offshore oil rig on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 An oil platform (or oil rig, offshore platform, oil production platform, and similar terms) is a large structure with facilities to extract and process
An oil platform (or oil rig, offshore platform, oil production platform, and similar terms) is a large structure with facilities to extract and process
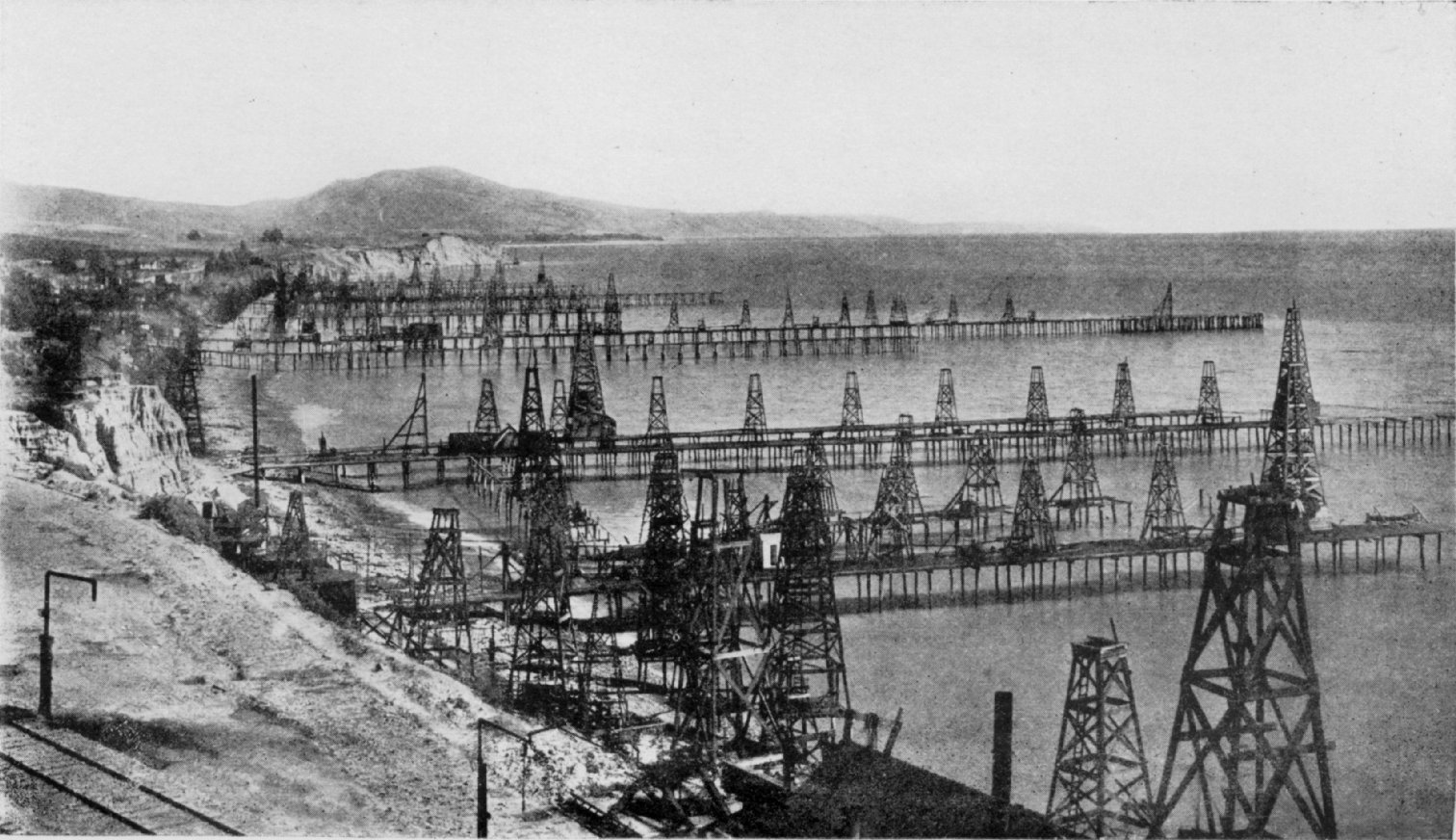 Around 1891, the first submerged oil wells were drilled from platforms built on piles in the fresh waters of the
Around 1891, the first submerged oil wells were drilled from platforms built on piles in the fresh waters of the
 Notable offshore basins include:
* the
Notable offshore basins include:
* the
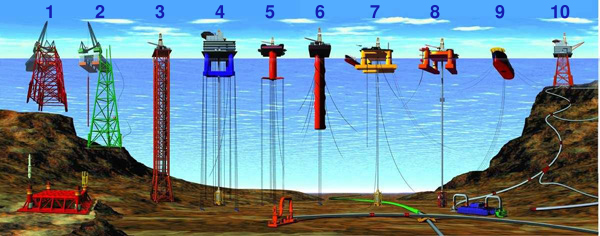 * 1) & 2) Conventional fixed platforms (deepest: Shell's Bullwinkle in 1991 at 412 m/1,353 ft GOM)
* 3) Compliant tower (deepest: ChevronTexaco's Petronius in 1998 at 534 m /1,754 ft GOM)
* 4) & 5) Vertically moored tension leg and mini-tension leg platform (deepest: ConocoPhillips’ Magnolia in 2004 1,425 m/4,674 ft GOM)
* 6) Spar (deepest: Shell's Perdido in 2010, 2,450 m/8,000 ft GOM)
* 7) & 8) Semi-submersibles (deepest: Shell's NaKika in 2003, 1920 m/6,300 ft GOM)
* 9) Floating production, storage, and offloading facility (deepest: 2005, 1,345 m/4,429 ft Brazil)
* 10) Sub-sea completion and tie-back to host facility (deepest: Shell's Coulomb tie to NaKika 2004, 2,307 m/ 7,570 ft)
: (Numbered from left to right; all records from 2005 data)
* 1) & 2) Conventional fixed platforms (deepest: Shell's Bullwinkle in 1991 at 412 m/1,353 ft GOM)
* 3) Compliant tower (deepest: ChevronTexaco's Petronius in 1998 at 534 m /1,754 ft GOM)
* 4) & 5) Vertically moored tension leg and mini-tension leg platform (deepest: ConocoPhillips’ Magnolia in 2004 1,425 m/4,674 ft GOM)
* 6) Spar (deepest: Shell's Perdido in 2010, 2,450 m/8,000 ft GOM)
* 7) & 8) Semi-submersibles (deepest: Shell's NaKika in 2003, 1920 m/6,300 ft GOM)
* 9) Floating production, storage, and offloading facility (deepest: 2005, 1,345 m/4,429 ft Brazil)
* 10) Sub-sea completion and tie-back to host facility (deepest: Shell's Coulomb tie to NaKika 2004, 2,307 m/ 7,570 ft)
: (Numbered from left to right; all records from 2005 data)
 These platforms are built on
These platforms are built on
 Jack-up Mobile Drilling Units (or jack-ups), as the name suggests, are rigs that can be jacked up above the sea using legs that can be lowered, much like jacks. These MODUs (Mobile Offshore Drilling Units) are typically used in water depths up to , although some designs can go to depth. They are designed to move from place to place, and then anchor themselves by deploying their legs to the ocean bottom using a
Jack-up Mobile Drilling Units (or jack-ups), as the name suggests, are rigs that can be jacked up above the sea using legs that can be lowered, much like jacks. These MODUs (Mobile Offshore Drilling Units) are typically used in water depths up to , although some designs can go to depth. They are designed to move from place to place, and then anchor themselves by deploying their legs to the ocean bottom using a
 The main types of floating production systems are FPSO (floating production, storage, and offloading system). FPSOs consist of large monohull structures, generally (but not always) shipshaped, equipped with processing facilities. These platforms are moored to a location for extended periods, and do not actually drill for oil or gas. Some variants of these applications, called FSO (floating storage and offloading system) or FSU (floating storage unit), are used exclusively for storage purposes, and host very little process equipment. This is one of the best sources for having floating production.
