Pike (weapon) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A pike is a very long thrusting spear formerly used in European warfare from the
A pike is a very long thrusting spear formerly used in European warfare from the
 The pike was a long weapon, varying considerably in size, from long. Generally, a spear becomes a pike when it is too long to be wielded with one hand in combat. It was approximately in weight, with the 16th century military writer Sir John Smythe recommending lighter rather than heavier pikes. It had a wooden shaft with an iron or steel spearhead affixed. The shaft near the head was often reinforced with metal strips called "cheeks" or langets. When the troops of opposing armies both carried the pike, it often grew in a sort of arms race, getting longer in both shaft and head length to give one side's pikemen an edge in combat. The extreme length of such weapons required a strong wood such as well-seasoned
The pike was a long weapon, varying considerably in size, from long. Generally, a spear becomes a pike when it is too long to be wielded with one hand in combat. It was approximately in weight, with the 16th century military writer Sir John Smythe recommending lighter rather than heavier pikes. It had a wooden shaft with an iron or steel spearhead affixed. The shaft near the head was often reinforced with metal strips called "cheeks" or langets. When the troops of opposing armies both carried the pike, it often grew in a sort of arms race, getting longer in both shaft and head length to give one side's pikemen an edge in combat. The extreme length of such weapons required a strong wood such as well-seasoned
 The pike, being unwieldy, was typically used in a deliberate, defensive manner, often alongside other missile and melee weapons. However, better-trained troops were capable of using the pike in an aggressive attack with each rank of pikemen being trained to hold their pikes so that they presented enemy infantry with four or five layers of spearheads bristling from the front of the formation.
As long as it kept good order, such a formation could roll right over enemy infantry, but it did have weaknesses. The men were all moving forward facing in a single direction and could not turn quickly or efficiently to protect the vulnerable flanks or rear of the formation. Nor could they maintain cohesion over uneven ground, as the Scots discovered to their cost at the Battle of Flodden. The huge block of men carrying such unwieldy spears could be difficult to maneuver in any way other than straightforward movement.
As a result, such mobile pike formations sought to have supporting troops protect their flanks or would maneuver to smash the enemy before they could be outflanked themselves. There was also the risk that the formation would become disordered, leading to a confused melee in which pikemen had the vulnerabilities mentioned above.
According to Sir John Smythe, there were two ways for two opposing pike formations to confront one another: cautious or aggressive. The cautious approach involved fencing at the length of the pike, while the aggressive approach involved quickly closing distance, with each of the first five ranks giving a single powerful thrust. In the aggressive approach, the first rank would then immediately resort to swords and daggers if the thrusts from the first five ranks failed to break the opposing pike formation. Smythe considered the cautious approach laughable.
Although primarily a military weapon, the pike could be surprisingly effective in single combat and a number of 16th-century sources explain how it was to be used in a dueling situation; fencers of the time often practiced with and competed against each other with long staves in place of pikes. George Silver considered the pike one of the more advantageous weapons for single combat in the open, giving it odds over all weapons shorter than or the sword and dagger/shield combination.
The pike, being unwieldy, was typically used in a deliberate, defensive manner, often alongside other missile and melee weapons. However, better-trained troops were capable of using the pike in an aggressive attack with each rank of pikemen being trained to hold their pikes so that they presented enemy infantry with four or five layers of spearheads bristling from the front of the formation.
As long as it kept good order, such a formation could roll right over enemy infantry, but it did have weaknesses. The men were all moving forward facing in a single direction and could not turn quickly or efficiently to protect the vulnerable flanks or rear of the formation. Nor could they maintain cohesion over uneven ground, as the Scots discovered to their cost at the Battle of Flodden. The huge block of men carrying such unwieldy spears could be difficult to maneuver in any way other than straightforward movement.
As a result, such mobile pike formations sought to have supporting troops protect their flanks or would maneuver to smash the enemy before they could be outflanked themselves. There was also the risk that the formation would become disordered, leading to a confused melee in which pikemen had the vulnerabilities mentioned above.
According to Sir John Smythe, there were two ways for two opposing pike formations to confront one another: cautious or aggressive. The cautious approach involved fencing at the length of the pike, while the aggressive approach involved quickly closing distance, with each of the first five ranks giving a single powerful thrust. In the aggressive approach, the first rank would then immediately resort to swords and daggers if the thrusts from the first five ranks failed to break the opposing pike formation. Smythe considered the cautious approach laughable.
Although primarily a military weapon, the pike could be surprisingly effective in single combat and a number of 16th-century sources explain how it was to be used in a dueling situation; fencers of the time often practiced with and competed against each other with long staves in place of pikes. George Silver considered the pike one of the more advantageous weapons for single combat in the open, giving it odds over all weapons shorter than or the sword and dagger/shield combination.
