Outer Solar System on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Solar System
naming guidelines document
. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''
''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''
. is the
 The Solar System formed 4.568 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a region within a large
The Solar System formed 4.568 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a region within a large  Within 50 million years, the pressure and density of hydrogen in the centre of the protostar became great enough for it to begin
Within 50 million years, the pressure and density of hydrogen in the centre of the protostar became great enough for it to begin

 The
The
 The Sun is the Solar System's star and by far its most massive component. Its large mass (332,900 Earth masses), which comprises 99.86% of all the mass in the Solar System,
produces temperatures and densities in its core high enough to sustain nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. This releases an enormous amount of
The Sun is the Solar System's star and by far its most massive component. Its large mass (332,900 Earth masses), which comprises 99.86% of all the mass in the Solar System,
produces temperatures and densities in its core high enough to sustain nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. This releases an enormous amount of
 Outside of the main part of the Sun's atmosphere extends the
Outside of the main part of the Sun's atmosphere extends the
 The inner Solar System is the region comprising the
The inner Solar System is the region comprising the
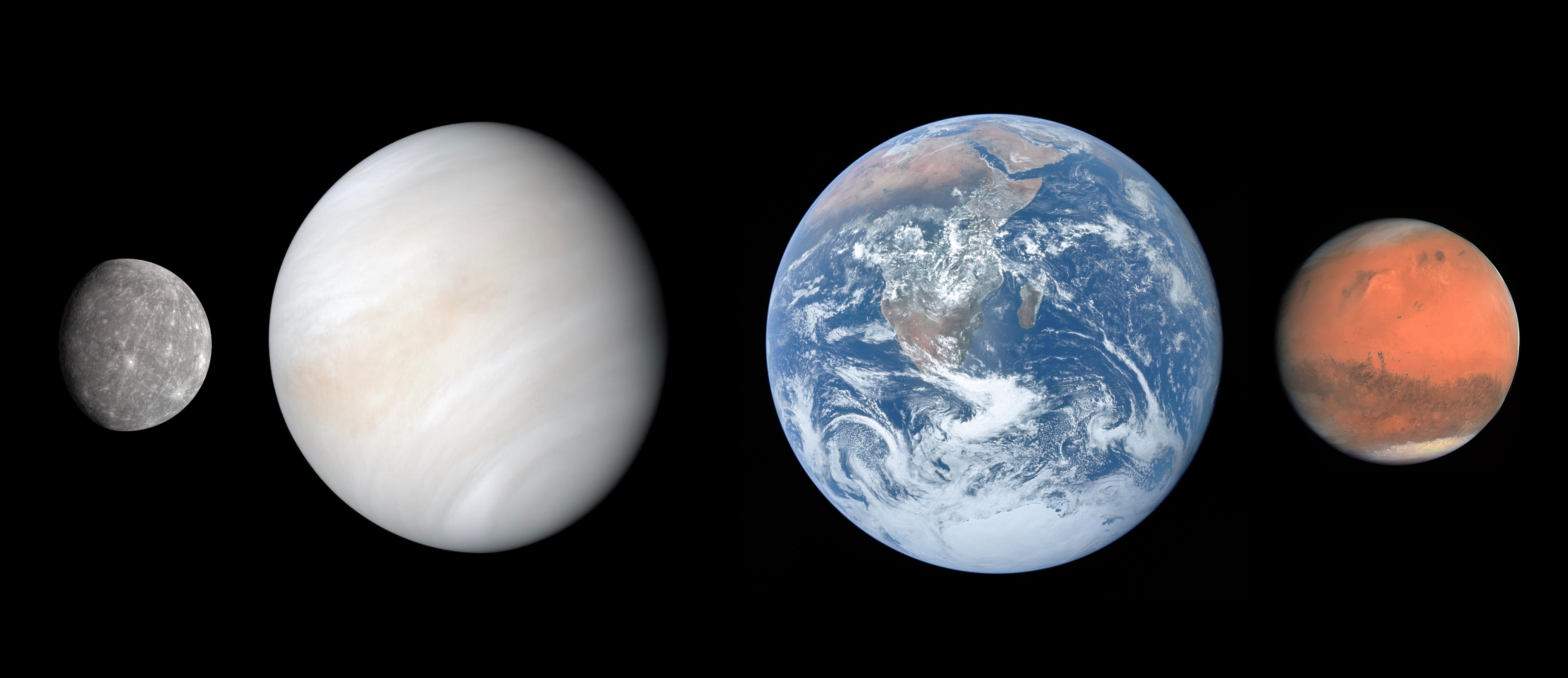 The four terrestrial or inner planets have dense, rocky compositions, few or no
The four terrestrial or inner planets have dense, rocky compositions, few or no
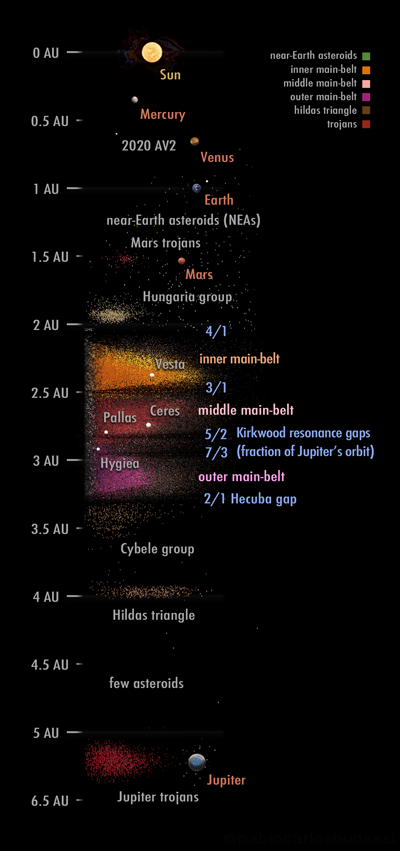 Asteroids except for the largest, Ceres, are classified as small Solar System bodies and are composed mainly of refractory rocky and metallic minerals, with some ice. They range from a few metres to hundreds of kilometres in size. Asteroids smaller than one meter are usually called
Asteroids except for the largest, Ceres, are classified as small Solar System bodies and are composed mainly of refractory rocky and metallic minerals, with some ice. They range from a few metres to hundreds of kilometres in size. Asteroids smaller than one meter are usually called
 The outer region of the Solar System is home to the
The outer region of the Solar System is home to the
 The four outer planets, also called giant planets or Jovian planets, collectively make up 99% of the mass known to orbit the Sun. Jupiter and Saturn are together more than 400 times the mass of Earth and consist overwhelmingly of the gases hydrogen and helium, hence their designation as
The four outer planets, also called giant planets or Jovian planets, collectively make up 99% of the mass known to orbit the Sun. Jupiter and Saturn are together more than 400 times the mass of Earth and consist overwhelmingly of the gases hydrogen and helium, hence their designation as
 Comets are small Solar System bodies, typically only a few kilometres across, composed largely of volatile ices. They have highly eccentric orbits, generally a perihelion within the orbits of the inner planets and an aphelion far beyond Pluto. When a comet enters the inner Solar System, its proximity to the Sun causes its icy surface to sublimate and ionise, creating a
Comets are small Solar System bodies, typically only a few kilometres across, composed largely of volatile ices. They have highly eccentric orbits, generally a perihelion within the orbits of the inner planets and an aphelion far beyond Pluto. When a comet enters the inner Solar System, its proximity to the Sun causes its icy surface to sublimate and ionise, creating a

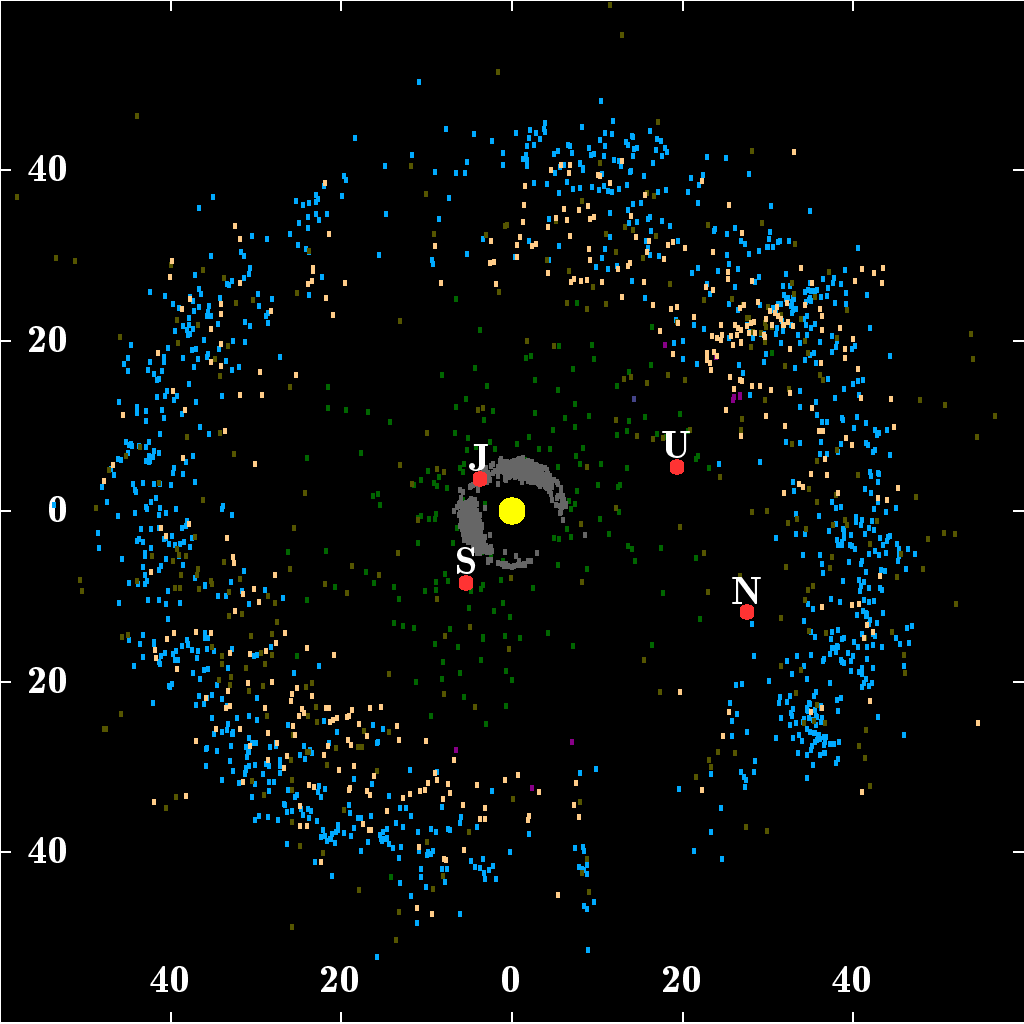
 Inside the orbit of Neptune is the planetary region of the Solar System. Beyond the orbit of Neptune lies the area of the " trans-Neptunian region", with the doughnut-shaped Kuiper belt, home of Pluto and several other dwarf planets, and an overlapping disc of scattered objects, which is tilted toward the plane of the Solar System and reaches much further out than the Kuiper belt. The entire region is still largely unexplored. It appears to consist overwhelmingly of many thousands of small worlds—the largest having a diameter only a fifth that of Earth and a mass far smaller than that of the Moon—composed mainly of rock and ice. This region is sometimes described as the "third zone of the Solar System", enclosing the inner and the outer Solar System.
Inside the orbit of Neptune is the planetary region of the Solar System. Beyond the orbit of Neptune lies the area of the " trans-Neptunian region", with the doughnut-shaped Kuiper belt, home of Pluto and several other dwarf planets, and an overlapping disc of scattered objects, which is tilted toward the plane of the Solar System and reaches much further out than the Kuiper belt. The entire region is still largely unexplored. It appears to consist overwhelmingly of many thousands of small worlds—the largest having a diameter only a fifth that of Earth and a mass far smaller than that of the Moon—composed mainly of rock and ice. This region is sometimes described as the "third zone of the Solar System", enclosing the inner and the outer Solar System.
