ontogenesis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an



 The figure above shows how the development of a pig, cow,
The figure above shows how the development of a pig, cow, 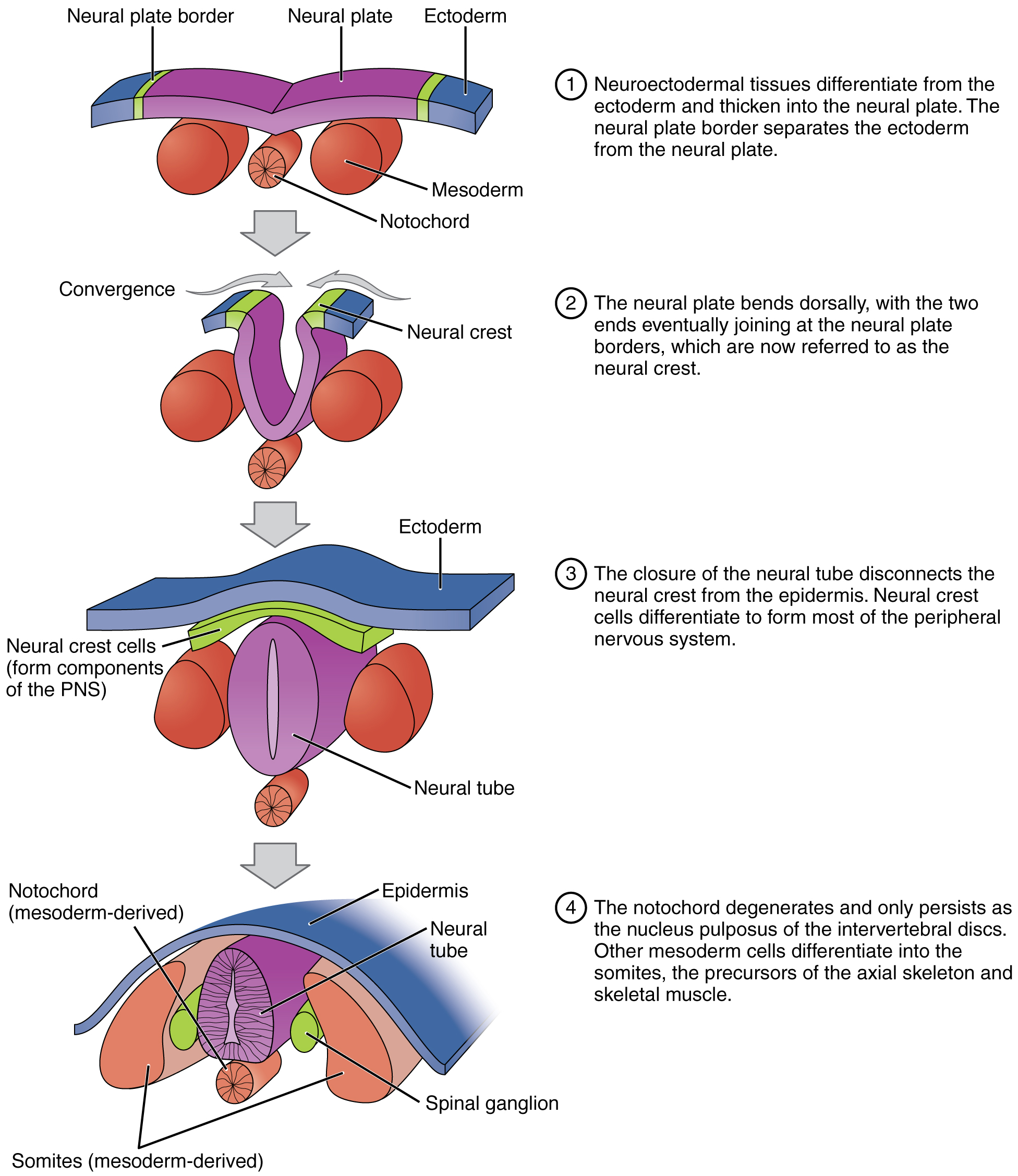

organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells ( cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and fu ...
