petrol-paraffin engine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A petrol-paraffin engine, TVO engine (United Kingdom) or gasoline-kerosene engine (
A petrol-paraffin engine, TVO engine (United Kingdom) or gasoline-kerosene engine (
 A petrol-paraffin engine differs from a single-fuel
A petrol-paraffin engine differs from a single-fuel
 Petrol-paraffin fuelling is suitable for
Petrol-paraffin fuelling is suitable for
 A petrol-paraffin engine, TVO engine (United Kingdom) or gasoline-kerosene engine (
A petrol-paraffin engine, TVO engine (United Kingdom) or gasoline-kerosene engine (North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
) is an old-fashioned type of dual-fuel
A flexible-fuel vehicle (FFV) or dual-fuel vehicle (colloquially called a flex-fuel vehicle) is an alternative fuel vehicle with an internal combustion engine designed to run on more than one fuel, usually gasoline blended with either ethanol o ...
internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combus ...
with spark-ignition
A spark-ignition engine (SI engine) is an internal combustion engine, generally a petrol engine, where the combustion process of the air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark from a spark plug. This is in contrast to compression-ignition engines, t ...
, designed to start on petrol (gasoline
Gasoline (; ) or petrol (; ) (see ) is a transparent, petroleum-derived flammable liquid that is used primarily as a fuel in most spark-ignited internal combustion engines (also known as petrol engines). It consists mostly of organic co ...
) and then to switch to run on paraffin (kerosene
Kerosene, paraffin, or lamp oil is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid which is derived from petroleum. It is widely used as a fuel in aviation as well as households. Its name derives from el, κηρός (''keros'') meaning "wax", and was regi ...
) once the engine is warm. The grade of paraffin used is known as tractor vaporising oil
Tractor vaporising oil (TVO) is a fuel for petrol-paraffin engines. It is seldom made or used today. In the United Kingdom and Australia, after the Second World War, it was commonly used for tractors until diesel engines became commonplace, esp ...
in the UK.
Advantages
The advantages of the petrol-paraffin engine are that (compared to petrol): # Paraffin can be cheaper and/or more readily available # Being less flammable, paraffin is safer to store # Being less volatile, paraffin is less likely to go "stale" in the tank. Some of these advantages have become illusory since paraffin, once widely available as a cheap fuel, has become rarer and more expensive, particularly in developed countries. Also, while some older vessels still use marine petrol-paraffin engines, most inboard marine engines now tend to be diesels.Equipment
 A petrol-paraffin engine differs from a single-fuel
A petrol-paraffin engine differs from a single-fuel petrol engine
A petrol engine (gasoline engine in American English) is an internal combustion engine designed to run on petrol (gasoline). Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends (such as ''E ...
in that two independent fuel tanks containing petrol and paraffin (respectively) are required, but both fuels may be supplied through the same carburetor
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main meteri ...
or fuel injection
Fuel injection is the introduction of fuel in an internal combustion engine, most commonly automotive engines, by the means of an injector. This article focuses on fuel injection in reciprocating piston and Wankel rotary engines.
All comp ...
system. An example of a fuel-injected petrol-paraffin engine is the Hesselman engine
The Hesselman engine is a hybrid between a petrol engine and a Diesel engine. It was designed and introduced in 1925 by Sweden, Swedish engineer Jonas Hesselman (1877-1957). It represented the first use of direct Gasoline direct injection, gaso ...
.