The world's first floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) facility is in production. See the section on particularly large examples below.
The main types of floating production systems are FPSO (floating production, storage, and offloading system). FPSOs consist of large monohull structures, generally (but not always) shipshaped, equipped with processing facilities. These platforms are moored to a location for extended periods, and do not actually drill for oil or gas. Some variants of these applications, called FSO (floating storage and offloading system) or FSU (floating storage unit), are used exclusively for storage purposes, and host very little process equipment. This is one of the best sources for having floating production.
The world's first floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) facility is in production. See the section on particularly large examples below.
 Spars are moored to the seabed like TLPs, but whereas a TLP has vertical tension tethers, a spar has more conventional mooring lines. Spars have to-date been designed in three configurations: the "conventional" one-piece cylindrical hull; the "truss spar", in which the midsection is composed of truss elements connecting the upper buoyant hull (called a hard tank) with the bottom soft tank containing permanent ballast; and the "cell spar", which is built from multiple vertical cylinders. The spar has more inherent stability than a TLP since it has a large counterweight at the bottom and does not depend on the mooring to hold it upright. It also has the ability, by adjusting the mooring line tensions (using chain-jacks attached to the mooring lines), to move horizontally and to position itself over wells at some distance from the main platform location. The first production spar was Kerr-McGee's Neptune, anchored in in the Gulf of Mexico; however, spars (such as
Spars are moored to the seabed like TLPs, but whereas a TLP has vertical tension tethers, a spar has more conventional mooring lines. Spars have to-date been designed in three configurations: the "conventional" one-piece cylindrical hull; the "truss spar", in which the midsection is composed of truss elements connecting the upper buoyant hull (called a hard tank) with the bottom soft tank containing permanent ballast; and the "cell spar", which is built from multiple vertical cylinders. The spar has more inherent stability than a TLP since it has a large counterweight at the bottom and does not depend on the mooring to hold it upright. It also has the ability, by adjusting the mooring line tensions (using chain-jacks attached to the mooring lines), to move horizontally and to position itself over wells at some distance from the main platform location. The first production spar was Kerr-McGee's Neptune, anchored in in the Gulf of Mexico; however, spars (such as
 The Petronius Platform is a compliant tower in the Gulf of Mexico modeled after the Hess Baldpate platform, which stands above the ocean floor. It is one of the world's tallest structures.
The Hibernia Gravity Base Structure, Hibernia platform in Canada is the world's heaviest offshore platform, located on the Jeanne D'Arc Basin, in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of
The Petronius Platform is a compliant tower in the Gulf of Mexico modeled after the Hess Baldpate platform, which stands above the ocean floor. It is one of the world's tallest structures.
The Hibernia Gravity Base Structure, Hibernia platform in Canada is the world's heaviest offshore platform, located on the Jeanne D'Arc Basin, in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of
 In British waters, the cost of removing all platform rig structures entirely was estimated in 2013 at £30 billion.
Aquatic organisms invariably attach themselves to the undersea portions of oil platforms, turning them into artificial reefs. In the Gulf of Mexico and offshore California, the waters around oil platforms are popular destinations for sports and commercial fishermen, because of the greater numbers of fish near the platforms. The United States and Brunei have active Rigs-to-Reefs programs, in which former oil platforms are left in the sea, either in place or towed to new locations, as permanent artificial reefs. In the US Gulf of Mexico, as of September 2012, 420 former oil platforms, about 10 percent of decommissioned platforms, have been converted to permanent reefs.
On the US Pacific coast, marine biologist Milton Love has proposed that oil platforms off California be retained as artificial reefs, instead of being dismantled (at great cost), because he has found them to be havens for many of the species of fish which are otherwise declining in the region, in the course of 11 years of research. Love is funded mainly by government agencies, but also in small part by the California Artificial Reef Enhancement Program. Professional diving#Scientific diving, Divers have been used to assess the fish populations surrounding the platforms.
In British waters, the cost of removing all platform rig structures entirely was estimated in 2013 at £30 billion.
Aquatic organisms invariably attach themselves to the undersea portions of oil platforms, turning them into artificial reefs. In the Gulf of Mexico and offshore California, the waters around oil platforms are popular destinations for sports and commercial fishermen, because of the greater numbers of fish near the platforms. The United States and Brunei have active Rigs-to-Reefs programs, in which former oil platforms are left in the sea, either in place or towed to new locations, as permanent artificial reefs. In the US Gulf of Mexico, as of September 2012, 420 former oil platforms, about 10 percent of decommissioned platforms, have been converted to permanent reefs.
On the US Pacific coast, marine biologist Milton Love has proposed that oil platforms off California be retained as artificial reefs, instead of being dismantled (at great cost), because he has found them to be havens for many of the species of fish which are otherwise declining in the region, in the course of 11 years of research. Love is funded mainly by government agencies, but also in small part by the California Artificial Reef Enhancement Program. Professional diving#Scientific diving, Divers have been used to assess the fish populations surrounding the platforms.
Oil Rig Disasters
Listing of oil rig accidents
Oil Rig Photos
Collection of pictures of drilling rigs and production platforms
Overview of Conventional Platforms
Pictorial treatment on the installation of platforms which extend from the seabed to the ocean surface {{DEFAULTSORT:Oil Platform Oil platforms, Offshore engineering Petroleum production Drilling technology Natural gas technology Structural engineering


 An oil platform (or oil rig, offshore platform, oil production platform, and similar terms) is a large structure with facilities to extract and process
An oil platform (or oil rig, offshore platform, oil production platform, and similar terms) is a large structure with facilities to extract and process petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
and natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
that lie in rock formations beneath the seabed
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'.
The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of ...
. Many oil platforms will also have facilities to accommodate the workers, although it is also common to have a separate accommodation platform bridge linked to the production platform. Most commonly, oil platforms engage in activities on the continental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
, though they can also be used in lakes, inshore waters, and inland seas. Depending on the circumstances, the platform may be fixed
Fixed may refer to:
* ''Fixed'' (EP), EP by Nine Inch Nails
* ''Fixed'', an upcoming 2D adult animated film directed by Genndy Tartakovsky
* Fixed (typeface), a collection of monospace bitmap fonts that is distributed with the X Window System
* ...
to the ocean floor, consist of an artificial island
An artificial island is an island that has been constructed by people rather than formed by natural means. Artificial islands may vary in size from small islets reclaimed solely to support a single pillar of a building or structure to those tha ...