(both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Pro ...
of the egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the study of the entirety of an organism's lifespan.
Ontogeny is the developmental history of an organism within its own lifetime, as distinct from phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological s ...
, which refers to the evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
ary history of a species. Another way to think of ontogeny is that it is the process of an organism going through all of the developmental stages over its lifetime. The developmental history includes all the developmental events that occur during the existence of an organism, beginning with the changes in the egg at the time of fertilization and events from the time of birth or hatching and afterward (i.e., growth, remolding of body shape, development of secondary sexual characteristics, etc.). While developmental (i.e., ontogenetic) processes can influence subsequent evolutionary (e.g., phylogenetic) processes (see evolutionary developmental biology
Evolutionary developmental biology (informally, evo-devo) is a field of biological research that compares the developmental processes of different organisms to infer how developmental processes evolved.
The field grew from 19th-century beginn ...
and recapitulation theory
The theory of recapitulation, also called the biogenetic law or embryological parallelism—often expressed using Ernst Haeckel's phrase "ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny"—is a historical hypothesis that the development of the embryo of an a ...
), individual organisms develop (ontogeny), while species evolve (phylogeny).
Ontogeny, embryology
Embryology (from Greek ἔμβρυον, ''embryon'', "the unborn, embryo"; and -λογία, '' -logia'') is the branch of animal biology that studies the prenatal development of gametes (sex cells), fertilization, and development of embr ...
and developmental biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and differentiation of st ...
are closely related studies and those terms are sometimes used interchangeably. Aspects of ontogeny are morphogenesis
Morphogenesis (from the Greek ''morphê'' shape and ''genesis'' creation, literally "the generation of form") is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of deve ...
, the development of form and shape of an organism; tissue growth; and cellular differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular ...
. The term ontogeny has also been used in cell biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living an ...
to describe the development of various cell types within an organism. Ontogeny is a useful field of study in many disciplines, including developmental biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and differentiation of st ...
, cell biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living an ...
, genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar work ...
, developmental psychology
Developmental psychology is the scientific study of how and why humans grow, change, and adapt across the course of their lives. Originally concerned with infants and children, the field has expanded to include adolescence, adult developme ...
, developmental cognitive neuroscience
Developmental cognitive neuroscience is an interdisciplinary scientific field devoted to understanding psychological processes and their neurological bases in the developing organism. It examines how the mind changes as children grow up, interrelat ...
, and developmental psychobiology. Ontogeny is used in anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of be ...
as the process through which each of us embodies the history of our own making.Toren, Christina. "Comparison and ontogeny." Anthropology, by comparison (2002): 187.
Etymology
The word ''ontogeny'' comes from theGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
''on'' meaning a being, individual; and existence, and from the suffix ''-geny'' from the Greek -''geniea'', meaning genesis, origin, and mode of production.
History
The term ontogeny was coined byErnst Haeckel
Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel (; 16 February 1834 – 9 August 1919) was a German zoologist, naturalist, eugenicist, philosopher, physician, professor, marine biologist and artist. He discovered, described and named thousands of new s ...
, a German zoologist and evolutionist in the 1860s. Haeckel, born in Germany on February 16, 1834, was also a strong supporter of Darwinism
Darwinism is a theory of biological evolution developed by the English naturalist Charles Darwin (1809–1882) and others, stating that all species of organisms arise and develop through the natural selection of small, inherited variations tha ...