 Although very long spears had been used since the dawn of organized warfare (notably illustrated in art showing Sumerian and Minoan warriors and hunters), the earliest recorded use of a pike-like weapon in the tactical method described above involved the
Although very long spears had been used since the dawn of organized warfare (notably illustrated in art showing Sumerian and Minoan warriors and hunters), the earliest recorded use of a pike-like weapon in the tactical method described above involved the
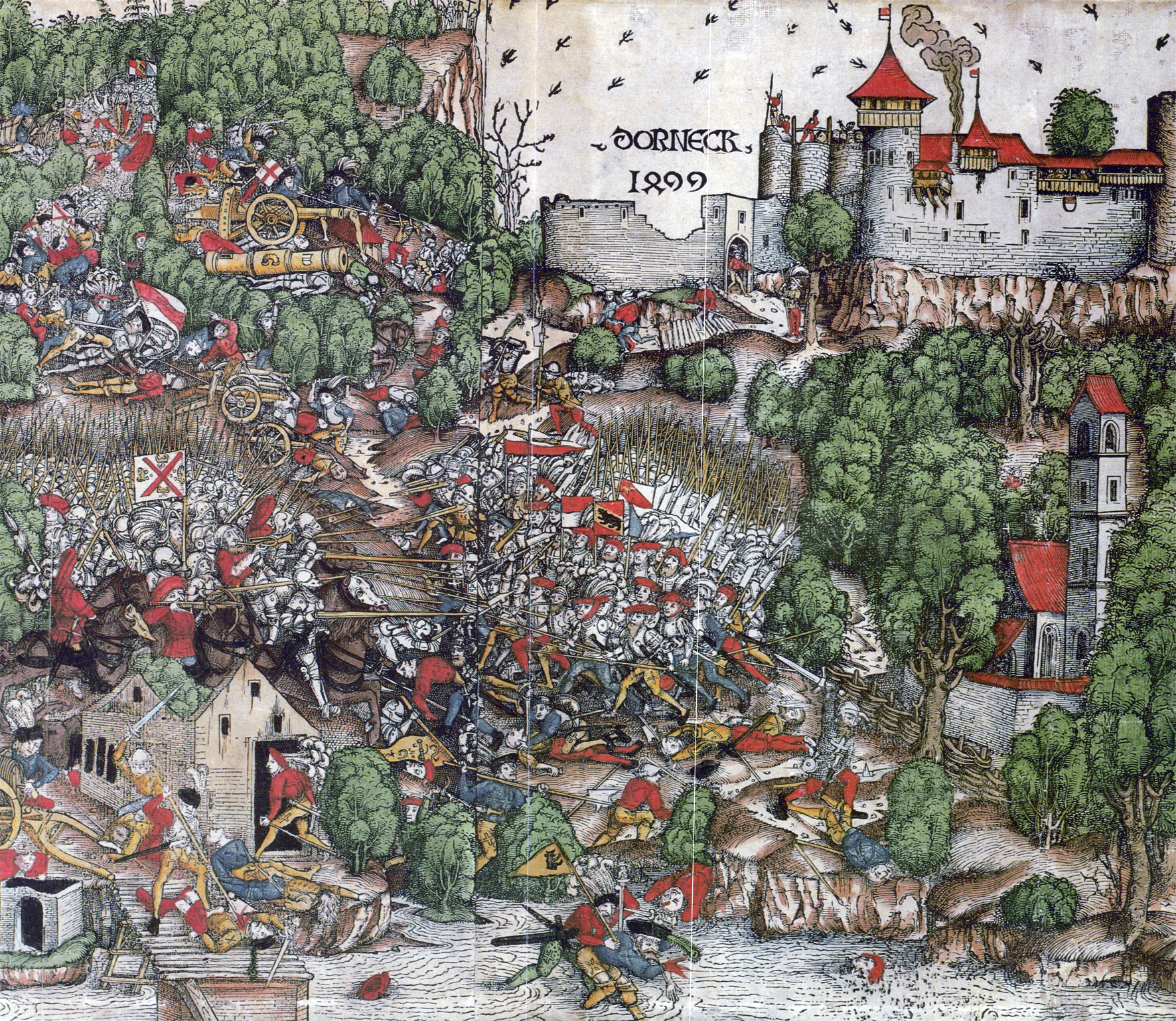 Medieval pike formations tended to have better success when they operated in an aggressive fashion. The Scots at the Battle of Stirling Bridge (1297), for example, utilized the momentum of their charge to overrun an English army while the Englishmen were crossing a narrow bridge. At the Battle of Laupen (1339), Bernese pikemen overwhelmed the infantry forces of the opposing Habsburg/Burgundian army with a massive charge before wheeling over to strike and rout the Austro-Burgundian horsemen as well. At the same time however such aggressive action required considerable tactical cohesiveness or suitable terrain to protect the vulnerable flanks of the pike formations especially from the attack of mounted man-at-arms. When these features were not available, militia often suffered costly failures, such as at the battles of Mons-en-Pevele (1304), Cassel (1328), Roosebeke (1382) and Othee (1408). The constant success of the Swiss mercenaries in the later period was attributed to their extreme discipline and tactical unity due to semi-professional nature, allowing a pike block to somewhat alleviate the threat presented by flanking attacks.
It was not uncommon for aggressive pike formations to be composed of dismounted men-at-arms, as at the
Medieval pike formations tended to have better success when they operated in an aggressive fashion. The Scots at the Battle of Stirling Bridge (1297), for example, utilized the momentum of their charge to overrun an English army while the Englishmen were crossing a narrow bridge. At the Battle of Laupen (1339), Bernese pikemen overwhelmed the infantry forces of the opposing Habsburg/Burgundian army with a massive charge before wheeling over to strike and rout the Austro-Burgundian horsemen as well. At the same time however such aggressive action required considerable tactical cohesiveness or suitable terrain to protect the vulnerable flanks of the pike formations especially from the attack of mounted man-at-arms. When these features were not available, militia often suffered costly failures, such as at the battles of Mons-en-Pevele (1304), Cassel (1328), Roosebeke (1382) and Othee (1408). The constant success of the Swiss mercenaries in the later period was attributed to their extreme discipline and tactical unity due to semi-professional nature, allowing a pike block to somewhat alleviate the threat presented by flanking attacks.