, or float
Float may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music Albums
* ''Float'' (Aesop Rock album), 2000
* ''Float'' (Flogging Molly album), 2008
* ''Float'' (Styles P album), 2013
Songs
* "Float" (Tim and the Glory Boys song), 2022
* "Float", by Bush ...
. In some arrangements the main facility may have storage facilities for the processed oil. Remote subsea
Subsea technology involves fully submerged ocean equipment, operations, or applications, especially when some distance offshore, in deep ocean waters, or on the seabed. The term ''subsea'' is frequently used in connection with oceanography, marin ...
wells may also be connected to a platform by flow lines and by umbilical connections. These sub-sea facilities may include of one or more subsea wells or manifold centres for multiple wells.
Offshore drilling presents environmental challenges, both from the produced hydrocarbons and the materials used during the drilling operation. Controversies include the ongoing US offshore drilling debate
The United States offshore drilling debate is an ongoing debate in the United States about whether, the extent to which, in which areas, and under what conditions, further offshore drilling should be allowed in U.S.-administered waters.
The iss ...
.
There are many different types of facilities from which offshore drilling operations take place. These include bottom-founded drilling rigs ( jackup barges and swamp barges), combined drilling and production facilities, either bottom-founded or floating platforms, and deepwater mobile offshore drilling units (MODU), including semi-submersibles and drillships. These are capable of operating in water depths up to . In shallower waters, the mobile units are anchored to the seabed. However, in deeper water (more than ), the semisubmersible
Semi-submersible may refer to a self-propelled vessel, such as:
*Heavy-lift ship, which partially submerge to allow their cargo (another ship) to float into place for transport
*Narco-submarine, some of which remained partially on the surface
*Se ...
s or drillship
A drillship is a merchant vessel designed for use in exploratory offshore drilling of new oil and gas wells or for scientific drilling purposes. In recent years the vessels have been used in deepwater and ultra-deepwater applications, equipped ...
s are maintained at the required drilling location using dynamic positioning
Dynamic positioning (DP) is a computer-controlled system to automatically maintain a vessel's position and heading by using its own propellers and thrusters. Position reference sensors, combined with wind sensors, motion sensors and gyrocompass ...
.
History
 Around 1891, the first submerged oil wells were drilled from platforms built on piles in the fresh waters of the
Around 1891, the first submerged oil wells were drilled from platforms built on piles in the fresh waters of the Grand Lake St. Marys
Grand Lake St. Marys State Park is a public recreation area located on Grand Lake in Mercer and Auglaize counties, Ohio. Grand Lake is the largest inland lake in Ohio in terms of area, but is shallow, with an average depth of only . The stat ...
(a.k.a. Mercer County Reservoir) in Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
. The wide but shallow reservoir was built from 1837 to 1845 to provide water to the Miami and Erie Canal
The Miami and Erie Canal was a canal that ran from Cincinnati to Toledo, Ohio, creating a water route between the Ohio River and Lake Erie. Construction on the canal began in 1825 and was completed in 1845 at a cost to the state government of $ ...
.
Around 1896, the first submerged oil wells in salt water were drilled in the portion of the Summerland field extending under the Santa Barbara Channel
The Santa Barbara Channel is a portion of the Southern California Bight and separates the mainland of California from the northern Channel Islands. It is generally south of the city of Santa Barbara, and west of the Oxnard Plain in Ventura Count ...
in California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
. The wells were drilled from piers extending from land out into the channel.
Other notable early submerged drilling activities occurred on the Canadian side of Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
since 1913 and Caddo Lake
Caddo Lake (french: Lac Caddo) is a lake and bayou (wetland) on the border between Texas and Louisiana, in northern Harrison County and southern Marion County in Texas and western Caddo Parish in Louisiana. The lake is named after the Caddoan ...
in Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
in the 1910s. Shortly thereafter, wells were drilled in tidal zones along the Gulf Coast
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South, is the coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The coastal states that have a shoreline on the Gulf of Mexico are Texas, Louisiana, Mississ ...
of Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
and Louisiana. The Goose Creek field near Baytown, Texas
Baytown is a city in the U.S. state of Texas, within Harris and Chambers counties. Located in the Houston–The Woodlands–Sugar Land metropolitan statistical area, it lies on the northern side of the Galveston Bay complex near the outlets of t ...
is one such example. In the 1920s, drilling was done from concrete platforms in Lake Maracaibo
Lake Maracaibo (Spanish: Lago de Maracaibo; Anu: Coquivacoa) is a lagoon in northwestern Venezuela, the largest lake in South America and one of the oldest on Earth, formed 36 million years ago in the Andes Mountains. The fault in the northern se ...
, Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
.
The oldest offshore well recorded in Infield's offshore database is the Bibi Eibat well which came on stream in 1923 in Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
. Landfill was used to raise shallow portions of the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
.
In the early 1930s, the Texas Company developed the first mobile steel barges for drilling in the brackish coastal areas of the gulf.
In 1937, Pure Oil Company
Pure Oil Company was an American petroleum company founded in 1914 and sold to what is now Union Oil Company of California in 1965. The Pure Oil name returned in 1993 as a cooperative (based in Rock Hill, South Carolina since 2008) which has grow ...
(now Chevron Corporation
Chevron Corporation is an American multinational energy corporation. The second-largest direct descendant of Standard Oil, and originally known as the Standard Oil Company of California (shortened to Socal or CalSo), it is headquartered in S ...
) and its partner Superior Oil Company
Superior Oil Company was an American oil company founded in 1921 in Coalinga, California, by William Myron Keck,
Superior Oil began as a drilling contracting firm and grew into the exploration and production of oil and natural gas. In 1930 the com ...
(now part of ExxonMobil Corporation
ExxonMobil Corporation (commonly shortened to Exxon) is an American multinational oil and gas corporation headquartered in Irving, Texas. It is the largest direct descendant of John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil, and was formed on November 3 ...
) used a fixed platform to develop a field in of water, one mile (1.6 km) offshore of Calcasieu Parish, Louisiana
Calcasieu Parish (; french: Paroisse de Calcasieu) is a parish located on the southwestern border of the U.S. state of Louisiana. As of the 2020 census, the population was 216,785. The parish seat is Lake Charles.
Calcasieu Parish is part of ...
.
In 1938, Humble Oil built a mile-long wooden trestle with railway tracks into the sea at McFadden Beach on the Gulf of Mexico, placing a derrick at its end – this was later destroyed by a hurricane.
In 1945, concern for American control of its offshore oil reserves caused President Harry Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. A leader of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 34th vice president from January to April 1945 under Franklin ...
to issue an Executive Order unilaterally extending American territory to the edge of its continental shelf, an act that effectively ended the 3-mile limit
The three-mile limit refers to a traditional and now largely obsolete conception of the international law of the seas which defined a country's territorial waters, for the purposes of trade regulation and exclusivity, as extending as far as the r ...
