radius (anatomy) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The radius or radial bone is one of the two large




 The long narrow
The long narrow
 Specific fracture types of the radius include:
*Proximal radius fracture. A fracture within the capsule of the
Specific fracture types of the radius include:
*Proximal radius fracture. A fracture within the capsule of the 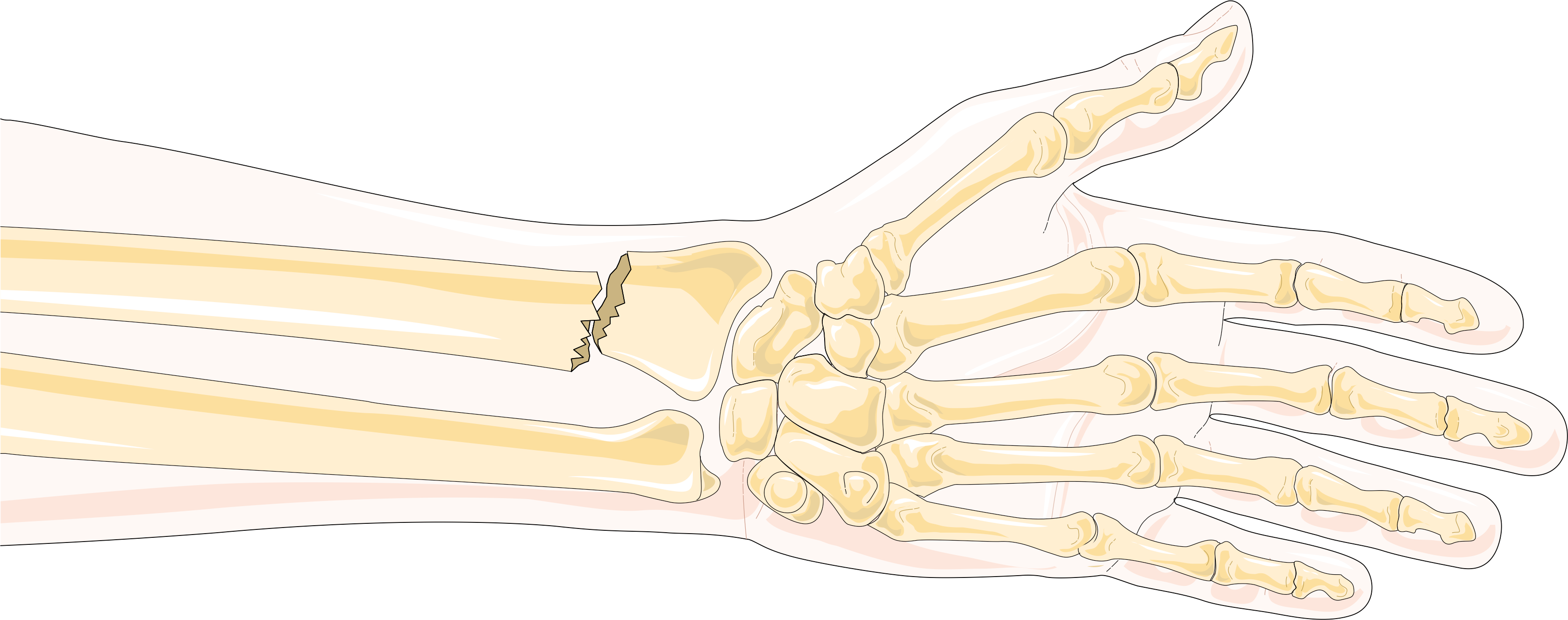 **
**
bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
s of the forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in ...
, the other being the ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
. It extends from the lateral
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Healthcare
*Lateral (anatomy), an anatomical direction
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
* Lateral release (surgery), a surgical procedure on the side of a kneecap
Phonetics
*Lateral co ...
side of the elbow
The elbow is the region between the arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and the me ...
to the thumb side of the wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carp ...
and runs parallel to the ulna. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. It is a long bone, prism
Prism usually refers to:
* Prism (optics), a transparent optical component with flat surfaces that refract light
* Prism (geometry), a kind of polyhedron
Prism may also refer to:
Science and mathematics
* Prism (geology), a type of sedimentary ...
-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally.
The radius is part of two joints
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
: the elbow
The elbow is the region between the arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and the me ...
and the wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carp ...
. At the elbow, it joins with the capitulum of the humerus
In human anatomy of the arm, the capitulum of the humerus is a smooth, rounded eminence on the lateral portion of the distal articular surface of the humerus. It articulates with the cupshaped depression on the head of the radius, and is limite ...
