Rotating Biological Contactor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A rotating biological contactor or RBC is a
 A properly designed RBC produced a very high quality final effluent. However both the organic and hydraulic loading had to be addressed in the design phase.
In the 1980s problems were encountered in the USA prompting the Environmental Agency to commission a number of reports.
These reports identified a number of issues and criticized the RBC process. One author suggested that since manufacturers were aware of the problem, the problems would be resolved and suggested that design engineers should specify a long life.
A properly designed RBC produced a very high quality final effluent. However both the organic and hydraulic loading had to be addressed in the design phase.
In the 1980s problems were encountered in the USA prompting the Environmental Agency to commission a number of reports.
These reports identified a number of issues and criticized the RBC process. One author suggested that since manufacturers were aware of the problem, the problems would be resolved and suggested that design engineers should specify a long life.
Design Criteria for Rotating Biological Contactors
Implementing Rotating Biological Contactor Solutions
Applying the Rotating Biological Contactor Process
Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources - Wastewater Operator Certification. Biological Treatment - Attached-Growth Processes Study Guide, February 2016 Edition
Penn State Harrisburg Environmental Training Center Wastewater Treatment Plant Operator Certification Training - Module 21: Rotating Biological Contactors
{{Wastewater Environmental engineering Chemical equipment Biodegradable waste management Waste treatment technology Water treatment
biological
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary in ...
fixed-film treatment process used in the secondary treatment
Secondary treatment is the removal of biodegradable organic matter (in solution or suspension) from sewage or similar kinds of wastewater. The aim is to achieve a certain degree of effluent quality in a sewage treatment plant suitable for the in ...
of wastewater following primary treatment
Sewage treatment (or domestic wastewater treatment, municipal wastewater treatment) is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable for discharge to the surrounding envi ...
. The primary treatment process involves removal of grit, sand and coarse suspended material through a screening process, followed by settling of suspended solids. The RBC process allows the wastewater to come in contact with a biological film in order to remove pollutant
A pollutant or novel entity is a substance or energy introduced into the environment that has undesired effects, or adversely affects the usefulness of a resource. These can be both naturally forming (i.e. minerals or extracted compounds like o ...
s in the wastewater before discharge of the treated wastewater to the environment
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
* Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or ...
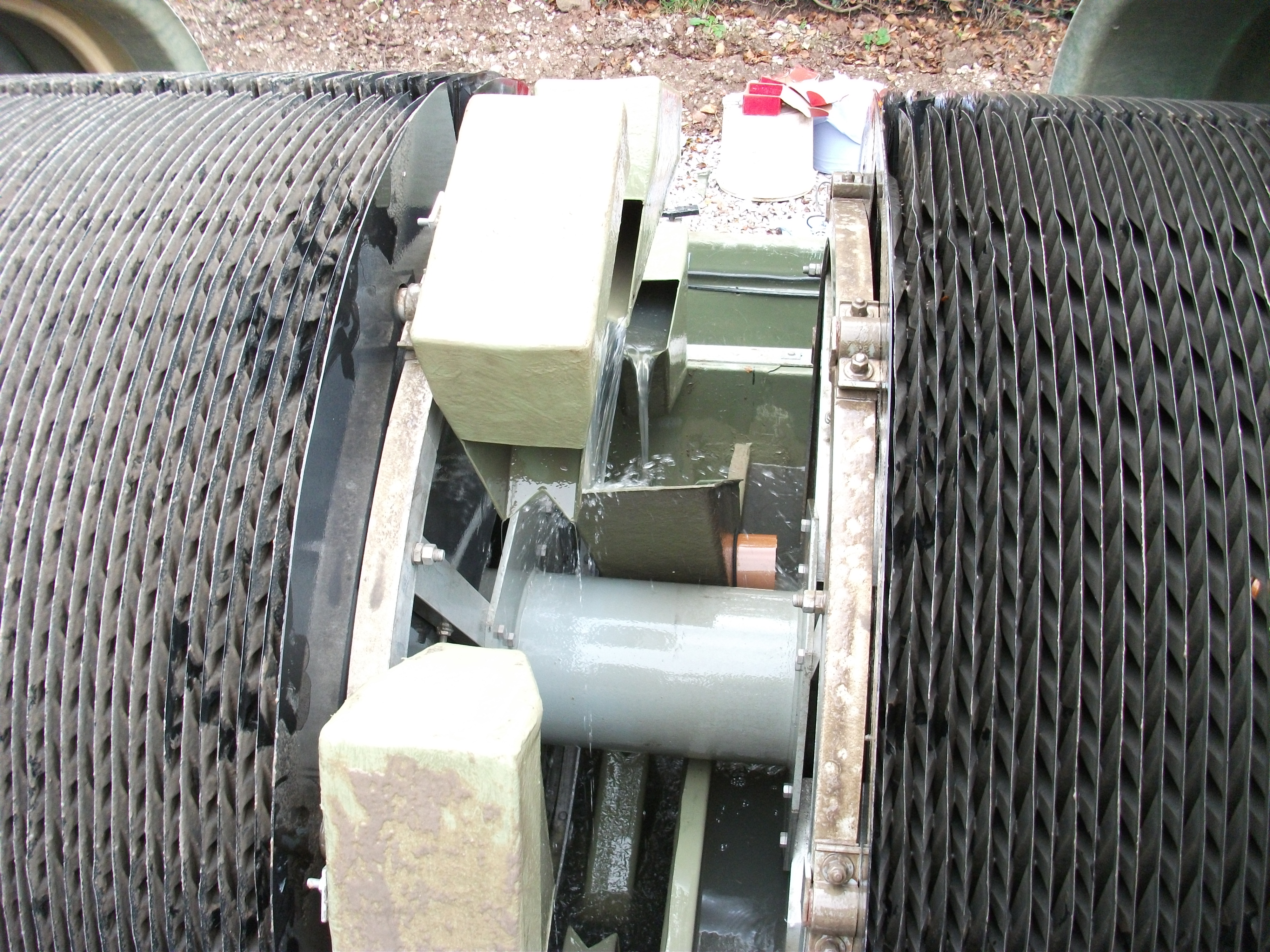
, usually a body of water (river, lake or ocean). A rotating biological contactor is a type of secondary (biological) treatment process. It consists of a series of closely spaced, parallel discs mounted on a rotating shaft which is supported just above the surface of the wastewater. Microorganisms grow on the surface of the discs where biological degradation
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradat ...
of the wastewater pollutants takes place.
