pulmonary contusion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A pulmonary contusion, also known as lung contusion, is a
 Pulmonary contusion and laceration are injuries to the lung tissue.
Pulmonary contusion and laceration are injuries to the lung tissue.
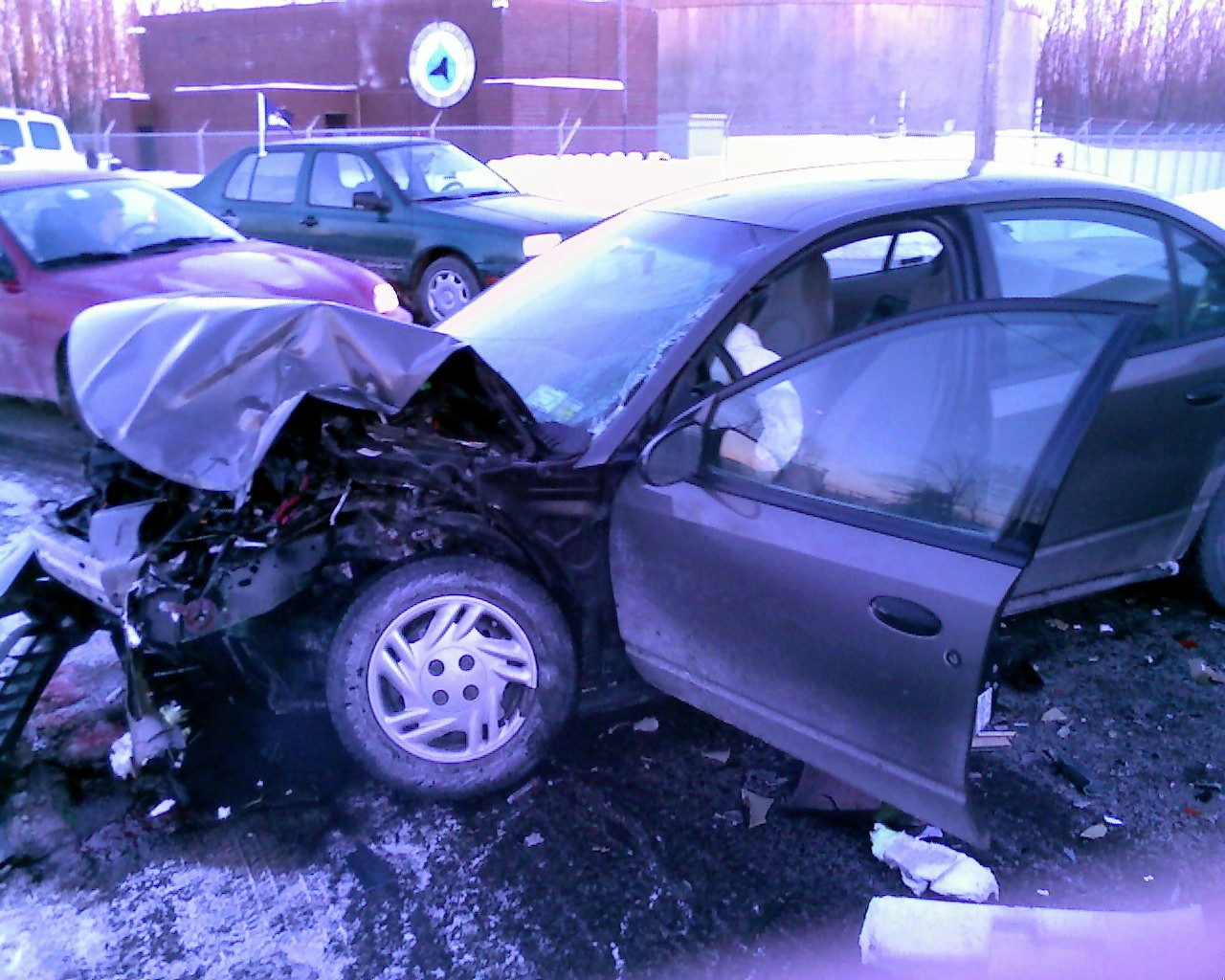 Pulmonary contusion is the most common injury found in blunt chest trauma, occurring in 25–35% of cases.
It is usually caused by the rapid deceleration that results when the moving chest strikes a fixed object. About 70% of cases result from motor vehicle collisions, most often when the chest strikes the inside of the car. Falls,
assaults,
and sports injuries are other causes.
Pulmonary contusion can also be caused by explosions; the organs most vulnerable to
Pulmonary contusion is the most common injury found in blunt chest trauma, occurring in 25–35% of cases.
It is usually caused by the rapid deceleration that results when the moving chest strikes a fixed object. About 70% of cases result from motor vehicle collisions, most often when the chest strikes the inside of the car. Falls,
assaults,
and sports injuries are other causes.
Pulmonary contusion can also be caused by explosions; the organs most vulnerable to
 Pulmonary contusion results in bleeding and fluid leakage into lung tissue, which can become stiffened and lose its normal elasticity. The water content of the lung increases over the first 72 hours after injury, potentially leading to frank
Pulmonary contusion results in bleeding and fluid leakage into lung tissue, which can become stiffened and lose its normal elasticity. The water content of the lung increases over the first 72 hours after injury, potentially leading to frank

 Computed tomography (CT scanning) is a more sensitive test for pulmonary contusion, and it can identify
Computed tomography (CT scanning) is a more sensitive test for pulmonary contusion, and it can identify
 Pulmonary
Pulmonary
 Positive pressure ventilation, in which air is forced into the lungs, is needed when oxygenation is significantly impaired.
Positive pressure ventilation, in which air is forced into the lungs, is needed when oxygenation is significantly impaired.
 Pulmonary contusion usually resolves itself without causing permanent complications; however it may also have long-term ill effects on respiratory function. Most contusions resolve in five to seven days after the injury. Signs detectable by radiography are usually gone within 10 days after the injury—when they are not, other conditions, such as pneumonia, are the likely cause. Chronic lung disease correlates with the size of the contusion and can interfere with an individual's ability to return to work.
Pulmonary contusion usually resolves itself without causing permanent complications; however it may also have long-term ill effects on respiratory function. Most contusions resolve in five to seven days after the injury. Signs detectable by radiography are usually gone within 10 days after the injury—when they are not, other conditions, such as pneumonia, are the likely cause. Chronic lung disease correlates with the size of the contusion and can interfere with an individual's ability to return to work.