 The scattered disc, which overlaps the Kuiper belt but extends out to near 500 AU, is thought to be the source of short-period comets. Scattered-disc objects are believed to have been perturbed into erratic orbits by the gravitational influence of Neptune's early outward migration. Most scattered disc objects (SDOs) have perihelia within the Kuiper belt but aphelia far beyond it (some more than 150 AU from the Sun). SDOs' orbits can also be inclined up to 46.8° from the ecliptic plane. Some astronomers consider the scattered disc to be merely another region of the Kuiper belt and describe scattered-disc objects as "scattered Kuiper belt objects". Some astronomers also classify centaurs as inward-scattered Kuiper belt objects along with the outward-scattered residents of the scattered disc.
The scattered disc, which overlaps the Kuiper belt but extends out to near 500 AU, is thought to be the source of short-period comets. Scattered-disc objects are believed to have been perturbed into erratic orbits by the gravitational influence of Neptune's early outward migration. Most scattered disc objects (SDOs) have perihelia within the Kuiper belt but aphelia far beyond it (some more than 150 AU from the Sun). SDOs' orbits can also be inclined up to 46.8° from the ecliptic plane. Some astronomers consider the scattered disc to be merely another region of the Kuiper belt and describe scattered-disc objects as "scattered Kuiper belt objects". Some astronomers also classify centaurs as inward-scattered Kuiper belt objects along with the outward-scattered residents of the scattered disc.
 The Sun's
The Sun's
 The Solar System is surrounded by the
The Solar System is surrounded by the
 Humanity's knowledge of the Solar System has grown incrementally over the centuries. Up to the
Humanity's knowledge of the Solar System has grown incrementally over the centuries. Up to the
A Tediously Accurate Map of the Solar System (web based scroll map scaled to the Moon being 1 pixel)
NASA's Eyes-on-the-Solar-System
NASA's Solar System Exploration
NASA's Solar System Simulator
{{Authority control Planetary science Space science Planetary systems with eight confirmed planets
Capitalization
Capitalization (American English) or capitalisation (British English) is writing a word with its first letter as a capital letter (uppercase letter) and the remaining letters in lower case, in writing systems with a case distinction. The term ...
of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreac ...
, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document
. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''
Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the first and foundational historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP). It traces the historical development of the English language, providing a c ...
'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''
. is the
gravitationally
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the strong ...
bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse
Gravitational collapse is the contraction of an astronomical object due to the influence of its own gravity, which tends to draw matter inward toward the center of gravity. Gravitational collapse is a fundamental mechanism for structure formatio ...
of a giant interstellar molecular cloud
A molecular cloud, sometimes called a stellar nursery (if star formation is occurring within), is a type of interstellar cloud, the density and size of which permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydroge ...
. The vast majority (99.86%) of the system's mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different ele ...
is in the Sun, with most of the remaining mass contained in the planet Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
. The four inner system planets— Mercury, Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
, Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
and Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
—are terrestrial planet
A terrestrial planet, telluric planet, or rocky planet, is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate rocks or metals. Within the Solar System, the terrestrial planets accepted by the IAU are the inner planets closest to the Sun: Mercury, ...
s, being composed primarily of rock and metal. The four giant planet
The giant planets constitute a diverse type of planet much larger than Earth. They are usually primarily composed of low-boiling-point materials (volatiles), rather than rock or other solid matter, but massive solid planets can also exist. The ...
s of the outer system are substantially larger and more massive than the terrestrials. The two largest, Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
and Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
, are gas giant
A gas giant is a giant planet composed mainly of hydrogen and helium. Gas giants are also called failed stars because they contain the same basic elements as a star. Jupiter and Saturn are the gas giants of the Solar System. The term "gas giant" ...
s, being composed mainly of hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
and helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic ta ...
; the next two, Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus ( Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars), grandfather of Zeus (Jupiter) and father of ...
and Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 time ...
, are ice giant
An ice giant is a giant planet composed mainly of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium, such as oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur. There are two ice giants in the Solar System: Uranus and Neptune.
In astrophysics and planetary ...
s, being composed mostly of volatile substances with relatively high melting points compared with hydrogen and helium, such as water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
, ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous ...
, and methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane ...
. All eight planets have nearly circular orbit
A circular orbit is an orbit with a fixed distance around the barycenter; that is, in the shape of a circle.
Listed below is a circular orbit in astrodynamics or celestial mechanics under standard assumptions. Here the centripetal force is ...
s that lie near the plane of Earth's orbit
Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance of 149.60 million km (92.96 million mi) in a counterclockwise direction as viewed from above the Northern Hemisphere. One complete orbit takes days (1 sidereal year), during which time Earth ...
, called the ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agains ...
.
There are an unknown number of smaller dwarf planet
A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit of the Sun, smaller than any of the eight classical planets but still a world in its own right. The prototypical dwarf planet is Pluto. The interest of dwarf planets to ...
s and innumerable small Solar System bodies orbiting the Sun. Six of the major planets, the six largest possible dwarf planets, and many of the smaller bodies are orbited by natural satellite
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are often colloquially referred to as ''moons'' ...
s, commonly called "moons" after Earth's Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
. Two natural satellites, Jupiter's moon Ganymede and Saturn's moon Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
, are larger but not more massive than Mercury, the smallest terrestrial planet, and Jupiter's moon Callisto is nearly as large. Each of the giant planets and some smaller bodies are encircled by planetary ring
A ring system is a disc or ring, orbiting an astronomical object, that is composed of solid material such as dust and moonlets, and is a common component of satellite systems around giant planets. A ring system around a planet is also known ...
s of ice, dust and moonlets. The asteroid belt
The asteroid belt is a torus-shaped region in the Solar System, located roughly between the orbits of the planets Jupiter and Mars. It contains a great many solid, irregularly shaped bodies, of many sizes, but much smaller than planets, c ...
, which lies between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, contains objects composed of rock, metal and ice. Beyond Neptune's orbit lie the Kuiper belt
The Kuiper belt () is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 tim ...
and scattered disc
The scattered disc (or scattered disk) is a distant circumstellar disc in the Solar System that is sparsely populated by icy small solar system bodies, which are a subset of the broader family of trans-Neptunian objects. The scattered-disc obje ...
, which are populations of objects composed mostly of ice and rock.
In the outer reaches of the Solar System lies a class of minor planets called detached object
Detached objects are a dynamical class of minor planets in the outer reaches of the Solar System and belong to the broader family of trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs). These objects have orbits whose points of closest approach to the Sun ( perihel ...
s. There is considerable debate as to how many such objects there will prove to be. Some of these objects are large enough to have rounded under their own gravity and thus to be categorized as dwarf planets. Astronomers generally accept about nine objects as dwarf planets: the asteroid , the Kuiper-belt objects Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the S ...
, , , , and , and the scattered-disc objects , , and . Various small-body populations, including comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ...
s, centaurs
A centaur ( ; grc, κένταυρος, kéntauros; ), or occasionally hippocentaur, is a creature from Greek mythology with the upper body of a human and the lower body and legs of a horse.
Centaurs are thought of in many Greek myths as bein ...
and interplanetary dust cloud
The interplanetary dust cloud, or zodiacal cloud (as the source of the zodiacal light), consists of cosmic dust (small particles floating in outer space) that pervades the space between planets within planetary systems, such as the Solar System ...
s, freely travel between the regions of the Solar System.
The solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the sol ...
, a stream of charged particles flowing outwards from the Sun, creates a bubble-like region of interplanetary medium
The interplanetary medium (IPM) or interplanetary space consists of the mass and energy which fills the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding ...
in the interstellar medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstella ...
known as the heliosphere
The heliosphere is the magnetosphere, astrosphere and outermost atmospheric layer of the Sun. It takes the shape of a vast, bubble-like region of space. In plasma physics terms, it is the cavity formed by the Sun in the surrounding interstell ...
. The heliopause is the point at which pressure from the solar wind is equal to the opposing pressure of the interstellar medium; it extends out to the edge of the scattered disc. The Oort cloud
The Oort cloud (), sometimes called the Öpik–Oort cloud, first described in 1950 by the Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, is a theoretical concept of a cloud of predominantly icy planetesimals proposed to surround the Sun at distances ranging from ...
, which is thought to be the source for long-period comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena are ...
s, may also exist at a distance roughly a thousand times further than the heliosphere. The Solar System is located 26,000 light-years from the center
The Center () is the fifth tallest skyscraper in Hong Kong, after International Commerce Centre, Two International Finance Centre (88 storeys), Central Plaza and Bank of China Tower. With a height of , it comprises 73 storeys. The center is ...
of the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
galaxy
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System ...
in the Orion Arm
The Orion Arm is a minor spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy that is across and approximately in length, containing the Solar System, including Earth. It is also referred to by its full name, the Orion–Cygnus Arm, as well as Local Arm, Orion ...
, which contains most of the visible stars in the night sky
The night sky is the nighttime appearance of celestial objects like stars, planets, and the Moon, which are visible in a clear sky between sunset and sunrise, when the Sun is below the horizon.
Natural light sources in a night sky in ...
. The nearest stars are within the so-called Local Bubble, with the closest, Proxima Centauri
Proxima Centauri is a small, low-mass star located away from the Sun in the southern constellation of Centaurus. Its Latin name means the 'nearest tarof Centaurus'. It was discovered in 1915 by Robert Innes and is the nearest-k ...
, at 4.2441 light-years.
Formation and evolution
 The Solar System formed 4.568 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a region within a large
The Solar System formed 4.568 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a region within a large molecular cloud
A molecular cloud, sometimes called a stellar nursery (if star formation is occurring within), is a type of interstellar cloud, the density and size of which permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydroge ...
. This initial cloud was likely several light-years across and probably birthed several stars. As is typical of molecular clouds, this one consisted mostly of hydrogen, with some helium, and small amounts of heavier elements fused by previous generations of stars. As the region that would become the Solar System, known as the pre-solar nebula, collapsed, conservation of angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum (rarely, moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed sy ...
caused it to rotate faster. The centre, where most of the mass collected, became increasingly hotter than the surrounding disc. As the contracting nebula rotated faster, it began to flatten into a protoplanetary disc with a diameter of roughly and a hot, dense protostar
A protostar is a very young star that is still gathering mass from its parent molecular cloud. The protostellar phase is the earliest one in the process of stellar evolution. For a low-mass star (i.e. that of the Sun or lower), it lasts about 50 ...
at the centre. The planets formed by accretion
Accretion may refer to:
Science
* Accretion (astrophysics), the formation of planets and other bodies by collection of material through gravity
* Accretion (meteorology), the process by which water vapor in clouds forms water droplets around nucl ...
from this disc, in which dust and gas gravitationally attracted each other, coalescing to form ever larger bodies. Hundreds of protoplanets may have existed in the early Solar System, but they either merged or were destroyed or ejected, leaving the planets, dwarf planets, and leftover minor bodies.
Due to their higher boiling points, only metals and silicates could exist in solid form in the warm inner Solar System close to the Sun, and these would eventually form the rocky planets of Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. Because metallic elements only comprised a very small fraction of the solar nebula, the terrestrial planets could not grow very large. The giant planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune) formed further out, beyond the frost line, the point between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter where material is cool enough for volatile icy compounds to remain solid. The ices that formed these planets were more plentiful than the metals and silicates that formed the terrestrial inner planets, allowing them to grow massive enough to capture large atmospheres of hydrogen and helium, the lightest and most abundant elements. Leftover debris that never became planets congregated in regions such as the asteroid belt, Kuiper belt, and Oort cloud. The Nice model
The Nice () model is a scenario for the dynamical evolution of the Solar System. It is named for the location of the Côte d'Azur Observatory—where it was initially developed in 2005—in Nice, France.
It proposes the migration of the giant ...
is an explanation for the creation of these regions and how the outer planets could have formed in different positions and migrated to their current orbits through various gravitational interactions.
 Within 50 million years, the pressure and density of hydrogen in the centre of the protostar became great enough for it to begin
Within 50 million years, the pressure and density of hydrogen in the centre of the protostar became great enough for it to begin thermonuclear fusion
Thermonuclear fusion is the process of atomic nuclei combining or “fusing” using high temperatures to drive them close enough together for this to become possible. There are two forms of thermonuclear fusion: ''uncontrolled'', in which the re ...
