prohibition of alcohol on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the
 Some kind of limitation on the trade in alcohol can be seen in the
Some kind of limitation on the trade in alcohol can be seen in the

 Prohibition in the United States focused on the manufacture, transportation, and sale of alcoholic beverages; exceptions were made for medicinal and religious uses. Alcohol consumption was never illegal under federal law. Nationwide Prohibition did not begin in the United States until January 1920, when the
Prohibition in the United States focused on the manufacture, transportation, and sale of alcoholic beverages; exceptions were made for medicinal and religious uses. Alcohol consumption was never illegal under federal law. Nationwide Prohibition did not begin in the United States until January 1920, when the 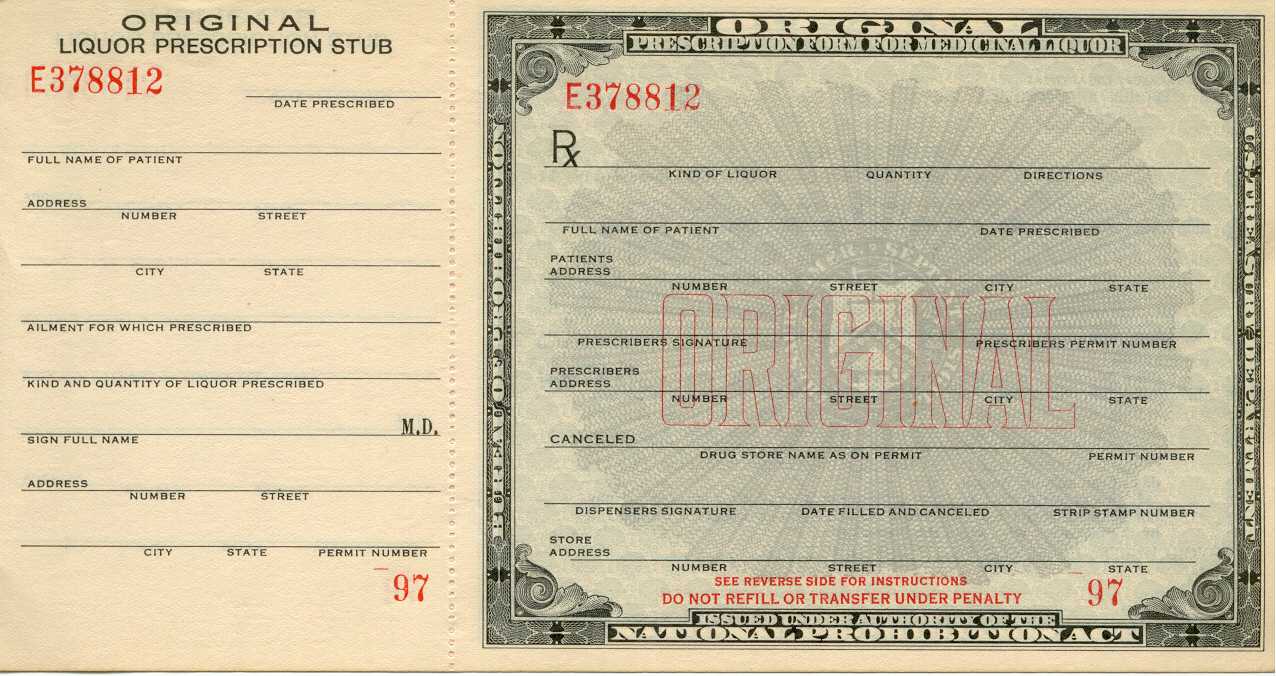 Initially, alcohol consumption nosedived to about 30% of its pre-Prohibition levels, but within a few years, the illicit market grew to roughly two-thirds. Illegal
Initially, alcohol consumption nosedived to about 30% of its pre-Prohibition levels, but within a few years, the illicit market grew to roughly two-thirds. Illegal
 The
The
Prohibition
– View Videos
online
* Cherrington, Ernest. ''America and the world liquor problem'' (1922
online
* Forsyth, Jessie, ''Collected Writings of Jessie Forsyth 1847–1937: The Good Templars and Temperance Reform on Three Continents'' ed by David M. Fahey (1988). * Gefou-Madianou, Dimitra, ed. ''Alcohol, gender, and culture'' (London: Routledge, 1992). * Heath, Dwight B. ed; ''International Handbook on Alcohol and Culture'' Greenwood Press, (1995). * Henius, Max. ''Modern liquor legislation and systems in Finland, Norway, Denmark and Sweden'' (1931). * Herlihy, Patricia. ''The Alcoholic Empire: Vodka & Politics in Late Imperial Russia'' (Oxford University Press, 2002). * Okrent, Daniel. ''Last Call; The Rise and Fall of Prohibition''. (New York: Scribner, 2010) in USA. * Schrad, Mark Lawrence. ''Smashing the Liquor Machine: A Global History of Prohibition'' (Oxford UP, 2021
excerpt
* Schrad, Mark Lawrence. ''The Political Power of Bad Ideas: Networks, Institutions, and the Global Prohibition Wave'' (2010) * Szymanski, Ann-Marie E. ''Pathways to Prohibition: Radicals, Moderates, and Social Movement Outcomes'' (Duke University Press, 2003) 325 pp. * Tyrrell, Ian. ''Woman's World/Woman's Empire: The Woman's Christian Temperance Union in International Perspective, 1880–1930'' (U of North Carolina Press, 1991). * White, Helene R. (ed.), ''Society, Culture and Drinking Patterns Reexamined'', (Rutgers Center of Alcohol Studies, 1991). * White, Stephen.''Russia Goes Dry: Alcohol, State and Society'' (1995). {{Authority control
 Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture
Manufacturing is the creation or Production (economics), production of goods with the help of equipment, Work (human activity), labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary secto ...
, storage (whether in barrel
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, ...
s or in bottle
A bottle is a narrow-necked container made of an impermeable material (such as glass, plastic or aluminium) in various shapes and sizes that stores and transports liquids. Its mouth, at the bottling line, can be sealed with an internal s ...
s), transport
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land ( rail and road), water, cable, pipelin ...
ation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic beverage
An alcoholic beverage (also called an alcoholic drink, adult beverage, or a drink) is a drink that contains ethanol, a type of Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol that acts Alcohol (drug), as a drug and is produced by Ethanol fermentation, fermentat ...
s. The word is also used to refer to a period of time during which such bans are enforced.
