pattern formation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The science of pattern formation deals with the visible, ( statistically) orderly outcomes of
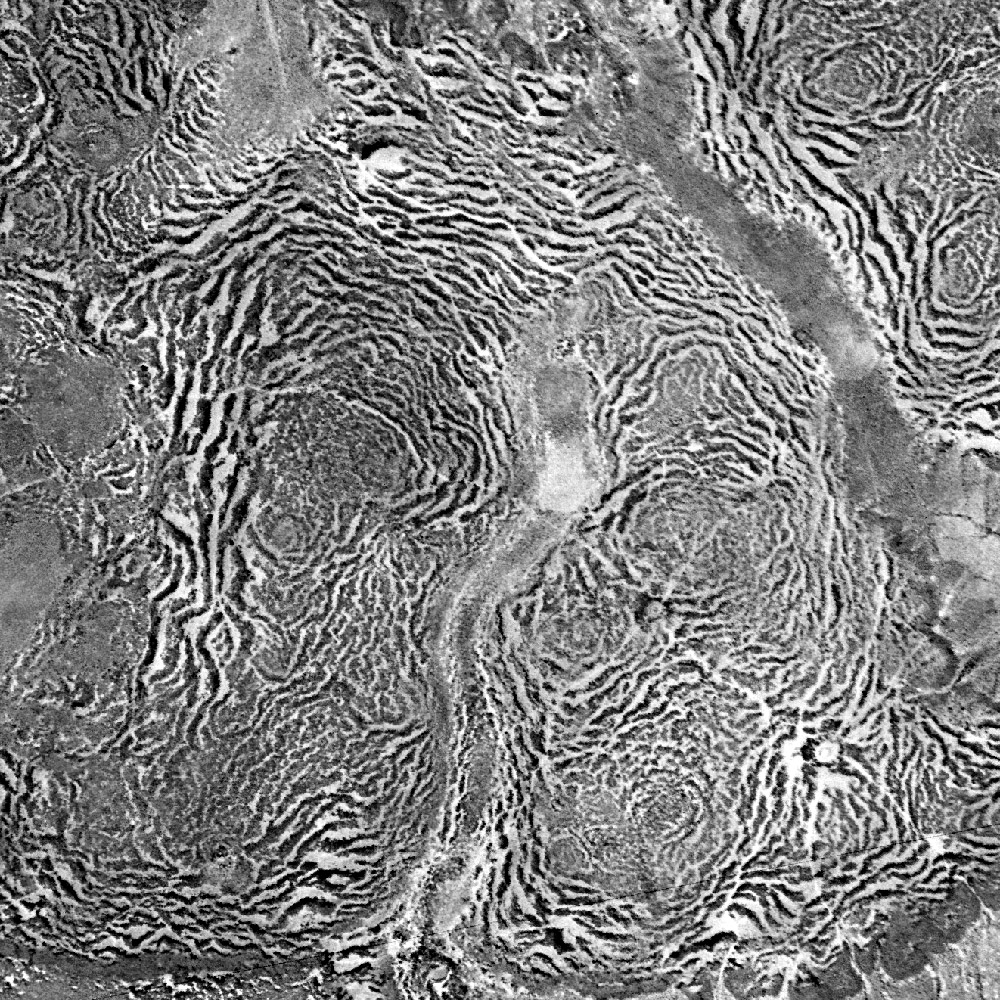 Vegetation patterns such as
Vegetation patterns such as
self-organization
Self-organization, also called spontaneous order in the social sciences, is a process where some form of overall order arises from local interactions between parts of an initially disordered system. The process can be spontaneous when suff ...
and the common principles behind similar patterns in nature
Patterns in nature are visible regularities of form found in the natural world. These patterns recur in different contexts and can sometimes be modelled mathematically. Natural patterns include symmetries, trees, spirals, meanders, waves, ...
.
In developmental biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and differentiation of stem ...
, pattern formation refers to the generation of complex organizations of cell fates in space and time. The role of genes in pattern formation is an aspect of morphogenesis
Morphogenesis (from the Greek ''morphê'' shape and ''genesis'' creation, literally "the generation of form") is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of dev ...
, the creation of diverse anatomies from similar genes, now being explored in the science of evolutionary developmental biology
Evolutionary developmental biology (informally, evo-devo) is a field of biological research that compares the developmental processes of different organisms to infer how developmental processes evolved.
The field grew from 19th-century begin ...
or evo-devo. The mechanisms involved are well seen in the anterior-posterior patterning of embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm ...
s from the model organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the working ...
