Ring Strain on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In 
 Small trans-cycloalkenes have so much ring strain they cannot exist for extended periods of time. For instance, the smallest trans-cycloalkane that has been isolated is
Small trans-cycloalkenes have so much ring strain they cannot exist for extended periods of time. For instance, the smallest trans-cycloalkane that has been isolated is
 In some molecules, torsional strain can contribute to ring strain in addition to angle strain. One example of such a molecule is
In some molecules, torsional strain can contribute to ring strain in addition to angle strain. One example of such a molecule is
/ref> The H-C-H bond angle is 115° whereas 106° is expected as in the CH2 groups of propane. *
organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J ...
, ring strain is a type of instability that exists when bonds in a molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and b ...
form angles that are abnormal. Strain is most commonly discussed for small rings such as cyclopropane
Cyclopropane is the cycloalkane with the molecular formula (CH2)3, consisting of three methylene groups (CH2) linked to each other to form a ring. The small size of the ring creates substantial ring strain in the structure. Cyclopropane itself i ...
s and cyclobutane
Cyclobutane is a cycloalkane and organic compound with the formula (CH2)4. Cyclobutane is a colourless gas and commercially available as a liquefied gas. Derivatives of cyclobutane are called cyclobutanes. Cyclobutane itself is of no commerci ...
s, whose internal angles are substantially smaller than the idealized value of approximately 109°. Because of their high strain, the heat of combustion
The heating value (or energy value or calorific value) of a substance, usually a fuel or food (see food energy), is the amount of heat released during the combustion of a specified amount of it.
The ''calorific value'' is the total energy rele ...
for these small rings is elevated.
Ring strain results from a combination of angle strain, conformational strain or Pitzer strain (torsional eclipsing interactions), and transannular strain, also known as van der Waals strain Van der Waals strain is strain resulting from Van der Waals repulsion when two substituents in a molecule approach each other with a distance less than the sum of their Van der Waals radii.
Van der Waals strain is also called Van der Waals rep ...
or Prelog strain. The simplest examples of angle strain are small cycloalkanes such as cyclopropane and cyclobutane.
Ring strain energy can be attributed to the energy required for the distortion of bond and bond angles in order to close a ring.
Ring strain energy is believed to be the cause of accelerated rates in altering ring reactions. Its interactions with traditional bond energies change the enthalpies of compounds effecting the kinetics and thermodynamics of ring strain reactions.

History
Ring strain theory was first developed by German chemist Adolf von Bayer in 1890. Previously, the only bonds believed to exist were torsional and steric; however, Bayer's theory became based on the interactions between the two strains. Bayer's theory was based on the assumption that ringed compounds were flat. Later, around the same time, Hermann Sachse formed his postulation that compound rings were not flat and potentially existed in a "chair" formation. Ernst Mohr later combined the two theories to explain the stability of six-membered rings and their frequency in nature, as well as the energy levels of other ring structures.Angle strain (Baeyer strain)
Alkanes
In alkanes, optimum overlap ofatomic orbital
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any ...
s is achieved at 109.5°. The most common cyclic compounds have five or six carbons in their ring. Adolf von Baeyer
Johann Friedrich Wilhelm Adolf von Baeyer (; 31 October 1835 – 20 August 1917) was a German chemist who synthesised indigo and developed a nomenclature for cyclic compounds (that was subsequently extended and adopted as part of the IUPAC org ...
received a Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
in 1905 for the discovery of the Baeyer strain theory, which was an explanation of the relative stabilities of cyclic molecules in 1885.Wade, L. G. "Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes." Organic Chemistry. 6th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2006. 103-122. Print.
Angle strain occurs when bond angles deviate from the ideal bond angles to achieve maximum bond strength in a specific chemical conformation
In chemistry, conformational isomerism is a form of stereoisomerism in which the isomers can be interconverted just by rotations about formally single bonds (refer to figure on single bond rotation). While any two arrangements of atoms in a mol ...
. Angle strain typically affects cyclic molecules, which lack the flexibility of acyclic molecules.
Angle strain destabilizes a molecule, as manifested in higher reactivity and elevated heat of combustion
The heating value (or energy value or calorific value) of a substance, usually a fuel or food (see food energy), is the amount of heat released during the combustion of a specified amount of it.
The ''calorific value'' is the total energy rele ...
. Maximum bond strength results from effective overlap of atomic orbitals in a chemical bond. A quantitative measure for angle strain is strain energy. Angle strain and torsional strain combine to create ring strain that affects cyclic molecules.
:
Normalized energies that allow comparison of ring strains are obtained by measuring per methylene group
In organic chemistry, a methylene group is any part of a molecule that consists of two hydrogen atoms bound to a carbon atom, which is connected to the remainder of the molecule by two single bonds. The group may be represented as , where th ...
(CH2) of the molar heat of combustion in the cycloalkanes.
:combustion per CH2 − 658.6 kJ = strain per CH2
The value 658.6 kJ per mole is obtained from an unstrained long-chain alkane.
Cycloalkanes generally have less ring strain than cycloalkenes, which is seen when comparing cyclopropane and cyclopropene.
