Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many
nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excre ...
s, resulting in health problems.
Specifically, it is "a
deficiency, excess, or imbalance of
energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of ...
,
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
and
other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues and form.
Malnutrition is not receiving the correct amount of nutrition. Malnutrition is increasing in children under the age of five due to providers who cannot afford or do not have access to adequate nutrition.
Malnutrition is a category of diseases that includes
undernutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues ...
and
overnutrition
Overnutrition (also known as hyperalimentation) is a form of malnutrition in which the intake of nutrients is oversupplied. The amount of nutrients exceeds the amount required for normal growth, development, and metabolism.
The term can also ref ...
. Undernutrition is a lack of nutrients, which can result in
stunted growth
Stunted growth is a reduced growth rate in human development. It is a primary manifestation of malnutrition (or more precisely undernutrition) and recurrent infections, such as diarrhea and helminthiasis, in early childhood and even before birth ...
,
wasting
In medicine, wasting, also known as wasting syndrome, refers to the process by which a debilitating disease causes muscle and fat tissue to "waste" away. Wasting is sometimes referred to as "acute malnutrition" because it is believed that ep ...
, and
underweight
An underweight person is a person whose body weight is considered too low to be healthy. A person who is underweight is malnourished.
Assessment
The body mass index, a ratio of a person's weight to their height, has traditionally been used ...
. A surplus of nutrients causes overnutrition, which can result in
obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
. In some
developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
, overnutrition in the form of obesity is beginning to appear within the same communities as undernutrition.
Most clinical studies use the term 'malnutrition' to refer to undernutrition. However, the use of 'malnutrition' instead of 'undernutrition' makes it impossible to distinguish between undernutrition and overnutrition, a less acknowledged form of malnutrition.
Accordingly, a 2019 report by
The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal and one of the oldest of its kind. It is also the world's highest-impact academic journal. It was founded in England in 1823.
The journal publishes original research articles ...
Commission suggested expanding the definition of malnutrition to include "all its forms, including obesity, undernutrition, and other
dietary risks." The
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
and The Lancet Commission have also identified "
e double burden of malnutrition," which occurs from "the coexistence of overnutrition (overweight and obesity) alongside undernutrition (stunted growth and wasting)."
[Ghattas, H., Acharya, Y., Jamaluddine, Z., Assi, M., El Asmar, K. and Jones, A., 2020. The child-level double burden of malnutrition in the MENA and LAC regions: Prevalence and social determinants. Maternal & Child Nutrition, 16(2).]
Prevalence
It is estimated that nearly one in three persons globally has at least one form of malnutrition: wasting, stunting, vitamin or mineral deficiency, overweight, obesity, or diet-related noncommunicable diseases. Undernutrition is more common in
developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
. Stunting is more prevalent in urban slums than in rural areas.
[Murarkar, S., Gothankar, J., Doke, P., Pore, P., Lalwani, S., Dhumale, G., Quraishi, S., Patil, R., Waghachavare, V., Dhobale, R., Rasote, K., Palkar, S. and Malshe, N., 2020. Prevalence and determinants of undernutrition among under-five children residing in urban slums and rural area, Maharashtra, India: a community-based cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health, 20(1).] Studies on malnutrition have the population categorised into different groups including infants, under-five children, children, adolescents, pregnant women, adults and the elderly population. The use of different growth references in different studies leads to variances in the undernutrition prevalence reported in different studies. Some of the growth references used in studies include the
National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) growth charts, WHO reference 2007, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) growth charts, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), WHO reference 1995, Obesity Task Force (IOTF) criteria and Indian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP) growth charts.
In children
The prevalence of undernutrition is highest among children under five.
In 2020, 149 million children under five years old were stunted, 45 million were wasted, and 38.9 million were overweight or obese.
The following year, an estimated 45% of deaths in children were linked to undernutrition.
The prevalence of wasting among children under five in South Asia was reported to be 16% moderately or severely wasted.
In Asia, India has one of the highest burden of wasting with over 20% wasted children. However, the burden of undernutrition among under-five children in African countries is much higher. A pooled analysis of the prevalence of chronic undernutrition among under-five children in East Africa was identified to be 33.3%. This prevalence of undernutrition among under-five children ranged from 21.9% in Kenya to 53% in Burundi. In Tanzania, the prevalence of stunting, among children under five varied from 41% in lowland and 64.5% in highland areas. Undernutrition by underweight and wasting was 11.5% and 2.5% in lowland and 22.% and 1.4% in the highland areas of Tanzania respectively. In South Sudan, the prevalence of undernutrition explained by stunting, underweight and wasting in under-five children were 23.8%, 4.8% and 2.3% respectively.
Vitamin A deficiency
Vitamin A deficiency (VAD) or hypovitaminosis A is a lack of vitamin A in blood and tissues. It is common in poorer countries, especially among children and women of reproductive age, but is rarely seen in more developed countries. Nyctalopia (ni ...
affects one third of children under age 5 around the world,
[World Health Organization, Global prevalence of vitamin A deficiency in populations at risk 1995–2005, WHO orld health organisationglobal database on vitamin A deficiency.] leading to 670,000 deaths and 250,000–500,000 cases of
blindness
Visual impairment, also known as vision impairment, is a medical definition primarily measured based on an individual's better eye visual acuity; in the absence of treatment such as correctable eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment� ...
.
In adults
As of June 2021, 1.9 billion adults were overweight or obese, and 462 million adults were underweight.
Globally, two billion people had
iodine deficiency
Iodine deficiency is a lack of the trace element iodine, an essential nutrient in the diet. It may result in metabolic problems such as goiter, sometimes as an endemic goiter as well as congenital iodine deficiency syndrome due to untreated cong ...
in 2017. In 2020, 900 million women and children had anemia, which is often caused by iron deficiency.
Certain groups have higher rates of undernutrition, including
elderly
Old age refers to ages nearing or surpassing the life expectancy of human beings, and is thus the end of the human life cycle. Terms and euphemisms for people at this age include old people, the elderly (worldwide usage), OAPs (British usage ...
people and women (in particular while
pregnant
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ca ...
or
breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be expressed by hand or pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that bre ...
children
A child ( : children) is a human being between the stages of birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. The legal definition of ''child'' generally refers to a minor, otherwise known as a person younger ...
under five years of age). Undernutrition is an increasing health problem in people aged over 65 years, even in developed countries, especially among nursing home residents and in acute care hospitals. In the elderly, undernutrition is more commonly due to physical, psychological, and social factors, not a lack of food. Age-related reduced dietary intake due to chewing and swallowing problems, sensory decline, depression, imbalanced gut microbiome, poverty and loneliness are major contributors to undernutrition in the elderly population.
Recent increase
There has been an increase in world hunger over the past decade. In 2015, 795 million people (about one in ten people on earth) had undernutrition.
In 2020, one in nine people in the world—or 820 million people worldwide—was hungry.
These increases are partially related to the ongoing
COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
, which continues to highlight the weaknesses of current food and health systems. It has contributed to
food insecurity
Food security speaks to the availability of food in a country (or geography) and the ability of individuals within that country (geography) to access, afford, and source adequate foodstuffs. According to the United Nations' Committee on World ...
, increasing hunger worldwide; meanwhile, lower physical activity during
lockdown
A lockdown is a restriction policy for people, community or a country to stay where they are, usually due to specific risks (such as COVID-19) that could possibly harm the people if they move and interact freely.
The term is used for a prison ...
s has contributed to increases in overweight and obesity.
In 2020, experts estimated that by the end of the year, the pandemic could double the number of people at risk of suffering acute hunger. Similarly, experts estimate that the
prevalence
In epidemiology, prevalence is the proportion of a particular population found to be affected by a medical condition (typically a disease or a risk factor such as smoking or seatbelt use) at a specific time. It is derived by comparing the number o ...
of moderate and severe wasting could increase by 14% due to COVID-19; coupled with reductions in nutrition and health services coverage, this could result in over 128,000 additional deaths among children under 5 in 2020 alone.