, and in a separate region, with the ulna at the radial notch
The radial notch of the ulna (lesser sigmoid cavity) is a narrow, oblong, articular depression on the lateral side of the coronoid process; it receives the circumferential articular surface of the head of the radius.
It is concave from before bac ...
. At the wrist, the radius forms a joint with the ulna bone.
The corresponding bone in the lower leg
The human leg, in the general word sense, is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh or sometimes even the hip or gluteal region. However, the definition in human anatomy refers only to the section of the lower limb e ...
is the fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity i ...
.
Structure



 The long narrow
The long narrow medullary cavity
The medullary cavity (''medulla'', innermost part) is the central cavity of bone shafts where red bone marrow and/or yellow bone marrow ( adipose tissue) is stored; hence, the medullary cavity is also known as the marrow cavity.
Located in the m ...
is enclosed in a strong wall of compact bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and ...
. It is thickest along the interosseous border and thinnest at the extremities, same over the cup-shaped articular surface (fovea) of the head.
The trabeculae
A trabecula (plural trabeculae, from Latin for "small beam") is a small, often microscopic, tissue element in the form of a small beam, strut or rod that supports or anchors a framework of parts within a body or organ. A trabecula generally has ...
of the spongy tissue are somewhat arched at the upper end and pass upward from the compact layer of the shaft to the ''fovea capituli'' (the humerus's cup-shaped articulatory notch); they are crossed by others parallel to the surface of the fovea. The arrangement at the lower end is somewhat similar. It is missing in radial aplasia
Radial aplasia is a congenital defect which affects the formation of the radius bone in the arm. The radius is the lateral bone (thumb side) which connects the humerus of the upper arm to the wrist via articulation with the carpal bones. A child ...
.
The radius has a body and two extremities. The upper extremity of the radius consists of a somewhat cylindrical head articulating with the ulna and the humerus, a neck, and a radial tuberosity
Beneath the neck of the radius, on the medial side, is an eminence, the radial tuberosity; its surface is divided into:
* a ''posterior, rough portion'', for the insertion of the tendon of the biceps brachii.
* an ''anterior, smooth portion'', on w ...
. The body of the radius is self-explanatory, and the lower extremity of the radius is roughly quadrilateral in shape, with articular surfaces for the ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
, scaphoid
The scaphoid bone is one of the carpal bones of the wrist. It is situated between the hand and forearm on the thumb side of the wrist (also called the lateral or radial side). It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. The scaphoid bone i ...
and lunate bone
The lunate bone (semilunar bone) is a carpal bone in the human hand. It is distinguished by its deep concavity and crescentic outline. It is situated in the center of the proximal row carpal bones, which lie between the ulna and radius and the h ...
s. The distal end of the radius forms two palpable points, radially the styloid process and Lister's tubercle
Lister's tubercle or dorsal tubercle of radius is a bony prominence located at the Anatomical terms of location, distal end of the radius (bone), radius. It is Palpation, palpable on the dorsum (anatomy)#human anatomy, dorsum of the wrist.
Struct ...
on the ulnar side. Along with the proximal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
and distal radioulnar articulation
The distal radioulnar articulation (also known as the distal radioulnar joint, or inferior radioulnar joint) is a synovial pivot joint between the two bones in the forearm; the radius and ulna. It is one of two joints between the radius and ulna ...
s, an interosseous membrane
An interosseous membrane is a thick dense fibrous sheet of connective tissue that spans the space between two bones, forming a type of syndesmosis joint.
Interosseous membranes in the human body:
* Interosseous membrane of forearm
* Interosseou ...
originates medially along the length of the body of the radius to attach the radius to the ulna.
Near the wrist
The distal end of the radius is large and of quadrilateral form. ;Joint surfaces It is provided with two articular surfaces – one below, for thecarpus
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal ...
, and another at the medial side, for the ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
.
* The ''carpal'' articular surface is triangular, concave, smooth, and divided by a slight antero-posterior ridge into two parts. Of these, the lateral, triangular, articulates with the scaphoid bone
The scaphoid bone is one of the carpal bones of the wrist. It is situated between the hand and forearm on the thumb side of the wrist (also called the lateral or radial side). It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. The scaphoid bone is ...
; the medial, quadrilateral, with the lunate bone
The lunate bone (semilunar bone) is a carpal bone in the human hand. It is distinguished by its deep concavity and crescentic outline. It is situated in the center of the proximal row carpal bones, which lie between the ulna and radius and the h ...
