puntians (Ὀπούντιοι) and Ozolians (Ὀζολοί) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Land of Punt (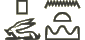 '' pwnt''; alternate Egyptological readings ''Pwene''(''t'') /pu:nt/) was an ancient kingdom known from Ancient Egyptian trade records. It produced and exported
'' pwnt''; alternate Egyptological readings ''Pwene''(''t'') /pu:nt/) was an ancient kingdom known from Ancient Egyptian trade records. It produced and exported
 The earliest recorded ancient Egyptian expedition to Punt was organized by
The earliest recorded ancient Egyptian expedition to Punt was organized by  A report of that five-ship voyage survives on
A report of that five-ship voyage survives on
 At times, the ancient Egyptians called Punt ''Ta netjer'' ('' tꜣ nṯr''), meaning "God's Land". This referred to the fact that it was among the regions of the Sun God, that is, the regions located in the direction of the sunrise, to the East of Egypt. These eastern regions' resources included products used in temples, notably incense. Older literature maintained that the label "God's Land", when interpreted as "Holy Land" or "Land of the gods/ancestors", meant that the ancient Egyptians viewed the Land of Punt as their ancestral homeland. W. M.
At times, the ancient Egyptians called Punt ''Ta netjer'' ('' tꜣ nṯr''), meaning "God's Land". This referred to the fact that it was among the regions of the Sun God, that is, the regions located in the direction of the sunrise, to the East of Egypt. These eastern regions' resources included products used in temples, notably incense. Older literature maintained that the label "God's Land", when interpreted as "Holy Land" or "Land of the gods/ancestors", meant that the ancient Egyptians viewed the Land of Punt as their ancestral homeland. W. M. 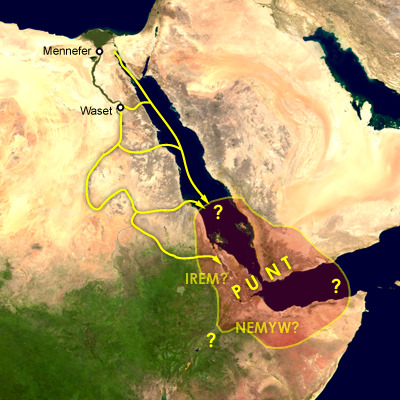
Queen Hatasu, and Her Expedition to the Land of Punt
by Amelia Ann Blanford Edwards (1891) * * at Deir el-Bahri * discussion by Dr. Karl H. Leser
;News reports on Wadi Gawasis excavations
(Boston University Bridge, 18 March 2005). Excavations at Wadi Gawasis, possibly the ancient Egyptian port Saaw.
Remains of ancient Egyptian seafaring ships discovered
(New Scientist, 23 March 2005). * *
4,000-year-old shipyard unearthed in Egypt
(MSNBC, 6 March 2006). {{DEFAULTSORT:Land of Punt Geography of ancient Egypt Ancient Somalia Countries in ancient Africa History of the Red Sea Foreign contacts of ancient Egypt Historical regions Lost places South Arabia Former kingdoms
Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
: 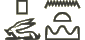 '' pwnt''; alternate Egyptological readings ''Pwene''(''t'') /pu:nt/) was an ancient kingdom known from Ancient Egyptian trade records. It produced and exported
'' pwnt''; alternate Egyptological readings ''Pwene''(''t'') /pu:nt/) was an ancient kingdom known from Ancient Egyptian trade records. It produced and exported gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
, aromatic resin
In polymer chemistry and materials science, resin is a solid or highly viscous substance of plant or synthetic origin that is typically convertible into polymers. Resins are usually mixtures of organic compounds. This article focuses on n ...
s, blackwood, ebony
Ebony is a dense black/brown hardwood, coming from several species in the genus '' Diospyros'', which also contains the persimmons. Unlike most woods, ebony is dense enough to sink in water. It is finely textured and has a mirror finish when ...
, ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals i ...
and wild animals.Shaw & Nicholson, p. 231. It is possible that it corresponds to Opone
Opone ( grc, Οπώνη) was an ancient proto-Somali city situated in the Horn of Africa. It is primarily known for its trade with the Ancient Egyptians, Romans, Greeks, Persians, and the states of ancient India. Through archaeological remains, t ...
in Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constituti ...