. Haeckel suggested that ontogeny briefly and sometimes incompletely recapitulated or repeated phylogeny in his 1866 book, ''Generelle Morphologie der Organismen'' ("General Morphology of Organisms"). Even though his book was widely read, the scientific community was not very convinced or interested in his ideas, so he turned to producing more publications to get more attention. In 1866, Haeckel and others imagined development as producing new structures after earlier additions to the developing organism have been established. He proposed that individual development followed developmental stages of previous generations and that the future generations would add something new to this process, and that there was a causal parallelism between an animal's ontogeny and phylogeny. In addition, Haeckel suggested a biogenetic law that ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny, based on the idea that the successive and progressive origin of new species was based on the same laws as the successive and progressive origin of new embryonic structures. According to Haeckel, development produced novelties, and natural selection would eliminate species that had become outdated or obsolete. Though his view of development and evolution wasn't justifiable, future embryologists tweaked and collaborated with Haeckel's proposals and showed how new morphological structures can occur by the hereditary modification of embryonic development. Marine biologist Walter Garstang
Walter Garstang FLS FZS (9 February 1868 – 23 February 1949), a Fellow of Lincoln College, Oxford and Professor of Zoology at the University of Leeds, was one of the first to study the functional biology of marine invertebrate larvae. His ...
reversed Haeckel's relationship between ontogeny and phylogeny, stating that ontogeny creates phylogeny, not recapitulates it.
A seminal 1963 paper by Nikolaas Tinbergen
Nikolaas "Niko" Tinbergen (; ; 15 April 1907 – 21 December 1988) was a Dutch biologist and ornithologist who shared the 1973 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Karl von Frisch and Konrad Lorenz for their discoveries concerning the ...
named ontogeny as one of the four primary questions of biology, along with Julian Huxley's three others: causation, survival value and evolution. Tinbergen emphasized that the change of behavioral ''machinery'' during development was distinct from the change in behavior during development. We can conclude that the thrush itself, i.e. its behavioral machinery, has changed only if the behavior change occurred while the environment was held constant...When we turn from description to causal analysis, and ask in what way the observed change in behavior machinery has been brought about, the natural first step is to try and distinguish between environmental influences and those within the animal...In ontogeny the conclusion that a certain change is internally controlled (is 'innate') is reached by ''elimination''. Tinbergen was concerned that the elimination of environmental factors is difficult to establish, and the use of the word innate is often misleading.
Developmental stages
Development of an organism happens through fertilization, cleavage, blastulation, gastrulation, organogenesis, and metamorphosis into an adult. Each species ofanimal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage ...
has a slightly different journey through these stages, since some stages might be shorter or longer when compared to other species, and where the offspring develops is different for each animal type (e.g., in a hard egg shell, uterus, soft egg shell, on a plant leaf, etc.).
Fertilization
In humans, the process of fetal development starts aftersperm
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, ...
fertilizes an egg and they fuse together, kickstarting embryonic development
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm ...
. The fusion of egg and sperm into a zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism.
In multicell ...
changes the surrounding membrane to not allow any more sperm to penetrate the egg, so multiple fertilizations can be prevented. Fusion of a zygote also activates the egg so it can begin undergoing cell division. Each animal species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriat ...
might not have specifically a sperm and an egg, but two gametes that contain half of the species' typical genetic material and the membranes of these gametes fuse to start creating an offspring.
Cleavage
Not long after successful fertilization by sperm, the zygote undergoes many mitotic divisions, which are also non-sexual cell divisions. Cleavage is the process of cell division, so the starting zygote becomes a collection of identical cells which is a morula and contains cells called blastomeres. Cleavage prepares the zygote to become an embryo, which is from 2 weeks to 8 weeks after conception (fertilization) in humans.
Blastulation
After the zygote has become an embryo, it continues dividing into a hollow sphere of cells, which is ablastula
Blastulation is the stage in early animal embryonic development that produces the blastula. In mammalian development the blastula develops into the blastocyst with a differentiated inner cell mass and an outer trophectoderm. The blastula (fro ...