.
* The articular surface for the ''ulna'' is called the ulnar notch (''sigmoid cavity'') of the radius; it is narrow, concave, smooth, and articulates with the head of the ulna.
These two articular surfaces are separated by a prominent ridge, to which the base of the triangular articular disk is attached; this disk separates the wrist-joint from the distal radioulnar articulation.
;Other surfaces
This end of the bone has three non-articular surfaces – volar, dorsal, and lateral.
* The ''volar surface'', rough and irregular, affords attachment to the volar radiocarpal ligament.
* The ''dorsal surface'' is convex, affords attachment to the dorsal radiocarpal ligament
The dorsal radiocarpal ligament (posterior ligament) is less thick and strong than its volar counterpart, and has a proximal attachment to the posterior border of the distal radius. Its fibers run medially and inferiorly to form a distal attachment ...
, and is marked by three grooves. Enumerated from the lateral side:
** The ''first'' groove is broad, but shallow, and subdivided into two by a slight ridge: the lateral of these two, transmits the tendon of the extensor carpi radialis longus muscle
The extensor carpi radialis longus is one of the five main muscles that control movements at the wrist. This muscle is quite long, starting on the lateral side of the humerus, and attaching to the base of the second metacarpal bone (metacarpal of ...
; the medial, the tendon of the extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle
In human anatomy, extensor carpi radialis brevis is a muscle in the forearm that acts to extend and abduct the wrist. It is shorter and thicker than its namesake extensor carpi radialis longus which can be found above the proximal end of the exten ...
.
** The ''second'' is deep but narrow, and bounded laterally by a sharply defined ridge; it is directed obliquely from above downward and lateralward, and transmits the tendon of the extensor pollicis longus muscle
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis longus muscle (EPL) is a skeletal muscle located dorsally on the forearm. It is much larger than the extensor pollicis brevis, the origin of which it partly covers and acts to stretch the thumb together with ...
.
** The ''third'' is broad, for the passage of the tendons of the extensor indicis proprius
In human anatomy, the extensor indicis roprius'' is a narrow, elongated skeletal muscle in the deep layer of the dorsal forearm, placed medial to, and parallel with, the extensor pollicis longus. Its tendon goes to the index finger, which it exte ...
and extensor digitorum communis
The extensor digitorum muscle (also known as extensor digitorum communis) is a muscle of the posterior forearm present in humans and other animals. It extends the medial four digits of the hand. Extensor digitorum is innervated by the posterior int ...
.
* The ''lateral surface'' is prolonged obliquely downward into a strong, conical projection, the styloid process, which gives attachment by its base to the tendon of the brachioradialis, and by its apex to the radial collateral ligament of wrist joint. The lateral surface of this process is marked by a flat groove, for the tendons of the abductor pollicis longus
In human anatomy, the abductor pollicis longus (APL) is one of the extrinsic muscles of the hand. Its major function is to abduct the thumb at the wrist. Its tendon forms the anterior border of the anatomical snuffbox.
Structure
The abductor ...
muscle and extensor pollicis brevis
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis brevis is a skeletal muscle on the dorsal side of the forearm. It lies on the medial side of, and is closely connected with, the abductor pollicis longus. The extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) belongs to the ...
muscle.
Body
The body of the radius (or shaft of radius) is prismoid in form, narrower above than below, and slightly curved, so as to be convex lateralward. It presents three borders and three surfaces. ;Borders The volar border (''margo volaris; anterior border; palmar'';) extends from the lower part of thetuberosity
In the skeleton of humans and other animals, a tubercle, tuberosity or apophysis is a protrusion or eminence that serves as an attachment for skeletal muscles. The muscles attach by tendons, where the enthesis is the connective tissue between the ...
above to the anterior part of the base of the styloid process below, and separates the volar from the lateral surface. Its upper third is prominent, and from its oblique direction has received the name of the oblique line of the radius; it gives origin to the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle
Flexor digitorum superficialis (''flexor digitorum sublimis'') is an extrinsic flexor muscle of the fingers at the proximal interphalangeal joints.
It is in the anterior compartment of the forearm. It is sometimes considered to be the deepest pa ...
(also ''flexor digitorum sublimis'') and flexor pollicis longus muscle
The flexor pollicis longus (; FPL, Latin ''flexor'', bender; ''pollicis'', of the thumb; ''longus'', long) is a muscle in the forearm and hand that flexes the thumb. It lies in the same plane as the flexor digitorum profundus. This muscle is uniqu ...
