snake venoms on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other
File:Tetrapodophis amplectus 3483.jpg, ''
 There are about 3,900 species of snakes, ranging as far northward as the Arctic Circle in Scandinavia and southward through Australia. Snakes can be found on every continent except Antarctica, as well as in the sea, and as high as in the
There are about 3,900 species of snakes, ranging as far northward as the Arctic Circle in Scandinavia and southward through Australia. Snakes can be found on every continent except Antarctica, as well as in the sea, and as high as in the

 Pit vipers, pythons, and some boas have infrared-sensitive receptors in deep grooves on the snout, allowing them to "see" the radiated heat of warm-blooded prey. In pit vipers, the grooves are located between the nostril and the eye in a large "pit" on each side of the head. Other infrared-sensitive snakes have multiple, smaller labial pits lining the upper lip, just below the nostrils.
A snake tracks its prey using smell, collecting airborne particles with its
Pit vipers, pythons, and some boas have infrared-sensitive receptors in deep grooves on the snout, allowing them to "see" the radiated heat of warm-blooded prey. In pit vipers, the grooves are located between the nostril and the eye in a large "pit" on each side of the head. Other infrared-sensitive snakes have multiple, smaller labial pits lining the upper lip, just below the nostrils.
A snake tracks its prey using smell, collecting airborne particles with its  The underside of a snake is very sensitive to vibration, allowing the snake to detect approaching animals by sensing faint vibrations in the ground.
Snake vision varies greatly between species. Some have keen eyesight and others are only able to distinguish light from dark, but the important trend is that a snake's visual perception is adequate enough to track movements. Generally, vision is best in tree-dwelling snakes and weakest in burrowing snakes. Some have
The underside of a snake is very sensitive to vibration, allowing the snake to detect approaching animals by sensing faint vibrations in the ground.
Snake vision varies greatly between species. Some have keen eyesight and others are only able to distinguish light from dark, but the important trend is that a snake's visual perception is adequate enough to track movements. Generally, vision is best in tree-dwelling snakes and weakest in burrowing snakes. Some have

 The skeleton of most snakes consists solely of the skull, hyoid, vertebral column, and ribs, though henophidian snakes retain vestiges of the pelvis and rear limbs.
The skull consists of a solid and complete
The skeleton of most snakes consists solely of the skull, hyoid, vertebral column, and ribs, though henophidian snakes retain vestiges of the pelvis and rear limbs.
The skull consists of a solid and complete
 Cobras, vipers, and closely related species use
Cobras, vipers, and closely related species use

 Snake embryonic development initially follows similar steps as any vertebrate embryo. The snake embryo begins as a
Snake embryonic development initially follows similar steps as any vertebrate embryo. The snake embryo begins as a  The elongation in snake body is accompanied by a significant increase in
The elongation in snake body is accompanied by a significant increase in
 In regions where winters are too cold for snakes to tolerate while remaining active, local species will enter a period of Dormancy#Brumation, brumation. Unlike Dormancy#Hibernation, hibernation, in which the dormant mammals are actually asleep, brumating reptiles are awake but inactive. Individual snakes may brumate in burrows, under rock piles, or inside fallen trees, or large numbers of snakes may clump together in Hibernaculum (zoology), hibernacula.
In regions where winters are too cold for snakes to tolerate while remaining active, local species will enter a period of Dormancy#Brumation, brumation. Unlike Dormancy#Hibernation, hibernation, in which the dormant mammals are actually asleep, brumating reptiles are awake but inactive. Individual snakes may brumate in burrows, under rock piles, or inside fallen trees, or large numbers of snakes may clump together in Hibernaculum (zoology), hibernacula.
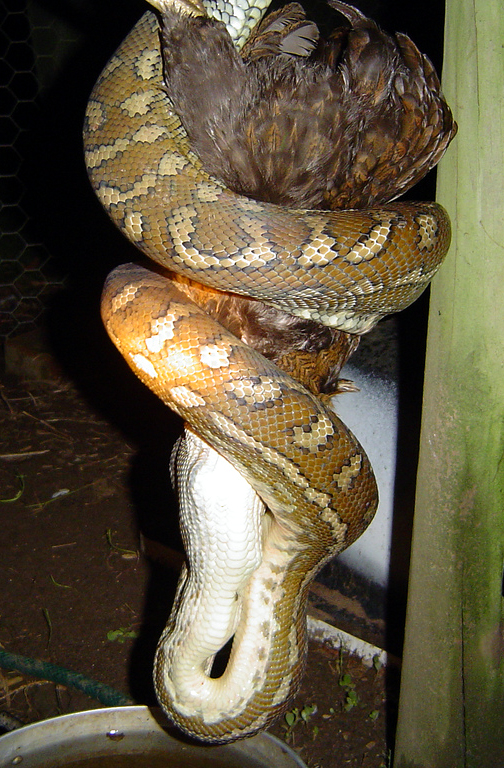
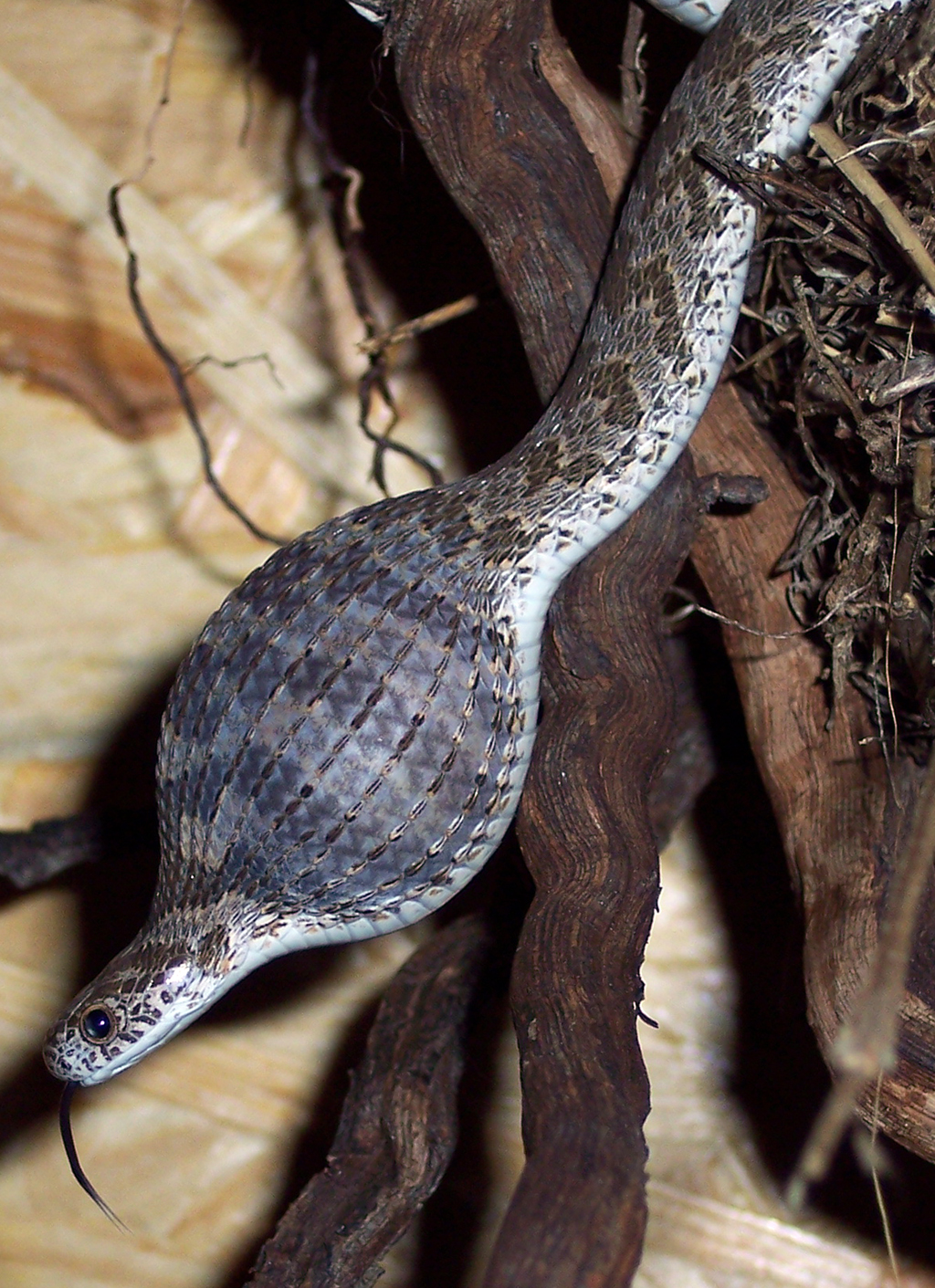 All snakes are hypercarnivore, strictly carnivorous, Predation, preying on small animals including lizards, frogs, other snakes, small mammals, birds, eggs, fish, snails, worms, and insects. Snakes cannot bite or tear their food to pieces so must swallow their prey whole. The eating habits of a snake are largely influenced by body size; smaller snakes eat smaller prey. Juvenile pythons might start out feeding on lizards or mice and graduate to small deer or antelope as an adult, for example.
The snake's jaw is a complex structure. Contrary to the popular belief that snakes can dislocate their jaws, they have an extremely flexible mandible, lower jaw, the two halves of which are not rigidly attached, and numerous other joints in the skull, which allow the snake to open its mouth wide enough to swallow prey whole, even if it is larger in diameter than the snake itself. For example, the Dasypeltis, African egg-eating snake has flexible jaws adapted for eating eggs much larger than the diameter of its head. This snake has no teeth, but does have bony protrusions on the inside edge of its Vertebral column, spine, which it uses to break the shell when eating eggs.
All snakes are hypercarnivore, strictly carnivorous, Predation, preying on small animals including lizards, frogs, other snakes, small mammals, birds, eggs, fish, snails, worms, and insects. Snakes cannot bite or tear their food to pieces so must swallow their prey whole. The eating habits of a snake are largely influenced by body size; smaller snakes eat smaller prey. Juvenile pythons might start out feeding on lizards or mice and graduate to small deer or antelope as an adult, for example.
The snake's jaw is a complex structure. Contrary to the popular belief that snakes can dislocate their jaws, they have an extremely flexible mandible, lower jaw, the two halves of which are not rigidly attached, and numerous other joints in the skull, which allow the snake to open its mouth wide enough to swallow prey whole, even if it is larger in diameter than the snake itself. For example, the Dasypeltis, African egg-eating snake has flexible jaws adapted for eating eggs much larger than the diameter of its head. This snake has no teeth, but does have bony protrusions on the inside edge of its Vertebral column, spine, which it uses to break the shell when eating eggs.
 The majority of snakes eat a variety of prey animals, but there is some specialization in certain species. King cobras and the Australian Vermicella annulata, bandy-bandy consume other snakes. Species of the family Pareidae have more teeth on the right side of their mouths than on the left, as they mostly prey on snails and the shells usually spiral clockwise.
Some snakes have a venomous bite, which they use to kill their prey before eating it. Other snakes kill their prey by
The majority of snakes eat a variety of prey animals, but there is some specialization in certain species. King cobras and the Australian Vermicella annulata, bandy-bandy consume other snakes. Species of the family Pareidae have more teeth on the right side of their mouths than on the left, as they mostly prey on snails and the shells usually spiral clockwise.
Some snakes have a venomous bite, which they use to kill their prey before eating it. Other snakes kill their prey by  After eating, snakes become dormant to allow the process of digestion to take place; this is an intense activity, especially after consumption of large prey. In species that feed only sporadically, the entire intestine enters a reduced state between meals to conserve energy. The digestive system is then 'up-regulated' to full capacity within 48 hours of prey consumption. Being
After eating, snakes become dormant to allow the process of digestion to take place; this is an intense activity, especially after consumption of large prey. In species that feed only sporadically, the entire intestine enters a reduced state between meals to conserve energy. The digestive system is then 'up-regulated' to full capacity within 48 hours of prey consumption. Being
 Lateral undulation is the sole mode of aquatic locomotion, and the most common mode of terrestrial locomotion. In this mode, the body of the snake alternately flexes to the left and right, resulting in a series of rearward-moving "waves". While this movement appears rapid, snakes have rarely been documented moving faster than two body-lengths per second, often much less. This mode of movement has the same net cost of transport (calories burned per meter moved) as running in lizards of the same mass.
Terrestrial lateral undulation is the most common mode of terrestrial locomotion for most snake species. In this mode, the posteriorly moving waves push against contact points in the environment, such as rocks, twigs, irregularities in the soil, etc. Each of these environmental objects, in turn, generates a reaction force directed forward and towards the midline of the snake, resulting in forward thrust while the lateral components cancel out. The speed of this movement depends upon the density of push-points in the environment, with a medium density of about 8 along the snake's length being ideal. The wave speed is precisely the same as the snake speed, and as a result, every point on the snake's body follows the path of the point ahead of it, allowing snakes to move through very dense vegetation and small openings.
When swimming, the waves become larger as they move down the snake's body, and the wave travels backwards faster than the snake moves forwards. Thrust is generated by pushing their body against the water, resulting in the observed slip. In spite of overall similarities, studies show that the pattern of muscle activation is different in aquatic versus terrestrial lateral undulation, which justifies calling them separate modes. All snakes can laterally undulate forward (with backward-moving waves), but only sea snakes have been observed reversing the motion (moving backwards with forward-moving waves).
Lateral undulation is the sole mode of aquatic locomotion, and the most common mode of terrestrial locomotion. In this mode, the body of the snake alternately flexes to the left and right, resulting in a series of rearward-moving "waves". While this movement appears rapid, snakes have rarely been documented moving faster than two body-lengths per second, often much less. This mode of movement has the same net cost of transport (calories burned per meter moved) as running in lizards of the same mass.
Terrestrial lateral undulation is the most common mode of terrestrial locomotion for most snake species. In this mode, the posteriorly moving waves push against contact points in the environment, such as rocks, twigs, irregularities in the soil, etc. Each of these environmental objects, in turn, generates a reaction force directed forward and towards the midline of the snake, resulting in forward thrust while the lateral components cancel out. The speed of this movement depends upon the density of push-points in the environment, with a medium density of about 8 along the snake's length being ideal. The wave speed is precisely the same as the snake speed, and as a result, every point on the snake's body follows the path of the point ahead of it, allowing snakes to move through very dense vegetation and small openings.
When swimming, the waves become larger as they move down the snake's body, and the wave travels backwards faster than the snake moves forwards. Thrust is generated by pushing their body against the water, resulting in the observed slip. In spite of overall similarities, studies show that the pattern of muscle activation is different in aquatic versus terrestrial lateral undulation, which justifies calling them separate modes. All snakes can laterally undulate forward (with backward-moving waves), but only sea snakes have been observed reversing the motion (moving backwards with forward-moving waves).