"freedom of the seas
Freedom of the seas ( la, mare liberum, lit. "free sea") is a principle in the law of the sea. It stresses freedom to navigate the oceans. It also disapproves of war fought in water. The freedom is to be breached only in a necessary inter ...
" regime.
In 1946, Magnolia Petroleum (now ExxonMobil
ExxonMobil Corporation (commonly shortened to Exxon) is an American multinational oil and gas corporation headquartered in Irving, Texas. It is the largest direct descendant of John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil, and was formed on November 30, ...
) drilled at a site off the coast, erecting a platform in of water off St. Mary Parish, Louisiana
St. Mary Parish (french: Paroisse de Sainte-Marie) is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana. As of the 2010 census, the population was 54,650. The parish seat is Franklin. The parish was created in 1811.
St. Mary Parish comprises th ...
.
In early 1947, Superior Oil erected a drilling/production platform in of water some 18 miles off Vermilion Parish, Louisiana
Vermilion Parish (french: Paroisse de Vermillion) is a parish located in the U.S. state of Louisiana, created in 1844. The parish seat is Abbeville. Vermilion Parish is part of the Lafayette metropolitan statistical area, and located in southern ...
. But it was Kerr-McGee
The Kerr-McGee Corporation, founded in 1929, was an American energy company involved in oil exploration, production of crude oil, natural gas, perchlorate and uranium mining and milling in various countries. On June 23, 2006, Anadarko Petroleum ...
Oil Industries (now part of Occidental Petroleum
Occidental Petroleum Corporation (often abbreviated Oxy in reference to its ticker symbol and logo) is an American company engaged in hydrocarbon exploration in the United States, and the Middle East as well as petrochemical manufacturing in the ...
), as operator for partners Phillips Petroleum
Phillips Petroleum Company was an American oil company incorporated in 1917 that expanded into petroleum refining, marketing and transportation, natural gas gathering and the chemicals sectors. It was Phillips Petroleum that first found oil in the ...
(ConocoPhillips
ConocoPhillips Company is an American multinational corporation engaged in hydrocarbon exploration and production. It is based in the Energy Corridor district of Houston, Texas.
The company has operations in 15 countries and has production in ...
) and Stanolind Oil & Gas ( BP), that completed its historic Ship Shoal Block 32 well in October 1947, months before Superior actually drilled a discovery from their Vermilion platform farther offshore. In any case, that made Kerr-McGee's well the first oil discovery drilled out of sight of land.
The British Maunsell Forts
The Maunsell Forts are armed towers built in the Thames and Mersey estuaries during the Second World War to help defend the United Kingdom. They were operated as army and navy forts, and named after their designer, Guy Maunsell. The forts were ...
constructed during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
are considered the direct predecessors of modern offshore platforms. Having been pre-constructed in a very short time, they were then floated to their location and placed on the shallow bottom of the Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the R ...
and the Mersey
The River Mersey () is in North West England. Its name derives from Old English and means "boundary river", possibly referring to its having been a border between the ancient kingdoms of Mercia and Northumbria. For centuries it has formed part ...
estuary.
In 1954, the first jackup oil rig was ordered by Zapata Oil
Emiliano Zapata Salazar (; August 8, 1879 – April 10, 1919) was a Mexican revolutionary. He was a leading figure in the Mexican Revolution of 1910–1920, the main leader of the people's revolution in the Mexican state of Morelos, and the i ...
. It was designed by R. G. LeTourneau
Robert Gilmour LeTourneau (November 30, 1888 – June 1, 1969), born in Richford, Vermont, he was a prolific inventor of earthmoving machinery and the founder of LeTourneau Technologies, Inc. His factories supplied LeTourneau machines which rep ...
and featured three electro-mechanically operated lattice-type legs. Built on the shores of the Mississippi river
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
by the LeTourneau Company, it was launched in December 1955, and christened "Scorpion". The Scorpion was put into operation in May 1956 off Port Aransas
Port Aransas ( ) is a city in Nueces County, Texas, United States. This city is 180 miles southeast of San Antonio. The population was 2,904 at the 2020 census. Port Aransas is the only established town on Mustang Island. It is located north of ...
, Texas. It was lost in 1969.
When offshore drilling moved into deeper waters of up to , fixed platform rigs were built, until demands for drilling equipment was needed in the to depth of the Gulf of Mexico, the first jack-up rigs
A jackup rig or a self-elevating unit is a type of mobile platform that consists of a buoyant hull fitted with a number of movable legs, capable of raising its hull over the surface of the sea. The buoyant hull enables transportation of the unit ...
began appearing from specialized offshore drilling contractors such as forerunners of ENSCO International.
The first semi-submersible
Semi-submersible may refer to a self-propelled vessel, such as:
*Heavy-lift ship, which partially submerge to allow their cargo (another ship) to float into place for transport
*Narco-submarine, some of which remained partially on the surface
*Se ...
resulted from an unexpected observation in 1961. Blue Water Drilling Company
Blue is one of the three primary colours in the RYB colour model (traditional colour theory), as well as in the RGB (additive) colour model. It lies between violet and cyan on the spectrum of visible light. The eye perceives blue when ob ...
owned and operated the four-column submersible Blue Water Rig No.1 in the Gulf of Mexico for Shell Oil Company
Shell USA, Inc. (formerly Shell Oil Company, Inc.) is the United States-based wholly owned subsidiary of Shell plc, a UK-based transnational corporation " oil major" which is amongst the largest oil companies in the world. Approximately 18,000 ...
. As the pontoons were not sufficiently buoyant to support the weight of the rig and its consumables, it was towed between locations at a draught midway between the top of the pontoons and the underside of the deck. It was noticed that the motions at this draught were very small, and Blue Water Drilling and Shell jointly decided to try operating the rig in its floating mode. The concept of an anchored, stable floating deep-sea platform had been designed and tested back in the 1920s by Edward Robert Armstrong
Edward Robert Armstrong (1876–1955) was a Canadian- American engineer and inventor who in 1927 proposed a series of "seadrome" floating airport platforms for airplanes to land on and refuel for transatlantic flights. While his original concept ...
for the purpose of operating aircraft with an invention known as the "seadrome". The first purpose-built drilling semi-submersible
Semi-submersible may refer to a self-propelled vessel, such as:
*Heavy-lift ship, which partially submerge to allow their cargo (another ship) to float into place for transport
*Narco-submarine, some of which remained partially on the surface
*Se ...
''Ocean Driller'' was launched in 1963. Since then, many semi-submersibles have been purpose-designed for the drilling industry mobile offshore fleet.
The first offshore drillship
A drillship is a merchant vessel designed for use in exploratory offshore drilling of new oil and gas wells or for scientific drilling purposes. In recent years the vessels have been used in deepwater and ultra-deepwater applications, equipped ...
was the ''CUSS 1'' developed for the Mohole project to drill into the Earth's crust.
As of June, 2010, there were over 620 mobile offshore drilling rigs (Jackups, semisubs, drillships, barges) available for service in the competitive rig fleet.
