Open data on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Open data is
Open data is
Martin Hilbert (2013), SSRN Scholarly Paper No. ID 2205145. Rochester, NY: Social Science Research Network; https://ssrn.com/abstract=2205145 * In scientific research, the rate of discovery is accelerated by better access to data. * Making data open helps combat "data rot" and ensure that scientific research data are preserved over time. * Statistical literacy benefits from open data. Instructors can use locally relevant data sets to teach statistical concepts to their students. It is generally held that factual data cannot be copyrighted. Publishers frequently add copyright statements (often forbidding re-use) to scientific data accompanying publications. It may be unclear whether the factual data embedded in full text are part of the copyright. While the human abstraction of facts from paper publications is normally accepted as legal there is often an implied restriction on the machine extraction by robots. Unlike open access, where groups of publishers have stated their concerns, open data is normally challenged by individual institutions. Their arguments have been discussed less in public discourse and there are fewer quotes to rely on at this time. Arguments against making all data available as open data include the following: * Government funding may not be used to duplicate or challenge the activities of the private sector (e.g. PubChem). * Governments have to be accountable for the efficient use of taxpayer's money: If public funds are used to aggregate the data and if the data will bring commercial (private) benefits to only a small number of users, the users should reimburse governments for the cost of providing the data. * Open data may lead to exploitation of, and rapid publication of results based on, data pertaining to developing countries by rich and well-equipped research institutes, without any further involvement and/or benefit to local communities ( helicopter research); similarly, to the historical open access to tropical forests that has led to the misappropriation ("Global Pillage") of plant genetic resources from developing countries. * The revenue earned by publishing data can be used to cover the costs of generating and/or disseminating the data, so that the dissemination can continue indefinitely. * The revenue earned by publishing data permits non-profit organizations to fund other activities (e.g. learned society publishing supports the society). * The government gives specific legitimacy for certain organizations to recover costs ( NIST in US,
Open Data – An Introduction
– from the
Video
of Tim Berners-Lee at
Six minute Video
of Tim Berners-Lee at
G8 Open Data Charter
Towards a Genealogy of Open Data
– research paper tracing different historical threads contributing to current conceptions of open data. {{Authority control Free culture movement

 Open data is
Open data is data
In the pursuit of knowledge, data (; ) is a collection of discrete Value_(semiotics), values that convey information, describing quantity, qualitative property, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of sy ...
that is openly accessible, exploitable, editable and shared by anyone for any purpose. Open data is licensed under an open license.
The goals of the open data movement are similar to those of other "open(-source)" movements such as open-source software, hardware, open content, open specifications
An open specification is a specification
A specification often refers to a set of documented requirements to be satisfied by a material, design, product, or service. A specification is often a type of technical standard.
There are different typ ...
, open education, open educational resources
Open educational resources (OER) are teaching, learning, and research materials intentionally created and licensed to be free for the end user to own, share, and in most cases, modify. The term "OER" describes publicly accessible materials and ...
, open government, open knowledge
Open knowledge (or free knowledge) is knowledge that is free to use, reuse, and redistribute without legal, social, or technological restriction. Open knowledge organizations and activists have proposed principles and methodologies related to th ...
, open access, open science, and the open web. The growth of the open data movement is paralleled by a rise in intellectual property rights. The philosophy behind open data has been long established (for example in the Mertonian tradition of science), but the term "open data" itself is recent, gaining popularity with the rise of the Internet and World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW), commonly known as the Web, is an information system enabling documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet.
Documents and downloadable media are made available to the network through web ...
and, especially, with the launch of open-data government initiatives such as Data.gov, Data.gov.uk and Data.gov.in.