 Pulmonary contusion can result in respiratory failure—about half of such cases occur within a few hours of the initial trauma. Other severe complications, including infections and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) occur in up to half of cases. Elderly people and those who have heart, lung, or kidney disease prior to the injury are more likely to stay longer in hospital and have complications from the injury. Complications occur in 55% of people with heart or lung disease and 13% of those without. Of people with pulmonary contusion alone, 17% develop ARDS, while 78% of people with at least two additional injuries develop the condition. A larger contusion is associated with an increased risk. In one study, 82% of people with 20% or more of the lung volume affected developed ARDS, while only 22% of people with less than 20% did so.
Pulmonary contusion can result in respiratory failure—about half of such cases occur within a few hours of the initial trauma. Other severe complications, including infections and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) occur in up to half of cases. Elderly people and those who have heart, lung, or kidney disease prior to the injury are more likely to stay longer in hospital and have complications from the injury. Complications occur in 55% of people with heart or lung disease and 13% of those without. Of people with pulmonary contusion alone, 17% develop ARDS, while 78% of people with at least two additional injuries develop the condition. A larger contusion is associated with an increased risk. In one study, 82% of people with 20% or more of the lung volume affected developed ARDS, while only 22% of people with less than 20% did so.
 A large amount of force is required to cause pulmonary contusion; a person injured with such force is likely to have other types of injuries as well. In fact, pulmonary contusion can be used to gauge the severity of trauma.
Up to three quarters of cases are accompanied by other chest injuries,
the most common of these being hemothorax and pneumothorax.
Flail chest is usually associated with significant pulmonary contusion, and the contusion, rather than the chest wall injury, is often the main cause of respiratory failure in people with these injuries.
Other indications of
A large amount of force is required to cause pulmonary contusion; a person injured with such force is likely to have other types of injuries as well. In fact, pulmonary contusion can be used to gauge the severity of trauma.
Up to three quarters of cases are accompanied by other chest injuries,
the most common of these being hemothorax and pneumothorax.
Flail chest is usually associated with significant pulmonary contusion, and the contusion, rather than the chest wall injury, is often the main cause of respiratory failure in people with these injuries.
Other indications of
 In 1761, the Italian anatomist
In 1761, the Italian anatomist
Chest Trauma - pulmonary contusion
trauma.org {{DEFAULTSORT:Pulmonary Contusion Chest trauma Medical emergencies Lung disorders
bruise
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur close ...
of the lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of ...
, caused by chest trauma. As a result of damage to capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
, blood and other fluids accumulate in the lung tissue. The excess fluid interferes with gas exchange
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liquid, a gas-permeable membrane, or a ...
, potentially leading to inadequate oxygen levels ( hypoxia). Unlike pulmonary laceration
A pulmonary laceration is a chest injury in which lung tissue is torn or cut.
An injury that is potentially more serious than pulmonary contusion, pulmonary laceration involves disruption of the architecture of the lung,
while pulmonary contusi ...
, another type of lung injury, pulmonary contusion does not involve a cut or tear of the lung tissue.
A pulmonary contusion is usually caused directly by blunt trauma
Blunt trauma, also known as blunt force trauma or non-penetrating trauma, is physical traumas, and particularly in the elderly who fall. It is contrasted with penetrating trauma which occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue ...
but can also result from explosion injuries or a shock wave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a me ...
associated with penetrating trauma
Penetrating trauma is an open wound injury that occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body, creating a deep but relatively narrow entry wound. In contrast, a blunt or ''non-penetrating'' trauma may have some deep da ...
. With the use of explosives during World Wars I and II, pulmonary contusion resulting from blasts gained recognition. In the 1960s its occurrence in civilians began to receive wider recognition, in which cases it is usually caused by traffic accidents. The use of seat belts and airbags reduces the risk to vehicle occupants.
Diagnosis is made by studying the cause of the injury, physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the pati ...
and chest radiography
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
. Typical signs and symptoms include direct effects of the physical trauma, such as chest pain and coughing up blood, as well as signs that the body is not receiving enough oxygen, such as cyanosis
Cyanosis is the change of body tissue color to a bluish-purple hue as a result of having decreased amounts of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Body tissues that show cyanosis are usually in locations ...
. The contusion frequently heals on its own with supportive care. Often nothing more than supplemental oxygen and close monitoring is needed; however, intensive care
Intensive care medicine, also called critical care medicine, is a medical specialty that deals with seriously or critically ill patients who have, are at risk of, or are recovering from conditions that may be life-threatening. It includes pro ...
may be required. For example, if breathing is severely compromised, mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move a ...
may be necessary. Fluid replacement
Fluid replacement or fluid resuscitation is the medical practice of replenishing bodily fluid lost through sweating, bleeding, fluid shifts or other pathologic processes. Fluids can be replaced with oral rehydration therapy (drinking), intravenous ...
may be required to ensure adequate blood volume, but fluids are given carefully since fluid overload
Hypervolemia, also known as fluid overload, is the medical condition where there is too much fluid in the blood. The opposite condition is hypovolemia, which is too little fluid volume in the blood. Fluid volume excess in the intravascular comp ...
can worsen pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive liquid accumulation in the tissue and air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause hypoxemia and respiratory failure. It is due ...
, which may be lethal.
The severity ranges from mild to severe: small contusions may have little or no impact on health, yet pulmonary contusion is the most common type of potentially lethal chest trauma. It occurs in 30–75% of severe chest injuries. The risk of death following a pulmonary contusion is between 14 and 40%. Pulmonary contusion is usually accompanied by other injuries. Although associated injuries are often the cause of death, pulmonary contusion is thought to cause death directly in a quarter to half of cases. Children are at especially high risk for the injury because the relative flexibility of their bones prevents the chest wall from absorbing force from an impact, causing it to be transmitted instead to the lung. Pulmonary contusion is associated with complications including pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severit ...
and acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin colo ...
, and it can cause long-term respiratory disability.
Classification
Pulmonary laceration
A pulmonary laceration is a chest injury in which lung tissue is torn or cut.
An injury that is potentially more serious than pulmonary contusion, pulmonary laceration involves disruption of the architecture of the lung,
while pulmonary contusi ...
, in which lung tissue is torn or cut, differs from pulmonary contusion in that the former involves disruption of the macroscopic
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or phenomena are large enough to be visible with the naked eye, without magnifying optical instruments. It is the opposite of microscopic.