History
 Some kind of limitation on the trade in alcohol can be seen in the
Some kind of limitation on the trade in alcohol can be seen in the Code of Hammurabi
The Code of Hammurabi is a Babylonian legal text composed 1755–1750 BC. It is the longest, best-organised, and best-preserved legal text from the ancient Near East. It is written in the Old Babylonian dialect of Akkadian, purportedly by Hamm ...
(c. 1772 BCE) specifically banning the selling of beer for money. It could only be bartered for barley: "If a beer seller do not receive barley as the price for beer, but if she receive money or make the beer a measure smaller than the barley measure received, they shall throw her into the water."
In the early twentieth century, much of the impetus for the prohibition movement in the Nordic countries and North America came from moralistic convictions of pietistic Protestants. Prohibition movements in the West coincided with the advent of women's suffrage
Women's suffrage is the right of women to vote in elections. Beginning in the start of the 18th century, some people sought to change voting laws to allow women to vote. Liberal political parties would go on to grant women the right to vot ...
, with newly empowered women as part of the political process strongly supporting policies that curbed alcohol consumption.
The first half of the 20th century saw periods of prohibition of alcoholic beverages in several countries:
* 1918 to 1920: Prohibition in Canada nationally, as well as in most provinces including:
**1901 to 1948 in Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island (PEI; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, but the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
** 1919 to 1919 in Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
* 1907 to 1992 in the Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic island group and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark.
They are located north-northwest of Scotland, and about halfway bet ...
; limited private imports from Denmark were allowed from 1928
* 1914 to 1925: Prohibition in the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic be ...
* 1915 to 1935: Prohibition in Iceland Prohibition in Iceland went into effect in 1915 and lasted, to some extent, until 1 March 1989 (since celebrated as "Beer Day"). The ban had originally prohibited all alcohol, but from 1922 legalized wine and in 1935 legalized all alcoholic beverag ...
(wine legal from 1922, but beer still prohibited until 1989)
* 1916 to 1927 in Norway (fortified wine and beer were also prohibited from 1917 to 1923)
* 1919 in the Hungarian Soviet Republic
The Socialist Federative Republic of Councils in Hungary ( hu, Magyarországi Szocialista Szövetséges Tanácsköztársaság) (due to an early mistranslation, it became widely known as the Hungarian Soviet Republic in English-language sources ( ...
, March 21 to August 1; called ''szesztilalom''
* 1919 to 1932 in Finland (called ''kieltolaki'', "ban law")
* 1920 to 1933: Prohibition in the United States
In the United States from 1920 to 1933, a nationwide constitutional law prohibited the production, importation, transportation, and sale of alcoholic beverages. The alcohol industry was curtailed by a succession of state legislatures, an ...
After several years, prohibition failed in North America and elsewhere. Rum-running or bootlegging became widespread, and organized crime
Organized crime (or organised crime) is a category of transnational, national, or local groupings of highly centralized enterprises run by criminals to engage in illegal activity, most commonly for profit. While organized crime is generally th ...
took control of the distribution of alcohol. Distilleries and breweries in Canada, Mexico and the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean ...
flourished as their products were either consumed by visiting Americans or illegally exported to the United States. Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at t ...
and Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Count ...
became notorious as havens for prohibition dodgers during the time known as the Roaring Twenties
The Roaring Twenties, sometimes stylized as Roaring '20s, refers to the 1920s decade in music and fashion, as it happened in Western society and Western culture. It was a period of economic prosperity with a distinctive cultural edge in th ...
- 75% of all alcohol smuggled into the United States crossed the Detroit-Windsor
Windsor may refer to:
Places Australia
* Windsor, New South Wales
** Municipality of Windsor, a former local government area
* Windsor, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane, Queensland
**Shire of Windsor, a former local government authority around Wi ...
border. Prohibition generally came to an end in the late 1920s or early 1930s in most of North America and Europe, although a few locations continued prohibition for many more years.
In some countries where the dominant religion forbids the use of alcohol, the production, sale, and consumption of alcoholic beverages is prohibited or restricted today. For example, in Saudi Arabia and Libya alcohol is banned; in Pakistan and Iran it is illegal with exceptions.
Effects
Generally, prohibition is not completely effective, and tends to drive the market underground instead.Prohibition worldwide

Africa
Nigeria
In the British colony of Nigeria, missionary forces demanded prohibition of liquor, which proved highly unpopular. Both Africans and British found illegal supplies such as secret stills, obtaining colonial liquor permits, and smuggling. The experiment began in 1890 and was repealed in 1939.South Africa
During the coronavirus outbreak of 2020, alcohol sales, and even the transportation of alcohol outside of one's home, was made illegal. This order came into effect during the nationwide lockdown on 27 March 2020. The purpose of the ban was intended to prevent drunken fights, reduce domestic violence, stop drunk driving, and eliminate the weekend binge-drinking so prevalent across South Africa. Police, medics, and analysts estimate—conservatively—that alcohol is involved in, or responsible for, at least 40% of all emergency hospital admissions. By reducing the number of people within hospitals, and of course within social gatherings, the goal of prohibition was to reduce the rate of transmission, and thus slow the spread of the virus. A 2022 study found that the alcohol prohibition reduced injury-induced mortality by at least 14% (a conservative estimate) and sharply reduced violent crime.South Asia
Afghanistan
Sale of alcohol is banned in Afghanistan.Bangladesh
In Bangladesh, alcohol is somewhat prohibited due to its proscription in the Islamic faith. The purchase and consumption is still allowed in the country. The Garo tribe consume a type of rice beer, and Christians in this country drink and purchase wine for theirholy communion
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instituted ...
.
India
In India alcohol is a state subject and individual states can legislate prohibition, but currently most states do not have prohibition and sale/consumption is freely available in 25 out of 29 states. Prohibition is in force in the states ofGujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
, Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West ...
and Nagaland
Nagaland () is a landlocked state in the northeastern region of India. It is bordered by the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh to the north, Assam to the west, Manipur to the south and the Sagaing Region of Myanmar to the east. Its capital cit ...