. These outer cells form a single epithelial layer, the blastoderm, that essentially encases the fluid-filled inside that is the blastocoel. The figure to the right shows the basic process that is modified in different species. Blastulation differs slightly in different species, but in mammals, the eight-cell stage embryo forms into a slightly different type of blastula, called a blastocyst. Other species such as sea stars, frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely Carnivore, carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order (biology), order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-f ...
s, chicks, and mice
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus'' ...
have all the same structures in this stage, yet the orientation of these features differs, plus these species have additional types of cells in this stage.

Gastrulation
After blastulation, the single-layered blastula expands and reorganizes into multiple layers, a gastrula (seen in the figure to the right).Reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates ( lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalia ...
s, bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s and mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur ...
s are triploblastic organisms, meaning the gastrula comprises three germ layer
A germ layer is a primary layer of cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans (animals that are sister taxa to the sponges) produce two or three p ...
s; the endoderm (inner layer), mesoderm (middle layer), and ectoderm (outer layer). As seen in the figure below, each germ layer will become multi-potent stem cells that can become a specific tissue depending on the germ layer and is what happens in humans. This differentiation of germ layers differs slightly, because not all of the organs and tissues below are in all organisms, but corresponding body systems can be substituted in place of these.
Organogenesis
In the figure below, human germ cells are able to differentiate into the specific organs and tissues they become later on in life. Germ cells are able to migrate to their final locations to rearrange themselves and some organs are made of two germ layers; one for the outside, the other for the inside. Theendoderm
Endoderm is the innermost of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and mesoderm (middle layer). Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gast ...
cells become the internal linings of organisms, such as the stomach, colon, small intestine, liver, and pancreas of the digestive system and the lungs. The mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical Emb ...
gives rise to other tissues not formed by the ectoderm, such as the heart, muscles, bones, blood, dermis of the skin, bone marrow, and the urogenital system. This germ layer is more specific for species, as it is the distinguishing layer of the three that can identify evolutionarily higher life-forms (e.g., bilateral organisms like humans) from lower-life forms (with radial symmetry). Lastly, the ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from t ...
is the outer layer of cells that become the epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water rel ...
and hair while being the precursor to the mammary glands, central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
, and the peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brai ...
s.

 The figure above shows how the development of a pig, cow,
The figure above shows how the development of a pig, cow, rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit sp ...
, and human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
offspring are similar when compared to one another. This figure shows how the germ layers can become different organs and tissues in evolutionarily higher life-forms and how these species essentially develop very similarly. Additionally, it shows how multiple species develop in a parallel manner but branch off to develop more specific features for the organism such as hooves, a tail, or ears. 
Neurulation
In developingvertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with ...
offspring, a neural tube
In the developing chordate (including vertebrates), the neural tube is the embryonic precursor to the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The neural groove gradually deepens as the neural fold become elevated, ...
is formed through either primary or secondary neurulation. Some species develop their spine and nervous system using both primary and secondary neurulation, while others use only primary or secondary neurulation. In human fetal development, primary neurulation occurs during weeks 3 and 4 of gestation to develop the brain and spinal cord. Then during weeks 5 and 6 of gestation, secondary neurulation forms the lower sacral and coccygeal cord.
= Primary Neurulation
= The diagram to the right illustrates primary neurulation, which is the process of cells surrounding the neural plate interacting with neural plate cells to proliferate, converge, and pinch off to form a hollow tube above thenotochord
In anatomy, the notochord is a flexible rod which is similar in structure to the stiffer cartilage. If a species has a notochord at any stage of its life cycle (along with 4 other features), it is, by definition, a chordate. The notochord consi ...
and mesoderm. This process is discontinuous and can start at different points along the cranial-caudal axis necessary for it to close. After the neural crest closes, the neural crest cells and ectoderm cells separate and the ectoderm becomes the epidermis surrounding this complex. The neural crest cells differentiate to become components of most of the peripheral nervous system in animals. Next, the notochord degenerates to become only the nucleus pulposus
An intervertebral disc (or intervertebral fibrocartilage) lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold t ...