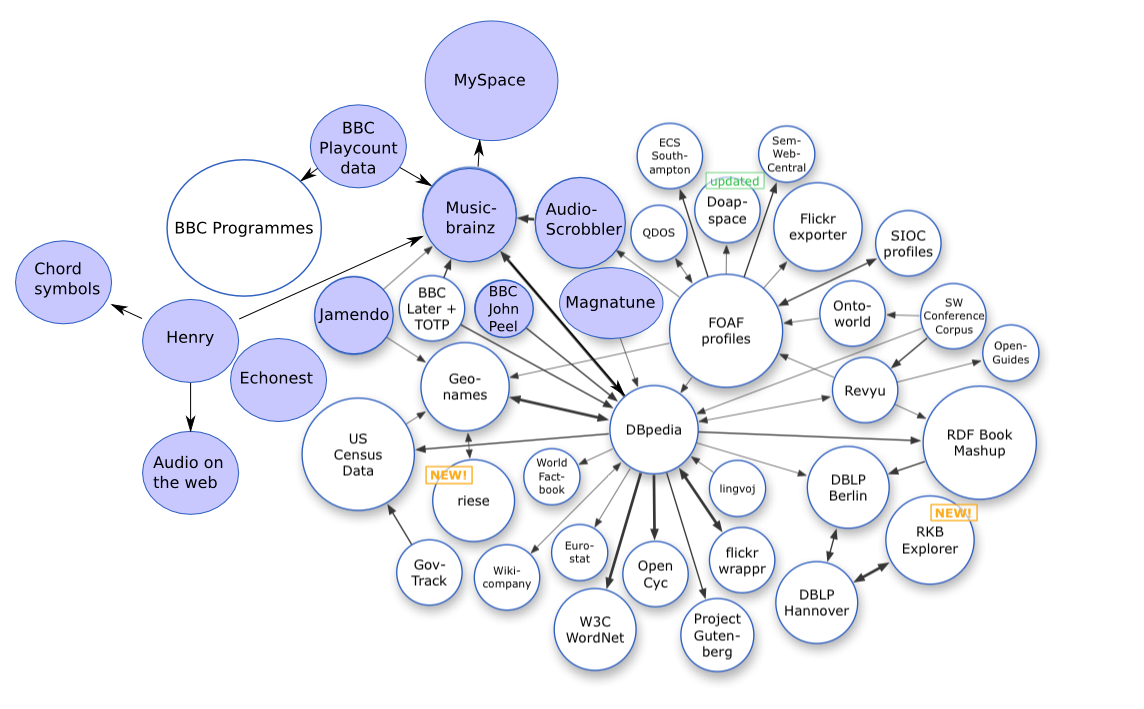
Open data can be linked data
In computing, linked data (often capitalized as Linked Data) is structured data which is interlinked with other data so it becomes more useful through semantic queries. It builds upon standard Web technologies such as HTTP, RDF and URIs, but ...
- referred to as linked open data.
One of the most important forms of open data is open government data (OGD), which is a form of open data created by ruling government institutions. Open government data's importance is born from it being a part of citizens' everyday lives, down to the most routine/mundane tasks that are seemingly far removed from government.
The abbreviation is sometimes used to indicate that the dataset or database in question complies with the principles of FAIR data and carries an explicit data‑capable open license.
Overview
The concept of open data is not new, but a formalized definition is relatively new. Open data as a phenomenon denotes that governmental data should be available to anyone with a possibility of redistribution in any form without any copyright restriction. One more definition is the Open Definition which can be summarized as "a piece of data is open if anyone is free to use, reuse, and redistribute it – subject only, at most, to the requirement to attribute and/or share-alike." Other definitions, including theOpen Data Institute
The Open Data Institute (ODI) is a non-profit private company limited by guarantee, based in the United Kingdom. Founded by Sir Tim Berners-Lee and Sir Nigel Shadbolt in 2012, the ODI’s mission is to connect, equip and inspire people around th ...
's "open data is data that anyone can access, use or share," have an accessible short version of the definition but refer to the formal definition. Open data may include non-textual material such as map
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes.
Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although ...
s, genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
s, connectome
A connectome () is a comprehensive map of neural connections in the brain, and may be thought of as its "wiring diagram". An organism's nervous system is made up of neurons which communicate through synapses. A connectome is constructed by tr ...
s, chemical compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element ...
s, mathematical and scientific formulae, medical data, and practice, bioscience and biodiversity.
A major barrier to the open data movement is the commercial value of data. Access to, or re-use of, data is often controlled by public or private organizations. Control may be through access restrictions, licenses
A license (or licence) is an official permission or permit to do, use, or own something (as well as the document of that permission or permit).
A license is granted by a party (licensor) to another party (licensee) as an element of an agreeme ...
, copyright
A copyright is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the exclusive right to copy, distribute, adapt, display, and perform a creative work, usually for a limited time. The creative work may be in a literary, artistic, educatio ...
, patents and charges for access or re-use. Advocates of open data argue that these restrictions detract from the common good and that data should be available without restrictions or fees.
