Pulmonary Trunk on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A pulmonary artery is an
 In order of blood flow, the pulmonary arteries start as the pulmonary trunk that leaves the fibrous pericardium ( parietal pericardium) of the ventricular outflow tract of
In order of blood flow, the pulmonary arteries start as the pulmonary trunk that leaves the fibrous pericardium ( parietal pericardium) of the ventricular outflow tract of
 The left main pulmonary artery then divides into two lobar arteries, one for each lobe of the left lung.
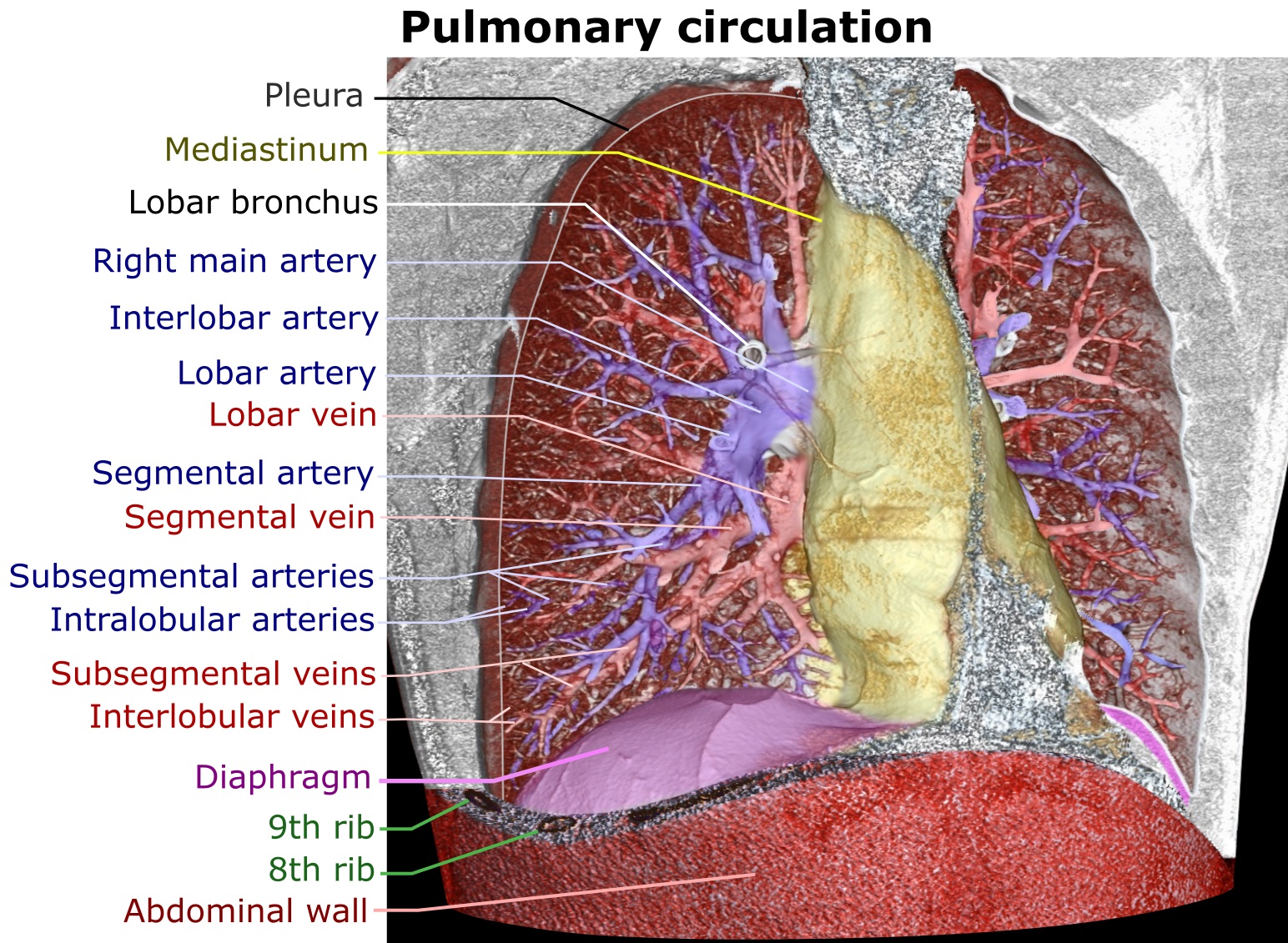
At the right root of the lung, it bifurcates into artery that supplies the right upper lobe of the lung, in front of the right upper lobe bronchus, and interlobar artery that supplies the right middle and inferior lobes of the lung, running together with bronchus intermedius.