of the intervertebral disc
An intervertebral disc (or intervertebral fibrocartilage) lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to h ...
s and the mesoderm cells differentiate to become the somite
The somites (outdated term: primitive segments) are a set of bilaterally paired blocks of paraxial mesoderm that form in the embryonic stage of somitogenesis, along the head-to-tail axis in segmented animals. In vertebrates, somites subdivide ...
s and skeletal muscle later on. Also during this stage, the neural crest cells become the spinal ganglions, which function as the brain in organisms like earthworm
An earthworm is a terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. They exhibit a tube-within-a-tube body plan; they are externally segmented with corresponding internal segmentation; and they usually have setae on all segments. T ...
s and arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s. In more advanced organisms like amphibian
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arbo ...
s, bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweig ...
s and mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur ...
s; the spinal ganglions consists of a cluster of nerve bodies positioned along the spinal cord at the dorsal and ventral roots of a spinal nerve, which is a pair of nerves that correspond to a vertebra of the spine.
= Secondary Neurulation
= In secondary neurulation, caudal and sacral regions of the spine are formed after primary neurulation is finished. This process initiates once primary neurulation is finished and the posterior neuropore closes, so the tail bud can proliferate and condense, then create a cavity and fuse with the central canal of the neural tube. Secondary neurulation occurs in the small region starting at the spinal tail bud up to the posterior neuropore, which is the open neural folds near the tail region that don't close through primary neurulation. As canalization progresses over the next few weeks, neurons and ependymal cells (cells that create cerebral spinal fluid) differentiate to become the tail end of the spinal cord. Next, the closed neural tube contains neuroepithelial cells that immediately divide after closure and a second type of cell forms; the neuroblast.Neuroblast
In vertebrates, a neuroblast or primitive nerve cell is a postmitotic cell that does not divide further, and which will develop into a neuron after a migration phase. In invertebrates such as ''Drosophila,'' neuroblasts are neural progenitor cell ...
cells form the mantle layer, which later becomes the gray matter
Grey matter is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil (dendrites and unmyelinated axons), glial cells (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), synapses, and capillaries. Grey matter is distingui ...
, which then gives rise to a marginal layer that becomes the white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribu ...
of the spinal cord. Secondary neurulation is seen in the neural tube of the lumbar and tail vertebrae of frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely Carnivore, carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order (biology), order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-f ...
s and chicks and in both instances, this process is like a continuation of gastrulation.

Larval and juvenile phases
In most species, the young organism that is just born or hatched is not sexually mature yet and in most animals, this young organism looks quite different than the adult form. This young organism is the larva and is the intermediate form before metamorphosing into an adult. A well known example of a larval form of an animal is thecaterpillar
Caterpillars ( ) are the larval stage of members of the order Lepidoptera (the insect order comprising butterflies and moths).
As with most common names, the application of the word is arbitrary, since the larvae of sawflies (suborder Sy ...
of butterflies
Butterflies are insects in the macrolepidopteran clade Rhopalocera from the order Lepidoptera, which also includes moths. Adult butterflies have large, often brightly coloured wings, and conspicuous, fluttering flight. The group comprises ...
and moth
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of w ...
s. Caterpillars keep growing and feeding in order for enough energy during the pupal stage, when necessary body parts for metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some inse ...
are grown. The juvenile phase is different in plants and animals, but in plants juvenility is an early phase of plant growth in which plants can't flower. In animals, the juvenile stage is most commonly found in social mammals, such as wild dogs, monkey
Monkey is a common name that may refer to most mammals of the infraorder Simiiformes, also known as the simians. Traditionally, all animals in the group now known as simians are counted as monkeys except the apes, which constitutes an incomple ...
s, apes, lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large cat of the genus '' Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphic; adu ...
s, wolves
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly un ...