Creators of data do not consider the need to state the conditions of ownership, licensing and re-use; instead presuming that not asserting copyright enters the data into the public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable. Because those rights have expired, ...
. For example, many scientists do not consider the data published with their work to be theirs to control and consider the act of publication in a journal to be an implicit release of data into the commons
The commons is the cultural and natural resources accessible to all members of a society, including natural materials such as air, water, and a habitable Earth. These resources are held in common even when owned privately or publicly. Commons c ...
. The lack of a license makes it difficult to determine the status of a data set A data set (or dataset) is a collection of data. In the case of tabular data, a data set corresponds to one or more database tables, where every column of a table represents a particular variable, and each row corresponds to a given record of the ...
and may restrict the use of data offered in an "Open" spirit. Because of this uncertainty it is possible for public or private organizations to aggregate said data, claim that it is protected by copyright, and then resell it.
The issue of indigenous knowledge
Traditional knowledge (TK), indigenous knowledge (IK) and local knowledge generally refer to knowledge systems embedded in the cultural traditions of regional, indigenous, or local communities. According to the World Intellectual Property Orga ...
(IK) poses a great challenge in terms of capturing, storage and distribution. Many societies in third-world countries lack the technicality processes of managing the IK.
At his presentation at the XML 2005 conference, Connolly displayed these two quotations regarding open data:
* "I want my data back." (Jon Bosak circa 1997)
* "I've long believed that customers of any application own the data they enter into it." (This quote refers to Veen's own heart-rate data.)
Major sources
Open data can come from any source. This section lists some of the fields that publish (or at least discuss publishing) a large amount of open data.In science
The concept of open access to scientific data was established with the formation of the World Data Center system, in preparation for the International Geophysical Year of 1957–1958. The International Council of Scientific Unions (now the International Council for Science) oversees several World Data Centres with the mission to minimize the risk of data loss and to maximize data accessibility. While the open-science-data movement long predates the Internet, the availability of fast, readily available networking has significantly changed the context ofOpen science data Open scientific data or open research data is a type of open data focused on publishing observations and results of scientific activities available for anyone to analyze and reuse. A major purpose of the drive for open data is to allow the verificat ...
, as publishing or obtaining data has become much less expensive and time-consuming.
The Human Genome Project was a major initiative that exemplified the power of open data. It was built upon the so-called Bermuda Principles, stipulating that: "All human genomic sequence information … should be freely available and in the public domain in order to encourage research and development and to maximize its benefit to society". More recent initiatives such as the Structural Genomics Consortium have illustrated that the open data approach can be used productively within the context of industrial R&D.
In 2004, the Science Ministers of all nations of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), which includes most developed countries of the world, signed a declaration which states that all publicly funded archive data should be made publicly available. Following a request and an intense discussion with data-producing institutions in member states, the OECD published in 2007 the ''OECD Principles and Guidelines for Access to Research Data from Public Funding'' as a ''soft-law'' recommendation.
Examples of open data in science:
* data.uni-muenster.de – Open data about scientific artifacts from the University of Muenster, Germany. Launched in 2011.
* Dataverse Network Project – archival repository software promoting data sharing
Data sharing is the practice of making data used for scholarly research available to other investigators. Many funding agencies, institutions, and publication venues have policies regarding data sharing because transparency and openness are consid ...
, persistent data citation, and reproducible research.
* linkedscience.org/data – Open scientific datasets encoded as Linked Data
In computing, linked data (often capitalized as Linked Data) is structured data which is interlinked with other data so it becomes more useful through semantic queries. It builds upon standard Web technologies such as HTTP, RDF and URIs, but ...
. Launched in 2011, ended 2018.
