polygonal number on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In

 Polygons with higher numbers of sides, such as pentagons and hexagons, can also be constructed according to this rule, although the dots will no longer form a perfectly regular lattice like above.
Polygons with higher numbers of sides, such as pentagons and hexagons, can also be constructed according to this rule, although the dots will no longer form a perfectly regular lattice like above.

 If is the number of sides in a polygon, the formula for the th -gonal number is
:
or
:
The th -gonal number is also related to the triangular numbers as follows:
:
Thus:
:
For a given -gonal number , one can find by
:
and one can find by
:.
If is the number of sides in a polygon, the formula for the th -gonal number is
:
or
:
The th -gonal number is also related to the triangular numbers as follows:
:
Thus:
:
For a given -gonal number , one can find by
:
and one can find by
:.
mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, a polygonal number is a number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual number ...
represented as dots or pebbles arranged in the shape of a regular polygon
In Euclidean geometry, a regular polygon is a polygon that is direct equiangular (all angles are equal in measure) and equilateral (all sides have the same length). Regular polygons may be either convex, star or skew. In the limit, a sequence ...
. The dots are thought of as alphas (units). These are one type of 2-dimensional figurate number
The term figurate number is used by different writers for members of different sets of numbers, generalizing from triangular numbers to different shapes (polygonal numbers) and different dimensions (polyhedral numbers). The term can mean
* polyg ...
s.
Definition and examples
The number 10 for example, can be arranged as atriangle
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. It is one of the basic shapes in geometry. A triangle with vertices ''A'', ''B'', and ''C'' is denoted \triangle ABC.
In Euclidean geometry, any three points, when non- colline ...
(see triangular number
A triangular number or triangle number counts objects arranged in an equilateral triangle. Triangular numbers are a type of figurate number, other examples being square numbers and cube numbers. The th triangular number is the number of dots i ...
):
:
But 10 cannot be arranged as a square
In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90- degree angles, π/2 radian angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length a ...
. The number 9, on the other hand, can be (see square number
In mathematics, a square number or perfect square is an integer that is the square of an integer; in other words, it is the product of some integer with itself. For example, 9 is a square number, since it equals and can be written as .
The u ...
):
:
Some numbers, like 36, can be arranged both as a square and as a triangle (see square triangular number):
:
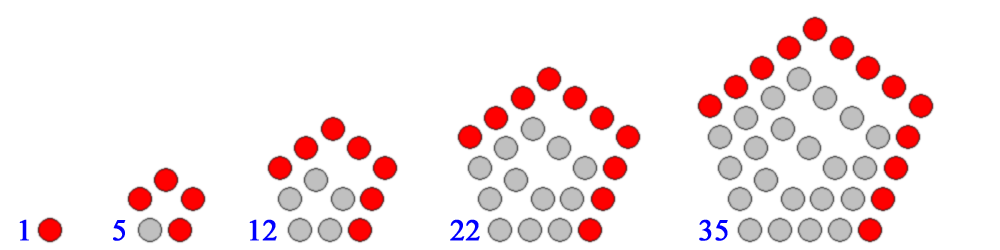
By convention, 1 is the first polygonal number for any number of sides. The rule for enlarging the polygon to the next size is to extend two adjacent arms by one point and to then add the required extra sides between those points. In the following diagrams, each extra layer is shown as in red.
Triangular numbers
:
Square numbers
: Polygons with higher numbers of sides, such as pentagons and hexagons, can also be constructed according to this rule, although the dots will no longer form a perfectly regular lattice like above.
Polygons with higher numbers of sides, such as pentagons and hexagons, can also be constructed according to this rule, although the dots will no longer form a perfectly regular lattice like above.
Pentagonal numbers
:
Hexagonal numbers
:
Formula
Every hexagonal number is also a triangular number
Applying the formula above: : to the case of 6 sides gives: : but since: : it follows that: : This shows that the th hexagonal number is also the th triangular number . We can find every hexagonal number by simply taking the odd-numbered triangular numbers: :1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21, 28, 36, 45, 55, 66, ...Table of values
The first 6 values in the column "sum of reciprocals", for triangular to octagonal numbers, come from a published solution to the general problem, which also gives a general formula for any number of sides, in terms of thedigamma function
In mathematics, the digamma function is defined as the logarithmic derivative of the gamma function:
:\psi(x)=\frac\ln\big(\Gamma(x)\big)=\frac\sim\ln-\frac.
It is the first of the polygamma functions. It is strictly increasing and strict ...
.
The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences
The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences (OEIS) is an online database of integer sequences. It was created and maintained by Neil Sloane while researching at AT&T Labs. He transferred the intellectual property and hosting of the OEIS to t ...
eschews terms using Greek prefixes (e.g., "octagonal") in favor of terms using numerals (i.e., "8-gonal").
A property of this table can be expressed by the following identity (see ):
:
with
:
Combinations
Some numbers, such as 36 which is both square and triangular, fall into two polygonal sets. The problem of determining, given two such sets, all numbers that belong to both can be solved by reducing the problem toPell's equation
Pell's equation, also called the Pell–Fermat equation, is any Diophantine equation of the form x^2 - ny^2 = 1, where ''n'' is a given positive nonsquare integer, and integer solutions are sought for ''x'' and ''y''. In Cartesian coordinates, ...
. The simplest example of this is the sequence of square triangular numbers.
The following table summarizes the set of -gonal -gonal numbers for small values of and .
:
In some cases, such as and , there are no numbers in both sets other than 1.
The problem of finding numbers that belong to three polygonal sets is more difficult. A computer search for pentagonal square triangular numbers has yielded only the trivial value of 1, though a proof that there are no other such numbers has yet to be found.
The number 1225 is hecatonicositetragonal (), hexacontagonal (), icosienneagonal (), hexagonal, square, and triangular.
The only polygonal set that is contained entirely in another polygonal set is the set of hexagonal numbers, which is contained in the set of triangular numbers.
See also
* Centered polygonal number * Polyhedral number * Fermat polygonal number theorem *Notes
References
*'' The Penguin Dictionary of Curious and Interesting Numbers'', David Wells (Penguin Books
Penguin Books is a British publishing, publishing house. It was co-founded in 1935 by Allen Lane with his brothers Richard and John, as a line of the publishers The Bodley Head, only becoming a separate company the following year.Polygonal numbers at PlanetMath
* *
* * Polygonal Number Counting Function: http://www.mathisfunforum.com/viewtopic.php?id=17853 {{Authority control Figurate numbers
* *
External links
** * Polygonal Number Counting Function: http://www.mathisfunforum.com/viewtopic.php?id=17853 {{Authority control Figurate numbers