, and more. In humans, puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a ...
marks the end of this stage and adolescence
Adolescence () is a transitional stage of physical and psychological development that generally occurs during the period from puberty to adulthood (typically corresponding to the age of majority). Adolescence is usually associated with the ...
follows. Some species begin puberty and reproduction before the juvenile stage is over, such as in female non-human primates. The larval and pupal stages can be seen in the figure to the right.
Metamorphosis
The process of an organism's body undergoing structural and physical changes after birth or hatching to become suitable for its adult environment ismetamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some inse ...
. For example, amphibian
Amphibians are four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terrestrial, fossorial, arbo ...
tadpoles have a maturation of liver enzymes, hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythroc ...
, and eye pigments, in addition to their nervous, digestive, and reproductive systems being remodeled. In all species, molting
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is the manner in which an animal routinely casts off a part of its body (often, but not always, an outer ...
and juvenile hormones appear to regulate these changes. The figure to the right shows the stages of life in butterflies and their metamorphosis transforms the caterpillar into a butterfly.
Adulthood
Adult
An adult is a human or other animal that has reached full growth. In human context, the term ''adult'' has meanings associated with social and legal concepts. In contrast to a " minor", a legal adult is a person who has attained the age of maj ...
hood is the stage of when physical and intellectual maturity have been achieved and this differs between species. In humans" \n\n\n\n\nThe robots exclusion standard, also known as the robots exclusion protocol or simply robots.txt, is a standard used by websites to indicate to visiting web crawlers and other web robots which portions of the site they are allowed to visi ...
, adulthood is thought to be around 20 or 21 years old and is the longest stage of life, but in all species it ends with death. In dogs, small breeds (e.g., Yorkshire Terrier, Chihuahua Chihuahua may refer to:
Places
* Chihuahua (state), a Mexican state
**Chihuahua (dog), a breed of dog named after the state
**Chihuahua cheese, a type of cheese originating in the state
**Chihuahua City, the capital city of the state
**Chihuahua Mu ...
, Cocker Spaniel, etc.) physically mature faster than large breeds (e.g., Saint Bernard, Great Dane
The Great Dane is a large sized dog breed originating from Germany. The Great Dane descends from hunting dogs from the Middle Ages used to hunt wild boar and deer, and as guardians of German nobility. It is one of the largest breeds in the worl ...
, Golden Retriever
The Golden Retriever is a Scottish breed of retriever dog of medium size. It is characterised by a gentle and affectionate nature and a striking golden coat. It is commonly kept as a pet and is among the most frequently registered breeds ...
, etc.), so adulthood is reached anywhere from 12 to 24 months or 1 to 2 years. In contrast, many insect species have long larval stages and the adult stage is only for reproduction. The silkworm moth
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of w ...
s don't have mouthparts and don't feed, so they have to consume enough food during the larval stage for energy to survive and mate.
Senescence
Senescence
Senescence () or biological aging is the gradual deterioration of functional characteristics in living organisms. The word ''senescence'' can refer to either cellular senescence or to senescence of the whole organism. Organismal senescence invol ...
is when cells stop dividing but don't die, but these cells can build up and cause problems in the body. These cells can release substances that cause inflammation and can damage healthy nearby cells. Senescence can be induced by un-repaired DNA damage (e.g., from radiation, old age, etc.) or other cellular stress and also is the state of being old.
Ontogenetic allometry
Most organisms undergo allometric changes inshape
A shape or figure is a graphical representation of an object or its external boundary, outline, or external surface, as opposed to other properties such as color, texture, or material type.
A plane shape or plane figure is constrained to lie ...
as they grow and mature, while others engage in metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some inse ...
. Even reptiles (non-avian sauropsids, e.g., crocodilians
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period (Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living ...
, turtles
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked tu ...
, snakes
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
, and lizards
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia altho ...
), in which the offspring are often viewed as miniature adults, show a variety of ontogenetic changes in morphology and physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemic ...
.