 Most often employed by colubroid snakes ( colubrids,
Most often employed by colubroid snakes ( colubrids,
 The movement of snakes in arboreal habitats has only recently been studied. While on tree branches, snakes use several modes of locomotion depending on species and bark texture. In general, snakes will use a modified form of concertina locomotion on smooth branches, but will laterally undulate if contact points are available. Snakes move faster on small branches and when contact points are present, in contrast to limbed animals, which do better on large branches with little 'clutter'.
Gliding snakes (''Chrysopelea'') of Southeast Asia launch themselves from branch tips, spreading their ribs and laterally undulating as they glide between trees. These snakes can perform a controlled glide for hundreds of feet depending upon launch altitude and can even turn in midair.
The movement of snakes in arboreal habitats has only recently been studied. While on tree branches, snakes use several modes of locomotion depending on species and bark texture. In general, snakes will use a modified form of concertina locomotion on smooth branches, but will laterally undulate if contact points are available. Snakes move faster on small branches and when contact points are present, in contrast to limbed animals, which do better on large branches with little 'clutter'.
Gliding snakes (''Chrysopelea'') of Southeast Asia launch themselves from branch tips, spreading their ribs and laterally undulating as they glide between trees. These snakes can perform a controlled glide for hundreds of feet depending upon launch altitude and can even turn in midair.
 In some parts of the world, especially in India, snake charming is a roadside show performed by a charmer. In such a show, the snake charmer carries a basket containing a snake that he seemingly charms by playing tunes with his flutelike musical instrument, to which the snake responds. The snake is in fact responding to the movement of the flute, not the sound it makes, as snakes lack external ears (though they do have internal ears).
The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 in India technically prohibits snake charming on the grounds of reducing animal cruelty. Other types of snake charmers use a snake and mongoose show, where the two animals have a mock fight; however, this is not very common, as the animals may be seriously injured or killed. Snake charming as a profession is dying out in India because of competition from modern forms of entertainment and environment laws proscribing the practice. Many Indians have never seen snake charming and it is becoming a folktale of the past.
In some parts of the world, especially in India, snake charming is a roadside show performed by a charmer. In such a show, the snake charmer carries a basket containing a snake that he seemingly charms by playing tunes with his flutelike musical instrument, to which the snake responds. The snake is in fact responding to the movement of the flute, not the sound it makes, as snakes lack external ears (though they do have internal ears).
The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 in India technically prohibits snake charming on the grounds of reducing animal cruelty. Other types of snake charmers use a snake and mongoose show, where the two animals have a mock fight; however, this is not very common, as the animals may be seriously injured or killed. Snake charming as a profession is dying out in India because of competition from modern forms of entertainment and environment laws proscribing the practice. Many Indians have never seen snake charming and it is becoming a folktale of the past.
 Although snakes are not commonly thought of as food, their consumption is acceptable in some cultures and may even be considered a delicacy. Snake soup is popular in Cantonese cuisine, consumed by locals in the autumn to warm their bodies. Western cultures document the consumption of snakes only under extreme circumstances of hunger, with the exception of cooked rattlesnake meat, which is commonly consumed in Texas and parts of the Midwestern United States.
Although snakes are not commonly thought of as food, their consumption is acceptable in some cultures and may even be considered a delicacy. Snake soup is popular in Cantonese cuisine, consumed by locals in the autumn to warm their bodies. Western cultures document the consumption of snakes only under extreme circumstances of hunger, with the exception of cooked rattlesnake meat, which is commonly consumed in Texas and parts of the Midwestern United States.
 In Asian countries such as China, Taiwan, Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, and Cambodia, drinking the blood of a snake—particularly the cobra—is believed to increase sexual virility. When possible, the blood is drained while the cobra is still alive, and it is usually mixed with some form of liquor to improve the taste.
The use of snakes in alcohol is accepted in some Asian countries. In such cases, one or more snakes are left to steep in a jar or container of liquor, as this is claimed to make the liquor stronger (as well as more expensive). One example of this is the Trimeresurus flavoviridis, Habu snake, which is sometimes placed in the Okinawan liqueur ''Habushu'' (ブ酒), also known as "Habu Sake".
Snake wine (蛇酒) is an alcoholic beverage produced by infusing whole snakes in Chinese alcoholic beverages, rice wine or grain alcohol. First recorded as being consumed in China during the Western Zhou dynasty, this drink is considered an important curative and is believed to reinvigorate a person according to traditional Chinese medicine.
In Asian countries such as China, Taiwan, Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, and Cambodia, drinking the blood of a snake—particularly the cobra—is believed to increase sexual virility. When possible, the blood is drained while the cobra is still alive, and it is usually mixed with some form of liquor to improve the taste.
The use of snakes in alcohol is accepted in some Asian countries. In such cases, one or more snakes are left to steep in a jar or container of liquor, as this is claimed to make the liquor stronger (as well as more expensive). One example of this is the Trimeresurus flavoviridis, Habu snake, which is sometimes placed in the Okinawan liqueur ''Habushu'' (ブ酒), also known as "Habu Sake".
Snake wine (蛇酒) is an alcoholic beverage produced by infusing whole snakes in Chinese alcoholic beverages, rice wine or grain alcohol. First recorded as being consumed in China during the Western Zhou dynasty, this drink is considered an important curative and is believed to reinvigorate a person according to traditional Chinese medicine.




 In Mesopotamia, ancient Mesopotamia, Nirah, the messenger god of Ištaran, was represented as a serpent on ''kudurrus'', or boundary marker, boundary stones. Representations of two intertwined serpents are common in Sumerian art and Neo-Sumerian artwork and still appear sporadically on cylinder seals and amulets until as late as the thirteenth century BC. The horned viper (''Cerastes cerastes'') appears in Kassites, Kassite and Neo-Assyrian Empire, Neo-Assyrian kudurrus and is invoked in Assyrian texts as a magical protective entity. A dragon-like creature with horns, the body and neck of a snake, the forelegs of a lion, and the hind-legs of a bird appears in Mesopotamian art from the Akkadian Period until the Hellenistic Period (323 BC–31 BC). This creature, known in Akkadian language, Akkadian as the ''mušḫuššu'', meaning "furious serpent", was used as a symbol for particular deities and also as a general protective emblem. It seems to have originally been the attendant of the Underworld god Ninazu, but later became the attendant to the Hurrian religion, Hurrian storm-god Tishpak, as well as, later, Ninazu's son Ningishzida, the Babylonian national god Marduk, the scribal god Nabu, and the Assyrian national god Ashur.
In History of Egypt, Egyptian history, the snake occupies a primary role with the Nile cobra adorning the crown of the pharaoh in ancient times. It was snake worship, worshipped as one of the gods and was also used for sinister purposes: murder of an adversary and ritual suicide (Cleopatra VII of Egypt, Cleopatra). The ouroboros was a well-known ancient Egyptian symbol of a serpent swallowing its own tail. The precursor to the ouroboros was the "Many-Faced", a serpent with five heads, who, according to the Amduat, the oldest surviving Book of the Dead, Book of the Afterlife, was said to coil around the corpse of the sun god Ra protectively. The earliest surviving depiction of a "true" ouroboros comes from the gilded shrines in KV62, the tomb of Tutankhamun. In the early centuries AD, the ouroboros was adopted as a symbol by Gnosticism, Gnostic Christians and chapter 136 of the ''Pistis Sophia'', an early Gnostic text, describes "a great dragon whose tail is in its mouth". In medieval alchemy, the ouroboros became a typical western dragon with wings, legs, and a tail.
In the Bible, King Nahash of Ammon, whose name means "Snake", is depicted very negatively, as a particularly cruel and despicable enemy of the ancient Hebrews.
In Mesopotamia, ancient Mesopotamia, Nirah, the messenger god of Ištaran, was represented as a serpent on ''kudurrus'', or boundary marker, boundary stones. Representations of two intertwined serpents are common in Sumerian art and Neo-Sumerian artwork and still appear sporadically on cylinder seals and amulets until as late as the thirteenth century BC. The horned viper (''Cerastes cerastes'') appears in Kassites, Kassite and Neo-Assyrian Empire, Neo-Assyrian kudurrus and is invoked in Assyrian texts as a magical protective entity. A dragon-like creature with horns, the body and neck of a snake, the forelegs of a lion, and the hind-legs of a bird appears in Mesopotamian art from the Akkadian Period until the Hellenistic Period (323 BC–31 BC). This creature, known in Akkadian language, Akkadian as the ''mušḫuššu'', meaning "furious serpent", was used as a symbol for particular deities and also as a general protective emblem. It seems to have originally been the attendant of the Underworld god Ninazu, but later became the attendant to the Hurrian religion, Hurrian storm-god Tishpak, as well as, later, Ninazu's son Ningishzida, the Babylonian national god Marduk, the scribal god Nabu, and the Assyrian national god Ashur.
In History of Egypt, Egyptian history, the snake occupies a primary role with the Nile cobra adorning the crown of the pharaoh in ancient times. It was snake worship, worshipped as one of the gods and was also used for sinister purposes: murder of an adversary and ritual suicide (Cleopatra VII of Egypt, Cleopatra). The ouroboros was a well-known ancient Egyptian symbol of a serpent swallowing its own tail. The precursor to the ouroboros was the "Many-Faced", a serpent with five heads, who, according to the Amduat, the oldest surviving Book of the Dead, Book of the Afterlife, was said to coil around the corpse of the sun god Ra protectively. The earliest surviving depiction of a "true" ouroboros comes from the gilded shrines in KV62, the tomb of Tutankhamun. In the early centuries AD, the ouroboros was adopted as a symbol by Gnosticism, Gnostic Christians and chapter 136 of the ''Pistis Sophia'', an early Gnostic text, describes "a great dragon whose tail is in its mouth". In medieval alchemy, the ouroboros became a typical western dragon with wings, legs, and a tail.
In the Bible, King Nahash of Ammon, whose name means "Snake", is depicted very negatively, as a particularly cruel and despicable enemy of the ancient Hebrews.
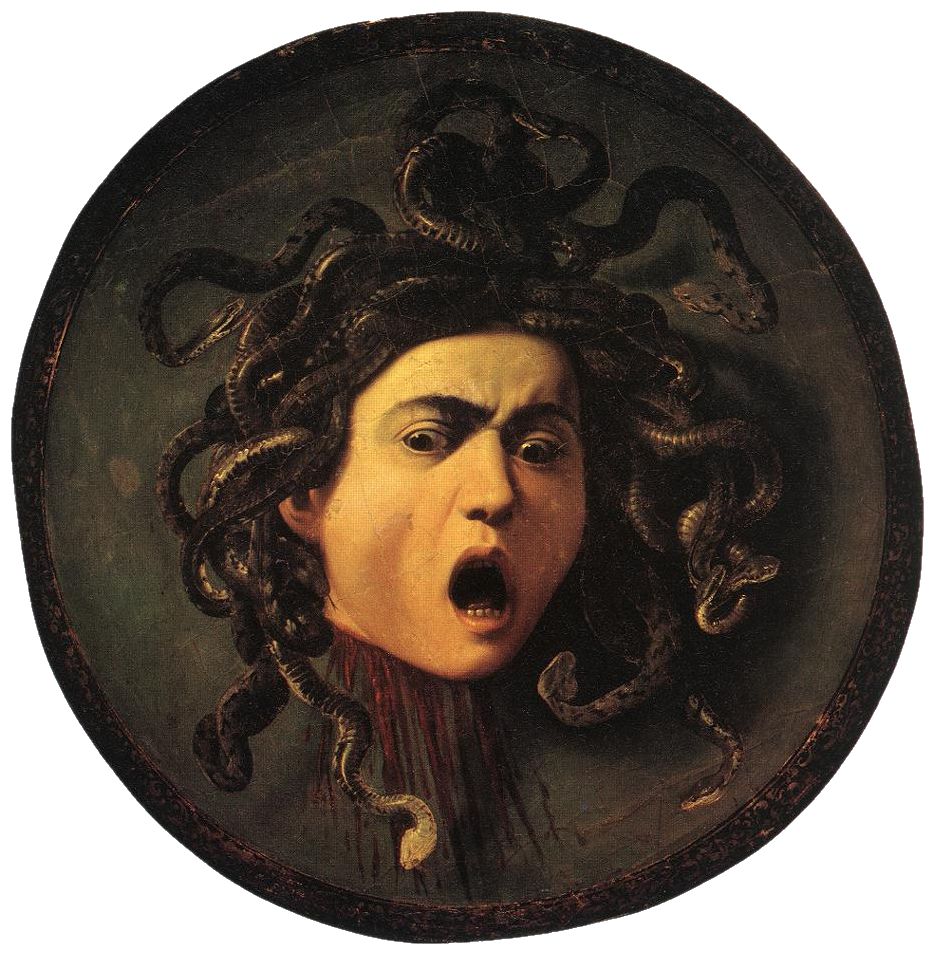 The ancient Greeks used the Gorgoneion, a depiction of a hideous face with serpents for hair, as an Apotropaic magic, apotropaic symbol to ward off evil. In a Greek mythology, Greek myth described by Pseudo-Apollodorus in his ''Bibliotheca (Pseudo-Apollodorus), Bibliotheca'', Medusa was a Gorgon with serpents for hair whose gaze turned all those who looked at her to stone and was slain by the hero Perseus. In the Roman poet Ovid's ''Metamorphoses'', Medusa is said to have once been a beautiful priestess of Athena, whom Athena turned into a serpent-haired monster after she was raped by the god Poseidon in Athena's temple. In another myth referenced by the Boeotian poet Hesiod and described in detail by Pseudo-Apollodorus, the hero Heracles is said to have slain the Lernaean Hydra, a multiple-headed serpent which dwelt in the swamps of Lerna.
The legendary account of the foundation of Ancient Thebes (Boeotia), Thebes mentioned a monster snake guarding the spring from which the new settlement was to draw its water. In fighting and killing the snake, the companions of the founder Cadmus all perished – leading to the term "Cadmean victory" (i.e. a victory involving one's own ruin).
The ancient Greeks used the Gorgoneion, a depiction of a hideous face with serpents for hair, as an Apotropaic magic, apotropaic symbol to ward off evil. In a Greek mythology, Greek myth described by Pseudo-Apollodorus in his ''Bibliotheca (Pseudo-Apollodorus), Bibliotheca'', Medusa was a Gorgon with serpents for hair whose gaze turned all those who looked at her to stone and was slain by the hero Perseus. In the Roman poet Ovid's ''Metamorphoses'', Medusa is said to have once been a beautiful priestess of Athena, whom Athena turned into a serpent-haired monster after she was raped by the god Poseidon in Athena's temple. In another myth referenced by the Boeotian poet Hesiod and described in detail by Pseudo-Apollodorus, the hero Heracles is said to have slain the Lernaean Hydra, a multiple-headed serpent which dwelt in the swamps of Lerna.
