Nuclear War on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
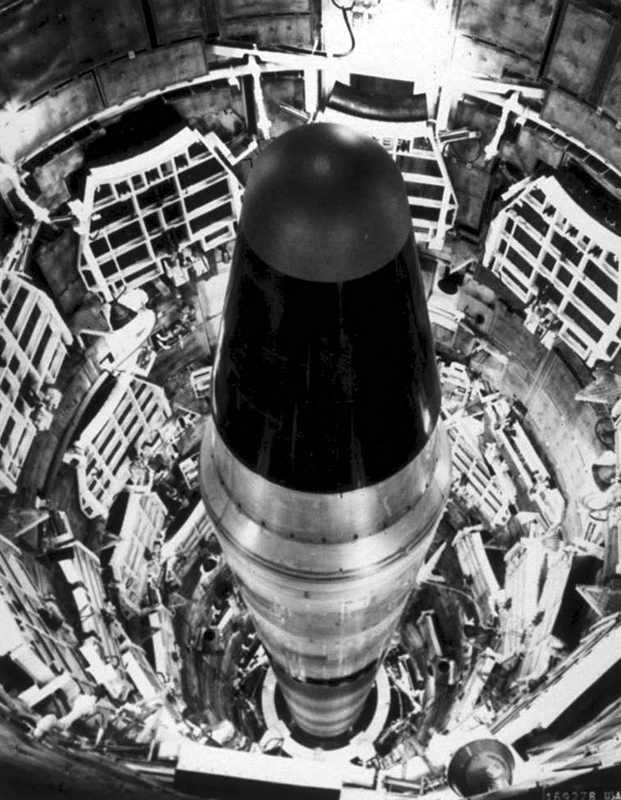 Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a theoretical
Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a theoretical
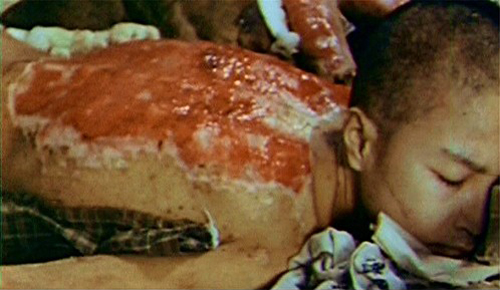 On August 6, 1945, the uranium-type nuclear weapon codenamed "
On August 6, 1945, the uranium-type nuclear weapon codenamed "
. TIME. September 20, 1976. The concept of a "
The concept of a "
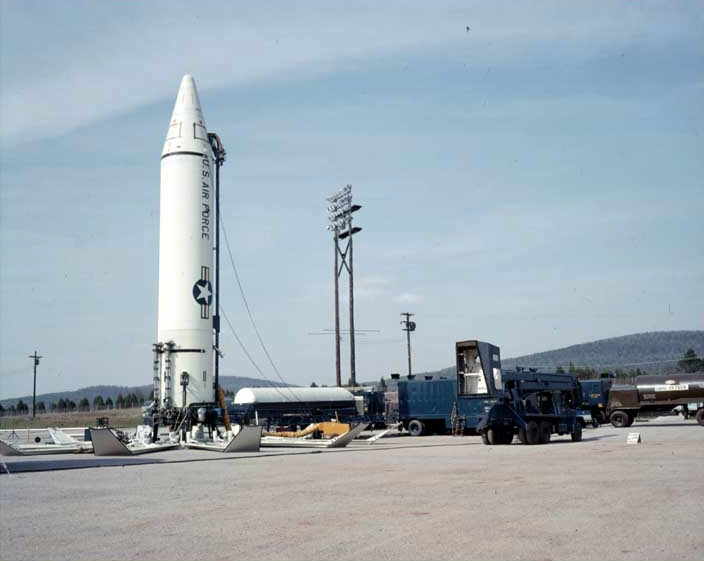 In 1960, the United States developed its first Single Integrated Operational Plan, a range of targeting options, and described launch procedures and target sets against which nuclear weapons would be launched, variants of which were in use from 1961 to 2003. That year also saw the start of the Missile Defense Alarm System, an American system of 12 early-warning satellites that provided limited notice of Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile launches between 1960 and 1966. The Ballistic Missile Early Warning System was completed in 1964.
The most powerful atomic bomb ever made, the Tsar Bomba, was tested by the Soviets on October 30, 1961. It was 50 megatons, or equal to 50 million tons of regular explosives. A complex and worrisome situation developed in 1962, in what is called the Cuban Missile Crisis. The Soviet Union placed medium-range ballistic missiles from the United States, possibly as a direct response to American Jupiter missiles placed in Turkey. After intense negotiations, the Soviets ended up removing the missiles from Cuba and decided to institute a massive weapons-building program of their own. In exchange, the United States dismantled its launch sites in Turkey, although this was done secretly and not publicly revealed for over two decades. First Secretary Nikita Khrushchev did not even reveal this part of the agreement when he came under fire by political opponents for mishandling the crisis. Communication delays during the crisis led to the establishment of the Moscow–Washington hotline to allow reliable, direct communications between the two nuclear powers.
By the late 1960s, the number of ICBMs and warheads was so high on both sides that it was believed that both the United States and the Soviet Union were capable of completely destroying the infrastructure and a large proportion of the population of the other country. Thus, by some western game theorists, a balance of power in international relations, balance of power system known as
In 1960, the United States developed its first Single Integrated Operational Plan, a range of targeting options, and described launch procedures and target sets against which nuclear weapons would be launched, variants of which were in use from 1961 to 2003. That year also saw the start of the Missile Defense Alarm System, an American system of 12 early-warning satellites that provided limited notice of Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile launches between 1960 and 1966. The Ballistic Missile Early Warning System was completed in 1964.
The most powerful atomic bomb ever made, the Tsar Bomba, was tested by the Soviets on October 30, 1961. It was 50 megatons, or equal to 50 million tons of regular explosives. A complex and worrisome situation developed in 1962, in what is called the Cuban Missile Crisis. The Soviet Union placed medium-range ballistic missiles from the United States, possibly as a direct response to American Jupiter missiles placed in Turkey. After intense negotiations, the Soviets ended up removing the missiles from Cuba and decided to institute a massive weapons-building program of their own. In exchange, the United States dismantled its launch sites in Turkey, although this was done secretly and not publicly revealed for over two decades. First Secretary Nikita Khrushchev did not even reveal this part of the agreement when he came under fire by political opponents for mishandling the crisis. Communication delays during the crisis led to the establishment of the Moscow–Washington hotline to allow reliable, direct communications between the two nuclear powers.
By the late 1960s, the number of ICBMs and warheads was so high on both sides that it was believed that both the United States and the Soviet Union were capable of completely destroying the infrastructure and a large proportion of the population of the other country. Thus, by some western game theorists, a balance of power in international relations, balance of power system known as
 In the late 1970s and, particularly, during the early 1980s under U.S. President Ronald Reagan, the United States renewed its commitment to a more powerful military, which required a large increase in spending on U.S. military programs. These programs, which were originally part of the defense budget of U.S. President Jimmy Carter, included spending on conventional and nuclear weapons systems. Under Reagan, defensive systems like the Strategic Defense Initiative were emphasized as well.