''Drosophila melanogaster
''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (the taxonomic order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the " vinegar fly" or "pomace fly". Starting with ...
'' (a fruit fly), one of the first organisms to have its morphogenesis studied, and in the eyespots of butterflies, whose development is a variant of the standard (fruit fly) mechanism.
Patterns in nature
Examples of pattern formation can be found in biology, physics, and science, and can readily be simulated with computer graphics, as described in turn below.Biology
Biological patterns such as animal markings, the segmentation of animals, andphyllotaxis
In botany, phyllotaxis () or phyllotaxy is the arrangement of leaves on a plant stem. Phyllotactic spirals form a distinctive class of patterns in nature.
Leaf arrangement
The basic arrangements of leaves on a stem are opposite and alternat ...
are formed in different ways.
In developmental biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and differentiation of stem ...
, pattern formation describes the mechanism by which initially equivalent cells in a developing tissue in an embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm ...
assume complex forms and functions. Embryogenesis
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm ...
, such as of the fruit fly ''Drosophila'', involves coordinated control of cell fates. Pattern formation is genetically controlled, and often involves each cell in a field sensing and responding to its position along a morphogen
A morphogen is a substance whose non-uniform distribution governs the pattern of tissue development in the process of morphogenesis or pattern formation, one of the core processes of developmental biology, establishing positions of the various ...
gradient, followed by short distance cell-to-cell communication through cell signaling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellula ...
pathways to refine the initial pattern. In this context, a field of cells is the group of cells whose fates are affected by responding to the same set positional information cues. This conceptual model was first described as the French flag model in the 1960s. More generally, the morphology of organisms is patterned by the mechanisms of evolutionary developmental biology
Evolutionary developmental biology (informally, evo-devo) is a field of biological research that compares the developmental processes of different organisms to infer how developmental processes evolved.
The field grew from 19th-century begin ...
, such as changing the timing and positioning of specific developmental events in the embryo.
Possible mechanisms of pattern formation in biological systems include the classical reaction–diffusion model proposed by Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher, and theoretical biologist. Turing was highly influential in the development of theoretical co ...
and the more recently found elastic instability
Elastic instability is a form of instability occurring in elastic systems, such as buckling of beams and plates subject to large compressive loads.
There are a lot of ways to study this kind of instability. One of them is to use the method of in ...
mechanism which is thought to be responsible for the fold patterns on the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting o ...
of higher animals, among other things.
Growth of colonies
Bacterial colonies show a large variety of patterns formed during colony growth. The resulting shapes depend on the growth conditions. In particular, stresses (hardness of the culture medium, lack of nutrients, etc.) enhance the complexity of the resulting patterns. Other organisms such asslime mould
Slime mold or slime mould is an informal name given to several kinds of unrelated eukaryotic organisms with a life cycle that includes a free-living single-celled stage and the formation of spores. Spores are often produced in macroscopic m ...
s display remarkable patterns caused by the dynamics of chemical signaling. Cellular embodiment (elongation and adhesion) can also have an impact on the developing patterns.
Vegetation patterns
 Vegetation patterns such as
Vegetation patterns such as tiger bush
Tiger bush, or brousse tigrée in the French language, is a patterned vegetation community and ground consisting of alternating bands of trees, shrubs, or grass separated by bare ground or low herb cover, that run roughly parallel to contour ...
and fir wave
A fir wave is a set of alternating bands of fir trees in sequential stages of development, observed in forests on exposed mountain slopes in several areas, including northeastern North America and Japan. Fir waves develop by wave-regeneration fol ...
s form for different reasons. Tiger bush consists of stripes of bushes on arid slopes in countries such as Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languages The
''SpiralZoom.com''
an educational website about the science of pattern formation, spirals in nature, and spirals in the mythic imagination.
'15-line Matlab code'
A simple 15-line Matlab program to simulate 2D pattern formation for reaction-diffusion model. {{DEFAULTSORT:Pattern Formation Developmental biology Articles containing video clips
Brusselator
The Brusselator is a theoretical model for a type of autocatalytic reaction.
The Brusselator model was proposed by Ilya Prigogine and his collaborators at the Université Libre de Bruxelles.
It is a portmanteau of Brussels and oscillator ...
model developed by Ilya Prigogine
Viscount Ilya Romanovich Prigogine (; russian: Илья́ Рома́нович Приго́жин; 28 May 2003) was a physical chemist and Nobel laureate noted for his work on dissipative structures, complex systems, and irreversibility.