The legendary account of the foundation of Ancient Thebes (Boeotia), Thebes mentioned a monster snake guarding the spring from which the new settlement was to draw its water. In fighting and killing the snake, the companions of the founder Cadmus all perished – leading to the term "Cadmean victory" (i.e. a victory involving one's own ruin).
 Three medical symbols involving snakes that are still used today are Bowl of Hygieia, symbolizing pharmacy, and the Caduceus and
Three medical symbols involving snakes that are still used today are Bowl of Hygieia, symbolizing pharmacy, and the Caduceus and

BBC Nature:
Snake news, and video clips from BBC programmes past and present.
at Life is Short but Snakes are Long {{Authority control Snakes, Cenomanian first appearances Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Extant Cenomanian first appearances
squamates
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest order of reptiles, comprising lizards, snakes, and amphisbaenians (worm lizards), which are collectively known as squamates or scaled reptiles. With over 10,900 species, it ...
, snakes are ectothermic
An ectotherm (from the Greek () "outside" and () "heat") is an organism in which internal physiological sources of heat are of relatively small or of quite negligible importance in controlling body temperature.Davenport, John. Animal Life ...
, amniote vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
s covered in overlapping scales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number w ...
. Many species of snakes have skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
s with several more joints than their lizard ancestors, enabling them to swallow prey much larger than their heads (cranial kinesis Cranial kinesis is the term for significant movement of skull bones relative to each other in addition to movement at the joint between the upper and lower jaw. It is usually taken to mean relative movement between the upper jaw and the braincase.
...
). To accommodate their narrow bodies, snakes' paired organs (such as kidneys) appear one in front of the other instead of side by side, and most have only one functional lung. Some species retain a pelvic girdle
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The p ...
with a pair of vestigial
Vestigiality is the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on co ...
claws on either side of the cloaca. Lizards have evolved elongate bodies without limbs or with greatly reduced limbs about twenty-five times independently via convergent evolution
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last com ...
, leading to many lineages of legless lizard
Legless lizard may refer to any of several groups of lizards that have independently lost limbs or reduced them to the point of being of no use in locomotion.Pough ''et al.'' 1992. Herpetology: Third Edition. Pearson Prentice Hall:Pearson Education ...
s. These resemble snakes, but several common groups of legless lizards have eyelids and external ears, which snakes lack, although this rule is not universal (see Amphisbaenia, Dibamidae
Dibamidae or blind skinks is a family of lizards characterized by their elongated cylindrical body and an apparent lack of limbs. Female dibamids are entirely limbless and the males retain small flap-like hind limbs, which they use to grip their ...
, and Pygopodidae
Pygopodidae, commonly known as legless lizards, snake-lizards, or flap-footed lizards, is a family of squamates with reduced or absent limbs, and are a type of gecko. At least 35 species are placed in two subfamilies and eight genera. They hav ...
).
Living snakes are found on every continent except Antarctica, and on most smaller land masses; exceptions include some large islands, such as Ireland, Iceland, Greenland, the Hawaiian archipelago
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kur ...
, and the islands of New Zealand, as well as many small islands of the Atlantic and central Pacific oceans. Additionally, sea snakes
Sea snakes, or coral reef snakes, are elapid snakes that inhabit marine environments for most or all of their lives. They belong to two subfamilies, Hydrophiinae and Laticaudinae. Hydrophiinae also includes Australasian terrestrial snakes, wher ...
are widespread throughout the Indian and Pacific oceans. Around thirty families
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideal ...
are currently recognized, comprising about 520 genera and about 3,900 species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
. They range in size from the tiny, Barbados threadsnake to the reticulated python
The reticulated python (''Malayopython reticulatus'') is a python species native to South and Southeast Asia. It is the world's longest snake, and is among the three heaviest. It is listed as least concern on the IUCN Red List because of its w ...
of in length. The fossil species '' Titanoboa cerrejonensis'' was long. Snakes are thought to have evolved from either burrowing or aquatic lizards, perhaps during the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
period, with the earliest known fossils dating to between 143 and 167 Ma ago. The diversity of modern snakes appeared during the Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''pal ...
epoch ( 66 to 56 Ma ago, after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event (also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction) was a sudden mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million years ago. With the ...
). The oldest preserved descriptions of snakes can be found in the Brooklyn Papyrus.
Most species of snake are nonvenomous and those that have venom use it primarily to kill and subdue prey rather than for self-defense. Some possess venom that is potent enough to cause painful injury or death to humans. Nonvenomous snakes either swallow prey alive or kill by constriction
Constriction is a method used by various snake species to kill or subdue their prey. Although some species of venomous and mildly venomous snakes do use constriction to subdue their prey, most snakes which use constriction lack venom. The snake i ...
.
Etymology
The English word ''snake'' comes fromOld English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
, itself from Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic bran ...
(cf.
The abbreviation ''cf.'' (short for the la, confer/conferatur, both meaning "compare") is used in writing to refer the reader to other material to make a comparison with the topic being discussed. Style guides recommend that ''cf.'' be used onl ...
Germanic 'ring snake', Swedish 'grass snake'), from Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo- ...
root 'to crawl to creep', which also gave ''sneak'' as well as Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
'snake'. The word ousted '' adder'', as ''adder'' went on to narrow in meaning, though in Old English was the general word for snake. The other term, ''serpent'', is from French, ultimately from Indo-European 'to creep', which also gave Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
() 'I crawl'.
Evolution
The fossil record of snakes is relatively poor because snake skeletons are typically small and fragile makingfossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
ization uncommon. Fossils readily identifiable as snakes (though often retaining hind limbs) first appear in the fossil record during the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
period. The earliest known true snake fossils (members of the crown group Serpentes) come from the marine simoliophiids, the oldest of which is the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', ...
( Cenomanian age) '' Haasiophis terrasanctus'', dated to between 112 and 94 million years old.
Based on comparative anatomy, there is consensus that snakes descended from lizards. Python
Python may refer to:
Snakes
* Pythonidae, a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia
** ''Python'' (genus), a genus of Pythonidae found in Africa and Asia
* Python (mythology), a mythical serpent
Computing
* Python (pro ...
s and boa
Kwon Bo-ah (; born November 5, 1986), known professionally as BoA, is a South Korean singer, songwriter, dancer, record producer and actress. One of the most successful and influential Korean entertainers, she has been dubbed the " Queen of K- ...
s—primitive groups among modern snakes—have vestigial hind limbs: tiny, clawed digits known as anal spurs, which are used to grasp during mating. The families Leptotyphlopidae
The Leptotyphlopidae (commonly called slender blind snakes or thread snakes) are a family of snakes found in North America, South America, Africa and Asia. All are fossorial and adapted to burrowing, feeding on ants and termites. Two subfamilies ...
and Typhlopidae
The Typhlopidae are a family of blind snakes. They are found mostly in the tropical regions of Africa, Asia, the Americas, and all mainland Australia and various islands. The rostral scale overhangs the mouth to form a shovel-like burrowing str ...
also possess remnants of the pelvic girdle, appearing as horny projections when visible.
Front limbs are nonexistent in all known snakes. This is caused by the evolution of their Hox gene
Hox genes, a subset of homeobox genes, are a group of related genes that specify regions of the body plan of an embryo along the head-tail axis of animals. Hox proteins encode and specify the characteristics of 'position', ensuring that the cor ...
s, controlling limb morphogenesis
Morphogenesis (from the Greek ''morphê'' shape and ''genesis'' creation, literally "the generation of form") is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of deve ...
. The axial skeleton of the snakes' common ancestor, like most other tetrapods, had regional specializations consisting of cervical (neck), thoracic (chest), lumbar (lower back), sacral (pelvic), and caudal (tail) vertebrae. Early in snake evolution, the Hox gene expression in the axial skeleton responsible for the development of the thorax became dominant. As a result, the vertebrae anterior to the hindlimb buds (when present) all have the same thoracic-like identity (except from the atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geograp ...
, axis
An axis (plural ''axes'') is an imaginary line around which an object rotates or is symmetrical. Axis may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis
* Axis (mathematics), a designator for a Cartesian-coordinat ...
, and 1–3 neck vertebrae). In other words, most of a snake's skeleton is an extremely extended thorax. Ribs are found exclusively on the thoracic vertebrae. Neck, lumbar and pelvic vertebrae are very reduced in number (only 2–10 lumbar and pelvic vertebrae are present), while only a short tail remains of the caudal vertebrae. However, the tail is still long enough to be of important use in many species, and is modified in some aquatic and tree-dwelling species.
Many modern snake groups originated during the Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''pal ...
, alongside the adaptive radiation
In evolutionary biology, adaptive radiation is a process in which organisms diversify rapidly from an ancestral species into a multitude of new forms, particularly when a change in the environment makes new resources available, alters biotic int ...
of mammals following the extinction of (non-avian) dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s. The expansion of grasslands in North America also led to an explosive radiation among snakes. Previously, snakes were a minor component of the North American fauna, but during the Miocene, the number of species and their prevalence increased dramatically with the first appearances of viper
The Viperidae (vipers) are a family of snakes found in most parts of the world, except for Antarctica, Australia, Hawaii, Madagascar, and various other isolated islands. They are venomous and have long (relative to non-vipers), hinged fangs tha ...
s and elapid
Elapidae (, commonly known as elapids ; grc, ἔλλοψ ''éllops'' "sea-fish") is a family of snakes characterized by their permanently erect fangs at the front of the mouth. Most elapids are venomous, with the exception of the genus Emydoce ...
s in North America and the significant diversification of Colubridae (including the origin of many modern genera such as Nerodia
''Nerodia'' is a genus of nonvenomous colubrid snakes commonly referred to as water snakes due to their aquatic behavior. The genus includes nine species, all native to North America.
Description
''Nerodia'' species vary greatly, but all are ...
, Lampropeltis, Pituophis, and Pantherophis
''Pantherophis'' is a genus of nonvenomous colubrid snakes endemic to central and eastern regions of North America. It consists of the North American ratsnakes, the foxsnakes, and the cornsnakes. The genus, which contains 10 recognized spec ...
).
Fossils
There is fossil evidence to suggest that snakes may have evolved from burrowing lizards, during theCretaceous Period
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of t ...
. An early fossil snake relative, '' Najash rionegrina'', was a two-legged burrowing animal with a sacrum, and was fully terrestrial
Terrestrial refers to things related to land or the planet Earth.
Terrestrial may also refer to:
* Terrestrial animal, an animal that lives on land opposed to living in water, or sometimes an animal that lives on or near the ground, as opposed to ...
. One extant analog of these putative ancestors is the earless monitor ''Lanthanotus
The earless monitor lizard (''Lanthanotus borneensis'') is a semiaquatic, brown lizard native to the Southeast Asian island of Borneo. It is the only living species in the family Lanthanotidae and it is related to the true monitor lizards.
Taxo ...
'' of Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and ea ...
(though it also is semiaquatic
In biology, semiaquatic can refer to various types of animals that spend part of their time in water, or plants that naturally grow partially submerged in water. Examples are given below.
Semiaquatic animals
Semi aquatic animals include:
* Ve ...
). Subterranean species evolved bodies streamlined for burrowing, and eventually lost their limbs. According to this hypothesis, features such as the transparent
Transparency, transparence or transparent most often refer to:
* Transparency (optics), the physical property of allowing the transmission of light through a material
They may also refer to:
Literal uses
* Transparency (photography), a still, ...
, fused eyelids ( brille) and loss of external ears evolved to cope with fossorial difficulties, such as scratched cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical ...
s and dirt in the ears. Some primitive snakes are known to have possessed hindlimbs, but their pelvic bones lacked a direct connection to the vertebrae. These include fossil species like ''Haasiophis
''Haasiophis'', consisting of the sole species ''Haasiophis terrasanctus'', is an extinct genus of snakes with hind limbs. It is one of three genera of Cenomanian snakes known to have possessed hindlimbs.
Etymology
The genus was named in hon ...
'', ''Pachyrhachis
''Pachyrhachis'' (from el, παχύς , 'thick' and el, ῥάχῐς , 'spine') is an extinct genus of snake with well developed hind legs known from fossils discovered in Ein Yabrud, near Ramallah, in the central West Bank. It is a relatively ...
'' and ''Eupodophis
''Eupodophis'' is an extinct genus of snake from the Late Cretaceous period. It has two small hind legs and is considered a transitional form between Cretaceous lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 sp ...
'', which are slightly older than ''Najash
''Najash'' is an extinct genus of basal snake from the Late Cretaceous Candeleros Formation of Patagonia. Like a number of other Cretaceous and living snakes it retained hindlimbs, but ''Najash'' is unusual in having well-developed legs that e ...
''.
This hypothesis was strengthened in 2015 by the discovery of a 113-million-year-old fossil of a four-legged snake in Brazil that has been named '' Tetrapodophis amplectus''. It has many snake-like features, is adapted for burrowing and its stomach indicates that it was preying on other animals. It is currently uncertain if ''Tetrapodophis'' is a snake or another species, in the squamate
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest order of reptiles, comprising lizards, snakes, and amphisbaenians (worm lizards), which are collectively known as squamates or scaled reptiles. With over 10,900 species, it ...
order, as a snake-like body has independently evolved at least 26 times. ''Tetrapodophis'' does not have distinctive snake features in its spine and skull. A study in 2021 places the animal in a group of extinct marine lizards from the Cretaceous period known as dolichosaurs and not directly related to snakes.
An alternative hypothesis, based on morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
* Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
* Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies ...
, suggests the ancestors of snakes were related to mosasaur
Mosasaurs (from Latin ''Mosa'' meaning the 'Meuse', and Greek ' meaning 'lizard') comprise a group of extinct, large marine reptiles from the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains were discovered in a limestone quarry at Maastricht on ...
s—extinct aquatic reptiles from the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
—forming the clade Pythonomorpha
Pythonomorpha was originally proposed by paleontologist Edward Drinker Cope (1869) as a reptilian order comprising mosasaurs, which he believed to be close relatives of Ophidia ( snakes). The etymology of the term Pythonomorpha comes from the Gre ...
. According to this hypothesis, the fused, transparent eyelids of snakes are thought to have evolved to combat marine conditions (corneal water loss through osmosis), and the external ears were lost through disuse in an aquatic environment. This ultimately led to an animal similar to today's sea snake
Sea snakes, or coral reef snakes, are elapid snakes that inhabit marine environments for most or all of their lives. They belong to two subfamilies, Hydrophiinae and Laticaudinae. Hydrophiinae also includes Australasian terrestrial snakes, wher ...
s. In the Late Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
, snakes recolonized land, and continued to diversify into today's snakes. Fossilized snake remains are known from early Late Cretaceous marine sediments, which is consistent with this hypothesis; particularly so, as they are older than the terrestrial ''Najash rionegrina''. Similar skull structure, reduced or absent limbs, and other anatomical features found in both mosasaurs and snakes lead to a positive cladistical correlation, although some of these features are shared with varanids.