; the surface above the line gives insertion to part of the supinator muscle. The middle third of the volar border is indistinct and rounded. The lower fourth is prominent, and gives insertion to the pronator quadratus muscle
Pronator quadratus is a square-shaped muscle on the distal forearm that acts to pronate (turn so the palm faces downwards) the hand.
Structure
Its fibres run perpendicular to the direction of the arm, running from the most distal quarter of the a ...
, and attachment to the dorsal carpal ligament
The extensor retinaculum (dorsal carpal ligament, or posterior annular ligament) is an anatomical term for the thickened part of the antebrachial fascia that holds the tendons of the extensor muscles in place. It is located on the back of the fore ...
; it ends in a small tubercle, into which the tendon of the brachioradialis muscle
The brachioradialis is a muscle of the forearm that flexes the forearm at the elbow. It is also capable of both pronation and supination, depending on the position of the forearm. It is attached to the distal styloid process of the radius by wa ...
is inserted.
The dorsal border (''margo dorsalis; posterior border'') begins above at the back of the neck, and ends below at the posterior part of the base of the styloid process; it separates the posterior from the lateral surface. is indistinct above and below, but well-marked in the middle third of the bone.
The interosseous border (''internal border; crista interossea; interosseous crest;'') begins above, at the back part of the tuberosity
In the skeleton of humans and other animals, a tubercle, tuberosity or apophysis is a protrusion or eminence that serves as an attachment for skeletal muscles. The muscles attach by tendons, where the enthesis is the connective tissue between the ...
, and its upper part is rounded and indistinct; it becomes sharp and prominent as it descends, and at its lower part divides into two ridges which are continued to the anterior and posterior margins of the ulnar notch. To the posterior of the two ridges the lower part of the interosseous membrane
An interosseous membrane is a thick dense fibrous sheet of connective tissue that spans the space between two bones, forming a type of syndesmosis joint.
Interosseous membranes in the human body:
* Interosseous membrane of forearm
* Interosseou ...
is attached, while the triangular surface between the ridges gives insertion to part of the pronator quadratus muscle
Pronator quadratus is a square-shaped muscle on the distal forearm that acts to pronate (turn so the palm faces downwards) the hand.
Structure
Its fibres run perpendicular to the direction of the arm, running from the most distal quarter of the a ...
. This crest separates the volar from the dorsal surface, and gives attachment to the interosseous membrane. The connection between the two bones is actually a joint referred to as a syndesmosis
In anatomy, fibrous joints are joints connected by fibrous tissue, consisting mainly of collagen. These are fixed joints where bones are united by a layer of white fibrous tissue of varying thickness. In the skull the joints between the bones ar ...
joint.
;Surfaces
The volar surface (''facies volaris; anterior surface'') is concave in its upper three-fourths, and gives origin to the flexor pollicis longus muscle
The flexor pollicis longus (; FPL, Latin ''flexor'', bender; ''pollicis'', of the thumb; ''longus'', long) is a muscle in the forearm and hand that flexes the thumb. It lies in the same plane as the flexor digitorum profundus. This muscle is uniqu ...
; it is broad and flat in its lower fourth, and affords insertion to the Pronator quadratus. A prominent ridge limits the insertion of the Pronator quadratus below, and between this and the inferior border is a triangular rough surface for the attachment of the volar radiocarpal ligament. At the junction of the upper and middle thirds of the volar surface is the nutrient foramen, which is directed obliquely upward.
The dorsal surface (''facies dorsalis; posterior surface'') is convex, and smooth in the upper third of its extent, and covered by the Supinator. Its middle third is broad, slightly concave, and gives origin to the Abductor pollicis longus
In human anatomy, the abductor pollicis longus (APL) is one of the extrinsic muscles of the hand. Its major function is to abduct the thumb at the wrist. Its tendon forms the anterior border of the anatomical snuffbox.
Structure
The abductor ...
above, and the extensor pollicis brevis muscle
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis brevis is a skeletal muscle on the dorsal side of the forearm. It lies on the medial side of, and is closely connected with, the abductor pollicis longus. The extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) belongs to the ...
below. Its lower third is broad, convex, and covered by the tendons of the muscles which subsequently run in the grooves on the lower end of the bone.