Although COVID-19 is less severe in children than in adults, the risk of severe disease increases with undernutrition.
Other major causes of hunger include manmade conflicts,
climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
s, and
economic
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with th ...
downturns.
Definitions
Undernutrition
Undernutrition can occur either due to protein-energy wasting or as a result of
micronutrient
Micronutrients are essential dietary elements required by organisms in varying quantities throughout life to orchestrate a range of physiological functions to maintain health. Micronutrient requirements differ between organisms; for example, huma ...
deficiencies.
[Morley, J., 2012. Undernutrition in older adults. Family Practice, 29(suppl 1), pp.i89-i93.] It adversely affects physical and mental functioning, and causes changes in body composition and body cell mass. Undernutrition is a major health problem, causing the highest mortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of d ...
in children, and is responsible for long-lasting physiologic
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical a ...
effects. It is a barrier to the complete physical and mental development of children.starvation
Starvation is a severe deficiency in caloric energy intake, below the level needed to maintain an organism's life. It is the most extreme form of malnutrition. In humans, prolonged starvation can cause permanent organ damage and eventually, de ...
, chronic hunger, Severe Acute Malnutrition (SAM), and/or Moderate Acute Malnutrition (MAM).
The signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showi ...
of micronutrient deficiencies
Micronutrient deficiency or dietary deficiency is not enough of one or more of the micronutrients required for optimal plant or animal health. In humans and other animals they include both vitamin deficiencies and mineral deficiencies, whereas in p ...
depend on which micronutrient is lacking.infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
s and frequently feel cold.
Micronutrient malnutrition
Micronutrient malnutrition results from inadequate intake of vitamins and minerals.iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , ...
, Vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin and an essential nutrient for humans. It is a group of organic compounds that includes retinol, retinal (also known as retinaldehyde), retinoic acid, and several provitamin A carotenoids (most notably ...
, and iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
are the most common. Children and pregnant women in low-income countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreeme ...
are at especially high risk for micronutrient deficiencies.Anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, t ...
is most commonly caused by iron deficiency, but can also result from other micronutrient deficiencies and diseases. This condition can have major health consequences.
It is possible to have overnutrition simultaneously with micronutrient deficiencies; this condition is termed the '
double burden of malnutrition
''.
Protein-energy malnutrition
'Undernutrition' sometimes refers specifically to protein–energy malnutrition (PEM).calorie restriction
Calorie restriction (caloric restriction or energy restriction) is a dietary regimen that reduces intake of energy from caloric foods & beverages without incurring malnutrition. "Reduce" can be defined relative to the subject's previous intake b ...
in that calorie restriction may not result in negative health effects. Hypoalimentation (underfeeding) is one cause of undernutrition.
Two forms of PEM are kwashiorkor
Kwashiorkor ( , ) is a form of severe protein malnutrition characterized by edema and an enlarged liver with fatty infiltrates. It is thought to be caused by sufficient calorie intake, but with insufficient protein consumption (or lack of go ...
and marasmus
Marasmus is a form of severe malnutrition characterized by energy deficiency. It can occur in anyone with severe malnutrition but usually occurs in children. Body weight is reduced to less than 62% of the normal (expected) body weight for the a ...
; both commonly coexist. ''Kwashiorkor'' is primarily caused by inadequate protein intake.
''Kwashiorkor'' is primarily caused by inadequate protein intake.edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area ma ...
, wasting, liver enlargement, hypoalbuminaemia
Hypoalbuminemia (or hypoalbuminaemia) is a medical sign in which the level of albumin in the blood is low. This can be due to decreased production in the liver, increased loss in the gastrointestinal tract or kidneys, increased use in the body, or ...
, and steatosis; the condition may also cause depigmentation
Depigmentation is the lightening of the skin or loss of pigment. Depigmentation of the skin can be caused by a number of local and systemic conditions. The pigment loss can be partial (injury to the skin) or complete (caused by vitiligo). It can b ...
of skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
and hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals.
The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and fi ...
.Ga language
Ga is a Kwa language spoken in Ghana, in and around the capital Accra. There are also some speakers in Togo, Benin and Western Nigeria. It has a phonemic distinction between three vowel lengths.
Classification
Ga is a Kwa language, part ...
of coastal Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and Tog ...
in West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali ...
. It means "the sickness the baby gets when the next baby is born," as it often occurs when the older child is deprived of breastfeeding and weaned to a diet composed largely of carbohydrates.metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run ...
to adapt in order to prolong survival.edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area ma ...
; minimal subcutaneous fat
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and macro ...
; and abnormal serum albumin levels.famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompan ...
, significant food restriction, or severe anorexia
Anorexia nervosa, often referred to simply as anorexia, is an eating disorder characterized by low weight, food restriction, body image disturbance, fear of gaining weight, and an overpowering desire to be thin. ''Anorexia'' is a term of Gre ...
.
Overnutrition
Excessive consumption of energy-dense foods and drinks and limited physical activity causes overnutrition. It causes overweight, defined as a body mass index (BMI)
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms and hei ...
of 25 or more, and can lead to obesity (a BMI of 30 or more).diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
, certain cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
s, and cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, ...
. Hence identifying and addressing the immediate risk factors has become a major health priority. The recent evidence on the impact of diet-induced obesity in fathers and mothers around the time of conception is identified to negatively program the health outcomes of multiple generations.
Classifying malnutrition
Definition by Gomez & Galvan
In 1956, Gómez and Galvan studied factors associated with death in a group of undernourished children in a hospital in Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital and largest city of Mexico, and the most populous city in North America. One of the world's alpha cities, it is located in the Valley o ...
, Mexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
. They defined three categories of malnutrition: first, second, and third degree.median
In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic f ...
weight for their age.arbitrary
Arbitrariness is the quality of being "determined by chance, whim, or impulse, and not by necessity, reason, or principle". It is also used to refer to a choice made without any specific criterion or restraint.
Arbitrary decisions are not necess ...
" and for not considering overweight as a form of malnutrition. Also, height alone may not be the best indicator of malnutrition; children who are born prematurely
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between ...
may be considered short for their age even if they have good nutrition.
Definition by Waterlow
In the 1970s, John Conrad Waterlow established a new classification system for malnutrition.
Effects
 Malnutrition weakens every part of the
Malnutrition weakens every part of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
.zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, and vitamins).tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, ...
. It also raises the risk of HIV transmission from mother to child, and increases replication of the virus.scurvy
Scurvy is a deficiency disease, disease resulting from a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, feeling tired and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, anemia, decreased red blood cells, gum disease, ch ...
and rickets
Rickets is a condition that results in weak or soft bones in children, and is caused by either dietary deficiency or genetic causes. Symptoms include bowed legs, stunted growth, bone pain, large forehead, and trouble sleeping. Complications ma ...
. As malnutrition worsens, those affected have less energy and experience impairment in brain functions. This can make it difficult (or impossible) for them to perform the tasks needed to acquire food, earn an income
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. Fo ...
, or gain an education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty ...
.
Malnutrition can also cause acute problems, like hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose bel ...
(low blood sugar
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the b ...
). This condition can cause lethargy, limpness, seizure
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with lo ...
s, and loss of consciousness
Loss may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music
* ''Loss'' (Bass Communion album) (2006)
* ''Loss'' (Mull Historical Society album) (2001)
*"Loss", a song by God Is an Astronaut from their self-titled album (2008)
* Losses "(Lil Tjay son ...
. Children are particularly at risk and can become hypoglycemic after 4 to 6 hours without food. Dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water, with an accompanying disruption of metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds free water intake, usually due to exercise, disease, or high environmental temperature. Mil ...
can also occur in malnourished people, and can be life-threatening, especially in babies and small children.