It was not uncommon for aggressive pike formations to be composed of dismounted men-at-arms, as at the
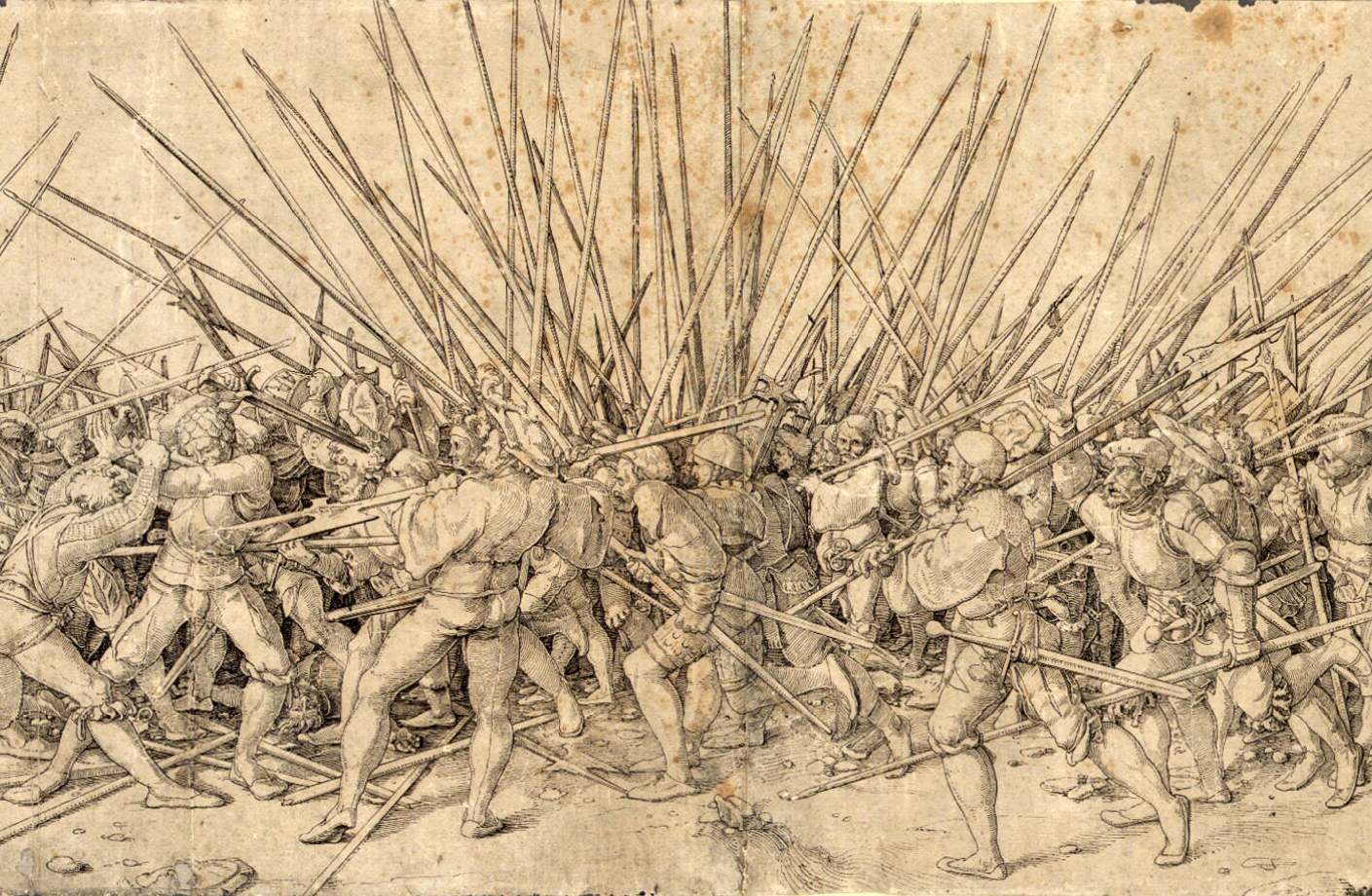
 The Swiss solved the pike's earlier problems and brought a renaissance to pike warfare in the 15th century, establishing strong training regimens to ensure they were masters of handling the ''Spiess'' (the German term for "skewer") on maneuvers and in combat; they also introduced marching to drums for this purpose. This meant that the pike blocks could rise to the attack, making them less passive and more aggressive formations, but sufficiently well trained that they could go on the defensive when attacked by cavalry. German soldiers known as Landsknechts later adopted Swiss methods of pike handling.
The Scots predominantly used shorter spears in their schiltron formation; their attempt to adopt the longer Continental pike was dropped for general use after its ineffective use led to humiliating defeat at the Battle of Flodden.
Such Swiss and Landsknecht phalanxes also contained men armed with two-handed swords, or '' Zweihänder'', and
The Swiss solved the pike's earlier problems and brought a renaissance to pike warfare in the 15th century, establishing strong training regimens to ensure they were masters of handling the ''Spiess'' (the German term for "skewer") on maneuvers and in combat; they also introduced marching to drums for this purpose. This meant that the pike blocks could rise to the attack, making them less passive and more aggressive formations, but sufficiently well trained that they could go on the defensive when attacked by cavalry. German soldiers known as Landsknechts later adopted Swiss methods of pike handling.
The Scots predominantly used shorter spears in their schiltron formation; their attempt to adopt the longer Continental pike was dropped for general use after its ineffective use led to humiliating defeat at the Battle of Flodden.
Such Swiss and Landsknecht phalanxes also contained men armed with two-handed swords, or '' Zweihänder'', and
 Shorter versions of pikes called ''boarding pikes'' were also used on warships—typically to repel
Shorter versions of pikes called ''boarding pikes'' were also used on warships—typically to repel Cambio della guardia al Quirinale – Infantry Passing out Parade
8:41. youtube.com for the President of the Italian Republic at the Quirinal Palace in Rome, Italy.
 A pike is a very long thrusting spear formerly used in European warfare from the
A pike is a very long thrusting spear formerly used in European warfare from the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Ren ...
and most of the Early Modern Period, and were wielded by foot soldiers deployed in pike square formation, until it was largely replaced by bayonet-equipped muskets. The pike was particularly well-known as the primary weapon of Swiss mercenary
The Swiss mercenaries (german: Reisläufer) were a powerful infantry force constituted by professional soldiers originating from the cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy. They were notable for their service in foreign armies, especially among th ...
and German Landsknecht units. A similar weapon, the sarissa, had been used in antiquity
Antiquity or Antiquities may refer to:
Historical objects or periods Artifacts
*Antiquities, objects or artifacts surviving from ancient cultures
Eras
Any period before the European Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries) but still within the histo ...
by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
's Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North Ma ...
phalanx infantry.