Biogr ...
and collaborators is one such example that exhibits Turing instability. Pattern formation in chemical systems often involve oscillatory chemical kinetics or autocatalytic reactions such as Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction or Briggs–Rauscher reaction. In industrial applications such as chemical reactors, pattern formation can lead to temperature hot spots which can reduce the yield or create hazardous safety problems such as a thermal runaway
Thermal runaway describes a process that is accelerated by increased temperature, in turn releasing energy that further increases temperature. Thermal runaway occurs in situations where an increase in temperature changes the conditions in a way ...
. The emergence of pattern formation can be studied by mathematical modeling and simulation of the underlying reaction-diffusion system.
Similarly as in chemical systems, patterns can develop in a weakly ionized plasma of a positive column of a glow discharge. In such cases creation and annihilation of charged particles due to collisions of atoms corresponds to reactions in chemical systems. Corresponding processes are essentially non-linear and lead in a discharge tube to formation of striations with regular or random character.
* Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction
* Liesegang rings
* Ionization waves
Physics
When a planar body of fluid under the influence of gravity is heated from below, Rayleigh-Bénard convection can form organized cells in hexagons or other shapes. These patterns form on the surface of the sun and in the mantle of the Earth as well as during more pedestrian processes. The interaction between rotation, gravity, and convection can cause planetary atmospheres to form patterns, as is seen in Saturn's hexagon and theGreat Red Spot
The Great Red Spot is a persistent high-pressure region in the atmosphere of Jupiter, producing an anticyclonic storm that is the largest in the Solar System. Located 22 degrees south of Jupiter's equator, it produces wind-speeds up to 432&nbs ...
and stripes of Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth t ...
. The same processes cause ordered cloud formations on Earth, such as stripes and rolls.
In the 1980s Lugiato and Lefever developed a model of light propagation in an optical cavity that results in pattern formation by the exploitation of nonlinear effects.
Precipitating and solidifying materials can crystallize into intricate patterns, such as those seen in snowflakes and dendritic crystals.
Mathematics
Sphere packing
In geometry, a sphere packing is an arrangement of non-overlapping spheres within a containing space. The spheres considered are usually all of identical size, and the space is usually three-dimensional Euclidean space. However, sphere packi ...
s and coverings. Mathematics underlies the other pattern formation mechanisms listed.
Computer graphics
Some types ofautomata
An automaton (; plural: automata or automatons) is a relatively self-operating machine, or control mechanism designed to automatically follow a sequence of operations, or respond to predetermined instructions.Automaton – Definition and More ...
have been used to generate organic-looking textures for more realistic shading
Shading refers to the depiction of depth perception in 3D models (within the field of 3D computer graphics) or illustrations (in visual art) by varying the level of darkness. Shading tries to approximate local behavior of light on the object's ...
of 3d objects.
A popular Photoshop plugin, KPT 6, included a filter called 'KPT reaction'. Reaction produced reaction–diffusion style patterns based on the supplied seed image.
A similar effect to the 'KPT reaction' can be achieved with convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions ( and ) that produces a third function (f*g) that expresses how the shape of one is modified by the other. The term ''convolution'' ...
functions in digital image processing
Digital image processing is the use of a digital computer to process digital images through an algorithm. As a subcategory or field of digital signal processing, digital image processing has many advantages over analog image processing. It all ...
, with a little patience, by repeatedly sharpening and blurring an image in a graphics editor. If other filters are used, such as emboss
EMBOSS is a free open source software analysis package developed for the needs of the molecular biology and bioinformatics user community. The software automatically copes with data in a variety of formats and even allows transparent retrieval of ...
or edge detection
Edge detection includes a variety of mathematical methods that aim at identifying edges, curves in a digital image at which the image brightness changes sharply or, more formally, has discontinuities. The same problem of finding discontinuitie ...
, different types of effects can be achieved.
Computers are often used to simulate
A simulation is the imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time. Simulations require the use of models; the model represents the key characteristics or behaviors of the selected system or process, whereas the ...
the biological, physical or chemical processes that lead to pattern formation, and they can display the results in a realistic way. Calculations using models like reaction–diffusion or MClone are based on the actual mathematical equations designed by the scientists to model the studied phenomena.
References
Bibliography
*External links
''SpiralZoom.com''
an educational website about the science of pattern formation, spirals in nature, and spirals in the mythic imagination.
'15-line Matlab code'
A simple 15-line Matlab program to simulate 2D pattern formation for reaction-diffusion model. {{DEFAULTSORT:Pattern Formation Developmental biology Articles containing video clips