Rotating biological contactors (RBCs) are capable of withstanding surges in organic load. To be successful, micro-organisms need both oxygen to live and food to grow. Oxygen is obtained from the atmosphere as the disks rotate. As the micro-organisms grow, they build up on the media until they are sloughed off due to shear forces provided by the rotating discs in the sewage. Effluent from the RBC is then passed through a clarifier where the sloughed biological solids in suspension settle as a sludge.
Operation
The rotating packs of disks (known as the media) are contained in a tank or trough and rotate at between 2 and 5 revolutions per minute. Commonly used plastics for the media are polyethylene, PVC and expanded polystyrene. The shaft is aligned with the flow of wastewater so that the discs rotate at right angles to the flow, with several packs usually combined to make up a treatment train. About 40% of the disc area is immersed in the wastewater. Biological growth is attached to the surface of the disc and forms a slime layer. The discs contact the wastewater with the atmospheric air for oxidation as it rotates. The rotation helps to slough off excess solids. The disc system can be staged in series to obtain nearly any detention time or degree of removal required. Since the systems are staged, the culture of the later stages can be acclimated to the slowly degraded materials. The discs consist of plastic sheets ranging from 2 to 4 m in diameter and are up to 10 mm thick. Several modules may be arranged in parallel and/or in series to meet the flow and treatment requirements. The discs are submerged in waste water to about 40% of their diameter. Approximately 95% of the surface area is thus alternately submerged in waste water and then exposed to the atmosphere above the liquid. Carbonaceous substrate is removed in the initial stage of RBC. Carbon conversion may be completed in the first stage of a series of modules, with nitrification being completed after the 5th stage. Most design of RBC systems will include a minimum of 4 or 5 modules in series to obtain nitrification of waste water. As the biofilm biomass changes from Carbon metabolizing to nitrifying, a visual colour change from grey/beige to brown can be seen which is illustrated by the adjacent photo.
Biofilms
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular po ...
, which are biological growths that become attached to the discs, assimilate the organic materials (measured as BOD5) in the wastewater. Aeration
Aeration (also called aerification or aeriation) is the process by which air is circulated through, mixed with or dissolved in a liquid or other substances that act as a fluid (such as soil). Aeration processes create additional surface area in t ...
is provided by the rotating action, which exposes the media to the air after contacting them with the wastewater, facilitating the degradation of the pollutants being removed. The degree of wastewater treatment is related to the amount of media surface area and the quality and volume of the inflowing wastewater.
RBC's regularly achieve the following effluent parameters for treated waste water: BOD5: 20 mg/L, Suspended Solids: 30 mg/L and Ammonia N: 20 mg/L. They consume very low power and make little noise due to the slow rotation of the rotor (2-5 RPM). They are generally considered very robust and low maintenance systems. Better discharge effluent parameters can be achieved by adding a tertiary polishing filter after the RBC to lower BOD5, SS and Ammonia Nitrogen. An additional UV or Chlorination step can achieve effluent parameters that make the water suitable for irrigation or toilet flushing.