One of the world's deepest hubs is currently the Perdido in the Gulf of Mexico, floating in 2,438 meters of water. It is operated by Royal Dutch Shell
Shell plc is a British multinational oil and gas company headquartered in London, England. Shell is a public limited company with a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange (LSE) and secondary listings on Euronext Amsterdam and the New Yo ...
and was built at a cost of $3 billion. The deepest operational platform is the Petrobras America Cascade FPSO in the Walker Ridge 249 field in 2,600 meters of water.
Main offshore basins
 Notable offshore basins include:
* the
Notable offshore basins include:
* the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
* the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
(offshore Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
, Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
, Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
, Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama (state song), Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County, Al ...
and Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
)
* California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
(in the Los Angeles Basin
The Los Angeles Basin is a sedimentary basin located in Southern California, in a region known as the Peninsular Ranges. The basin is also connected to an anomalous group of east-west trending chains of mountains collectively known as the Tr ...
and Santa Barbara Channel
The Santa Barbara Channel is a portion of the Southern California Bight and separates the mainland of California from the northern Channel Islands. It is generally south of the city of Santa Barbara, and west of the Oxnard Plain in Ventura Count ...
, part of the Ventura Basin)
* the Caspian Sea (notably some major fields offshore Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
)
* the Campos and Santos Basin
The Santos Basin ( pt, Bacia de Santos) is an approximately large mostly offshore sedimentary basin. It is located in the south Atlantic Ocean, some southeast of Santos, Brazil. The basin is one of the Brazilian basins to have resulted from th ...
s off the coasts of Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
* Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
and Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
(Atlantic Canada
Atlantic Canada, also called the Atlantic provinces (french: provinces de l'Atlantique), is the region of Eastern Canada comprising the provinces located on the Atlantic coast, excluding Quebec. The four provinces are New Brunswick, Newfoundlan ...
)
* several fields off West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Maurit ...
most notably west of Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
and Angola
, national_anthem = " Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordina ...
* offshore fields in South East Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
and Sakhalin
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh: ...
, Russia
* major offshore oil fields are located in the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Persis, Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a Mediterranean sea (oceanography), me ...
such as Safaniya, Manifa and Marjan which belong to Saudi Arabia and are developed by Saudi Aramco.
* fields in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
(Mumbai High, K G Basin-East Coast Of India, Tapti Field, Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
, India)
* the Taranaki Basin
The Taranaki Basin is an onshore-offshore Cretaceous rift basin on the West Coast of New Zealand. Development of rifting was the result of extensional stresses during the breakup of Gondwanaland. The basin later underwent fore-arc and intra-arc ba ...
in New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
* the Kara Sea
The Kara Sea (russian: Ка́рское мо́ре, ''Karskoye more'') is a marginal sea, separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and from the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya archipelago. ...
north of Siberia
* the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
off the coasts of Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., ...
and Canada's Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. ...
* the offshore fields in the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to t ...
Types
Larger lake- and sea-based offshore platforms anddrilling rig
A drilling rig is an integrated system that drills wells, such as oil or water wells, or holes for piling and other construction purposes, into the earth's subsurface. Drilling rigs can be massive structures housing equipment used to drill wat ...
for oil.
 * 1) & 2) Conventional fixed platforms (deepest: Shell's Bullwinkle in 1991 at 412 m/1,353 ft GOM)
* 3) Compliant tower (deepest: ChevronTexaco's Petronius in 1998 at 534 m /1,754 ft GOM)
* 4) & 5) Vertically moored tension leg and mini-tension leg platform (deepest: ConocoPhillips’ Magnolia in 2004 1,425 m/4,674 ft GOM)
* 6) Spar (deepest: Shell's Perdido in 2010, 2,450 m/8,000 ft GOM)
* 7) & 8) Semi-submersibles (deepest: Shell's NaKika in 2003, 1920 m/6,300 ft GOM)
* 9) Floating production, storage, and offloading facility (deepest: 2005, 1,345 m/4,429 ft Brazil)
* 10) Sub-sea completion and tie-back to host facility (deepest: Shell's Coulomb tie to NaKika 2004, 2,307 m/ 7,570 ft)
: (Numbered from left to right; all records from 2005 data)
* 1) & 2) Conventional fixed platforms (deepest: Shell's Bullwinkle in 1991 at 412 m/1,353 ft GOM)
* 3) Compliant tower (deepest: ChevronTexaco's Petronius in 1998 at 534 m /1,754 ft GOM)
* 4) & 5) Vertically moored tension leg and mini-tension leg platform (deepest: ConocoPhillips’ Magnolia in 2004 1,425 m/4,674 ft GOM)
* 6) Spar (deepest: Shell's Perdido in 2010, 2,450 m/8,000 ft GOM)
* 7) & 8) Semi-submersibles (deepest: Shell's NaKika in 2003, 1920 m/6,300 ft GOM)
* 9) Floating production, storage, and offloading facility (deepest: 2005, 1,345 m/4,429 ft Brazil)
* 10) Sub-sea completion and tie-back to host facility (deepest: Shell's Coulomb tie to NaKika 2004, 2,307 m/ 7,570 ft)
: (Numbered from left to right; all records from 2005 data)
Fixed platforms
 These platforms are built on
These platforms are built on concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most wi ...
or steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
legs, or both, anchored directly onto the seabed, supporting the deck with space for drilling rigs, production facilities and crew quarters. Such platforms are, by virtue of their immobility, designed for very long term use (for instance the Hibernia platform). Various types of structure are used: steel jacket, concrete caisson, floating steel, and even floating concrete. Steel jackets are structural sections made of tubular steel members, and are usually piled into the seabed. To see more details regarding Design, construction and installation of such platforms refer to: and.
Concrete caisson structures, pioneered by the Condeep
Condeep is a make of gravity-based structure for oil platforms invented and patented by engineer Olav Mo in 1972, which were fabricated by Norwegian Contractors in Stavanger, Norway.Fagerberg; Mowery; Verspagen, p.192 ''Condeep'' is an abbrevia ...
concept, often have in-built oil storage in tanks below the sea surface and these tanks were often used as a flotation capability, allowing them to be built close to shore (Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
fjord
In physical geography, a fjord or fiord () is a long, narrow inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Alaska, Antarctica, British Columbia, Chile, Denmark, Germany, Greenland, the Faroe Islands, Ice ...
s and Scottish firth
Firth is a word in the English and Scots languages used to denote various coastal waters in the United Kingdom, predominantly within Scotland. In the Northern Isles, it more usually refers to a smaller inlet. It is linguistically cognate to ''fj ...
s are popular because they are sheltered and deep enough) and then floated to their final position where they are sunk to the seabed. Fixed platforms are economically feasible for installation in water depths up to about .
Compliant towers
These platforms consist of slender, flexible towers and a pile foundation supporting a conventional deck for drilling and production operations. Compliant towers are designed to sustain significant lateral deflections and forces, and are typically used in water depths ranging from .Semi-submersible platform
These platforms have hulls (columns and pontoons) of sufficientbuoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the p ...
to cause the structure to float, but of weight sufficient to keep the structure upright. Semi-submersible platforms can be moved from place to place and can be ballasted up or down by altering the amount of flooding in buoyancy tanks. They are generally anchored by combinations of chain, wire rope or polyester rope, or both, during drilling and/or production operations, though they can also be kept in place by the use of dynamic positioning
Dynamic positioning (DP) is a computer-controlled system to automatically maintain a vessel's position and heading by using its own propellers and thrusters. Position reference sensors, combined with wind sensors, motion sensors and gyrocompass ...
