pericardial tamponade on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cardiac tamponade, also known as pericardial tamponade (), is the buildup of fluid in the pericardium (the sac around the
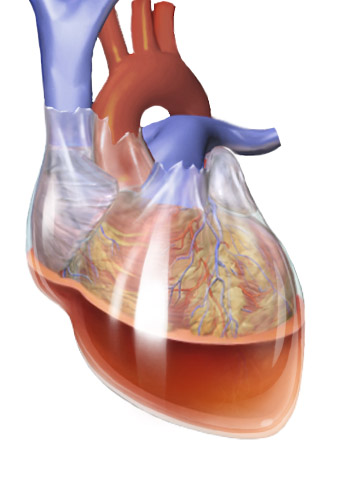 The pericardium, the double-walled sac surrounding the heart, consists of a fibrous pericardium layer on the outside and a double-layered serous pericardium on the inside. Between the two layers of the serous pericardium is the pericardial space, which is filled with lubricating serous fluid that prevents friction as the heart contracts. The outer layer of the heart is made of fibrous tissue which does not easily stretch, so once excess fluid begins to enter the pericardial space, pressure starts to increase. Consequently, the heart becomes compressed due to its inability to fully relax.
If fluid continues to accumulate, each successive diastolic period leads to less blood entering the ventricles. Eventually, increasing pressure on the heart forces the
The pericardium, the double-walled sac surrounding the heart, consists of a fibrous pericardium layer on the outside and a double-layered serous pericardium on the inside. Between the two layers of the serous pericardium is the pericardial space, which is filled with lubricating serous fluid that prevents friction as the heart contracts. The outer layer of the heart is made of fibrous tissue which does not easily stretch, so once excess fluid begins to enter the pericardial space, pressure starts to increase. Consequently, the heart becomes compressed due to its inability to fully relax.
If fluid continues to accumulate, each successive diastolic period leads to less blood entering the ventricles. Eventually, increasing pressure on the heart forces the
heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to ...
), resulting in compression of the heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to ...
. Onset may be rapid or gradual. Symptoms typically include those of obstructive shock
Obstructive shock is one of the four types of shock, caused by a physical obstruction in the flow of blood. Obstruction can occur at the level of the great vessels or the heart itself. Causes include pulmonary embolism, cardiac tamponade, and tens ...
including shortness of breath, weakness, lightheadedness, and cough. Other symptoms may relate to the underlying cause.
Common causes of cardiac tamponade include cancer, kidney failure, chest trauma
A chest injury, also known as chest trauma, is any form of physical injury to the chest including the ribs, heart and lungs. Chest injuries account for 25% of all deaths from traumatic injury. Typically chest injuries are caused by blunt mechanisms ...
, myocardial infarction, and pericarditis. Other causes include connective tissues diseases, hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as po ...
, aortic rupture, autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly a ...
, and complications of cardiac surgery
Cardiac surgery, or cardiovascular surgery, is surgery on the heart or great vessels performed by cardiac surgeons. It is often used to treat complications of ischemic heart disease (for example, with coronary artery bypass grafting); to cor ...
. In Africa, tuberculosis is a relatively common cause.
Diagnosis may be suspected based on low blood pressure, jugular venous distension, or quiet heart sounds
Heart sounds are the noises generated by the beating heart and the resultant flow of blood through it. Specifically, the sounds reflect the turbulence created when the heart valves snap shut. In cardiac auscultation, an examiner may use a steth ...
(together known as Beck's triad). A pericardial rub
A pericardial friction rub, also pericardial rub, is an audible medical sign used in the diagnosis of pericarditis. Upon auscultation, this sign is an extra heart sound of to-and-fro character, typically with three components, two systolic and one ...
may be present in cases due to inflammation. The diagnosis may be further supported by specific electrocardiogram (ECG) changes, chest X-ray
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in me ...
, or an ultrasound of the heart. If fluid increases slowly the pericardial sac can expand to contain more than 2 liters; however, if the increase is rapid, as little as 200 mL can result in tamponade.
Tamponade is a medical emergency. When it results in symptoms, drainage is necessary. This can be done by pericardiocentesis
Pericardiocentesis (PCC), also called pericardial tap, is a medical procedure where fluid is aspirated from the pericardium (the sac enveloping the heart).
Anatomy and Physiology
The pericardium is a fibrous sac surrounding the heart composed o ...