, parts of Manipur
Manipur () ( mni, Kangleipak) is a state in Northeast India, with the city of Imphal as its capital. It is bounded by the Indian states of Nagaland to the north, Mizoram to the south and Assam to the west. It also borders two regions of ...
, and the union territory of Lakshadweep
Lakshadweep (), also known as Laccadives (), is a union territory of India. It is an archipelago of 36 islands in the Arabian sea, located off the Malabar Coast.
The name ''Lakshadweep'' means "one lakh islands" in Sanskrit, though the Lac ...
. All other States and union territories of India
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions.
History
Pre-indep ...
permit the sale of alcohol.
Election days and certain national holidays such as ''Independence Day
An independence day is an annual event commemorating the anniversary of a nation's independence or statehood, usually after ceasing to be a group or part of another nation or state, or more rarely after the end of a military occupation. Many ...
'' are meant to be ''dry days'' when liquor sale is not permitted but consumption is allowed. Some Indian states observe dry days on major religious festivals/occasions depending on the popularity of the festival in that region.
Maldives
TheMaldives
Maldives (, ; dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ, translit=Dhivehi Raajje, ), officially the Republic of Maldives ( dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ, translit=Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa, label=none, ), is an archipelag ...
ban the import of alcohol, x-raying all baggage on arrival. Alcoholic beverages are available only to foreign tourists on resort islands and may not be taken off the resort
A resort (North American English) is a self-contained commercial establishment that tries to provide most of a vacationer's wants, such as food, drink, swimming, lodging, sports, entertainment, and shopping, on the premises. The term ''resort ...
.
Pakistan
Pakistan allowed the free sale and consumption of alcohol for three decades from 1947, but restrictions were introduced byZulfikar Ali Bhutto
Zulfikar (or Zulfiqar) Ali Bhutto ( ur, , sd, ذوالفقار علي ڀٽو; 5 January 1928 – 4 April 1979), also known as Quaid-e-Awam ("the People's Leader"), was a Pakistani barrister, politician and statesman who served as the fourt ...
just weeks before he was removed as prime minister in 1977. Since then, only members of non-Muslim minorities such as Hindus
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
, Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ� ...
and Zoroastrians are allowed to apply for alcohol permits. The monthly quota is dependent upon one's income, but is actually about five bottles of liquor or 100 bottles of beer. In a country of 180 million, only about 60 outlets are allowed to sell alcohol. The Murree Brewery in Rawalpindi
Rawalpindi ( or ; Urdu, ) is a city in the Punjab province of Pakistan. It is the fourth largest city in Pakistan after Karachi, Lahore and Faisalabad, and third largest in Punjab after Lahore and Faisalabad. Rawalpindi is next to Pakistan ...
was once the only legal brewery, but today there are more. The ban officially is enforced by the country's Islamic Ideology Council, but it is not strictly policed. Members of religious minorities, however, often sell their liquor permits to Muslims as part of a continuing black market trade in alcohol.
Sri Lanka
In 1955 Sri Lanka passed a law prohibiting adult women from buying alcohol. In January 2018, Finance Minister Mangala Samaraweera announced that the law would be amended, allowing women to legally consume alcohol and work in venues that sell alcohol. The legalization was overruled by PresidentMaithripala Sirisena
Maithripala Yapa Sirisena ( si, පල්ලෙවත්ත ගමරාළලාගේ මෛත්රීපාල යාපා සිරිසේන; ta, பல்லேவத்த கமராளலாகே மைத்திரி� ...
several days later.
West Asia
Iran
Since the1979 Islamic Revolution
The Iranian Revolution ( fa, انقلاب ایران, Enqelâb-e Irân, ), also known as the Islamic Revolution ( fa, انقلاب اسلامی, Enqelâb-e Eslâmī), was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynas ...
, the sale and consumption of alcohol is banned in Iran. All people are banned from drinking alcohol but some people trade and sell it illegally.
Kuwait
The consumption, importation and brewing of, and trafficking in liquor is strictly against the law.Saudi Arabia
The sale, consumption, importation and brewing of, and trafficking in liquor is strictly against the law.Yemen
Alcohol is banned in Yemen.Southeast Asia
Brunei
InBrunei
Brunei ( , ), formally Brunei Darussalam ( ms, Negara Brunei Darussalam, Jawi: , ), is a country located on the north coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia. Apart from its South China Sea coast, it is completely surrounded by th ...
, alcohol consumption and sale is banned in public. Non-Muslims are allowed to purchase a limited amount of alcohol from their point of embarcation overseas for their own private consumption, and non-Muslims who are at least the age of 18 are allowed to bring in not more than two bottles of liquor (about two litre
The litre (international spelling) or liter (American English spelling) (SI symbols L and l, other symbol used: ℓ) is a metric unit of volume. It is equal to 1 cubic decimetre (dm3), 1000 cubic centimetres (cm3) or 0.001 cubic metre (m3 ...
s) and twelve cans of beer per person into the country.
Indonesia
Alcohol sales are banned in small shops and convenience stores.Malaysia
Alcohol is banned only for Muslims in Malaysia due to its Islamic faith and sharia law. Nevertheless, alcoholic products can easily be found in supermarkets, specialty shops, and convenience stores all over the country. Non-halal
''Halal'' (; ar, حلال, ) is an Arabic word that translates to "permissible" in English. In the Quran, the word ''halal'' is contrasted with '' haram'' (forbidden). This binary opposition was elaborated into a more complex classification k ...
restaurants also typically sell alcohol.
Philippines
There are only restrictions during elections in the Philippines. Alcohol is prohibited to be sold, furnished, offered, bought, or took two days prior to an election. Hotels and restaurants may secure a prior exemption but even then they are only allowed to serve alcohol to non-Filipino citizens. Private consumption of alcohol hoarded prior to the ban period is tolerated. The PhilippineCommission on Elections
An election commission is a body charged with overseeing the implementation of electioneering process of any country. The formal names of election commissions vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, and may be styled an electoral commission, a c ...
may opt to extend the liquor ban. In the 2013 elections, there was a proposal that it be extended to five days. This was overturned by the Supreme Court.