Design
 The pike was a long weapon, varying considerably in size, from long. Generally, a spear becomes a pike when it is too long to be wielded with one hand in combat. It was approximately in weight, with the 16th century military writer Sir John Smythe recommending lighter rather than heavier pikes. It had a wooden shaft with an iron or steel spearhead affixed. The shaft near the head was often reinforced with metal strips called "cheeks" or langets. When the troops of opposing armies both carried the pike, it often grew in a sort of arms race, getting longer in both shaft and head length to give one side's pikemen an edge in combat. The extreme length of such weapons required a strong wood such as well-seasoned
The pike was a long weapon, varying considerably in size, from long. Generally, a spear becomes a pike when it is too long to be wielded with one hand in combat. It was approximately in weight, with the 16th century military writer Sir John Smythe recommending lighter rather than heavier pikes. It had a wooden shaft with an iron or steel spearhead affixed. The shaft near the head was often reinforced with metal strips called "cheeks" or langets. When the troops of opposing armies both carried the pike, it often grew in a sort of arms race, getting longer in both shaft and head length to give one side's pikemen an edge in combat. The extreme length of such weapons required a strong wood such as well-seasoned ash
Ash or ashes are the solid remnants of fires. Specifically, ''ash'' refers to all non-aqueous, non-gaseous residues that remain after something burns. In analytical chemistry, to analyse the mineral and metal content of chemical samples, ash ...
for the pole, which was tapered towards the point to prevent the pike from sagging on the ends, although drooping or slight flection of the shaft was always a problem in pike handling. It is a common mistake to refer to a bladed polearm as a pike; such weapons are more generally halberd
A halberd (also called halbard, halbert or Swiss voulge) is a two-handed pole weapon that came to prominent use during the 13th, 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. The word ''halberd'' is cognate with the German word ''Hellebarde'', deriving from ...
s, glaive
A glaive (or glave) is a European polearm, consisting of a single-edged blade on the end of a pole. It is similar to the Japanese naginata, the Chinese guandao, the Korean woldo, and the Russian sovnya.
Overview
Typically, the blade is arou ...
s or voulges.
The great length of the pikes allowed a great concentration of spearheads to be presented to the enemy, with their wielders at a greater distance, but also made pikes unwieldy in close combat. This meant that pikemen had to be equipped with an additional, shorter weapon such as a dagger
A dagger is a fighting knife with a very sharp point and usually two sharp edges, typically designed or capable of being used as a thrusting or stabbing weapon.State v. Martin, 633 S.W.2d 80 (Mo. 1982): This is the dictionary or popular-use def ...
or sword in order to defend themselves should the fighting degenerate into a melee. In general, however, pikemen attempted to avoid such disorganized combat, in which they were at a disadvantage. To compound their difficulties in a melee, the pikeman often did not have a shield, or had only a small shield which would be of limited use in close-quarters fighting.
Tactics
 The pike, being unwieldy, was typically used in a deliberate, defensive manner, often alongside other missile and melee weapons. However, better-trained troops were capable of using the pike in an aggressive attack with each rank of pikemen being trained to hold their pikes so that they presented enemy infantry with four or five layers of spearheads bristling from the front of the formation.
As long as it kept good order, such a formation could roll right over enemy infantry, but it did have weaknesses. The men were all moving forward facing in a single direction and could not turn quickly or efficiently to protect the vulnerable flanks or rear of the formation. Nor could they maintain cohesion over uneven ground, as the Scots discovered to their cost at the Battle of Flodden. The huge block of men carrying such unwieldy spears could be difficult to maneuver in any way other than straightforward movement.
As a result, such mobile pike formations sought to have supporting troops protect their flanks or would maneuver to smash the enemy before they could be outflanked themselves. There was also the risk that the formation would become disordered, leading to a confused melee in which pikemen had the vulnerabilities mentioned above.
According to Sir John Smythe, there were two ways for two opposing pike formations to confront one another: cautious or aggressive. The cautious approach involved fencing at the length of the pike, while the aggressive approach involved quickly closing distance, with each of the first five ranks giving a single powerful thrust. In the aggressive approach, the first rank would then immediately resort to swords and daggers if the thrusts from the first five ranks failed to break the opposing pike formation. Smythe considered the cautious approach laughable.
Although primarily a military weapon, the pike could be surprisingly effective in single combat and a number of 16th-century sources explain how it was to be used in a dueling situation; fencers of the time often practiced with and competed against each other with long staves in place of pikes. George Silver considered the pike one of the more advantageous weapons for single combat in the open, giving it odds over all weapons shorter than or the sword and dagger/shield combination.
The pike, being unwieldy, was typically used in a deliberate, defensive manner, often alongside other missile and melee weapons. However, better-trained troops were capable of using the pike in an aggressive attack with each rank of pikemen being trained to hold their pikes so that they presented enemy infantry with four or five layers of spearheads bristling from the front of the formation.
As long as it kept good order, such a formation could roll right over enemy infantry, but it did have weaknesses. The men were all moving forward facing in a single direction and could not turn quickly or efficiently to protect the vulnerable flanks or rear of the formation. Nor could they maintain cohesion over uneven ground, as the Scots discovered to their cost at the Battle of Flodden. The huge block of men carrying such unwieldy spears could be difficult to maneuver in any way other than straightforward movement.
As a result, such mobile pike formations sought to have supporting troops protect their flanks or would maneuver to smash the enemy before they could be outflanked themselves. There was also the risk that the formation would become disordered, leading to a confused melee in which pikemen had the vulnerabilities mentioned above.
According to Sir John Smythe, there were two ways for two opposing pike formations to confront one another: cautious or aggressive. The cautious approach involved fencing at the length of the pike, while the aggressive approach involved quickly closing distance, with each of the first five ranks giving a single powerful thrust. In the aggressive approach, the first rank would then immediately resort to swords and daggers if the thrusts from the first five ranks failed to break the opposing pike formation. Smythe considered the cautious approach laughable.
Although primarily a military weapon, the pike could be surprisingly effective in single combat and a number of 16th-century sources explain how it was to be used in a dueling situation; fencers of the time often practiced with and competed against each other with long staves in place of pikes. George Silver considered the pike one of the more advantageous weapons for single combat in the open, giving it odds over all weapons shorter than or the sword and dagger/shield combination.
History
Ancient Europe
 Although very long spears had been used since the dawn of organized warfare (notably illustrated in art showing Sumerian and Minoan warriors and hunters), the earliest recorded use of a pike-like weapon in the tactical method described above involved the
Although very long spears had been used since the dawn of organized warfare (notably illustrated in art showing Sumerian and Minoan warriors and hunters), the earliest recorded use of a pike-like weapon in the tactical method described above involved the Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North Ma ...
sarissa, used by the troops of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
's father, Philip II of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 382 – 21 October 336 BC) was the king ('' basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the ...
, and successive dynasties, which dominated warfare for several centuries in many countries.