Angle strain in alkenes
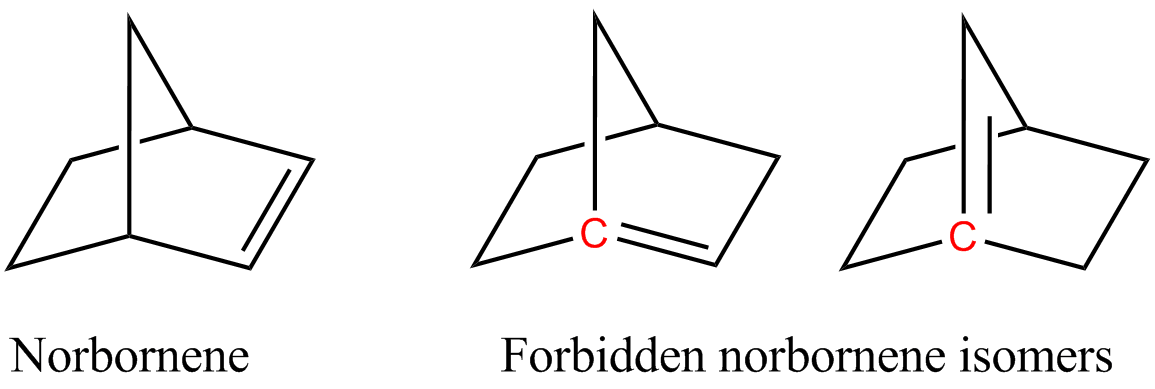
Cyclic alkenes are subject to strain resulting from distortion of the sp2-hybridized carbon centers. Illustrative is C60 where the carbon centres are pyramidalized. This distortion enhances the reactivity of this molecule. Angle strain also is the basis of Bredt's rule which dictates that bridgehead carbon centers are not incorporated in alkenes because the resulting alkene would be subject to extreme angle strain. Small trans-cycloalkenes have so much ring strain they cannot exist for extended periods of time. For instance, the smallest trans-cycloalkane that has been isolated is
Small trans-cycloalkenes have so much ring strain they cannot exist for extended periods of time. For instance, the smallest trans-cycloalkane that has been isolated is trans-cyclooctene
''trans''-Cyclooctene is a cyclic hydrocarbon with the formula ��(CH2)6CH=CH– where the two C–C single bonds adjacent to the double bond are on opposite sides of the latter's plane. It is a colorless liquid with a disagreeable odor.
Cycl ...
. Trans-cycloheptene has been detected via spectrophotometry
Spectrophotometry is a branch of electromagnetic spectroscopy concerned with the quantitative measurement of the reflection or transmission properties of a material as a function of wavelength. Spectrophotometry uses photometers, known as sp ...
for minute time periods, and trans-cyclohexene is thought to be an intermediate in some reactions. No smaller trans-cycloalkenes are known. On the contrary, while small cis-cycloalkenes do have ring strain, they have much less ring strain than small trans-cycloalkenes.
In general, the increased levels of unsaturation in alkenes leads to higher ring strain. Increasing unsaturation leads to greater ring strain in cyclopropene. Therefore, cyclopropene is an alkene that has the most ring strain between the two mentioned. The differing hybridizations and geometries between cyclopropene and cyclopropane contribute to the increased ring strain. Cyclopropene also has an increased angle strain, which also contributes to the greater ring strain. However, this trend does not always work for every alkane and alkene.
Torsional Strain (Pitzer Strain)
 In some molecules, torsional strain can contribute to ring strain in addition to angle strain. One example of such a molecule is
In some molecules, torsional strain can contribute to ring strain in addition to angle strain. One example of such a molecule is cyclopropane
Cyclopropane is the cycloalkane with the molecular formula (CH2)3, consisting of three methylene groups (CH2) linked to each other to form a ring. The small size of the ring creates substantial ring strain in the structure. Cyclopropane itself i ...
. Cyclopropane's carbon-carbon bonds form angles of 60°, far from the preferred angle of 109.5° angle in alkanes, so angle strain contributes most to cyclopropane's ring strain. However, as shown in the Newman projection
A Newman projection is a drawing that helps visualize the 3-dimensional structure of a molecule. This projection most commonly sights down a carbon-carbon bond, making it a very useful way to visualize the stereochemistry of alkanes. A Newman pro ...
of the molecule, the hydrogen atoms are eclipsed, causing some torsional strain as well.
Examples
In cycloalkanes, each carbon is bonded nonpolar covalently to two carbons and two hydrogen. The carbons have sp3 hybridization and should have ideal bond angles of 109.5°. Due to the limitations of cyclic structure, however, the ideal angle is only achieved in a six carbon ring —cyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula . Cyclohexane is non-polar. Cyclohexane is a colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive detergent-like odor, reminiscent of cleaning products (in which it is sometimes used). Cyclohe ...
in chair conformation. For other cycloalkanes, the bond angles deviate from ideal.