, as later known by the ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
, while some biblical scholars
Biblical studies is the academic application of a set of diverse disciplines to the study of the Bible (the Old Testament and New Testament).''Introduction to Biblical Studies, Second Edition'' by Steve Moyise (Oct 27, 2004) pages 11–12 For ...
have identified it with the biblical land of Put or Havilah
Havilah ( ''Ḥăwīlāh'') refers to both a land and people in several books of the Bible; the one mentioned in , while the other is mentioned in .
Biblical mentions
In one case, Havilah is associated with the Garden of Eden, that mentioned in ...
.
At times Punt is referred to as ''Ta netjer'' ('' tꜣ nṯr''), the "Land of the God". The exact location of Punt is debated by historians. Various locations have been offered, southeast of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, a Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
coastal region: Somaliland, Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constituti ...
, Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red ...
, northeast Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, Eritrea, and north-east Sudan. It is also possible that it covered both the Horn of Africa and Southern Arabia
South Arabia () is a historical region that consists of the southern region of the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia, mainly centered in what is now the Republic of Yemen, yet it has also historically included Najran, Jizan, Al-Bahah, and 'A ...
.Dimitri Meeks – Chapter 4 – "Locating Punt" from the book ''Mysterious Lands''", by David B. O'Connor and Stephen Quirke. Puntland
Puntland ( so, Puntland, ar, أرض البنط, it, Terra di Punt or ''Paese di Punt''), officially the Puntland State of Somalia ( so, Dowlad Goboleedka Puntland ee Soomaaliya, ar, ولاية أرض البنط الصومالية), is a F ...
, the Somali administrative region at the end of the Horn of Africa is named in reference to it.
Egyptian expeditions to Punt
 The earliest recorded ancient Egyptian expedition to Punt was organized by
The earliest recorded ancient Egyptian expedition to Punt was organized by Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the ...
Sahure
Sahure (also Sahura, meaning "He who is close to Re") was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the second ruler of the Fifth Dynasty (c. 2465 – c. 2325 BC). He reigned for about 13 years in the early 25th century BC during the Old Kingdom Period. ...
of the Fifth Dynasty
The Fifth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (notated Dynasty V) is often combined with Dynasties III, IV and VI under the group title the Old Kingdom. The Fifth Dynasty pharaohs reigned for approximately 150 years, from the early 25th century BC until ...
(25th century BC), returning with cargoes of ''antyue'' and Puntites. However, gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
from Punt is recorded as having been in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
as early as the time of Pharaoh Khufu
Khufu or Cheops was an ancient Egyptian monarch who was the second pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty, in the first half of the Old Kingdom period ( 26th century BC). Khufu succeeded his father Sneferu as king. He is generally accepted as having c ...
of the Fourth Dynasty
The Fourth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (notated Dynasty IV) is characterized as a "golden age" of the Old Kingdom of Egypt. Dynasty IV lasted from to 2494 BC. It was a time of peace and prosperity as well as one during which trade with other ...
.
Subsequently, there were more expeditions to Punt in the Sixth, Eleventh
In music or music theory, an eleventh is the note eleven scale degrees from the root of a chord and also the interval between the root and the eleventh. The interval can be also described as a compound fourth, spanning an octave plus a ...
, Twelfth and Eighteenth dynasties of Egypt. In the Twelfth Dynasty, trade with Punt was celebrated in popular literature in the ''Tale of the Shipwrecked Sailor
The "Tale of the Shipwrecked Sailor" is a Middle Kingdom story of an Ancient Egyptian voyage to "the King's mines".
Historical information
At least one source states that the papyrus having the story written upon it is located within the Imp ...
''.
In the reign of Mentuhotep III
Sankhkare Mentuhotep III (also Montuhotep III) of the Eleventh Dynasty was Pharaoh of Egypt during the Middle Kingdom. He was assigned a reign of 12 years in the Turin Canon.
Reign
Mentuhotep III succeeded his father Mentuhotep II to t ...
(11th dynasty, ca. 2000 BC), an officer named Hannu
Hannu, Hennu or Henenu was an Egyptian noble, serving as ''m-r-pr'' "majordomo" to Mentuhotep III in the 20th century BC. He reportedly re-opened the trade routes to Punt and Libya for the Middle Kingdom of Egypt. He was buried in a tomb in Dei ...
organized one or more voyages to Punt, but it is uncertain whether he personally traveled on these expeditions. Trading missions of the 12th dynasty pharaohs Senusret I
Senusret I (Middle Egyptian: z-n-wsrt; /suʀ nij ˈwas.ɾiʔ/) also anglicized as Sesostris I and Senwosret I, was the second pharaoh of the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt. He ruled from 1971 BC to 1926 BC (1920 BC to 1875 BC), and was one of the mo ...