Overview
When applied to physical phenomena a ...
architecture of the lung, while the latter does not. When lacerations fill with blood, the result is pulmonary hematoma
A pulmonary hematoma is a collection of blood within the tissue of the lung. It may result when a pulmonary laceration fills with blood. A lung laceration filled with air is called a pneumatocele. In some cases, both pneumatoceles and hematoma ...
, a collection of blood within the lung tissue. Contusion involves hemorrhage in the alveoli Alveolus (; pl. alveoli, adj. alveolar) is a general anatomical term for a concave cavity or pit.
Uses in anatomy and zoology
* Pulmonary alveolus, an air sac in the lungs
** Alveolar cell or pneumocyte
** Alveolar duct
** Alveolar macrophage
* M ...
(tiny air-filled sacs responsible for absorbing oxygen), but a hematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is ...
is a discrete clot of blood not interspersed with lung tissue. A collapsed lung can result when the pleural cavity
The pleural cavity, pleural space, or interpleural space is the potential space between the pleurae of the pleural sac that surrounds each lung. A small amount of serous pleural fluid is maintained in the pleural cavity to enable lubrication b ...
(the space outside the lung) accumulates blood ( hemothorax) or air (pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve i ...
) or both ( hemopneumothorax). These conditions do not inherently involve damage to the lung tissue itself, but they may be associated with it. Injuries to the chest wall are also distinct from but may be associated with lung injuries. Chest wall injuries include rib fractures and flail chest
Flail chest is a life-threatening medical condition that occurs when a segment of the rib cage breaks due to trauma and becomes detached from the rest of the chest wall. Two of the symptoms of flail chest are chest pain and shortness of breath. ...
, in which multiple ribs are broken so that a segment of the ribcage is detached from the rest of the chest wall and moves independently.
Signs and symptoms
Presentation may be subtle; people with mild contusion may have no symptoms at all. However, pulmonary contusion is frequently associated with signs (objective indications) andsymptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showi ...
s (subjective states), including those indicative of the lung injury itself and of accompanying injuries. Because gas exchange
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liquid, a gas-permeable membrane, or a ...
is impaired, signs of low blood oxygen saturation, such as low concentrations of oxygen in arterial blood gas and cyanosis
Cyanosis is the change of body tissue color to a bluish-purple hue as a result of having decreased amounts of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Body tissues that show cyanosis are usually in locations ...
(bluish color of the skin and mucous membranes) are commonly associated. Dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing di ...
(painful breathing or difficulty breathing) is commonly seen, and tolerance for exercise may be lowered. Rapid breathing
Tachypnea, also spelt tachypnoea, is a respiratory rate greater than normal, resulting in abnormally rapid and shallow breathing.
In adult humans at rest, any respiratory rate of 1220 per minute is considered clinically normal, with tachypnea b ...
and a rapid heart rate are other signs. With more severe contusions, breath sounds
Respiratory sounds, also known as lung sounds or breath sounds, refer to the specific sounds generated by the movement of air through the respiratory system. These may be easily audible or identified through auscultation of the respiratory system ...
heard through a stethoscope may be decreased, or rales
Crackles are the clicking, rattling, or crackling noises that may be made by one or both lungs of a human with a respiratory disease during inhalation. They are usually heard only with a stethoscope ("on auscultation"). Pulmonary crackles are a ...
(an abnormal crackling sound in the chest accompanying breathing) may be present. People with severe contusions may have bronchorrhea (the production of watery sputum
Sputum is mucus that is coughed up from the lower airways (the trachea and bronchi). In medicine, sputum samples are usually used for a naked eye examination, microbiological investigation of respiratory infections and cytological investigatio ...
). Wheezing and coughing are other signs. Coughing up blood or bloody sputum is present in up to half of cases. Cardiac output
In cardiac physiology, cardiac output (CO), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols Q, \dot Q, or \dot Q_ , edited by Catherine E. Williamson, Phillip Bennett is the volumetric flow rate of the heart's pumping output: th ...
(the volume of blood pumped by the heart) may be reduced, and hypotension
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the di ...
(low blood pressure) is frequently present. The area of the chest wall near the contusion may be tender or painful due to associated chest wall injury.
Signs and symptoms take time to develop, and as many as half of cases are asymptomatic
In medicine, any disease is classified asymptomatic if a patient tests as carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. Whenever a medical condition fails to show noticeable symptoms after a diagnosis it might be considered a ...
at the initial presentation. The more severe the injury, the more quickly symptoms become apparent. In severe cases, symptoms may occur as quickly as three or four hours after the trauma. Hypoxemia
Hypoxemia is an abnormally low level of oxygen in the blood. More specifically, it is oxygen deficiency in arterial blood. Hypoxemia has many causes, and often causes hypoxia as the blood is not supplying enough oxygen to the tissues of the bod ...
(low oxygen concentration in the arterial blood) typically becomes progressively worse over 24–48 hours after injury. In general, pulmonary contusion tends to worsen slowly over a few days, but it may also cause rapid deterioration or death if untreated.
Causes
 Pulmonary contusion is the most common injury found in blunt chest trauma, occurring in 25–35% of cases.
It is usually caused by the rapid deceleration that results when the moving chest strikes a fixed object. About 70% of cases result from motor vehicle collisions, most often when the chest strikes the inside of the car. Falls,
assaults,
and sports injuries are other causes.
Pulmonary contusion can also be caused by explosions; the organs most vulnerable to
Pulmonary contusion is the most common injury found in blunt chest trauma, occurring in 25–35% of cases.
It is usually caused by the rapid deceleration that results when the moving chest strikes a fixed object. About 70% of cases result from motor vehicle collisions, most often when the chest strikes the inside of the car. Falls,
assaults,
and sports injuries are other causes.
Pulmonary contusion can also be caused by explosions; the organs most vulnerable to blast injuries
A blast injury is a complex type of physical trauma resulting from direct or indirect exposure to an explosion. Blast injuries occur with the detonation of high-order explosives as well as the deflagration of low order explosives. These injur ...
are those that contain gas, such as the lungs. Blast lung is severe pulmonary contusion, bleeding, or edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area ma ...
with damage to alveoli and blood vessels, or a combination of these.
This is the primary cause of death among people who initially survive an explosion.
Unlike other mechanisms of injury in which pulmonary contusion is often found alongside other injuries, explosions can cause pulmonary contusion without damage to the chest wall.