* systemanaturae.org – Open scientific datasets related to wildlife classified by animal species. Launched in 2015.In government
There are a range of different arguments for government open data. Some advocates say that making government information available to the public as machine readable open data can facilitate government transparency, accountability and public participation. "Open data can be a powerful force for public accountability—it can make existing information easier to analyze, process, and combine than ever before, allowing a new level of public scrutiny." Governments that enable public viewing of data can help citizens engage within the governmental sectors and "add value to that data." Open data experts have nuanced the impact that opening government data may have on government transparency and accountability. In a widely cited paper, scholars David Robinson and Harlan Yu contend that governments may project a veneer of transparency by publishing machine-readable data that does not actually make government more transparent or accountable. Drawing from earlier studies on transparency and anticorruption, World Bank political scientist Tiago C. Peixoto extended Yu and Robinson’s argument by highlighting a minimal chain of events necessary for open data to lead to accountability: # relevant data is disclosed; # the data is widely disseminated and understood by the public; # the public reacts to the content of the data; and # public officials either respond to the public’s reaction or are sanctioned by the public through institutional means. Some make the case that opening up official information can support technological innovation and economic growth by enabling third parties to develop new kinds of digital applications and services. Several national governments have created websites to distribute a portion of the data they collect. It is a concept for a collaborative project in the municipal Government to create and organize culture for Open Data or Open government data. Additionally, other levels of government have established open data websites. There are many government entities pursuing Open Data in Canada. Data.gov lists the sites of a total of 40 US states and 46 US cities and counties with websites to provide open data, e.g., the state ofMaryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, the state of California, US and New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
.
At the international level, the United Nations has an open data website that publishes statistical data from member states and UN agencies, and the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
published a range of statistical data relating to developing countries. The European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body ...
has created two portals for the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
: the EU Open Data Portal
Before data.europa.eu, the EU Open Data Portal was the point of access to public data published by the EU institutions, agencies and other bodies. On April 21, 2021 it was consolidated to the data.europa.eu portal, together with the European Data ...
which gives access to open data from the EU institutions, agencies and other bodies and the European Data Portal that provides datasets from local, regional and national public bodies across Europe. The two portals were consolidated to data.europa.eu on April 21, 2021.
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
is the first country to release standard processes and guidelines under a Creative Commons license for spread usage in the Public Administration. The open model is called the Open Data Management Cycle and was adopted in several regions such as Veneto
it, Veneto (man) it, Veneta (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 = ...
and Umbria
it, Umbro (man) it, Umbra (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, ...
Main cities like Reggio Calabria and Genova
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of G ...
have adopted this model.
In October 2015, the Open Government Partnership launched the International Open Data Charter, a set of principles and best practices for the release of governmental open data formally adopted by seventeen governments of countries, states and cities during the OGP Global Summit in Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
.
In non-profit organizations
Manynon-profit organizations
A nonprofit organization (NPO) or non-profit organisation, also known as a non-business entity, not-for-profit organization, or nonprofit institution, is a legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public or social benefit, in co ...
offer open access to their data, as long it does not undermine their users', members' or third party's privacy rights. In comparison to for-profit corporation A for-profit corporation is an organization which aims to earn profit through its operations and is concerned with its own interests, unlike those of the public (non-profit corporation).
Structure
A for-profit corporation is usually an organization ...
s, they do not seek to monetize their data. OpenNWT launched a website offering open data of elections. CIAT offers open data to anybody who is willing to conduct big data analytics in order to enhance the benefit of international agricultural research. DBLP
DBLP is a computer science bibliography website. Starting in 1993 at Universität Trier in Germany, it grew from a small collection of HTML files and became an organization hosting a database and logic programming bibliography site. Since Novem ...
, which is owned by a non-profit organization Dagstuhl
Dagstuhl is a computer science research center in Germany, located in and named after a district of the town of Wadern, Merzig-Wadern, Saarland.
Location
Following the model of the mathematical center at Oberwolfach, the center is installed i ...
, offers its database of scientific publications from computer science as open data. Non-profit hospitality exchange services offer trustworthy teams of scientists access to their anonymized data for publication of insights to the benefit of humanity. Open Icecat provides product data-sheets and e-commerce usage statistics as open data. Before becoming a for-profit corporation A for-profit corporation is an organization which aims to earn profit through its operations and is concerned with its own interests, unlike those of the public (non-profit corporation).
Structure
A for-profit corporation is usually an organization ...
in 2011, Couchsurfing
CouchSurfing is a hospitality exchange service by which users can request homestays or interact with other people who are interested in travel. It is accessible via a website and mobile app. It uses a subscription business model, and while ho ...
offered 4 research teams access to its social network
A social network is a social structure made up of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), sets of dyadic ties, and other social interactions between actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for ...
ing data. In 2015, non-profit hospitality exchange services Bewelcome and Warm Showers
Warm Showers (WS) is a non-profit hospitality exchange service for people engaging in bicycle touring. The platform is a gift economy — hosts are not supposed to charge for lodging and are not bound. The legal form is a Colorado 501(c)(3) non ...
provided their data for public research.