, Amenemhat II and Amenemhat IV had also successfully navigated their way to and from the mysterious land of Punt.Joyce Tyldesley, Hatchepsut: The Female Pharaoh, Penguin Books, 1996 hardback, p.145
In the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Hatshepsut
Hatshepsut (; also Hatchepsut; Egyptian: '' ḥꜣt- špswt'' "Foremost of Noble Ladies"; or Hatasu c. 1507–1458 BC) was the fifth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. She was the second historically confirmed female pharaoh, af ...
built a Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
fleet to facilitate trade between the head of the Gulf of Aqaba
The Gulf of Aqaba ( ar, خَلِيجُ ٱلْعَقَبَةِ, Khalīj al-ʿAqabah) or Gulf of Eilat ( he, מפרץ אילת, Mifrátz Eilát) is a large gulf at the northern tip of the Red Sea, east of the Sinai Peninsula and west of the Arabian ...
and points south as far as Punt to bring mortuary goods to Karnak
The Karnak Temple Complex, commonly known as Karnak (, which was originally derived from ar, خورنق ''Khurnaq'' "fortified village"), comprises a vast mix of decayed temples, pylons, chapels, and other buildings near Luxor, Egypt. Constr ...
in exchange for Nubian gold. Hatshepsut personally made the most famous ancient Egyptian expedition that sailed to Punt. Her artists revealing much about the royals, inhabitants, habitation and variety of trees on the island, revealing it as the "Land of the Gods, a region far to the east in the direction of the sunrise, blessed with products for religious purposes", where traders returned with gold, ivory, ebony
Ebony is a dense black/brown hardwood, coming from several species in the genus '' Diospyros'', which also contains the persimmons. Unlike most woods, ebony is dense enough to sink in water. It is finely textured and has a mirror finish when ...
, incense
Incense is aromatic biotic material that releases fragrant smoke when burnt. The term is used for either the material or the aroma. Incense is used for aesthetic reasons, religious worship, aromatherapy, meditation, and ceremony. It may also b ...
, aromatic resins, animal skins, live animals, eye-makeup cosmetics, fragrant woods, and cinnamon. During the reign of Queen Hatshepsut
Hatshepsut (; also Hatchepsut; Egyptian: '' ḥꜣt- špswt'' "Foremost of Noble Ladies"; or Hatasu c. 1507–1458 BC) was the fifth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. She was the second historically confirmed female pharaoh, af ...
in the 15th century BC, ships regularly crossed the Red Sea in order to obtain bitumen, copper, carved amulets, naptha
Naphtha ( or ) is a flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixture.
Mixtures labelled ''naphtha'' have been produced from natural gas condensates, petroleum distillates, and the distillation of coal tar and peat. In different industries and regions '' ...
and other goods transported overland and down the Dead Sea to Elat at the head of the gulf of Aqaba where they were joined with frankincense and myrrh coming north both by sea and overland along trade routes through the mountains running north along the east coast of the Red Sea.
 A report of that five-ship voyage survives on
A report of that five-ship voyage survives on relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term '' relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
s in Hatshepsut's mortuary temple at Deir el-Bahri
Deir el-Bahari or Dayr al-Bahri ( ar, الدير البحري, al-Dayr al-Baḥrī, the Monastery of the North) is a complex of mortuary temples and tombs located on the west bank of the Nile, opposite the city of Luxor, Egypt. This is a part of ...
.Tyldesley, Hatchepsut, p.149 Throughout the temple texts, Hatshepsut "maintains the fiction that her envoy" Chancellor Nehsi, who is mentioned as the head of the expedition, had travelled to Punt "in order to extract tribute from the natives" who admit their allegiance to the Egyptian pharaoh.Tyldesley, Hatchepsut, p.147 In reality, Nehsi's expedition was a simple trading mission to a land, Punt, which was by this time a well-established trading post. Moreover, Nehsi's visit to Punt was not inordinately brave since he was "accompanied by at least five shiploads of gyptian
Windel Beneto Edwards (born 25 October 1983), better known by his stage name Gyptian (), is a Jamaican reggae singer. He often appears with roots reggae songs within the reggae subgenre dancehall.