Signs
There are many different signs of dehydration in malnourished people. These can include sunken eyes; a very dry mouth; decreased urine output and/or dark urine; increased heart rate with decreasing blood pressure; and altered mental status
An altered level of consciousness is any measure of arousal other than normal. Level of consciousness (LOC) is a measurement of a person's arousability and responsiveness to stimuli from the environment.
A mildly depressed level of consciousne ...
.
Cognitive development
Protein-calorie malnutrition can cause cognitive impairment
Cognitive deficit is an inclusive term to describe any characteristic that acts as a barrier to the cognition process.
The term may describe
* deficits in overall intelligence (as with intellectual disabilities),
* specific and restricted defici ...
s. This most commonly occurs in people who were malnourished during a "critical period ... from the final third of gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pr ...
to the first 2 years of life". For example, in children under two years of age, iron deficiency anemia is likely to affect brain function acutely, and probably also chronically. Similarly, folate
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing an ...
deficiency has been linked to neural tube defect
Neural tube defects (NTDs) are a group of birth defects in which an opening in the spine or cranium remains from early in human development. In the third week of pregnancy called gastrulation, specialized cells on the dorsal side of the embryo b ...
s.
Iodine deficiency is "the most common preventable cause of mental impairment worldwide."infant
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used t ...
s, lowers intelligence by 10 to 15 I.Q. points, shaving incalculable potential off a nation's development."cretinism
Congenital iodine deficiency syndrome is a medical condition present at birth marked by impaired physical and mental development, due to insufficient thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism) often caused by insufficient dietary iodine during pregnancy. It ...
and dwarfism
Dwarfism is a condition wherein an organism is exceptionally small, and mostly occurs in the animal kingdom. In humans, it is sometimes defined as an adult height of less than , regardless of sex; the average adult height among people with dw ...
. These effects occur most commonly in mountain villages. However, 16 percent of the world's people have at least mild goiter (a swollen thyroid gland
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans it is in the neck and consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thy ...
in the neck)."
Causes & risk factors
Social and political
Social conditions have a significant influence on the health of people. The social determinants of undernutrition mainly include poor education, poverty, disease burden and lack of women's empowerment.[Bhutta, Z., Ahmed, T., Black, R., Cousens, S., Dewey, K., Giugliani, E., Haider, B., Kirkwood, B., Morris, S., Sachdev, H. and Shekar, M., 2008. What works? Interventions for maternal and child undernutrition and survival. The Lancet, 371(9610), pp.417-440.] Identifying and addressing these determinants can eliminate undernutrition in the long term.food prices
Food prices refer to the average price level for food across countries, regions and on a global scale. Food prices have an impact on producers and consumers of food.
Price levels depend on the food production process, including food marketing ...
is a major factor preventing low income households from getting nutritious food [ For example, Khan and Kraemer (2009) found that in ]Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
, low socioeconomic status
Socioeconomic status (SES) is an economic and sociological combined total measure of a person's work experience and of an individual's or family's economic access to resources and social position in relation to others. When analyzing a family's ...
was associated with chronic malnutrition since it inhibited purchase of nutritious foods (like milk, meat, poultry
Poultry () are domesticated birds kept by humans for their eggs, their meat or their feathers. These birds are most typically members of the superorder Galloanserae (fowl), especially the order Galliformes (which includes chickens, qu ...
, and fruits).technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, scien ...
. However, in the developing world, eighty percent of malnourished children live in countries that produce food surpluses, according to estimates from the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).economist
An economist is a professional and practitioner in the social sciences, social science discipline of economics.
The individual may also study, develop, and apply theories and concepts from economics and write about economic policy. Within this ...
Amartya Sen
Amartya Kumar Sen (; born 3 November 1933) is an Indian economist and philosopher, who since 1972 has taught and worked in the United Kingdom and the United States. Sen has made contributions to welfare economics, social choice theory, economi ...
observes that, in recent decades, famine has always been a problem of food distribution
Food distribution is the process where a general population is supplied with food. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) considers food distribution as a subset of the food system. The process and methodology behind food distribution varies ...
, purchasing power
Purchasing power is the amount of goods and services that can be purchased with a unit of currency. For example, if one had taken one unit of currency to a store in the 1950s, it would have been possible to buy a greater number of items than would ...
, and/or poverty, since there has always been enough food for everyone in the world.sociopolitical
Political sociology is an interdisciplinary field of study concerned with exploring how governance and society interact and influence one another at the micro to macro levels of analysis. Interested in the social causes and consequences of how ...
causes of malnutrition. For example, the population of a community might be at increased risk for malnutrition if government is poor and the area lacks health-related services. On a smaller scale, certain households or individuals may be at an even higher risk due to differences in income levels, access to land, or levels of education. Community plays a crucial role in addressing the social causes of malnutrition. For example, communities with high social support and knowledge sharing about social protection programs can enable better public service demands. Better public service demands and social protection programs minimise the risk of malnutrition in these communities.
It is argued that commodity
In economics, a commodity is an economic good, usually a resource, that has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to who produced them.
The price of a co ...
speculators are increasing the cost of food. As the real-estate bubble in the United States was collapsing, it is said that trillions of dollars moved to invest in food and primary commodities, causing the 2007–2008 food price crisis
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is inges ...
.
The use of biofuel
Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels, such as oil. According to the United States Energy Information Administration ...
s as a replacement for traditional fuels raises the price of food. The United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
special rapporteur
A rapporteur is a person who is appointed by an organization to report on the proceedings of its meetings. The term is a French-derived word.
For example, Dick Marty was appointed ''rapporteur'' by the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Eur ...
on the right to food
The right to food, and its variations, is a human right protecting the right of people to feed themselves in dignity, implying that sufficient food is available, that people have the means to access it, and that it adequately meets the individual ...
, Jean Ziegler proposes that agricultural waste, such as corn cobs
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
and banana leaves, should be used as fuel instead of crop
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. When the plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. Most crops are cultivated in agriculture or hydropon ...
s.
In some developing countries, overnutrition (in the form of obesity) is beginning to appear in the same communities where malnutrition occurs. Overnutrition increases with urbanisation, food commercialisation and technological developments and increases physical inactivity. Variations in the health status of individuals in the same society are associated with the societal structure and an individual's socioeconomic status which leads to income inequality, racism, educational differences and lack of opportunities.
Diseases & conditions
Infectious diseases
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
which increase nutrient requirements, such as gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea and gastro, is an inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of energy, and dehydr ...
, pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severit ...
, malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. ...
, and measles
Measles is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by measles virus. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, ...
, can cause malnutrition.[ So can some chronic illnesses, especially ]HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ...
.
Malnutrition can also result from abnormal nutrient loss due to diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin w ...
or chronic small bowel illnesses, like Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea (which may be bloody if inflammation is severe), fever, abdominal distensi ...
or untreated coeliac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barle ...
.bariatric surgery
Bariatric surgery (or weight loss surgery) includes a variety of procedures performed on people who are obese. Long term weight loss through the standard of care procedures ( Roux en-Y bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and biliopancreatic diversio ...
can also cause malnutrition.
Dietary practices
Undernutrition
Undernutrition due to lack of adequate breastfeeding is associated with the deaths of an estimated one million children annually. Illegal advertising of breast-milk substitutes contributed to malnutrition and continued three decades after its 1981 prohibition under the ''WHO International Code of Marketing Breast Milk Substitutes''.
Maternal malnutrition can also factor into the poor health or death of a baby. Over 800,000 neonatal deaths have occurred because of deficient growth of the fetus
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal dev ...
in the mother's womb.
Deriving too much of one's diet from a single source, such as eating almost exclusively potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Uni ...
, maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American English, North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous ...
or rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
, can cause malnutrition. This may either be from a lack of education about proper nutrition, or from only having access to a single food source.iron deficiency
Iron deficiency, or sideropenia, is the state in which a body lacks enough iron to supply its needs. Iron is present in all cells in the human body and has several vital functions, such as carrying oxygen to the tissues from the lungs as a key ...
or zinc deficiency can also increase risk of death.[UNICEF (2013)]
Improving Child Nutrition – The achievable imperative for global progress
UNICEF
Overnutrition
 Overnutrition caused by
Overnutrition caused by overeating
Overeating occurs when an individual consumes more calories in relation to the energy that is expended via physical activity or expelled via excretion, leading to weight gain and often obesity. Overeating is the defining characteristic of bin ...
is also a form of malnutrition. In the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, more than half of all adults are now overweight—a condition that, like hunger, increases susceptibility to disease and disability, reduces worker productivity
Productivity is the efficiency of production of goods or services expressed by some measure. Measurements of productivity are often expressed as a ratio of an aggregate output to a single input or an aggregate input used in a production proces ...
, and lowers life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
.surplus
Surplus may refer to:
* Economic surplus, one of various supplementary values
* Excess supply, a situation in which the quantity of a good or service supplied is more than the quantity demanded, and the price is above the equilibrium level determ ...
of non-nutritious food. Increased sedentary lifestyle
Sedentary lifestyle is a Lifestyle (social sciences), lifestyle type, in which one is physically inactive and does little or no physical movement and or exercise. A person living a sedentary lifestyle is often sitting or lying down while enga ...
s also contribute to overnutrition. Yale University
Yale University is a private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. Established in 1701 as the Collegiate School, it is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and among the most prestigious in the w ...
psychologist Kelly Brownell calls this a "toxic food environment
A food environment is the "physical presence of food that affects a person’s diet, a person’s proximity to food store locations, the distribution of food stores, food service, and any physical entity by which food may be obtained, or a connect ...
," where fat- and sugar-laden foods have taken precedence over healthy nutritious foods.per capita
''Per capita'' is a Latin phrase literally meaning "by heads" or "for each head", and idiomatically used to mean "per person". The term is used in a wide variety of social sciences and statistical research contexts, including government statistic ...
in the United States than in any other country. This mass consumption of fast food results from its affordability and accessibility. Fast food, which is low in cost and nutrition, is high in calories. Due to increasing urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly th ...
and automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, namely by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines ...
, people are living more sedentary lifestyles. These factors combine to make weight gain difficult to avoid.China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, consumption of high-fat foods has increased, while consumption of rice and other goods has decreased. Overeating leads to many diseases, such as
Overeating leads to many diseases, such as heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, h ...
and diabetes, that may be fatal.
Agricultural productivity
Local food shortages can be caused by a lack of arable land
Arable land (from the la, arabilis, "able to be ploughed") is any land capable of being ploughed and used to grow crops.''Oxford English Dictionary'', "arable, ''adj''. and ''n.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 2013. Alternatively, for th ...
, adverse weather, and/or poorer farming skills (like inadequate crop rotation
Crop rotation is the practice of growing a series of different types of crops in the same area across a sequence of growing seasons. It reduces reliance on one set of nutrients, pest and weed pressure, and the probability of developing resistant ...
). They can also occur in areas which lack the technology or resources needed for the higher yields found in modern agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
. These resources include fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
s, pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. This includes herbicide, insecticide, nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, microbicide, fungicide, and ...
s, irrigation, Agricultural machinery, machinery, and storage facilities. As a result of widespread poverty, farmers and governments cannot provide enough of these resources to improve local yields.
Additionally, the World Bank and some wealthy donor countries have pressured developing countries to use free market policies. Even as the United States and Europe extensively subsidy, subsidized their own farmers, they urged developing countries to cut or eliminate subsidized agricultural inputs, like fertilizer.[ Fertilizer is also increasingly unavailable because Western Environmental movement, environmental groups have fought to end its use due to environmental concerns. The Green Revolution pioneers Norman Borlaug and Keith Rosenberg cited as the obstacle to feeding Africa by .]
Future threats
In the future, variety of factors could potentially disrupt global food supply and cause widespread malnutrition.
Global warming is of importance to food security. Almost all malnourished people (95%) live in the tropics and subtropics, where the climate is relatively stable. According to the latest Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change reports, temperature increases in these regions are "very likely."
Prevention
 Reducing malnutrition is key part of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal 2 (SDG2), "Zero Hunger," which aims to reduce malnutrition, undernutrition, and stunted child growth. Managing severe acute undernutrition in a community setting has received significant research attention.
Reducing malnutrition is key part of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal 2 (SDG2), "Zero Hunger," which aims to reduce malnutrition, undernutrition, and stunted child growth. Managing severe acute undernutrition in a community setting has received significant research attention.
Food security
In the 1950s and 1960s, the Green Revolution aimed to bring modern Western agricultural techniques (like nitrogen fertilizers and pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are meant to control pests. This includes herbicide, insecticide, nematicide, molluscicide, piscicide, avicide, rodenticide, bactericide, insect repellent, animal repellent, microbicide, fungicide, and ...
s) to Asia. Investments in agriculture, such as fund fertilizers and seeds, increased food harvests and thus food production. Consequently, food prices and malnutrition decreased (as they had earlier in Western nations).[
The Green Revolution was possible in Asia because of existing infrastructure and institutions, such as a system of roads and public seed companies that made seeds available. These resources were in short supply in Africa, decreasing the Green Revolution's impact on the continent.
For example, almost five million of the 13 million people in Malawi used to need emergency food aid. However, in the early 2000s, the Malawian government changed its agricultural policies, and implemented subsidies for fertilizer and seed introduced against World Bank strictures. By 2007, farmers were producing record-breaking corn harvests. Corn production leaped to 3.4 million in 2007 compared to 1.2 million in 2005, making Malawi a major food exporter.]
Economics
Many aid groups have found that giving cash assistance (or cash vouchers) is more effective than donating food. Particularly in areas where food is available but unaffordable, giving cash assistance is a cheaper, faster, and more efficient way to deliver help to the hungry. Food banks and soup kitchens address malnutrition in places where people lack money to buy food. A basic income has been proposed as a way to ensure that everyone has enough money to buy food and other basic needs. This is a form of social security in which all citizens or residents of a country regularly receive an unconditional sum of money, either from a government or some other public institution, in addition to any income received from elsewhere.
Food banks and soup kitchens address malnutrition in places where people lack money to buy food. A basic income has been proposed as a way to ensure that everyone has enough money to buy food and other basic needs. This is a form of social security in which all citizens or residents of a country regularly receive an unconditional sum of money, either from a government or some other public institution, in addition to any income received from elsewhere.
Successful initiatives
Ethiopia pioneered a program that later became part of the World Bank's prescribed method for coping with a food crisis. Through the country's main food assistance program, the Productive Safety Net Program, Ethiopia provided rural residents who were chronically short of food a chance to work for food or cash. Foreign aid organizations like the World Food Program were then able to buy food locally from surplus areas to distribute in areas with a shortage of food. Aid organizations now view the Ethiopian program as a model of how to best help hungry nations.
Successful initiatives also include Brazil, Brazil's recycling program for Biodegradable waste, organic waste, which benefits farmers, the urban poor, and the city in general. City residents separate organic waste from their garbage, bag it, and then exchange it for fresh fruit and vegetables from local farmers. This reduces the country's waste while giving the urban poor a steady supply of nutritious food.
World population
Restricting population size is a proposed solution to malnutrition. Thomas Malthus argues that population growth can be controlled by natural disasters and by voluntary limits through "moral restraint." Robert Chapman suggests that government policies are a necessary ingredient for curtailing global population growth. The United Nations recognizes that poverty and malnutrition (as well as the environment) are interdependent and complementary with population growth. According to the World Health Organisation, "Family planning is key to slowing unsustainable population growth and the resulting negative impacts on the economy, environment, and national and regional development efforts". However, more than 200 million women worldwide lack adequate access to family planning services.
There are Theories of famines, different theories about what causes famine. Some theorists, like the Indian economist
An economist is a professional and practitioner in the social sciences, social science discipline of economics.