In addition to blunt trauma
Blunt trauma, also known as blunt force trauma or non-penetrating trauma, is physical traumas, and particularly in the elderly who fall. It is contrasted with penetrating trauma which occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue ...
, penetrating trauma
Penetrating trauma is an open wound injury that occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body, creating a deep but relatively narrow entry wound. In contrast, a blunt or ''non-penetrating'' trauma may have some deep da ...
can cause pulmonary contusion.
Contusion resulting from penetration by a rapidly moving projectile usually surrounds the path along which the projectile traveled through the tissue. The pressure wave forces tissue out of the way, creating a temporary cavity; the tissue readily moves back into place, but it is damaged. Pulmonary contusions that accompany gun and knife wounds are not usually severe enough to have a major effect on outcome; penetrating trauma causes less widespread lung damage than does blunt trauma. An exception is shotgun wounds, which can seriously damage large areas of lung tissue through a blast injury mechanism.
Mechanism
The physical processes behind pulmonary contusion are poorly understood. However, it is known that lung tissue can be crushed when the chest wall bends inward on impact. Three other possible mechanisms have been suggested: theinertia
Inertia is the idea that an object will continue its current motion until some force causes its speed or direction to change. The term is properly understood as shorthand for "the principle of inertia" as described by Newton in his first law ...
l effect, the spall
Spall are fragments of a material that are broken off a larger solid body. It can be produced by a variety of mechanisms, including as a result of projectile impact, corrosion, weathering, cavitation, or excessive rolling pressure (as in a ball ...
ing effect, and the implosion effect.
* In the inertial effect, the lighter alveolar tissue is sheared from the heavier hilar structures, an effect similar to diffuse axonal injury in head injury. It results from the fact that different tissues have different densities, and therefore different rates of acceleration or deceleration.
* In the spalling effect, lung tissue bursts or is sheared where a shock wave meets the lung tissue, at interfaces between gas and liquid. The alveolar walls form such a gas-liquid interface with the air in the alveoli.
The spalling effect occurs in areas with large differences in density; particles of the denser tissue are spalled (thrown) into the less dense particles.
* The implosion effect occurs when a pressure wave passes through a tissue containing bubbles of gas: the bubbles first implode, then rebound and expand beyond their original volume.
The air bubbles cause many tiny explosions, resulting in tissue damage; the overexpansion of gas bubbles stretches and tears alveoli.
This effect is thought to occur microscopically when the pressure in the airways increases sharply.
Contusion usually occurs on the lung directly under the site of impact, but, as with traumatic brain injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity (ranging from mild traumatic brain injury TBI/concussionto severe traumatic br ...
, a contrecoup Contrecoup may refer to:
* Coup contrecoup injury
In head injury, a coup injury occurs under the site of impact with an object, and a contrecoup injury occurs on the side opposite the area that was hit. Coup and contrecoup injuries are associated ...
contusion may occur at the site opposite the impact as well. A blow to the front of the chest may cause contusion on the back of the lungs because a shock wave travels through the chest and hits the curved back of the chest wall; this reflects the energy onto the back of the lungs, concentrating it. (A similar mechanism may occur at the front of the lungs when the back is struck.)
The amount of energy transferred to the lung is determined in a large part by the compliance (flexibility) of the chest wall. Children's chests are more flexible because their ribs are more elastic and there is less ossification
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in ...
of their intercostal cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck ...
. Therefore, their chest walls bend, absorbing less of the force and transmitting more of it to the underlying organs.
An adult's more bony chest wall absorbs more of the force itself rather than transmitting it. Thus children commonly get pulmonary contusions without fractures overlying them, while elderly people are more likely to develop fractures than contusions. One study found that pulmonary contusions were accompanied by fractures 62% of the time in children and 80% of the time in adults.
Pathophysiology
pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive liquid accumulation in the tissue and air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause hypoxemia and respiratory failure. It is due ...
in more serious cases. As a result of these and other pathological processes, pulmonary contusion progresses over time and can cause hypoxia (insufficient oxygen).
Bleeding and edema
In contusions, torncapillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
leak fluid into the tissues around them. The membrane between alveoli and capillaries is torn; damage to this capillary–alveolar membrane and small blood vessels causes blood and fluids to leak into the alveoli and the interstitial space (the space surrounding cells) of the lung. With more severe trauma, there is a greater amount of edema, bleeding, and tearing of the alveoli. Pulmonary contusion is characterized by microhemorrhages (tiny bleeds) that occur when the alveoli Alveolus (; pl. alveoli, adj. alveolar) is a general anatomical term for a concave cavity or pit.
Uses in anatomy and zoology
* Pulmonary alveolus, an air sac in the lungs
** Alveolar cell or pneumocyte
** Alveolar duct
** Alveolar macrophage
* M ...
are traumatically separated from airway structures and blood vessels. Blood initially collects in the interstitial space, and then edema occurs by an hour or two after injury. An area of bleeding in the contused lung is commonly surrounded by an area of edema. In normal gas exchange
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liquid, a gas-permeable membrane, or a ...
, carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
diffuses across the endothelium
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the ve ...
of the capillaries, the interstitial space, and across the alveolar epithelium; oxygen diffuses in the other direction. Fluid accumulation interferes with gas exchange, and can cause the alveoli to fill with proteins and collapse due to edema and bleeding. The larger the area of the injury, the more severe respiratory compromise will be.
Consolidation and collapse
Pulmonary contusion can cause parts of the lung to consolidate, alveoli to collapse, andatelectasis
Atelectasis is the collapse or closure of a lung resulting in reduced or absent gas exchange. It is usually unilateral, affecting part or all of one lung. It is a condition where the alveoli are deflated down to little or no volume, as distinct ...
(partial or total lung collapse) to occur. Consolidation occurs when the parts of the lung that are normally filled with air fill with material from the pathological condition, such as blood. Over a period of hours after the injury, the alveoli in the injured area thicken and may become consolidated. A decrease in the amount of surfactant
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension between two liquids, between a gas and a liquid, or interfacial tension between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsion#Emulsifiers , ...
produced also contributes to the collapse and consolidation of alveoli; inactivation of surfactant increases their surface tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) t ...
. Reduced production of surfactant can also occur in surrounding tissue that was not originally injured.
Inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
of the lungs, which can result when components of blood enter the tissue due to contusion, can also cause parts of the lung to collapse. Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
s, neutrophils
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying ...