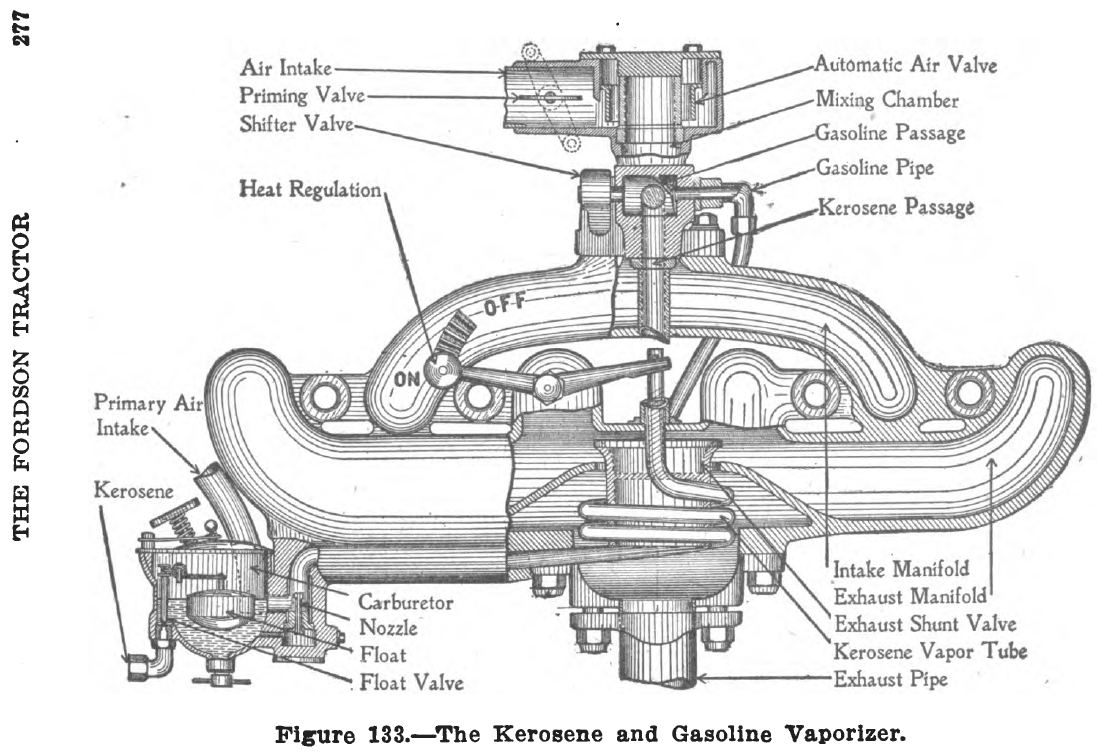
Paraffin is less volatile than petrol, and will not normally ignite at ambient temperatures, so the petrol-paraffin engine is started using petrol, and only when the engine has attained a sufficient operating temperature
An operating temperature is the allowable temperature range of the local ambient environment at which an electrical or mechanical device operates. The device will operate effectively within a specified temperature range which varies based on the de ...
will the engine be switched to paraffin. This switching can be done manually or automatically. Some engines use a vaporizer
Vaporizer or vaporiser may refer to:
*Anesthetic vaporizer, a device used in the administration of anesthesia
* Electronic cigarette, or a part of one (often called a "PV" or "personal vaporizer")
*Humidifier, a household appliance that increases ...
, which uses heat from the exhaust manifold
In automotive engineering, an exhaust manifold collects the exhaust gases from multiple cylinders into one pipe. The word ''manifold'' comes from the Old English word ''manigfeald'' (from the Anglo-Saxon ''manig'' anyand ''feald'' old and refe ...
to vaporize
Vaporization (or vaporisation) of an element or compound is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor. There are two types of vaporization: evaporation and boiling. Evaporation is a surface phenomenon, whereas boiling is a bulk phenomeno ...
the fuel entering the intake system.
Applications
Traditional applications
Petrol-paraffin engines were traditionally found inmotor boat
A motorboat, speedboat or powerboat is a boat that is exclusively powered by an engine.
Some motorboats are fitted with inboard engines, others have an outboard motor installed on the rear, containing the internal combustion engine, the gea ...
s, fishing vessel
A fishing vessel is a boat or ship used to catch fish in the sea, or on a lake or river. Many different kinds of vessels are used in commercial, artisanal and recreational fishing.
The total number of fishing vessels in the world in 2016 was es ...
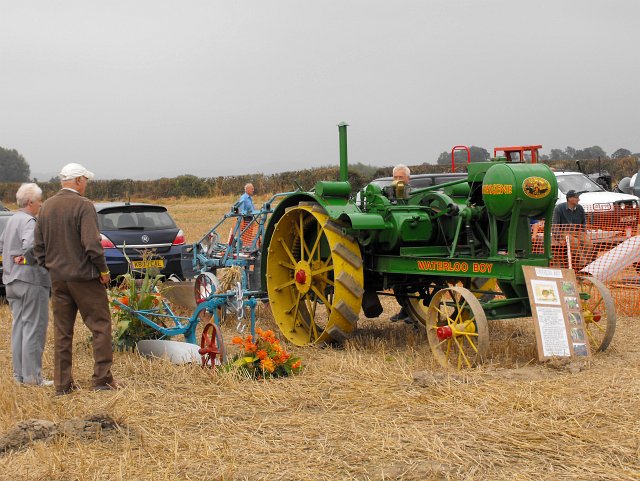
s, small tractor
A tractor is an engineering vehicle specifically designed to deliver a high tractive effort (or torque) at slow speeds, for the purposes of hauling a trailer or machinery such as that used in agriculture, mining or construction. Most common ...