. The temperature, reaction rate
The reaction rate or rate of reaction is the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place, defined as proportional to the increase in the concentration of a product per unit time and to the decrease in the concentration of a reactant per uni ...
, pressure, and density increased until hydrostatic equilibrium
In fluid mechanics, hydrostatic equilibrium (hydrostatic balance, hydrostasy) is the condition of a fluid or plastic solid at rest, which occurs when external forces, such as gravity, are balanced by a pressure-gradient force. In the planeta ...
was achieved: the thermal pressure counterbalancing the force of gravity. At this point, the Sun became a main-sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar ...
star. The main-sequence phase, from beginning to end, will last about 10 billion years for the Sun compared to around two billion years for all other phases of the Sun's pre-remnant
Remnant or remnants may refer to:
Religion
* Remnant (Bible), a recurring theme in the Bible
* Remnant (Seventh-day Adventist belief), the remnant theme in the Seventh-day Adventist Church
* ''The Remnant'' (newspaper), a traditional Catholic n ...
life combined. Solar wind from the Sun created the heliosphere
The heliosphere is the magnetosphere, astrosphere and outermost atmospheric layer of the Sun. It takes the shape of a vast, bubble-like region of space. In plasma physics terms, it is the cavity formed by the Sun in the surrounding interstell ...
and swept away the remaining gas and dust from the protoplanetary disc into interstellar space. As helium accumulates at its core the Sun is growing brighter; early in its main-sequence life its brightness was 70% that of what it is today.
The Solar System will remain roughly as it is known today until the hydrogen in the core of the Sun has been entirely converted to helium, which will occur roughly 5 billion years from now. This will mark the end of the Sun's main-sequence life. At that time, the core of the Sun will contract with hydrogen fusion occurring along a shell surrounding the inert helium, and the energy output will be greater than at present. The outer layers of the Sun will expand to roughly 260 times its current diameter, and the Sun will become a red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses ()) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface temperature around o ...
. Because of its increased surface area, the surface of the Sun will be cooler ( at its coolest) than it is on the main sequence.
The expanding Sun is expected to vaporize Mercury as well as Venus, and render Earth uninhabitable (possibly destroying it as well). Eventually, the core will be hot enough for helium fusion; the Sun will burn helium for a fraction of the time it burned hydrogen in the core. The Sun is not massive enough to commence the fusion of heavier elements, and nuclear reactions in the core will dwindle. Its outer layers will be ejected into space, leaving behind a dense white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
, half the original mass of the Sun but only the size of Earth. The ejected outer layers will form what is known as a planetary nebula
A planetary nebula (PN, plural PNe) is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.
The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelate ...
, returning some of the material that formed the Sun—but now enriched with heavier elements like carbon—to the interstellar medium.
Structure and composition
The word ''solar'' means "pertaining to the Sun", which is derived from theLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
word ''sol'', meaning Sun. The Sun is the dominant gravitational member of the Solar System, and its planetary system is maintained in a relatively stable, slowly evolving state by following isolated, gravitationally bound
The gravitational binding energy of a system is the minimum energy which must be added to it in order for the system to cease being in a gravitationally bound state. A gravitationally bound system has a lower (''i.e.'', more negative) gravitati ...
orbits around the Sun.
Orbits
The planets and other large objects in orbit around the Sun lie near the plane of Earth's orbit, known as the ecliptic. Smaller icy objects such as comets frequently orbit at significantly greater angles to this plane. Most of the planets in the Solar System have secondary systems of their own, being orbited by natural satellites called moons. Many of the largest natural satellites are in synchronous rotation, with one face permanently turned toward their parent. The four giant planets have planetary rings, thin bands of tiny particles that orbit them in unison. As a result of theformation of the Solar System
The formation of the Solar System began about 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a ...
, planets and most other objects orbit the Sun in the same direction that the Sun is rotating. That is, counter-clockwise, as viewed from above Earth's north pole. There are exceptions, such as Halley's Comet
Halley's Comet or Comet Halley, officially designated 1P/Halley, is a short-period comet visible from Earth every 75–79 years. Halley is the only known short-period comet that is regularly visible to the naked eye from Earth, and thus the on ...
. Most of the larger moons orbit their planets in prograde direction, matching the planetary rotation; Neptune's moon Triton
Triton commonly refers to:
* Triton (mythology), a Greek god
* Triton (moon), a satellite of Neptune
Triton may also refer to:
Biology
* Triton cockatoo, a parrot
* Triton (gastropod), a group of sea snails
* ''Triton'', a synonym of ''Triturus'' ...
is the largest to orbit in the opposite, retrograde manner. Most larger objects rotate around their own axes in the prograde direction relative to their orbit, though the rotation of Venus is retrograde.
To a good first approximation, Kepler's laws of planetary motion
In astronomy, Kepler's laws of planetary motion, published by Johannes Kepler between 1609 and 1619, describe the orbits of planets around the Sun. The laws modified the heliocentric theory of Nicolaus Copernicus, replacing its circular orb ...
describe the orbits of objects about the Sun. These laws stipulate that each object travels along an ellipse
In mathematics, an ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. It generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse in ...
with the Sun at one focus, which causes the body's distance from the Sun to vary over the course of its year. A body's closest approach to the Sun is called its ''perihelion
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion.
General description
There are two apsides in any elli ...
'', whereas its most distant point from the Sun is called its ''aphelion
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion.
General description
There are two apsides in any ell ...
''. The orbits of the planets are nearly circular, but many comets, asteroids, and Kuiper belt objects follow highly elliptical orbits. Kepler's laws only account for the influence of the Sun's gravity upon an orbiting body, not the gravitational pulls of different bodies upon each other. On a human time scale, these additional perturbations can be accounted for using numerical models, but the planetary system can change chaotically over billions of years.
The angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum (rarely, moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed syst ...
of the Solar System is a measure of the total amount of orbital and rotational momentum possessed by all its moving components. Although the Sun dominates the system by mass, it accounts for only about 2% of the angular momentum. The planets, dominated by Jupiter, account for most of the rest of the angular momentum due to the combination of their mass, orbit, and distance from the Sun, with a possibly significant contribution from comets.
Composition
The overall structure of the charted regions of the Solar System consists of the Sun, four smaller inner planets surrounded by a belt of mostly rocky asteroids, and four giant planets surrounded by the Kuiper belt of mostly icy objects. Astronomers sometimes informally divide this structure into separate regions. The inner Solar System includes the four terrestrial planets and the asteroid belt. The outer Solar System is beyond the asteroids, including the four giant planets. Since the discovery of the Kuiper belt, the outermost parts of the Solar System are considered a distinct region consisting of the objects beyond Neptune. The principal component of the Solar System is the Sun, a low-mass star that contains 99.86% of the system's known mass and dominates it gravitationally. The Sun's four largest orbiting bodies, the giant planets, account for 99% of the remaining mass, with Jupiter and Saturn together comprising more than 90%. The remaining objects of the Solar System (including the four terrestrial planets, the dwarf planets, moons,asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere. ...
s, and comets) together comprise less than 0.002% of the Solar System's total mass.
The Sun is composed of roughly 98% hydrogen and helium, as are Jupiter and Saturn. A composition gradient exists in the Solar System, created by heat and light pressure from the early Sun; those objects closer to the Sun, which are more affected by heat and light pressure, are composed of elements with high melting points. Objects farther from the Sun are composed largely of materials with lower melting points. The boundary in the Solar System beyond which those volatile substances could coalesce is known as the frost line, and it lies at roughly five times the Earth's distance from the Sun.
The objects of the inner Solar System are composed mostly of rocky materials, such as silicates
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name ...
, iron or nickel. Jupiter and Saturn are composed mainly of gases with extremely low melting points and high vapour pressure
Vapor pressure (or vapour pressure in English-speaking countries other than the US; see spelling differences) or equilibrium vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phase ...
, such as hydrogen, helium, and neon
Neon is a chemical element with the symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is a noble gas. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with about two-thirds the density of air. It was discovered (along with krypt ...
. Ices, like water, methane, ammonia, hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is poisonous, corrosive, and flammable, with trace amounts in ambient atmosphere having a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. The under ...
, and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
, have melting points up to a few hundred kelvins. They can be found as ices, liquids, or gases in various places in the Solar System. Icy substances comprise the majority of the satellites of the giant planets, as well as most of Uranus and Neptune (the so-called "ice giant
An ice giant is a giant planet composed mainly of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium, such as oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur. There are two ice giants in the Solar System: Uranus and Neptune.
In astrophysics and planetary ...
s") and the numerous small objects that lie beyond Neptune's orbit. Together, gases and ices are referred to as ''volatiles
Volatiles are the group of chemical elements and chemical compounds that can be readily vaporized. In contrast with volatiles, elements and compounds that are not readily vaporized are known as refractory substances.
On planet Earth, the term ...
''.
Distances and scales

astronomical unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au, or or AU) is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and approximately equal to or 8.3 light-minutes. The actual distance from Earth to the Sun varies by about 3% as Earth orbits ...
U() would be the distance from the Earth to the Sun if the planet's orbit were perfectly circular. For comparison, the radius of the Sun is . Thus, the Sun occupies 0.00001% (10−5 %) of the volume of a sphere with a radius the size of Earth's orbit, whereas Earth's volume is roughly one millionth (10−6) that of the Sun. Jupiter, the largest planet, is from the Sun and has a radius of , whereas the most distant planet, Neptune, is from the Sun.
With a few exceptions, the farther a planet or belt is from the Sun, the larger the distance between its orbit and the orbit of the next nearer object to the Sun. For example, Venus is approximately 0.33 AU farther out from the Sun than Mercury, whereas Saturn is 4.3 AU out from Jupiter, and Neptune lies 10.5 AU out from Uranus. Attempts have been made to determine a relationship between these orbital distances, like the Titius–Bode law
The Titius–Bode law (sometimes termed just Bode's law) is a formulaic prediction of spacing between planets in any given solar system. The formula suggests that, extending outward, each planet should be approximately twice as far from the Sun as ...
and Johannes Kepler's model based on the Platonic solid
In geometry, a Platonic solid is a convex, regular polyhedron in three-dimensional Euclidean space. Being a regular polyhedron means that the faces are congruent (identical in shape and size) regular polygons (all angles congruent and all e ...
s, but ongoing discoveries have invalidated these hypotheses.
Some Solar System model
Solar System models, especially mechanical models, called '' orreries'', that illustrate the relative positions and motions of the planets and moons in the Solar System have been built for centuries. While they often showed relative sizes, the ...
s attempt to convey the relative scales involved in the Solar System on human terms. Some are small in scale (and may be mechanical—called orreries)—whereas others extend across cities or regional areas. The largest such scale model, the Sweden Solar System
The Sweden Solar System is the world's largest permanent scale model of the Solar System. The Sun is represented by the Avicii Arena in Stockholm, the largest hemispherical building in the world. The inner planets can also be found in Stockhol ...
, uses the 110-metre (361 ft) Avicii Arena
Avicii Arena, originally known as Stockholm Globe Arena and previously as Ericsson Globe, but commonly referred to in Swedish simply as Globen (; "the Globe"), is an indoor arena located in Stockholm Globe City, Johanneshov district of Stockho ...
in Stockholm
Stockholm () is the capital and largest city of Sweden as well as the largest urban area in Scandinavia. Approximately 980,000 people live in the municipality, with 1.6 million in the urban area, and 2.4 million in the metropo ...
as its substitute Sun, and, following the scale, Jupiter is a 7.5-metre (25-foot) sphere at Stockholm Arlanda Airport
Stockholm Arlanda Airport is an international airport located in the Sigtuna Municipality of Sweden, near the town of Märsta, north of Stockholm and nearly south-east of Uppsala. The airport is located within Stockholm County and the provi ...
, 40 km (25 mi) away, whereas the farthest current object, Sedna, is a 10 cm (4 in) sphere in Luleå
Luleå ( , , locally ; smj, Luleju; fi, Luulaja) is a city on the coast of northern Sweden, and the capital of Norrbotten County, the northernmost county in Sweden. Luleå has 48,728 inhabitants in its urban core (2018) and is the seat of Lu ...