Other than election-related prohibition, alcohol is freely sold to anyone above the legal drinking age
The legal drinking age is the minimum age at which a person can legally consume alcoholic beverages. The minimum age alcohol can be legally consumed can be different from the age when it can be purchased in some countries. These laws vary between ...
.
Thailand
Alcohol sales are prohibited duringelections
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has opera ...
from 18:00 the day prior to voting, until the end of the day of voting itself. Alcohol is also prohibited on major Buddhist holy days, and sometimes on royal commemoration days, such as birthdays.
Thailand also enforces time-limited bans on alcohol on a daily basis. Alcohol can only be legally purchased in stores or restaurants between 11:00–14:00 and 17:00–midnight. The law is enforced by all major retailers (most notably 7-Eleven) and restaurants, but is frequently ignored by the smaller "mom and pop" stores. Hotels and resorts are exempt from the rules.
The consumption of alcohol is also banned at any time within 200 meters of a filling station (where sale of alcohol is also illegal), schools, temples or hospitals as well as on board any type of road vehicle regardless of whether it is being consumed by the driver or passenger.
At certain times of the year—Thai New Year (Songkran
Songkran is a term derived from the Sanskrit word, ' (or, more specifically, ') and used to refer to the traditional New Year celebrated in Bangladesh, Cambodia, Thailand, Laos, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, parts of northeast India, parts of Vietnam and ...
) is an example—the government may also enforce arbitrary bans on the sale and consumption of alcohol in specific public areas where large scale festivities are due to take place and large crowds are expected.
Thailand strictly regulates alcohol advertising, as specified in the Alcoholic Beverage Control Act, B.E. 2551 (2008) (ABCA). Sales of alcohol via "electronic channels" (internet) are prohibited.
Europe
Czech Republic
On 14 September 2012, the Government of theCzech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
banned all sales of alcoholic drinks with more than 20% alcohol. From this date, it was illegal to sell such alcoholic beverages in shops, supermarkets, bars, restaurants, filling stations, e-shop
Online shopping is a form of electronic commerce which allows consumers to directly buy goods or services from a seller over the Internet using a web browser or a mobile app. Consumers find a product of interest by visiting the website of the r ...
s etc. This measure was taken in response to the wave of methanol poisoning cases resulting in the deaths of 18 people in the Czech Republic. Since the beginning of the " methanol affair" the total number of deaths has increased to 25. The ban was to be valid until further notice, though restrictions were eased towards the end of September. The last bans on Czech alcohol with regard to the poisoning cases were lifted on 10 October 2012, when neighbouring Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the ...
and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
allowed its import once again.
Nordic countries
TheNordic countries
The Nordic countries (also known as the Nordics or ''Norden''; lit. 'the North') are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe and the North Atlantic. It includes the sovereign states of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sw ...
, with the exception of Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
, have had a strong temperance movement
The temperance movement is a social movement promoting temperance or complete abstinence from consumption of alcoholic beverages. Participants in the movement typically criticize alcohol intoxication or promote teetotalism, and its leaders emph ...
since the late-1800s, closely linked to the Christian revival
Christian revivalism is increased spiritual interest or renewal in the life of a church congregation or society, with a local, national or global effect. This should be distinguished from the use of the term "revival" to refer to an evangelis ...
movement of the late-nineteenth century, but also to several worker organisations. As an example, in 1910 the temperance organisations in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
had some 330,000 members, which was about 6% of a population of 5.5 million. This heavily influenced the decisions of Nordic politicians in the early 20th century.
In 1907, the Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic island group and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark.
They are located north-northwest of Scotland, and about halfway bet ...
passed a law prohibiting all sale of alcohol, which was in force until 1992. Very restricted private importation from Denmark was allowed from 1928 onwards.
In 1914, Sweden put in place a rationing system, the Bratt System
The Bratt System was a system that was used in Sweden (1919–1955) and similarly in Finland (1944–1970) to control alcohol consumption, by rationing of liquor. Every citizen allowed to consume alcohol was given a booklet called a m ...
, in force until 1955. A referendum in 1922 rejected an attempt to enforce total prohibition.
In 1915, Iceland instituted total prohibition. The ban for wine was lifted in 1922 and spirits in 1935, but beer remained prohibited until 1989 (circumvented by mixing light beer and spirits).
In 1916, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
prohibited distilled beverage
Liquor (or a spirit) is an alcoholic drink produced by distillation of grains, fruits, vegetables, or sugar, that have already gone through alcoholic fermentation. Other terms for liquor include: spirit drink, distilled beverage or hard l ...
s, and in 1917 the prohibition was extended to also include fortified wine
Fortified wine is a wine to which a distilled spirit, usually brandy, has been added. In the course of some centuries, winemakers have developed many different styles of fortified wine, including port, sherry, madeira, Marsala, Comma ...
and beer. The wine and beer ban was lifted in 1923, and in 1927 the ban of distilled beverages was also lifted.
In 1919, Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bot ...
enacted prohibition, as one of the first acts after independence from the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
. Four previous attempts to institute prohibition in the early twentieth century had failed due to opposition from the tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the ter ...
. After a development similar to the one in the United States during its prohibition, with large-scale smuggling
Smuggling is the illegal transportation of objects, substances, information or people, such as out of a house or buildings, into a prison, or across an international border, in violation of applicable laws or other regulations.
There are variou ...
and increasing violence and crime rates, public opinion turned against the prohibition, and after a national referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a Representative democr ...
where 70% voted for a repeal of the law, prohibition was abolished in early 1932.
Today, all Nordic countries except Denmark continue to have strict controls on the sale of alcohol, which is highly taxed (dutied) to the public. There are government monopolies in place for selling spirits, wine, and stronger beers in Norway (Vinmonopolet
Vinmonopolet ( en, The Wine Monopoly), symbolized by Ⓥ and colloquially shortened to Polet, is a government-owned alcoholic beverage retailer and the only company allowed to sell beverages containing an alcohol content higher than 4.75% in Nor ...