Applications to other fields
Anthropology
Comparing ourselves to others is something humans do all the time. The chapter "Comparison and ontogeny" from the book ''Anthropology, by Comparison'' by Christina Toren states: In doing so we are acknowledging not so much our sameness to others or our difference, but rather the commonality that resides in our difference. In other words, because each one of us is at once remarkably similar to, and remarkably different from, all other humans, it makes little sense to think of comparison in terms of a list of absolute similarities and a list of absolute differences. Rather, in respect of all other humans, we find similarities in the ways we are different from one another and differences in the ways we are the same. That we are able to do this is a function of the genuinely historical process that is human ontogeny.See also
*Developmental biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and differentiation of st ...
* Ernst Haeckel
Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel (; 16 February 1834 – 9 August 1919) was a German zoologist, naturalist, eugenicist, philosopher, physician, professor, marine biologist and artist. He discovered, described and named thousands of new s ...
* Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar work ...
* Recapitulation theory
The theory of recapitulation, also called the biogenetic law or embryological parallelism—often expressed using Ernst Haeckel's phrase "ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny"—is a historical hypothesis that the development of the embryo of an a ...
, the idea that ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological s ...
* Embryology
Embryology (from Greek ἔμβρυον, ''embryon'', "the unborn, embryo"; and -λογία, '' -logia'') is the branch of animal biology that studies the prenatal development of gametes (sex cells), fertilization, and development of embr ...
* Organogenesis
Organogenesis is the phase of embryonic development that starts at the end of gastrulation and continues until birth. During organogenesis, the three germ layers formed from gastrulation (the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) form the internal org ...
* Ontogeny (psychoanalysis)
Ontogeny in a psychoanalytical context is the development of the whole organism, viewed from the light of occurrences during the life, not in the last place in the pre-history of early childhood, which has become unconscious, according to Sigmun ...
* Phylogenetics
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups ...
* Phylogeny (psychoanalysis) Phylogeny in psychoanalysis is the study of the whole family or species of an organism in order to better understand the pre-history of it. It might have an unconscious influence on a patient, according to Sigmund Freud. After the possibilities of o ...
* Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes in ...
* Evo-devo (evolutionary developmental biology)
* Cellular differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular ...
* Cell biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living an ...
* Nikolaas Tinbergen
Nikolaas "Niko" Tinbergen (; ; 15 April 1907 – 21 December 1988) was a Dutch biologist and ornithologist who shared the 1973 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Karl von Frisch and Konrad Lorenz for their discoveries concerning the ...
* Metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some inse ...
* Morphology
* Physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemic ...
* Eco-evo-devo (ecological evolutionary developmental biology)
* Darwinism
Darwinism is a theory of biological evolution developed by the English naturalist Charles Darwin (1809–1882) and others, stating that all species of organisms arise and develop through the natural selection of small, inherited variations tha ...
* Fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Pro ...
* Cleavage
* Blastulation
* Gastrulation
Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula (a single-layered hollow sphere of cells), or in mammals the blastocyst is reorganized into a multilayered structure known as the gastrula. ...
* Germ layer
A germ layer is a primary layer of cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans (animals that are sister taxa to the sponges) produce two or three p ...
s
* Neurulation
Neurulation refers to the folding process in vertebrate embryos, which includes the transformation of the neural plate into the neural tube. The embryo at this stage is termed the neurula.
The process begins when the notochord induces the form ...
* Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the sp ...
* Metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Some inse ...
* Larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
...
* Adult
An adult is a human or other animal that has reached full growth. In human context, the term ''adult'' has meanings associated with social and legal concepts. In contrast to a " minor", a legal adult is a person who has attained the age of maj ...
hood
* Senescence
Senescence () or biological aging is the gradual deterioration of functional characteristics in living organisms. The word ''senescence'' can refer to either cellular senescence or to senescence of the whole organism. Organismal senescence invol ...
Notes and references
External links
* * {{Authority control Developmental biology