Early life
Born to a Seventh-day Adventist ...
marines" and greeted warmly by the chief of Punt and his immediate family. The Puntites "traded not only in their own produce of incense, ebony and short-horned cattle, but lsoin goods from other African states including gold, ivory and animal skins." According to the temple reliefs, the Land of Punt was ruled at that time by King Parahu and Queen Ati. This well illustrated expedition of Hatshepsut occurred in Year 9 of the female pharaoh's reign with the blessing of the god Amun:
While the Egyptians "were not particularly well versed in the hazards of sea travel, and the long voyage to Punt must have seemed something akin to a journey to the moon for present-day explorers... the rewards of btaining frankincense, ebony and myrrhclearly outweighed the risks." An extensive account of the expedition, based on the tableaux, was provided by Amelia Edwards
Amelia Ann Blanford Edwards (7 June 1831 – 15 April 1892), also known as Amelia B. Edwards, was an English novelist, journalist, traveller and Egyptologist. Her literary successes included the ghost story "The Phantom Coach" (1864), the novel ...
in 1891.
According to Stuart Tyson Smith, Egyptologist and professor of anthropology at University of California, Santa Barbara
The University of California, Santa Barbara (UC Santa Barbara or UCSB) is a public land-grant research university in Santa Barbara, California with 23,196 undergraduates and 2,983 graduate students enrolled in 2021–2022. It is part of the U ...
, "The scene of an expedition to Punt from Queen Hatshepsuis mortuary complex at Deir el-Bahri shows Puntites with red skin and facial features similar to Egyptians, long or bobbed hair, goatee beards, and kilts".
Hatshepsut's 18th dynasty successors, such as Thutmose III
Thutmose III (variously also spelt Tuthmosis or Thothmes), sometimes called Thutmose the Great, was the sixth pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty. Officially, Thutmose III ruled Egypt for almost 54 years and his reign is usually dated from 2 ...
and Amenhotep III, also continued the Egyptian tradition of trading with Punt.Tyldesley, Hatchepsut, pp.145–146 The trade with Punt continued into the start of the 20th dynasty before terminating prior to the end of Egypt's New Kingdom. Papyrus Harris I
Papyrus Harris I is also known as the Great Harris Papyrus and (less accurately) simply the Harris Papyrus (though there are a number of other papyri in the Harris collection). Its technical designation is ''Papyrus British Museum EA 9999''. At 41 ...
, a contemporary Egyptian document that details events that occurred in the reign of the early 20th dynasty king Ramesses III
Usermaatre Meryamun Ramesses III (also written Ramses and Rameses) was the second Pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty in Ancient Egypt. He is thought to have reigned from 26 March 1186 to 15 April 1155 BC and is considered to be the last great monar ...
, includes an explicit description of an Egyptian expedition's return from Punt:
After the end of the New Kingdom period, Punt became "an unreal and fabulous land of myths and legends." However, Egyptians continued to compose love songs about Punt, "When I hold my love close, and her arms steal around me, I'm like a man translated to Punt, or like someone out in the reedflats, when the world suddenly bursts into flower."
''Ta netjer''
Flinders Petrie
Sir William Matthew Flinders Petrie ( – ), commonly known as simply Flinders Petrie, was a British Egyptologist and a pioneer of systematic methodology in archaeology and the preservation of artefacts. He held the first chair of Egyp ...
believed that the Dynastic Race The dynastic race theory was the earliest thesis to attempt to explain how predynastic Egypt developed into the sophisticated monarchy of Dynastic Egypt. The theory holds that the earliest roots of the ancient Egyptian dynastic civilisation were i ...
came from or through Punt and that "Pan, or Punt, was a district at the south end of the Red Sea, which probably embraced both the African and Arabian shores." Moreover, E. A. Wallis Budge stated that "Egyptian tradition of the Dynastic Period held that the aboriginal home of the Egyptians was Punt...". James Breasted in 1906 argued that the term Ta netjer was not only applied to Punt, located southeast of Egypt, but also to regions of Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
east and northeast of Egypt, such as Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to Lebanon–Syria border, the north and east and Israel to Blue ...
, which was the source of wood for temples.
On the murals of the Hatshepsut temple at Deir el-Bahri, the King and Queen of Punt are depicted along with their retinue. Due to her unusual appearance, the Queen was sometimes hypothesized to have had advanced steatopygia or elephantiasis
Elephantiasis is the enlargement and hardening of limbs or body parts due to tissue swelling. It is characterised by edema, hypertrophy, and fibrosis of skin and subcutaneous tissues, due to obstruction of lymphatic vessels. It may affect the geni ...
.