, surgery to create a pericardial window
A pericardial window is a cardiac surgical procedure to create a fistula – or "window" – from the pericardial space to the pleural cavity. The purpose of the window is to allow a pericardial effusion or cardiac tamponade to drain from the ...
, or a pericardiectomy
Pericardiectomy is the surgical removal of part or most of the pericardium. This operation is most commonly used to relieve constrictive pericarditis, or to remove a pericardium that is calcified and fibrous. It may also be used for severe or recu ...
. Drainage may also be necessary to rule out infection or cancer. Other treatments may include the use of dobutamine or in those with low blood volume
Hypovolemia, also known as volume depletion or volume contraction, is a state of abnormally low extracellular fluid in the body. This may be due to either a loss of both salt and water or a decrease in blood volume. Hypovolemia refers to the loss ...
, intravenous fluids
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrie ...
. Those with few symptoms and no worrisome features can often be closely followed. The frequency of tamponade is unclear. One estimate from the United States places it at 2 per 10,000 per year.
Signs and symptoms
Onset may be rapid (acute) or more gradual (subacute). Signs of cardiac tamponade typically include those ofcardiogenic shock
Cardiogenic shock (CS) is a medical emergency resulting from inadequate blood flow due to the dysfunction of the ventricles of the heart.Textbooks of Internal MedicinHarrison's Principles of Internal Medicine 16th Edition, The McGraw-Hill Compan ...
including shortness of breath, weakness, lightheadedness, cough and those of Beck's triad e.g. jugular vein distention, quiet heart sounds and hypotension. Other symptoms may relate to the underlying cause.
Other general signs of shock (such as fast heart rate, shortness of breath and decreasing level of consciousness
An altered level of consciousness is any measure of arousal other than normal. Level of consciousness (LOC) is a measurement of a person's arousability and responsiveness to stimuli from the environment.
A mildly depressed level of consciousne ...
) may also occur. However, some of these signs may not be present in certain cases. A fast heart rate, although expected, may be absent in people with uremia
Uremia is the term for high levels of urea in the blood. Urea is one of the primary components of urine. It can be defined as an excess of amino acid and protein metabolism end products, such as urea and creatinine, in the blood that would be no ...
and hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as po ...
.
According to Reddy,Reddy PS, Curtiss EI, Uretsky BF. Spectrum of hemodynamic changes in cardiac tamponade. Am J Cardiol. 1990 Dec 15;66(20):1487-91. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(90)90540-h. PMID: 2251997. cardiac tamponade and its progression can be described in 3 different phases. In phase I, the required filling pressure increases due to the high stiffness of the ventricles. This is because of the accumulation of pericardial fluid in the pericardial cavity. During phase II, the pericardial pressure exceeds the ventricular filling pressure caused by the further accumulation of pericardial fluid. This results in a decrease in cardiac input and output. A further decrease of cardiac input and output is typical in phase III of the progression of cardiac tamponade. This is caused by the equilibration of left ventricular filling and pericardial pressure, leading to “severe deterioration of end-organ perfusion.” Some of the symptoms, as a consequence, include abdominal pain due to liver engorgement.
Causes
Cardiac tamponade is caused by a large or uncontrolledpericardial effusion
A pericardial effusion is an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pericardial cavity. The pericardium is a two-part membrane surrounding the heart: the outer fibrous connective membrane and an inner two-layered serous membrane. The two layers of t ...
, i.e. the buildup of fluid inside the pericardium. This commonly occurs as a result of chest trauma
A chest injury, also known as chest trauma, is any form of physical injury to the chest including the ribs, heart and lungs. Chest injuries account for 25% of all deaths from traumatic injury. Typically chest injuries are caused by blunt mechanisms ...
(both blunt and penetrating), but can also be caused by myocardial infarction, myocardial rupture
Myocardial rupture is a laceration of the ventricles or atria of the heart, of the interatrial or interventricular septum, or of the papillary muscles. It is most commonly seen as a serious sequela of an acute myocardial infarction (heart at ...
, cancer (most often Hodgkin lymphoma), uremia
Uremia is the term for high levels of urea in the blood. Urea is one of the primary components of urine. It can be defined as an excess of amino acid and protein metabolism end products, such as urea and creatinine, in the blood that would be no ...
, pericarditis, or cardiac surgery, and rarely occurs during retrograde aortic dissection
Aortic dissection (AD) occurs when an injury to the innermost layer of the aorta allows blood to flow between the layers of the aortic wall, forcing the layers apart. In most cases, this is associated with a sudden onset of severe chest or ...
