Rigging on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
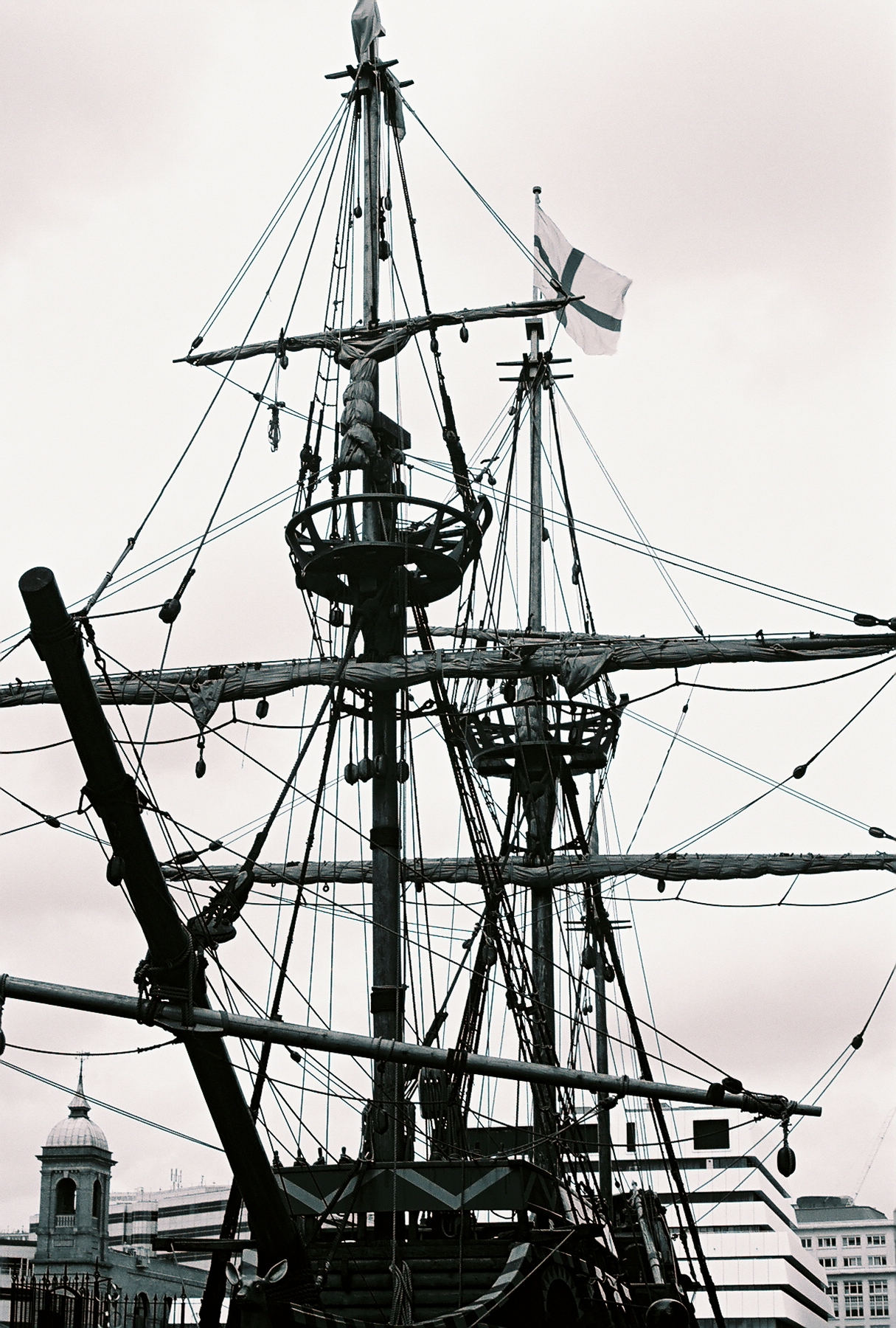

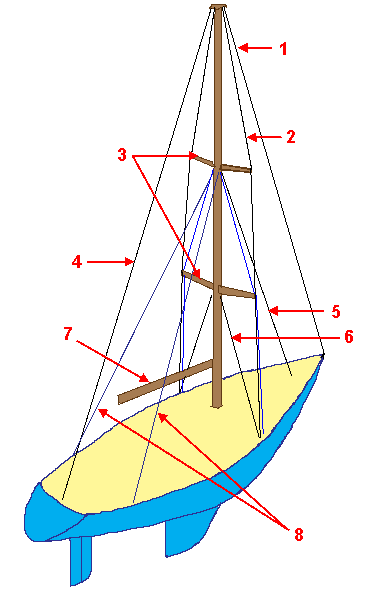
 Rigging comprises the system of ropes, cables and chains, which support a
Rigging comprises the system of ropes, cables and chains, which support a
Photos of different types of ship rigging
at GlobalSecurity.org {{Authority control Sailing rigs and rigging Marine occupations



 Rigging comprises the system of ropes, cables and chains, which support a
Rigging comprises the system of ropes, cables and chains, which support a sailing ship
A sailing ship is a sea-going vessel that uses sails mounted on masts to harness the power of wind and propel the vessel. There is a variety of sail plans that propel sailing ships, employing square-rigged or fore-and-aft sails. Some ships ...
or sail boat's masts—''standing rigging'', including shrouds
Shroud usually refers to an item, such as a cloth, that covers or protects some other object. The term is most often used in reference to ''burial sheets'', mound shroud, grave clothes, winding-cloths or winding-sheets, such as the famous Shr ...
and stays—and which adjust the position of the vessel's sails and spars to which they are attached—the ''running rigging'', including halyards, braces, sheets and vangs.