After the fall of the last successor of Macedon, the pike largely fell out of use for the next 1000 or so years. The one exception to this appears to have been in Germany, where Tacitus recorded Germanic tribesmen in the 2nd century AD as using "over-long spears". He consistently refers to the spears used by the Germans as being "massive" and "very long" suggesting that he is describing in essence a pike. Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
, in his De Bello Gallico, describes the Helvetii as fighting in a tight, phalanx-like formation with spears jutting out over their shields. Caesar was probably describing an early form of the shieldwall so popular in later times.
Medieval Europe revival
In theMiddle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, the principal users of the pike were urban militia troops such as the Flemings
The Flemish or Flemings ( nl, Vlamingen ) are a Germanic ethnic group native to Flanders, Belgium, who speak Dutch. Flemish people make up the majority of Belgians, at about 60%.
"''Flemish''" was historically a geographical term, as all in ...
or the peasant array of the lowland Scots. For example, the Scots used a spear formation known as the '' schiltron'' in several battles during the Wars of Scottish Independence
The Wars of Scottish Independence were a series of military campaigns fought between the Kingdom of Scotland and the Kingdom of England in the late 13th and early 14th centuries.
The First War (1296–1328) began with the English invasion of ...
including the Battle of Bannockburn in 1314, and the Flemings used their ''geldon'' long spear to absorb the attack of French knights at the Battle of the Golden Spurs in 1302, before other troops in the Flemish formation counterattacked the stalled knights with goedendags. Both battles were seen by contemporaries as stunning victories of commoners over superbly equipped, mounted, military professionals, where victory was owed to the use of the pike and the brave resistance of the commoners who wielded them.
These formations were essentially immune to the attacks of mounted men-at-arms as long as the knights obligingly threw themselves on the spear wall and the foot soldiers remained steady under the morale challenge of facing a cavalry charge, but the closely packed nature of pike formations rendered them vulnerable to enemy archers and crossbowmen who could shoot them down with impunity, especially when the pikemen did not have adequate armor. Many defeats, such as at Roosebeke and Halidon Hill, were suffered by the militia pike armies when faced by cunning foes who employed their archers and crossbowmen to thin the ranks of the pike blocks before charging in with their (often dismounted) men-at-arms.
 Medieval pike formations tended to have better success when they operated in an aggressive fashion. The Scots at the Battle of Stirling Bridge (1297), for example, utilized the momentum of their charge to overrun an English army while the Englishmen were crossing a narrow bridge. At the Battle of Laupen (1339), Bernese pikemen overwhelmed the infantry forces of the opposing Habsburg/Burgundian army with a massive charge before wheeling over to strike and rout the Austro-Burgundian horsemen as well. At the same time however such aggressive action required considerable tactical cohesiveness or suitable terrain to protect the vulnerable flanks of the pike formations especially from the attack of mounted man-at-arms. When these features were not available, militia often suffered costly failures, such as at the battles of Mons-en-Pevele (1304), Cassel (1328), Roosebeke (1382) and Othee (1408). The constant success of the Swiss mercenaries in the later period was attributed to their extreme discipline and tactical unity due to semi-professional nature, allowing a pike block to somewhat alleviate the threat presented by flanking attacks.
It was not uncommon for aggressive pike formations to be composed of dismounted men-at-arms, as at the
Medieval pike formations tended to have better success when they operated in an aggressive fashion. The Scots at the Battle of Stirling Bridge (1297), for example, utilized the momentum of their charge to overrun an English army while the Englishmen were crossing a narrow bridge. At the Battle of Laupen (1339), Bernese pikemen overwhelmed the infantry forces of the opposing Habsburg/Burgundian army with a massive charge before wheeling over to strike and rout the Austro-Burgundian horsemen as well. At the same time however such aggressive action required considerable tactical cohesiveness or suitable terrain to protect the vulnerable flanks of the pike formations especially from the attack of mounted man-at-arms. When these features were not available, militia often suffered costly failures, such as at the battles of Mons-en-Pevele (1304), Cassel (1328), Roosebeke (1382) and Othee (1408). The constant success of the Swiss mercenaries in the later period was attributed to their extreme discipline and tactical unity due to semi-professional nature, allowing a pike block to somewhat alleviate the threat presented by flanking attacks.
It was not uncommon for aggressive pike formations to be composed of dismounted men-at-arms, as at the Battle of Sempach
The Battle of Sempach was fought on 9 July 1386, between Leopold III, Duke of Austria and the Old Swiss Confederacy. The battle was a decisive Swiss victory in which Duke Leopold and numerous Austrian nobles died. The victory helped turn the loo ...
(1386), where the dismounted Austrian vanguard, using their lances as pikes, had some initial success against their predominantly halberd
A halberd (also called halbard, halbert or Swiss voulge) is a two-handed pole weapon that came to prominent use during the 13th, 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. The word ''halberd'' is cognate with the German word ''Hellebarde'', deriving from ...
-equipped Swiss adversaries. Dismounted Italian men-at-arms also used the same method to defeat the Swiss at the Battle of Arbedo (1422). Equally, well-armored Scottish nobles (accompanied even by King James IV) were recorded as forming the leading ranks of Scottish pike blocks at the Battle of Flodden (1513), incidentally rendering the whole formation resistant to English archery.
Renaissance Europe heyday

 The Swiss solved the pike's earlier problems and brought a renaissance to pike warfare in the 15th century, establishing strong training regimens to ensure they were masters of handling the ''Spiess'' (the German term for "skewer") on maneuvers and in combat; they also introduced marching to drums for this purpose. This meant that the pike blocks could rise to the attack, making them less passive and more aggressive formations, but sufficiently well trained that they could go on the defensive when attacked by cavalry. German soldiers known as Landsknechts later adopted Swiss methods of pike handling.
The Scots predominantly used shorter spears in their schiltron formation; their attempt to adopt the longer Continental pike was dropped for general use after its ineffective use led to humiliating defeat at the Battle of Flodden.
Such Swiss and Landsknecht phalanxes also contained men armed with two-handed swords, or '' Zweihänder'', and
The Swiss solved the pike's earlier problems and brought a renaissance to pike warfare in the 15th century, establishing strong training regimens to ensure they were masters of handling the ''Spiess'' (the German term for "skewer") on maneuvers and in combat; they also introduced marching to drums for this purpose. This meant that the pike blocks could rise to the attack, making them less passive and more aggressive formations, but sufficiently well trained that they could go on the defensive when attacked by cavalry. German soldiers known as Landsknechts later adopted Swiss methods of pike handling.