, 912 km (567 mi) away.
If the Sun–Neptune distance is scaled to , then the Sun would be about in diameter (roughly two-thirds the diameter of a golf ball), the giant planets would be all smaller than about , and Earth's diameter along with that of the other terrestrial planets would be smaller than a flea () at this scale.
Sun
 The Sun is the Solar System's star and by far its most massive component. Its large mass (332,900 Earth masses), which comprises 99.86% of all the mass in the Solar System,
produces temperatures and densities in its core high enough to sustain nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. This releases an enormous amount of
The Sun is the Solar System's star and by far its most massive component. Its large mass (332,900 Earth masses), which comprises 99.86% of all the mass in the Solar System,
produces temperatures and densities in its core high enough to sustain nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. This releases an enormous amount of energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of ...
, mostly radiated into space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consi ...
as electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visib ...
peaking in visible light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 t ...
.
Because the Sun fuses hydrogen into helium at its core, it is a main-sequence star. More specifically, it is a G2-type main-sequence star, where the type designation refers to its effective temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature ...
. Hotter main-sequence stars are more luminous. The Sun's temperature is intermediate between that of the hottest stars and that of the coolest stars. Stars brighter and hotter than the Sun are rare, whereas substantially dimmer and cooler stars, known as red dwarf
''Red Dwarf'' is a British science fiction comedy franchise created by Rob Grant and Doug Naylor, which primarily consists of a television sitcom that aired on BBC Two between 1988 and 1999, and on Dave since 2009, gaining a cult following. ...
s, make up about 75% of the stars in the Milky Way.
The Sun is a population I star; it has a higher abundance of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium ("metals
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typical ...
" in astronomical parlance) than the older population II stars. Elements heavier than hydrogen and helium were formed in the cores of ancient and exploding stars, so the first generation of stars had to die before the universe could be enriched with these atoms. The oldest stars contain few metals, whereas stars born later have more. This higher metallicity is thought to have been crucial to the Sun's development of a planetary system
A planetary system is a set of gravitationally bound non- stellar objects in or out of orbit around a star or star system. Generally speaking, systems with one or more planets constitute a planetary system, although such systems may also consi ...
because the planets form from the accretion of "metals".
Environment and habitability
 Outside of the main part of the Sun's atmosphere extends the
Outside of the main part of the Sun's atmosphere extends the heliosphere
The heliosphere is the magnetosphere, astrosphere and outermost atmospheric layer of the Sun. It takes the shape of a vast, bubble-like region of space. In plasma physics terms, it is the cavity formed by the Sun in the surrounding interstell ...
and dominates the Solar planetary system
A planetary system is a set of gravitationally bound non- stellar objects in or out of orbit around a star or star system. Generally speaking, systems with one or more planets constitute a planetary system, although such systems may also consi ...
. The vast majority of the heliosphere is occupied by a near-vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or " void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often ...
known as the interplanetary medium
The interplanetary medium (IPM) or interplanetary space consists of the mass and energy which fills the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding ...
. Along with light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm), corresponding to frequencies of 750–420 t ...
, the Sun radiates a continuous stream of charged particles (a plasma) called the solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the sol ...
. This stream of particles spreads outwards at speeds from to , creating a tenuous atmosphere that permeates the interplanetary medium out to at least . Activity on the Sun's surface, such as solar flare
A solar flare is an intense localized eruption of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other sol ...
s and coronal mass ejection
A coronal mass ejection (CME) is a significant release of plasma and accompanying magnetic field from the Sun's corona into the heliosphere. CMEs are often associated with solar flares and other forms of solar activity, but a broadly accept ...
s, disturbs the heliosphere, creating space weather
Space weather is a branch of space physics and aeronomy, or heliophysics, concerned with the time varying conditions within the Solar System, including the solar wind, emphasizing the space surrounding the Earth, including conditions in the ...
and causing geomagnetic storms. The largest structure within the heliosphere is the heliospheric current sheet, a spiral form created by the actions of the Sun's rotating magnetic field on the interplanetary medium.
Earth's magnetic field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magneti ...
stops its atmosphere from being stripped away by the solar wind. Venus and Mars do not have magnetic fields, and as a result the solar wind is causing their atmospheres to gradually bleed away into space. Coronal mass ejections and similar events blow a magnetic field and huge quantities of material from the surface of the Sun. The interaction of this magnetic field and material with Earth's magnetic field funnels charged particles into Earth's upper atmosphere, where its interactions create aurorae
An aurora (plural: auroras or aurorae), also commonly known as the polar lights, is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly seen in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). Auroras display dynamic patterns of bri ...
seen near the magnetic poles.
The heliosphere and planetary magnetic fields (for those planets that have them) partially shield the Solar System from high-energy interstellar particles called cosmic ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own ...
s. The density of cosmic rays in the interstellar medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstella ...
and the strength of the Sun's magnetic field change on very long timescales, so the level of cosmic-ray penetration in the Solar System varies, though by how much is unknown.
The interplanetary medium is home to at least two disc-like regions of cosmic dust
Cosmic dust, also called extraterrestrial dust, star dust or space dust, is dust which exists in outer space, or has fallen on Earth. Most cosmic dust particles measure between a few molecules and 0.1 mm (100 micrometers). Larger particles are c ...
. The first, the zodiacal dust cloud, lies in the inner Solar System and causes the zodiacal light
The zodiacal light (also called false dawn when seen before sunrise) is a faint glow of diffuse sunlight scattered by interplanetary dust. Brighter around the Sun, it appears in a particularly dark night sky to extend from the Sun's direction ...
. It may have been formed by collisions within the asteroid belt brought on by gravitational interactions with the planets; a more recent proposed origin is the planet Mars. The second dust cloud extends from about to about , and was probably created by collisions within the Kuiper belt.
The zone of hability of the Solar System is located in the Inner Solar System. Beside the Solar conditions for hability on Solar System objects such as Earth, habitability might be possibly in subsurface oceans of various Outer Solar System moons.
Inner Solar System
 The inner Solar System is the region comprising the
The inner Solar System is the region comprising the terrestrial planets
A terrestrial planet, telluric planet, or rocky planet, is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate rocks or metals. Within the Solar System, the terrestrial planets accepted by the IAU are the inner planets closest to the Sun: Mercury, ...
and the asteroid belt
The asteroid belt is a torus-shaped region in the Solar System, located roughly between the orbits of the planets Jupiter and Mars. It contains a great many solid, irregularly shaped bodies, of many sizes, but much smaller than planets, c ...
. Composed mainly of silicate
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is a ...
s and metals, the objects of the inner Solar System are relatively close to the Sun; the radius of this entire region is less than the distance between the orbits of Jupiter and Saturn. This region is also within the frost line, which is a little less than from the Sun.
Inner planets
 The four terrestrial or inner planets have dense, rocky compositions, few or no
The four terrestrial or inner planets have dense, rocky compositions, few or no moons
A natural satellite is, in the most common usage, an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet, or small Solar System body (or sometimes another natural satellite). Natural satellites are often colloquially referred to as ''moons'' ...
, and no ring systems. They are composed largely of refractory
In materials science, a refractory material or refractory is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat, pressure, or chemical attack, and retains strength and form at high temperatures. Refractories are polycrystalline, polyphase, ...
minerals such as the silicateswhich form their crusts and mantlesand metals such as iron and nickel which form their cores. Three of the four inner planets (Venus, Earth and Mars) have atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A ...
s substantial enough to generate weather; all have impact craters and tectonic
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents ...
surface features, such as rift valley
A rift valley is a linear shaped lowland between several highlands or mountain ranges created by the action of a geologic rift. Rifts are formed as a result of the pulling apart of the lithosphere due to extensional tectonics. The linear d ...
s and volcanoes. The term ''inner planet'' should not be confused with ''inferior planet
In the Solar System, a planet is said to be inferior or interior with respect to another planet if its orbit lies inside the other planet's orbit around the Sun. In this situation, the latter planet is said to be superior to the former. In the ...
'', which designates those planets that are closer to the Sun than Earth is (i.e. Mercury and Venus).
Mercury
Mercury ( from the Sun) is the closest planet to the Sun. The smallest planet in the Solar System (), Mercury has no natural satellites. The dominant geological features are impact craters or basins with ejecta blankets, the remains of early volcanic activity including magma flows, and lobed ridges or rupes that were probably produced by a period of contraction early in the planet's history. Mercury's very tenuous atmosphere consists of solar-wind particles trapped by Mercury's magnetic field, as well as atoms blasted off its surface by the solar wind. Its relatively large iron core and thin mantle have not yet been adequately explained. Hypotheses include that its outer layers were stripped off by a giant impact, or that it was prevented from fully accreting by the young Sun's energy. There have been searches for "Vulcanoid
The vulcanoids are a hypothetical population of asteroids that orbit the Sun in a dynamically stable zone inside the orbit of the planet Mercury. They are named after the hypothetical planet Vulcan, which was proposed on the basis of irregularit ...
s", asteroids in stable orbits between Mercury and the Sun, but none have been discovered.
Venus
Venus ( from the Sun) is close in size to Earth () and, like Earth, has a thick silicate mantle around an iron core, a substantial atmosphere, and evidence of internal geological activity. It is much drier than Earth, and its atmosphere is ninety times as dense. Venus has no natural satellites. It is the hottest planet, with surface temperatures over , mainly due to the amount ofgreenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (), carbon dioxide (), methane ...
es in the atmosphere. The planet has no magnetic field that would prevent depletion of its substantial atmosphere, which suggests that its atmosphere is being replenished by volcanic eruptions. A relatively young planetary surface displays extensive evidence of volcanic activity, but is devoid of plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label= Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of larg ...
. It may undergo resurfacing episodes on a time scale of 700 million years.
Earth
Earth ( from the Sun) is the largest and densest of the inner planets, the only one known to have current geological activity, and the only place where life is known to exist. Its liquidhydrosphere
The hydrosphere () is the combined mass of water found on, under, and above the surface of a planet, minor planet, or natural satellite. Although Earth's hydrosphere has been around for about 4 billion years, it continues to change in shape. This ...
is unique among the terrestrial planets, and it is the only planet where plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label= Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of larg ...
has been observed. Earth's atmosphere is radically different from those of the other planets, having been altered by the presence of life to contain 21% free oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
. The planetary magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior d ...
shields the surface from solar and cosmic radiation, limiting atmospheric stripping and maintaining habitability. It has one natural satellite, the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
, the only large satellite of a terrestrial planet in the Solar System.
Mars
Mars ( from the Sun) is smaller than Earth and Venus (). It has an atmosphere of mostly carbon dioxide with a surface pressure of ; roughly 0.6% of that of Earth but sufficient to support weather phenomena. Its surface, peppered with volcanoes, such asOlympus Mons
Olympus Mons (; Latin for Mount Olympus) is a large shield volcano on Mars. The volcano has a height of over 21.9 km (13.6 mi or 72,000 ft) as measured by the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA). Olympus Mons is about two and a ha ...
, and rift valleys, such as Valles Marineris
Valles Marineris (; Latin for '' Mariner Valleys'', named after the ''Mariner 9'' Mars orbiter of 1971–72 which discovered it) is a system of canyons that runs along the Martian surface east of the Tharsis region. At more than long, wide and ...
, shows geological activity that may have persisted until as recently as 2 million years ago. Its red colour comes from iron oxide
Iron oxides are chemical compounds composed of iron and oxygen. Several iron oxides are recognized. All are black magnetic solids. Often they are non-stoichiometric. Oxyhydroxides are a related class of compounds, perhaps the best known of wh ...
(rust) in its soil. Mars has two tiny natural satellites (Deimos Deimos, a Greek word for ''dread'', may refer to:
* Deimos (deity), one of the sons of Ares and Aphrodite in Greek mythology
* Deimos (moon), the smaller and outermost of Mars' two natural satellites
* Elecnor Deimos, a Spanish aerospace company
* ...
and Phobos) thought to be either captured asteroids, or ejected debris from a massive impact early in Mars's history.