The individual may also study, develop, and apply theories and concepts from economics and write about economic policy. Within this ...
Amartya Sen, believe that the world has more than enough resources to sustain its population. In this view, malnutrition is caused by unequal distribution of resources and under- or unutilized arable land. For example, Sen argues that "no matter how a famine is caused, methods of breaking it call for a large supply of food in the Public Distribution System, public distribution system. This applies not only to organizing rationing and control, but also to undertaking work programmes and other methods of increasing purchasing power
Purchasing power is the amount of goods and services that can be purchased with a unit of currency. For example, if one had taken one unit of currency to a store in the 1950s, it would have been possible to buy a greater number of items than would ...
for those hit by Theories of famines#Failure of exchange entitlements, shifts in exchange entitlements in a general inflationary situation."
Food sovereignty
Food sovereignty is one suggested policy framework to resolve access issues. In this framework, people (rather than international market forces) have the right to define their own food, agricultural, livestock, and fishery systems. Food First is one of the primary think tanks working to build support for food sovereignty. Neoliberalism, Neoliberals advocate for an increasing role of the free market.
Health facilities
Another possible long-term solution to malnutrition is to increase access to health facilities in rural parts of the world. These facilities could monitor undernourished children, act as supplemental food distribution centers, and provide education on dietary needs. Similar facilities have already proven very successful in countries such as Peru and Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and Tog ...
.
Breastfeeding
In 2016, estimates suggested that more widespread breastfeeding could prevent about 823,000 deaths annually of children under age 5.
Barriers to breastfeeding
Breastfeeding is noted as one of the most Cost-effectiveness analysis, cost-effective medical interventions benefiting child health.
21st century global initiatives
Starting around 2009, there was renewed international media and political attention focused on malnutrition. This resulted in part from spikes in food prices and the Financial crisis of 2007–2008, 2008 financial crisis. Additionally, there was an emerging consensus that combating malnutrition is one of the most cost-effective ways to contribute to development. This led to the 2010 launch of the UN's ''Scaling up Nutrition'' movement (SUN).
In April 2012, a number of countries signed the Food Assistance Convention, the world's first legally binding international agreement on food aid. The following month, the Copenhagen Consensus recommended that politicians and private sector Philanthropy, philanthropists should prioritize interventions against hunger and malnutrition in order to maximize the effectiveness of aid spending. The Consensus recommended prioritizing these interventions ahead of any others, including the fights against malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. ...
and AIDS.
In June 2015, the European Union and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation launched a partnership to combat undernutrition, especially in children. The program was first implemented in Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the mo ...
, Burundi, Ethiopia, Kenya, Laos and Niger. It aimed to help these countries improve information and analysis about nutrition, enabling them to develop effective national nutrition policies.
Also in 2015, the UN's Food and Agriculture Organization created a partnership aimed at ending hunger in Africa by 2025. The African Union, African Union's Comprehensive Africa Agriculture Development Programme (CAADP) provided the framework for the partnership. It includes a variety of interventions, including support for improved food production, a strengthening of social protection, and integration of the right to food
The right to food, and its variations, is a human right protecting the right of people to feed themselves in dignity, implying that sufficient food is available, that people have the means to access it, and that it adequately meets the individual ...
into national legislation.
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations#Online campaign against hunger, EndingHunger campaign is an online communication campaign whose goal is to raise awareness about hunger. The campaign has created viral videos depicting Celebrity, celebrities voicing their anger about the large number of hungry people in the world.
After the Millennium Development Goals expired in 2015, the Sustainable Development Goals became the main global policy focus to reduce hunger and poverty. In particular, Goal 2: Zero Hunger sets globally agreed-upon targets to wipe out hunger, end all forms of malnutrition, and make Sustainable agriculture, agriculture sustainable. The partnership Compact2025 develops and disseminates evidence-based advice to politicians and other decision-makers, with the goal of ending hunger and undernutrition by 2025. The International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) led the partnership, with the involvement of UN organisations, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and private foundations.
Treatment


Improving nutrition
Efforts to improve nutrition are some of the common forms of development aid.
Identifying malnourishment
Measuring children is crucial to identifying malnourishment. In 2000, the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) established the International Micronutrient Malnutrition Prevention and Control (IMMPaCt) program. It tested children for malnutrition by conducting a three-dimensional scan, using an iPad or a Tablet computer, tablet. Its objective was to help doctors provide more efficient treatments.
Medical management
It is often possible to manage severe malnutrition within a person's home, using therapeutic food#Ready-to-Use Therapeutic Food, ready-to-use therapeutic foods.
Bangladeshi model
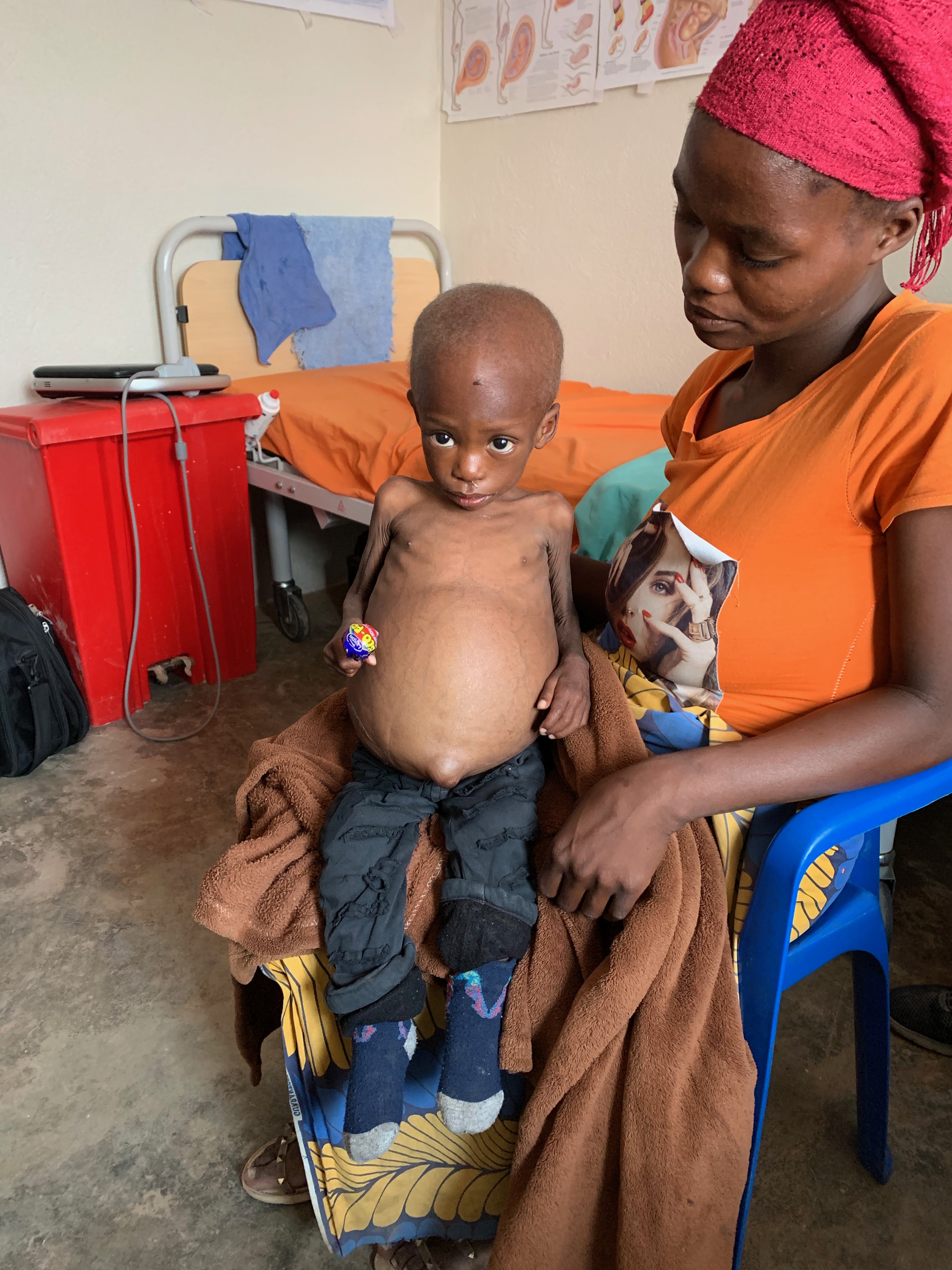 In response to child malnutrition, the Bangladesh, Bangladeshi government recommends ten steps for treating severe malnutrition:
In response to child malnutrition, the Bangladesh, Bangladeshi government recommends ten steps for treating severe malnutrition:
Therapeutic foods
Due in part to limited research on supplementary feeding, there is little evidence that this strategy is beneficial. A 2015 systematic review of 32 studies found that there are limited benefits when children under 5 receive supplementary feeding, especially among younger, poorer, and more undernourished children.