. Semi-submersibles can be used in water depths from .
Jack-up drilling rigs
 Jack-up Mobile Drilling Units (or jack-ups), as the name suggests, are rigs that can be jacked up above the sea using legs that can be lowered, much like jacks. These MODUs (Mobile Offshore Drilling Units) are typically used in water depths up to , although some designs can go to depth. They are designed to move from place to place, and then anchor themselves by deploying their legs to the ocean bottom using a
Jack-up Mobile Drilling Units (or jack-ups), as the name suggests, are rigs that can be jacked up above the sea using legs that can be lowered, much like jacks. These MODUs (Mobile Offshore Drilling Units) are typically used in water depths up to , although some designs can go to depth. They are designed to move from place to place, and then anchor themselves by deploying their legs to the ocean bottom using a rack and pinion
A rack and pinion is a type of linear actuator that comprises a circular gear (the '' pinion'') engaging a linear gear (the ''rack''). Together, they convert rotational motion into linear motion. Rotating the pinion causes the rack to be driven ...
gear system on each leg.
Drillships
A drillship is a maritime vessel that has been fitted with drilling apparatus. It is most often used for exploratory drilling of new oil or gas wells in deep water but can also be used for scientific drilling. Early versions were built on a modified tanker hull, but purpose-built designs are used today. Most drillships are outfitted with adynamic positioning
Dynamic positioning (DP) is a computer-controlled system to automatically maintain a vessel's position and heading by using its own propellers and thrusters. Position reference sensors, combined with wind sensors, motion sensors and gyrocompass ...
system to maintain position over the well. They can drill in water depths up to .
Floating production systems
 The main types of floating production systems are FPSO (floating production, storage, and offloading system). FPSOs consist of large monohull structures, generally (but not always) shipshaped, equipped with processing facilities. These platforms are moored to a location for extended periods, and do not actually drill for oil or gas. Some variants of these applications, called FSO (floating storage and offloading system) or FSU (floating storage unit), are used exclusively for storage purposes, and host very little process equipment. This is one of the best sources for having floating production.
The world's first floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) facility is in production. See the section on particularly large examples below.
The main types of floating production systems are FPSO (floating production, storage, and offloading system). FPSOs consist of large monohull structures, generally (but not always) shipshaped, equipped with processing facilities. These platforms are moored to a location for extended periods, and do not actually drill for oil or gas. Some variants of these applications, called FSO (floating storage and offloading system) or FSU (floating storage unit), are used exclusively for storage purposes, and host very little process equipment. This is one of the best sources for having floating production.
The world's first floating liquefied natural gas (FLNG) facility is in production. See the section on particularly large examples below.
Tension-leg platform
TLPs are floating platforms tethered to the seabed in a manner that eliminates most vertical movement of the structure. TLPs are used in water depths up to about . The "conventional" TLP is a 4-column design that looks similar to a semisubmersible. Proprietary versions include the Seastar and MOSES mini TLPs; they are relatively low cost, used in water depths between . Mini TLPs can also be used as utility, satellite or early production platforms for larger deepwater discoveries.Gravity-based structure
A GBS can either be steel or concrete and is usually anchored directly onto the seabed. Steel GBS are predominantly used when there is no or limited availability of crane barges to install a conventional fixed offshore platform, for example in the Caspian Sea. There are several steel GBS's in the world today (e.g. offshore Turkmenistan Waters (Caspian Sea) and offshore New Zealand). Steel GBS do not usually providehydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and hydrophobic, and their odors are usually weak or ex ...
storage capability. It is mainly installed by pulling it off the yard, by either wet-tow or/and dry-tow, and self-installing by controlled ballasting of the compartments with sea water. To position the GBS during installation, the GBS may be connected to either a transportation barge or any other barge (provided it is large enough to support the GBS) using strand jacks. The jacks shall be released gradually whilst the GBS is ballasted to ensure that the GBS does not sway too much from target location.
Spar platforms
Brent Spar
Brent Spar, or Brent E, was a North Sea oil storage and tanker loading buoy in the Brent oilfield, operated by Shell UK. With the completion of a pipeline connection to the oil terminal at Sullom Voe in Shetland, the storage facility had cont ...
) were previously used as FSOs.
Eni's Devil's Tower
Devils Tower (also known as Bear Lodge Butte) is a butte, possibly laccolithic, composed of igneous rock in the Bear Lodge Ranger District of the Black Hills, near Hulett and Sundance in Crook County, northeastern Wyoming, above the Belle Fo ...
located in of water in the Gulf of Mexico, was the world's deepest spar until 2010. The world's deepest platform as of 2011 was the Perdido spar in the Gulf of Mexico, floating in 2,438 metres of water. It is operated by Royal Dutch Shell
Shell plc is a British multinational oil and gas company headquartered in London, England. Shell is a public limited company with a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange (LSE) and secondary listings on Euronext Amsterdam and the New Yo ...
and was built at a cost of $3 billion.
The first truss spars were Kerr-McGee's Boomvang and Nansen.
The first (and, as of 2010, only) cell spar is Kerr-McGee's Red Hawk.
Normally unmanned installations (NUI)
These installations, sometimes called toadstools, are small platforms, consisting of little more than awell bay
A well bay is an area of an oil platform where the Christmas trees and wellheads are located. It normally consists of two levels, a lower where the wellheads are accessed and an upper where the Xmas Trees are accessed often along with the various ...
, helipad
A helipad is a landing area or platform for helicopters and powered lift aircraft.
While helicopters and powered lift aircraft are able to operate on a variety of relatively flat surfaces, a fabricated helipad provides a clearly marked hard s ...
and emergency shelter. They are designed to be operated remotely under normal conditions, only to be visited occasionally for routine maintenance or well work
A well intervention, or well work, is any operation carried out on an oil or gas well during, or at the end of, its productive life that alters the state of the well or well geometry, provides well diagnostics, or manages the production of the wel ...
.
Conductor support systems
These installations, also known as satellite platforms, are small unmanned platforms consisting of little more than awell bay
A well bay is an area of an oil platform where the Christmas trees and wellheads are located. It normally consists of two levels, a lower where the wellheads are accessed and an upper where the Xmas Trees are accessed often along with the various ...
and a small process plant
An oil production plant is a facility which processes production fluids from oil wells in order to separate out key components and prepare them for export. Typical oil well production fluids are a mixture of oil, gas and produced water. An oil prod ...
. They are designed to operate in conjunction with a static production platform which is connected to the platform by flow lines or by umbilical cable
An umbilical cable or umbilical is a cable and/or hose that supplies required consumables to an apparatus, like a rocket, or to a person, such as a diver or astronaut. It is named by analogy with an umbilical cord. An umbilical can, for example, ...
, or both.
Particularly large examples
 The Petronius Platform is a compliant tower in the Gulf of Mexico modeled after the Hess Baldpate platform, which stands above the ocean floor. It is one of the world's tallest structures.