Asteroid belt
 Asteroids except for the largest, Ceres, are classified as small Solar System bodies and are composed mainly of refractory rocky and metallic minerals, with some ice. They range from a few metres to hundreds of kilometres in size. Asteroids smaller than one meter are usually called
Asteroids except for the largest, Ceres, are classified as small Solar System bodies and are composed mainly of refractory rocky and metallic minerals, with some ice. They range from a few metres to hundreds of kilometres in size. Asteroids smaller than one meter are usually called meteoroid
A meteoroid () is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space.
Meteoroids are defined as objects significantly smaller than asteroids, ranging in size from grains to objects up to a meter wide. Objects smaller than this are classified as mi ...
s and micrometeoroids (grain-sized), with the exact division between the two categories being debated over the years. As of 2017, the IAU designates asteroids having diameter between about 30 micrometre
The micrometre (American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American and British English spelling differences# ...
s and 1 metre as micrometeroids, and terms smaller particles "dust".
The asteroid belt occupies the orbit between Mars and Jupiter, between from the Sun. It is thought to be remnants from the Solar System's formation that failed to coalesce because of the gravitational interference of Jupiter. The asteroid belt contains tens of thousands, possibly millions, of objects over one kilometre in diameter. Despite this, the total mass of the asteroid belt is unlikely to be more than a thousandth of that of Earth. The asteroid belt is very sparsely populated; spacecraft routinely pass through without incident.
Ceres
Ceres ( from the Sun) is the largest asteroid, aprotoplanet
A protoplanet is a large planetary embryo that originated within a protoplanetary disc and has undergone internal melting to produce a differentiated interior. Protoplanets are thought to form out of kilometer-sized planetesimals that gravitation ...
, and a dwarf planet. It has a diameter of slightly under and a mass large enough for its own gravity to pull it into a spherical shape. Ceres was considered a planet when it was discovered in 1801, but as further observations revealed additional asteroids, it became common to consider it as one of the minor rather than major planets. It was then reclassified again as a dwarf planet in 2006 when the IAU definition of planet was established.
Pallas and Vesta
Pallas
Pallas may refer to:
Astronomy
* 2 Pallas asteroid
** Pallas family, a group of asteroids that includes 2 Pallas
* Pallas (crater), a crater on Earth's moon
Mythology
* Pallas (Giant), a son of Uranus and Gaia, killed and flayed by Athena
* Pa ...
(2.77 AU from the Sun) and Vesta (2.36 AU from the Sun) are the largest asteroids in the asteroid belt, after Ceres. They are the other two protoplanets that survive more or less intact. At about in diameter, they were large enough to have developed planetary geology in the past, but both have suffered large impacts and been battered out of being round. Fragments from impacts upon these two bodies survive elsewhere in the asteroid belt, as the Pallas family The Pallas family (''adj. Palladian''; ) is a small asteroid family of B-type asteroids at very high inclinations in the intermediate asteroid belt.
The namesake of the family is 2 Pallas, an extremely large asteroid with a mean diameter of about 5 ...
and Vesta family
The Vesta family (adj. ''Vestian''; ) is a family of asteroids. The cratering family is located in the inner asteroid belt in the vicinity of its namesake and principal body, 4 Vesta. It is one of the largest asteroid families with more than ...
. Both were considered planets upon their discoveries in 1802 and 1807 respectively, and then like Ceres generally considered as minor planets with the discovery of more asteroids. Some authors today have begun to consider Pallas and Vesta as planets again, along with Ceres, under geophysical definitions of the term.
Asteroid groups
Asteroids in the asteroid belt are divided into asteroid groups and families based on their orbital characteristics.Kirkwood gap
A Kirkwood gap is a gap or dip in the distribution of the semi-major axes (or equivalently of the orbital periods) of the orbits of main-belt asteroids. They correspond to the locations of orbital resonances with Jupiter.
For example, there ...
s are sharp dips in the distribution of asteroid orbits that correspond to orbital resonance
In celestial mechanics, orbital resonance occurs when orbiting bodies exert regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually because their orbital periods are related by a ratio of small integers. Most commonly, this relationsh ...
s with Jupiter. Asteroid moon
A minor-planet moon is an astronomical object that orbits a minor planet as its natural satellite. , there are 457 minor planets known or suspected to have moons. Discoveries of minor-planet moons (and binary objects, in general) are important ...
s are asteroids that orbit larger asteroids. They are not as clearly distinguished as planetary moons, sometimes being almost as large as their partners (e.g. that of 90 Antiope
Antiope (minor planet designation: 90 Antiope) is a double asteroid in the outer asteroid belt. It was discovered on October 1, 1866, by Robert Luther. In 2000, it was found to consist of two almost-equally-sized bodies orbiting each other. At ...
). The asteroid belt includes main-belt comet
Active asteroids are small Solar System bodies that have asteroid-like orbits but show comet-like visual characteristics. That is, they show comae, tails, or other visual evidence of mass-loss (like a comet), but their orbit remains within Jup ...
s, which may have been the source of Earth's water.
Jupiter trojan
The Jupiter trojans, commonly called trojan asteroids or simply trojans, are a large group of asteroids that share the planet Jupiter's orbit around the Sun. Relative to Jupiter, each trojan librates around one of Jupiter's stable Lagrange p ...
s are located in either of Jupiter's L4 or L5 points (gravitationally stable regions leading and trailing a planet in its orbit); the term is also used for small bodies in any other planetary or satellite Lagrange point
In celestial mechanics, the Lagrange points (; also Lagrangian points or libration points) are points of equilibrium for small-mass objects under the influence of two massive orbiting bodies. Mathematically, this involves the solution of t ...
. Hilda asteroids
The Hilda asteroids (adj. ''Hildian'') are a dynamical group of more than 5,000 asteroids located beyond the asteroid belt but within Jupiter's orbit, in a 3:2 orbital resonance with Jupiter. The namesake is the asteroid 153 Hilda.
Hildas move ...
are in a 2:3 resonance with Jupiter; that is, they go around the Sun three times for every two Jupiter orbits. The inner Solar System contains near-Earth asteroids
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body whose orbit brings it into proximity with Earth. By convention, a Solar System body is a NEO if its closest approach to the Sun ( perihelion) is less than 1.3 astronomical units (AU ...
, many of which cross the orbits of the inner planets. Some of them are potentially hazardous objects.
Outer Solar System
 The outer region of the Solar System is home to the
The outer region of the Solar System is home to the giant planet
The giant planets constitute a diverse type of planet much larger than Earth. They are usually primarily composed of low-boiling-point materials (volatiles), rather than rock or other solid matter, but massive solid planets can also exist. The ...
s and their large moons. The centaurs
A centaur ( ; grc, κένταυρος, kéntauros; ), or occasionally hippocentaur, is a creature from Greek mythology with the upper body of a human and the lower body and legs of a horse.
Centaurs are thought of in many Greek myths as bein ...
and many short-period comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena are ...
s also orbit in this region. Due to their greater distance from the Sun, the solid objects in the outer Solar System contain a higher proportion of volatiles, such as water, ammonia, and methane than those of the inner Solar System because the lower temperatures allow these compounds to remain solid.
Outer planets
 The four outer planets, also called giant planets or Jovian planets, collectively make up 99% of the mass known to orbit the Sun. Jupiter and Saturn are together more than 400 times the mass of Earth and consist overwhelmingly of the gases hydrogen and helium, hence their designation as
The four outer planets, also called giant planets or Jovian planets, collectively make up 99% of the mass known to orbit the Sun. Jupiter and Saturn are together more than 400 times the mass of Earth and consist overwhelmingly of the gases hydrogen and helium, hence their designation as gas giant
A gas giant is a giant planet composed mainly of hydrogen and helium. Gas giants are also called failed stars because they contain the same basic elements as a star. Jupiter and Saturn are the gas giants of the Solar System. The term "gas giant" ...
s. Uranus and Neptune are far less massiveless than 20 Earth masses () eachand are composed primarily of ices. For these reasons, some astronomers suggest they belong in their own category, ice giants. All four giant planets have rings, although only Saturn's ring system is easily observed from Earth. The term ''superior planet
In the Solar System, a planet is said to be inferior or interior with respect to another planet if its orbit lies inside the other planet's orbit around the Sun. In this situation, the latter planet is said to be superior to the former. In the ref ...
'' designates planets outside Earth's orbit and thus includes both the outer planets and Mars.
The ring–moon systems of Jupiter, Saturn, and Uranus are like miniature versions of the Solar System; that of Neptune is significantly different, having been disrupted by the capture of its largest moon Triton.
Jupiter
Jupiter ( from the Sun), at , is 2.5 times the mass of all the other planets put together. It is composed largely ofhydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
and helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic ta ...
. Jupiter's strong internal heat creates semi-permanent features in its atmosphere, such as cloud bands and the Great Red Spot
The Great Red Spot is a persistent high-pressure region in the atmosphere of Jupiter, producing an anticyclonic storm that is the largest in the Solar System. Located 22 degrees south of Jupiter's equator, it produces wind-speeds up to 432&nb ...
. The planet possesses a 4.2– strength magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior d ...
that spans 22–29 million km, making it, in certain respects, the largest object in the Solar System. Jupiter has 80 known satellites. The four largest, Ganymede, Callisto, Io, and Europa
Europa may refer to:
Places
* Europe
* Europa (Roman province), a province within the Diocese of Thrace
* Europa (Seville Metro), Seville, Spain; a station on the Seville Metro
* Europa City, Paris, France; a planned development
* Europa Clif ...
, are called the Galilean moons
The Galilean moons (), or Galilean satellites, are the four largest moons of Jupiter: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. They were first seen by Galileo Galilei in December 1609 or January 1610, and recognized by him as satellites of Jupite ...
: they show similarities to the terrestrial planets, such as volcanism and internal heating. Ganymede, the largest satellite in the Solar System, is larger than Mercury; Callisto is almost as large.
Saturn
Saturn ( from the Sun), distinguished by its extensive ring system, has several similarities to Jupiter, such as its atmospheric composition andmagnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior d ...
. Although Saturn has 60% of Jupiter's volume, it is less than a third as massive, at . Saturn is the only planet of the Solar System that is less dense than water. The rings of Saturn are made up of small ice and rock particles. Saturn has 83 confirmed satellites composed largely of ice. Two of these, Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
and Enceladus
Enceladus is the sixth-largest moon of Saturn (19th largest in the Solar System). It is about in diameter, about a tenth of that of Saturn's largest moon, Titan. Enceladus is mostly covered by fresh, clean ice, making it one of the most refle ...
, show signs of geological activity; they, as well as five other Saturnian moons (Iapetus
In Greek mythology, Iapetus (; ; grc, Ἰαπετός, Iapetós), also Japetus, is a Titan, the son of Uranus and Gaia and father of Atlas (mythology), Atlas, Prometheus, Epimetheus (mythology), Epimetheus, and Menoetius (mythology), Menoetius. ...
, Rhea, Dione, Tethys, and Mimas), are large enough to be round. Titan, the second-largest moon in the Solar System, is bigger than Mercury and the only satellite in the Solar System to have a substantial atmosphere.
Uranus
Uranus ( from the Sun), at , has the lowest mass of the outer planets. Uniquely among the planets, it orbits the Sun on its side; itsaxial tilt
In astronomy, axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis and its orbital axis, which is the line perpendicular to its orbital plane; equivalently, it is the angle between its equatorial plane and orb ...
is over ninety degrees to the ecliptic. This gives the planet extreme seasonal variation as each pole points toward and then away from the Sun. It has a much colder core than the other giant planets and radiates very little heat into space. As a consequence, it has the coldest planetary atmosphere in the Solar System. Uranus has 27 known satellites, the largest ones being Titania, Oberon
Oberon () is a king of the fairies in medieval and Renaissance literature. He is best known as a character in William Shakespeare's play ''A Midsummer Night's Dream'', in which he is King of the Fairies and spouse of Titania, Queen of the Fairi ...
, Umbriel, Ariel, and Miranda. Like the other giant planets, it possesses a ring system and magnetosphere.