Another major shift in nuclear doctrine was the development and the improvement of the submarine-launched, nuclear-armed, ballistic missile, or Submarine-launched ballistic missile, SLBM. It was hailed by many military theorists as a weapon that would make nuclear war less likely. SLBMs—which can move with "stealth" (greatly lessened detectability) virtually anywhere in the world—give a nation a "second strike" capability (i.e., after absorbing a "first strike"). Before the advent of the SLBM, thinkers feared that a nation might be tempted to initiate a first strike if it felt confident that such a strike would incapacitate the nuclear arsenal of its enemy, making retaliation impossible. With the advent of SLBMs, no nation could be certain that a first strike would incapacitate its enemy's entire nuclear arsenal. To the contrary, it would have to fear a near-certain retaliatory second strike from SLBMs. Thus, a first strike was a much less feasible (or desirable) option, and a deliberately initiated nuclear war was thought to be less likely to start.
However, it was soon realized that submarines could approach enemy coastlines undetected and decrease the warning time (the time between detection of the missile launch and the impact of the missile) from as much as half an hour to possibly under three minutes. This effect was especially significant to the United States, Britain and China, whose capitals of Washington, D.C., Washington D.C., London, and Beijing all lay within 100 miles (160 km) of their coasts. Moscow was much more secure from this type of threat, due to its considerable distance from the sea. This greatly increased the credibility of a "surprise first strike" by one faction and (theoretically) made it possible to knock out or disrupt the chain of command of a target nation before any counterstrike could be ordered (known as a "decapitation strike"). It strengthened the notion that a nuclear war could possibly be "won", resulting not only in greatly increased tensions and increasing calls for fail-deadly control systems, but also in a dramatic increase in military spending. The submarines and their missile systems were very expensive, and one fully equipped nuclear-powered and nuclear-armed missile submarine could cost more than the entire Measures of national income and output#Gross National Product, GNP of a developing country. It was also calculated, however, that the greatest cost came in the development of ''both'' sea- and land-based anti-submarine defenses and in improving and strengthening the "chain of command", and as a result, military spending skyrocketed.
In the late 1970s and, particularly, during the early 1980s under U.S. President Ronald Reagan, the United States renewed its commitment to a more powerful military, which required a large increase in spending on U.S. military programs. These programs, which were originally part of the defense budget of U.S. President Jimmy Carter, included spending on conventional and nuclear weapons systems. Under Reagan, defensive systems like the Strategic Defense Initiative were emphasized as well.
Another major shift in nuclear doctrine was the development and the improvement of the submarine-launched, nuclear-armed, ballistic missile, or Submarine-launched ballistic missile, SLBM. It was hailed by many military theorists as a weapon that would make nuclear war less likely. SLBMs—which can move with "stealth" (greatly lessened detectability) virtually anywhere in the world—give a nation a "second strike" capability (i.e., after absorbing a "first strike"). Before the advent of the SLBM, thinkers feared that a nation might be tempted to initiate a first strike if it felt confident that such a strike would incapacitate the nuclear arsenal of its enemy, making retaliation impossible. With the advent of SLBMs, no nation could be certain that a first strike would incapacitate its enemy's entire nuclear arsenal. To the contrary, it would have to fear a near-certain retaliatory second strike from SLBMs. Thus, a first strike was a much less feasible (or desirable) option, and a deliberately initiated nuclear war was thought to be less likely to start.
However, it was soon realized that submarines could approach enemy coastlines undetected and decrease the warning time (the time between detection of the missile launch and the impact of the missile) from as much as half an hour to possibly under three minutes. This effect was especially significant to the United States, Britain and China, whose capitals of Washington, D.C., Washington D.C., London, and Beijing all lay within 100 miles (160 km) of their coasts. Moscow was much more secure from this type of threat, due to its considerable distance from the sea. This greatly increased the credibility of a "surprise first strike" by one faction and (theoretically) made it possible to knock out or disrupt the chain of command of a target nation before any counterstrike could be ordered (known as a "decapitation strike"). It strengthened the notion that a nuclear war could possibly be "won", resulting not only in greatly increased tensions and increasing calls for fail-deadly control systems, but also in a dramatic increase in military spending. The submarines and their missile systems were very expensive, and one fully equipped nuclear-powered and nuclear-armed missile submarine could cost more than the entire Measures of national income and output#Gross National Product, GNP of a developing country. It was also calculated, however, that the greatest cost came in the development of ''both'' sea- and land-based anti-submarine defenses and in improving and strengthening the "chain of command", and as a result, military spending skyrocketed.
 As a consequence of the September 11 attacks, American forces immediately increased their readiness to the highest level in 28 years, closing the blast doors of the NORAD's Cheyenne Mountain Complex, Cheyenne Mountain Operations Center for the first time due to a non-exercise event. But unlike similar increases during the Cold War, Russia immediately decided to stand down a large military exercise in the Arctic region, in order to minimize the risk of incidents, rather than following suit.
The former chair of the
As a consequence of the September 11 attacks, American forces immediately increased their readiness to the highest level in 28 years, closing the blast doors of the NORAD's Cheyenne Mountain Complex, Cheyenne Mountain Operations Center for the first time due to a non-exercise event. But unlike similar increases during the Cold War, Russia immediately decided to stand down a large military exercise in the Arctic region, in order to minimize the risk of incidents, rather than following suit.
The former chair of the  Another potential geopolitical issue that is considered particularly worrisome by military analysts is a possible conflict between the
Another potential geopolitical issue that is considered particularly worrisome by military analysts is a possible conflict between the
by Morten Bremer Mærli, Bellona Foundation
"Possibility of Nuclear War in Asia: An Indian Perspective"
a project of United Service Institution of India, USI, Discusses the possibility of a nuclear war in Asia from the
"Presidency in the Nuclear Age"
conference and forum at the John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum, JFK Library, Boston, October 12, 2009. Four panels: "The Race to Build the Bomb and the Decision to Use It", "Cuban Missile Crisis and the First Nuclear Test Ban Treaty", "The Cold War and the Nuclear Arms Race", and "Nuclear Weapons, Terrorism, and the Presidency". * Tom Stevenson, "A Tiny Sun" (review of Fred Kaplan (journalist), Fred Kaplan, ''The Bomb: Presidents, Generals, and the Secret History of Nuclear War'', Simon and Schuster, 2021, 384 pp.; and Keir A. Lieber and Daryl G. Press, ''The Myth of the Nuclear Revolution: Power Politics in the Atomic Age'', Cornell, 2020, 180 pp.), ''London Review of Books'', vol. 44, no. 4 (24 February 2022), pp. 29–32. "Nuclear strategists systematically underestimate the chances of nuclear accident... [T]here have been too many close calls for accidental use to be discounted." (p. 32.)
Fallout: After a Nuclear Attack
– slideshow by ''Life magazine'' *
The Effects of Nuclear War
'' (1979) — handbook produced by the United States Office of Technology Assessment (hosted by the Federation of American Scientists) *
Nuclear Attack Planning Base – 1990
' (1987) — assessment of the effects of a major Soviet attack on the United States produced by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (hosted by the Federation of American Scientists) *
Nuclear War Survival Skills
' (1979/1987) — handbook produced by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (use menu at left to navigate)
Ground Zero: A Javascript simulation of the effects of a nuclear explosion in a city
British RAF manual on the effects of nuclear explosions dated 1955
by Alan F. Philips, M.D.
Interactive Timeline of the Nuclear Age
Annotated bibliography on nuclear warfare from the Alsos Digital Library for Nuclear Issues
* DeVolpi, Alexander, Vladimir E. Minkov, Vadim A. Simonenko, and George S. Stanford. 2004. ''Nuclear Shadowboxing: Contemporary Threats from Cold War Weaponry'', Vols. 1 and 2. Fidlar Doubleday.