However, specially formulated foods do appear to be useful in treating moderate acute malnutrition in the developing world.
Micronutrient supplementation
According to the World Bank, treating malnutrition - mostly by fortifying foods with micronutrients - improves lives more quickly than other forms of aid, and at a lower cost.diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin w ...
, Zinc deficiency, zinc supplementation is recommended following an initial four-hour rehydration period. Daily zinc supplementation can help reduce the severity and duration of the diarrhea. Additionally, continuing daily zinc supplementation for ten to fourteen days makes diarrhea less likely to recur in the next two to three months.[The Treatment of Diarrhoea: A manual for physicians and other senior health workers](_blank)
World Health Organization, 2005. See especially Ch. 4 "Management of Acute Diarrhoea (Without Blood)" and Ch. 8 "Management of Diarrhoea With Severe Malnutrition."
Malnourished children also need both potassium and magnesium.[National Guidelines for the Management of Severely Malnourished Children in Bangladesh](_blank)
, Institute of Public Health Nutrition, Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh, May 2008, page 18 (19 in PDF) and following pages. Within two to three hours of starting rehydration, children should be encouraged to take food, particularly foods rich in potassium
Treating diarrhea
Preventing dehydration
Food and drink can help prevent dehydration in malnourished people with diarrhea. Eating (or breastfeeding, among infants) should resume as soon as possible.
Oral rehydration therapy
If prevention has failed and dehydration develops, the preferred treatment is rehydration through oral rehydration therapy (ORT). In severely undernourished children with diarrhea, rehydration should be done slowly, according to the World Health Organization.
Oral rehydration solutions consist of clean water mixed with small amounts of sugars and salts. These solutions help restore normal electrolyte levels, provide a source of carbohydrates, and help with fluid replacement.
Reduced-Osmotic concentration, osmolarity ORS is the current standard of care for oral rehydration therapy, with reasonably wide availability. Introduced in 2003 by WHO and UNICEF, reduced-osmolarity solutions contain lower concentrations of sodium and glucose than original ORS preparations. Reduced-osmolarity ORS has the added benefit of reducing stool volume and vomiting while simultaneously preventing dehydration. Packets of reduced-osmolarity ORS include glucose, table salt, potassium chloride, and trisodium citrate. For general use, each packet should be mixed with a liter of water. However, for malnourished children, experts recommend adding a packet of ORS to two liters of water, along with an extra 50 grams of sucrose and some stock potassium solution.
People who have no access to commercially available ORS can make a homemade version using water, sugar, and table salt. Experts agree that homemade ORS preparations should include one Litre, liter (34 Fluid ounce, oz.) of clean water and 6 teaspoons of sugar; however, they disagree about whether they should contain half a teaspoon of table salt or a full teaspoon. Most sources recommend using half a teaspoon of salt per liter of water.[Family Practice Notebook](_blank)
Oral Rehydration Solution, Scott Moses, MD, February 1, 2014. However, people with malnutrition have an excess of body sodium.
Low blood sugar
Hypoglycemia, whether known or suspected, can be treated with a mixture of sugar and water. If the patient is conscious, the initial dose of sugar and water can be given by mouth. Otherwise, they should receive glucose by intravenous or nasogastric tube. If seizures occur (and continue after glucose is given), rectal diazepam may be helpful. Blood sugar levels should be re-checked on two hour intervals.
Hypothermia
Hypothermia (dangerously low Human body temperature, core body temperature) can occur in malnutrition, particularly in children. Mild hypothermia causes confusion trembling, and clumsiness; more severe cases can be fatal. Keeping malnourished children warm can prevent or treat hypothermia. Covering the child (including their head) in blankets is one method. Another method is to warm the child through direct skin-to-skin contact with their mother or father, then covering both parent and child.
Warming methods are usually most important at night.
Epidemiology

 The figures provided in this section on epidemiology all refer to ''undernutrition'' even if the term malnutrition is used which, by definition, could also apply to too much nutrition.
The Global Hunger Index (GHI) is a multidimensional statistical tool used to describe the state of countries' hunger situation. The GHI measures progress and failures in the global fight against hunger.
The figures provided in this section on epidemiology all refer to ''undernutrition'' even if the term malnutrition is used which, by definition, could also apply to too much nutrition.
The Global Hunger Index (GHI) is a multidimensional statistical tool used to describe the state of countries' hunger situation. The GHI measures progress and failures in the global fight against hunger.
People affected
The United Nations estimated that there were 821 million undernourished people in the world in 2017. This is using the UN's definition of 'undernourishment', where it refers to insufficient consumption of raw calories, and so does not necessarily include people who lack micro nutrients.[ The undernourishment occurred despite the world's farmers producing enough food to feed around 12 billion people—almost double the current world population.
Malnutrition, as of 2010, was the cause of 1.4% of all disability adjusted life years.]
Mortality
 Mortality due to malnutrition accounted for 58 percent of the total mortality in 2006: "In the world, approximately 62 million people, all causes of death combined, die each year. One in twelve people worldwide is malnourished and according to the Save the Children 2012 report, one in four of the world's children are chronically malnourished. In 2006, more than 36 million died of hunger or diseases due to deficiencies in micronutrients".
In 2010 protein-energy malnutrition resulted in 600,000 deaths down from 883,000 deaths in 1990.
Mortality due to malnutrition accounted for 58 percent of the total mortality in 2006: "In the world, approximately 62 million people, all causes of death combined, die each year. One in twelve people worldwide is malnourished and according to the Save the Children 2012 report, one in four of the world's children are chronically malnourished. In 2006, more than 36 million died of hunger or diseases due to deficiencies in micronutrients".
In 2010 protein-energy malnutrition resulted in 600,000 deaths down from 883,000 deaths in 1990.iodine deficiency
Iodine deficiency is a lack of the trace element iodine, an essential nutrient in the diet. It may result in metabolic problems such as goiter, sometimes as an endemic goiter as well as congenital iodine deficiency syndrome due to untreated cong ...
and iron deficiency anemia, result in another 84,000 deaths.zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, for example, account for 1 million. Malnutrition in the first two years is irreversible. Malnourished children grow up with worse health and lower education achievement. Their own children tend to be smaller. Malnutrition was previously seen as something that exacerbates the problems of diseases such as measles, pneumonia and diarrhea, but malnutrition actually causes diseases, and can be fatal in its own right.
History
Hunger has been a perennial human problem. However, until the early 20th century, there was relatively little awareness of the qualitative aspects of malnutrition.
Throughout history, various peoples have known the importance of eating certain foods to prevent symptoms now associated with malnutrition. Yet such knowledge appears to have been repeatedly lost and then re-discovered. For example, the ancient Egyptians reportedly knew the symptoms of scurvy
Scurvy is a deficiency disease, disease resulting from a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, feeling tired and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, anemia, decreased red blood cells, gum disease, ch ...