Policies and strategies
At a small level, a business or research organization's policies and strategies towards open data will vary, sometimes greatly. One common strategy employed is the use of a data commons. A data commons is an interoperable software and hardware platform that aggregates (or collocates) data, data infrastructure, and data-producing and data-managing applications in order to better allow a community of users to manage, analyze, and share their data with others over both short- and long-term timelines. Ideally, this interoperable cyberinfrastructure should be robust enough "to facilitate transitions between stages in the life cycle of a collection" of data and information resources while still being driven by common data models and workspace tools enabling and supporting robust data analysis. The policies and strategies underlying a data commons will ideally involve numerous stakeholders, including the data commons service provider, data contributors, and data users. Grossman ''et al'' suggests six major considerations for a data commons strategy that better enables open data in businesses and research organizations. Such a strategy should address the need for: * permanent, persistent digital IDs, which enable access controls for datasets; * permanent, discoverable metadata associated with each digital ID; * application programming interface (API)-based access, tied to an authentication and authorization service; * data portability; * data "peering," without access, egress, and ingress charges; and * a rationed approach to users computing data over the data commons. Beyond individual businesses and research centers, and at a more macro level, countries like Germany have launched their own official nationwide open data strategies, detailing how data management systems and data commons should be developed, used, and maintained for the greater public good.Arguments for and against
Opening government data is only a waypoint on the road to improving education, improving government, and building tools to solve other real-world problems. While many arguments have been made categorically, the following discussion of arguments for and against open data highlights that these arguments often depend highly on the type of data and its potential uses. Arguments made on behalf of open data include the following: * "Data belongs to thehuman race
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
". Typical examples are genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding g ...
s, data on organisms, medical science, environmental data following the Aarhus Convention.
* Public money
Government spending or expenditure includes all government consumption, investment, and transfer payments. In national income accounting, the acquisition by governments of goods and services for current use, to directly satisfy the individual o ...
was used to fund the work, and so it should be universally available.
* It was created by or at a government institution (this is common in US National Laboratories and government agencies).
* Facts cannot legally be copyrighted.
* Sponsors of research do not get full value unless the resulting data are freely available.
* Restrictions on data re-use create an anticommons.
* Data are required for the smooth process of running communal human activities and are an important enabler of socio-economic development (health care, education, economic productivity, etc.)."Big Data for Development: From Information- to Knowledge Societies"Martin Hilbert (2013), SSRN Scholarly Paper No. ID 2205145. Rochester, NY: Social Science Research Network; https://ssrn.com/abstract=2205145 * In scientific research, the rate of discovery is accelerated by better access to data. * Making data open helps combat "data rot" and ensure that scientific research data are preserved over time. * Statistical literacy benefits from open data. Instructors can use locally relevant data sets to teach statistical concepts to their students. It is generally held that factual data cannot be copyrighted. Publishers frequently add copyright statements (often forbidding re-use) to scientific data accompanying publications. It may be unclear whether the factual data embedded in full text are part of the copyright. While the human abstraction of facts from paper publications is normally accepted as legal there is often an implied restriction on the machine extraction by robots. Unlike open access, where groups of publishers have stated their concerns, open data is normally challenged by individual institutions. Their arguments have been discussed less in public discourse and there are fewer quotes to rely on at this time. Arguments against making all data available as open data include the following: * Government funding may not be used to duplicate or challenge the activities of the private sector (e.g. PubChem). * Governments have to be accountable for the efficient use of taxpayer's money: If public funds are used to aggregate the data and if the data will bring commercial (private) benefits to only a small number of users, the users should reimburse governments for the cost of providing the data. * Open data may lead to exploitation of, and rapid publication of results based on, data pertaining to developing countries by rich and well-equipped research institutes, without any further involvement and/or benefit to local communities ( helicopter research); similarly, to the historical open access to tropical forests that has led to the misappropriation ("Global Pillage") of plant genetic resources from developing countries. * The revenue earned by publishing data can be used to cover the costs of generating and/or disseminating the data, so that the dissemination can continue indefinitely. * The revenue earned by publishing data permits non-profit organizations to fund other activities (e.g. learned society publishing supports the society). * The government gives specific legitimacy for certain organizations to recover costs ( NIST in US,
Ordnance Survey
Ordnance Survey (OS) is the national mapping agency for Great Britain. The agency's name indicates its original military purpose (see ordnance and surveying), which was to map Scotland in the wake of the Jacobite rising of 1745. There was a ...
in UK).