An in depth history of American air weapons and nuclear bombs from the reference book ''American Combat Planes of the 20th Century'' by Ray Wagner
NUKEMAP3D
– a 3D nuclear weapons effects simulator powered by Google Maps. {{DEFAULTSORT:Nuclear Warfare Nuclear warfare, Nuclear weapons, Warfare
 Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a theoretical
Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a theoretical military conflict
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regu ...
or prepared political strategy that deploys nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
ry. Nuclear weapons are weapons of mass destruction
A weapon of mass destruction (WMD) is a chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear, or any other weapon that can kill and bring significant harm to numerous individuals or cause great damage to artificial structures (e.g., buildings), natu ...
; in contrast to conventional warfare
Conventional warfare is a form of warfare conducted by using conventional weapons and battlefield tactics between two or more states in open confrontation. The forces on each side are well-defined and fight by using weapons that target primari ...
, nuclear warfare can produce destruction in a much shorter time and can have a long-lasting radiological
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'', such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visib ...
result. A major nuclear exchange would likely have long-term effects, primarily from the fallout
Nuclear fallout is the residual radioactive material propelled into the upper atmosphere following a nuclear blast, so called because it "falls out" of the sky after the explosion and the shock wave has passed. It commonly refers to the radioac ...
released, and could also lead to secondary effects, such as "nuclear winter
Nuclear winter is a severe and prolonged global climatic cooling effect that is hypothesized to occur after widespread firestorms following a large-scale nuclear war. The hypothesis is based on the fact that such fires can inject soot into t ...
", nuclear famine
Nuclear famine is a hypothesized famine considered a potential threat following global or regional nuclear exchange. It is thought that even subtle cooling effects resulting from a regional nuclear exchange could have a substantial impact on agri ...
and societal collapse
Societal collapse (also known as civilizational collapse) is the fall of a complex human society characterized by the loss of cultural identity and of socioeconomic complexity, the downfall of government, and the rise of violence. Possible cause ...
. A global thermonuclear war with Cold War-era stockpiles, or even with the current smaller stockpiles, may lead to various scenarios including the extinction of the human race.
To date, the only use of nuclear weapons in armed conflict occurred in 1945 with the American atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
The United States detonated two atomic bombs over the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki on 6 and 9 August 1945, respectively. The two bombings killed between 129,000 and 226,000 people, most of whom were civilians, and remain the onl ...
. On August 6, 1945, a uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
gun-type device (code name "Little Boy
"Little Boy" was the type of atomic bomb dropped on the Japanese city of Hiroshima on 6 August 1945 during World War II, making it the first nuclear weapon used in warfare. The bomb was dropped by the Boeing B-29 Superfortress ''Enola Gay'' p ...
") was detonated over the Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
ese city of Hiroshima
is the capital of Hiroshima Prefecture in Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 1,199,391. The gross domestic product (GDP) in Greater Hiroshima, Hiroshima Urban Employment Area, was US$61.3 billion as of 2010. Kazumi Matsui ...
. Three days later, on August 9, a plutonium
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exh ...
implosion-type device (code name "Fat Man
"Fat Man" (also known as Mark III) is the codename for the type of nuclear bomb the United States detonated over the Japanese city of Nagasaki on 9 August 1945. It was the second of the only two nuclear weapons ever used in warfare, the fir ...
") was detonated over the Japanese city of Nagasaki
is the capital and the largest city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan.
It became the sole port used for trade with the Portuguese and Dutch during the 16th through 19th centuries. The Hidden Christian Sites in the ...
. Together, these two bombings resulted in the deaths of approximately 200,000 people and contributed to the surrender of Japan
The surrender of the Empire of Japan in World War II was announced by Emperor Hirohito on 15 August and formally signed on 2 September 1945, bringing the war's hostilities to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Na ...
, which occurred without any further use of nuclear weapons in the conflict.
After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, nuclear weapons were also developed by the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
(1949), the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
(1952), France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
(1960), and the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
(1964), which contributed to the state of conflict and extreme tension that became known as the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
. In 1974, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, and in 1998, Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
, two countries that were openly hostile toward each other, developed nuclear weapons. Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
(1960s) and North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and T ...
(2006) are also thought to have developed stocks of nuclear weapons, though it is not known how many. The Israeli government has never admitted nor denied having nuclear weapons, although it is known to have constructed the reactor and reprocessing plant necessary for building nuclear weapons. South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
also manufactured several complete nuclear weapons in the 1980s, but subsequently became the first country to voluntarily destroy their domestically made weapons stocks and abandon further production (1990s). Nuclear weapons have been detonated on over 2,000 occasions for testing purposes and demonstrations.
After the dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
in 1991 and the resultant end of the Cold War, the threat of a major nuclear war between the two nuclear superpowers was generally thought to have declined. Since then, concern over nuclear weapons has shifted to the prevention of localized nuclear conflicts resulting from nuclear proliferation
Nuclear proliferation is the spread of nuclear weapons, fissionable material, and weapons-applicable nuclear technology and information to nations not recognized as " Nuclear Weapon States" by the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Wea ...
, and the threat of nuclear terrorism
Nuclear terrorism refers to any person or persons detonating a nuclear weapon as an act of terrorism (i.e., illegal or immoral use of violence for a political or religious cause). Some definitions of nuclear terrorism include the sabotage of a ...
. However, the threat of nuclear war is considered to have resurged after the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. A ...
, particularly with regard to Russian threats to use nuclear weapons during the invasion.
Since 1947, the Doomsday Clock
The Doomsday Clock is a symbol that represents the likelihood of a man-made global catastrophe, in the opinion of the members of the ''Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists''. Maintained since 1947, the clock is a metaphor for threats to humanity ...
of the ''Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists
The ''Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists'' is a nonprofit organization concerning science and global security issues resulting from accelerating technological advances that have negative consequences for humanity. The ''Bulletin'' publishes conte ...
'' has visualized how close the world is to a nuclear war. The Doomsday Clock reached high points in 1953, when the Clock was set to two minutes until midnight after the U.S. and the Soviet Union began testing hydrogen bombs, and in 2018, following the failure of world leaders to address tensions relating to nuclear weapons and climate change issues. Since 2020, the Clock has been set at 100 seconds to midnight, the closest it's ever been. The most recent advance of the Clock's time setting was justified by the perceived increased danger of both nuclear warfare and climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
, intensified by government disinformation
Disinformation is false information deliberately spread to deceive people. It is sometimes confused with misinformation, which is false information but is not deliberate.
The English word ''disinformation'' comes from the application of the ...
campaigns and other information warfare
Information warfare (IW) (as different from cyber warfare that attacks computers, software, and command control systems) is a concept involving the battlespace use and management of information and communication technology (ICT) in pursuit of a ...
.
Types of nuclear warfare
The possibility of using nuclear weapons in war is usually divided into two subgroups, each with different effects and potentially fought with different types of nuclear armaments. The first, a limited nuclear war (sometimes ''attack'' or ''exchange''), refers to the controlled use of nuclear weapons, whereby the implicit threat exists that a nations can still escalate their use of nuclear weapons. For example, using a small number of nuclear weapons against strictly military targets could be escalated through increasing the number of weapons used, or escalated through the selection of different targets. Limited attacks are thought to be a more credible response against attacks that do not justify all-out retaliation, such as an enemy's limited use of nuclear weapons. The second, a full-scale nuclear war, could consist of large numbers of nuclear weapons used in an attack aimed at an entire country, including military, economic, and civilian targets. Such an attack would almost certainly destroy the entire economic, social, and military infrastructure of the target nation, and would likely have a devastating effect on Earth's biosphere. SomeCold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
strategists such as Henry Kissinger
Henry Alfred Kissinger (; ; born Heinz Alfred Kissinger, May 27, 1923) is a German-born American politician, diplomat, and geopolitical consultant who served as United States Secretary of State and National Security Advisor under the presid ...
argued that a limited nuclear war could be possible between two heavily armed superpowers (such as the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
). Some predict, however, that a limited war could potentially " escalate" into a full-scale nuclear war. Others have called limited nuclear war "global nuclear holocaust in slow motion", arguing that—once such a war took place—others would be sure to follow over a period of decades, effectively rendering the planet uninhabitable in the same way that a "full-scale nuclear war" between superpowers would, only taking a much longer (and arguably more agonizing) path to the same result.
Even the most optimistic predictions of the effects of a major nuclear exchange foresee the death of many millions of victims within a very short period of time. Such predictions usually include the breakdown of institutions, government, professional and commercial, vital to the continuation of civilization. The resulting loss of vital affordances (food, water and electricity production and distribution, medical and information services, etc.) would account for millions more deaths. More pessimistic predictions argue that a full-scale nuclear war could potentially bring about the extinction of the human race, or at least its ''near'' extinction, with only a relatively small number of survivors (mainly in remote areas) and a reduced quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
and life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
for centuries afterward. However, such predictions, assuming total war
Total war is a type of warfare that includes any and all civilian-associated resources and infrastructure as legitimate military targets, mobilizes all of the resources of society to fight the war, and gives priority to warfare over non-com ...
with nuclear arsenals at Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
highs, have not been without criticism. Such a horrific catastrophe as global nuclear warfare would almost certainly cause permanent damage to most complex life on the planet, its ecosystems, and the global climate.
A study presented at the annual meeting of the American Geophysical Union
The American Geophysical Union (AGU) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization of Earth, atmospheric, ocean, hydrologic, space, and planetary scientists and enthusiasts that according to their website includes 130,000 people (not members). AGU's ...
in December 2006 asserted that even a small-scale regional nuclear war could produce as many direct fatalities as all of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
and disrupt the global climate for a decade or more. In a regional nuclear conflict scenario in which two opposing nations in the subtropics
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° nort ...
each used 50 Hiroshima-sized nuclear weapons (c. 15 kiloton each) on major population centers, the researchers predicted fatalities ranging from 2.6 million to 16.7 million per country. The authors of the study estimated that as much as five million tons of soot
Soot ( ) is a mass of impure carbon particles resulting from the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons. It is more properly restricted to the product of the gas-phase combustion process but is commonly extended to include the residual pyrolysed ...
could be released, producing a cooling of several degrees over large areas of North America and Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
(including most of the grain-growing regions). The cooling would last for years and could be "catastrophic", according to the researchers.
Either a limited or full-scale nuclear exchange could occur during an ''accidental nuclear war'', in which the use of nuclear weapons is triggered unintentionally. Postulated triggers for this scenario have included malfunctioning early warning devices and/or targeting computers, deliberate malfeasance by rogue military commanders, consequences of an accidental straying of warplanes into enemy airspace, reactions to unannounced missile tests during tense diplomatic periods, reactions to military exercises, mistranslated or miscommunicated messages, and others.
A number of these scenarios actually occurred during the Cold War, though none resulted in the use of nuclear weapons. Many such scenarios have been depicted in popular culture
Popular culture (also called mass culture or pop culture) is generally recognized by members of a society as a set of practices, beliefs, artistic output (also known as, popular art or mass art) and objects that are dominant or prevalent in a ...
, such as in the 1959 film '' On the Beach'', the 1962 novel ''Fail-Safe
In engineering, a fail-safe is a design feature or practice that in the event of a specific type of failure, inherently responds in a way that will cause minimal or no harm to other equipment, to the environment or to people. Unlike inherent safe ...
'' (released as a film in 1964); the film '' Dr. Strangelove or: How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Love the Bomb'', also released in 1964; the film ''WarGames
''WarGames'' is a 1983 American science fiction techno-thriller film written by Lawrence Lasker and Walter F. Parkes and directed by John Badham. The film, which stars Matthew Broderick, Dabney Coleman, John Wood, and Ally Sheedy, follow ...
'', released in 1983.
History
1940s
Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
During the final stages ofWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
in 1945, the United States conducted atomic raids on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima
is the capital of Hiroshima Prefecture in Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 1,199,391. The gross domestic product (GDP) in Greater Hiroshima, Hiroshima Urban Employment Area, was US$61.3 billion as of 2010. Kazumi Matsui ...
and Nagasaki
is the capital and the largest city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan.
It became the sole port used for trade with the Portuguese and Dutch during the 16th through 19th centuries. The Hidden Christian Sites in the ...
, the first on August 6, 1945, and the second on August 9, 1945. These two events were the only times nuclear weapons have been used in combat
Combat (French for ''fight'') is a purposeful violent conflict meant to physically harm or kill the opposition. Combat may be armed (using weapons) or unarmed ( not using weapons). Combat is sometimes resorted to as a method of self-defense, or ...
.
For six months before the atomic bombings, the U.S. 20th Air Force
The Twentieth Air Force (Air Forces Strategic) (20th AF) is a numbered air force of the United States Air Force Global Strike Command (AFGSC). It is headquartered at Francis E. Warren Air Force Base, Wyoming.
20 AF's primary mission is Interco ...
under General
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". O ...
Curtis LeMay
Curtis Emerson LeMay (November 15, 1906 – October 1, 1990) was an American Air Force general who implemented a controversial strategic bombing campaign in the Pacific theater of World War II. He later served as Chief of Staff of the U.S. Air ...
executed low-level incendiary raids against Japanese cities. The worst air raid to occur during the process was not the nuclear attacks, but the ''Operation Meetinghouse'' raid on Tokyo. On the night of March 9–10, 1945, ''Operation Meetinghouse'' commenced and 334 Boeing B-29 Superfortress
The Boeing B-29 Superfortress is an American four-engined propeller-driven heavy bomber, designed by Boeing and flown primarily by the United States during World War II and the Korean War. Named in allusion to its predecessor, the B-17 Fl ...
bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped from an air ...
s took off to raid, with 279 of them dropping 1,665 tons of incendiaries
Incendiary weapons, incendiary devices, incendiary munitions, or incendiary bombs are weapons designed to start fires or destroy sensitive equipment using fire (and sometimes used as anti-personnel weaponry), that use materials such as napalm, th ...
and explosive
An explosive (or explosive material) is a reactive substance that contains a great amount of potential energy that can produce an explosion if released suddenly, usually accompanied by the production of light, heat, sound, and pressure. An expl ...
s on Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.46 ...
. The bombing was meant to burn wooden buildings and indeed the bombing caused fire that created a 50 m/s wind, which is comparable to tornadoes. Each bomber carried 6 tons of bombs. A total of 381,300 bombs, which amount to 1,783 tons of bombs, were used in the bombing. Within a few hours of the raid, it had killed an estimated 100,000 people and destroyed of the city and 267,000 buildings in a single night — the deadliest bombing raid in military aviation
Military aviation comprises military aircraft and other flying machines for the purposes of conducting or enabling aerial warfare, including national airlift ( air cargo) capacity to provide logistical supply to forces stationed in a war thea ...
history other than the atomic raids on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. By early August 1945, an estimated 450,000 people had died as the U.S. had intensely firebombed a total of 67 Japanese cities.
In late June 1945, as the U.S. wrapped up the two-and-a-half-month Battle of Okinawa
The , codenamed Operation Iceberg, was a major battle of the Pacific War fought on the island of Okinawa by United States Army (USA) and United States Marine Corps (USMC) forces against the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA). The initial invasion of ...
(which cost the lives of 260,000 people, including 150,000 civilians), it was faced with the prospect of invading the Japanese home islands
The Japanese archipelago (Japanese: 日本列島, ''Nihon rettō'') is a group of 6,852 islands that form the country of Japan, as well as the Russian island of Sakhalin. It extends over from the Sea of Okhotsk in the northeast to the East Chin ...
in an operation codenamed Operation Downfall
Operation Downfall was the proposed Allied plan for the invasion of the Japanese home islands near the end of World War II. The planned operation was canceled when Japan surrendered following the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, ...
. Based on the U.S. casualties from the preceding island-hopping campaigns, American commanders estimated that between 50,000 and 500,000 U.S. troops would die and at least 600,000–1,000,000 others would be injured while invading the Japanese home islands. The U.S. manufacture of 500,000 Purple Heart
The Purple Heart (PH) is a United States military decoration awarded in the name of the President to those wounded or killed while serving, on or after 5 April 1917, with the U.S. military. With its forerunner, the Badge of Military Merit, ...
s from the anticipated high level of casualties during the U.S. invasion of Japan gave a demonstration of how deadly and costly it would be. President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ...
Harry S. Truman realized he could not afford such a horrendous casualty rate, especially since over 400,000 American combatants had already died fighting in both the European and the Pacific theaters of the war.
On July 26, 1945, the United States, the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, and the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeas ...
issued a Potsdam Declaration
The Potsdam Declaration, or the Proclamation Defining Terms for Japanese Surrender, was a statement that called for the surrender of all Japanese armed forces during World War II. On July 26, 1945, United States President Harry S. Truman, Uni ...
that called for the unconditional surrender
An unconditional surrender is a surrender in which no guarantees are given to the surrendering party. It is often demanded with the threat of complete destruction, extermination or annihilation.
In modern times, unconditional surrenders most ofte ...
of Japan. It stated that if Japan did not surrender, it would face "prompt and utter destruction". The Japanese government ignored this ultimatum, sending a message that they were not going to surrender. In response to the rejection, President Truman authorized the dropping of the atomic bombs. At the time of its use, there were only two atomic bombs available, and despite the fact that more were in production back in mainland U.S., the third bomb wouldn't be available for combat until September.
 On August 6, 1945, the uranium-type nuclear weapon codenamed "
On August 6, 1945, the uranium-type nuclear weapon codenamed "Little Boy
"Little Boy" was the type of atomic bomb dropped on the Japanese city of Hiroshima on 6 August 1945 during World War II, making it the first nuclear weapon used in warfare. The bomb was dropped by the Boeing B-29 Superfortress ''Enola Gay'' p ...
" was detonated over the Japanese city of Hiroshima
is the capital of Hiroshima Prefecture in Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 1,199,391. The gross domestic product (GDP) in Greater Hiroshima, Hiroshima Urban Employment Area, was US$61.3 billion as of 2010. Kazumi Matsui ...
with an energy of about , destroying nearly 50,000 buildings (including the headquarters
Headquarters (commonly referred to as HQ) denotes the location where most, if not all, of the important functions of an organization are coordinated. In the United States, the corporate headquarters represents the entity at the center or the to ...
of the 2nd General Army and Fifth Division) and killing approximately 70,000 people, including 20,000 Japanese combatants and 20,000 Korean slave laborers.Adams, S. & Crawford, A.. 2000. ''World War II.'' First edition. Printed in association with the Imperial War Museum. Eyewitness Books series. New York, Doring Kindersley Limited Three days later, on August 9, a plutonium-type nuclear weapon codenamed "Fat Man
"Fat Man" (also known as Mark III) is the codename for the type of nuclear bomb the United States detonated over the Japanese city of Nagasaki on 9 August 1945. It was the second of the only two nuclear weapons ever used in warfare, the fir ...
" was used against the Japanese city of Nagasaki, with the explosion equivalent to about , destroying 60% of the city and killing approximately 35,000 people, including 23,200–28,200 Japanese munitions workers, 2,000 Korean slave laborers, and 150 Japanese combatants. The industrial damage in Nagasaki was high, partly owing to the inadvertent targeting of the industrial zone, leaving 68–80 percent of the non-dock industrial production destroyed.
Six days after the detonation over Nagasaki, Japan announced its surrender to the Allied Powers on August 15, 1945, signing the Instrument of Surrender on September 2, 1945, officially ending the Pacific War
The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War, was the theater of World War II that was fought in Asia, the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and Oceania. It was geographically the largest theater of the war, including the vas ...
and, therefore, World War II, as Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
had already signed its Instrument of Surrender on May 8, 1945, ending the war in Europe. The two atomic bombings led, in part, to post-war Japan's adopting of the Three Non-Nuclear Principles, which forbade the nation from developing nuclear armaments.
Immediately after the Japan bombings
After the successful Trinity nuclear test July 16, 1945, which was the very first nuclear detonation, theManhattan project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
lead manager J. Robert Oppenheimer
J. Robert Oppenheimer (; April 22, 1904 – February 18, 1967) was an American theoretical physicist. A professor of physics at the University of California, Berkeley, Oppenheimer was the wartime head of the Los Alamos Laboratory and is oft ...
recalled:
Immediately after the atomic bombings of Japan, the status of atomic weapons in international and military relations was unclear. Presumably, the United States hoped atomic weapons could offset the Soviet Union's larger conventional ground forces in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whi ...
, and possibly be used to pressure Soviet leader Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet Union, Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as Ge ...
into making concessions. Under Stalin, the Soviet Union pursued its own atomic capabilities through a combination of scientific research and espionage
Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information ( intelligence) from non-disclosed sources or divulging of the same without the permission of the holder of the information for a tang ...
directed against the American program. The Soviets believed that the Americans, with their limited nuclear arsenal, were unlikely to engage in any new world wars, while the Americans were not confident they could prevent a Soviet takeover of Europe, despite their atomic advantage.
Within the United States, the authority to produce and develop nuclear weapons was removed from military control and put instead under the civilian control of the United States Atomic Energy Commission
The United States Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) was an agency of the United States government established after World War II by U.S. Congress to foster and control the peacetime development of atomic science and technology. President ...
. This decision reflected an understanding that nuclear weapons had unique risks and benefits that were separate from other military technology known at the time.
For several years after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, the United States developed and maintained a strategic force based on the Convair B-36
The Convair B-36 "Peacemaker" is a strategic bomber that was built by Convair and operated by the United States Air Force (USAF) from 1949 to 1959. The B-36 is the largest mass-produced piston-engined aircraft ever built. It had the longest win ...
bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped from an air ...
that would be able to attack any potential enemy from bomber bases in the United States. It deployed atomic bombs around the world for potential use in conflicts. Over a period of a few years, many in the American defense community became increasingly convinced of the invincibility of the United States to a nuclear attack. Indeed, it became generally believed that the threat of nuclear war would deter any strike against the United States.
Many proposals were suggested to put all American nuclear weapons under international control (by the newly formed United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
, for example) as an effort to deter both their usage and an arms race
An arms race occurs when two or more groups compete in military superiority. It consists of a competition between two or more states to have superior armed forces; a competition concerning production of weapons, the growth of a military, and ...
. However, no terms could be arrived at that would be agreed upon by both the United States and the Soviet Union.
On August 29, 1949, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
tested its first nuclear weapon at Semipalatinsk
Semey ( kk, Семей, Semei, سەمەي; cyrl, Семей ), until 2007 known as Semipalatinsk (russian: Семипала́тинск) and in 1917–1920 as Alash-kala ( kk, Алаш-қала, ''Alaş-qala''), is a city in eastern Kazakhst ...
in Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
(see also Soviet atomic bomb project
The Soviet atomic bomb project was the classified research and development program that was authorized by Joseph Stalin in the Soviet Union to develop nuclear weapons during and after World War II.
Although the Soviet scientific community disc ...
). Scientists in the United States from the Manhattan Project had warned that, in time, the Soviet Union would certainly develop nuclear capabilities of its own. Nevertheless, the effect upon military thinking and planning in the United States was dramatic, primarily because American military strategists had not anticipated the Soviets would "catch up" so soon. However, at this time, they had not discovered that the Soviets had conducted significant nuclear espionage of the project from spies at Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory (often shortened as Los Alamos and LANL) is one of the sixteen research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy (DOE), located a short distance northwest of Santa Fe, New Mexico, ...
, the most significant of which was done by the theoretical physicist Klaus Fuchs
Klaus Emil Julius Fuchs (29 December 1911 – 28 January 1988) was a German theoretical physicist and atomic spy who supplied information from the American, British and Canadian Manhattan Project to the Soviet Union during and shortly af ...
. The first Soviet bomb was more or less a deliberate copy of the Fat Man
"Fat Man" (also known as Mark III) is the codename for the type of nuclear bomb the United States detonated over the Japanese city of Nagasaki on 9 August 1945. It was the second of the only two nuclear weapons ever used in warfare, the fir ...
plutonium
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exh ...
device. In the same year the first US-Soviet nuclear war plan was penned in the US with Operation Dropshot
Operation Dropshot was the United States Department of Defense code name for a contingency plan for a possible nuclear and conventional war with the USSR and its allies in order to counter the anticipated Soviet takeover of Western Europe, the ...
.
With the monopoly over nuclear technology broken, worldwide nuclear proliferation accelerated. The United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
tested its first independent atomic bomb in 1952, followed by France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
developing its first atomic bomb
Trinity was the code name of the first detonation of a nuclear weapon. It was conducted by the United States Army at 5:29 a.m. on July 16, 1945, as part of the Manhattan Project. The test was conducted in the Jornada del Muerto desert abo ...
in 1960 and then China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
developing its first atomic bomb
Trinity was the code name of the first detonation of a nuclear weapon. It was conducted by the United States Army at 5:29 a.m. on July 16, 1945, as part of the Manhattan Project. The test was conducted in the Jornada del Muerto desert abo ...
in 1964. While much smaller than the arsenals of the United States and the Soviet Union, Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
's nuclear reserves were nevertheless a significant factor in strategic planning during the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
. A top-secret White paper
A white paper is a report or guide that informs readers concisely about a complex issue and presents the issuing body's philosophy on the matter. It is meant to help readers understand an issue, solve a problem, or make a decision. A white paper ...
, compiled by the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
and produced for the British Government in 1959, estimated that British V bombers carrying nuclear weapons were capable of destroying key cities and military targets in the Soviet Union, with an estimated 16 million deaths in the Soviet Union (half of whom were estimated to be killed on impact and the rest fatally injured) ''before'' bomber aircraft from the U.S. Strategic Air Command reached their targets.
1950s
Although the Soviet Union had nuclear weapon capabilities at the beginning of theCold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
, the United States still had an advantage in terms of bombers and weapons. In any exchange of hostilities, the United States would have been capable of bombing the Soviet Union, whereas the Soviet Union would have more difficulty carrying out the reverse mission.
The widespread introduction of jet-powered interceptor aircraft
An interceptor aircraft, or simply interceptor, is a type of fighter aircraft designed specifically for the defensive interception role against an attacking enemy aircraft, particularly bombers and reconnaissance aircraft. Aircraft that are ...
upset this imbalance somewhat by reducing the effectiveness of the American bomber fleet. In 1949 Curtis LeMay
Curtis Emerson LeMay (November 15, 1906 – October 1, 1990) was an American Air Force general who implemented a controversial strategic bombing campaign in the Pacific theater of World War II. He later served as Chief of Staff of the U.S. Air ...
was placed in command of the Strategic Air Command and instituted a program to update the bomber fleet to one that was all-jet. During the early 1950s the B-47 Stratojet
The Boeing B-47 Stratojet (Boeing company designation Model 450) is a retired American long-range, six-engined, turbojet-powered strategic bomber designed to fly at high subsonic speed and at high altitude to avoid enemy interceptor aircraft. ...
and B-52 Stratofortress
The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress is an American long-range, subsonic, jet-powered strategic bomber. The B-52 was designed and built by Boeing, which has continued to provide support and upgrades. It has been operated by the United States Air ...
were introduced, providing the ability to bomb the Soviet Union more easily. Before the development of a capable strategic missile force in the Soviet Union, much of the war-fighting doctrine held by western nations revolved around using a large number of smaller nuclear weapons in a tactical role. It is debatable whether such use could be considered "limited" however because it was believed that the United States would use its own strategic weapons (mainly bombers at the time) should the Soviet Union deploy any kind of nuclear weapon against civilian targets. Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur (26 January 18805 April 1964) was an American military leader who served as General of the Army for the United States, as well as a field marshal to the Philippine Army. He had served with distinction in World War I, was ...
, an American general, was fired by President Harry Truman
Harry S. Truman (May 8, 1884December 26, 1972) was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. A leader of the Democratic Party, he previously served as the 34th vice president from January to April 1945 under Franklin ...
, partially because he persistently requested permission to use his own discretion in deciding whether to utilize atomic weapons on the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
in 1951 during the Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Korean War
, partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict
, image = Korean War Montage 2.png
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Clockwise from top:{ ...
. Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong pronounced ; also Romanization of Chinese, romanised traditionally as Mao Tse-tung. (26 December 1893 – 9 September 1976), also known as Chairman Mao, was a Chinese communist revolutionary who was the List of national founde ...
, China's communist leader, gave the impression that he would welcome a nuclear war with the capitalists because it would annihilate what he viewed as their "imperialist" system.Instant Wisdom: Beyond the Little Red Book. TIME. September 20, 1976.
 The concept of a "
The concept of a "Fortress North America
Fortress North America is a term used both during the Second World War and more often in the Cold War to refer to the option of defending Canada and the United States against their enemies if the rest of the world were lost to them.
In the perio ...
" emerged during the Second World War and persisted into the Cold War to refer to the option of defending Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by to ...
and the United States against their enemies if the rest of the world were lost to them. This option was rejected with the formation of NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
and the decision to permanently station troops in Europe.
In the summer of 1951, Project Vista
Project Vista was a top secret study conducted by prominent physicists, researchers, military officers, and staff at California Institute of Technology from April 1 to December 1, 1951. The project got its name from the Vista del Arroyo Hotel ...
started, in which project analysts such as Robert F. Christy looked at how to defend Western Europe from a Soviet invasion. The emerging development of tactical nuclear weapons
A tactical nuclear weapon (TNW) or non-strategic nuclear weapon (NSNW) is a nuclear weapon that is designed to be used on a battlefield in military situations, mostly with friendly forces in proximity and perhaps even on contested friendly territo ...
was looked upon as a means to give Western forces a qualitative advantage over the Soviet numerical supremacy in conventional weapons.
Several scares about the increasing ability of the Soviet Union's strategic bomber forces surfaced during the 1950s. The defensive response by the United States was to deploy a fairly strong "layered defense" consisting of interceptor aircraft
An interceptor aircraft, or simply interceptor, is a type of fighter aircraft designed specifically for the defensive interception role against an attacking enemy aircraft, particularly bombers and reconnaissance aircraft. Aircraft that are ...
and anti-aircraft missiles, like the Nike
Nike often refers to:
* Nike (mythology), a Greek goddess who personifies victory
* Nike, Inc., a major American producer of athletic shoes, apparel, and sports equipment
Nike may also refer to:
People
* Nike (name), a surname and feminine give ...
, and guns, like the M51 Skysweeper
The M51 Skysweeper (Gun, M51, Antiaircraft or Gun automatic, 75-mm T83E6, and E7, recoil mechanism, and loader rammer) was an anti-aircraft gun deployed in the early 1950s by both the U.S. Army and U.S. Air Force. It was the first such gun to ...
, near larger cities. However, this was a small response compared to the construction of a huge fleet of nuclear bombers. The principal nuclear strategy
Nuclear strategy involves the development of doctrines and strategies for the production and use of nuclear weapons.
As a sub-branch of military strategy, nuclear strategy attempts to match nuclear weapons as means to political ends. In add ...
was to massively penetrate the Soviet Union. Because such a large area could not be defended against this overwhelming attack in any credible way, the Soviet Union would lose any exchange.
This logic became ingrained in American nuclear doctrine and persisted for much of the duration of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
. As long as the strategic American nuclear forces could overwhelm their Soviet counterparts, a Soviet pre-emptive strike could be averted. Moreover, the Soviet Union could not afford to build any reasonable counterforce, as the economic output of the United States was far larger than that of the Soviets, and they would be unable to achieve "nuclear parity".
Soviet nuclear doctrine, however, did not match American nuclear doctrine. Soviet military planners assumed they could win a nuclear war. Therefore, they ''expected'' a large-scale nuclear exchange, followed by a "conventional war" which itself would involve heavy use of tactical nuclear weapon
A tactical nuclear weapon (TNW) or non-strategic nuclear weapon (NSNW) is a nuclear weapon that is designed to be used on a battlefield in military situations, mostly with friendly forces in proximity and perhaps even on contested friendly territo ...
s. American doctrine rather assumed that Soviet doctrine was similar, with the ''mutual'' in mutually assured destruction
Mutual assured destruction (MAD) is a doctrine of military strategy and national security policy which posits that a full-scale use of nuclear weapons by an attacker on a nuclear-armed defender with second-strike capabilities would cause the ...
necessarily requiring that the other side see things in much the same way, rather than believing—as the Soviets did—that they could fight a large-scale, "combined nuclear and conventional" war.
In accordance with their doctrine, the Soviet Union conducted large-scale military exercises to explore the possibility of defensive and offensive warfare
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regu ...
during a nuclear war
Nuclear warfare, also known as atomic warfare, is a theoretical military conflict or prepared political strategy that deploys nuclear weaponry. Nuclear weapons are weapons of mass destruction; in contrast to conventional warfare, nuclear wa ...
. The exercise, under the code name of "Totskoye nuclear exercise, Snowball", involved the detonation of a nuclear bomb about twice as powerful as that which fell on Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Nagasaki and an army of approximately 45,000 soldiers on maneuvers through the hypocenter immediately after the blast. The exercise was conducted on September 14, 1954, under command of Marshal of the Soviet Union, Marshal Georgy Zhukov to the north of Totskoye village in Orenburg Oblast, Russia.
A revolution in nuclear strategic thought occurred with the introduction of the intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM), which the Soviet Union first successfully tested in August 1957. In order to deliver a warhead to a target, a missile was much faster and more cost-effective than a bomber, and enjoyed a higher survivability due to the enormous difficulty of interception of the ICBMs (due to their high altitude and extreme speed). The Soviet Union could now afford to achieve nuclear parity with the United States in raw numbers, although for a time, they appeared to have chosen not to.
Photos of Soviet missile sites set off a wave of panic in the U.S. military, something the launch of Sputnik would do for the American public a few months later. Politicians, notably then-United States Senate, U.S. Senator John Fitzgerald Kennedy, John F. Kennedy suggested that a "missile gap" existed between the Soviet Union and the United States. The US military gave missile development programs the highest national priority, and several reconnaissance aircraft, spy aircraft and reconnaissance satellites were designed and deployed to observe Soviet progress.
Early ICBMs and bombers were relatively inaccurate, which led to the concept of countervalue strikes — attacks directly on the enemy population, which would theoretically lead to a collapse of the enemy's will to fight. During the Cold War, the Soviet Union invested in extensive protected civilian infrastructure, such as large "nuclear-proof" bunkers and non-perishable food stores. By comparison, smaller scale civil defense programs were instituted in the United States starting in the 1950s, where schools and other public buildings had basements stocked with non-perishable food supplies, canned water, first aid, and dosimeter and Geiger counter radiation-measuring devices. Many of the locations were given "fallout shelter" designation signs. CONELRAD radio information systems were adopted, whereby the commercial radio sector (later supplemented by the National Emergency Alarm Repeaters) would broadcast on two AM broadcasting, AM radio frequencies in the event of a Civil Defense (CD) emergency. These two frequencies, 640 and 1240 kHz, were marked with small CD triangles on the tuning dial of radios of the period, as can still be seen on 1950s-vintage radios on online auction sites and museums. A few backyard fallout shelters were built by private individuals.
Henry Kissinger
Henry Alfred Kissinger (; ; born Heinz Alfred Kissinger, May 27, 1923) is a German-born American politician, diplomat, and geopolitical consultant who served as United States Secretary of State and National Security Advisor under the presid ...
's view on tactical nuclear war in his controversial 1957 book ''Nuclear Weapons and Foreign Policy'' was that any nuclear weapon exploded in air burst mode that was below 500 kilotons in yield and thus averting serious fallout, may be more decisive and less costly in human lives than a protracted conventional war.
A list of targets made by the United States was released sometime during December 2015 by the U.S. National Archives and Records Administration. The language used to describe targets is "designated ground zeros". The list was released after a request was made during 2006 by William Burr who belongs to a research group at George Washington University, and belongs to a previously Classified information#Secret, top-secret 800-page document. The list is entitled "Atomic Weapons Requirements Study for 1959" and was produced by U.S. Strategic Air Command during the year 1956.
1960s
 In 1960, the United States developed its first Single Integrated Operational Plan, a range of targeting options, and described launch procedures and target sets against which nuclear weapons would be launched, variants of which were in use from 1961 to 2003. That year also saw the start of the Missile Defense Alarm System, an American system of 12 early-warning satellites that provided limited notice of Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile launches between 1960 and 1966. The Ballistic Missile Early Warning System was completed in 1964.