, or while the person is taking anticoagulant therapy. The effusion can occur rapidly (as in the case of trauma or myocardial rupture), or over a more gradual period of time (as in cancer). The fluid involved is often blood, but pus
Pus is an exudate, typically white-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammation during bacterial or fungal infection. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection ...
is also found in some circumstances.
Surgery
One of the most common settings for cardiac tamponade is in the first 7 days after heart surgery. After heart surgery, chest tubes are placed to drain blood. These chest tubes, however, are prone to clot formation. When a chest tube becomes occluded or clogged, the blood that should be drained can accumulate around the heart, leading to tamponade.Pathophysiology
 The pericardium, the double-walled sac surrounding the heart, consists of a fibrous pericardium layer on the outside and a double-layered serous pericardium on the inside. Between the two layers of the serous pericardium is the pericardial space, which is filled with lubricating serous fluid that prevents friction as the heart contracts. The outer layer of the heart is made of fibrous tissue which does not easily stretch, so once excess fluid begins to enter the pericardial space, pressure starts to increase. Consequently, the heart becomes compressed due to its inability to fully relax.
If fluid continues to accumulate, each successive diastolic period leads to less blood entering the ventricles. Eventually, increasing pressure on the heart forces the
The pericardium, the double-walled sac surrounding the heart, consists of a fibrous pericardium layer on the outside and a double-layered serous pericardium on the inside. Between the two layers of the serous pericardium is the pericardial space, which is filled with lubricating serous fluid that prevents friction as the heart contracts. The outer layer of the heart is made of fibrous tissue which does not easily stretch, so once excess fluid begins to enter the pericardial space, pressure starts to increase. Consequently, the heart becomes compressed due to its inability to fully relax.
If fluid continues to accumulate, each successive diastolic period leads to less blood entering the ventricles. Eventually, increasing pressure on the heart forces the septum
In biology, a septum (Latin for ''something that encloses''; plural septa) is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as septate.
Examples
Human anatomy
* Interatr ...
to bend in towards the left ventricle, leading to a decrease in stroke volume. This causes the development of obstructive shock
Obstructive shock is one of the four types of shock, caused by a physical obstruction in the flow of blood. Obstruction can occur at the level of the great vessels or the heart itself. Causes include pulmonary embolism, cardiac tamponade, and tens ...
, which if left untreated may lead to cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. It is a medical emergency that, without immediate medical intervention, will result in sudden cardiac death within minutes. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and possi ...
(often presenting as pulseless electrical activity
Pulseless electrical activity (PEA) refers to cardiac arrest in which the electrocardiogram shows a heart rhythm that should produce a pulse, but does not. Pulseless electrical activity is found initially in about 55% of people in cardiac arrest.
...
). The decrease in stroke volume can also ultimately lead to a decrease in cardiac output, which could be signaled by tachycardia and hypotension.
Diagnosis
The three classic signs, known as Beck's triad, are low blood pressure, jugular-venous distension, and muffledheart sounds
Heart sounds are the noises generated by the beating heart and the resultant flow of blood through it. Specifically, the sounds reflect the turbulence created when the heart valves snap shut. In cardiac auscultation, an examiner may use a steth ...
. Other signs may include pulsus paradoxus
Pulsus paradoxus, also paradoxic pulse or paradoxical pulse, is an abnormally large decrease in stroke volume, systolic blood pressure and pulse wave amplitude during inspiration. The normal fall in pressure is less than 10 mmHg. When the drop i ...
(a drop of at least 10 mmHg in arterial blood pressure with inspiration), and ST segment changes on the electrocardiogram, which may also show low voltage QRS complexes.
Medical imaging
Tamponade can often be diagnosed radiographically.Echocardiography
An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart.
It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound.
Echocardiography has become routinely used in th ...
, which is the diagnostic test of choice, often demonstrates an enlarged pericardium or collapsed ventricles. A large cardiac tamponade will show as an enlarged globular-shaped heart on chest x-ray. During inspiration, the negative pressure in the thoracic cavity will cause increased pressure into the right ventricle. This increased pressure in the right ventricle will cause the interventricular septum to bulge towards the left ventricle, leading to decreased filling of the left ventricle. At the same time, right ventricle volume is markedly diminished and sometimes it can collapse.
