pneumatic trough on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A pneumatic trough is a piece of laboratory apparatus used for collecting gases, such as
A pneumatic trough is a piece of laboratory apparatus used for collecting gases, such as
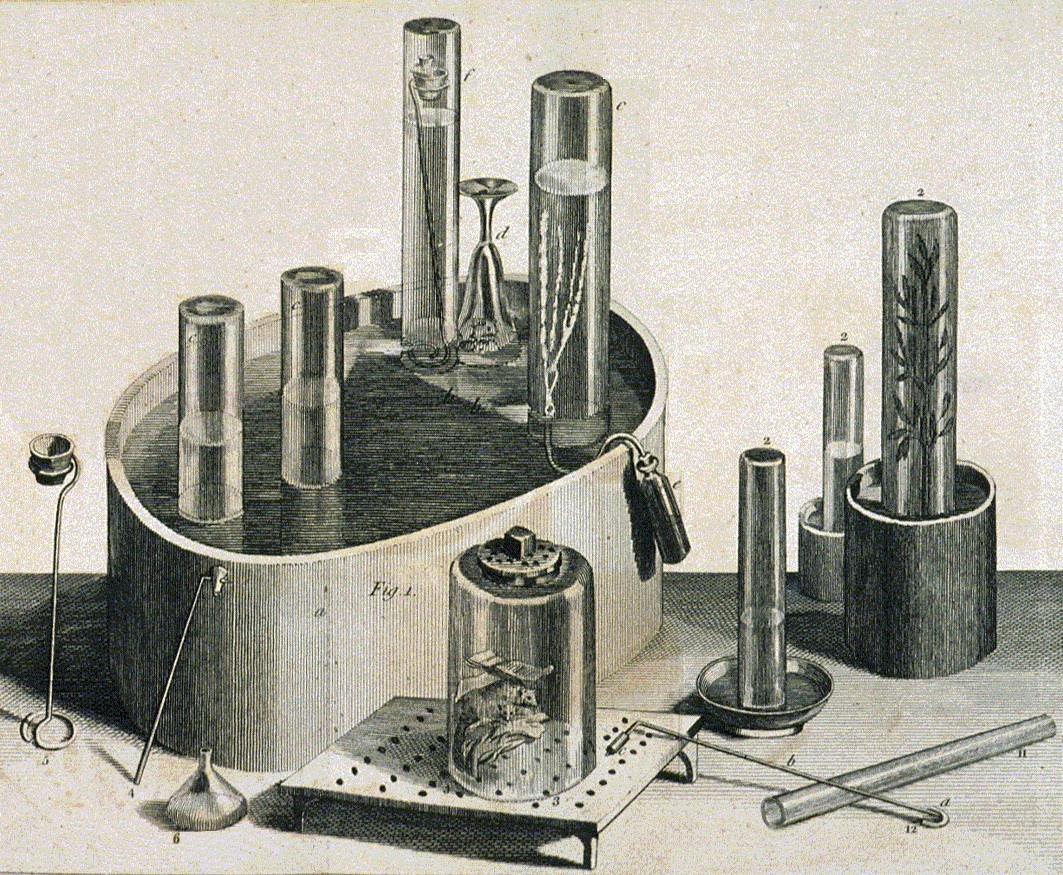 The bottle is filled with water, inverted, and placed into the pneumatic trough already containing water. The outlet tube from the gas-generating apparatus is inserted into the opening of the bottle so that gas can bubble up through it, displacing the water within.
The bottle is filled with water, inverted, and placed into the pneumatic trough already containing water. The outlet tube from the gas-generating apparatus is inserted into the opening of the bottle so that gas can bubble up through it, displacing the water within.
 A pneumatic trough is a piece of laboratory apparatus used for collecting gases, such as
A pneumatic trough is a piece of laboratory apparatus used for collecting gases, such as hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
and nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
.It is mainly made of glass or various fibres and are of various sizes.It was invented by Stephen Hales.
Description
Four items are required for gas collection with a pneumatic trough: * The trough itself, which is a large glass dish or a similar container. * A gas bottle (or bulb), to hold the gas collected. * A way to support the gas bottle or bulb, such as a beehive shelf or a hanger (as with Stephen Hales' design). * A liquid in the trough.Liquid
Pneumatic troughs require a liquid such as water. Scientists also have used mercury in pneumatic troughs, but usually only for the collection of water-soluble gases. Health and safety issues surrounding mercury generally prohibit its use in modern-day pneumatic troughs.Usage
 The bottle is filled with water, inverted, and placed into the pneumatic trough already containing water. The outlet tube from the gas-generating apparatus is inserted into the opening of the bottle so that gas can bubble up through it, displacing the water within.
The bottle is filled with water, inverted, and placed into the pneumatic trough already containing water. The outlet tube from the gas-generating apparatus is inserted into the opening of the bottle so that gas can bubble up through it, displacing the water within.
See also
* Eudiometer *Pneumatic chemistry
In the history of science, pneumatic chemistry is an area of scientific research of the seventeenth, eighteenth, and early nineteenth centuries. Important goals of this work were the understanding of the physical properties of gases and how the ...
* Joseph Priestley
Joseph Priestley (; 24 March 1733 – 6 February 1804) was an English chemist, natural philosopher, separatist theologian, grammarian, multi-subject educator, and liberal political theorist. He published over 150 works, and conducted exp ...
* Stephen Hales
Stephen Hales (17 September 16774 January 1761) was an English clergyman who made major contributions to a range of scientific fields including botany, pneumatic chemistry and physiology. He was the first person to measure blood pressure. He al ...
References
Further reading
* {{science-stub Laboratory equipment