, and other inflammatory cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multi ...
s and blood components can enter the lung tissue and release factors that lead to inflammation, increasing the likelihood of respiratory failure. In response to inflammation, excess mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
is produced, potentially plugging parts of the lung and leading to their collapse. Even when only one side of the chest is injured, inflammation may also affect the other lung. Uninjured lung tissue may develop edema, thickening of the septa of the alveoli, and other changes. If this inflammation is severe enough, it can lead to dysfunction of the lungs like that seen in acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Ventilation/perfusion mismatch
Normally, the ratio of ventilation to perfusion is about one-to-one; the volume of air entering the alveoli ( ventilation) is about equal to that of blood in the capillaries around them (perfusion
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ or a tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion is measured as the rate at which blood is deliver ...
).
This ratio is reduced in pulmonary contusion; fluid-filled alveoli cannot fill with air, oxygen does not fully saturate the hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythroc ...
, and the blood leaves the lung without being fully oxygenated.
Insufficient inflation of the lungs, which can result from inadequate mechanical ventilation or an associated injury such as flail chest, can also contribute to the ventilation/perfusion mismatch. As the mismatch between ventilation and perfusion grows, blood oxygen saturation is reduced. Pulmonary hypoxic vasoconstriction, in which blood vessels near the hypoxic alveoli constrict (narrow their diameter) in response to the lowered oxygen levels, can occur in pulmonary contusion. The vascular resistance increases in the contused part of the lung, leading to a decrease in the amount of blood that flows into it, directing blood to better-ventilated areas. Although reducing blood flow to the unventilated alveoli is a way to compensate for the fact that blood passing unventilated alveoli is not oxygenated, the oxygenation of the blood remains lower than normal. If it is severe enough, the hypoxemia resulting from fluid in the alveoli cannot be corrected just by giving supplemental oxygen; this problem is the cause of a large portion of the fatalities that result from trauma.
Diagnosis
To diagnose pulmonary contusion, health professionals use clues from a physical examination, information about the event that caused the injury, andradiography
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeu ...
. Laboratory findings may also be used; for example, arterial blood gasses may show insufficient oxygen and excessive carbon dioxide even in someone receiving supplemental oxygen. However, blood gas levels may show no abnormality early in the course of pulmonary contusion.
X-ray

Chest X-ray
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in me ...
is the most common method used for diagnosis, and may be used to confirm a diagnosis already made using clinical signs
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showin ...
. Consolidated areas appear white on an X-ray film.
Contusion is not typically restricted by the anatomical boundaries of the lobes or segments of the lung. The X-ray appearance of pulmonary contusion is similar to that of aspiration, and the presence of hemothorax or pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve i ...
may obscure the contusion on a radiograph. Signs of contusion that progress after 48 hours post-injury are likely to be actually due to aspiration, pneumonia, or ARDS.
Although chest radiography is an important part of the diagnosis, it is often not sensitive enough to detect the condition early after the injury. In a third of cases, pulmonary contusion is not visible on the first chest radiograph performed. It takes an average of six hours for the characteristic white regions to show up on a chest X-ray, and the contusion may not become apparent for 48 hours. When a pulmonary contusion is apparent in an X-ray, it suggests that the trauma to the chest was severe and that a CT scan might reveal other injuries that were missed with X-ray.
Computed tomography
 Computed tomography (CT scanning) is a more sensitive test for pulmonary contusion, and it can identify
Computed tomography (CT scanning) is a more sensitive test for pulmonary contusion, and it can identify abdominal
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the to ...
, chest, or other injuries that accompany the contusion. In one study, chest X-ray detected pulmonary contusions in 16.3% of people with serious blunt trauma, while CT detected them in 31.2% of the same people.
Unlike X-ray, CT scanning can detect the contusion almost immediately after the injury. However, in both X-ray and CT a contusion may become more visible over the first 24–48 hours after trauma as bleeding and edema into lung tissues progress.
CT scanning also helps determine the size of a contusion, which is useful in determining whether a patient needs mechanical ventilation; a larger volume of contused lung on CT scan is associated with an increased likelihood that ventilation will be needed. CT scans also help differentiate between contusion and pulmonary hematoma
A pulmonary hematoma is a collection of blood within the tissue of the lung. It may result when a pulmonary laceration fills with blood. A lung laceration filled with air is called a pneumatocele. In some cases, both pneumatoceles and hematoma ...
, which may be difficult to tell apart otherwise. However, pulmonary contusions that are visible on CT but not chest X-ray are usually not severe enough to affect outcome or treatment.
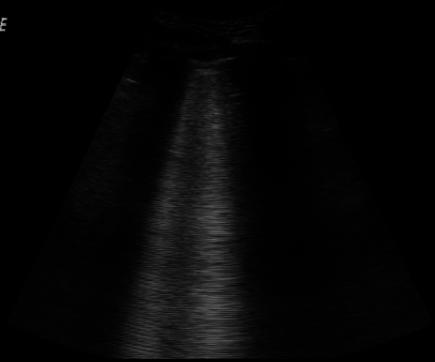
Ultrasound
 Pulmonary
Pulmonary ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
, performed at the bedside or on the accident scene, is being explored as a diagnosis for pulmonary contusion. Its use is still not widespread, being limited to facilities which are comfortable with its use for other applications, like pneumothorax, airway management, and hemothorax. Accuracy has been found to be comparable to CT scanning.
Prevention
Prevention of pulmonary contusion is similar to that of other chest trauma. Airbags in combination with seat belts can protect vehicle occupants by preventing the chest from striking the interior of the vehicle during a collision, and by distributing forces involved in the crash more evenly across the body. However, in rare cases, an airbag causes pulmonary contusion in a person who is not properly positioned when it deploys. Child restraints such as carseats protect children in vehicle collisions from pulmonary contusion. Equipment exists for use in some sports to prevent chest and lung injury; for example, in softball the catcher is equipped with a chest protector. Athletes who do not wear such equipment, such as basketball players, can be trained to protect their chests from impacts. Protective garments can also prevent pulmonary contusion in explosions. Although traditionalbody armor
Body armor, also known as body armour, personal armor or armour, or a suit or coat of armor, is protective clothing designed to absorb or deflect physical attacks. Historically used to protect military personnel, today it is also used by variou ...
made from rigid plates or other heavy materials protects from projectiles generated by a blast, it does not protect against pulmonary contusion, because it does not prevent the blast's shock wave from being transferred to the lung. Special body armor has been designed for military personnel at high risk for blast injuries; these garments can prevent a shock wave from being propagated across the chest wall to the lung, and thus protect wearers from blast lung injuries. These garments alternate layers of materials with high and low acoustic impedance (the product of a material's density and a wave's velocity through it) in order to "decouple" the blast wave, preventing its propagation into the tissues.