), Finland (Alko
Alko Inc is the national alcoholic beverage retailing monopoly in Finland. It is the only store in the country which retails beer over 5.5% ABV, wine (except in vineyards) and spirits. Alcoholic beverages are also sold in licensed restaurant ...
), Sweden ( Systembolaget), Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
( Vínbúðin), and the Faroe Islands (Rúsdrekkasøla Landsins
Rúsdrekkasøla Landsins, or simply Rúsan, is the national alcoholic beverage retailing monopoly of the Faroe Islands, following the model of neighbouring Nordic alcohol monopolies Vinmonopolet, Systembolaget, Vínbúð and Alko. The company w ...
). Bars and restaurants may, however, import alcoholic beverages directly or through other companies.
Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland ...
, which is part of the Kingdom of Denmark
The Danish Realm ( da, Danmarks Rige; fo, Danmarkar Ríki; kl, Danmarkip Naalagaaffik), officially the Kingdom of Denmark (; ; ), is a sovereign state located in Northern Europe and Northern North America. It consists of metropolitan Denma ...
, does not share its easier controls on the sale of alcohol. Greenland has (like Denmark) sales in food shops, but prices are typically high. Private import when travelling from Denmark is only allowed in small quantities.
Russian Empire and the Soviet Union
In theRussian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
, a limited version of a Dry Law was introduced in 1914. It continued through the turmoil of the Russian Revolution of 1917
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
and the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
into the period of Soviet Russia
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
until 1925.
United Kingdom
Although the sale or consumption of commercial alcohol has never been prohibited by law in the United Kingdom, various groups in the UK have campaigned for the prohibition of alcohol; including theSociety of Friends
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belie ...
(Quakers), The Methodist Church and other non-conformists, as well as temperance movements such as Band of Hope
Hope UK is a United Kingdom Christian charity based in London, England which educates children and young people about drug and alcohol abuse. Local meetings started in 1847 and a formal organisation was established in 1855 with the name The Unite ...
and temperance Chartist movements of the nineteenth century.
Formed in 1853 and inspired by the Maine law
The Maine Law (or "Maine Liquor Law"), passed on June 2, 1851 in Maine, was the first statutory implementation of the developing temperance movement in the United States.
History
Temperance activist Neal Dow helped craft the Maine liquor law w ...
in the United States, the United Kingdom Alliance
The United Kingdom Alliance (UKA) was a temperance movement in the United Kingdom founded in 1853 in Manchester to work for the prohibition of the trade in alcohol in the United Kingdom. This occurred in a context of support for the type of law ...
aimed at promoting a similar law prohibiting the sale of alcohol in the UK. This hard-line group of prohibitionists was opposed by other temperance organisations who preferred moral persuasion to a legal ban. This division in the ranks limited the effectiveness of the temperance movement as a whole. The impotence of legislation in this field was demonstrated when the Sale of Beer Act 1854, which restricted Sunday opening hours, had to be repealed, following widespread rioting. In 1859, a prototype prohibition bill was overwhelmingly defeated in the House of Commons.
On 22 March 1917, during the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
at a crowded meeting in the Queen's Hall
The Queen's Hall was a concert hall in Langham Place, London, Langham Place, London, opened in 1893. Designed by the architect Thomas Knightley, it had room for an audience of about 2,500 people. It became London's principal concert venue. Fro ...
in London (chaired by Alfred Booth
Alfred Booth (24 February 1893 – 19 December 1965) was a British Congregational lay preacher and politician.
Booth served with the Lancashire Fusiliers during World War I. In 1933, he was elected to Bolton Borough Council, and he was Mayo ...
) many influential people including Agnes Weston
Dame Agnes Elizabeth Weston, GBE (26 March 1840 – 23 October 1918), also known as Aggie Weston, was an English philanthropist noted for her work with the Royal Navy. For over twenty years, she lived and worked among the sailors of the Royal Na ...
spoke, or letters from them were read out, against alcohol consumption, calling for prohibition; General Sir Reginald Hart wrote to the meeting that "Every experienced officer knew that practically all unhappiness and crime in the Army is due to drink". At the meeting, Lord Channing
Francis Allston Channing, 1st Baron Channing (21 March 1841 – 20 February 1926), known as Sir Francis Channing, Bt, between 1906 and 1912, was an American-born British barrister, academic, and Liberal Party politician.
Background and educati ...
said that it was a pity that the whole Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filin ...
did not follow the example of King George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936.
Born during the reign of his grandmother Qu ...
and Lord Kitchener when in 1914 those two spoke calling for complete prohibition for the duration of the war.
Edwin Scrymgeour
Edwin Scrymgeour (28 July 1866 – 1 February 1947) was a British politician who served as a Member of Parliament (MP) for Dundee in Scotland. He is the only person ever elected to the House of Commons on a prohibitionist ticket, as the ca ...
served as Member of Parliament for Dundee between 15 November 1922 and 8 October 1931. He remains the only person to have ever been elected to the House of Commons on a prohibitionist ticket. In 1922, he defeated incumbent Liberal member Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
; winning the seat for the
Scottish Prohibition Party, which he had founded in 1901, and for which he had stood for election successfully as a Dundee Burgh Councillor in 1905 and unsuccessfully as a parliamentary candidate between 1908 and 1922.
North America
Canada
Indigenous peoples in Canada
In Canada, Indigenous groups comprise the First Nations, Inuit and Métis. Although ''Indian'' is a term still commonly used in legal documents, the descriptors ''Indian'' and '' Eskimo'' have fallen into disuse in Canada, and most consider th ...
were subject to prohibitory alcohol laws under the ''Indian Act
The ''Indian Act'' (, long name ''An Act to amend and consolidate the laws respecting Indians'') is a Canadian act of Parliament that concerns registered Indians, their bands, and the system of Indian reserves. First passed in 1876 and still ...
'' of 1876. Sections of the ''Indian Act'' regarding liquor were not repealed for over a hundred years, until 1985.
An official, but non-binding, federal referendum on prohibition was held in 1898. Prime Minister Wilfrid Laurier's government chose not to introduce a federal bill on prohibition, mindful of the strong antipathy in Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirte ...