Genetic studies in recent years have indicated snakes are not as closely related to monitor lizards as was once believed—and therefore not to mosasaurs, the proposed ancestor in the aquatic scenario of their evolution. However, more evidence links mosasaurs to snakes than to varanids. Fragmented remains found from the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
and Early Cretaceous indicate deeper fossil records for these groups, which may potentially refute either hypothesis.
Tetrapodophis
''Tetrapodophis'' (greek meaning "four-footed snake") is an extinct genus of lizard from the Early Cretaceous. ''Tetrapodophis'' was previously thought to be one of the oldest members of Ophidia (Snakes and their extinct relatives). However, this ...
''
File:Eupodophis at Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences, Brussels.jpg, '' Eupodophis descouensi''
File:Eupodophis descouensi Holotype.jpg, '' Eupodophis descouensi''
File:Eupodophis descouensi Holotype hind leg.jpg, ''Eupodophis
''Eupodophis'' is an extinct genus of snake from the Late Cretaceous period. It has two small hind legs and is considered a transitional form between Cretaceous lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 sp ...
descouensi'' hind leg
Genetic basis of snake evolution
Both fossils andphylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
studies demonstrate that snakes evolved from lizards, hence the question became which genetic changes led to limb loss in the snake ancestor. Limb loss is actually very common in extant reptiles and has happened dozens of times within skinks, anguids, and other lizards.
In 2016, two studies reported that limb loss in snakes is associated with DNA mutations in the Zone of Polarizing Activity Regulatory Sequence (ZRS), a regulatory region of the sonic hedgehog gene which is critically required for limb development. More advanced snakes have no remnants of limbs, but basal snakes such as pythons and boas do have traces of highly reduced, vestigial hind limbs. Python embryos even have fully developed hind limb buds, but their later development is stopped by the DNA mutations in the ZRS.
Distribution
Himalayan Mountains
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 ...
of Asia. There are numerous islands from which snakes are absent, such as Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
, Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
, and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
(although New Zealand's waters are infrequently visited by the yellow-bellied sea snake
The yellow-bellied sea snake (''Hydrophis platurus'') is a venomous species of snake from the subfamily Hydrophiinae (the sea snakes) found in tropical oceanic waters around the world except for the Atlantic Ocean. For many years, it was place ...
and the banded sea krait
The yellow-lipped sea krait (''Laticauda colubrina''), also known as the banded sea krait or colubrine sea krait, is a species of venomous sea snake found in tropical Indo-Pacific oceanic waters. The snake has distinctive black stripes and a ye ...
).
Taxonomy
All modern snakes are grouped within the suborder Serpentes inLinnean taxonomy
Linnaean taxonomy can mean either of two related concepts:
# The particular form of biological classification (taxonomy) set up by Carl Linnaeus, as set forth in his ''Systema Naturae'' (1735) and subsequent works. In the taxonomy of Linnaeus t ...
, part of the order Squamata
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest order of reptiles, comprising lizards, snakes, and amphisbaenians (worm lizards), which are collectively known as squamates or scaled reptiles. With over 10,900 species ...
, though their precise placement within squamates remains controversial.
The two infraorder
Order ( la, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and ...
s of Serpentes are: Alethinophidia
:''Common names: advanced snakes.''
The Alethinophidia are an infraorder of snakes that includes all snakes other than blind snakes and thread snakes. Snakes have long been grouped into families within Alethinophidia based on their morphology, ...
and Scolecophidia
The Scolecophidia, commonly known as blind snakes or thread snakes, are an infraorder of snakes. They range in length from . All are fossorial (adapted for burrowing). Five families and 39 genera are recognized. The Scolecophidia infraorder is mo ...
. This separation is based on morphological characteristics and mitochondrial DNA sequence similarity. Alethinophidia is sometimes split into Henophidia and Caenophidia
The Caenophidia are a derived clade of alethinophidian snakes, which contains over 80% of all the extant species of snakes. The largest family is Colubridae, but it also includes at least seven other families, at least four of which were once ...
, with the latter consisting of "colubroid" snakes ( colubrids, vipers
The Viperidae (vipers) are a family of snakes found in most parts of the world, except for Antarctica, Australia, Hawaii, Madagascar, and various other isolated islands. They are venomous and have long (relative to non-vipers), hinged fangs th ...
, elapids
Elapidae (, commonly known as elapids ; grc, ἔλλοψ ''éllops'' "sea-fish") is a family of snakes characterized by their permanently erect fangs at the front of the mouth. Most elapids are venomous, with the exception of the genus Emydocep ...
, hydrophiids, and atractaspids) and acrochordids, while the other alethinophidian families comprise Henophidia. While not extant today, the Madtsoiidae
Madtsoiidae is an extinct family of mostly Gondwanan snakes with a fossil record extending from early Cenomanian ( Upper Cretaceous) to late Pleistocene strata located in South America, Africa, India, Australia and Southern Europe. Madts ...
, a family of giant, primitive, python-like snakes, was around until 50,000 years ago in Australia, represented by genera such as '' Wonambi''.
There are numerous debates in the systematics within the group. For instance, many sources classify Boidae
The Boidae, commonly known as boas or boids, are a family of nonvenomous snakes primarily found in the Americas, as well as Africa, Europe, Asia, and some Pacific Islands. Boas include some of the world's largest snakes, with the green anacond ...
and Pythonidae
The Pythonidae, commonly known as pythons, are a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia. Among its members are some of the largest snakes in the world. Ten genera and 42 species are currently recognized.
Distributi ...
as one family, while some keep the Elapidae
Elapidae (, commonly known as elapids ; grc, ἔλλοψ ''éllops'' "sea-fish") is a family of snakes characterized by their permanently erect fangs at the front of the mouth. Most elapids are venomous, with the exception of the genus Emydoce ...
and Hydrophiidae
Hydrophiinae is a subfamily of venomous snakes in the family Elapidae. It contains most sea snakes and many genera of venomous land snakes found in Australasia, such as the taipans (''Oxyuranus''), tiger snakes (''Notechis''), brown snakes (''P ...
(sea snakes) separate for practical reasons despite their extremely close relation.
Recent molecular studies support the monophyly
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic gro ...
of the clades
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
of modern snakes, scolecophidians, typhlopids + anomalepidids, alethinophidians, core alethinophidians, uropeltids (''Cylindrophis'', ''Anomochilus'', uropeltines), macrostomatans, booids, boids, pythonids and caenophidians.
Families
Legless lizards
While snakes are limbless reptiles, evolved from (and grouped with) lizards, there are many other species of lizards that have lost their limbs independently but which superficially look similar to snakes. These include theslowworm
The slow worm (''Anguis fragilis'') is a reptile native to western Eurasia. It is also called a deaf adder, a slowworm, a blindworm, or regionally, a long-cripple and hazelworm. These legless lizards are also sometimes called common slowworms. T ...
and glass snake.
Other serpentine tetrapods that are unrelated to snakes include caecilian
Caecilians (; ) are a group of limbless, vermiform or serpentine amphibians. They mostly live hidden in the ground and in stream substrates, making them the least familiar order of amphibians. Caecilians are mostly distributed in the tropics o ...
s (amphibians), amphisbaenians (near-lizard squamates), and the extinct aistopods (amphibians).
Biology

Size
The now extinct '' Titanoboa cerrejonensis'' was in length. By comparison, the largest extant snakes are thereticulated python
The reticulated python (''Malayopython reticulatus'') is a python species native to South and Southeast Asia. It is the world's longest snake, and is among the three heaviest. It is listed as least concern on the IUCN Red List because of its w ...
, measuring about long, and the green anaconda
The green anaconda (''Eunectes murinus''), also known as the giant Emerald anaconda, common anaconda, common water boa or sucuri, is a boa species found in South America. It is the heaviest and one of the longest known extant snake species. Lik ...
, which measures about long and is considered the heaviest snake on Earth at .
At the other end of the scale, the smallest extant snake is '' Leptotyphlops carlae'', with a length of about . Most snakes are fairly small animals, approximately in length.
Perception
 Pit vipers, pythons, and some boas have infrared-sensitive receptors in deep grooves on the snout, allowing them to "see" the radiated heat of warm-blooded prey. In pit vipers, the grooves are located between the nostril and the eye in a large "pit" on each side of the head. Other infrared-sensitive snakes have multiple, smaller labial pits lining the upper lip, just below the nostrils.
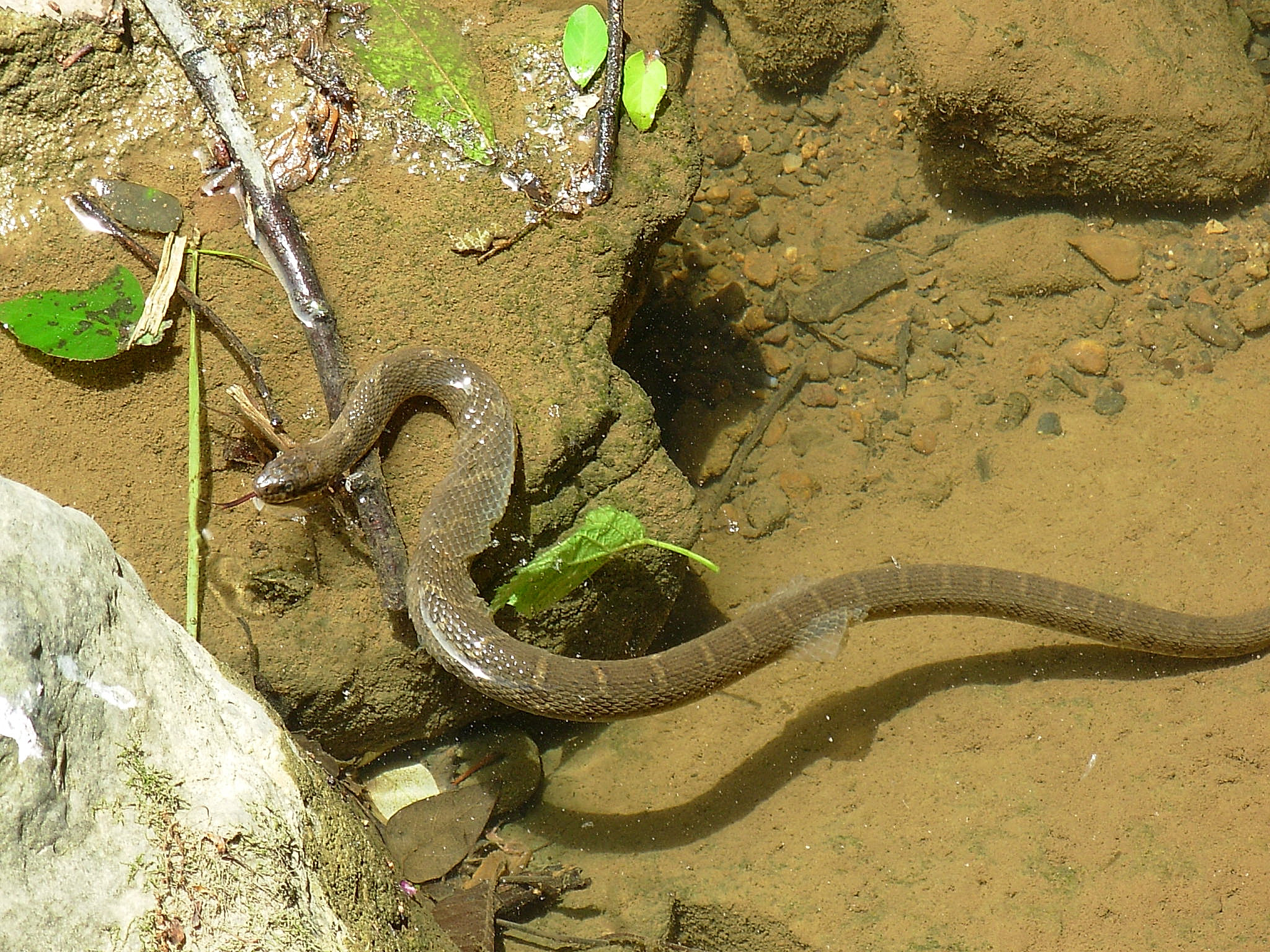
A snake tracks its prey using smell, collecting airborne particles with its
Pit vipers, pythons, and some boas have infrared-sensitive receptors in deep grooves on the snout, allowing them to "see" the radiated heat of warm-blooded prey. In pit vipers, the grooves are located between the nostril and the eye in a large "pit" on each side of the head. Other infrared-sensitive snakes have multiple, smaller labial pits lining the upper lip, just below the nostrils.
A snake tracks its prey using smell, collecting airborne particles with its forked tongue
A forked tongue is a tongue split into two distinct tines at the tip; this is a feature common to many species of reptiles. Reptiles smell using the tip of their tongue, and a forked tongue allows them to sense from which direction a smell is co ...
, then passing them to the vomeronasal organ
The vomeronasal organ (VNO), or Jacobson's organ, is the paired auxiliary olfactory (smell) sense organ located in the soft tissue of the nasal septum, in the nasal cavity just above the roof of the mouth (the hard palate) in various tetrapods. T ...
or ''Jacobson's organ'' in the mouth for examination. The fork in the tongue provides a sort of directional sense of smell and taste simultaneously. The snake's tongue is constantly in motion, sampling particles from the air, ground, and water, analyzing the chemicals found, and determining the presence of prey or predators in the local environment. In water-dwelling snakes, such as the anaconda
Anacondas or water boas are a group of large snakes of the genus '' Eunectes''. They are found in tropical South America. Four species are currently recognized.
Description
Although the name applies to a group of snakes, it is often used ...
, the tongue functions efficiently underwater.
 The underside of a snake is very sensitive to vibration, allowing the snake to detect approaching animals by sensing faint vibrations in the ground.
Snake vision varies greatly between species. Some have keen eyesight and others are only able to distinguish light from dark, but the important trend is that a snake's visual perception is adequate enough to track movements. Generally, vision is best in tree-dwelling snakes and weakest in burrowing snakes. Some have
The underside of a snake is very sensitive to vibration, allowing the snake to detect approaching animals by sensing faint vibrations in the ground.
Snake vision varies greatly between species. Some have keen eyesight and others are only able to distinguish light from dark, but the important trend is that a snake's visual perception is adequate enough to track movements. Generally, vision is best in tree-dwelling snakes and weakest in burrowing snakes. Some have binocular vision
In biology, binocular vision is a type of vision in which an animal has two eyes capable of facing the same direction to perceive a single three-dimensional image of its surroundings. Binocular vision does not typically refer to vision where an ...