Molecules with a high amount of ring strain consist of three, four, and some five-membered rings, including: cyclopropanes, cyclopropene
Cyclopropene is an organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest cycloalkene. Because the ring is highly strained, cyclopropene is difficult to prepare and highly reactive. This colorless gas has been the subject for many fundamental st ...
s, cyclobutanes, cyclobutene
Cyclobutene is a cycloalkene. It is of interest in research but currently has no practical applications. It is a colorless easily condensed gas. A modern synthesis involves the 2-step dehydration of cyclobutanol. The compound was first prepared ...
s, ,1,1 ropellanes, ,2,2 ropellanes, epoxides
In organic chemistry, an epoxide is a cyclic ether () with a three-atom ring. This ring approximates an equilateral triangle, which makes it strained, and hence highly reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale f ...
, aziridines, cyclopentenes, and norbornenes. These molecules have bond angles between ring atoms which are more acute than the optimal tetrahedral (109.5°) and trigonal planar (120°) bond angles required by their respective sp3 and sp2 bonds. Because of the smaller bond angles, the bonds have higher energy and adopt more p-character to reduce the energy of the bonds. In addition, the ring structures of cyclopropanes/enes and cyclclobutanes/enes offer very little conformational flexibility. Thus, the substituents of ring atoms exist in an eclipsed conformation in cyclopropanes and between gauche and eclipsed in cyclobutanes, contributing to higher ring strain energy in the form of Van der Waals repulsion.
*cyclopropane
Cyclopropane is the cycloalkane with the molecular formula (CH2)3, consisting of three methylene groups (CH2) linked to each other to form a ring. The small size of the ring creates substantial ring strain in the structure. Cyclopropane itself i ...
, C3H6 — the C-C-C bond angles are 60° whereas tetrahedral 109.5° bond angles are expected. The intense angle strain leads to nonlinear orbital overlap of its sp3 orbitals. Because of the bond's instability, cyclopropane is more reactive than other alkanes. Since any three points make a plane and cyclopropane has only three carbons, cyclopropane is planar.Anslyn, Eric V., and Dennis A. Dougherty. "Chapter 2: Strain and Stability." Modern Physical Organic Chemistry. Sausalito, CA: University Science, 2006. 100-09. Print/ref> The H-C-H bond angle is 115° whereas 106° is expected as in the CH2 groups of propane. *
cyclobutane
Cyclobutane is a cycloalkane and organic compound with the formula (CH2)4. Cyclobutane is a colourless gas and commercially available as a liquefied gas. Derivatives of cyclobutane are called cyclobutanes. Cyclobutane itself is of no commerci ...
, C4H8 — if it was completely square planar its bond angles would be 90° whereas tetrahedral 109.5° bond angles are expected. However, the actual C-C-C bond angle is 88° because it has a slightly folded form to relieve some torsional strain at the expense of slightly more angle strain. The high strain energy of cyclobutane is primarily from angle strain.
*cyclopentane
Cyclopentane (also called C pentane) is a highly flammable alicyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula C5H10 and CAS number 287-92-3, consisting of a ring of five carbon atoms each bonded with two hydrogen atoms above and below the plane. It occ ...
, C5H10 — if it was a completely regular planar pentagon its bond angles would be 108°, but tetrahedral 109.5° bond angles are expected. However, it has an unfixed puckered shape that undulates up and down.
*cyclohexane, C6H12 — Although the chair conformation is able to achieve ideal angles, the unstable half-chair conformation has angle strain in the C-C-C angles which range from 109.86° to 119.07°.
* ethylene oxide, CH2OCH2
* cubane, C8H8
Ring strain can be considerably higher in bicyclic systems. For example, bicyclobutane, C4H6, is noted for being one of the most strained compounds that is isolatable on a large scale; its strain energy is estimated at 63.9 kcal mol−1 (267 kJ mol−1).
Cyclopropane has a lesser amount of ring strain since it has the least amount of unsaturation; as a result, increasing the amount of unsaturation leads to greater ring strain. For example, cyclopropene has a greater amount of ring strain than cyclopropane because it has more unsaturation.
Applications
The potential energy and unique bonding structure contained in the bonds of molecules with ring strain can be used to drive reactions inorganic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one o ...
. Examples of such reactions are Ring opening metathesis polymerisation, photo-induced ring opening of cyclobutene
Cyclobutene is a cycloalkene. It is of interest in research but currently has no practical applications. It is a colorless easily condensed gas. A modern synthesis involves the 2-step dehydration of cyclobutanol. The compound was first prepared ...
s, and nucleophilic ring-opening of epoxides
In organic chemistry, an epoxide is a cyclic ether () with a three-atom ring. This ring approximates an equilateral triangle, which makes it strained, and hence highly reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale f ...
and aziridines.
Increased potential energy from ring strain also can be used to increase the energy released by explosives or increase their shock sensitivity. For example, the shock sensitivity of the explosive 1,3,3-Trinitroazetidine
1,3,3-Trinitroazetidine (TNAZ) is a highly energetic heterocyclic compound that has been considered as a potential replacement for TNT because of its low melting point (101 °C) and good thermal stability (up to 240 °C). TNAZ was first s ...
could partially or primarily explained by its ring strain.
See also
* Strain (chemistry) * Alkane stereochemistryReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ring Strain Chemical bonding Physical organic chemistry