s, light railway
A light railway is a railway built at lower costs and to lower standards than typical "heavy rail": it uses lighter-weight track, and may have more steep gradients and tight curves to reduce civil engineering costs. These lighter standards allow ...
locomotive
A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the Power (physics), motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, Motor coach (rail), motor ...
s, and stationary auxiliary engines, but not in cars or motorcycles.
The Milnes-Daimler motor bus of 1904 (based on the Cannstatt Daimler lorry), operated in London by Thomas Tilling
The Tilling Group was one of two conglomerates that controlled almost all of the major bus operators in the United Kingdom between World Wars I and II and until nationalisation in 1948.
Tilling, together with the other conglomerate, British El ...
, ran on either petrol or paraffin, but for starting the engine, or frequent stop-start work, petrol continuously was the preferable option. The airflow from the carburettor
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main meterin ...
was heated by diverted exhaust gas
Exhaust gas or flue gas is emitted as a result of the combustion of fuels such as natural gas, gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, fuel oil, biodiesel blends, or coal. According to the type of engine, it is discharged into the atmosphere through an ...
.
Design
 Petrol-paraffin fuelling is suitable for
Petrol-paraffin fuelling is suitable for four-stroke cycle
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either directi ...
piston engines and wankel engine
The Wankel engine (, ) is a type of internal combustion engine using an Eccentric (mechanism), eccentric rotary combustion engine, rotary design to convert pressure into rotating motion. It was invented by German engineer Felix Wankel, and desi ...
s. A petrol/paraffin engine tends to run hotter whilst burning paraffin, and so the cooling system must be sufficiently robust. Being slower burning, the paraffin requires the longer combustion period that a four-stroke engine can provide; so two-stroke
A two-stroke (or two-stroke cycle) engine is a type of internal combustion engine that completes a Thermodynamic power cycle, power cycle with two strokes (up and down movements) of the piston during one power cycle, this power cycle being comple ...
versions are rare J.A.P.
JA Prestwich Industries, was a British engineering equipment manufacturing company named after founder John Alfred Prestwich, which was formed in 1951 by the amalgamation of J.A.Prestwich and Company Limited and Pencils Ltd.
History
John Pres ...
used their 16H engine on TVO. Although modern petrol engines may have compression ratios typically between 9:1 and 12:1, a petrol-paraffin engine requires a lower compression ratio
The compression ratio is the ratio between the volume of the cylinder and combustion chamber in an internal combustion engine at their maximum and minimum values.
A fundamental specification for such engines, it is measured two ways: the stati ...
of 8:1 or less, to avoid pre-ignition of the fuel-air mixture which would cause damage from engine knocking
In spark ignition internal combustion engines, knocking (also knock, detonation, spark knock, pinging or pinking) occurs when combustion of some of the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder does not result from propagation of the flame front ignite ...
. Most existing petrol aero-engines have low compression ratios, around 8:1 or 9:1, making dual-fuel conversions viable.
Fuel
The fuel used in petrol-paraffin engines was known asTractor vaporising oil
Tractor vaporising oil (TVO) is a fuel for petrol-paraffin engines. It is seldom made or used today. In the United Kingdom and Australia, after the Second World War, it was commonly used for tractors until diesel engines became commonplace, esp ...
(TVO) in the United Kingdom and as Power kerosene in Australia. TVO was withdrawn from sale by UK suppliers in 1974 but has been re-introduced by at least one supplier.
Naphthalene locomotive
A railway locomotive using ''solid''naphthalene
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromati ...
was built by Schneider-Creusot
Schneider et Cie, also known as Schneider-Creusot for its birthplace in the French town of Le Creusot, was a historic French iron and steel-mill company which became a major arms manufacturer. In the 1960s, it was taken over by the Belgian Empain ...
in France in 1913. It was a 70 bhp petrol-paraffin engine, but using solid naphthalene rather than paraffin, simply as a cheaper fuel. The naphthalene was melted and vaporised by a water jacket, heated by the engine.
References
{{Reflist, 30em Internal combustion piston engines Gasoline engines