Treatment
No treatment is known to speed the healing of a pulmonary contusion; the main care is supportive. Attempts are made to discover injuries accompanying the contusion, to prevent additional injury, and to provide supportive care while waiting for the contusion to heal. Monitoring, including keeping track offluid balance
Fluid balance is an aspect of the homeostasis of organisms in which the amount of water in the organism needs to be controlled, via osmoregulation and behavior, such that the concentrations of electrolytes ( salts in solution) in the various b ...
, respiratory function, and oxygen saturation using pulse oximetry is also required as the patient's condition may progressively worsen.
Monitoring for complications such as pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severit ...
and acute respiratory distress syndrome is of critical importance.
Treatment aims to prevent respiratory failure
Respiratory failure results from inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system, meaning that the arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, or both cannot be kept at normal levels. A drop in the oxygen carried in the blood is known as hypoxemia; a rise ...
and to ensure adequate blood oxygenation. Supplemental oxygen can be given and it may be warmed and humidified. When the contusion does not respond to other treatments, extracorporeal membranous oxygenation may be used, pumping blood from the body into a machine that oxygenates it and removes carbon dioxide prior to pumping it back in.
Ventilation
 Positive pressure ventilation, in which air is forced into the lungs, is needed when oxygenation is significantly impaired.
Positive pressure ventilation, in which air is forced into the lungs, is needed when oxygenation is significantly impaired. Noninvasive
Minimally invasive procedures (also known as minimally invasive surgeries) encompass surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed, thereby reducing wound healing time, associated pain, and risk of infection. Surgery by definiti ...
positive pressure ventilation including continuous positive airway pressure
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is a form of positive airway pressure (PAP) ventilation in which a constant level of pressure greater than atmospheric pressure is continuously applied to the upper respiratory tract of a person. The ...
(CPAP) and bi-level positive airway pressure (BiPAP), may be used to improve oxygenation and treat atelectasis: air is blown into the airways at a prescribed pressure via a face mask. Noninvasive ventilation has advantages over invasive methods because it does not carry the risk of infection that intubation does, and it allows normal coughing, swallowing, and speech. However, the technique may cause complications; it may force air into the stomach or cause aspiration of stomach contents, especially when level of consciousness
An altered level of consciousness is any measure of arousal other than normal. Level of consciousness (LOC) is a measurement of a person's arousability and responsiveness to stimuli from the environment.
A mildly depressed level of consciou ...
is decreased.
People with signs of inadequate respiration or oxygenation may need to be intubated
Intubation (sometimes entubation) is a medical procedure involving the insertion of a tube into the body. Patients are generally anesthetized beforehand. Examples include tracheal intubation, and the balloon tamponade with a Sengstaken-Blak ...
and mechanically ventilated. Mechanical ventilation aims to reduce pulmonary edema and increase oxygenation. Ventilation can reopen collapsed alveoli, but it is harmful for them to be repeatedly opened, and positive pressure ventilation can also damage the lung by overinflating it.
Intubation is normally reserved for when respiratory problems occur, but most significant contusions do require intubation, and it may be done early in anticipation of this need. People with pulmonary contusion who are especially likely to need ventilation include those with prior severe lung disease
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side ...
or kidney problems; the elderly; those with a lowered level of consciousness; those with low blood oxygen or high carbon dioxide levels; and those who will undergo operations with anesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), ...
. Larger contusions have been correlated with a need for ventilation for longer periods of time.
Pulmonary contusion or its complications such as acute respiratory distress syndrome may cause lungs to lose compliance
Compliance can mean:
Healthcare
* Compliance (medicine), a patient's (or doctor's) adherence to a recommended course of treatment
* Compliance (physiology), the tendency of a hollow organ to resist recoil toward its original dimensions (this is a ...
(stiffen), so higher pressures may be needed to give normal amounts of air and oxygenate the blood adequately. Positive end-expiratory pressure
Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) is the pressure in the lungs (alveolar pressure) above atmospheric pressure (the pressure outside of the body) that exists at the end of expiration. The two types of PEEP are extrinsic PEEP (PEEP applied ...
(PEEP), which delivers air at a given pressure at the end of the expiratory cycle, can reduce edema and keep alveoli from collapsing.
PEEP is considered necessary with mechanical ventilation; however, if the pressure is too great it can expand the size of the contusion and injure the lung. When the compliance of the injured lung differs significantly from that of the uninjured one, the lungs can be ventilated independently with two ventilators in order to deliver air at different pressures; this helps avoid injury from overinflation while providing adequate ventilation.
Fluid therapy
The administration of fluid therapy in individuals with pulmonary contusion is controversial. Excessive fluid in the circulatory system ( hypervolemia) can worsen hypoxia because it can cause fluid leakage from injured capillaries (pulmonary edema), which are more permeable than normal. However, low blood volume (hypovolemia
Hypovolemia, also known as volume depletion or volume contraction, is a state of abnormally low extracellular fluid in the body. This may be due to either a loss of both salt and water or a decrease in blood volume. Hypovolemia refers to the los ...
) resulting from insufficient fluid has an even worse impact, potentially causing hypovolemic shock
Shock may refer to:
Common uses Collective noun
*Shock, a historic commercial term for a group of 60, see English numerals#Special names
* Stook, or shock of grain, stacked sheaves
Healthcare
* Shock (circulatory), circulatory medical emerge ...
; for people who have lost large amounts of blood, fluid resuscitation is necessary. A lot of the evidence supporting the idea that fluids should be withheld from people with pulmonary contusion came from animal studies, not clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, diet ...
s with humans; human studies have had conflicting findings on whether fluid resuscitation worsens the condition. Current recommendations suggest giving enough fluid to ensure sufficient blood flow but not giving any more fluid than necessary. For people who do require large amounts of intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrie ...
fluid, a catheter
In medicine, a catheter (/ˈkæθətər/) is a thin tubing (material), tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgi ...
may be placed in the pulmonary artery
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and ...
to measure the pressure within it. Measuring pulmonary artery pressure allows the clinician to give enough fluids to prevent shock without exacerbating edema.
Diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics i ...
s, drugs that increase urine output to reduce excessive fluid in the system, can be used when fluid overload does occur, as long as there is not a significant risk of shock. Furosemide
Furosemide is a loop diuretic medication used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It may also be used for the treatment of high blood pressure. It can be taken by injection into a vein or by mo ...
, a diuretic used in the treatment of pulmonary contusion, also relaxes the smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non- striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit ...
in the veins of the lungs, thereby decreasing pulmonary venous resistance and reducing the pressure in the pulmonary capillaries.
Supportive care
Retaining secretions in the airways can worsen hypoxia and lead to infections. Thus, an important part of treatment ispulmonary toilet Pulmonary hygiene, formerly referred to as pulmonary toilet,
is a set of methods used to clear mucus and secretions from the airways. The word ''pulmonary'' refers to the lungs. The word ''toilet'', related to the French ''toilette'', refers ...
, the use of suction, deep breathing, coughing, and other methods to remove material such as mucus and blood from the airways. Chest physical therapy makes use of techniques such as breathing exercises, stimulation of coughing, suctioning, percussion, movement, vibration, and drainage to rid the lungs of secretions, increase oxygenation, and expand collapsed parts of the lungs. People with pulmonary contusion, especially those who do not respond well to other treatments, may be positioned with the uninjured lung lower than the injured one to improve oxygenation. Inadequate pulmonary toilet can result in pneumonia. People who do develop infections are given antibiotics. No studies have yet shown a benefit of using antibiotics as a preventative measure before infection occurs, although some doctors do recommend prophylactic antibiotic use even without scientific evidence of its benefit. However, this can cause the development of antibiotic resistant
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistance. P ...
strains of bacteria, so giving antibiotics without a clear need is normally discouraged. For people who are at especially high risk of developing infections, the sputum
Sputum is mucus that is coughed up from the lower airways (the trachea and bronchi). In medicine, sputum samples are usually used for a naked eye examination, microbiological investigation of respiratory infections and cytological investigatio ...
can be culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
d to test for the presence of infection-causing bacteria; when they are present, antibiotics are used.
Pain control is another means to facilitate the elimination of secretions. A chest wall injury can make coughing painful, increasing the likelihood that secretions will accumulate in the airways. Chest injuries also contribute to hypoventilation
Hypoventilation (also known as respiratory depression) occurs when ventilation is inadequate (''hypo'' meaning "below") to perform needed respiratory gas exchange. By definition it causes an increased concentration of carbon dioxide (hypercapni ...
(inadequate breathing) because the chest wall movement involved in breathing adequately is painful. Insufficient expansion of the chest may lead to atelectasis
Atelectasis is the collapse or closure of a lung resulting in reduced or absent gas exchange. It is usually unilateral, affecting part or all of one lung. It is a condition where the alveoli are deflated down to little or no volume, as distinct ...
, further reducing oxygenation of the blood. Analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It ...
s (pain medications) can be given to reduce pain. Injection of anesthetics into nerves in the chest wall, called nerve block
Nerve block or regional nerve blockade is any deliberate interruption of signals traveling along a nerve, often for the purpose of pain relief. Local anesthetic nerve block (sometimes referred to as simply "nerve block") is a short-term block, ...
ade, is another approach to pain management; this does not depress respiration the way some pain medications can.
Prognosis
Fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which connective tissue replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of perma ...
of the lungs can occur, resulting in dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing di ...
(shortness of breath), low blood oxygenation, and reduced functional residual capacity for as long as six years after the injury. As late as four years post-injury, decreased functional residual capacity has been found in most pulmonary contusion patients studied. During the six months after pulmonary contusion, up to 90% of people have difficulty breathing. In some cases, dyspnea persists for an indefinite period. Contusion can also permanently reduce the compliance of the lungs.
Complications
 Pulmonary contusion can result in respiratory failure—about half of such cases occur within a few hours of the initial trauma. Other severe complications, including infections and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) occur in up to half of cases. Elderly people and those who have heart, lung, or kidney disease prior to the injury are more likely to stay longer in hospital and have complications from the injury. Complications occur in 55% of people with heart or lung disease and 13% of those without. Of people with pulmonary contusion alone, 17% develop ARDS, while 78% of people with at least two additional injuries develop the condition. A larger contusion is associated with an increased risk. In one study, 82% of people with 20% or more of the lung volume affected developed ARDS, while only 22% of people with less than 20% did so.
Pulmonary contusion can result in respiratory failure—about half of such cases occur within a few hours of the initial trauma. Other severe complications, including infections and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) occur in up to half of cases. Elderly people and those who have heart, lung, or kidney disease prior to the injury are more likely to stay longer in hospital and have complications from the injury. Complications occur in 55% of people with heart or lung disease and 13% of those without. Of people with pulmonary contusion alone, 17% develop ARDS, while 78% of people with at least two additional injuries develop the condition. A larger contusion is associated with an increased risk. In one study, 82% of people with 20% or more of the lung volume affected developed ARDS, while only 22% of people with less than 20% did so.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severit ...
, another potential complication, develops in as many as 20% of people with pulmonary contusion. Contused lungs are less able to remove bacteria than uninjured lungs, predisposing them to infection. Intubation and mechanical ventilation further increase the risk of developing pneumonia; the tube is passed through the nose or mouth into the airways, potentially tracking bacteria from the mouth or sinuses into them. Also, intubation prevents coughing, which would clear bacteria-laden secretions from the airways, and secretions pool near the tube's cuff and allow bacteria to grow. The sooner the endotracheal tube
A tracheal tube is a catheter that is inserted into the trachea for the primary purpose of establishing and maintaining a patent airway and to ensure the adequate exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Many different types of tracheal tubes ar ...
is removed, the lower the risk of pneumonia, but if it is removed too early and has to be put back in, the risk of pneumonia rises. People who are at risk for pulmonary aspiration
Pulmonary aspiration is the entry of material such as pharyngeal secretions, food or drink, or stomach contents from the oropharynx or gastrointestinal tract, into the larynx (voice box) and lower respiratory tract, the portions of the respi ...
(e.g. those with lowered level of consciousness due to head injuries) are especially likely to get pneumonia. As with ARDS, the chances of developing pneumonia increase with the size of the contusion. Children and adults have been found to have similar rates of complication with pneumonia and ARDS.