Differential diagnosis
Initial diagnosis of cardiac tamponade can be challenging, as there is a broad differential diagnosis. The differential includes possible diagnoses based on symptoms, time course, mechanism of injury, patient history. Rapid onset cardiac tamponade may also appear similar to pleural effusions, shock, pulmonary embolism, and tension pneumothorax. If symptoms appeared more gradually, the differential diagnosis includes acute heart failure. In a person with trauma presenting withpulseless electrical activity
Pulseless electrical activity (PEA) refers to cardiac arrest in which the electrocardiogram shows a heart rhythm that should produce a pulse, but does not. Pulseless electrical activity is found initially in about 55% of people in cardiac arrest.
...
in the absence of hypovolemia and tension pneumothorax, the most likely diagnosis is cardiac tamponade.American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma (2007). ''Advanced Trauma Life Support for Doctors, 7th Edition''. Chicago: American College of Surgeons
In addition to the diagnostic complications afforded by the wide-ranging differential diagnosis for chest pain, diagnosis can be additionally complicated by the fact that people will often be weak or faint at presentation. For instance, a fast rate of breathing and difficulty breathing on exertion that progresses to air hunger at rest can be a key diagnostic symptom, but it may not be possible to obtain such information from people who are unconscious or who have convulsions at presentation.
Treatment
Pre-hospital care
Initial treatment given will usually be supportive in nature, for example administration of oxygen, and monitoring. There is little care that can be provided pre-hospital other than general treatment for shock. Some teams have performed an emergencythoracotomy
A thoracotomy is a surgical procedure to gain access into the pleural space of the chest. It is performed by surgeons (emergency physicians or paramedics under certain circumstances) to gain access to the thoracic organs, most commonly the he ...
to release clotting in the pericardium caused by a penetrating chest injury.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment is the key to survival with tamponade. Some pre-hospital providers will have facilities to provide pericardiocentesis
Pericardiocentesis (PCC), also called pericardial tap, is a medical procedure where fluid is aspirated from the pericardium (the sac enveloping the heart).
Anatomy and Physiology
The pericardium is a fibrous sac surrounding the heart composed o ...
, which can be life-saving. If the person has already suffered a cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. It is a medical emergency that, without immediate medical intervention, will result in sudden cardiac death within minutes. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and possi ...
, pericardiocentesis alone cannot ensure survival, and so rapid evacuation to a hospital is usually the more appropriate course of action.
Hospital management
Initial management in hospital is by pericardiocentesis. This involves the insertion of a needle through the skin and into the pericardium and aspirating fluid under ultrasound guidance preferably. This can be done laterally through the intercostal spaces, usually the fifth, or as a subxiphoid approach. A left parasternal approach begins 3 to 5 cm left of the sternum to avoid the left internal mammary artery, in the 5thintercostal space
The intercostal space (ICS) is the anatomic space between two ribs (Lat. costa). Since there are 12 ribs on each side, there are 11 intercostal spaces, each numbered for the rib superior to it.
Structures in intercostal space
* several kinds ...
. Often, a cannula
A cannula (; Latin meaning 'little reed'; plural or ) is a tube that can be inserted into the body, often for the delivery or removal of fluid or for the gathering of samples. In simple terms, a cannula can surround the inner or outer surfaces ...
is left in place during resuscitation following initial drainage so that the procedure can be performed again if the need arises. If facilities are available, an emergency pericardial window
A pericardial window is a cardiac surgical procedure to create a fistula – or "window" – from the pericardial space to the pleural cavity. The purpose of the window is to allow a pericardial effusion or cardiac tamponade to drain from the ...
may be performed instead, during which the pericardium is cut open to allow fluid to drain. Following stabilization of the person, surgery is provided to seal the source of the bleed and mend the pericardium.
Following heart surgery, the amount of chest tube drainage is monitored. If the drainage volume drops off, and the blood pressure goes down, this can suggest a tamponade due to chest tube clogging. In that case, the person is taken back to the operating room for an emergency reoperation.
If aggressive treatment is offered immediately and no complications arise (shock, AMI or arrhythmia, heart failure, aneurysm, carditis, embolism, or rupture), or they are dealt with quickly and fully contained, then adequate survival is still a distinct possibility.
Epidemiology
The frequency of tamponade is unclear. One estimate from the United States places it at 2 per 10,000 per year. It is estimated to occur in 2% of those with stab or gunshot wounds to the chest.References
External links
{{Trauma , state=autocollapse Chest trauma Pericardial disorders Disorders of fascia Heart diseases Medical emergencies Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate