States Geography of Canada Climate of the United States Climate of CanadaBelt
Belt may refer to:
Apparel
* Belt (clothing), a leather or fabric band worn around the waist
* Championship belt, a type of trophy used primarily in combat sports
* Colored belts, such as a black belt or red belt, worn by martial arts practit ...