Associated injuries
thoracic
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the crea ...
trauma may be associated, including fracture of the sternum and bruising of the chest wall. Over half of fractures of the scapula are associated with pulmonary contusion. The contusion is frequently found underlying fracture sites. When accompanied by a fracture, it is usually concentrated into a specific location—the contusion is more diffuse when there is no fracture. Pulmonary laceration
A pulmonary laceration is a chest injury in which lung tissue is torn or cut.
An injury that is potentially more serious than pulmonary contusion, pulmonary laceration involves disruption of the architecture of the lung,
while pulmonary contusi ...
s may result from the same blunt or penetrating forces that cause contusion. Lacerations can result in pulmonary hematomas; these are reported to develop in 4–11% of pulmonary contusions.
Epidemiology
Pulmonary contusion is found in 30–75% of severe cases of chest injury, making it the most common serious injury to occur in association withthoracic
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the crea ...
trauma.
Of people who have multiple injuries with an injury severity score of over 15, pulmonary contusion occurs in about 17%. It is difficult to determine the death rate ( mortality) because pulmonary contusion rarely occurs by itself. Usually, deaths of people with pulmonary contusion result from other injuries, commonly traumatic brain injury. It is controversial whether pulmonary contusion with flail chest
Flail chest is a life-threatening medical condition that occurs when a segment of the rib cage breaks due to trauma and becomes detached from the rest of the chest wall. Two of the symptoms of flail chest are chest pain and shortness of breath. ...
is a major factor in mortality on its own or whether it merely contributes to mortality in people with multiple injuries. The estimated mortality rate of pulmonary contusion ranges from 14 to 40%, depending on the severity of the contusion itself and on associated injuries. When the contusions are small, they do not normally increase the chance of death or poor outcome for people with blunt chest trauma; however, these chances increase with the size of the contusion. One study found that 35% of people with multiple significant injuries including pulmonary contusion die. In another study, 11% of people with pulmonary contusion alone died, while the number rose to 22% in those with additional injuries. Pulmonary contusion is thought to be the direct cause of death in a quarter to a half of people with multiple injuries (polytrauma Polytrauma and multiple trauma are medical terms describing the condition of a person who has been subjected to multiple traumatic injuries, such as a serious head injury in addition to a serious burn. The term is defined via an Injury Severity Sc ...
) who die. An accompanying flail chest increases the morbidity
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
and mortality to more than twice that of pulmonary contusion alone.
Pulmonary contusion is the most common cause of death among vehicle occupants involved in accidents, and it is thought to contribute significantly in about a quarter of deaths resulting from vehicle collisions. As vehicle use has increased, so has the number of auto accidents, and with it the number of chest injuries. However an increase in the number of airbags installed in modern cars may be decreasing the incidence of pulmonary contusion. Use of child restraint systems has brought the approximate incidence of pulmonary contusion in children in vehicle accidents from 22% to 10%.
Differences in the bodies of children and adults lead to different manifestations of pulmonary contusion and associated injuries; for example, children have less body mass, so the same force is more likely to lead to trauma in multiple body systems. Since their chest walls are more flexible, children are more vulnerable to pulmonary contusion than adults are, and thus suffer from the injury more commonly.
Pulmonary contusion has been found in 53% of children with chest injuries requiring hospitalization. Children in forceful impacts suffer twice as many pulmonary contusions as adults with similar injury mechanisms, yet have proportionately fewer rib fractures. The rates of certain types of injury mechanisms differ between children and adults; for example, children are more often hit by cars as pedestrians. Some differences in children's physiology might be advantageous (for example they are less likely to have other medical conditions), and thus they have been predicted to have a better outcome.
However, despite these differences, children with pulmonary contusion have similar mortality rates to adults.
History
 In 1761, the Italian anatomist
In 1761, the Italian anatomist Giovanni Battista Morgagni
Giovanni Battista Morgagni (25 February 1682 – 6 December 1771) was an Italian anatomist, generally regarded as the father of modern anatomical pathology, who taught thousands of medical students from many countries during his 56 years as Prof ...
was first to describe a lung injury that was not accompanied by injury to the chest wall overlying it. Nonetheless, it was the French military surgeon Guillaume Dupuytren who is thought to have coined the term ''pulmonary contusion'' in the 19th century.
It still was not until the early 20th century that pulmonary contusion and its clinical significance began to receive wide recognition. With the use of explosives during World War I came many casualties with no external signs of chest injury but with significant bleeding in the lungs. Studies of World War I injuries by D.R. Hooker showed that pulmonary contusion was an important part of the concussive injury that results from explosions.
Pulmonary contusion received further attention during World War II, when the bombings of Britain caused blast injuries and associated respiratory problems in both soldiers and civilians. Also during this time, studies with animals placed at varying distances from a blast showed that protective gear could prevent lung injuries. These findings suggested that an impact to the outside of the chest wall was responsible for the internal lesions. In 1945, studies identified a phenomenon termed "wet lung", in which the lungs accumulated fluid and were simultaneously less able to remove it. They attributed the respiratory failure often seen in blunt chest trauma in part to excessive fluid resuscitation, and the question of whether and how much to administer fluids has remained controversial ever since.
During the Vietnam War, combat again provided the opportunity for study of pulmonary contusion; research during this conflict played an important role in the development of the modern understanding of its treatment. The condition also began to be more widely recognized in a non-combat context in the 1960s, and symptoms and typical findings with imaging techniques such as X-ray were described. Before the 1960s, it was believed that the respiratory insufficiency seen in flail chest was due to "paradoxical motion" of the flail segment of the chest wall (the flail segment moves in the opposite direction as the chest wall during respiration), so treatment was aimed at managing the chest wall injury, not the pulmonary contusion.
For example, positive pressure ventilation was used to stabilize the flail segment from within the chest. It was first proposed in 1965 that this respiratory insufficiency is most often due to injury of the lung rather than to the chest wall, and a group led by J.K. Trinkle confirmed this hypothesis in 1975.
Hence the modern treatment prioritizes the management of pulmonary contusion. Animal studies performed in the late 1960s and 1970s shed light on the pathophysiological processes involved in pulmonary contusion. Studies in the 1990s revealed a link between pulmonary contusion and persistent respiratory difficulty for years after the injury in people in whom the injury coexisted with flail chest. In the next decade studies demonstrated that function in contused lungs improves for years after the injury.
References
External links
Chest Trauma - pulmonary contusion
trauma.org {{DEFAULTSORT:Pulmonary Contusion Chest trauma Medical emergencies Lung disorders