, where both eyes are capable of focusing on the same point, an example of this being the Asian vine snake. Most snakes focus by moving the lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements ...
back and forth in relation to the retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then ...
. Diurnal snakes have round pupils and many nocturnal snakes have slit pupils. Most species possess three visual pigments and are probably able to see two primary colors in daylight. It has been concluded that the last common ancestors of all snakes had UV-sensitive vision, but most snakes that depend on their eyesight to hunt in daylight have evolved lenses that act like sunglasses for filtering out the UV-light, which probably also sharpens their vision by improving the contrast.
Skin
The skin of a snake is covered inscales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number w ...
. Contrary to the popular notion of snakes being slimy (because of possible confusion of snakes with worm
Worms are many different distantly related bilateral animals that typically have a long cylindrical tube-like body, no limbs, and no eyes (though not always).
Worms vary in size from microscopic to over in length for marine polychaete wo ...
s), snakeskin
Snakeskin may either refer to the skin of a live snake, the shed skin of a snake after molting, or to a type of leather that is made from the hide of a dead snake. Snakeskin and scales can have varying patterns and color formations, providing prot ...
has a smooth, dry texture. Most snakes use specialized belly scales to travel, allowing them to grip surfaces. The body scales may be smooth, keeled, or granular. The eyelids of a snake are transparent "spectacle" scales, also known as brille, which remain permanently closed.
The shedding of scales is called '' ecdysis'' (or in normal usage, ''molting'' or ''sloughing''). Snakes shed the complete outer layer of skin in one piece.Smith, Malcolm A. ''The Fauna of British India, Including Ceylon and Burma
''The Fauna of British India'' (short title) with long titles including ''The Fauna of British India, Including Ceylon and Burma'', and ''The Fauna of British India Including the Remainder of the Oriental Region'' is a series of scientific books th ...
''. Vol I, Loricata and Testudines. p. 30. Snake scales are not discrete, but extensions of the epidermis—hence they are not shed separately but as a complete outer layer during each molt, akin to a sock being turned inside out.
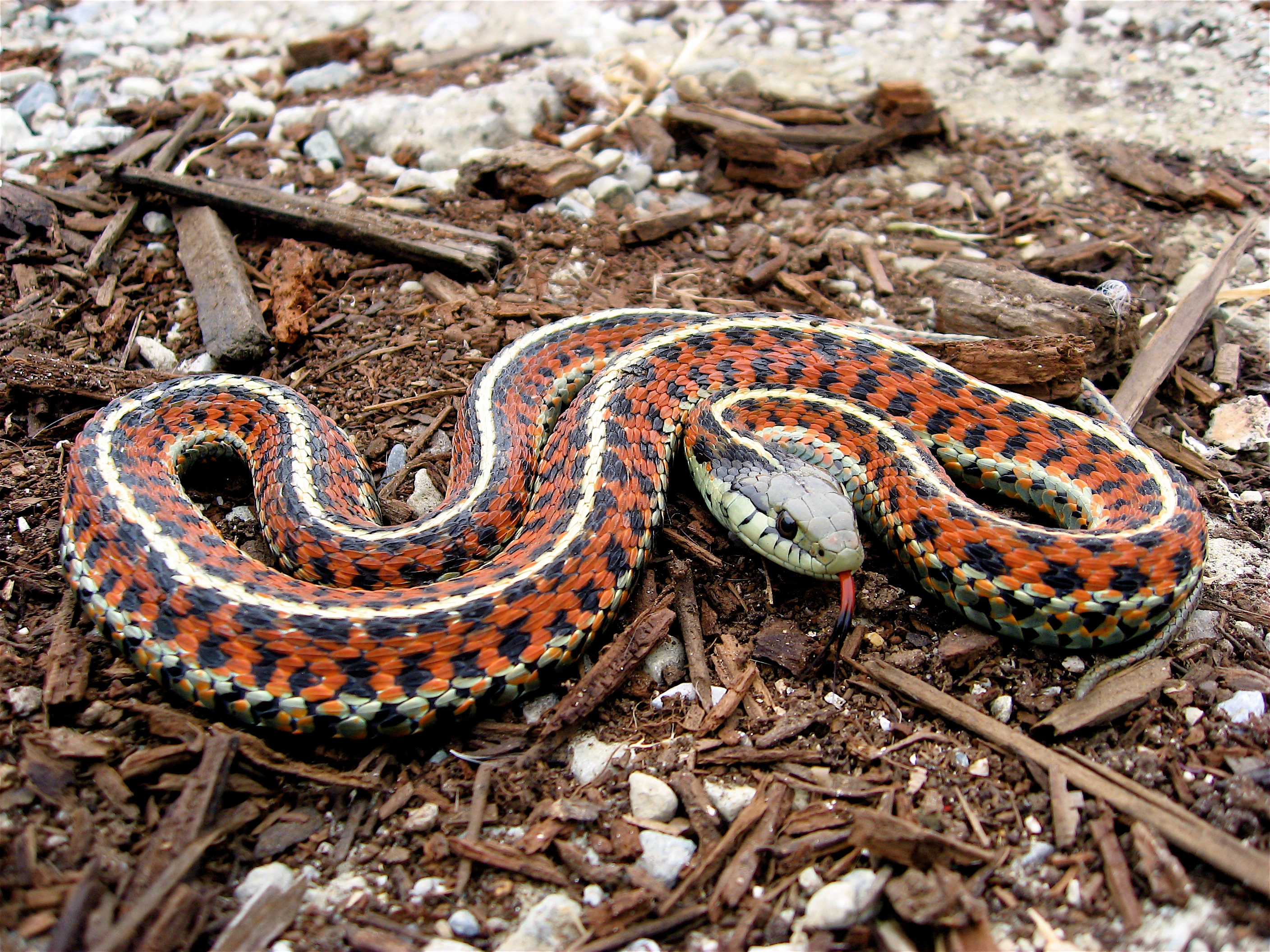
Snakes have a wide diversity of skin coloration patterns which are often related to behavior, such as the tendency to have to flee from predators. Snakes that are at a high risk of predation tend to be plain, or have longitudinal stripes, providing few reference points to predators, thus allowing the snake to escape without being noticed. Plain snakes usually adopt active hunting strategies, as their pattern allows them to send little information to prey about motion. Blotched snakes usually use ambush-based strategies, likely because it helps them blend into an environment with irregularly shaped objects, like sticks or rocks. Spotted patterning can similarly help snakes to blend into their environment.
The shape and number of scales on the head, back, and belly are often characteristic and used for taxonomic purposes. Scales are named mainly according to their positions on the body. In "advanced" (Caenophidia
The Caenophidia are a derived clade of alethinophidian snakes, which contains over 80% of all the extant species of snakes. The largest family is Colubridae, but it also includes at least seven other families, at least four of which were once ...
n) snakes, the broad belly scales and rows of dorsal scales correspond to the vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
e, allowing these to be counted without the need for dissection.
Molting
Molting
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is the manner in which an animal routinely casts off a part of its body (often, but not always, an outer ...
(or "ecdysis") serves a number of purposes. It allows old, worn skin to be replaced and it can remove parasites such as mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear e ...
s and tick
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by ...
s that live in the skin. It's also been observed in snakes that molting can be synced to mating cycles. Shedding skin can release pheromones and revitalize color and patterns of the skin to increase attraction of mates. Renewal of the skin by molting supposedly allows growth in some animals such as insects, but this has been disputed in the case of snakes.
Molting occurs periodically throughout the life of a snake. Before each molt, the snake stops eating and often hides or moves to a safe place. Just before shedding, the skin becomes dull and dry looking and the snake's eyes turn cloudy or blue-colored. The inner surface of the old skin liquefies, causing it to separate from the new skin beneath it. After a few days, the eyes become clear and the snake "crawls" out of its old skin, which splits close to the snake's mouth. The snake rubs its body against rough surfaces to aid in the shedding of its old skin. In many cases, the cast skin peels backward over the body from head to tail in one piece, like pulling a sock off inside-out, revealing a new, larger, brighter layer of skin which has formed underneath.
A young snake that is still growing may shed its skin up to four times a year, but an older snake may shed only once or twice a year. The discarded skin carries a perfect imprint of the scale pattern, so it is usually possible to identify the snake from the cast skin if it is reasonably intact. This periodic renewal has led to the snake being a symbol of healing
With physical trauma or disease suffered by an organism, healing involves the repairing of damaged tissue(s), organs and the biological system as a whole and resumption of (normal) functioning. Medicine includes the process by which the cells ...
and medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pr ...
, as pictured in the Rod of Asclepius
In Greek mythology, the Rod of Asclepius (⚕; grc, Ράβδος του Ασκληπιού, , sometimes also spelled Asklepios), also known as the Staff of Aesculapius and as the asklepian, is a serpent-entwined rod wielded by the Greek god A ...
.
Scale counts can sometimes be used to identify the sex of a snake when the species is not distinctly sexually dimorphic
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most ani ...
. A probe is fully inserted into the cloaca, marked at the point where it stops, then removed and measured against the subcaudal scales.Rosenfeld (1989), p. 11. The scalation count determines whether the snake is a male or female, as the hemipenes
A hemipenis (plural hemipenes) is one of a pair of intromittent organs of male squamates (snakes, lizards and worm lizards). Hemipenes are usually held inverted within the body, and are everted for reproduction via erectile tissue, much like ...
of a male will probe to a different depth (usually longer) than the cloaca of a female.
Skeleton
 The skeleton of most snakes consists solely of the skull, hyoid, vertebral column, and ribs, though henophidian snakes retain vestiges of the pelvis and rear limbs.
The skull consists of a solid and complete
The skeleton of most snakes consists solely of the skull, hyoid, vertebral column, and ribs, though henophidian snakes retain vestiges of the pelvis and rear limbs.
The skull consists of a solid and complete neurocranium
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, or brain-pan is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calvaria or skul ...
, to which many of the other bones are only loosely attached, particularly the highly mobile jaw bones, which facilitate manipulation and ingestion of large prey items. The left and right sides of the lower jaw are joined only by a flexible ligament at the anterior tips, allowing them to separate widely, and the posterior end of the lower jaw bones articulate with a quadrate bone
The quadrate bone is a skull bone in most tetrapods, including amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, birds), and early synapsids.
In most tetrapods, the quadrate bone connects to the quadratojugal and squamosal bones in the skull, and forms upper pa ...
, allowing further mobility. The mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
and quadrate bones can pick up ground-borne vibrations; because the sides of the lower jaw can move independently of one another, a snake resting its jaw on a surface has sensitive stereo auditory perception, used for detecting the position of prey. The jaw–quadrate–stapes
The ''stapes'' or stirrup is a bone in the middle ear of humans and other animals which is involved in the conduction of sound vibrations to the inner ear. This bone is connected to the oval window by its annular ligament, which allows the foo ...
pathway is capable of detecting vibrations on the angstrom
The angstromEntry "angstrom" in the Oxford online dictionary. Retrieved on 2019-03-02 from https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/angstrom.Entry "angstrom" in the Merriam-Webster online dictionary. Retrieved on 2019-03-02 from https://www.m ...
scale, despite the absence of an outer ear and the lack of an impedance matching
In electronics, impedance matching is the practice of designing or adjusting the input impedance or output impedance of an electrical device for a desired value. Often, the desired value is selected to maximize power transfer or minimize si ...
mechanism—provided by the ossicles in other vertebrates—for receiving vibrations from the air.
The hyoid is a small bone located posterior and ventral to the skull, in the 'neck' region, which serves as an attachment for the muscles of the snake's tongue, as it does in all other tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids ( pelycosaurs, extinct t ...
s.
The vertebral column consists of between 200 and 400 vertebrae, or sometimes more. The body vertebrae each have two ribs articulating with them. The tail vertebrae are comparatively few in number (often less than 20% of the total) and lack ribs. The vertebrae have projections that allow for strong muscle attachment, enabling locomotion without limbs.
Caudal autotomy
Autotomy (from the Greek ''auto-'', "self-" and ''tome'', "severing", αὐτοτομία) or self-amputation, is the behaviour whereby an animal sheds or discards one or more of its own appendages, usually as a self-defense mechanism to elude ...
(self-amputation of the tail), a feature found in some lizards, is absent in most snakes. In the rare cases where it does exist in snakes, caudal autotomy is intervertebral (meaning the separation of adjacent vertebrae), unlike that in lizards, which is intravertebral, i.e. the break happens along a predefined fracture plane present on a vertebra.
In some snakes, most notably boas and pythons, there are vestiges of the hindlimbs in the form of a pair of pelvic spur
Pelvic spurs are the externally visible portion of the vestigial remnants of legs found on each side of the cloaca in primitive snakes, such as boas and pythons. The remnants of a pelvis and femur, which have no connection with the spine, simply ...
s. These small, claw-like protrusions on each side of the cloaca are the external portion of the vestigial hindlimb skeleton, which includes the remains of an ilium and femur.
Snakes are polyphyodont
A polyphyodont is any animal whose teeth are continually replaced. In contrast, diphyodonts are characterized by having only two successive sets of teeth.
Polyphyodonts include most toothed fishes, many reptiles such as crocodiles and geckos, ...
s with teeth that are continuously replaced.
Internal organs
Snakes and other non- archosaur (crocodilia
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian stage) and are the closest livi ...
ns, dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s + bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s and allies) reptiles have a three-chambered heart that controls the circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
via the left and right atrium, and one ventricle. Internally, the ventricle is divided into three interconnected cavities: the cavum arteriosum, the cavum pulmonale, and the cavum venosum. The cavum venosum receives deoxygenated blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
from the right atrium and the cavum arteriosum receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium. Located beneath the cavum venosum is the cavum pulmonale, which pumps blood to the pulmonary trunk.
The snake's heart is encased in a sac, called the ''pericardium
The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made o ...
'', located at the bifurcation
Bifurcation or bifurcated may refer to:
Science and technology
* Bifurcation theory, the study of sudden changes in dynamical systems
** Bifurcation, of an incompressible flow, modeled by squeeze mapping the fluid flow
* River bifurcation, the ...
of the bronchi
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. ...
. The heart is able to move around, owing to the lack of a diaphragm; this adjustment protects the heart from potential damage when large ingested prey is passed through the esophagus
The esophagus ( American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to ...
. The spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
is attached to the gall bladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although ...
and pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an en ...
and filters the blood. The thymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or ''T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. ...
, located in fatty tissue above the heart, is responsible for the generation of immune cells in the blood. The cardiovascular system of snakes is unique for the presence of a renal portal system in which the blood from the snake's tail passes through the kidneys before returning to the heart.