. Much later, in the 14th century, Crusades, Crusaders sometimes used anti-scurvy measures - for example, ensuring that Citrus, citrus fruits were planted on Mediterranean islands, for use on sea journeys. However, for several centuries, Europeans appear to have forgotten the importance of these measures. They rediscovered this knowledge in the 18th century, and by the early 19th century, the Royal Navy was issuing frequent rations of Lemon, lemon juice to every crewman on their ships. This massively reduced scurvy deaths among British sailors, which in turn gave the British a significant advantage in the Napoleonic Wars. Later on in the 19th century, the Royal Navy replaced lemons with limes (unaware at the time that lemons are far more effective at preventing scurvy).
Special populations
Undernutrition is an important determinant of maternal and child health, accounting for more than a third of child deaths and more than 10 percent of the total global disease burden according to 2008 studies.
Children
 Undernutrition adversely affects the cognitive development of children, contributing to poor earning capacity and poverty in adulthood. The development of childhood undernutrition coincides with the introduction of complementary weaning foods which are usually nutrient deficient. The World Health Organization estimates that malnutrition accounts for 54 percent of child mortality worldwide,
Undernutrition adversely affects the cognitive development of children, contributing to poor earning capacity and poverty in adulthood. The development of childhood undernutrition coincides with the introduction of complementary weaning foods which are usually nutrient deficient. The World Health Organization estimates that malnutrition accounts for 54 percent of child mortality worldwide,[Prüss-Üstün, A., Bos, R., Gore, F., Bartram, J. (2008)]
Safer water, better health – Costs, benefits and sustainability of interventions to protect and promote health
World Health Organization (WHO), Geneva, Switzerland Over 90% of the stunted children below five years of age live in sub-Saharan Africa and South Central Asia.
Women

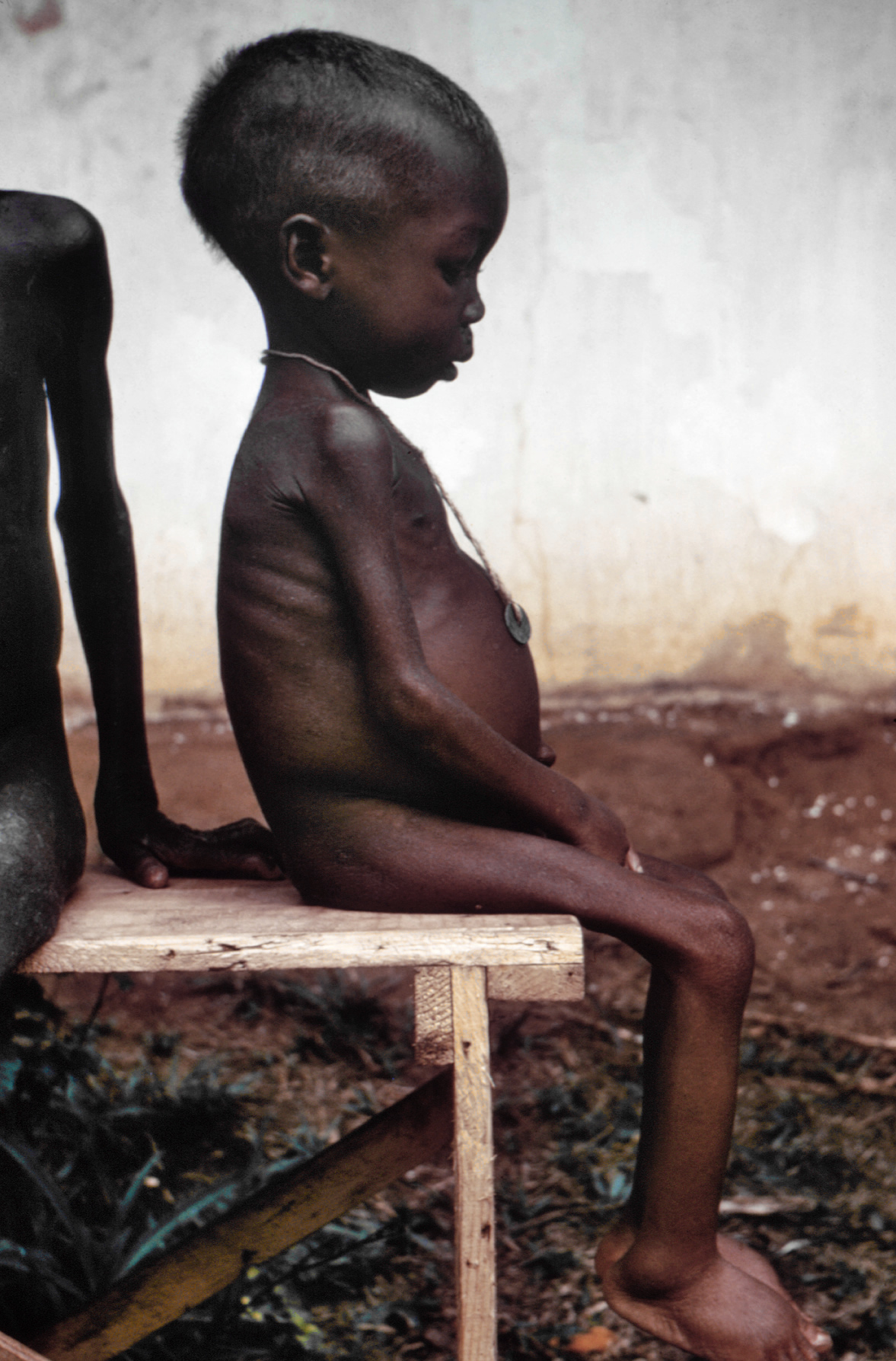 Researchers from the Centre for World Food Studies in 2003 found that the gap between levels of undernutrition in men and women is generally small, but that the gap varies from region to region and from country to country.
Researchers from the Centre for World Food Studies in 2003 found that the gap between levels of undernutrition in men and women is generally small, but that the gap varies from region to region and from country to country.
Physiology
Women have unique nutritional requirements, and in some cases need more nutrients than men; for example, women need twice as much calcium as men.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, women must ingest enough nutrients for themselves and their child, so they need significantly more protein and calories during these periods, as well as more vitamins and minerals (especially iron, iodine, calcium, folic acid, and vitamins A, C, and K).developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
and increased the risk of death during childbirth.
Educating children
"Action for Healthy Kids, Action for healthy kids" has created several methods to teach children about nutrition. They introduce 2 different topics, self-awareness which teaches children about taking care of their own health and social awareness, which is how culinary arts vary from culture to culture. As well as its importance when it comes to nutrition. They include eBooks, tips, cooking clubs. including facts about vegetables and fruits.
Team Nutrition has created "MyPlate, MyPlate eBooks" this includes 8 different eBooks to download for free. These eBooks contain drawings to color, audio narration, and a large number of characters to make nutrition lessons entertaining for children.
According to the FAO, women are often responsible for preparing food and have the chance to educate their children about beneficial food and health habits, giving mothers another chance to improve the nutrition of their children.
Elderly
 Malnutrition and being underweight are more common in the elderly than in adults of other ages.
Malnutrition and being underweight are more common in the elderly than in adults of other ages.