The right and left main pulmonary (lungs) arteries give off branches that supplies the corresponding
The left main pulmonary artery then divides into two lobar arteries, one for each lobe of the left lung.
At the right root of the lung, it bifurcates into artery that supplies the right upper lobe of the lung, in front of the right upper lobe bronchus, and interlobar artery that supplies the right middle and inferior lobes of the lung, running together with bronchus intermedius.
The right and left main pulmonary (lungs) arteries give off branches that supplies the corresponding
File:Relations of the aorta, trachea, esophagus and other heart structures.png, Image showing ''main pulmonary artery'' coursing ventrally to the aortic root and
artery
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pu ...
in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
from the right side of the heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as ca ...
to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as ca ...
, and the smallest ones are the arterioles, which lead to the capillaries that surround the pulmonary alveoli
A pulmonary alveolus (plural: alveoli, from Latin ''alveolus'', "little cavity"), also known as an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide. Al ...
.
Structure
The pulmonary arteries areblood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide awa ...
s that carry systemic venous blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the microcirculation of the lungs. Unlike in other organs where arteries supply oxygenated blood, the blood carried by the pulmonary arteries is deoxygenated, as it is venous blood returning to the heart. The main pulmonary arteries emerge from the right side of the heart, and then split into smaller arteries that progressively divide and become arterioles, eventually narrowing into the capillary microcirculation of the lungs where gas exchange occurs.
Pulmonary trunk
 In order of blood flow, the pulmonary arteries start as the pulmonary trunk that leaves the fibrous pericardium ( parietal pericardium) of the ventricular outflow tract of
In order of blood flow, the pulmonary arteries start as the pulmonary trunk that leaves the fibrous pericardium ( parietal pericardium) of the ventricular outflow tract of right ventricle
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the uppe ...
(also known as infundibulum or conus arteriosus. The outflow track runs superiorly and to the left, posterior to the pulmonary valve. The pulmonary trunk bifurcates into right and left pulmonary arteries below the arch of aorta
The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch () is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea.
Structure
The aorta begins a ...
and in front of the left main bronchus. Pulmonary trunk is short and wideapproximately in length and - in diameter.
The pulmonary trunk splits into the right and the left main pulmonary artery. The left main pulmonary artery is shorter than the right, passes behind and downwards the descending aorta and above the left main bronchus to the root of the left lung. Above, the left main pulmonary artery is connected to the concavity of the proximal descending aorta by the ligamentum arteriosum
The ligamentum arteriosum (arterial ligament), also known as the Ligament of Botallo or Harvey's ligament, is a small ligament attaching the aorta to the pulmonary artery. It serves no function in adults but is the remnant of the ductus arteriosus ...
. The right pulmonary artery pass across the midline of the body, below the carina of trachea
In anatomy, the carina or tracheal bifurcation is a ridge of cartilage in the trachea that occurs between the division of the two main bronchi.
Structure
The carina occurs at the lower end of the trachea (usually at the level of the 4th to 5th ...
, and comes in front of the right main bronchus.
Branches
lung lobe
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side ...
s. In such cases it is termed lobar arteries. The lobar arteries branch into segmental arteries (roughly 1 for each segment). Segmental arteries run together with segmental bronchi, at the posterolateral surfaces of the bronchi. These in turn branch into subsegmental pulmonary arteries. These eventually form intralobular arteries. The pulmonary arteries supply the alveoli of the lungs. In contrast, bronchial arteries
In human anatomy, the bronchial arteries supply the lungs with nutrition and oxygenated blood. Although there is much variation, there are usually two bronchial arteries that run to the left lung, and one to the right lung and are a vital part ...
, that has different origins, supply the bronchi of the lungs.
Development
The pulmonary arteries originate from the truncus arteriosus and the sixth pharyngeal arch. The truncus arteriosus is a structure that forms during the development of the heart as a successor to the conus arteriosus. By the third week of development, the endocardial tubes have developed a swelling in the part closest to the heart. The swelling is known as the bulbus cordis and the upper part of this swelling develops into the truncus arteriosus. The structure is ultimately mesodermal in origin. During development of the heart, the heart tissues undergo folding, and the truncus arteriosus is exposed to what will eventually be both the left and right ventricles. As a septum develops between the two ventricles of the heart, two bulges form on either side of the truncus arteriosus. These progressively enlarge until the trunk splits into the aorta and pulmonary arteries. During early development, the ductus arteriosus connects the pulmonary trunk and theaortic arch
The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch () is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea.
Structure
The aorta begins ...
, allowing blood to bypass the lungs.