Proposed locations
Horn of Africa
The majority opinion places Punt in Northeastern Africa, based on the fact that the products of Punt (as depicted in the Hatshepsut illustrations) were abundantly found in the Horn of Africa but were less common or sometimes absent in Arabia. These products included gold and aromatic resins such as myrrh, frankincense, andebony
Ebony is a dense black/brown hardwood, coming from several species in the genus '' Diospyros'', which also contains the persimmons. Unlike most woods, ebony is dense enough to sink in water. It is finely textured and has a mirror finish when ...
; the wild animals depicted in Punt included giraffes, baboons, hippopotami
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extan ...
, and leopards. Richard Pankhurst states: "unt
The University of North Texas (UNT) is a public research university in Denton, Texas. It was founded as a nonsectarian, coeducational, private teachers college in 1890 and was formally adopted by the state 11 years later."Denton Normal School," ...
has been identified with territory on both the Arabian and the Horn of Africa coasts. Consideration of the articles that the Egyptians obtained from Punt, notably gold and ivory, suggests, however, that these were primarily of African origin. ... This leads us to suppose that the term Punt probably applied more to African than Arabian territory."
In 2003, Ian Shaw wrote that "There is still some debate regarding the precise location of Punt, which was once identified with the region of modern Somalia. A strong argument has now been made for its location in either southern Sudan or the Eritrean region of Ethiopia, where the indigenous plants and animals equate most closely with those depicted in the Egyptian reliefs and paintings".
According to Simon Najovits, the area comprising Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constituti ...
, Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red ...
, the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; ...
coast of Eritrea and Sudan in the Horn of Africa is considered the most likely location .
In June 2018, Polish archaeologists who have been conducting research in The Temple of Hatshepsut since 1961 discovered the only depiction of a secretary bird (''Sagittarius serpentarius
The secretarybird or secretary bird (''Sagittarius serpentarius'') is a large, mostly terrestrial bird of prey. Endemic to Africa, it is usually found in the open grasslands and savanna of the sub-Saharan region. John Frederick Miller describe ...
'') known from ancient Egypt in the Bas-reliefs from the Portico of Punt that depicted the great Pharaonic expedition to the Land of Punt. The secretary bird lives only in the African open grasslands and savannah, it is listed among the birds found in Sudan, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, Eritrea, Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red ...
, and Somaliland, the bird is not found in Arabia.
Recently it has been suggested that Punt might be located in the Eastern desert in Sudan and the northern Horn of Africa where the Gash Group The Gash Group is a neolithic, prehistoric culture that flourished around 3000 to 1800 BC in Eritrea and the Eastern Sudan. It was followed by the Jebel Mokram Group. The name Gash relates to the river in Eritrea with the same name.
Description ...
(about 3000 to 1800 BC) and later the Jebel Mokram Group flourished. Especially at Gash Group sites, many Egyptian pottery vessels and Egyptian faience beads were found, indicating close contacts with Egypt. Found Red Sea shells demonstrate contact with the Red Sea coast.
Arabian peninsula
Dimitri Meeks disagrees with the Horn of Africa hypothesis and points to ancient inscriptions that locate Punt in the western coast of the Arabian Peninsula, from theGulf of Aqaba
The Gulf of Aqaba ( ar, خَلِيجُ ٱلْعَقَبَةِ, Khalīj al-ʿAqabah) or Gulf of Eilat ( he, מפרץ אילת, Mifrátz Eilát) is a large gulf at the northern tip of the Red Sea, east of the Sinai Peninsula and west of the Arabian ...
to Yemen, he has written that "Texts locating Punt beyond doubt to the south are in the minority, but they are the only ones cited in the current consensus about the location of the country. Punt, we are told by the Egyptians, is situated – in relation to the Nile Valley – both to the north, in contact with the countries of the Near East of the Mediterranean area, and also to the east or south-east, while its furthest borders are far away to the south. Only the Arabian Peninsula satisfies all these indications."
Others
Some scholars have argued that Punt is the early Pandyan island ofTamraparni
Tamraparni (Sanskrit for "with copper leaves" or "red-leaved") is an older name for multiple distinct places, including Sri Lanka, Tirunelveli in India, and the Thamirabarani River that flows through Tirunelveli.
As a name for Sri Lanka
The r ...
, present day Sri Lanka. An artifact datable to the Fifth Dynasty was originally stated to be made from ''Diospyros ebenum
''Diospyros ebenum'', or Ceylon ebony ( si, කළුවර ''Kaluwara''), is a species of tree in the genus Diospyros and the family Ebenaceae. The tree produces valuable black wood.