The lateral surface (''facies lateralis; external surface'') is convex throughout its entire extent and is known as the convexity of the radius, curving outwards to be convex at the side. Its upper third gives insertion to the supinator muscle. About its center is a rough ridge, for the insertion of the pronator teres muscle
The pronator teres is a muscle (located mainly in the forearm) that, along with the pronator quadratus, serves to pronate the forearm (turning it so that the palm faces posteriorly when from the anatomical position). It has two attachments, to t ...
. Its lower part is narrow, and covered by the tendons of the abductor pollicis longus muscle
In human anatomy, the abductor pollicis longus (APL) is one of the extrinsic muscles of the hand. Its major function is to abduct the thumb at the wrist. Its tendon forms the anterior border of the anatomical snuffbox.
Structure
The abductor ...
and extensor pollicis brevis muscle
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis brevis is a skeletal muscle on the dorsal side of the forearm. It lies on the medial side of, and is closely connected with, the abductor pollicis longus. The extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) belongs to the ...
.
Near the elbow
The upper extremity of the radius (or proximal extremity) presents a head, neck, and tuberosity. * The radial ''head'' has a cylindrical form, and on its upper surface is a shallow cup or fovea for articulation with thecapitulum
capitulum (plural capitula) may refer to:
*the Latin word for chapter
** an index or list of chapters at the head of a gospel manuscript
** a short reading in the Liturgy of the Hours
*** derived from which, it is the Latin for the assembly known ...
(or capitellum) of the humerus. The circumference of the head is smooth; it is broad medially where it articulates with the radial notch of the ulna, narrow in the rest of its extent, which is embraced by the annular ligament. The deepest point in the fovea is not axi-symmetric with the long axis of the radius, creating a cam effect during pronation and supination.
* The head is supported on a round, smooth, and constricted portion called the ''neck'', on the back of which is a slight ridge for the insertion of part of the supinator muscle.
* Beneath the neck, on the medial side, is an eminence, the ''radial tuberosity
Beneath the neck of the radius, on the medial side, is an eminence, the radial tuberosity; its surface is divided into:
* a ''posterior, rough portion'', for the insertion of the tendon of the biceps brachii.
* an ''anterior, smooth portion'', on w ...
''; its surface is divided into a posterior, rough portion, for the insertion of the tendon of the biceps brachii muscle
The biceps or biceps brachii ( la, musculus biceps brachii, "two-headed muscle of the arm") is a large muscle that lies on the front of the upper arm between the shoulder and the elbow. Both heads of the muscle arise on the scapula and join t ...
, and an anterior, smooth portion, on which a bursa is interposed between the tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability ...
and the bone.
Development
The radius isossified
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in t ...
from ''three'' centers: one for the body, and one for each extremity. That for the body makes its appearance near the center of the bone, during the eighth week of fetal
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal develo ...
life.
Ossification commences in the lower end between 9 and 26 months of age. The ossification center for the upper end appears by the fifth year.
The upper epiphysis
The epiphysis () is the rounded end of a long bone, at its joint with adjacent bone(s). Between the epiphysis and diaphysis (the long midsection of the long bone) lies the metaphysis, including the epiphyseal plate (growth plate). At the jo ...
fuses with the body at the age of seventeen or eighteen years, the lower about the age of twenty.
An additional center sometimes found in the radial tuberosity
Beneath the neck of the radius, on the medial side, is an eminence, the radial tuberosity; its surface is divided into:
* a ''posterior, rough portion'', for the insertion of the tendon of the biceps brachii.
* an ''anterior, smooth portion'', on w ...
, appears about the fourteenth or fifteenth year.
Function
Muscle attachments
The biceps muscle inserts on theradial tuberosity
Beneath the neck of the radius, on the medial side, is an eminence, the radial tuberosity; its surface is divided into:
* a ''posterior, rough portion'', for the insertion of the tendon of the biceps brachii.
* an ''anterior, smooth portion'', on w ...
of the upper extremity of the bone. The upper third of the body of the bone attaches to the supinator, the flexor digitorum superficialis
Flexor digitorum superficialis (''flexor digitorum sublimis'') is an extrinsic flexor muscle of the fingers at the proximal interphalangeal joints.
It is in the anterior compartment of the forearm. It is sometimes considered to be the deepest pa ...
, and the flexor pollicis longus
The flexor pollicis longus (; FPL, Latin ''flexor'', bender; ''pollicis'', of the thumb; ''longus'', long) is a muscle in the forearm and hand that flexes the thumb. It lies in the same plane as the flexor digitorum profundus. This muscle is un ...
muscles.
The middle third of the body attaches to the extensor ossis metacarpi pollicis, extensor primi internodii pollicis, and the pronator teres muscles.
