ring singularity on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A ring singularity or ringularity is the gravitational singularity of a rotating
 When a spherical non-rotating body of a critical radius collapses under its own
When a spherical non-rotating body of a critical radius collapses under its own
Spinning Black Holes
' (Lecture at the University of Canterbury, timecod
49m8s
/ref> possible for the Kerr black hole to act as a sort of
black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravitation, gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts t ...
, or a Kerr black hole
The Kerr metric or Kerr geometry describes the geometry of empty spacetime around a rotating uncharged axially symmetric black hole with a quasispherical event horizon. The Kerr metric is an exact solution of the Einstein field equations of ge ...
, that is shaped like a ring.
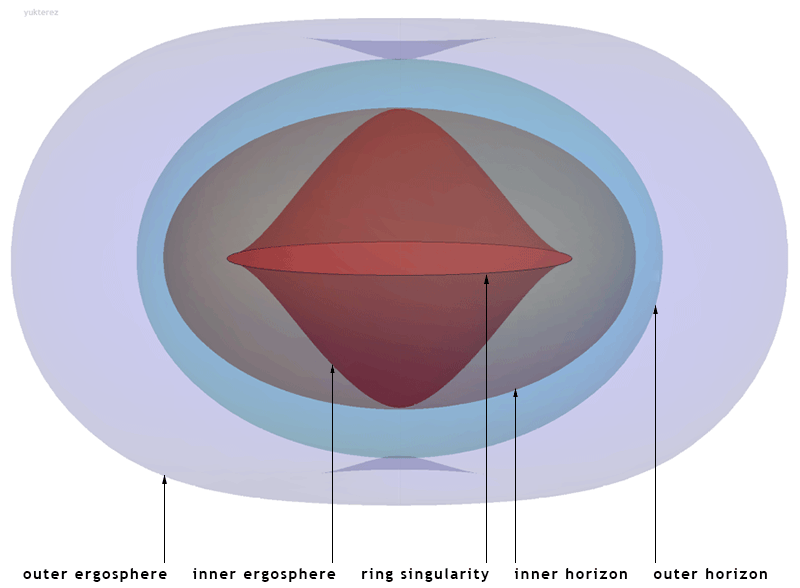
Description of a ring singularity
 When a spherical non-rotating body of a critical radius collapses under its own
When a spherical non-rotating body of a critical radius collapses under its own gravitation
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stron ...
under general relativity, theory suggests it will collapse to a single point. This is not the case with a rotating black hole (a Kerr black hole
The Kerr metric or Kerr geometry describes the geometry of empty spacetime around a rotating uncharged axially symmetric black hole with a quasispherical event horizon. The Kerr metric is an exact solution of the Einstein field equations of ge ...
). With a fluid rotating body, its distribution of mass is not spherical (it shows an equatorial bulge), and it has angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum (rarely, moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed syst ...
. Since a point cannot support rotation
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional ...
or angular momentum in classical physics (general relativity being a classical theory), the minimal shape of the singularity that can support these properties is instead a ring with zero thickness but non-zero radius, and this is referred to as a ringularity or Kerr singularity.
A rotating hole's rotational frame-dragging effects, described by the Kerr metric, causes spacetime in the vicinity of the ring to undergo curvature in the direction of the ring's motion. Effectively this means that different observers placed around a Kerr black hole who are asked to point to the hole's apparent center of gravity
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the balance point) is the unique point where the weight function, weighted relative position (vector), position of the distributed mass sums to zero. Thi ...
may point to different points on the ring. Falling objects will begin to acquire angular momentum from the ring before they actually strike it, and the path taken by a perpendicular light ray (initially traveling toward the ring's center) will curve in the direction of ring motion before intersecting with the ring.
Traversability and nakedness
An observer crossing the event horizon of a non-rotating and uncharged black hole (aSchwarzschild black hole
In Einstein's theory of general relativity, the Schwarzschild metric (also known as the Schwarzschild solution) is an
exact solution to the Einstein field equations that describes the gravitational field outside a spherical mass, on the assumpti ...
) cannot avoid the central singularity, which lies in the future world line
The world line (or worldline) of an object is the path that an object traces in 4-dimensional spacetime. It is an important concept in modern physics, and particularly theoretical physics.
The concept of a "world line" is distinguished from con ...
of everything within the horizon. Thus one cannot avoid spaghettification
In astrophysics, spaghettification (sometimes referred to as the noodle effect) is the vertical stretching and horizontal compression of objects into long thin shapes (rather like spaghetti) in a very strong, non-homogeneous gravitational field ...
by the tidal forces of the central singularity.
This is not necessarily true with a Kerr black hole. An observer falling into a Kerr black hole may be able to avoid the central singularity by making clever use of the inner event horizon associated with this class of black hole. This makes it theoretically (but not likely practically)Roy Kerr: Spinning Black Holes
' (Lecture at the University of Canterbury, timecod
49m8s
/ref> possible for the Kerr black hole to act as a sort of
wormhole
A wormhole (Einstein-Rosen bridge) is a hypothetical structure connecting disparate points in spacetime, and is based on a special Solutions of the Einstein field equations, solution of the Einstein field equations.
A wormhole can be visualize ...
, possibly even a traversable wormhole.
The Kerr singularity as a "toy" wormhole
The Kerr singularity can also be used as a mathematical tool to study the wormhole "field line problem". If a particle is passed through a wormhole, the continuity equations for the electric field suggest that the field lines should not be broken. When an electrical charge passes through a wormhole, the particle's charge field lines appear to emanate from the entry mouth and the exit mouth gains a charge density deficit due to Bernoulli's principle. (For mass, the entry mouth gains mass density and the exit mouth gets a mass density deficit.) Since a Kerr singularity has the same feature, it also allows this issue to be studied.Existence of ring singularities
It is generally expected that since the usual collapse to apoint singularity
Point or points may refer to:
Places
* Point, Lewis, a peninsula in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland
* Point, Texas, a city in Rains County, Texas, United States
* Point, the NE tip and a ferry terminal of Lismore, Scotland, Lismore, Inner Hebrides, ...
under general relativity involves arbitrarily dense conditions, quantum effects
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, ...
may become significant and prevent the singularity forming ("quantum fuzz"). Without quantum gravitational effects, there is good reason to suspect that the interior geometry of a rotating black hole is not the Kerr geometry. The inner event horizon of the Kerr geometry is probably not stable, due to the infinite blue-shifting of infalling radiation. This observation was supported by the investigation of charged black holes which exhibited similar "infinite blueshifting" behavior. While much work has been done, the realistic gravitational collapse of objects into rotating black holes, and the resultant geometry, continues to be an active research topic.
See also
*Black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravitation, gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts t ...
* Black hole electron
* Gravitational singularity
*Geon (physics)
In theoretical general relativity, a geon is a nonsingular electromagnetic or gravitational wave which is held together in a confined region by the gravitational attraction of its own field energy. They were first investigated theoretically in 195 ...
Further reading
* Thorne, Kip, '' Black Holes and Time Warps: Einstein's Outrageous Legacy'', W. W. Norton & Company; Reprint edition, January 1, 1995, . * Matt Visser, ''Lorentzian Wormholes: from Einstein to Hawking'' (AIP press, 1995)References
{{Black holes Black holes Wormhole theory