The Hibernia Gravity Base Structure, Hibernia platform in Canada is the world's heaviest offshore platform, located on the Jeanne D'Arc Basin, in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of
The Petronius Platform is a compliant tower in the Gulf of Mexico modeled after the Hess Baldpate platform, which stands above the ocean floor. It is one of the world's tallest structures.
The Hibernia Gravity Base Structure, Hibernia platform in Canada is the world's heaviest offshore platform, located on the Jeanne D'Arc Basin, in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
. This ''gravity base structure'' (GBS), which sits on the ocean floor, is high and has storage capacity for of crude oil in its high caisson. The platform acts as a small concrete island with serrated outer edges designed to withstand the impact of an iceberg. The GBS contains production storage tanks and the remainder of the void space is filled with ballast with the entire structure weighing in at 1.2 million tons.
Royal Dutch Shell
Shell plc is a British multinational oil and gas company headquartered in London, England. Shell is a public limited company with a primary listing on the London Stock Exchange (LSE) and secondary listings on Euronext Amsterdam and the New Yo ...
has developed the first FLNG, Floating Liquefied Natural Gas (FLNG) facility, which is situated approximately 200 km off the coast of Western Australia. It is the largest floating offshore facility. It is approximately 488m long and 74m wide with Displacement (ship), displacement of around 600,000t when fully ballasted.
Maintenance and supply
A typical oil production platform is self-sufficient in energy and water needs, housing electrical generation, water desalinators and all of the equipment necessary to process oil and gas such that it can be either delivered directly onshore by pipeline or to a Floating production storage and offloading, floating platform or tanker loading facility, or both. Elements in the oil/gas production process include wellhead, production manifold, production separator, glycol process to dry gas, gas compressors, Water injection (oil production), water injection pumps, oil/gas export metering and main oil line pumps. Larger platforms are assisted by smaller ESVs (emergency support vessels) like the United Kingdom, British Iolair that are summoned when something has gone wrong, ''e.g.'' when a search and rescue operation is required. During normal operations, platform supply vessel, PSVs (platform supply vessels) keep the platforms provisioned and supplied, and anchor handling tug supply vessel, AHTS vessels can also supply them, as well as tow them to location and serve as standby rescue and firefighting vessels.Crew
Essential personnel
Not all of the following personnel are present on every platform. On smaller platforms, one worker can perform a number of different jobs. The following also are not names officially recognized in the industry: *OIM (offshore installation manager) who is the ultimate authority during his/her shift and makes the essential decisions regarding the operation of the platform; *operations team leader (OTL); *Offshore Methods Engineer (OME) who defines the installation methodology of the platform; *offshore operations engineer (OOE) who is the senior technical authority on the platform; *PSTL or operations coordinator for managing crew changes; *dynamic positioning operator, navigation, ship or vessel maneuvering (MODU), station keeping, fire and gas systems operations in the event of incident; *automation systems specialist, to configure, maintain and troubleshoot the process control systems (PCS), process safety systems, emergency support systems and vessel management systems; *second mate to meet manning requirements of flag state, operates fast rescue craft, cargo operations, fire team leader; *third mate to meet manning requirements of flag state, operate fast rescue craft, cargo operations, fire team leader; *ballast control operator to operate fire and gas systems; *crane operators to operate the cranes for lifting cargo around the platform and between boats; *scaffolders to rig up scaffolding for when it is required for workers to work at height; *coxswains to maintain the lifeboats and manning them if necessary; *control room operators, especially FPSO or production platforms; *catering crew, including people tasked with performing essential functions such as cooking, laundry and cleaning the accommodation; *production techs to run the production plant; *helicopter Aviator, pilot(s) living on some platforms that have a helicopter based offshore and transporting workers to other platforms or to shore on crew changes; *maintenance technicians (instrument, electrical or mechanical). *Fully qualified medic. *Radio operator to operate all radio communications. *Store Keeper, keeping the inventory well supplied *Technician to record the fluid levels in tanksIncidental personnel
Drill crew will be on board if the installation is performing drilling operations. A drill crew will normally comprise: * Toolpusher * Driller (oil), Driller * Roughnecks * Roustabouts * Company man * Mud engineer * Motorman (drilling), Motorman See: Glossary of oilfield jargon * Derrickhand * Geologist * Welders and Welder Helpers Well services crew will be on board forwell work
A well intervention, or well work, is any operation carried out on an oil or gas well during, or at the end of, its productive life that alters the state of the well or well geometry, provides well diagnostics, or manages the production of the wel ...
. The crew will normally comprise:
* Well services supervisor
*Wireline (cabling), Wireline or coiled tubing operators
* Pump operator
* Pump hanger and ranger
Drawbacks
Risks
The nature of their operation—extraction of volatile substances sometimes under extreme pressure in a hostile environment—means risk; accidents and tragedies occur regularly. The U.S. Minerals Management Service reported 69 offshore deaths, 1,349 injuries, and 858 fires and explosions on offshore rigs in the Gulf of Mexico from 2001 to 2010. On July 6, 1988, 167 people died whenOccidental Petroleum
Occidental Petroleum Corporation (often abbreviated Oxy in reference to its ticker symbol and logo) is an American company engaged in hydrocarbon exploration in the United States, and the Middle East as well as petrochemical manufacturing in the ...
's Piper Alpha offshore production platform, on the Piper field in the UK sector of the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
, exploded after a gas leak. The resulting investigation conducted by Lord Cullen and publicized in the first Cullen Report was highly critical of a number of areas, including, but not limited to, management within the company, the design of the structure, and the Permit to Work System. The report was commissioned in 1988, and was delivered in November 1990. The accident greatly accelerated the practice of providing living accommodations on separate platforms, away from those used for extraction.
The offshore can be in itself a hazardous environment. In March 1980, the 'flotel' (floating hotel) platform ''Alexander L. Kielland (platform), Alexander L. Kielland'' capsized in a storm in the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
with the loss of 123 lives.
In 2001, ''Petrobras 36'' in Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
exploded and sank five days later, killing 11 people.
Given the number of grievances and conspiracy theories that involve the oil business, and the importance of gas/oil platforms to the economy, platforms in the United States are believed to be potential terrorist targets. Agencies and military units responsible for maritime counter-terrorism in the US (United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard, Navy SEALs, United States Marine Corps Force Reconnaissance, Marine Recon) often train for platform raids.
On April 21, 2010, the ''Deepwater Horizon'' platform, 52 nautical mile, miles off-shore of Venice, Louisiana, (property of Transocean and leased to BP) Deepwater Horizon oil spill, exploded, killing 11 people, and sank two days later. The resulting undersea gusher, conservatively estimated to exceed as of early June 2010, became the worst oil spill in US history, eclipsing the Exxon Valdez oil spill.
Ecological effects
 In British waters, the cost of removing all platform rig structures entirely was estimated in 2013 at £30 billion.