* Privacy concerns may require that access to data is limited to specific users or to sub-sets of the data.
* Collecting, 'cleaning', managing and disseminating data are typically labour- and/or cost-intensive processes – whoever provides these services should receive fair remuneration for providing those services.
* Sponsors do not get full value unless their data is used appropriately – sometimes this requires quality management, dissemination and branding efforts that can best be achieved by charging fees to users.
* Often, targeted end-users cannot use the data without additional processing (analysis, apps etc.) – if anyone has access to the data, none may have an incentive to invest in the processing required to make data useful (typical examples include biological, medical, and environmental data).
* There is no control to the secondary use (aggregation) of open data.
Relation to other open activities
The goals of the Open Data movement are similar to those of other "Open" movements. * Open access is concerned with making scholarly publications freely available on the internet. In some cases, these articles include open datasets as well. *Open specifications
An open specification is a specification
A specification often refers to a set of documented requirements to be satisfied by a material, design, product, or service. A specification is often a type of technical standard.
There are different typ ...
are documents describing file types or protocols, where the documents are openly licensed. These specifications are primarily meant to improve different software handling the same file types or protocols, but monopolists forced by law into open specifications might make it more difficult.
* Open content is concerned with making resources aimed at a human audience (such as prose, photos, or videos) freely available.
* Open knowledge
Open knowledge (or free knowledge) is knowledge that is free to use, reuse, and redistribute without legal, social, or technological restriction. Open knowledge organizations and activists have proposed principles and methodologies related to th ...
. Open Knowledge International
Open Knowledge Foundation (OKF) is a global, non-profit network that promotes and shares information at no charge, including both content and data. It was founded by Rufus Pollock on 20 May 2004 in Cambridge, UK. It is incorporated in England an ...
argues for openness in a range of issues including, but not limited to, those of open data. It covers (a) scientific, historical, geographic or otherwise (b) Content such as music, films, books (c) Government and other administrative information. Open data is included within the scope of the Open Knowledge Definition, which is alluded to in Science Commons' Protocol for Implementing Open Access Data.
* Open notebook science refers to the application of the Open Data concept to as much of the scientific process as possible, including failed experiments and raw experimental data.
* Open-source software
Open-source software (OSS) is computer software that is released under a license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to use, study, change, and distribute the software and its source code to anyone and for any purpose. Op ...
is concerned with the open-source license
An open-source license is a type of license for computer software and other products that allows the source code, blueprint or design to be used, modified and/or shared under defined terms and conditions. This allows end users and commercial compa ...
s under which computer programs can be distributed and is not normally concerned primarily with data.
* Open educational resources
Open educational resources (OER) are teaching, learning, and research materials intentionally created and licensed to be free for the end user to own, share, and in most cases, modify. The term "OER" describes publicly accessible materials and ...
are freely accessible, openly licensed documents and media that are useful for teaching, learning, and assessing as well as for research purposes.
* Open research/ open science/open science data Open scientific data or open research data is a type of open data focused on publishing observations and results of scientific activities available for anyone to analyze and reuse. A major purpose of the drive for open data is to allow the verificat ...
(linked open science) means an approach to open and interconnect scientific assets like data, methods and tools with linked data
In computing, linked data (often capitalized as Linked Data) is structured data which is interlinked with other data so it becomes more useful through semantic queries. It builds upon standard Web technologies such as HTTP, RDF and URIs, but ...
techniques to enable transparent, reproducible and interdisciplinary research.
*Open-GLAM (Galleries, Library, Archives, and Museums) is an initiative and network that supports exchange and collaboration between cultural institutions that support open access to their digitalized collections. The GLAM-Wiki Initiative helps cultural institutions share their openly licensed resources with the world through collaborative projects with experienced Wikipedia
Wikipedia is a multilingual free online encyclopedia written and maintained by a community of volunteers, known as Wikipedians, through open collaboration and using a wiki-based editing system. Wikipedia is the largest and most-read refer ...
editors. Open Heritage Data is associated with Open GLAM, as openly licensed data in the heritage sector is now frequently used in research, publishing, and programming, particularly in the Digital Humanities
Digital humanities (DH) is an area of scholarly activity at the intersection of computing or Information technology, digital technologies and the disciplines of the humanities. It includes the systematic use of digital resources in the humanitie ...