. As a result, Canadian prohibition was instead enacted through laws passed by the provinces during the first twenty years of the 20th century, especially during the 1910s. Canada did, however, enact a national prohibition from 1918 to 1920 as a temporary wartime measure. Much of the rum-running during prohibition took place in Windsor, Ontario. The provinces later repealed their prohibition laws, mostly during the 1920s, although some local municipalities remain dry.
Mexico
Some communities in theChiapas
Chiapas (; Tzotzil and Tzeltal: ''Chyapas'' ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Chiapas), is one of the states that make up the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 124 municipalities ...
state of southern Mexico are under the control of the libertarian socialist
Libertarian socialism, also known by various other names, is a left-wing,Diemer, Ulli (1997)"What Is Libertarian Socialism?" The Anarchist Library. Retrieved 4 August 2019. anti-authoritarian, anti-statist and libertarianLong, Roderick T. (20 ...
Zapatista Army of National Liberation
The Zapatista Army of National Liberation (, EZLN), often referred to as the Zapatistas (Mexican ), is a far-left political and militant group that controls a substantial amount of territory in Chiapas, the southernmost state of Mexico.
Since ...
, and often ban alcohol as part of what was described as "a collective decision". This prohibition has been used by many villages as a way to decrease domestic violence and has generally been favored by women. This prohibition, however, is not recognized by federal Mexican law as the Zapatista movement is strongly opposed by the federal government.
The sale and purchase of alcohol is prohibited on and the night before certain national holidays, such as '' Natalicio de Benito Juárez'' (birthdate of Benito Juárez
Benito Pablo Juárez García (; 21 March 1806 – 18 July 1872) was a Mexican liberal politician and lawyer who served as the 26th president of Mexico from 1858 until his death in office in 1872. As a Zapotec, he was the first indigenous pre ...
) and '' Día de la Revolución'', which are meant to be dry nationally. The same "dry law" applies to the days before presidential elections every six years.
United States
 Prohibition in the United States focused on the manufacture, transportation, and sale of alcoholic beverages; exceptions were made for medicinal and religious uses. Alcohol consumption was never illegal under federal law. Nationwide Prohibition did not begin in the United States until January 1920, when the
Prohibition in the United States focused on the manufacture, transportation, and sale of alcoholic beverages; exceptions were made for medicinal and religious uses. Alcohol consumption was never illegal under federal law. Nationwide Prohibition did not begin in the United States until January 1920, when the Eighteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution
The Eighteenth Amendment (Amendment XVIII) of the United States Constitution established the prohibition of alcohol in the United States. The amendment was proposed by Congress on December 18, 1917, and was ratified by the requisite number of ...
went into effect. The 18th amendment was ratified in 1919, and was repealed in December 1933 with the ratification of the Twenty-first Amendment.
Concern over excessive alcohol consumption began during the American colonial era, when fines were imposed for drunken behavior and for selling liquor without a license. In the mid-19th century evangelical Protestants denounced drinking as sinful and demanded the prohibition of the sale of beer, wine and liquor. Apart from Maine, they had limited success until the early 20th century. By the 1840s the temperance movement
The temperance movement is a social movement promoting temperance or complete abstinence from consumption of alcoholic beverages. Participants in the movement typically criticize alcohol intoxication or promote teetotalism, and its leaders emph ...
was actively encouraging individuals to immediately stop drinking. However, the issue of slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
, and then the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polici ...
, overshadowed the temperance movement until the 1870s.
Prohibition was a major reform movement from the 1870s until the 1920s, when nationwide prohibition went into effect. It was supported by evangelical Protestant churches, especially the Methodists, Baptists
Baptists form a major branch of Protestantism distinguished by baptizing professing Christian believers only (believer's baptism), and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul com ...
, Presbyterians
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their n ...
, Disciples of Christ
The Christian Church (Disciples of Christ) is a mainline Protestant Christian denomination in the United States and Canada. The denomination started with the Restoration Movement during the Second Great Awakening, first existing during the 19th ...
, Congregationalists
Congregational churches (also Congregationalist churches or Congregationalism) are Protestant churches in the Calvinist tradition practising congregationalist church governance, in which each congregation independently and autonomously runs i ...
, Quakers, and Scandinavian Lutherans. Opposition came from Catholics, Episcopalians, and German Lutherans. The Women's Crusade
The Woman's Crusade was a temperance campaign in the United States in 1873-1874. It was a series of non-violent protests fighting against the dangers of alcoholism.
Background
Many women in Cleveland, Ohio were inspired by a speech given by Dio ...
of 1873 and the Woman's Christian Temperance Union
The Woman's Christian Temperance Union (WCTU) is an international temperance organization, originating among women in the United States Prohibition movement. It was among the first organizations of women devoted to social reform with a program th ...
(WCTU), founded in 1874, were means through which certain women organized and demanded political action, well before they were granted the vote. The WCTU and the Prohibition Party
The Prohibition Party (PRO) is a political party in the United States known for its historic opposition to the sale or consumption of alcoholic beverages and as an integral part of the temperance movement. It is the oldest existing third party ...
were major players until the 20th century, when the Anti-Saloon League
The Anti-Saloon League (now known as the ''American Council on Addiction and Alcohol Problems'') is an organization of the temperance movement that lobbied for prohibition in the United States in the early 20th century.
Founded in 1893 in Ober ...
emerged as the movement's leader. By 1913, 9 states had statewide prohibition and 31 others had local option laws in effect. The League then turned their efforts toward attaining a constitutional amendment and grassroots support for nationwide prohibition. The German American
German Americans (german: Deutschamerikaner, ) are Americans who have full or partial German ancestry. With an estimated size of approximately 43 million in 2019, German Americans are the largest of the self-reported ancestry groups by the Unite ...
community was the base of the beer industry and became a pariah when the U.S. declared war on Germany in 1917. A new constitutional amendment passed Congress in December 1917 and was ratified by the states in 1919. It prohibited "the manufacture, sale, or transportation of intoxicating liquors within, the importation thereof into, or the exportation thereof." On October 28, 1919, Congress passed the National Prohibition Act, known as the Volstead Act
The National Prohibition Act, known informally as the Volstead Act, was an act of the 66th United States Congress, designed to carry out the intent of the 18th Amendment (ratified January 1919), which established the prohibition of alcoholic d ...