Secondary clarification
Secondary clarifiers following RBCs are identical in design to conventional humus tanks, as used downstream oftrickling filter
A trickling filter is a type of wastewater treatment system. It consists of a fixed bed of rocks, coke, gravel, slag, polyurethane foam, sphagnum peat moss, ceramic, or plastic media over which sewage or other wastewater flows downward an ...
s. Sludge is generally removed daily, or pumped automatically to the primary settlement tank for co-settlement. Regular sludge removal reduces the risk of anaerobic conditions from developing within the sludge, with subsequent sludge flotation due to the release of gases.
History
The first RBC was installed in West Germany in 1959, later it was introduced in the United States and Canada. In the United States, rotating biological contactors are used for industries producing wastewaters high inbiochemical oxygen demand
Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) is the amount of dissolved oxygen (DO) needed (i.e. demanded) by aerobic biological organisms to break down organic material present in a given water sample at a certain temperature over a specific time period. T ...
(BOD) (e.g., petroleum industry and dairy industry). In the UK, the first GRP RBC's - manufactured by KEE Process Ltd. originally known as KLARGESTER - go back to 1955.
 A properly designed RBC produced a very high quality final effluent. However both the organic and hydraulic loading had to be addressed in the design phase.
In the 1980s problems were encountered in the USA prompting the Environmental Agency to commission a number of reports.
These reports identified a number of issues and criticized the RBC process. One author suggested that since manufacturers were aware of the problem, the problems would be resolved and suggested that design engineers should specify a long life.
A properly designed RBC produced a very high quality final effluent. However both the organic and hydraulic loading had to be addressed in the design phase.
In the 1980s problems were encountered in the USA prompting the Environmental Agency to commission a number of reports.
These reports identified a number of issues and criticized the RBC process. One author suggested that since manufacturers were aware of the problem, the problems would be resolved and suggested that design engineers should specify a long life.
Severn Trent
Severn Trent plc is a water company based in Coventry, England. It supplies 4.6 million households and business across the Midlands and Wales.
It is traded on the London Stock Exchange and a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. Severn Trent, the ...
Water Ltd, a large UK Water Company based in the Midlands, employed RBCs as the preferred process for their small works which amount to over 700 sites Consequently, long life was essential to compliance.
This issue was successfully addressed by Eric Findlay C Eng when he was employed by Severn Trent
Severn Trent plc is a water company based in Coventry, England. It supplies 4.6 million households and business across the Midlands and Wales.
It is traded on the London Stock Exchange and a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. Severn Trent, the ...
Water Ltd in the UK following a period of failure of a number of plants. As a result, the issue of short life failure became fully understood in the early 1990s when the correct process and hydraulic issues had been identified to produce a high quality nitrified effluent.
There are several other papers which address the whole issue of RBCs. Findlay also developed a system for repairing defective RBCs enabling shaft and frame life to be extended up to 30 years based on the Cranfield designed frame. Where additional capacity was required intermediate frames are used.KEE Process Website (1993)
https://www.keeservices.com/about/
See also
*Activated sludge
The activated sludge process is a type of biological wastewater treatment process for treating sewage or industrial wastewaters using aeration and a biological floc composed of bacteria and protozoa. It uses air (or oxygen) and microorganisms to ...
*Aerated lagoon
An aerated lagoon (or aerated pond) is a simple wastewater treatment system consisting of a pond with artificial aeration to promote the biological oxidation of wastewaters.
There are many other aerobic biological processes for treatment of waste ...
*Trickling filter
A trickling filter is a type of wastewater treatment system. It consists of a fixed bed of rocks, coke, gravel, slag, polyurethane foam, sphagnum peat moss, ceramic, or plastic media over which sewage or other wastewater flows downward an ...
* Industrial wastewater treatment
*List of waste water treatment technologies
This page consists of a list of wastewater treatment technologies:
See also
* Agricultural wastewater treatment
*Industrial wastewater treatment
* List of solid waste treatment technologies
* Waste treatment technologies
*Water purification
*Se ...
* Sewage treatment
References
External links
Design Criteria for Rotating Biological Contactors
Implementing Rotating Biological Contactor Solutions
Applying the Rotating Biological Contactor Process
Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources - Wastewater Operator Certification. Biological Treatment - Attached-Growth Processes Study Guide, February 2016 Edition
Penn State Harrisburg Environmental Training Center Wastewater Treatment Plant Operator Certification Training - Module 21: Rotating Biological Contactors
{{Wastewater Environmental engineering Chemical equipment Biodegradable waste management Waste treatment technology Water treatment