Neptune
Neptune ( from the Sun), though slightly smaller than Uranus, is more massive () and hence more dense. It radiates more internal heat than Uranus, but not as much as Jupiter or Saturn. Neptune has 14 known satellites. The largest,Triton
Triton commonly refers to:
* Triton (mythology), a Greek god
* Triton (moon), a satellite of Neptune
Triton may also refer to:
Biology
* Triton cockatoo, a parrot
* Triton (gastropod), a group of sea snails
* ''Triton'', a synonym of ''Triturus'' ...
, is geologically active, with geyser
A geyser (, ) is a spring characterized by an intermittent discharge of water ejected turbulently and accompanied by steam. As a fairly rare phenomenon, the formation of geysers is due to particular hydrogeological conditions that exist only i ...
s of liquid nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen—LN2—is nitrogen in a liquid state at low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about . It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, low viscosity liquid that is wid ...
. Triton is the only large satellite with a retrograde orbit, which indicates that it did not form with Neptune, but was probably captured from the Kuiper belt. Neptune is accompanied in its orbit by several minor planet
According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a minor planet is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the Sun that is exclusively classified as neither a planet nor a comet. Before 2006, the IAU officially used the term ''minor ...
s, termed Neptune trojan
Neptune trojans are bodies that orbit the Sun near one of the stable Lagrangian points of Neptune, similar to the trojans of other planets. They therefore have approximately the same orbital period as Neptune and follow roughly the same orbital ...
s, that either lead or trail the planet by about one-sixth of the way around the Sun, positions known as Lagrange point
In celestial mechanics, the Lagrange points (; also Lagrangian points or libration points) are points of equilibrium for small-mass objects under the influence of two massive orbiting bodies. Mathematically, this involves the solution of t ...
s.
Centaurs
The centaurs are icy comet-like bodies whose orbits have semi-major axes greater than Jupiter's () and less than Neptune's (). The largest known centaur,10199 Chariklo
10199 Chariklo is the largest confirmed centaur (small body of the outer Solar System). It orbits the Sun between Saturn and Uranus, grazing the orbit of Uranus. On 26 March 2014, astronomers announced the discovery of two rings (nickname ...
, has a diameter of about . The first centaur discovered, 2060 Chiron
2060 Chiron is a small Solar System body in the outer Solar System, orbiting the Sun between Saturn and Uranus. Discovered in 1977 by Charles Kowal, it was the first-identified member of a new class of objects now known as centaurs—bodies o ...
, has also been classified as a comet (95P) because it develops a coma just as comets do when they approach the Sun.
Comets
 Comets are small Solar System bodies, typically only a few kilometres across, composed largely of volatile ices. They have highly eccentric orbits, generally a perihelion within the orbits of the inner planets and an aphelion far beyond Pluto. When a comet enters the inner Solar System, its proximity to the Sun causes its icy surface to sublimate and ionise, creating a
Comets are small Solar System bodies, typically only a few kilometres across, composed largely of volatile ices. They have highly eccentric orbits, generally a perihelion within the orbits of the inner planets and an aphelion far beyond Pluto. When a comet enters the inner Solar System, its proximity to the Sun causes its icy surface to sublimate and ionise, creating a coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
: a long tail of gas and dust often visible to the naked eye.
Short-period comets have orbits lasting less than two hundred years. Long-period comets have orbits lasting thousands of years. Short-period comets are thought to originate in the Kuiper belt, whereas long-period comets, such as Hale–Bopp, are thought to originate in the Oort cloud. Many comet groups, such as the Kreutz sungrazers, formed from the breakup of a single parent. Some comets with hyperbolic orbits may originate outside the Solar System, but determining their precise orbits is difficult. Old comets whose volatiles have mostly been driven out by solar warming are often categorised as asteroids.
Trans-Neptunian region
 Inside the orbit of Neptune is the planetary region of the Solar System. Beyond the orbit of Neptune lies the area of the " trans-Neptunian region", with the doughnut-shaped Kuiper belt, home of Pluto and several other dwarf planets, and an overlapping disc of scattered objects, which is tilted toward the plane of the Solar System and reaches much further out than the Kuiper belt. The entire region is still largely unexplored. It appears to consist overwhelmingly of many thousands of small worlds—the largest having a diameter only a fifth that of Earth and a mass far smaller than that of the Moon—composed mainly of rock and ice. This region is sometimes described as the "third zone of the Solar System", enclosing the inner and the outer Solar System.
Inside the orbit of Neptune is the planetary region of the Solar System. Beyond the orbit of Neptune lies the area of the " trans-Neptunian region", with the doughnut-shaped Kuiper belt, home of Pluto and several other dwarf planets, and an overlapping disc of scattered objects, which is tilted toward the plane of the Solar System and reaches much further out than the Kuiper belt. The entire region is still largely unexplored. It appears to consist overwhelmingly of many thousands of small worlds—the largest having a diameter only a fifth that of Earth and a mass far smaller than that of the Moon—composed mainly of rock and ice. This region is sometimes described as the "third zone of the Solar System", enclosing the inner and the outer Solar System.
Kuiper belt
The Kuiper belt is a great ring of debris similar to the asteroid belt, but consisting mainly of objects composed primarily of ice. It extends between from the Sun. It is composed mainly of small Solar System bodies, although the largest few are probably large enough to be dwarf planets. There are estimated to be over 100,000 Kuiper belt objects with a diameter greater than , but the total mass of the Kuiper belt is thought to be only a tenth or even a hundredth the mass of Earth. Many Kuiper belt objects have multiple satellites, and most have orbits that take them outside the plane of the ecliptic. The Kuiper belt can be roughly divided into the " classical" belt and theresonant trans-Neptunian object
In astronomy, a resonant trans-Neptunian object is a trans-Neptunian object (TNO) in mean-motion orbital resonance with Neptune. The orbital periods of the resonant objects are in a simple integer relations with the period of Neptune, e.g. 1:2, ...
s. The latter have orbits whose periods are in a simple ratio to that of Neptune: for example, going around the Sun twice for every three times that Neptune does, or once for every two. The classical belt consists of objects having no resonance with Neptune, and extends from roughly . Members of the classical Kuiper belt are sometimes called "cubewanos", after the first of their kind to be discovered, originally designated 1992 QB1; they are still in near primordial, low-eccentricity orbits.
Pluto and Charon
The dwarf planet Pluto (with an average orbit of from the Sun) is the largest known object in the Kuiper belt. When discovered in 1930, it was considered to be the ninth planet; this changed in 2006 with the adoption of a formal definition of planet. Pluto has a relatively eccentric orbit inclined 17 degrees to the ecliptic plane and ranging from from the Sun at perihelion (within the orbit of Neptune) to at aphelion. Pluto has a 2:3 resonance with Neptune, meaning that Pluto orbits twice round the Sun for every three Neptunian orbits. Kuiper belt objects whose orbits share this resonance are called plutinos. Charon, the largest of Pluto's moons, is sometimes described as part of abinary system
A binary system is a system of two astronomical bodies which are close enough that their gravitational attraction causes them to orbit each other around a barycenter ''(also see animated examples)''. More restrictive definitions require that th ...
with Pluto, as the two bodies orbit a barycentre of gravity above their surfaces (i.e. they appear to "orbit each other"). Beyond Charon, four much smaller moons, Styx
In Greek mythology, Styx (; grc, Στύξ ) is a river that forms the boundary between Earth (Gaia) and the Underworld. The rivers Acheron, Cocytus, Lethe, Phlegethon, and Styx all converge at the centre of the underworld on a great marsh, ...
, Nix
Nix or NIX may refer to:
Places
* Nix, Alabama, an unincorporated community, United States
* Nix, Texas, a ghost town in southwestern Lampasas County, Texas, United States
* Nix (moon), a moon of Pluto
People
* Nix (surname), listing people wit ...
, Kerberos, and Hydra, orbit Pluto.
Others
Besides Pluto, astronomers generally agree that at least four other Kuiper belt objects are dwarf planets, and additional bodies have also been proposed: * Makemake (45.79 AU average from the Sun), although smaller than Pluto, is the largest known object in the ''classical'' Kuiper belt (that is, a Kuiper belt object not in a confirmed resonance with Neptune). Makemake is the brightest object in the Kuiper belt after Pluto. Discovered in 2005, it was officially named in 2009. Its orbit is far more inclined than Pluto's, at 29°. It has one known moon. *Haumea
, discoverer =
, discovered =
, earliest_precovery_date = March 22, 1955
, mpc_name = (136108) Haumea
, pronounced =
, adjectives = Haumean
, note = yes
, alt_names =
, named_after = Haumea
, mp_category =
, orbit_ref =
, epoc ...
(43.13 AU average from the Sun) is in an orbit similar to Makemake, except that it is in a temporary 7:12 orbital resonance with Neptune. Like Makemake, it was discovered in 2005. It has two known moons, Hiʻiaka and Namaka, and rotates so quickly (once every 3.9 hours) that it is stretched into an ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that may be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation.
An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a surface that may be defined as th ...
.
* (43.69 AU average from the Sun) is the second-largest known object in the classical Kuiper belt, after Makemake. Its orbit is significantly less eccentric and inclined than those of Makemake or Haumea. It has one known moon, Weywot.
* (39.40 AU average from the Sun) is in the same 2:3 orbital resonance with Neptune as Pluto, and is the largest such object after Pluto itself. Its eccentricity and inclination are similar to Pluto's, but its perihelion lies about 120° from that of Pluto. Thus, the phase of Orcus's orbit is opposite to Pluto's: Orcus is at aphelion (most recently in 2019) around when Pluto is at perihelion (most recently in 1989) and vice versa. For this reason, it has been called the ''anti-Pluto''.
It has one known moon, Vanth.
Scattered disc
Eris and Gonggong
(67.78 AU average from the Sun) is the largest known scattered disc object, and caused a debate about what constitutes a planet, because it is 25% more massive than Pluto and about the same diameter. It is the most massive of the known dwarf planets. It has one known moon, Dysnomia. Like Pluto, its orbit is highly eccentric, with a perihelion of 38.2 AU (roughly Pluto's distance from the Sun) and an aphelion of 97.6 AU, and steeply inclined to the ecliptic plane at an angle of 44°. (67.38 AU average from the Sun) is in a comparable orbit to Eris, except that it is in a 3:10 resonance with Neptune. It has one known moon, Xiangliu.Farthest regions
The point at which the Solar System ends and interstellar space begins is not precisely defined because its outer boundaries are shaped by two forces, the solar wind and the Sun's gravity. The limit of the solar wind's influence is roughly four times Pluto's distance from the Sun; this ''heliopause'', the outer boundary of theheliosphere
The heliosphere is the magnetosphere, astrosphere and outermost atmospheric layer of the Sun. It takes the shape of a vast, bubble-like region of space. In plasma physics terms, it is the cavity formed by the Sun in the surrounding interstell ...
, is considered the beginning of the interstellar medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstella ...
. The Sun's Hill sphere, the effective range of its gravitational dominance, is thought to extend up to a thousand times farther and encompasses the hypothetical Oort cloud
The Oort cloud (), sometimes called the Öpik–Oort cloud, first described in 1950 by the Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, is a theoretical concept of a cloud of predominantly icy planetesimals proposed to surround the Sun at distances ranging from ...
.
Edge of the heliosphere
 The Sun's
The Sun's stellar-wind bubble
A stellar-wind bubble is a cavity light-years across filled with hot gas blown into the interstellar medium by the high-velocity (several thousand km/s) stellar wind from a single massive star of type O or B. Weaker stellar winds also blow b ...
, the heliosphere
The heliosphere is the magnetosphere, astrosphere and outermost atmospheric layer of the Sun. It takes the shape of a vast, bubble-like region of space. In plasma physics terms, it is the cavity formed by the Sun in the surrounding interstell ...
, a region of space dominated by the Sun, has its boundary at the ''termination shock'', which is roughly 80–100 AU from the Sun upwind of the interstellar medium and roughly 200 AU from the Sun downwind. Here the solar wind collides with the interstellar medium and dramatically slows, condenses and becomes more turbulent, forming a great oval structure known as the ''heliosheath''. This structure has been theorized to look and behave very much like a comet's tail, extending outward for a further 40 AU on the upwind side but tailing many times that distance downwind. Evidence from the '' Cassini'' and Interstellar Boundary Explorer
Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX or Explorer 91 or SMEX-10) is a NASA satellite in Earth orbit that uses energetic neutral atoms (ENAs) to image the interaction region between the Solar System and interstellar space. The mission is par ...
spacecraft has suggested that it is forced into a bubble shape by the constraining action of the interstellar magnetic field, but the actual shape remains unknown.