The vestigial
Vestigiality is the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on co ...
left lung is often small or sometimes even absent, as snakes' tubular bodies require all of their organs to be long and thin. In the majority of species, only one lung is functional. This lung contains a vascularized anterior portion and a posterior portion that does not function in gas exchange. This 'saccular lung' is used for hydrostatic
Fluid statics or hydrostatics is the branch of fluid mechanics that studies the condition of the equilibrium of a floating body and submerged body "fluids at hydrostatic equilibrium and the pressure in a fluid, or exerted by a fluid, on an imme ...
purposes to adjust buoyancy in some aquatic snakes and its function remains unknown in terrestrial species. Many organs that are paired, such as kidneys
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; bloo ...
or reproductive organs
A sex organ (or reproductive organ) is any part of an animal or plant that is involved in sexual reproduction. The reproductive organs together constitute the reproductive system. In animals, the testis in the male, and the ovary in the female, a ...
, are staggered within the body, one located ahead of the other.
Snakes have no lymph nodes.
Venom
venom
Venom or zootoxin is a type of toxin produced by an animal that is actively delivered through a wound by means of a bite, sting, or similar action. The toxin is delivered through a specially evolved ''venom apparatus'', such as fangs or a st ...
to immobilize, injure, or kill their prey. The venom is modified saliva, delivered through fangs
A fang is a long, pointed tooth. In mammals, a fang is a modified maxillary tooth, used for biting and tearing flesh. In snakes, it is a specialized tooth that is associated with a venom gland (see snake venom). Spiders also have external fa ...
. The fangs of 'advanced' venomous snakes like viperids and elapids are hollow, allowing venom to be injected more effectively, and the fangs of rear-fanged snakes such as the boomslang simply have a groove on the posterior edge to channel venom into the wound. Snake venoms are often prey-specific, and their role in self-defense is secondary.
Venom, like all salivary secretions, is a predigestant that initiates the breakdown of food into soluble compounds, facilitating proper digestion. Even nonvenomous snakebites (like any animal bite) cause tissue damage.
Certain birds, mammals, and other snakes (such as kingsnake
Kingsnakes are colubrid New World members of the genus ''Lampropeltis'', which includes 26 species. Among these, about 45 subspecies are recognized. They are nonvenomous and ophiophagous in diet.
Description
Kingsnakes vary widely in size and ...
s) that prey on venomous snakes have developed resistance and even immunity to certain venoms. Venomous snakes include three families
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideal ...
of snakes, and do not constitute a formal taxonomic classification
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are give ...
group.
The colloquial
Colloquialism (), also called colloquial language, everyday language or general parlance, is the style (sociolinguistics), linguistic style used for casual (informal) communication. It is the most common functional style of speech, the idiom norm ...
term "poisonous snake" is generally an incorrect label for snakes. A poison is inhaled or ingested, whereas venom produced by snakes is injected into its victim via fangs. There are, however, two exceptions: ''Rhabdophis
''Rhabdophis'' is a genus of snakes in the subfamily Natricinae of the family Colubridae. Species in the genus ''Rhabdophis'' are generally called keelback snakes, and are found primarily in Southeast Asia.
Toxicity
''Rhabdophis'' is often thou ...
'' sequesters toxins from the toads it eats, then secretes them from nuchal glands to ward off predators; and a small unusual population of garter snake
Garter snake is a common name for generally harmless, small to medium-sized snakes belonging to the genus ''Thamnophis'' in the family Colubridae. Native to North and Central America, species in the genus ''Thamnophis'' can be found from the ...
s in the US state of Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. T ...
retains enough toxins in their livers from ingested newt
A newt is a salamander in the subfamily Pleurodelinae. The terrestrial juvenile phase is called an eft. Unlike other members of the family Salamandridae, newts are semiaquatic, alternating between aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Not all aqua ...
s to be effectively poisonous to small local predators (such as crow
A crow is a bird of the genus '' Corvus'', or more broadly a synonym for all of ''Corvus''. Crows are generally black in colour. The word "crow" is used as part of the common name of many species. The related term "raven" is not pinned scientifica ...
s and fox
Foxes are small to medium-sized, omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull, upright, triangular ears, a pointed, slightly upturned snout, and a long bushy tail (or ''brush'').
Twelve sp ...
es).
Snake venoms are complex mixtures of protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s, and are stored in venom glands at the back of the head. In all venomous snakes, these glands open through ducts into grooved or hollow teeth in the upper jaw. The proteins can potentially be a mix of neurotoxins (which attack the nervous system), hemotoxin
Hemotoxins, haemotoxins or hematotoxins are toxins that destroy red blood cells, disrupt blood clotting, and/or cause organ degeneration and generalized tissue damage. The term ''hemotoxin'' is to some degree a misnomer since toxins that damage t ...
s (which attack the circulatory system), cytotoxin
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are an immune cell or some types of venom, e.g. from the puff adder (''Bitis arietans'') or brown recluse spider (''Loxosceles reclusa'').
Cell physiology
Treating c ...
s (which attack the cells directly), bungarotoxins (related to neurotoxins, but also directly affect muscle tissue), and many other toxins that affect the body in different ways. Almost all snake venom contains ''hyaluronidase
Hyaluronidases are a family of enzymes that catalyse the degradation of hyaluronic acid (HA). Karl Meyer classified these enzymes in 1971, into three distinct groups, a scheme based on the enzyme reaction products. The three main types of hyal ...
'', an enzyme that ensures rapid diffusion of the venom.
Venomous snakes that use hemotoxins usually have fangs in the front of their mouths, making it easier for them to inject the venom into their victims. Some snakes that use neurotoxins (such as the mangrove snake) have fangs in the back of their mouths, with the fangs curled backwards. This makes it difficult both for the snake to use its venom and for scientists to milk them. Elapids, however, such as cobras and kraits are ''proteroglyphous
A snake skeleton consists primarily of the skull, vertebrae, and ribs, with only vestigial limb, vestigial remnants of the limbs.
Skull
The skull of a snake is a very complex structure, with numerous joints to allow the snake to swallow prey fa ...
''—they possess hollow fangs that cannot be erected toward the front of their mouths, and cannot "stab" like a viper. They must actually bite the victim.
It has been suggested that all snakes may be venomous to a certain degree, with harmless snakes having weak venom and no fangs. According to this theory, most snakes that are labelled "nonvenomous" would be considered harmless because they either lack a venom delivery method or are incapable of delivering enough to endanger a human. The theory postulates that snakes may have evolved from a common lizard ancestor that was venomous, and also that venomous lizards like the gila monster
The Gila monster (''Heloderma suspectum'', ) is a species of venomous lizard native to the Southwestern United States and the northwestern Mexican state of Sonora. It is a heavy, typically slow-moving reptile, up to long, and it is the only ve ...
, beaded lizard, monitor lizards, and the now-extinct mosasaurs
Mosasaurs (from Latin ''Mosa'' meaning the 'Meuse', and Greek ' meaning 'lizard') comprise a group of extinct, large marine reptiles from the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains were discovered in a limestone quarry at Maastricht on th ...
, may have derived from this same common ancestor. They share this "venom clade
Toxicofera (Greek for "those who bear toxins") is a proposed clade of scaled reptiles (squamates) that includes the Serpentes (snakes), Anguimorpha (monitor lizards, gila monster, and alligator lizards) and Iguania ( iguanas, agamas, and ch ...
" with various other sauria
Sauria is the clade containing the most recent common ancestor of archosaurs (such as crocodilians, dinosaurs, etc.) and lepidosaurs ( lizards and kin), and all its descendants. Since most molecular phylogenies recover turtles as more closely ...
n species.
Venomous snakes are classified in two taxonomic families:
* Elapid
Elapidae (, commonly known as elapids ; grc, ἔλλοψ ''éllops'' "sea-fish") is a family of snakes characterized by their permanently erect fangs at the front of the mouth. Most elapids are venomous, with the exception of the genus Emydoce ...
s – cobras including king cobras, kraits
''Bungarus'' is a genus of venomous elapid snakes, the kraits ("krait" is pronounced , rhyming with "kite"), found in South and Southeast Asia. The genus ''Bungarus'' has 16 species.
Distribution
Kraits are found in tropical Asia, from near Ir ...
, mamba
Mambas are fast moving highly venomous snakes of the genus ''Dendroaspis'' (which literally means "tree asp") in the family Elapidae. Four extant species are recognised currently; three of those four species are essentially arboreal and green ...
s, Australian copperheads, sea snake
Sea snakes, or coral reef snakes, are elapid snakes that inhabit marine environments for most or all of their lives. They belong to two subfamilies, Hydrophiinae and Laticaudinae. Hydrophiinae also includes Australasian terrestrial snakes, wher ...
s, and coral snake
Coral snakes are a large group of elapid snakes that can be divided into two distinct groups, the Old World coral snakes and New World coral snakes. There are 16 species of Old World coral snakes, in three genera (''Calliophis'', '' Hemibungar ...
s.
* Viperids – vipers, rattlesnakes, copperheads/ cottonmouths, and bushmasters.
There is a third family containing the ''opistoglyphous'' (rear-fanged) snakes (as well as the majority of other snake species):
* Colubrid
Colubridae (, commonly known as colubrids , from la, coluber, 'snake') is a family of snakes. With 249 genera, it is the largest snake family. The earliest species of the family date back to the Oligocene epoch. Colubrid snakes are found on ev ...
s – boomslangs, tree snakes, vine snakes, cat snakes, although not all colubrids are venomous.
Reproduction
Although a wide range of reproductive modes are used by snakes, all employinternal fertilization
Internal fertilization is the union of an egg and sperm cell during sexual reproduction inside the female body. Internal fertilization, unlike its counterpart, external fertilization, brings more control to the female with reproduction. For inte ...
. This is accomplished by means of paired, forked hemipenes
A hemipenis (plural hemipenes) is one of a pair of intromittent organs of male squamates (snakes, lizards and worm lizards). Hemipenes are usually held inverted within the body, and are everted for reproduction via erectile tissue, much like ...
, which are stored, inverted, in the male's tail.Capula (1989), p. 117. The hemipenes are often grooved, hooked, or spined—designed to grip the walls of the female's cloaca. The clitoris of the female snake consists of two structures located between the cloaca and the scent glands.
Most species of snakes lay eggs
Humans and human ancestors have scavenged and eaten animal eggs for millions of years. Humans in Southeast Asia had domesticated chickens and harvested their eggs for food by 1,500 BCE. The most widely consumed eggs are those of fowl, especial ...
which they abandon shortly after laying. However, a few species (such as the king cobra) construct nests and stay in the vicinity of the hatchlings after incubation. Most pythons coil around their egg-clutches and remain with them until they hatch. A female python will not leave the eggs, except to occasionally bask in the sun or drink water. She will even "shiver" to generate heat to incubate the eggs.
Some species of snake are ovoviviparous
Ovoviviparity, ovovivipary, ovivipary, or aplacental viviparity is a term used as a "bridging" form of reproduction between egg-laying oviparous and live-bearing viviparous reproduction. Ovoviviparous animals possess embryos that develop insi ...
and retain the eggs within their bodies until they are almost ready to hatch.Capula (1989), p. 118. Several species of snake, such as the boa constrictor
The boa constrictor (scientific name also ''Boa constrictor''), also called the red-tailed boa, is a species of large, non-venomous, heavy-bodied snake that is frequently kept and bred in captivity. The boa constrictor is a member of the family B ...
and green anaconda, are fully viviparous
Among animals, viviparity is development of the embryo inside the body of the parent. This is opposed to oviparity which is a reproductive mode in which females lay developing eggs that complete their development and hatch externally from the ...
, nourishing their young through a placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate mate ...
as well as a yolk sac
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though ''yolk sac'' is ...
; this is highly unusual among reptiles, and normally found in requiem sharks or placental mammals
Placental mammals (infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguishe ...
. Retention of eggs and live birth are most often associated with colder environments.

Sexual selection
Sexual selection is a mode of natural selection in which members of one biological sex choose mates of the other sex to mate with (intersexual selection), and compete with members of the same sex for access to members of the opposite sex ( ...
in snakes is demonstrated by the 3,000 species that each use different tactics in acquiring mates. Ritual combat between males for the females they want to mate with includes topping, a behavior exhibited by most viperids in which one male will twist around the vertically elevated fore body of its opponent and force it downward. It is common for neck-biting to occur while the snakes are entwined.
Facultative parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek grc, παρθένος, translit=parthénos, lit=virgin, label=none + grc, γένεσις, translit=génesis, lit=creation, label=none) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and developmen ...
is a natural form of reproduction in which growth and development of embryos occur without fertilization. ''Agkistrodon contortrix'' (copperhead) and ''Agkistrodon piscivorus'' (cottonmouth) can reproduce by facultative parthenogenesis, meaning that they are capable of switching from a sexual
Sex is the biological distinction of an organism between male and female.
Sex or SEX may also refer to:
Biology and behaviour
*Animal sexual behaviour
**Copulation (zoology)
**Human sexual activity
**Non-penetrative sex, or sexual outercourse
** ...
mode of reproduction to an asexual mode. The most likely type of parthenogenesis to occur is automixis
''Automixis'' is the fusion of (typically haploid) nuclei or gametes derived from the same individual. The term covers several reproductive mechanisms, some of which are parthenogenetic.
Diploidy might be restored by the doubling of the chromoso ...
with terminal fusion, a process in which two terminal products from the same meiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately r ...
fuse to form a diploid zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism.
In multicell ...
. This process leads to genome-wide homozygosity
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
...
, expression of deleterious recessive allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
s, and often to developmental abnormalities. Both captive-born and wild-born copperheads and cottonmouths appear to be capable of this form of parthenogenesis.
Reproduction in squamate
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest order of reptiles, comprising lizards, snakes, and amphisbaenians (worm lizards), which are collectively known as squamates or scaled reptiles. With over 10,900 species, it ...
reptiles is almost exclusively sexual. Males ordinarily have a ZZ pair of sex-determining chromosomes, and females a ZW pair. However, the Colombian Rainbow boa ('' Epicrates maurus'') can also reproduce by facultative parthenogenesis, resulting in production of WW female progeny. The WW females are likely produced by terminal automixis.
Embryonic Development
 Snake embryonic development initially follows similar steps as any vertebrate embryo. The snake embryo begins as a
Snake embryonic development initially follows similar steps as any vertebrate embryo. The snake embryo begins as a zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism.
In multicell ...
, undergoes rapid cell division, forms a germinal disc
The blastodisc, also called the germinal disc, is the embryo-forming part on the yolk of the egg of an animal that undergoes discoidal meroblastic cleavage. Discoidal cleavage occurs in those animals with a large proportion of yolk in their eggs, ...
, also called a blastodisc, then undergoes gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis
Organogenesis is the phase of embryonic development that starts at the end of gastrulation and continues until birth. During organogenesis, the three germ layers formed from gastrulation (the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) form the internal org ...
. Cell division and proliferation continues until an early snake embryo develops and the typical body shape of a snake can be observed. Multiple features differentiate the embryologic development of snakes from other vertebrates, two significant factors being the elongation of the body and the lack of limb development.