Etymology
According to theEncyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition
The ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' Eleventh Edition (1910–1911) is a 29-volume reference work, an edition of the '' Encyclopædia Britannica''. It was developed during the encyclopaedia's transition from a British to an American publication. S ...
"rigging" derives from Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Saxons happened wit ...
''wrigan'' or ''wringing'', "to clothe". The same source points out that "rigging" a sailing vessel refers to putting all the components in place to allow it to function, including the masts, spars, sails and the rigging.
Types of rigging
Rigging is divided into two classes, '' standing'', which supports the mast (and bowsprit), and ''running'', which controls the orientation of the sails and their degree of reefing. Configurations differ for each type of rigging, between ''fore-and-aft rig
A fore-and-aft rig is a sailing vessel rigged mainly with sails set along the line of the keel, rather than perpendicular to it as on a square rigged vessel.
Description
Fore-and-aft rigged sails include staysails, Bermuda rigged sails, ga ...
ged'' vessels and '' square-rigged'' vessels.
Standing
Standing rigging is cordage which is fixed in position. Standing rigging is almost always between a mast and the deck, using tension to hold the mast firmly in place. Due to its role, standing rigging is now most commonly made of steel cable. It was historically made of the same materials as running rigging, only coated in tar for added strength and protection from the elements.Fore-and-aft rigged vessels
Most fore-and-aft rigged vessels have the following types of standing rigging: a forestay, a backstay, and upper and lowershrouds
Shroud usually refers to an item, such as a cloth, that covers or protects some other object. The term is most often used in reference to ''burial sheets'', mound shroud, grave clothes, winding-cloths or winding-sheets, such as the famous Shr ...
(side stays).
Less common rigging configurations are diamond stays and jumpers. Both of these are used to keep a thin mast in column especially under the load of a large down wind sail or in strong wind.
Rigging parts include swageless terminals, swage terminal
A swage terminal is a product used to terminate wire. A swaging machine is used to terminate the wire. The wire is passed into a deep hole in the swage terminal which is then pressed onto the terminal by applying force. This type of product is use ...
s, shackle toggle terminals and fail-safe wire rigging insulators.
Square-rigged vessels
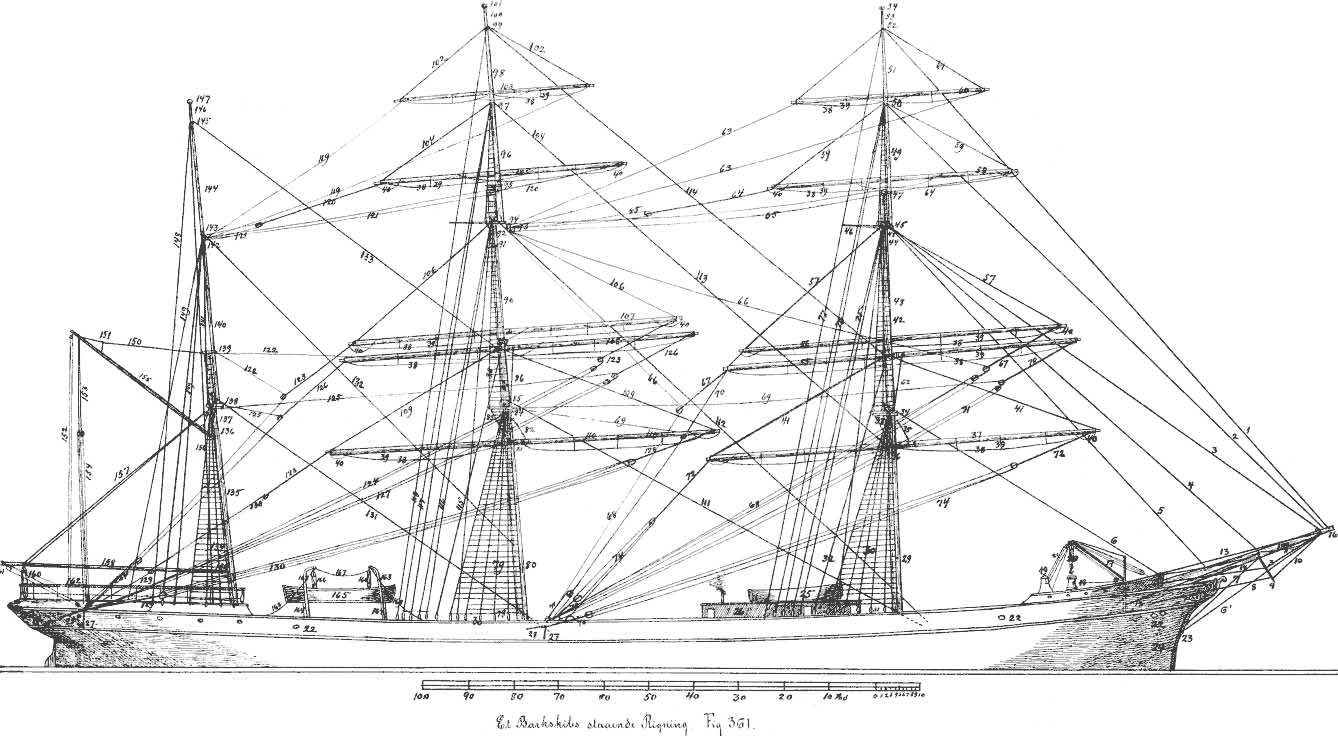
Whereas 20th-century square-rigged vessels were constructed of steel with steel standing rigging, prior vessels used wood masts with hemp-fiber standing rigging. As rigs became taller by the end of the 19th century, masts relied more heavily on successive spars, stepped one atop the other to form the whole, from bottom to top: the ''lower mast'', ''top mast'', and ''topgallant mast''. This construction relies heavily on support by a complex array of stays and shrouds. Each stay in either the fore-and-aft or athwartships direction has a corresponding one in the opposite direction providing counter-tension. Fore-and-aft the system of tensioning start with the stays that are anchored in front of each mast. Shrouds are tensioned by pairs of deadeyes, circular blocks that have the large-diameter line run around them, whilst multiple holes allow smaller line—''lanyards''—to pass multiple times between the two and thereby allow tensioning of the shroud. In addition to overlapping the mast below, the top mast and topgallant mast are supported laterally by shrouds that pass around either a platform, called a " top", or cross-wise beams, called "crosstrees