The outer boundary of the heliosphere, the ''heliopause'', is the point at which the solar wind finally terminates and is the beginning of interstellar space. ''Voyager 1
''Voyager 1'' is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. Launched 16 days after its twin '' Voyager 2'', ''V ...
'' and ''Voyager 2
''Voyager 2'' is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. As a part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, '' Voyager 1'', ...
'' passed the termination shock and entered the heliosheath at 94 and 84 AU from the Sun, respectively. ''Voyager 1'' was reported to have crossed the heliopause in August 2012, and ''Voyager 2'' in December 2018.
The shape and form of the outer edge of the heliosphere is likely affected by the fluid dynamics
In physics and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids— liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including ''aerodynamics'' (the study of air and other gases in motion) a ...
of interactions with the interstellar medium as well as solar magnetic fields prevailing to the south, e.g. it is bluntly shaped with the northern hemisphere extending 9 AU farther than the southern hemisphere. See Figures 1 and 2. Beyond the heliopause, at around 230 AU, lies the bow shock
In astrophysics, a bow shock occurs when the magnetosphere of an astrophysical object interacts with the nearby flowing ambient plasma such as the solar wind. For Earth and other magnetized planets, it is the boundary at which the speed of th ...
, a plasma "wake" left by the Sun as it travels through the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
.
Detached objects
(with an average orbit of 520 AU from the Sun) is a large, reddish object with a gigantic, highly elliptical orbit that takes it from about 76 AU at perihelion to 940 AU at aphelion and takes 11,400 years to complete. Mike Brown, who discovered the object in 2003, asserts that it cannot be part of thescattered disc
The scattered disc (or scattered disk) is a distant circumstellar disc in the Solar System that is sparsely populated by icy small solar system bodies, which are a subset of the broader family of trans-Neptunian objects. The scattered-disc obje ...
or the Kuiper belt because its perihelion is too distant to have been affected by Neptune's migration. He and other astronomers consider it to be the first in an entirely new population, sometimes termed "distant detached objects" (DDOs), which also may include the object , which has a perihelion of 45 AU, an aphelion of 415 AU, and an orbital period of 3,420 years. Brown terms this population the "inner Oort cloud" because it may have formed through a similar process, although it is far closer to the Sun. Sedna is very likely a dwarf planet, though its shape has yet to be determined. The second unequivocally detached object, with a perihelion farther than Sedna's at roughly 81 AU, is , discovered in 2012. Its aphelion is only about half that of Sedna's, at 458 AU.
Oort cloud
The Oort cloud is a hypothetical spherical cloud of up to a trillion icy objects that is thought to be the source for all long-period comets and to surround the Solar System at roughly 50,000 AU (around 1light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distance, astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 Orders of magnitude (numbers)#1012, trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 ...
(ly)) from the Sun, and possibly to as far as 100,000 AU (1.87 ly). It is thought to be composed of comets that were ejected from the inner Solar System by gravitational interactions with the outer planets. Oort cloud objects move very slowly, and can be perturbed by infrequent events, such as collisions, the gravitational effects of a passing star, or the galactic tide
A galactic tide is a tidal force experienced by objects subject to the gravitational field of a galaxy such as the Milky Way. Particular areas of interest concerning galactic tides include galactic collisions, the disruption of dwarf or satelli ...
, the tidal force
The tidal force is a gravitational effect that stretches a body along the line towards the center of mass of another body due to a gradient (difference in strength) in gravitational field from the other body; it is responsible for diverse phenomen ...
exerted by the Milky Way.
Boundaries
Much of the Solar System is still unknown. The Sun's gravitational field is estimated to dominate the gravitational forces of surrounding stars out to about two light-years (125,000 AU). Lower estimates for the radius of the Oort cloud, by contrast, do not place it farther than 50,000 AU. Most of the mass is orbiting in the region between 3,000 and 100,000 AU. Despite discoveries such as Sedna, the region between the Kuiper belt and the Oort cloud, an area tens of thousands of AU in radius, is still virtually unmapped. Learning about this region of space is difficult, because it depends upon inferences from those few objects whose orbits happen to be perturbed such that they fall closer to the Sun, and even then, detecting these objects has often been possible only when they happened to become bright enough to register as comets. Objects may yet be discovered in the Solar System's uncharted regions. The furthest known objects, such asComet West
Comet West, formally designated C/1975 V1, 1976 VI, and 1975n, was a comet described as one of the brightest objects to pass through the inner Solar System in 1976. It is often described as a "great comet."
History
It was discovered photograp ...
, have aphelia around 70,000 AU from the Sun.
Galactic context
The Solar System is located in theMilky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
, a barred spiral galaxy
A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in about two thirds of all spiral galaxies, and generally affect both the motions of stars and interstellar gas within spiral galaxies ...
with a diameter of about 100,000 light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distance, astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 Orders of magnitude (numbers)#1012, trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 ...
s containing more than 100 billion stars. The Sun resides in one of the Milky Way's outer spiral arms, known as the Orion–Cygnus Arm
The Orion Arm is a minor spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy that is across and approximately in length, containing the Solar System, including Earth. It is also referred to by its full name, the Orion–Cygnus Arm, as well as Local Arm, Orion ...
or Local Spur. The Sun lies about 26,660 light-years from the Galactic Center
The Galactic Center or Galactic Centre is the rotational center, the barycenter, of the Milky Way galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a compact ra ...
, and its speed around the center of the Milky Way is about 220 km/s, so that it completes one revolution every 240 million years. This revolution is known as the Solar System's galactic year
The galactic year, also known as a cosmic year, is the duration of time required for the Sun to orbit once around the center of the Milky Way Galaxy.
. The solar apex
The solar apex, or the apex of the Sun's way, refers to the direction that the Sun travels with respect to the local standard of rest. This is not to be confused with the Sun's apparent motion through all constellations of the zodiac, which ...
, the direction of the Sun's path through interstellar space, is near the constellation Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures.
The Romans adapted the ...
in the direction of the current location of the bright star Vega
Vega is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Lyra. It has the Bayer designation α Lyrae, which is Latinised to Alpha Lyrae and abbreviated Alpha Lyr or α Lyr. This star is relatively close at only from the Sun, a ...
. The plane of the ecliptic lies at an angle of about 60° to the galactic plane.
The Solar System's location in the Milky Way is a factor in the evolutionary history of life on Earth. Its orbit is close to circular, and orbits near the Sun are at roughly the same speed as that of the spiral arms. Therefore, the Sun passes through arms only rarely. Because spiral arms are home to a far larger concentration of supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or whe ...
e, gravitational instabilities, and radiation that could disrupt the Solar System, this has given Earth long periods of stability for life to evolve. However, the changing position of the Solar System relative to other parts of the Milky Way could explain periodic extinction events on Earth, according to the Shiva hypothesis or related theories, but this remains controversial.
The Solar System lies well outside the star-crowded environs of the galactic centre. Near the centre, gravitational tugs from nearby stars could perturb bodies in the Oort cloud
The Oort cloud (), sometimes called the Öpik–Oort cloud, first described in 1950 by the Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, is a theoretical concept of a cloud of predominantly icy planetesimals proposed to surround the Sun at distances ranging from ...
and send many comets into the inner Solar System, producing collisions with potentially catastrophic implications for life on Earth. The intense radiation of the galactic centre could also interfere with the development of complex life. Stellar flybys that pass within of the Sun occur roughly once every 100,000 years. The closest well-measured approach was Scholz's Star, which approached to of the Sun some , likely passing through the outer Oort cloud.
Celestial neighbourhood
 The Solar System is surrounded by the
The Solar System is surrounded by the Local Interstellar Cloud
The Local Interstellar Cloud (LIC), also known as the Local Fluff, is an interstellar cloud roughly across, through which the Solar System is moving. This feature overlaps a region around the Sun referred to as the solar neighborhood. It is un ...
, although it is not clear if it is embedded in the Local Interstellar Cloud or if it lies just outside the cloud's edge. Multiple other interstellar cloud
An interstellar cloud is generally an accumulation of gas, plasma, and dust in our and other galaxies. Put differently, an interstellar cloud is a denser-than-average region of the interstellar medium, the matter and radiation that exists in the ...
s also exist in the region within 300 light-years of the Sun, known as the Local Bubble. The latter feature is an hourglass-shaped cavity or superbubble
A superbubble or supershell is a cavity which is hundreds of light years across and is populated with hot (106 K) gas atoms, less dense than the surrounding interstellar medium, blown against that medium and carved out by multiple superno ...
in the interstellar medium roughly 300 light-years across. The bubble is suffused with high-temperature plasma, suggesting that it may be the product of several recent supernovae.
The Local Bubble is a small superbubble compared to the neighbouring wider Radcliffe Wave and ''Split'' linear structures (formerly Gould Belt
The Gould Belt is a local, partial ring of stars in the Milky Way, about 3,000 light-years long, tilted away from the galactic plane by about 16–20 degrees. It contains many O- and B-type stars, amounting to the nearest star-forming re ...
), each of which are some thousands of light-years in length. All these structures are part of the Orion Arm
The Orion Arm is a minor spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy that is across and approximately in length, containing the Solar System, including Earth. It is also referred to by its full name, the Orion–Cygnus Arm, as well as Local Arm, Orion ...
, which contains most of the stars in the Milky Way that are visible to the unaided eye. The density of all matter in the local neighborhood is ·pc−3.
Within ten light-years of the Sun there are relatively few stars, the closest being the triple star system Alpha Centauri
Alpha Centauri ( Latinized from α Centauri and often abbreviated Alpha Cen or α Cen) is a triple star system in the constellation of Centaurus. It consists of 3 stars: Alpha Centauri A (officially Rigil Kentaurus), Alpha Centa ...
, which is about 4.4 light-years away and may be in the Local Bubble's G-Cloud. Alpha Centauri A and B are a closely tied pair of Sun-like stars, whereas the closest star to Earth, the small red dwarf
''Red Dwarf'' is a British science fiction comedy franchise created by Rob Grant and Doug Naylor, which primarily consists of a television sitcom that aired on BBC Two between 1988 and 1999, and on Dave since 2009, gaining a cult following. ...
Proxima Centauri
Proxima Centauri is a small, low-mass star located away from the Sun in the southern constellation of Centaurus. Its Latin name means the 'nearest tarof Centaurus'. It was discovered in 1915 by Robert Innes and is the nearest-k ...
, orbits the pair at a distance of 0.2 light-year. In 2016, a potentially habitable exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
was found to be orbiting Proxima Centauri, called Proxima Centauri b
Proxima Centauri b (or Proxima b), sometimes referred to as Alpha Centauri Cb, is an exoplanet orbiting in the habitable zone of the red dwarf star Proxima Centauri, which is the closest star to the Sun and part of the triple star system Alp ...
, the closest confirmed exoplanet to the Sun.
The next closest known fusors to the Sun are the red dwarfs Barnard's Star
Barnard's Star is a red dwarf about six light-years from Earth in the constellation of Ophiuchus. It is the fourth-nearest-known individual star to the Sun after the three components of the Alpha Centauri system, and the closest star in t ...
(at 5.9 ly), Wolf 359 (7.8 ly), and Lalande 21185 (8.3 ly). The nearest brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs (also called failed stars) are substellar objects that are not massive enough to sustain nuclear fusion of ordinary hydrogen ( 1H) into helium in their cores, unlike a main-sequence star. Instead, they have a mass between the most ...
s belong to the binary Luhman 16 system (6.6 ly), and the closest known rogue
A rogue is a person or entity that flouts accepted norms of behavior.