.
Open Data as commons
Ideas and definitions
Formally both the definition of Open Data and commons revolve around the concept of shared resources with a low barrier to access. Substantially, digital commons include Open Data in that it includes resources maintained online, such as data. Overall, looking at operational principles of Open Data one could see the overlap between Open Data and (digital) commons in practice. Principles of Open Data are sometimes distinct depending on the type of data under scrutiny. Nonetheless, they are somewhat overlapping and their key rationale is the lack of barriers to the re-use of data(sets). Regardless of their origin, principles across types of Open Data hint at the key elements of the definition of commons. These are, for instance, accessibility, re-use, findability, non-proprietarily. Additionally, although to a lower extent, threats and opportunities associated with both Open Data and commons are similar. Synthesizing, they revolve around (risks and) benefits associated with (uncontrolled) use of common resources by a large variety of actors.The System
Both commons and Open Data can be defined by the features of the resources that fit under these concepts, but they can be defined by the characteristics of the systems their advocates push for. Governance is a focus for both Open Data and commons scholars. The key elements that outline commons and Open Data peculiarities are the differences (and maybe opposition) to the dominant market logics as shaped by capitalism. Perhaps it is this feature that emerges in the recent surge of the concept of commons as related to a more social look at digital technologies in the specific forms of digital and, especially, data commons.Real-life case
An exemplification of how the relationship between Open Data and commons and how their governance can potentially disrupt the market logic otherwise dominating big data is a project conducted by Human Ecosystem Relazioni in Bologna (Italy). See: https://www.he-r.it/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/HUB-report-impaginato_v1_small.pdf. This project aimed at extrapolating and identifying online social relations surrounding “collaboration” in Bologna. Data was collected from social networks and online platforms for citizens collaboration. Eventually data was analyzed for the content, meaning, location, timeframe, and other variables. Overall, online social relations for collaboration were analyzed based on network theory. The resulting dataset have been made available online as Open Data (aggregated and anonymized); nonetheless, individuals can reclaim all their data. This has been done with the idea of making data into a commons. This project exemplifies the relationship between Open Data and commons, and how they can disrupt the market logic driving big data use in two ways. First, it shows how such projects, following the rationale of Open Data somewhat can trigger the creation of effective data commons. The project itself was offering different types of support to social network platform users to have contents removed. Second, opening data regarding online social networks interactions has the potential to significantly reduce the monopolistic power of social network platforms on those data.Funders' mandates
Several funding bodies which mandate Open Access mandate Open Data. A good expression of requirements (truncated in places) is given by theCanadian Institutes of Health Research
The Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR; french: Instituts de recherche en santé du Canada; IRSC) is a federal agency responsible for funding health and medical research in Canada. Comprising 13 institutes, it is the successor to the M ...
(CIHR):
* to deposit bioinformatics, atomic and molecular coordinate data, experimental data into the appropriate public database immediately upon publication of research results.
* to retain original data sets for a minimum of five years after the grant. This applies to all data, whether published or not.
Other bodies active in promoting the deposition of data as well as full text include the Wellcome Trust. An academic paper published in 2013 advocated that Horizon 2020 (the science funding mechanism of the EU) should mandate that funded projects hand in their databases as "deliverables" at the end of the project, so that they can be checked for third party usability then shared.
Non-open data
Several mechanisms restrict access to or reuse of data (and several reasons for doing this are given above). They include: * making data available for a charge; * compilation in databases or websites to which only registered members or customers can have access; * use of a proprietary or closed technology or encryption which creates a barrier for access; * copyright statements claiming to forbid (or obfuscating) re-use of the data, including the use of "no derivatives" requirements; * patent forbidding re-use of the data (for example the 3-dimensional coordinates of some experimental protein structures have been patented); * restriction of robots to websites, with preference to certain search engines; * aggregating factual data into "databases" which may be covered by " database rights" or " database directives" (e.g.Directive on the legal protection of databases
The Directive 96/9/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 March 1996 on the legal protection of databases
is a directive of the European Union in the field of copyright law, made under the internal market provisions of the T ...