, to implement the new 18th Amendment. After a year's required delay, national prohibition began on January 16, 1920.
 Initially, alcohol consumption nosedived to about 30% of its pre-Prohibition levels, but within a few years, the illicit market grew to roughly two-thirds. Illegal
Initially, alcohol consumption nosedived to about 30% of its pre-Prohibition levels, but within a few years, the illicit market grew to roughly two-thirds. Illegal still
A still is an apparatus used to distill liquid mixtures by heating to selectively boil and then cooling to condense the vapor. A still uses the same concepts as a basic distillation apparatus, but on a much larger scale. Stills have been use ...
s flourished in remote rural areas as well as city slums, and large quantities were smuggled from Canada. Bootlegging became a major business activity for organized crime groups, under leaders such as Al Capone
Alphonse Gabriel Capone (; January 17, 1899 – January 25, 1947), sometimes known by the nickname "Scarface", was an American gangster and businessman who attained notoriety during the Prohibition era as the co-founder and boss of the ...
in Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Count ...
and Lucky Luciano
Charles "Lucky" Luciano (, ; born Salvatore Lucania ; November 24, 1897 – January 26, 1962) was an Italian-born gangster who operated mainly in the United States. Luciano started his criminal career in the Five Points gang and was instrumen ...
in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
.
Prohibition lost support during the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
, from 1929. The repeal movement was initiated and financed by the Association Against the Prohibition Amendment
The Association Against the Prohibition Amendment was established in 1918 and became a leading organization working for the repeal of prohibition in the United States. It was the first group created to fight Prohibition, also known as the 18th ...
, and Pauline Sabin, a wealthy Republican, founded the Women's Organization for National Prohibition Reform (WONPR). Repeal of Prohibition in the United States
The repeal of Prohibition in the United States was accomplished with the passage of the Twenty-first Amendment to the United States Constitution on December 5, 1933.
Background
In 1919, the requisite number of state legislatures ratified the Eig ...
was accomplished with the ratification of the Twenty-first Amendment on December 5, 1933. Under its terms, states were allowed to set their own laws for the control of alcohol.
Between 1832 and 1953, federal legislation prohibited the sale of alcohol to Native Americans, with very limited success. After 1953, Native American communities and reservations were permitted to pass their own local ordinance
A local ordinance is a law issued by a local government. such as a municipality, county, parish, prefecture, or the like.
China
In Hong Kong, all laws enacted by the territory's Legislative Council remain to be known as ''Ordinances'' () a ...
s governing the sale of alcoholic beverages.
In the 21st century, there are still counties and parishes within the United States known as " dry," where the sale of alcohol is prohibited or restricted.
South America
Venezuela
In Venezuela, twenty-four hours before every election, the government prohibits the sale and distribution of alcoholic beverages throughout the national territory, including the restriction to all dealers, liquor stores, supermarkets, restaurants, wineries, pubs, bars, public entertainment, clubs and any establishment that markets alcoholic beverages. The same is done duringHoly Week
Holy Week ( la, Hebdomada Sancta or , ; grc, Ἁγία καὶ Μεγάλη Ἑβδομάς, translit=Hagia kai Megale Hebdomas, lit=Holy and Great Week) is the most sacred week in the liturgical year in Christianity. In Eastern Churches, w ...
as a measure to reduce the alarming rate of road traffic accidents during these holidays.
Oceania
Australia
 The
The Australian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (commonly abbreviated as ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) until 1938, is a landlocked federal territory of Australia containing the national capital Canberra and some surrounding township#Aust ...
(then the Federal Capital Territory) was the first jurisdiction in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
to have prohibition laws. In 1911, King O'Malley
King O'Malley (2 July 1858? – 20 December 1953) was an American-born Australian politician who served in the House of Representatives from 1901 to 1917, and served two terms as Minister for Home Affairs (1910–1913; 1915–16). He is remember ...
, then Minister of Home Affairs, shepherded laws through Parliament preventing new issue or transfer of licences to sell alcohol, to address unruly behaviour among workers building the new capital city. Prohibition was partial, since possession of alcohol purchased outside of the Territory remained legal and the few pubs that had existing licences could continue to operate. The Federal Parliament repealed the laws after residents of the Federal Capital Territory voted for the end of them in a 1928 plebiscite.
Since then, some state governments and local councils have enacted dry areas. This is where the purchase or consumption of alcohol is only permitted in licensed areas such as liquor stores, clubs, cafes, bars, hotels, restaurants, and also private homes. In public places such as streets, parks, and squares, consumption is not permitted, but carrying bottles that were purchased at licensed venues is allowed. Almost all dry areas are small defined districts within larger urban or rural communities.
More recently, alcohol has been prohibited in many remote Indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
communities. Penalties for transporting alcohol into these "dry" communities are severe and can result in confiscation of any vehicles involved; in dry areas within the Northern Territory
The Northern Territory (commonly abbreviated as NT; formally the Northern Territory of Australia) is an Australian territory in the central and central northern regions of Australia. The Northern Territory shares its borders with Western Aust ...
, all vehicles used to transport alcohol are seized.
New Zealand
In New Zealand, prohibition was a moralistic reform movement begun in the mid-1880s by the Protestant evangelical and Nonconformist churches and theWoman's Christian Temperance Union
The Woman's Christian Temperance Union (WCTU) is an international temperance organization, originating among women in the United States Prohibition movement. It was among the first organizations of women devoted to social reform with a program th ...
and after 1890 by the Prohibition League. It assumed that individual virtue was all that was needed to carry the colony forward from a pioneering society to a more mature one, but it never achieved its goal of national prohibition. Both the Church of England and the largely Irish Catholic Church rejected prohibition as an intrusion of government into the church's domain, while the growing labor movement saw capitalism rather than alcohol as the enemy.Greg Ryan, "Drink and the Historians: Sober Reflections on Alcohol in New Zealand 1840–1914," ''New Zealand Journal of History'' (April 2010) Vol. 44, No. 1Richard Newman, "New Zealand's Vote for Prohibition in 1911", ''New Zealand Journal of History'', April 1975, Vol. 9, Issue 1, pp. 52–71
Reformers hoped that the women's vote, in which New Zealand was a pioneer, would swing the balance, but the women were not as well organized as in other countries. Prohibition had a majority in a national referendum in 1911, but needed a 60% vote to pass. The movement kept trying in the 1920s, losing three more referendums by close votes; it managed to keep in place a 6 pm closing hour for pubs and Sunday closing. The Depression and war years effectively ended the movement, but their 6 p.m. closing hour remained until October 1967 when it was extended to 10 pm.