Function
The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from theright ventricle
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the uppe ...
to the lungs. The blood here passes through capillaries adjacent to alveoli Alveolus (; pl. alveoli, adj. alveolar) is a general anatomical term for a concave cavity or pit.
Uses in anatomy and zoology
* Pulmonary alveolus, an air sac in the lungs
** Alveolar cell or pneumocyte
** Alveolar duct
** Alveolar macrophage
* M ...
and becomes oxygenated as part of the process of respiration.
In contrast to the ''pulmonary arteries'', the bronchial arteries
In human anatomy, the bronchial arteries supply the lungs with nutrition and oxygenated blood. Although there is much variation, there are usually two bronchial arteries that run to the left lung, and one to the right lung and are a vital part ...
supply nutrition to the lungs themselves.
Pressure
The pulmonary artery pressure (PA pressure) is a measure of the blood pressure found in the main pulmonary artery. This is measured by inserting a catheter into the main pulmonary artery. The mean pressure is typically 9–18 mmHg, and thewedge pressure
The pulmonary wedge pressure (PWP), also called pulmonary arterial wedge pressure (PAWP), pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP), pulmonary artery occlusion pressure (PAOP), or cross-sectional pressure, is the pressure measured by wedging a pulm ...
measured in the left atrium may be 6–12 mmHg. The wedge pressure may be elevated in left heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, Fatigue (medical), exc ...
, mitral valve stenosis, and other conditions, such as sickle cell disease.
Clinical significance
The pulmonary artery is relevant in a number of clinical states. Pulmonary hypertension is used to describe an increase in the pressure of the pulmonary artery, and may be defined as a mean pulmonary artery pressure of greater than 25 mmHg. As can be measured on a CT scan, a diameter of more than 29 mm diameter is often used as a cut-off to indicate pulmonary hypertension. In chest X-rays, diameter of descending pulmonary artery more than 16 mm indicates pulmonary hypertension. This may occur as a result of heart problems such as heart failure, lung or airway disease such as COPD or scleroderma, or thromboembolic disease such as pulmonary embolism or emboli seen in sickle cell anaemia. Most recently, computational fluid based tools (non-invasive) have been proposed to be at par with the current clinical tests (invasive) of pulmonary hypertension. Pulmonary embolism refers to an embolus that lodges in the pulmonary circulation. This may arise from adeep venous thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enla ...
, especially after a period of immobility. A pulmonary embolus is a common cause of death in patients with cancer and stroke. A large pulmonary embolus that becomes lodged in the bifurcation of the pulmonary trunk with extensions into both the left and right main pulmonary arteries is called a ''saddle embolus''.
Several animal models have been utilized for investigating pulmonary artery related pathologies. Porcine model of pulmonary artery is the most frequently used and it was recently found that their mechanical properties vary with every subsequent branching.
Additional images
trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air- breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from t ...
, and the ''right pulmonary artery'' passes dorsally to the ascending aorta
The ascending aorta (AAo) is a portion of the aorta commencing at the upper part of the base of the left ventricle, on a level with the lower border of the third costal cartilage behind the left half of the sternum.
Structure
It passes obliqu ...
, while the ''left pulmonary artery'' passes ventrally to the descending aorta.
File:Illu pulmonary circuit.jpg, Pulmonary circuit
File:Gray503.png, Transverse section of thorax, showing relations of pulmonary artery.
File:Slide16444 (1).jpg, alt=Original image from Anatomist 90, Pulmonary artery
File:Slide44uru.JPG, Pulmonary artery.Deep dissection.Anterior view.
File:Computed tomograph of pulmonary vessels.jpg, CT scan of a normal lung, with different levels of pulmonary arteries.
File:Bronchial anatomy.jpg, Bronchial anatomy
See also
*Pulmonary artery sling
Pulmonary artery sling is a rare condition in which the blood vessels between the heart and the lungs have formed incorrectly before birth. It is a type of cardiovascular condition called a vascular ring.The main treatment is surgery. Symptoms ...
* Rasmussen's aneurysm Rasmussen's aneurysm is a pulmonary artery aneurysm associated with a cavitary lung lesion. It was originally described by Fritz Valdemar Rasmussen in association with cavitary lung lesions of tuberculosis,Rasmussen, V. On hemoptysis, especially wh ...
References
External links
* – "Heart: The Pericardial sac and Great vessels" * – "Heart: Openings of Great Vessels into the Pericardial Sac" * – " Mediastinal surface of the right lung" * – "Mediastinal surface of the left lung" * {{DEFAULTSORT:Pulmonary Artery Arteries of the thorax