Crosstrees are the two horizontal spars at the upper ends of the topmasts of sailing ships, used to anchor the shrouds from the topgallant mast. Similarly, they may be mounted at the upper end of the topgallant to anchor the shrouds from the r ...
". Each additional mast segment is supported fore and aft by a series of stays that lead forward. These lines are countered in tension by backstays, which are secured along the sides of the vessel behind the shrouds.
Running
Running rigging is the cordage used to control the shape and position of the sails. Materials have evolved from the use of Manilla rope to synthetic fibers, which includedacron
Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and fo ...
, nylon
Nylon is a generic designation for a family of synthetic polymers composed of polyamides ( repeating units linked by amide links).The polyamides may be aliphatic or semi-aromatic.
Nylon is a silk-like thermoplastic, generally made from pet ...
and kevlar.
Running rigging varies between ''fore-and-aft rigged'' vessels and ''square-rigged'' vessels. They have common functions between them for supporting, shaping and orienting sails, which employ different mechanisms. For supporting sails, halyards (sometimes haulyards), are used to raise sails and control luff tension. On gaff-rig
Gaff rig is a sailing rig (configuration of sails, mast and stays) in which the sail is four-cornered, fore-and-aft rigged, controlled at its peak and, usually, its entire head by a spar (pole) called the ''gaff''. Because of the size and sh ...
ged vessels, topping lifts hold the yards across the top of the sail aloft. Sail shape is usually controlled by lines that pull at the corners of the sail, including the outhaul at the clew and the downhaul at the tack
TACK is a group of archaea acronym for Thaumarchaeota (now Nitrososphaerota), Aigarchaeota, Crenarchaeota (now Thermoproteota), and Korarchaeota, the first groups discovered. They are found in different environments ranging from acidophilic ...
on fore-and-aft rigs. The orientation of sails to the wind is controlled primarily by sheets, but also by braces, which position the yard arms
A yard is a spar on a mast from which sails are set. It may be constructed of timber or steel or from more modern materials such as aluminium or carbon fibre. Although some types of fore and aft rigs have yards, the term is usually used to desc ...
with respect to the wind on square-rigged vessels.
See also
*Full-rigged ship
A full-rigged ship or fully rigged ship is a sailing vessel's sail plan with three or more masts, all of them square-rigged. A full-rigged ship is said to have a ship rig or be ship-rigged. Such vessels also have each mast stepped in three s ...
* Bermuda rig
A Bermuda rig, Bermudian rig, or Marconi rig is a configuration of mast and rigging for a type of sailboat and is the typical configuration for most modern sailboats. This configuration was developed in Bermuda in the 1600s; the term ''Marconi'' ...
* Lateen rig
* Junk rig
* Shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to bef ...
* Superstructure
References
Further reading
* * * * *External links
Photos of different types of ship rigging
at GlobalSecurity.org {{Authority control Sailing rigs and rigging Marine occupations