The lower quarter of the body attaches to the pronator quadratus muscle and the tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability ...
of the supinator longus.
Clinical significance
Radial aplasia
Radial aplasia is a congenital defect which affects the formation of the radius bone in the arm. The radius is the lateral bone (thumb side) which connects the humerus of the upper arm to the wrist via articulation with the carpal bones. A child ...
refers to the congenital absence or shortness of the radius.
Fracture
 Specific fracture types of the radius include:
*Proximal radius fracture. A fracture within the capsule of the
Specific fracture types of the radius include:
*Proximal radius fracture. A fracture within the capsule of the elbow
The elbow is the region between the arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the lateral and the me ...
joint results in the fat pad sign
The fat pad sign, also known as the sail sign, is a potential finding on elbow radiography which suggests a fracture of one or more bones at the elbow. It is may indicate an occult fracture that is not directly visible. Its name derives from th ...
or "sail sign" which is a displacement of the fat pad A fat pad (aka haversian gland) is a mass of closely packed fat cells surrounded by fibrous tissue septa.TheFreeDictionary > Fat padCiting: Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 8th edition. 2009 They may be extensively supplied with capillaries and nerve end ...
at the elbow.
 **
**Essex-Lopresti fracture
The Essex-Lopresti fracture is a fracture of the radial head of the forearm with concomitant dislocation of the distal radio-ulnar joint along with disruption of the thin interosseous membrane which holds them together.radial head with concomitant dislocation of the distal radio-ulnar joint with disruption of the
at Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics online *Radial shaft fracture *
interosseous membrane
An interosseous membrane is a thick dense fibrous sheet of connective tissue that spans the space between two bones, forming a type of syndesmosis joint.
Interosseous membranes in the human body:
* Interosseous membrane of forearm
* Interosseou ...
.Essex Lopresti fractureat Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics online *Radial shaft fracture *
Distal radius fracture
A distal radius fracture, also known as wrist fracture, is a break of the part of the radius bone which is close to the wrist. Symptoms include pain, bruising, and rapid-onset swelling. The ulna bone may also be broken.
In younger people, thes ...
**Galeazzi fracture
The Galeazzi fracture is a fracture of the distal third of the radius with dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint. It classically involves an isolated fracture of the junction of the distal third and middle third of the radius with associated ...
– a fracture of the radius with dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint
** Colles' fracture – a distal fracture of the radius with dorsal (posterior) displacement of the wrist and hand
**Smith's fracture
A Smith's fracture, is a fracture of the distal radius.
Although it can also be caused by a direct blow to the dorsal forearm or by a fall with the wrist flexed, the most common mechanism of injury for Smith's fracture occurs in a palmar fall w ...
– a distal fracture of the radius with volar (ventral) displacement of the wrist and hand
**Barton's fracture
A Barton's fracture is a type of wrist injury where there is a broken bone associated with a dislocated bone in the wrist, typically occurring after falling on top of a bent wrist. It is an intra-articular fracture of the distal radius with disloc ...
– an intra-articular fracture
An intraarticular fracture is a bone fracture in which the break crosses into the surface of a joint. This always results in damage to the cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protec ...
of the distal radius with dislocation of the radiocarpal joint
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal ...
.
History
The word ''radius'' isLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
for "ray". In the context of the radius bone, a ray can be thought of rotating around an axis line extending diagonally from center of capitulum
capitulum (plural capitula) may refer to:
*the Latin word for chapter
** an index or list of chapters at the head of a gospel manuscript
** a short reading in the Liturgy of the Hours
*** derived from which, it is the Latin for the assembly known ...
to the center of distal ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
. While the ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
is the major contributor to the elbow joint, the radius primarily contributes to the wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carp ...
joint.
The radius is named so because the radius (bone) acts like the radius (of a circle). It rotates around the ulna and the far end (where it joins to the bones of the hand), known as the styloid process of the radius, is the distance from the ulna (center of the circle) to the edge of the radius (the circle). The ulna acts as the center point to the circle because when the arm is rotated the ulna does not move.
Animals
In four-legged animals, the radius is the main load-bearing bone of the lower forelimb. Its structure is similar in most terrestrialtetrapods
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids ( pelycosaurs, extinct therapsi ...
, but it may be fused with the ulna in some mammals (such as horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million yea ...
s) and reduced or modified in animals with flippers or vestigial forelimbs.
Gallery
References
{{Authority control Long bones Bones of the upper limb