);
* time-limited access to resources such as e-journal
An academic journal or scholarly journal is a periodical publication in which scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. Academic journals serve as permanent and transparent forums for the presentation, scrutiny, and d ...
s (which on traditional print were available to the purchaser indefinitely);
* "webstacles", or the provision of single data points as opposed to tabular queries or bulk downloads of data set A data set (or dataset) is a collection of data. In the case of tabular data, a data set corresponds to one or more database tables, where every column of a table represents a particular variable, and each row corresponds to a given record of the ...
s; and
* political, commercial or legal pressure on the activity of organisations providing Open Data (for example the American Chemical Society
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a scientific society based in the United States that supports scientific inquiry in the field of chemistry. Founded in 1876 at New York University, the ACS currently has more than 155,000 members at all ...
lobbied the US Congress to limit funding to the National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late ...
for its Open PubChem data).
See also
* List of open data *Open knowledge
Open knowledge (or free knowledge) is knowledge that is free to use, reuse, and redistribute without legal, social, or technological restriction. Open knowledge organizations and activists have proposed principles and methodologies related to th ...
* Open content
* Openness
Openness is an overarching concept or philosophy that is characterized by an emphasis on transparency and collaboration. That is, openness refers to "accessibility of knowledge, technology and other resources; the transparency of action; the per ...
* Creative Commons license
A Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted "work".A "work" is any creative material made by a person. A painting, a graphic, a book, a song/lyric ...
* Data curation Data curation is the organization and integration of data collected from various sources. It involves annotation, publication and presentation of the data such that the value of the data is maintained over time, and the data remains available for re ...
* Data governance
Data governance is a term used on both a macro and a micro level. The former is a political concept and forms part of international relations and Internet governance; the latter is a data management concept and forms part of corporate data govern ...
* Data management
* Data publishing
* Data sharing
Data sharing is the practice of making data used for scholarly research available to other investigators. Many funding agencies, institutions, and publication venues have policies regarding data sharing because transparency and openness are consid ...
* Demand responsive transport
Demand-responsive transport (DRT), also known as demand-responsive transit, demand-responsive service,
US National Trans ...
* US National Trans ...
Digital preservation
In library and archival science, digital preservation is a formal endeavor to ensure that digital information of continuing value remains accessible and usable. It involves planning, resource allocation, and application of preservation methods and ...
* FAIR data principles
* International Open Data Day
* Linked data
In computing, linked data (often capitalized as Linked Data) is structured data which is interlinked with other data so it becomes more useful through semantic queries. It builds upon standard Web technologies such as HTTP, RDF and URIs, but ...
and Linked open data
In computing, linked data (often capitalized as Linked Data) is structured data which is interlinked with other data so it becomes more useful through semantic queries. It builds upon standard Web technologies such as HTTP, RDF and URIs, but r ...
* Open catalogue
* Open energy system databases
* Open Icecat
* Urban informatics
Urban informatics refers to the study of people creating, applying and using information and communication technology and data in the context of cities and urban environments. It sits at the conjunction of urban science, geomatics, and informatics ...
* Wikidata
Wikidata is a collaboratively edited multilingual knowledge graph hosted by the Wikimedia Foundation. It is a common source of open data that Wikimedia projects such as Wikipedia, and anyone else, can use under the CC0 public domain license ...
References
External links
Open Data – An Introduction
– from the
Open Knowledge Foundation
Open Knowledge Foundation (OKF) is a global, non-profit network that promotes and shares information at no charge, including both content and data. It was founded by Rufus Pollock on 20 May 2004 in Cambridge, UK. It is incorporated in England a ...
Video
of Tim Berners-Lee at
TED (conference)
TED Conferences, LLC (Technology, Entertainment, Design) is an American-Canadian non-profit media organization that posts international talks online for free distribution under the slogan "ideas worth spreading". TED was founded by Richard Sa ...
2009 calling for "Raw Data Now"
Six minute Video
of Tim Berners-Lee at
TED (conference)
TED Conferences, LLC (Technology, Entertainment, Design) is an American-Canadian non-profit media organization that posts international talks online for free distribution under the slogan "ideas worth spreading". TED was founded by Richard Sa ...
2010 showing examples of open data
G8 Open Data Charter
Towards a Genealogy of Open Data
– research paper tracing different historical threads contributing to current conceptions of open data. {{Authority control Free culture movement