 The elongation in snake body is accompanied by a significant increase in
The elongation in snake body is accompanied by a significant increase in vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
count (mice have 60 vertebrae, whereas snakes may have over 300). This increase in vertebrae is due to an increase in somite
The somites (outdated term: primitive segments) are a set of bilaterally paired blocks of paraxial mesoderm that form in the embryonic stage of somitogenesis, along the head-to-tail axis in segmented animals. In vertebrates, somites subdivide ...
s during embryogenesis, leading to an increased number of vertebrae which develop. Somites are formed at the presomitic mesoderm due to a set of oscillatory genes that direct the somitogenesis clock. The snake somitogenesis clock operates at a frequency 4 times that of a mouse (after correction for developmental time), creating more somites, and therefore creating more vertebrae. This difference in clock speed is believed to be caused by differences in ''Lunatic fringe'' gene expression, a gene involved in the somitogenesis clock.
There is ample literature focusing on the limb development/lack of development in snake embryos and the gene expression associated with the different stages. In Henophidia, basal snakes, such as the python, embryos in early development exhibit a hind limb bud that develops with some cartilage and a cartilaginous pelvic element, however this degenerates before hatching. This presence of vestigial development suggests that some snakes are still undergoing hind limb reduction before they are eliminated. There is no evidence in basal snakes of forelimb rudiments and no examples of snake forelimb bud initiation in embryo, so little is known regarding the loss of this trait. Recent studies suggests that hind limb reduction could be due to mutations in enhancers for the Sonic hedgehog, SSH gene, however other studies suggested that mutations within the Hox gene, Hox Genes or their enhancers could contribute to snake limblessness. Since multiple studies have found evidence suggesting different genes played a role in the loss of limbs in snakes, it is likely that multiple gene mutations had an additive effect leading to limb loss in snakes
Behavior
Winter dormancy
 In regions where winters are too cold for snakes to tolerate while remaining active, local species will enter a period of Dormancy#Brumation, brumation. Unlike Dormancy#Hibernation, hibernation, in which the dormant mammals are actually asleep, brumating reptiles are awake but inactive. Individual snakes may brumate in burrows, under rock piles, or inside fallen trees, or large numbers of snakes may clump together in Hibernaculum (zoology), hibernacula.
In regions where winters are too cold for snakes to tolerate while remaining active, local species will enter a period of Dormancy#Brumation, brumation. Unlike Dormancy#Hibernation, hibernation, in which the dormant mammals are actually asleep, brumating reptiles are awake but inactive. Individual snakes may brumate in burrows, under rock piles, or inside fallen trees, or large numbers of snakes may clump together in Hibernaculum (zoology), hibernacula.
Feeding and diet
 All snakes are hypercarnivore, strictly carnivorous, Predation, preying on small animals including lizards, frogs, other snakes, small mammals, birds, eggs, fish, snails, worms, and insects. Snakes cannot bite or tear their food to pieces so must swallow their prey whole. The eating habits of a snake are largely influenced by body size; smaller snakes eat smaller prey. Juvenile pythons might start out feeding on lizards or mice and graduate to small deer or antelope as an adult, for example.
The snake's jaw is a complex structure. Contrary to the popular belief that snakes can dislocate their jaws, they have an extremely flexible mandible, lower jaw, the two halves of which are not rigidly attached, and numerous other joints in the skull, which allow the snake to open its mouth wide enough to swallow prey whole, even if it is larger in diameter than the snake itself. For example, the Dasypeltis, African egg-eating snake has flexible jaws adapted for eating eggs much larger than the diameter of its head. This snake has no teeth, but does have bony protrusions on the inside edge of its Vertebral column, spine, which it uses to break the shell when eating eggs.
All snakes are hypercarnivore, strictly carnivorous, Predation, preying on small animals including lizards, frogs, other snakes, small mammals, birds, eggs, fish, snails, worms, and insects. Snakes cannot bite or tear their food to pieces so must swallow their prey whole. The eating habits of a snake are largely influenced by body size; smaller snakes eat smaller prey. Juvenile pythons might start out feeding on lizards or mice and graduate to small deer or antelope as an adult, for example.
The snake's jaw is a complex structure. Contrary to the popular belief that snakes can dislocate their jaws, they have an extremely flexible mandible, lower jaw, the two halves of which are not rigidly attached, and numerous other joints in the skull, which allow the snake to open its mouth wide enough to swallow prey whole, even if it is larger in diameter than the snake itself. For example, the Dasypeltis, African egg-eating snake has flexible jaws adapted for eating eggs much larger than the diameter of its head. This snake has no teeth, but does have bony protrusions on the inside edge of its Vertebral column, spine, which it uses to break the shell when eating eggs.
 The majority of snakes eat a variety of prey animals, but there is some specialization in certain species. King cobras and the Australian Vermicella annulata, bandy-bandy consume other snakes. Species of the family Pareidae have more teeth on the right side of their mouths than on the left, as they mostly prey on snails and the shells usually spiral clockwise.
Some snakes have a venomous bite, which they use to kill their prey before eating it. Other snakes kill their prey by
The majority of snakes eat a variety of prey animals, but there is some specialization in certain species. King cobras and the Australian Vermicella annulata, bandy-bandy consume other snakes. Species of the family Pareidae have more teeth on the right side of their mouths than on the left, as they mostly prey on snails and the shells usually spiral clockwise.
Some snakes have a venomous bite, which they use to kill their prey before eating it. Other snakes kill their prey by constriction
Constriction is a method used by various snake species to kill or subdue their prey. Although some species of venomous and mildly venomous snakes do use constriction to subdue their prey, most snakes which use constriction lack venom. The snake i ...
, while some swallow their prey when it is still alive.
 After eating, snakes become dormant to allow the process of digestion to take place; this is an intense activity, especially after consumption of large prey. In species that feed only sporadically, the entire intestine enters a reduced state between meals to conserve energy. The digestive system is then 'up-regulated' to full capacity within 48 hours of prey consumption. Being
After eating, snakes become dormant to allow the process of digestion to take place; this is an intense activity, especially after consumption of large prey. In species that feed only sporadically, the entire intestine enters a reduced state between meals to conserve energy. The digestive system is then 'up-regulated' to full capacity within 48 hours of prey consumption. Being ectothermic
An ectotherm (from the Greek () "outside" and () "heat") is an organism in which internal physiological sources of heat are of relatively small or of quite negligible importance in controlling body temperature.Davenport, John. Animal Life ...
("cold-blooded"), the surrounding temperature plays an important role in the digestion process. The ideal temperature for snakes to digest food is . There is a huge amount of metabolism, metabolic energy involved in a snake's digestion, for example the surface body temperature of the South American rattlesnake (''Crotalus durissus'') increases by as much as during the digestive process. If a snake is disturbed after having eaten recently, it will often vomiting, regurgitate its prey to be able to escape the perceived threat. When undisturbed, the digestive process is highly efficient; the snake's digestive enzymes dissolve and absorb everything but the prey's hair (or feathers) and claws, which are excreted along with uric acid, waste.
Hooding and spitting
Hooding (expansion of the neck area) is a visual deterrent, mostly seen in cobras (elapids), and is primarily controlled by rib muscles. Hooding can be accompanied by spitting venom towards the threatening object, and producing a specialized sound; hissing. Studies on captive cobras showed that 13 to 22% of the body length is raised during hooding.Locomotion
The lack of limbs does not impede the movement of snakes. They have developed several different modes of locomotion to deal with particular environments. Unlike the gaits of limbed animals, which form a continuum, each mode of snake locomotion is discrete and distinct from the others; transitions between modes are abrupt.Lateral undulation
 Lateral undulation is the sole mode of aquatic locomotion, and the most common mode of terrestrial locomotion. In this mode, the body of the snake alternately flexes to the left and right, resulting in a series of rearward-moving "waves". While this movement appears rapid, snakes have rarely been documented moving faster than two body-lengths per second, often much less. This mode of movement has the same net cost of transport (calories burned per meter moved) as running in lizards of the same mass.
Terrestrial lateral undulation is the most common mode of terrestrial locomotion for most snake species. In this mode, the posteriorly moving waves push against contact points in the environment, such as rocks, twigs, irregularities in the soil, etc. Each of these environmental objects, in turn, generates a reaction force directed forward and towards the midline of the snake, resulting in forward thrust while the lateral components cancel out. The speed of this movement depends upon the density of push-points in the environment, with a medium density of about 8 along the snake's length being ideal. The wave speed is precisely the same as the snake speed, and as a result, every point on the snake's body follows the path of the point ahead of it, allowing snakes to move through very dense vegetation and small openings.
When swimming, the waves become larger as they move down the snake's body, and the wave travels backwards faster than the snake moves forwards. Thrust is generated by pushing their body against the water, resulting in the observed slip. In spite of overall similarities, studies show that the pattern of muscle activation is different in aquatic versus terrestrial lateral undulation, which justifies calling them separate modes. All snakes can laterally undulate forward (with backward-moving waves), but only sea snakes have been observed reversing the motion (moving backwards with forward-moving waves).
Lateral undulation is the sole mode of aquatic locomotion, and the most common mode of terrestrial locomotion. In this mode, the body of the snake alternately flexes to the left and right, resulting in a series of rearward-moving "waves". While this movement appears rapid, snakes have rarely been documented moving faster than two body-lengths per second, often much less. This mode of movement has the same net cost of transport (calories burned per meter moved) as running in lizards of the same mass.
Terrestrial lateral undulation is the most common mode of terrestrial locomotion for most snake species. In this mode, the posteriorly moving waves push against contact points in the environment, such as rocks, twigs, irregularities in the soil, etc. Each of these environmental objects, in turn, generates a reaction force directed forward and towards the midline of the snake, resulting in forward thrust while the lateral components cancel out. The speed of this movement depends upon the density of push-points in the environment, with a medium density of about 8 along the snake's length being ideal. The wave speed is precisely the same as the snake speed, and as a result, every point on the snake's body follows the path of the point ahead of it, allowing snakes to move through very dense vegetation and small openings.
When swimming, the waves become larger as they move down the snake's body, and the wave travels backwards faster than the snake moves forwards. Thrust is generated by pushing their body against the water, resulting in the observed slip. In spite of overall similarities, studies show that the pattern of muscle activation is different in aquatic versus terrestrial lateral undulation, which justifies calling them separate modes. All snakes can laterally undulate forward (with backward-moving waves), but only sea snakes have been observed reversing the motion (moving backwards with forward-moving waves).
Sidewinding
 Most often employed by colubroid snakes ( colubrids,
Most often employed by colubroid snakes ( colubrids, elapids
Elapidae (, commonly known as elapids ; grc, ἔλλοψ ''éllops'' "sea-fish") is a family of snakes characterized by their permanently erect fangs at the front of the mouth. Most elapids are venomous, with the exception of the genus Emydocep ...
, and vipers
The Viperidae (vipers) are a family of snakes found in most parts of the world, except for Antarctica, Australia, Hawaii, Madagascar, and various other isolated islands. They are venomous and have long (relative to non-vipers), hinged fangs th ...
) when the snake must move in an environment that lacks irregularities to push against (rendering lateral undulation impossible), such as a slick mud flat, or a sand dune, sidewinding is a modified form of lateral undulation in which all of the body segments oriented in one direction remain in contact with the ground, while the other segments are lifted up, resulting in a peculiar "rolling" motion. This mode of locomotion overcomes the slippery nature of sand or mud by pushing off with only static portions on the body, thereby minimizing slipping. The static nature of the contact points can be shown from the tracks of a sidewinding snake, which show each belly scale imprint, without any smearing. This mode of locomotion has very low caloric cost, less than of the cost for a lizard to move the same distance. Contrary to popular belief, there is no evidence that sidewinding is associated with the sand being hot.
Concertina
When push-points are absent, but there is not enough space to use sidewinding because of lateral constraints, such as in tunnels, snakes rely on concertina locomotion. In this mode, the snake braces the posterior portion of its body against the tunnel wall while the front of the snake extends and straightens. The front portion then flexes and forms an anchor point, and the posterior is straightened and pulled forwards. This mode of locomotion is slow and very demanding, up to seven times the cost of laterally undulating over the same distance. This high cost is due to the repeated stops and starts of portions of the body as well as the necessity of using active muscular effort to brace against the tunnel walls.Arboreal
 The movement of snakes in arboreal habitats has only recently been studied. While on tree branches, snakes use several modes of locomotion depending on species and bark texture. In general, snakes will use a modified form of concertina locomotion on smooth branches, but will laterally undulate if contact points are available. Snakes move faster on small branches and when contact points are present, in contrast to limbed animals, which do better on large branches with little 'clutter'.
Gliding snakes (''Chrysopelea'') of Southeast Asia launch themselves from branch tips, spreading their ribs and laterally undulating as they glide between trees. These snakes can perform a controlled glide for hundreds of feet depending upon launch altitude and can even turn in midair.
The movement of snakes in arboreal habitats has only recently been studied. While on tree branches, snakes use several modes of locomotion depending on species and bark texture. In general, snakes will use a modified form of concertina locomotion on smooth branches, but will laterally undulate if contact points are available. Snakes move faster on small branches and when contact points are present, in contrast to limbed animals, which do better on large branches with little 'clutter'.
Gliding snakes (''Chrysopelea'') of Southeast Asia launch themselves from branch tips, spreading their ribs and laterally undulating as they glide between trees. These snakes can perform a controlled glide for hundreds of feet depending upon launch altitude and can even turn in midair.
Rectilinear
The slowest mode of snake locomotion is rectilinear locomotion, which is also the only one where the snake does not need to bend its body laterally, though it may do so when turning. In this mode, the belly scales are lifted and pulled forward before being placed down and the body pulled over them. Waves of movement and stasis pass posteriorly, resulting in a series of ripples in the skin. The ribs of the snake do not move in this mode of locomotion and this method is most often used by large Pythonidae, pythons,boa
Kwon Bo-ah (; born November 5, 1986), known professionally as BoA, is a South Korean singer, songwriter, dancer, record producer and actress. One of the most successful and influential Korean entertainers, she has been dubbed the " Queen of K- ...
s, and Viperidae, vipers when stalking prey across open ground as the snake's movements are subtle and harder to detect by their prey in this manner.