Aquatic organisms invariably attach themselves to the undersea portions of oil platforms, turning them into artificial reefs. In the Gulf of Mexico and offshore California, the waters around oil platforms are popular destinations for sports and commercial fishermen, because of the greater numbers of fish near the platforms. The United States and Brunei have active Rigs-to-Reefs programs, in which former oil platforms are left in the sea, either in place or towed to new locations, as permanent artificial reefs. In the US Gulf of Mexico, as of September 2012, 420 former oil platforms, about 10 percent of decommissioned platforms, have been converted to permanent reefs.
On the US Pacific coast, marine biologist Milton Love has proposed that oil platforms off California be retained as artificial reefs, instead of being dismantled (at great cost), because he has found them to be havens for many of the species of fish which are otherwise declining in the region, in the course of 11 years of research. Love is funded mainly by government agencies, but also in small part by the California Artificial Reef Enhancement Program. Professional diving#Scientific diving, Divers have been used to assess the fish populations surrounding the platforms.
In British waters, the cost of removing all platform rig structures entirely was estimated in 2013 at £30 billion.
Aquatic organisms invariably attach themselves to the undersea portions of oil platforms, turning them into artificial reefs. In the Gulf of Mexico and offshore California, the waters around oil platforms are popular destinations for sports and commercial fishermen, because of the greater numbers of fish near the platforms. The United States and Brunei have active Rigs-to-Reefs programs, in which former oil platforms are left in the sea, either in place or towed to new locations, as permanent artificial reefs. In the US Gulf of Mexico, as of September 2012, 420 former oil platforms, about 10 percent of decommissioned platforms, have been converted to permanent reefs.
On the US Pacific coast, marine biologist Milton Love has proposed that oil platforms off California be retained as artificial reefs, instead of being dismantled (at great cost), because he has found them to be havens for many of the species of fish which are otherwise declining in the region, in the course of 11 years of research. Love is funded mainly by government agencies, but also in small part by the California Artificial Reef Enhancement Program. Professional diving#Scientific diving, Divers have been used to assess the fish populations surrounding the platforms.
Effects on the environment
Offshore oil production involves environmental risks, most notably oil spills from oil tankers or pipelines transporting oil from the platform to onshore facilities, and from leaks and accidents on the platform. Produced water is also generated, which is water brought to the surface along with the oil and gas; it is usually highly saline and may include dissolved or unseparated hydrocarbons. Offshore rigs are shut down during hurricanes. In the Gulf of Mexico hurricanes are increasing because of the increasing number of oil platforms that heat surrounding air with methane, it is estimated that U.S. Gulf of Mexico, oil and gas facilities emit approximately 500000 tons of methane emissions, methane each year, corresponding to a loss of produced gas of 2.9 percent. The increasing number of oil rigs also increase movement of oil tankers which also increases levels which directly warm water in the zone, warm waters are a key factor for hurricanes to form. To reduce the amount of carbon emissions otherwise released into the atmosphere, methane pyrolysis of natural gas pumped up by oil platforms is a possible alternative to flaring for consideration. Methane pyrolysis produces non-polluting hydrogen in high volume from this natural gas at low cost. This process operates at around 1000 °C and removes carbon in a solid form from the methane, producing hydrogen. The carbon can then be pumped underground and is not released into the atmosphere. It is being evaluated in such research laboratories as Karlsruhe Liquid-metal Laboratory (KALLA). and the chemical engineering team at University of California – Santa BarbaraRepurposing
If not Decommission (ship), decommissioned, old Semi-submersible platform#Mobile offshore drilling units (MODU), platforms can be repurposed to Carbon capture and storage, pump into rocks below the seabed. Odyssey (launch platform), Others have been Sea Launch#Launches, converted to launch rockets into space, and SpaceX floating launch platform, more are being redesigned for use with heavy-lift launch vehicles.Challenges
Offshore oil and gas production is more challenging than land-based installations due to the remote and harsher environment. Much of the innovation in the offshore petroleum sector concerns overcoming these challenges, including the need to provide very large production facilities. Production and drilling facilities may be very large and a large investment, such as the Troll A platform standing on a depth of 300 meters. Another type of offshore platform may float with a mooring system to maintain it on location. While a floating system may be lower cost in deeper waters than a fixed platform, the dynamic nature of the platforms introduces many challenges for the drilling and production facilities. The ocean can add several thousand meters or more to the fluid column. The addition increases the equivalent circulating density and downhole pressures in drilling wells, as well as the energy needed to lift produced fluids for separation on the platform. The trend today is to conduct more of the production operationssubsea
Subsea technology involves fully submerged ocean equipment, operations, or applications, especially when some distance offshore, in deep ocean waters, or on the seabed. The term ''subsea'' is frequently used in connection with oceanography, marin ...
, by separating water from oil and re-injecting it rather than Pumping (oil well), pumping it up to a platform, or by flowing to onshore, with no installations visible above the sea. Subsea installations help to exploit resources at progressively deeper waters—locations that had been inaccessible—and overcome challenges posed by sea ice such as in the Barents Sea. One such challenge in shallower environments is Seabed gouging by ice, seabed gouging by drifting ice features (means of protecting offshore installations against ice action includes burial in the seabed).
Offshore manned facilities also present logistics and human resources challenges. An offshore oil platform is a small community in itself with cafeteria, sleeping quarters, management and other support functions. In the North Sea, staff members are transported by helicopter for a two-week shift. They usually receive higher salaries than onshore workers do. Supplies and waste are transported by ship, and the supply deliveries need to be carefully planned because storage space on the platform is limited. Today, much effort goes into relocating as many of the personnel as possible onshore, where management and technical experts are in touch with the platform by video conferencing. An onshore job is also more attractive for the aging workforce in the petroleum industry, at least in the western world. These efforts among others are contained in the established term integrated operations. The increased use of subsea facilities helps achieve the objective of keeping more workers onshore. Subsea facilities are also easier to expand, with new separators or different modules for different oil types, and are not limited by the fixed floor space of an above-water installation.
Deepest platforms
The world's deepest oil platform is the floating Perdido (oil platform), Perdido, which is a Spar (platform), spar platform in the Gulf of Mexico in a water depth of . Non-floating compliant towers and fixed platforms, by water depth: * Petronius Platform, * Baldpate Platform, * Troll A, Troll A Platform, * Bullwinkle Platform, * Pompano Platform, * Benguela-Belize Lobito-Tomboco Platform, * Gullfaks C, Gullfaks C Platform, * Tombua Landana Platform, * Harmony Platform,See also
* List of tallest oil platforms * Accommodation platform * Chukchi Cap * Conductor support system * Deep sea mining * Deepwater drilling * Drillship * North Sea oil * Offshore geotechnical engineering * Offshore oil and gas in the United States * Oil drilling * Protocol for the Suppression of Unlawful Acts against the Safety of Fixed Platforms Located on the Continental Shelf * SAR201 * Shallow water drilling * Submarine pipeline * TEMPSC * Texas TowersReferences
External links
Oil Rig Disasters
Listing of oil rig accidents
Oil Rig Photos
Collection of pictures of drilling rigs and production platforms
Overview of Conventional Platforms
Pictorial treatment on the installation of platforms which extend from the seabed to the ocean surface {{DEFAULTSORT:Oil Platform Oil platforms, Offshore engineering Petroleum production Drilling technology Natural gas technology Structural engineering