Rogue or rogues may also refer to:
Companies
* Rogue Ales, a microbrewery in Newport, Oregon
* Rogue Arts, a film production company
* Rogue Entertainment, a software co ...
or free-floating planetary-mass object at less than 10 Jupiter masses is the sub-brown dwarf
A sub-brown dwarf or planetary-mass brown dwarf is an astronomical object that formed in the same manner as stars and brown dwarfs (i.e. through the collapse of a gas cloud) but that has a planetary mass, therefore by definition below the limi ...
WISE 0855−0714
WISE 0855−0714 (full designation WISE J085510.83−071442.5, or W0855 for short) is a sub-brown dwarf () from Earth, therefore the fourth- closest star or (sub-) brown dwarf system to the Sun, the discovery of which was announced in ...
(7.4 ly).
Just beyond at 8.6 ly lies Sirius
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. Its name is derived from the Greek word , or , meaning 'glowing' or 'scorching'. The star is designated α Canis Majoris, Latinized to Alpha Canis Majoris, and abbreviated Alpha CM ...
, the brightest star in Earth's night sky
The night sky is the nighttime appearance of celestial objects like stars, planets, and the Moon, which are visible in a clear sky between sunset and sunrise, when the Sun is below the horizon.
Natural light sources in a night sky in ...
, with roughly twice the Sun's mass, orbited by the closest white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
to Earth, Sirius B. Other stars within ten light-years are the binary red-dwarf system Luyten 726-8
Luyten 726-8, also known as Gliese 65, is a binary star system that is one of Earth's nearest neighbors, at about 8.7 light years from Earth in the constellation Cetus. The two component stars are both flare stars with the variable s ...
(8.7 ly) and the solitary red dwarf Ross 154
Ross 154 (V1216 Sgr) is a star in the southern zodiac constellation of Sagittarius. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 10.44, making it much too faint to be seen with the naked eye. At a minimum, viewing Ross 154 requires a telescope ...
(9.7 ly). The closest solitary Sun-like star to the Solar System is Tau Ceti at 11.9 light-years. It has roughly 80% of the Sun's mass but only about half of its luminosity.
The nearest and unaided-visible group of stars beyond the immediate celestial neighbourhood is the Ursa Major Moving Group at roughly 80 light-years, which is within the Local Bubble, like the nearest as well as unaided-visible star cluster
Star clusters are large groups of stars. Two main types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters are tight groups of ten thousand to millions of old stars which are gravitationally bound, while open clusters are more loosely cl ...
the Hyades, which lie at its edge. The closest star-forming regions are the Corona Australis Molecular Cloud, the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex
The Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex is a complex of interstellar clouds with different nebulae, particularly dark nebulae which is centered 1° south of the star ρ Ophiuchi, which it among others extends to, of the constellation Ophiuchus. At an es ...
and the Taurus Molecular Cloud; the latter lies just beyond the Local Bubble and is part of the Radcliffe wave.
Comparison with extrasolar systems
Compared to many extrasolar systems, the Solar System stands out in lacking planets interior to the orbit of Mercury. The known Solar System also lackssuper-Earth
A super-Earth is an extrasolar planet with a mass higher than Earth's, but substantially below those of the Solar System's ice giants, Uranus and Neptune, which are 14.5 and 17 times Earth's, respectively.
The term "super-Earth" refers only to ...
s, planets between one and ten times as massive as the Earth, although the hypothetical Planet Nine
Planet Nine is a hypothetical planet in the outer region of the Solar System. Its gravitational effects could explain the peculiar clustering of orbits for a group of extreme trans-Neptunian objects (ETNOs), bodies beyond Neptune that orbit ...
, if it does exist, could be a super-Earth beyond the Solar System as we understand it today. Uncommonly, it has only small rocky planets and large gas giants; elsewhere planets of intermediate size are typical—both rocky and gas—so there is no "gap" as seen between the size of Earth and of Neptune (with a radius 3.8 times as large). As many of these super-Earths are closer to their respective stars than Mercury is to the sun, a hypothesis has arisen that all planetary systems start with many close-in planets, and that typically a sequence of their collisions causes consolidation of mass into few larger planets, but in case of the Solar System the collisions caused their destruction and ejection.
The orbits of Solar System planets are nearly circular. Compared to other systems, they have smaller orbital eccentricity
In astrodynamics, the orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a dimensionless parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect circle. A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values bet ...
. Although there are attempts to explain it partly with a bias in the radial-velocity detection method and partly with long interactions of a quite high number of planets, the exact causes remain undetermined.
Humanity's perspective
 Humanity's knowledge of the Solar System has grown incrementally over the centuries. Up to the
Humanity's knowledge of the Solar System has grown incrementally over the centuries. Up to the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Ren ...
–Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
, astronomers from Europe to India believed Earth to be stationary at the centre of the Universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the univers ...
and categorically different from the divine or ethereal objects that moved through the sky. Although the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
philosopher Aristarchus of Samos
Aristarchus of Samos (; grc-gre, Ἀρίσταρχος ὁ Σάμιος, ''Aristarkhos ho Samios''; ) was an ancient Greek astronomer and mathematician who presented the first known heliocentric model that placed the Sun at the center of the ...
had speculated on a heliocentric
Heliocentrism (also known as the Heliocentric model) is the astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun at the center of the universe. Historically, heliocentrism was opposed to geocentrism, which placed the Earth ...
reordering of the cosmos, Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (; pl, Mikołaj Kopernik; gml, Niklas Koppernigk, german: Nikolaus Kopernikus; 19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulat ...
was the first person known to have developed a mathematically predictive heliocentric system. Heliocentrism did not triumph immediately over geocentrism, but the work of Copernicus had its champions, notably Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws ...
. Using a heliocentric model that improved upon Copernicus by allowing orbits to be elliptical as well as circular, and the precise observational data of Tycho Brahe
Tycho Brahe ( ; born Tyge Ottesen Brahe; generally called Tycho (14 December 154624 October 1601) was a Danish astronomer, known for his comprehensive astronomical observations, generally considered to be the most accurate of his time. He was ...
, Kepler produced the ''Rudolphine Tables
The ''Rudolphine Tables'' ( la, Tabulae Rudolphinae) consist of a star catalogue and planetary tables published by Johannes Kepler in 1627, using observational data collected by Tycho Brahe (1546–1601). The tables are named in memory of Rudolf ...
'', which enabled accurate computations of the positions of the then-known planets. Pierre Gassendi
Pierre Gassendi (; also Pierre Gassend, Petrus Gassendi; 22 January 1592 – 24 October 1655) was a French philosopher, Catholic priest, astronomer, and mathematician. While he held a church position in south-east France, he also spent much t ...
used them to predict a transit of Mercury in 1631, and Jeremiah Horrocks
Jeremiah Horrocks (16183 January 1641), sometimes given as Jeremiah Horrox (the Latinised version that he used on the Emmanuel College register and in his Latin manuscripts), – See footnote 1 was an English astronomer. He was the first person ...
did the same for a transit of Venus
frameless, upright=0.5
A transit of Venus across the Sun takes place when the planet Venus passes directly between the Sun and a superior planet, becoming visible against (and hence obscuring a small portion of) the solar disk. During a tr ...
in 1639. This provided a strong vindication of heliocentrism and Kepler's elliptical orbits.
In the 17th century, Galileo
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He was ...
publicized the use of the telescope in astronomy; he and Simon Marius
Simon Marius ( latinized form of Simon Mayr; 10 January 1573 – 5 January 1625) was a German astronomer. He was born in Gunzenhausen, near Nuremberg, but spent most of his life in the city of Ansbach. He is most known for being among the first ...
independently discovered that Jupiter had four satellites in orbit around it. Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , , ; also spelled Huyghens; la, Hugenius; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor, who is regarded as one of the greatest scientists o ...
followed on from these observations by discovering Saturn's moon Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
and the shape of the rings of Saturn
The rings of Saturn are the most extensive ring system of any planet in the Solar System. They consist of countless small particles, ranging in size from micrometers to meters, that orbit around Saturn. The ring particles are made almost entir ...
. In 1677, Edmond Halley
Edmond (or Edmund) Halley (; – ) was an English astronomer, mathematician and physicist. He was the second Astronomer Royal in Britain, succeeding John Flamsteed in 1720.
From an observatory he constructed on Saint Helena in 1676–77, H ...
observed a transit of Mercury across the Sun, leading him to realise that observations of the solar parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening, nearby object ...
of a planet (more ideally using the transit of Venus) could be used to trigonometrically determine the distances between Earth, Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
, and the Sun. Halley's friend Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, Theology, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosophy, natural philosopher"), widely ...
, in his magisterial ''Principia Mathematica
The ''Principia Mathematica'' (often abbreviated ''PM'') is a three-volume work on the foundations of mathematics written by mathematician–philosophers Alfred North Whitehead and Bertrand Russell and published in 1910, 1912, and 1913. ...
'' of 1687, demonstrated that celestial bodies are not quintessentially different from Earthly ones: the same laws of motion and of gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stro ...
apply on Earth and in the skies.
The term "Solar System" entered the English language by 1704, when John Locke
John Locke (; 29 August 1632 – 28 October 1704) was an English philosopher and physician, widely regarded as one of the most influential of Enlightenment thinkers and commonly known as the "father of liberalism". Considered one of ...
used it to refer to the Sun, planets, and comets. In 1705, Halley realised that repeated sightings of a comet were of the same object, returning regularly once every 75–76 years. This was the first evidence that anything other than the planets repeatedly orbited the Sun, though Seneca had theorized this about comets in the 1st century. Careful observations of the 1769 transit of Venus allowed astronomers to calculate the average Earth–Sun distance as , only 0.8% greater than the modern value. Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus ( Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars), grandfather of Zeus (Jupiter) and father of ...
, having occasionally been observed since antiquity, was recognized to be a planet orbiting beyond Saturn by 1783. In 1838, Friedrich Bessel successfully measured a stellar parallax
Stellar parallax is the apparent shift of position of any nearby star (or other object) against the background of distant objects, and a basis for determining (through trigonometry) the distance of the object. Created by the different orbital p ...
, an apparent shift in the position of a star created by Earth's motion around the Sun, providing the first direct, experimental proof of heliocentrism. Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 time ...
was identified as a planet some years later, in 1846, thanks to its gravitational pull causing a slight but detectable variation in the orbit of Uranus.
In the 20th century, humans began their space exploration around the Solar System, starting with placing telescopes in space. Since then, humans have landed on the Moon during the Apollo program; the Apollo 13
Apollo 13 (April 1117, 1970) was the seventh crewed mission in the Apollo space program and the third meant to land on the Moon. The craft was launched from Kennedy Space Center on April 11, 1970, but the lunar landing was aborted aft ...
mission marked the furthest any human has been away from Earth at . All eight planets have been visited by space probes; the outer planets were first visited by the ''Voyager'' spacecraft, one of which (''Voyager 1
''Voyager 1'' is a space probe launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, as part of the Voyager program to study the outer Solar System and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. Launched 16 days after its twin '' Voyager 2'', ''V ...
'') is the furthest object made by humankind and the first in interstellar space. In addition, probes have also returned samples from comets and asteroids, as well as flown through the Sun's corona and made fly-bys of Kuiper belt objects. Six of the planets (all but Uranus and Neptune) have or had a dedicated orbiter.
See also
*List of gravitationally rounded objects of the Solar System
This is a list of most likely gravitationally rounded objects of the Solar System, which are objects that have a rounded, ellipsoidal shape due to their own gravity (but are not necessarily in hydrostatic equilibrium). Apart from the Sun itself, ...
* List of Solar System objects by size
This article includes a list of the most massive known objects of the Solar System and partial lists of smaller objects by observed mean radius. These lists can be sorted according to an object's radius and mass and, for the most massive objects, ...
* Lists of geological features of the Solar System
* List of Solar System extremes
This article describes extreme locations of the Solar System. Entries listed in bold are Solar System-wide extremes.
By feature
By class
By object
By distance
* List of Solar System objects most distant from the Sun
See also
* ...
* Outline of the Solar System
Notes
References
External links
*A Tediously Accurate Map of the Solar System (web based scroll map scaled to the Moon being 1 pixel)
NASA's Eyes-on-the-Solar-System
NASA's Solar System Exploration
NASA's Solar System Simulator
{{Authority control Planetary science Space science Planetary systems with eight confirmed planets