Interactions with humans

Bite
Snakes do not ordinarily prey on humans. Unless startled or injured, most snakes prefer to avoid contact and will not attack humans. With the exception of large constrictors, nonvenomous snakes are not a threat to humans. The bite of a nonvenomous snake is usually harmless; their teeth are not adapted for tearing or inflicting a deep puncture wound, but rather grabbing and holding. Although the possibility of infection and tissue damage is present in the bite of a nonvenomous snake, venomous snakes present far greater hazard to humans. The World Health Organization (WHO) lists snakebite under the "other neglected conditions" category. Documented deaths resulting from snake bites are uncommon. Nonfatal bites from venomous snakes may result in the need for amputation of a limb or part thereof. Of the roughly 725 species of venomous snakes worldwide, only 250 are able to kill a human with one bite. Australia averages only one fatal snake bite per year. In India, 250,000 snakebites are recorded in a single year, with as many as 50,000 recorded initial deaths. The WHO estimates that on the order of 100,000 people die each year as a result of snake bites, and around three times as many amputations and other permanent disabilities are caused by snakebites annually. The treatment for a snakebite is as variable as the bite itself. The most common and effective method is through antivenom (or antivenin), a serum made from the venom of the snake. Some antivenom is species-specific (monovalent) while some is made for use with multiple species in mind (polyvalent). In the United States for example, all species of venomous snakes are pit vipers, with the exception of thecoral snake
Coral snakes are a large group of elapid snakes that can be divided into two distinct groups, the Old World coral snakes and New World coral snakes. There are 16 species of Old World coral snakes, in three genera (''Calliophis'', '' Hemibungar ...
. To produce antivenom, a mixture of the venoms of the different species of rattlesnakes, copperheads, and cottonmouths is injected into the body of a horse in ever-increasing dosages until the horse is immunized. Blood is then extracted from the immunized horse. The serum is separated and further purified and freeze-dried. It is reconstituted with sterile water and becomes antivenom. For this reason, people who are allergic to horses are more likely to have an allergic reaction to antivenom. Antivenom for the more dangerous species (such as mamba
Mambas are fast moving highly venomous snakes of the genus ''Dendroaspis'' (which literally means "tree asp") in the family Elapidae. Four extant species are recognised currently; three of those four species are essentially arboreal and green ...
s, taipans, and cobras) is made in a similar manner in India, South Africa, and Australia, although these antivenoms are species-specific.
Snake charmers
 In some parts of the world, especially in India, snake charming is a roadside show performed by a charmer. In such a show, the snake charmer carries a basket containing a snake that he seemingly charms by playing tunes with his flutelike musical instrument, to which the snake responds. The snake is in fact responding to the movement of the flute, not the sound it makes, as snakes lack external ears (though they do have internal ears).
The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 in India technically prohibits snake charming on the grounds of reducing animal cruelty. Other types of snake charmers use a snake and mongoose show, where the two animals have a mock fight; however, this is not very common, as the animals may be seriously injured or killed. Snake charming as a profession is dying out in India because of competition from modern forms of entertainment and environment laws proscribing the practice. Many Indians have never seen snake charming and it is becoming a folktale of the past.
In some parts of the world, especially in India, snake charming is a roadside show performed by a charmer. In such a show, the snake charmer carries a basket containing a snake that he seemingly charms by playing tunes with his flutelike musical instrument, to which the snake responds. The snake is in fact responding to the movement of the flute, not the sound it makes, as snakes lack external ears (though they do have internal ears).
The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 in India technically prohibits snake charming on the grounds of reducing animal cruelty. Other types of snake charmers use a snake and mongoose show, where the two animals have a mock fight; however, this is not very common, as the animals may be seriously injured or killed. Snake charming as a profession is dying out in India because of competition from modern forms of entertainment and environment laws proscribing the practice. Many Indians have never seen snake charming and it is becoming a folktale of the past.
Trapping
The ''Irulas'' tribe of Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu in India have been hunter-gatherers in the hot, dry plains forests, and have practiced the art of snake catching for generations. They have a vast knowledge of snakes in the field. They generally catch the snakes with the help of a simple stick. Earlier, the ''Irulas'' caught thousands of snakes for the snake-skin industry. After the complete ban of the snake-skin industry in India and protection of all snakes under the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972, Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972, they formed the Irula Snake Catcher's Cooperative and switched to catching snakes for removal of venom, releasing them in the wild after four extractions. The venom so collected is used for producing life-saving antivenom, biomedical research and for other medicinal products. The ''Irulas'' are also known to eat some of the snakes they catch and are very useful in rat extermination in the villages. Despite the existence of snake charmers, there have also been professional snake catchers or Wrangler (profession), wranglers. Modern-day snake trapping involves a herpetologist using a long stick with a V- shaped end. Some television show hosts, like Bill Haast, Austin Stevens, Steve Irwin, and Jeff Corwin, prefer to catch them using bare hands.Consumption
 Although snakes are not commonly thought of as food, their consumption is acceptable in some cultures and may even be considered a delicacy. Snake soup is popular in Cantonese cuisine, consumed by locals in the autumn to warm their bodies. Western cultures document the consumption of snakes only under extreme circumstances of hunger, with the exception of cooked rattlesnake meat, which is commonly consumed in Texas and parts of the Midwestern United States.
Although snakes are not commonly thought of as food, their consumption is acceptable in some cultures and may even be considered a delicacy. Snake soup is popular in Cantonese cuisine, consumed by locals in the autumn to warm their bodies. Western cultures document the consumption of snakes only under extreme circumstances of hunger, with the exception of cooked rattlesnake meat, which is commonly consumed in Texas and parts of the Midwestern United States.
 In Asian countries such as China, Taiwan, Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, and Cambodia, drinking the blood of a snake—particularly the cobra—is believed to increase sexual virility. When possible, the blood is drained while the cobra is still alive, and it is usually mixed with some form of liquor to improve the taste.
The use of snakes in alcohol is accepted in some Asian countries. In such cases, one or more snakes are left to steep in a jar or container of liquor, as this is claimed to make the liquor stronger (as well as more expensive). One example of this is the Trimeresurus flavoviridis, Habu snake, which is sometimes placed in the Okinawan liqueur ''Habushu'' (ブ酒), also known as "Habu Sake".
Snake wine (蛇酒) is an alcoholic beverage produced by infusing whole snakes in Chinese alcoholic beverages, rice wine or grain alcohol. First recorded as being consumed in China during the Western Zhou dynasty, this drink is considered an important curative and is believed to reinvigorate a person according to traditional Chinese medicine.
In Asian countries such as China, Taiwan, Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, and Cambodia, drinking the blood of a snake—particularly the cobra—is believed to increase sexual virility. When possible, the blood is drained while the cobra is still alive, and it is usually mixed with some form of liquor to improve the taste.
The use of snakes in alcohol is accepted in some Asian countries. In such cases, one or more snakes are left to steep in a jar or container of liquor, as this is claimed to make the liquor stronger (as well as more expensive). One example of this is the Trimeresurus flavoviridis, Habu snake, which is sometimes placed in the Okinawan liqueur ''Habushu'' (ブ酒), also known as "Habu Sake".
Snake wine (蛇酒) is an alcoholic beverage produced by infusing whole snakes in Chinese alcoholic beverages, rice wine or grain alcohol. First recorded as being consumed in China during the Western Zhou dynasty, this drink is considered an important curative and is believed to reinvigorate a person according to traditional Chinese medicine.
Pets
In the Western world, some snakes are kept as pets, especially docile species such as the ball python and corn snake. To meet the demand, a herpetoculture, captive breeding industry has developed. Snakes bred in captivity are considered preferable to specimens caught in the wild and tend to make better pets. Compared with more traditional types of companion animal, snakes can be very low-maintenance pets; they require minimal space, as most common species do not exceed in length, and can be fed relatively infrequently—usually once every five to 14 days. Certain snakes have a lifespan of more than 40 years if given proper care.Symbolism


 The ancient Greeks used the Gorgoneion, a depiction of a hideous face with serpents for hair, as an Apotropaic magic, apotropaic symbol to ward off evil. In a Greek mythology, Greek myth described by Pseudo-Apollodorus in his ''Bibliotheca (Pseudo-Apollodorus), Bibliotheca'', Medusa was a Gorgon with serpents for hair whose gaze turned all those who looked at her to stone and was slain by the hero Perseus. In the Roman poet Ovid's ''Metamorphoses'', Medusa is said to have once been a beautiful priestess of Athena, whom Athena turned into a serpent-haired monster after she was raped by the god Poseidon in Athena's temple. In another myth referenced by the Boeotian poet Hesiod and described in detail by Pseudo-Apollodorus, the hero Heracles is said to have slain the Lernaean Hydra, a multiple-headed serpent which dwelt in the swamps of Lerna.
The legendary account of the foundation of Ancient Thebes (Boeotia), Thebes mentioned a monster snake guarding the spring from which the new settlement was to draw its water. In fighting and killing the snake, the companions of the founder Cadmus all perished – leading to the term "Cadmean victory" (i.e. a victory involving one's own ruin).
The ancient Greeks used the Gorgoneion, a depiction of a hideous face with serpents for hair, as an Apotropaic magic, apotropaic symbol to ward off evil. In a Greek mythology, Greek myth described by Pseudo-Apollodorus in his ''Bibliotheca (Pseudo-Apollodorus), Bibliotheca'', Medusa was a Gorgon with serpents for hair whose gaze turned all those who looked at her to stone and was slain by the hero Perseus. In the Roman poet Ovid's ''Metamorphoses'', Medusa is said to have once been a beautiful priestess of Athena, whom Athena turned into a serpent-haired monster after she was raped by the god Poseidon in Athena's temple. In another myth referenced by the Boeotian poet Hesiod and described in detail by Pseudo-Apollodorus, the hero Heracles is said to have slain the Lernaean Hydra, a multiple-headed serpent which dwelt in the swamps of Lerna.
The legendary account of the foundation of Ancient Thebes (Boeotia), Thebes mentioned a monster snake guarding the spring from which the new settlement was to draw its water. In fighting and killing the snake, the companions of the founder Cadmus all perished – leading to the term "Cadmean victory" (i.e. a victory involving one's own ruin).
 Three medical symbols involving snakes that are still used today are Bowl of Hygieia, symbolizing pharmacy, and the Caduceus and
Three medical symbols involving snakes that are still used today are Bowl of Hygieia, symbolizing pharmacy, and the Caduceus and Rod of Asclepius
In Greek mythology, the Rod of Asclepius (⚕; grc, Ράβδος του Ασκληπιού, , sometimes also spelled Asklepios), also known as the Staff of Aesculapius and as the asklepian, is a serpent-entwined rod wielded by the Greek god A ...
, which are symbols denoting medicine in general.
One of the etymologies proposed for the common female first name ''Linda (given name), Linda'' is that it might derive from Old German ''Lindi'' or ''Linda'', meaning a serpent.
India is often called the land of snakes and is steeped in tradition regarding snakes. Snakes are worshipped as gods even today with many women pouring milk on snake pits (despite snakes' aversion for milk). The cobra is seen on the neck of Shiva and Vishnu is depicted often as sleeping on a seven-headed snake or within the coils of a serpent. There are also several temples in India solely for cobras sometimes called ''Nagraj'' (King of Snakes) and it is believed that snakes are symbols of fertility. There is a Hindu festival called Nag Panchami each year on which day snakes are venerated and prayed to. See also ''Nāga''.
In India there is another mythology about snakes. Commonly known in Hindi as "Ichchhadhari Nag, Ichchhadhari" snakes. Such snakes can take the form of any living creature, but prefer human form. These mythical snakes possess a valuable gem called "Mani", which is more brilliant than diamond. There are many stories in India about greedy people trying to possess this gem and ending up getting killed.
The Snake (zodiac), snake is one of the 12 celestial animals of Chinese zodiac, in the Chinese calendar.
Many ancient Peruvian cultures worshipped nature. They emphasized animals and often depicted snakes in their art.
Religion
Snakes are used in Hinduism as a part of ritual worship. In the annual Nag Panchami festival, participants worship either live cobras or images of Nāgas. Lord Shiva is depicted in most images with a snake coiled around his neck. Puranas, Puranic literature includes various stories associated with snakes, for example Shesha is said to hold all the planets of the Universe on his hoods and to constantly sing the glories of Vishnu from all his mouths. Other notable snakes in Hinduism are Vasuki, Takshaka, Karkotaka, and Pingala. The term ''Nāga'' is used to refer to entities that take the form of large snakes in Hinduism and Buddhism. Snakes have been widely revered in many cultures, such as in ancient Greece where the serpent was seen as a healer. Asclepius carried a serpent wound around his wand, a symbol seen today on many ambulances. In Judaism, the snake of brass is also a symbol of healing, of one's life being saved from imminent death. In religious terms, the snake and jaguar were arguably the most important animals in ancient Mesoamerica. "In states of ecstasy, lords dance a serpent dance; great descending snakes adorn and support buildings from Chichen Itza to Tenochtitlan, and the Nahuatl word ''coatl'' meaning serpent or twin, forms part of primary deities such as Mixcoatl, Quetzalcoatl, and Coatlicue." In the Maya calendar, Maya and Aztec calendars, the fifth day of the week was known as Snake Day. In some parts of Christianity, the redemptive work of Jesus, Jesus Christ is compared to saving one's life through beholding the Nehushtan (serpent of brass). Snake handling in Christianity, Snake handlers use snakes as an integral part of church worship, to demonstrate their faith in divine protection. However, more commonly in Christianity, the serpent has been depicted as a representative of evil and sly plotting, as seen in the description in Book of Genesis, Genesis of a snake tempting Eve in the Garden of Eden. Saint Patrick is purported to have expelled all snakes from Ireland while converting the country to Christianity in the 5th century, thus explaining the absence of snakes there. In Christianity and Judaism, the snake makes its infamous appearance in the first book of the Bible when a serpent appears before Adam and Eve and tempts them with the forbidden fruit from the Tree of Knowledge of Good and Evil, Tree of Knowledge. The snake returns in the Book of Exodus when Moses turns his staff into a snake as a sign of God's power, and later when he makes the Nehushtan, a bronze snake on a pole that when looked at cured the people of bites from the snakes that plagued them in the desert. The serpent makes its final appearance symbolizing Satan in the Book of Revelation: "And he laid hold on the dragon the old serpent, which is the devil and Satan, and bound him for a thousand years." In Neo-Paganism and Wicca, the snake is seen as a symbol of wisdom and knowledge. Additionally, snakes are sometimes associated with Hecate, the Greek goddess of witchcraft.
Medicine
Several compounds from snake venoms are being researched as potential treatments or preventatives for pain, cancers, arthritis, stroke, heart disease, hemophilia, and hypertension, and to control bleeding (e.g. during surgery).See also
* Limbless vertebrates * List of Serpentes families * List of snakes * Ophiology * Snakebot * Snake detection theory * Snake skeleton * Spinal osteoarthropathy (reptile disease) * ''The New Encyclopedia of Snakes'' * The Snakes of Europe and Snakes of Europe Wikibooks:Snakes of Europe, a wikibook * Venomous snake * *References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* * * * *BBC Nature:
Snake news, and video clips from BBC programmes past and present.
at Life is Short but Snakes are Long {{Authority control Snakes, Cenomanian first appearances Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Extant Cenomanian first appearances