The Scots predominantly used shorter spears in their schiltron formation; their attempt to adopt the longer Continental pike was dropped for general use after its ineffective use led to humiliating defeat at the Battle of Flodden.
Such Swiss and Landsknecht phalanxes also contained men armed with two-handed swords, or '' Zweihänder'', and halberd
A halberd (also called halbard, halbert or Swiss voulge) is a two-handed pole weapon that came to prominent use during the 13th, 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. The word ''halberd'' is cognate with the German word ''Hellebarde'', deriving from ...
iers for close combat against both infantry and attacking cavalry.
The Swiss were confronted with the German ''Landsknecht'' who used similar tactics as the Swiss, but more pikes in the more difficult ''German thrust'' (german: deutscher Stoß: holding a pike that had its weight in the lower 1/3 at the end with two hands), which was utilized in a more flexible attacking column.
The high military reputation of the Swiss and the ''Landsknechts'' again led to the employment of mercenary units across Europe in order to train other armies in their tactics. These two, and others who had adopted their tactics, faced off in several wars, leading to a series of developments as a result.
These formations had great successes on the battlefield, starting with the astonishing victories of the Swiss cantons against Charles the Bold of Burgundy in the Burgundian Wars
The Burgundian Wars (1474–1477) were a conflict between the Burgundian State and the Old Swiss Confederacy and its allies. Open war broke out in 1474, and the Duke of Burgundy, Charles the Bold, was defeated three times on the battlefield in th ...
, in which the Swiss participated in 1476 and 1477. In the battles of Grandson
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideall ...
, Morat and Nancy, the Swiss not only successfully resisted the attacks of enemy knights, as the relatively passive Scottish and Flemish infantry squares had done in the earlier Middle Ages, but also marched to the attack with great speed and in good formation, their attack columns steamrolling the Burgundian forces, sometimes with great massacre.
The deep pike attack column remained the primary form of effective infantry combat for the next forty years, and the Swabian War saw the first conflict in which both sides had large formations of well-trained pikemen. After that war, its combatants—the Swiss (thereafter generally serving as mercenaries) and their Landsknecht imitators—would often face each other again in the Italian Wars, which would become in many ways the military proving ground of the Renaissance.
The so-called '' Schefflin'' was a polearm, closely related to the pike, which from the late 1400s and throughout the 16th century saw widespread use in the German-speaking world. It served as a multipurpose weapon for both infantry (in the manner of pikes) and light cavalry (in the manner of demi-lances). Characteristically, it featured a large, hollow-made and leaf-shaped head of about 50 centimetres or more, which was attached to a long and slender shaft. Apart from being used by soldiers in battle, a tassel fixed to the socket of the head together with optional further embellishment made the ''Schefflin'' an appropriate main weapon for princely bodyguards and courtly officials. There seems to be a close relation between the contemporary German term ''Schefflin'' and the West European terms ''javeline'' (French) and ''javelin'' (English), both referring to some type of cavalry spear. Although rarely noticed, many of these weapons have survived to this day. Some pieces, of which many are said to have been used by the personal entourage of Henry VIII, are kept at the Royal Armouries in Leeds.
Ancient China
Pikes and long halberds were in use in ancient China from theWarring States period
The Warring States period () was an era in History of China#Ancient China, ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded ...
since the 5th century BC. Infantrymen used a variety of long polearm weapons, but the most popular was the dagger-axe, pike-like long spear, and the ''ji''. The dagger-axe and ''ji'' came in various lengths, from 9 to 18 feet; the weapon consisted of a thrusting spear with a slashing blade appended to it. Dagger-axes and ''ji'' were an extremely popular weapon in various kingdoms, especially for the Qin state and Qin Dynasty, and possibly the succeeding Han Dynasty, who produced 18-foot-long halberd and pike-like weapons, as well as 22 foot long pikes during the war against Xiongnu.
Classical Japan
During the continuous European development of the pike, Japan experienced a parallel evolution of pole weapons. In Classical Japan, the Japanese style of warfare was generally fast-moving and aggressive, with far shallower formations than their European equivalents. The naginata and yari were more commonly used than swords for Japanese ashigaru foot soldiers and dismountedsamurai
were the hereditary military nobility and officer caste of medieval and early-modern Japan from the late 12th century until their abolition in 1876. They were the well-paid retainers of the '' daimyo'' (the great feudal landholders). They ...
due to their greater reach. Naginata, first used around 750 AD, had curved sword-like blades on wooden shafts with often spiked metal counterweights. They were typically used with a slashing action and forced the introduction of shin guards as cavalry battles became more important. Yari were spears of varying lengths; their straight blades usually had sharpened edges or protrusions from the central blade, and were fitted to a hollowed shaft with an extremely long tang.
Medieval Japan
During the later half of the 16th century inMedieval Japan
The first human inhabitants of the Japanese archipelago have been traced to Japanese Paleolithic, prehistoric times around 30,000 BC. The Jōmon period, named after its cord-marked pottery, was followed by the Yayoi period in the first millenni ...
, pikes used were generally long, but sometimes up to in length. By this point, pikemen were becoming the main forces in armies. They formed lines, combined with arquebusiers and spearmen. Formations were generally only two or three rows deep.
Pike and shot
In the aftermath of the Italian Wars, from the late 15th century to the late 16th century, most European armies adopted the use of the pike, often in conjunction with primitive firearms such as the arquebus andcaliver
An arquebus ( ) is a form of long gun that appeared in Europe and the Ottoman Empire during the 15th century. An infantryman armed with an arquebus is called an arquebusier.
Although the term ''arquebus'', derived from the Dutch word ''Haakbus ...
, to form large pike and shot formations.
The quintessential example of this development was the Spanish tercio, which consisted of a large square of pikemen with small, mobile squadrons of arquebusiers moving along its perimeter, as well as traditional men-at-arms. These three elements formed a mutually supportive combination of tactical roles: the arquebusiers harried the enemy line, the pikemen protected the arquebusiers from enemy cavalry charges, and the men-at-arms, typically armed with swords and javelins, fought off enemy pikemen when two opposing squares made contact. The Tercio deployed smaller numbers of pikemen than the huge Swiss and Landsknecht columns, and their formation ultimately proved to be much more flexible on the battlefield.
