polynomial expansion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
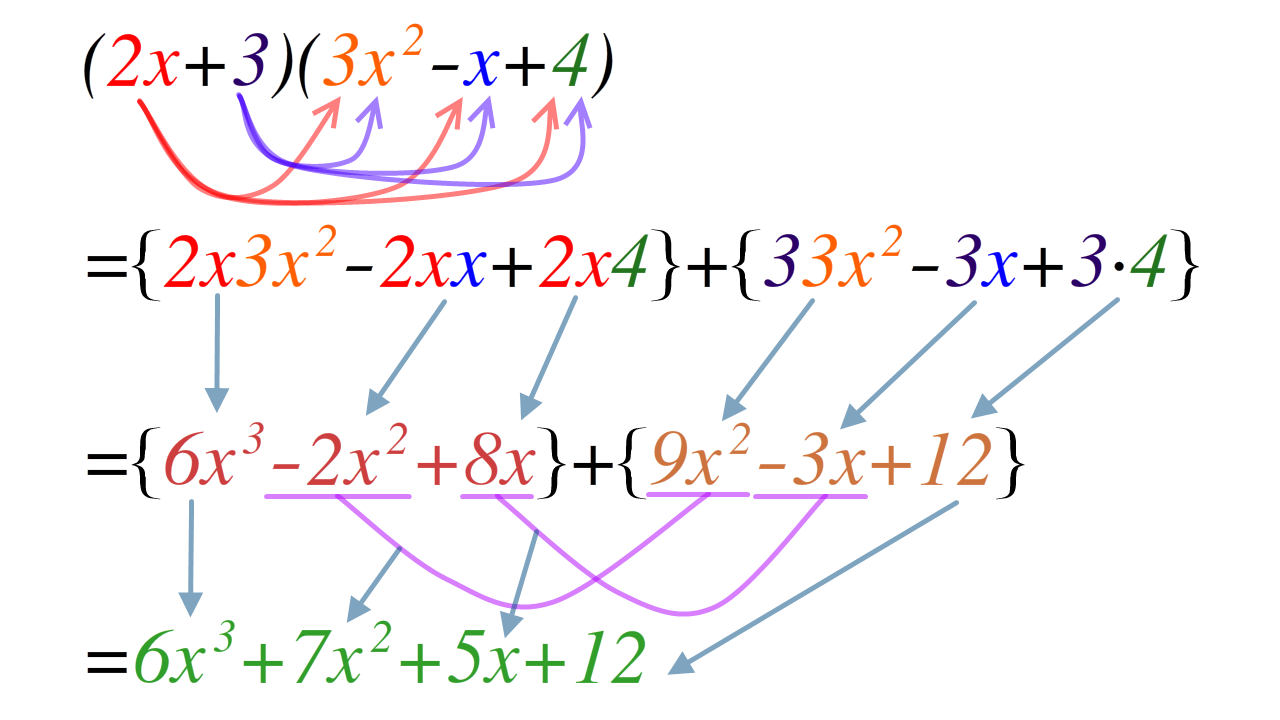 To multiply two factors, each term of the first factor must be multiplied by each term of the other factor. If both factors are
To multiply two factors, each term of the first factor must be multiplied by each term of the other factor. If both factors are
Review of Algebra: Expansion
Expand page
quickmath.com
Online Calculator with Symbolic Calculations
livephysics.com {{DEFAULTSORT:Polynomial Expansion Polynomials de:Ausmultiplizieren
mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, an expansion of a product of sums expresses it as a sum of products by using the fact that multiplication distributes over addition. Expansion of a polynomial expression can be obtained by repeatedly replacing subexpressions that multiply two other subexpressions, at least one of which is an addition, by the equivalent sum of products, continuing until the expression becomes a sum of (repeated) products. During the expansion, simplifications such as grouping of like terms or cancellations of terms may also be applied. Instead of multiplications, the expansion steps could also involve replacing powers of a sum of terms by the equivalent expression obtained from the binomial formula
In elementary algebra, the binomial theorem (or binomial expansion) describes the algebraic expansion of powers of a binomial. According to the theorem, it is possible to expand the polynomial into a sum involving terms of the form , where the ...
; this is a shortened form of what would happen if the power were treated as a repeated multiplication, and expanded repeatedly. It is customary to reintroduce powers in the final result when terms involve products of identical symbols.
Simple examples of polynomial expansions are the well known rules
:
:
when used from left to right. A more general single-step expansion will introduce all products of a term of one of the sums being multiplied with a term of the other:
:
An expansion which involves multiple nested rewrite steps is that of working out a Horner scheme
In mathematics and computer science, Horner's method (or Horner's scheme) is an algorithm for polynomial evaluation. Although named after William George Horner, this method is much older, as it has been attributed to Joseph-Louis Lagrange by Hor ...
to the (expanded) polynomial it defines, for instance
:.
The opposite process of trying to write an expanded polynomial as a product is called polynomial factorization
In mathematics and computer algebra, factorization of polynomials or polynomial factorization expresses a polynomial with coefficients in a given field (mathematics), field or in the integers as the product of irreducible polynomial, irreducible ...
.
Expansion of a polynomial written in factored form
 To multiply two factors, each term of the first factor must be multiplied by each term of the other factor. If both factors are
To multiply two factors, each term of the first factor must be multiplied by each term of the other factor. If both factors are binomial
Binomial may refer to:
In mathematics
*Binomial (polynomial), a polynomial with two terms
* Binomial coefficient, numbers appearing in the expansions of powers of binomials
*Binomial QMF, a perfect-reconstruction orthogonal wavelet decomposition
...
s, the FOIL rule
In secondary school, ''FOIL'' is a mnemonic for the standard method of multiplying two binomials—hence the method may be referred to as the FOIL method. The word ''FOIL'' is an acronym for the four terms of the product:
* First ("first" ...
can be used, which stands for "First Outer Inner Last," referring to the terms that are multiplied together. For example, expanding
:
yields
:
Expansion of (x+y)n
: When expanding , a special relationship exists between the coefficients of the terms when written in order of descending powers of ''x'' and ascending powers of ''y''. The coefficients will be the numbers in the (''n'' + 1)th row ofPascal's triangle
In mathematics, Pascal's triangle is a triangular array of the binomial coefficients that arises in probability theory, combinatorics, and algebra. In much of the Western world, it is named after the French mathematician Blaise Pascal, although ot ...
(since Pascal's triangle starts with row and column number of 0).
For example, when expanding , the following is obtained:
:
See also
*Polynomial factorization
In mathematics and computer algebra, factorization of polynomials or polynomial factorization expresses a polynomial with coefficients in a given field (mathematics), field or in the integers as the product of irreducible polynomial, irreducible ...
*Factorization
In mathematics, factorization (or factorisation, see American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), English spelling differences) or factoring consists of writing a number or another mathematical object as a p ...
*Multinomial theorem
In mathematics, the multinomial theorem describes how to expand a power of a sum in terms of powers of the terms in that sum. It is the generalization of the binomial theorem from binomials to multinomials.
Theorem
For any positive integer ...
External links
DiscussionReview of Algebra: Expansion
University of Akron
The University of Akron is a public research university in Akron, Ohio. It is part of the University System of Ohio. As a STEM-focused institution, it focuses on industries such as polymers, advanced materials, and engineering. It is classified ...
Online toolsExpand page
quickmath.com
Online Calculator with Symbolic Calculations
livephysics.com {{DEFAULTSORT:Polynomial Expansion Polynomials de:Ausmultiplizieren