For many years, referendums were held for individual towns or electorates, often coincident with general elections. The ballots determined whether these individual areas would be "dry" – that is, alcohol could not be purchased or consumed in public in these areas. One notable example was the southern city of Invercargill
Invercargill ( , mi, Waihōpai is the southernmost and westernmost city in New Zealand, and one of the southernmost cities in the world. It is the commercial centre of the Southland region. The city lies in the heart of the wide expanse ...
, which was dry from 1907 to 1943. People wanting alcohol usually travelled to places outside the city (such as the nearby township of Lorneville or the town of Winton) to drink in the local pubs or purchase alcohol to take back home. The last bastion of this 'dry' area remains in force in the form of a licensing trust that still to this day governs the sale of liquor in Invercargill. The city does not allow the sale of alcohol (beer and wine included) in supermarkets unlike the remainder of New Zealand, and all form of alcohol regardless of the sort can only be sold in bars and liquor stores.
Prohibition was of limited success in New Zealand as—like in other countries—it led to organised bootlegging. The most famous bootlegged alcohol in New Zealand was that produced in the Hokonui Hills
The Hokonui Hills, also known as ''The Hokonui Mountains'' or simply ''The Hokonui'', are a range of hills in central Southland, New Zealand. They rise to 600 metres above the surrounding Southland Plains, of which the hills mark a northern extre ...
close to the town of Gore
Gore may refer to:
Places Australia
* Gore, Queensland
* Gore Creek (New South Wales)
* Gore Island (Queensland)
Canada
* Gore, Nova Scotia, a rural community
* Gore, Quebec, a township municipality
* Gore Bay, Ontario, a township on Manito ...
(not coincidentally, the nearest large town to Invercargill). Even today, the term "Hokonui" conjures up images of illicit whisky to many New Zealanders.
Elections
In many countries in Latin America, the Philippines, Thailand, Turkey, India, and several US states, the sale but not the consumption of alcohol is prohibited before and duringelection
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative democracy has operat ...
s.– View Videos
See also
*Bootleggers and Baptists
Bootleggers and Baptists is a concept put forth by regulatory economist Bruce Yandle,Pdf.
:''See also'':
...
* :''See also'':
...
Iron law of prohibition
The iron law of prohibition is a term coined by Richard Cowan in 1986 which posits that as law enforcement becomes more intense, the potency of prohibited substances increases. Cowan put it this way: "the harder the enforcement, the harder the d ...
* Legal drinking age
The legal drinking age is the minimum age at which a person can legally consume alcoholic beverages. The minimum age alcohol can be legally consumed can be different from the age when it can be purchased in some countries. These laws vary between ...
* List of countries with alcohol prohibition
The following countries have or had comprehensive prohibitions against alcohol. Particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoh ...
* Prohibition of drugs
The prohibition of drugs through sumptuary legislation or religious law is a common means of attempting to prevent the recreational use of certain intoxicating substances.
While some drugs are illegal to possess, many governments regulate t ...
* Prohibition Party
The Prohibition Party (PRO) is a political party in the United States known for its historic opposition to the sale or consumption of alcoholic beverages and as an integral part of the temperance movement. It is the oldest existing third party ...
* Scottish Prohibition Party
Notes
Further reading
* Barrows, Susanna, Robin Room, and Jeffrey Verhey (eds.), ''The Social History of Alcohol: Drinking and Culture in Modern Society'' (Berkeley, Calif: Alcohol Research Group, 1987). * Barrows, Susanna, and Robin Room (eds.), ''Drinking: Behavior and Belief in Modern History'' University of California Press, (1991). * Blocker, Jack S., David M. Fahey, and Ian R. Tyrrell eds. ''Alcohol and Temperance in Modern History: An International Encyclopedia'' 2 Vol. (2003). * * Cherrington, Ernest ed., ''Standard Encyclopaedia of the Alcohol Problem'' 6 volumes (1925–1930), comprehensive international coverage to late 1920sonline
* Cherrington, Ernest. ''America and the world liquor problem'' (1922
online
* Forsyth, Jessie, ''Collected Writings of Jessie Forsyth 1847–1937: The Good Templars and Temperance Reform on Three Continents'' ed by David M. Fahey (1988). * Gefou-Madianou, Dimitra, ed. ''Alcohol, gender, and culture'' (London: Routledge, 1992). * Heath, Dwight B. ed; ''International Handbook on Alcohol and Culture'' Greenwood Press, (1995). * Henius, Max. ''Modern liquor legislation and systems in Finland, Norway, Denmark and Sweden'' (1931). * Herlihy, Patricia. ''The Alcoholic Empire: Vodka & Politics in Late Imperial Russia'' (Oxford University Press, 2002). * Okrent, Daniel. ''Last Call; The Rise and Fall of Prohibition''. (New York: Scribner, 2010) in USA. * Schrad, Mark Lawrence. ''Smashing the Liquor Machine: A Global History of Prohibition'' (Oxford UP, 2021
excerpt
* Schrad, Mark Lawrence. ''The Political Power of Bad Ideas: Networks, Institutions, and the Global Prohibition Wave'' (2010) * Szymanski, Ann-Marie E. ''Pathways to Prohibition: Radicals, Moderates, and Social Movement Outcomes'' (Duke University Press, 2003) 325 pp. * Tyrrell, Ian. ''Woman's World/Woman's Empire: The Woman's Christian Temperance Union in International Perspective, 1880–1930'' (U of North Carolina Press, 1991). * White, Helene R. (ed.), ''Society, Culture and Drinking Patterns Reexamined'', (Rutgers Center of Alcohol Studies, 1991). * White, Stephen.''Russia Goes Dry: Alcohol, State and Society'' (1995). {{Authority control