Mixed formations of men quickly became the norm for European infantrymen, with many, but not all, seeking to imitate the Tercio; in England, a combination of bill
Bill(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
* Banknote, paper cash (especially in the United States)
* Bill (law), a proposed law put before a legislature
* Invoice, commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer
* Bill, a bird or animal's beak
Pla ...
men, longbow
A longbow (known as warbow in its time, in contrast to a hunting bow) is a type of tall Bow and arrow, bow that makes a fairly long Bow draw, draw possible. A longbow is not significantly Recurve bow, recurved. Its limbs are relatively narrow an ...
men, and men-at-arms remained the norm, though this changed when the supply of yew
Yew is a common name given to various species of trees.
It is most prominently given to any of various coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Taxus'':
* European yew or common yew (''Taxus baccata'')
* Pacific yew or western yew (''Taxus br ...
on the island dwindled.
The percentage of men who were armed with firearms in Tercio-like formations steadily increased as firearms advanced in technology. This advance is believed to be the demise of cavalry when in fact it revived it. From the late 16th century and into the 17th century, smaller pike formations were used, invariably defending attached musketeers, often as a central block with two sub-units of shooters, called "sleeves of shot", on either side of the pikes. Although the cheaper and versatile infantry increasingly adopted firearms, cavalry's proportion in the army remained high.
During the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I (" Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of r ...
(1642–1651) the New Model Army (1646–1660) initially had two musketeers for each pikeman. Two musketeers for each pikeman was not the agreed mix used throughout Europe, and when in 1658 Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three ...
, by then the Lord Protector, sent a contingent of the New Model Army to Flanders to support his French allies under the terms of their treaty of friendship (the Treaty of Paris, 1657) he supplied regiments with equal numbers of musketeers and pikemen.} On the battlefield, the musketeers lacked protection against enemy cavalry, and the two types of foot soldier supported each other.
The post Restoration English Army used pikemen and by 1697 (the last year of the Nine Years' War) English infantry battalions fighting in the Low Countries still had two musketeers to every pikemen and fought in the now traditional style of pikemen five ranks deep in the centre, with six ranks of musketeers on each side.
According to John Kersey
John Kersey the younger ( fl. 1720) was an English philologist and lexicographer of the late seventeenth and early eighteenth centuries. He is notable for editing three dictionaries in his lifetime: ''A New English Dictionary'' (1702), a revised ...
in 1706, the pike was typically in length.
End of the pike era
The mid 17th century to the early 18th century saw the decline of the pike in most European armies. This started with the profileration of theflintlock
Flintlock is a general term for any firearm that uses a flint-striking ignition mechanism, the first of which appeared in Western Europe in the early 16th century. The term may also apply to a particular form of the mechanism itself, also know ...
, which gave a musketeer both more powerful and a faster rate of fire than he before possessed, incentivizing a higher ratio of shot to pike. It continued with development of the plug bayonet, followed by the socket bayonet in the 1680s and 1690s. The plug bayonet did not replace the pike as it required a soldier surrender his ability to shoot to fix it, but the socket bayonet solved that issue. The bayonet added a long blade of up to 60 cm (24 inches) to the end of the musket, allowing the musket to act as a spear-like weapon when held out with both hands. Although they did not have the full reach of pikes, bayonets were effective against cavalry charges, which used to be the main weakness of musketeer formations, and allowed armies to massively expand their potential firepower by giving every infantryman a firearm; pikemen were no longer needed to protect musketeers from cavalry. Furthermore, improvements in artillery caused most European armies to abandon large formations in favor of multiple staggered lines, both to minimize casualties and to present a larger frontage for volley fire. Thick hedges of bayonets proved to be an effective anti-cavalry solution, and improved musket firepower was now so deadly that combat was often decided by shooting alone.
A common end date for the use of the pike in most infantry formations is 1700, such as the Prussian and Austrian armies. Others, including the Swedish and Russian armies, continued to use the pike as an effective weapon for several more decades, until the 1720s and 1730s (the Swedes of King Charles XII in particular using it to great effect until 1721). At the start of the Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swe ...
in 1700, Russian line infantry companies had 5 NCOs, 84 musketeers, and 18 pikemen, the musketeers initially being equipped with sword-like plug bayonets; they did not fully switch to socket bayonets until 1709. A Swedish company consisted of 82 musketeers, 48 pikemen, and 16 grenadiers.Gabriele Esposito. "Armies of the Great Northern War: 1700-1720." Osprey: 2019. Pages 10 and 16. The Army of the Holy Roman Empire maintained a ratio of 2 muskets to 1 pike in the middle to late 17th century, officially abandoning the pike in 1699. The French, meanwhile, had a ratio of 3-4 muskets to 1 pike by 1689. Both sides of the Wars of the Three Kingdoms
The Wars of the Three Kingdoms were a series of related conflicts fought between 1639 and 1653 in the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland, then separate entities united in a personal union under Charles I. They include the 1639 to 1640 Bi ...
in the 1640s and 1650s preferred a ratio of 2 muskets to 1 pike, but this was not always possible.
During the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
(1775–1783), pikes called "trench spears" made by local blacksmiths saw limited use until enough bayonets could be procured for general use by both Continental Army and attached militia units.
Throughout the Napoleonic era, the spontoon, a type of shortened pike that typically had a pair of blades or lugs mounted to the head, was retained as a symbol by some NCOs; in practice it was probably more useful for gesturing and signaling than as a weapon for combat.
As late as Poland's Kościuszko Uprising in 1794, the pike reappeared as a child of necessity which became, for a short period, a surprisingly effective weapon on the battlefield. In this case, General Thaddeus Kosciuszko, facing a shortage of firearms and bayonets to arm landless serf partisans recruited straight from the wheat fields, had their sickles and scythe
A scythe ( ) is an agriculture, agricultural hand tool for mowing grass or Harvest, harvesting Crop, crops. It is historically used to cut down or reaping, reap edible grain, grains, before the process of threshing. The scythe has been largely ...
s heated and straightened out into something resembling crude " war scythes". These weaponized agricultural accouterments were then used in battle as both cutting weapons, as well as makeshift pikes. The peasant
A peasant is a pre-industrial agricultural laborer or a farmer with limited land-ownership, especially one living in the Middle Ages under feudalism and paying rent, tax, fees, or services to a landlord. In Europe, three classes of peasa ...