Description
This middle-high evergreen tree grows very sl ...
'' wood, a tree which is originally of Southern India and Sri Lanka. However, such identification is now considered unconfirmed because of the unlikelihood of such an early contact between Egypt and the Indian subcontinent, together with the difficulty of correctly identifying a plant specimen dead for thousands of years.
Punt as depicted by Ancient Egypt
See also
*Ophir
Ophir (; ) is a port or region mentioned in the Bible, famous for its wealth. King Solomon received a shipment from Ophir every three years (1 Kings 10:22) which consisted of gold, silver, sandalwood, pearls, ivory, apes, and peacocks.
...
, an unidentified place mentioned in the Hebrew Bible as a source of riches for Solomon's Temple
* Tarshish
Tarshish ( Phoenician: ''TRŠŠ'', he, תַּרְשִׁישׁ ''Taršīš'', , ''Tharseis'') occurs in the Hebrew Bible with several uncertain meanings, most frequently as a place (probably a large city or region) far across the sea from Phoen ...
, another unidentified place mentioned in the Bible
Notes
References
* . * . * * Fattovich, Rodolfo. 1991. "The Problem of Punt in the Light of the Recent Field Work in the Eastern Sudan". In ''Akten des vierten internationalen Ägyptologen Kongresses, München 1985'', edited by Sylvia Schoske. Vol. 4 of 4 vols. Hamburg: Helmut Buske Verlag. 257–272. * ———. 1993. "Punt: The Archaeological Perspective". In ''Sesto congresso internazionale de egittologia: Atti'', edited by Gian Maria Zaccone and Tomaso Ricardi di Netro. Vol. 2 of 2 vols. Torino: Italgas. 399–405. * Herzog, Rolf. 1968. ''Punt''. Abhandlungen des Deutsches Archäologischen Instituts Kairo, Ägyptische Reihe 6. Glückstadt: Verlag J. J. Augustin. * * . * . * . * O'Connor, David (1994), ''Ancient Nubia: Egypt's Rival in Africa'', University of Pennsylvania Press, pp. 41–44. * Wicker, F. D. P. (July, 1998), "The Road to Punt", ''The Geographical Journal.'' Vol. 164, no. 2. 155-167Further reading
*Older literature
* Johannes Dümichen: ''Die Flotte einer ägyptischen Königin'', Leipzig, 1868. * *Wilhelm Max Müller
Wilhelm Max Müller (15 May 1862 – 12 July 1919) was a German-born American orientalist.
Biography
Müller was born at Gleißenberg, Germany. He received his higher education in Erlangen, Berlin, Munich, and Leipzig, where he received his ...
: ''Asien und Europa nach altägyptischen Denkmälern'', Leipzig, 1893.
* Adolf Erman
Johann Peter Adolf Erman (; 31 October 185426 June 1937) was a renowned German Egyptologist and lexicographer.
Life
Born in Berlin, he was the son of Georg Adolf Erman and grandson of Paul Erman and Friedrich Bessel.
Educated at Leipzig and ...
: ''Life in Ancient Egypt'', London, 1894.
* Édouard Naville
Henri Édouard Naville (14 June 1844 – 17 October 1926) was a Swiss archaeologist, Egyptologist and Biblical scholar.
Born in Geneva, he studied at the University of Geneva, King's College, London, and the Universities of Bonn, Paris, a ...
: "Deir-el-Bahri" in ''Egypt Exploration Fund, Memoirs XII, XIII, XIV, and XIX'', London, 1894 et seq.
* James Henry Breasted: ''A History of the Ancient Egyptians'', New York, 1908.
External links
* with quotes from Breasted (1906) and Petrie (1939)Queen Hatasu, and Her Expedition to the Land of Punt
by Amelia Ann Blanford Edwards (1891) * * at Deir el-Bahri * discussion by Dr. Karl H. Leser
;News reports on Wadi Gawasis excavations
(Boston University Bridge, 18 March 2005). Excavations at Wadi Gawasis, possibly the ancient Egyptian port Saaw.
Remains of ancient Egyptian seafaring ships discovered
(New Scientist, 23 March 2005). * *
4,000-year-old shipyard unearthed in Egypt
(MSNBC, 6 March 2006). {{DEFAULTSORT:Land of Punt Geography of ancient Egypt Ancient Somalia Countries in ancient Africa History of the Red Sea Foreign contacts of ancient Egypt Historical regions Lost places South Arabia Former kingdoms