See also
* Action Against Hunger
* ''A Place at the Table''
* Agrobiodiversity
* Child health and nutrition in Africa
* Childhood obesity
* Community Therapeutic Care
* Deficiency (medicine)
* Eating disorder
* Economic issues
* Famine scales
* Fome Zero (Zero Hunger)
* Food Donation Connection
* Homelessness
* Hunger in the United Kingdom
* Hunger in the United States
* Hunger marches
* The Hunger Project
* Income inequality
* Integrated Food Security Phase Classification
* Malnutrition in India
* Malnutrition in South Africa
* Malnutrition in Peru
* Malnutrition in Zimbabwe
* NutritionDay
* Nutrition and Education International
* Muselmann
* National Security Study Memorandum 200 (1974)
* Oxfam
* Poverty trap
* Project Open Hand
* Social programs
* Starvation response
* Sustainable fishery
* United Nations Millennium Declaration
* Vitamin deficiency
References
External links
*
Action Against Hunger , ACF-USA
Action Against Hunger , ACF-UK
Hunger Relief International , HRI
Hunger Relief research on IssueLab
The Global Food Security and Nutrition Forum (FSN Forum)
Ten Things you can do to Fight World Hunger
''The Nation'', May 13, 2009
United Nation 2007 report
World Food Programme , WFP
UN
WFP
{{Authority control
Malnutrition,
Global issues
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
Wikipedia infectious disease articles ready to translate
Health effects of food and nutrition
Limbic system
Motivation
Neuropsychology
Eating behaviors
Hazards of outdoor recreation
 ''Kwashiorkor'' is primarily caused by inadequate protein intake. Its symptoms include
''Kwashiorkor'' is primarily caused by inadequate protein intake. Its symptoms include  Malnutrition weakens every part of the
Malnutrition weakens every part of the  Overnutrition caused by
Overnutrition caused by  Overeating leads to many diseases, such as
Overeating leads to many diseases, such as  Reducing malnutrition is key part of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal 2 (SDG2), "Zero Hunger," which aims to reduce malnutrition, undernutrition, and stunted child growth. Managing severe acute undernutrition in a community setting has received significant research attention.
Reducing malnutrition is key part of the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal 2 (SDG2), "Zero Hunger," which aims to reduce malnutrition, undernutrition, and stunted child growth. Managing severe acute undernutrition in a community setting has received significant research attention.
 Food banks and soup kitchens address malnutrition in places where people lack money to buy food. A basic income has been proposed as a way to ensure that everyone has enough money to buy food and other basic needs. This is a form of social security in which all citizens or residents of a country regularly receive an unconditional sum of money, either from a government or some other public institution, in addition to any income received from elsewhere.
Food banks and soup kitchens address malnutrition in places where people lack money to buy food. A basic income has been proposed as a way to ensure that everyone has enough money to buy food and other basic needs. This is a form of social security in which all citizens or residents of a country regularly receive an unconditional sum of money, either from a government or some other public institution, in addition to any income received from elsewhere.


 In response to child malnutrition, the Bangladesh, Bangladeshi government recommends ten steps for treating severe malnutrition:
# Prevent or treat dehydration
# Prevent or treat low blood sugar
# Prevent or treat hypothermia, low body temperature
# Prevent or treat infection;
# Correct electrolyte imbalances
# Correct micronutrient deficiencies
# Start feeding cautiously
# Achieve catch-up growth
# Provide psychological support
# Prepare for discharge and follow-up after recovery
In response to child malnutrition, the Bangladesh, Bangladeshi government recommends ten steps for treating severe malnutrition:
# Prevent or treat dehydration
# Prevent or treat low blood sugar
# Prevent or treat hypothermia, low body temperature
# Prevent or treat infection;
# Correct electrolyte imbalances
# Correct micronutrient deficiencies
# Start feeding cautiously
# Achieve catch-up growth
# Provide psychological support
# Prepare for discharge and follow-up after recovery
 Undernutrition adversely affects the cognitive development of children, contributing to poor earning capacity and poverty in adulthood. The development of childhood undernutrition coincides with the introduction of complementary weaning foods which are usually nutrient deficient. The World Health Organization estimates that malnutrition accounts for 54 percent of child mortality worldwide, about 1 million children. There is a strong association between undernutrition and child mortality. Another estimate also by WHO states that childhood underweight is the cause for about 35% of all deaths of children under the age of five years worldwide.Prüss-Üstün, A., Bos, R., Gore, F., Bartram, J. (2008)
Undernutrition adversely affects the cognitive development of children, contributing to poor earning capacity and poverty in adulthood. The development of childhood undernutrition coincides with the introduction of complementary weaning foods which are usually nutrient deficient. The World Health Organization estimates that malnutrition accounts for 54 percent of child mortality worldwide, about 1 million children. There is a strong association between undernutrition and child mortality. Another estimate also by WHO states that childhood underweight is the cause for about 35% of all deaths of children under the age of five years worldwide.Prüss-Üstün, A., Bos, R., Gore, F., Bartram, J. (2008)
 Researchers from the Centre for World Food Studies in 2003 found that the gap between levels of undernutrition in men and women is generally small, but that the gap varies from region to region and from country to country. These small-scale studies showed that female undernutrition prevalence rates exceeded male undernutrition prevalence rates in South/Southeast Asia and Latin America and were lower in Sub-Saharan Africa. Datasets for Ethiopia and Zimbabwe reported undernutrition rates between 1.5 and 2 times higher in men than in women; however, in India and Pakistan, datasets rates of undernutrition were 1.5–2 times higher in women than in men. Intra-country variation also occurs, with frequent high gaps between regional undernutrition rates. Gender inequality in nutrition in some countries such as India is present in all stages of life.
Studies on nutrition concerning gender bias within households look at patterns of food allocation, and one study from 2003 suggested that women often receive a lower share of food requirements than men. Gender discrimination, gender roles, and social norms affecting women can lead to early marriage and childbearing, close birth spacing, and undernutrition, all of which contribute to malnourished mothers.
Within the household, there may be differences in levels of malnutrition between men and women, and these differences have been shown to vary significantly from one region to another, with problem areas showing relative deprivation of women. Samples of 1000 women in India in 2008 demonstrated that malnutrition in women is associated with poverty, lack of development and awareness, and illiteracy. The same study showed that gender discrimination in households can prevent a woman's access to sufficient food and healthcare. How socialization affects the health of women in Bangladesh, Najma Rivzi explains in an article about a research program on this topic. In some cases, such as in parts of Kenya in 2006, rates of malnutrition in pregnant women were even higher than rates in children.
Women in some societies are traditionally given less food than men since men are perceived to have heavier workloads. Household chores and agricultural tasks can in fact be very arduous and require additional energy and nutrients; however, physical activity, which largely determines energy requirements, is difficult to estimate.
Researchers from the Centre for World Food Studies in 2003 found that the gap between levels of undernutrition in men and women is generally small, but that the gap varies from region to region and from country to country. These small-scale studies showed that female undernutrition prevalence rates exceeded male undernutrition prevalence rates in South/Southeast Asia and Latin America and were lower in Sub-Saharan Africa. Datasets for Ethiopia and Zimbabwe reported undernutrition rates between 1.5 and 2 times higher in men than in women; however, in India and Pakistan, datasets rates of undernutrition were 1.5–2 times higher in women than in men. Intra-country variation also occurs, with frequent high gaps between regional undernutrition rates. Gender inequality in nutrition in some countries such as India is present in all stages of life.
Studies on nutrition concerning gender bias within households look at patterns of food allocation, and one study from 2003 suggested that women often receive a lower share of food requirements than men. Gender discrimination, gender roles, and social norms affecting women can lead to early marriage and childbearing, close birth spacing, and undernutrition, all of which contribute to malnourished mothers.
Within the household, there may be differences in levels of malnutrition between men and women, and these differences have been shown to vary significantly from one region to another, with problem areas showing relative deprivation of women. Samples of 1000 women in India in 2008 demonstrated that malnutrition in women is associated with poverty, lack of development and awareness, and illiteracy. The same study showed that gender discrimination in households can prevent a woman's access to sufficient food and healthcare. How socialization affects the health of women in Bangladesh, Najma Rivzi explains in an article about a research program on this topic. In some cases, such as in parts of Kenya in 2006, rates of malnutrition in pregnant women were even higher than rates in children.
Women in some societies are traditionally given less food than men since men are perceived to have heavier workloads. Household chores and agricultural tasks can in fact be very arduous and require additional energy and nutrients; however, physical activity, which largely determines energy requirements, is difficult to estimate.