"pikemen" armed with these crude instruments played a pivotal role in securing a near impossible victory against a far larger and better equipped Russian army at the Battle of Racławice
The Battle of Racławice was one of the first battles of the Polish-Lithuanian Kościuszko Uprising against Russia. It was fought on 4 April 1794 near the village of Racławice in Lesser Poland.Storozynski, A., 2009, The Peasant Prince, New Y ...
, which took place on 4 April 1794.
Civilian pikeman played a similar role, though outnumbered and outgunned, in the 1798 Rising
The Irish Rebellion of 1798 ( ga, Éirí Amach 1798; Ulster-Scots: ''The Hurries'') was a major uprising against British rule in Ireland. The main organising force was the Society of United Irishmen, a republican revolutionary group influenced ...
in Ireland four years later. Here, especially in the Wexford Rebellion and in Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 ...
, the pike was useful mainly as a weapon by men and women fighting on foot against cavalry armed with guns.
Improvised pikes, made from bayonets on poles, were used by escaped convicts during the Castle Hill rebellion
The Castle Hill convict rebellion was an 1804 convict rebellion in the Castle Hill area of Sydney, against the colonial authorities of the British colony of New South Wales. The rebellion culminated in a battle fought between convicts and the ...
of 1804.
As late as the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
, at the beginning of the 19th century, even the Russian militia (mostly landless peasants, like the Polish partisans before them) could be found carrying shortened pikes into battle. As the 19th century progressed, the obsolete pike would still find a use in such countries as Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
, generally in the hands of desperate peasant rebel
A rebel is a participant in a rebellion.
Rebel or rebels may also refer to:
People
* Rebel (given name)
* Rebel (surname)
* Patriot (American Revolution), during the American Revolution
* American Southerners, as a form of self-identification ...
s who did not have access to firearms. John Brown purchased a large number of pikes and brought them to his raid on Harpers Ferry.
One attempt to resurrect the pike as a primary infantry weapon occurred during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
(1861–1865) when the Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confeder ...
planned to recruit twenty regiments of pikemen in 1862. In April 1862 it was authorised that every Confederate infantry regiment would include two companies of pikemen, a plan supported by Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, towards the end of which he was appointed the overall commander of the Confederate States Army. He led the Army of Nor ...
. Many pikes were produced but were never used in battle and the plan to include pikemen in the army was abandoned.
 Shorter versions of pikes called ''boarding pikes'' were also used on warships—typically to repel
Shorter versions of pikes called ''boarding pikes'' were also used on warships—typically to repel boarding
Boarding may refer to:
*Boarding, used in the sense of "room and board", i.e. lodging and meals as in a:
** Boarding house
**Boarding school
*Boarding (horses) (also known as a livery yard, livery stable, or boarding stable), is a stable where ho ...
parties, up to the late 19th century.
The great Hawaiian warrior king Kamehameha I had an elite force of men armed with very long spears who seem to have fought in a manner identical to European pikemen, despite the usual conception of his people's general disposition for individualistic dueling as their method of close combat. It is not known whether Kamehameha himself introduced this tactic or if it was taken from the use of traditional Hawaiian weapons.
The pike was issued as a British Home Guard weapon in 1942 after the War Office acted on a letter from Winston Churchill saying ''"every man must have a weapon of some kind, be it only a mace or pike"''. However, these hand-held weapons never left the stores after the pikes had "generated an almost universal feeling of anger and disgust from the ranks of the Home Guard, demoralised the men and led to questions being asked in both Houses of Parliament". The pikes, made from obsolete Lee–Enfield
The Lee–Enfield or Enfield is a bolt-action, magazine-fed repeating rifle that served as the main firearm of the military forces of the British Empire and Commonwealth during the first half of the 20th century, and was the British Army's sta ...
rifle bayonet blades welded to a steel tube, took the name of ''"Croft's Pikes"'' after Henry Page Croft
Henry Page Croft, 1st Baron Croft (22 June 1881 – 7 December 1947) was a decorated British soldier and Conservative Party politician.
Early life and family
He was born at Fanhams Hall in Ware, Hertfordshire, England. He was the son of ...
, the Under-Secretary of State for War who attempted to defend the fiasco by stating that they were a "silent and effective weapon".
In Spain, beginning in 1715 and ending in 1977, there were night patrol guards in cities called ''serenos'' who carried a short pike of called ''chuzo''.
Pikes live on today only in ceremonial roles, being used to carry the colours
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associa ...
of an infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and mar ...
regiment and with the Company of Pikemen and Musketeers
The Company of Pikemen & Musketeers is a ceremonial unit of the Honourable Artillery Company (HAC), which provides a regiment for the Army Reserve and is associated with the City of London. The HAC is the oldest regiment in the British Army, though ...
of the Honourable Artillery Company, or by some of the infantry units on duty during their rotation as guard8:41. youtube.com
See also
* Pike square * Push of pike * Lance * Javelin * Kontos (weapon) * SpearReferences
Further reading
* Delbrück, Hans. ''History of the Art of War'', originally published in 1920; University of Nebraska Press (reprint), 1990 (trans. J. Renfroe Walter). Volume III: ''Medieval Warfare''. * Fegley, Randall. ''The Golden Spurs of Kortrijk: How the Knights of France Fell to the Foot Soldiers of Flanders in 1302'', Jefferson, NC: McFarland, 2002. * McPeak, William. ''Military Heritage'', 7(1), August 2005, pp. 10,12,13. * Oman, Charles. ''A History of the Art of War in the Sixteenth Century''. London: Methuen & Co., 1937. * Parker, Geoffrey. ''The Military Revolution: Military Innovation and the Rise of the West 1500–1800'', Cambridge University Press, 1996. * Smith, Goldwyn. ''Irish History and the Irish Question'', New York: McClure, Phillips & Co., 1905. * Vullaimy, C. E. ''Royal George: A Study of King George III, His Experiment in Monarchy, His Decline and Retirement'', D. Appleton-Century Company, Inc., 1937.External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Pike (Weapon) Spears Polearms Medieval polearms Renaissance-era weapons Warfare of the Early Modern period Articles containing video clips