The most powerful atomic bomb ever made, the Tsar Bomba, was tested by the Soviets on October 30, 1961. It was 50 megatons, or equal to 50 million tons of regular explosives. A complex and worrisome situation developed in 1962, in what is called the Cuban Missile Crisis. The Soviet Union placed medium-range ballistic missiles from the United States, possibly as a direct response to American Jupiter missiles placed in Turkey. After intense negotiations, the Soviets ended up removing the missiles from Cuba and decided to institute a massive weapons-building program of their own. In exchange, the United States dismantled its launch sites in Turkey, although this was done secretly and not publicly revealed for over two decades. First Secretary Nikita Khrushchev did not even reveal this part of the agreement when he came under fire by political opponents for mishandling the crisis. Communication delays during the crisis led to the establishment of the Moscow–Washington hotline to allow reliable, direct communications between the two nuclear powers.
By the late 1960s, the number of ICBMs and warheads was so high on both sides that it was believed that both the United States and the Soviet Union were capable of completely destroying the infrastructure and a large proportion of the population of the other country. Thus, by some western game theorists, a balance of power in international relations, balance of power system known as
In 1960, the United States developed its first Single Integrated Operational Plan, a range of targeting options, and described launch procedures and target sets against which nuclear weapons would be launched, variants of which were in use from 1961 to 2003. That year also saw the start of the Missile Defense Alarm System, an American system of 12 early-warning satellites that provided limited notice of Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile launches between 1960 and 1966. The Ballistic Missile Early Warning System was completed in 1964.
The most powerful atomic bomb ever made, the Tsar Bomba, was tested by the Soviets on October 30, 1961. It was 50 megatons, or equal to 50 million tons of regular explosives. A complex and worrisome situation developed in 1962, in what is called the Cuban Missile Crisis. The Soviet Union placed medium-range ballistic missiles from the United States, possibly as a direct response to American Jupiter missiles placed in Turkey. After intense negotiations, the Soviets ended up removing the missiles from Cuba and decided to institute a massive weapons-building program of their own. In exchange, the United States dismantled its launch sites in Turkey, although this was done secretly and not publicly revealed for over two decades. First Secretary Nikita Khrushchev did not even reveal this part of the agreement when he came under fire by political opponents for mishandling the crisis. Communication delays during the crisis led to the establishment of the Moscow–Washington hotline to allow reliable, direct communications between the two nuclear powers.
By the late 1960s, the number of ICBMs and warheads was so high on both sides that it was believed that both the United States and the Soviet Union were capable of completely destroying the infrastructure and a large proportion of the population of the other country. Thus, by some western game theorists, a balance of power in international relations, balance of power system known as mutually assured destruction
Mutual assured destruction (MAD) is a doctrine of military strategy and national security policy which posits that a full-scale use of nuclear weapons by an attacker on a nuclear-armed defender with second-strike capabilities would cause the ...
(or ''MAD'') came into being. It was thought that no full-scale exchange between the powers would result in an outright winner, with at best one side emerging the pyrrhic victory, pyrrhic victor. Thus both sides were stability-instability paradox, deterred from risking the initiation of a direct confrontation, instead being forced to engage in lower-intensity proxy wars.
During this decade the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
began to build subterranean infrastructure such as the Underground Project 131 following the Sino-Soviet split.
One drawback of the MAD doctrine was the possibility of a nuclear war occurring without either side intentionally striking first. Early Warning Systems (EWS) were notoriously error-prone. For example, on 78 occasions in 1979 alone, a "missile display conference" was called to evaluate detections that were "potentially threatening to the North American continent". Some of these were trivial errors and were spotted quickly, but several went to more serious levels. On September 26, 1983, Stanislav Petrov received convincing indications of an American first strike launch against the Soviet Union, but positively identified the warning as a false alarm. Though it is unclear what role Petrov's actions played in preventing a nuclear war during this incident, he has been honored by the United Nations for his actions.
Similar incidents happened many times in the United States, due to failed Integrated circuit, computer chips, misidentifications of large flights of geese, test programs, and bureaucratic failures to notify early warning military personnel of legitimate launches of test or weather missiles. For many years, the United States Air Force, U.S. Air Force's strategic bombers were kept airborne on a daily rotating basis "around the clock" (see Operation Chrome Dome), until the number and severity of List of military nuclear accidents, accidents, the 1968 Thule Air Base B-52 crash in particular, persuaded policymakers it was not worthwhile.
1970s
Israel responded to the Arab Yom Kippur War attack on 6 October 1973 by assembling 13 nuclear weapons in a tunnel under the Negev desert when Syrian tanks were sweeping in across the Golan Heights. On 8 October 1973, Israeli Prime Minister Golda Meir authorized Defense Minister Moshe Dayan to activate the 13 Israeli nuclear warheads and distribute them to Israeli air force units, with the intent that they be used if Israel began to be overrun.Nuclear Weapons in the Cold War, Bernard Brodie On 24 October 1973, as US President Richard Nixon was preoccupied with the Watergate scandal, Henry Kissinger ordered a DEFCON-3 alert preparing American B-52 nuclear bombers for war. Intelligence reports indicated that the USSR was preparing to defend Egypt in its Yom Kippur War with Israel. It had become apparent that if Israel had dropped nuclear weapons on Egypt or Syria, as it prepared to do, then the USSR would have retaliated against Israel, with the US then committed to providing Israeli assistance, possibly escalating to a general nuclear war. By the late 1970s, people in both theUnited States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
, along with the rest of the world, had been living with the concept of mutual assured destruction (MAD) for about a decade, and it became deeply ingrained into the psyche and popular culture of those countries.
On May 18, 1974, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
conducted its first nuclear test in the Pokhran test range. The name of the operation was Smiling Buddha, and India termed the test as a "peaceful nuclear explosion."
The Soviet Duga radar, Duga early warning over-the-horizon radar system was made operational in 1976. The extremely powerful radio transmissions needed for such a system led to much disruption of civilian shortwave broadcasts, earning it the nickname "Russian Woodpecker".
The idea that any nuclear conflict would eventually escalate was a challenge for military strategists. This challenge was particularly severe for the United States and its NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
allies. It was believed (until the 1970s) that a Soviet tank offensive into Western Europe would quickly overwhelm NATO conventional forces, leading to the necessity of the West escalating to the use of tactical nuclear weapons, one of which was the W-70.
This strategy had one major (and possibly critical) flaw, which was soon realized by military analysts but highly underplayed by the U.S. military: conventional NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two N ...
forces in the European theatre of war were far outnumbered by similar Soviet and Warsaw Pact forces, and it was assumed that in case of a major Soviet attack (commonly envisioned as the "Red tanks rolling towards the North Sea" scenario) that NATO—in the face of quick conventional defeat—would soon have no other choice but to resort to tactical nuclear strikes against these forces. Most analysts agreed that once the first nuclear exchange had occurred, escalation to global nuclear war would likely become inevitable. The Warsaw Pact's vision of an atomic war between NATO and Warsaw Pact forces was simulated in the top-secret exercise Seven Days to the River Rhine in 1979. The British government exercised their vision of a Soviet nuclear attack with Square Leg in early 1980.
Large hardened nuclear weapon storage areas were built across European countries in anticipation of local US and European forces falling back as the conventional NATO defense from the Soviet Union, named REFORGER, was believed to only be capable of stalling the Soviets for a short time.
1980s
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
developed a nuclear weapon capability during the 1970s and early 1980s. It was operational for a brief period before being dismantled in the early 1990s.
According to the 1980 United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
report ''General and Complete Disarmament: Comprehensive Study on Nuclear Weapons: Report of the Secretary-General'', it was estimated that there were a total of about 40,000 Historical nuclear weapons stockpiles and nuclear tests by country, nuclear warheads in existence at that time, with a potential combined explosive yield of approximately 13,000 TNT equivalent, megatons. By comparison, the largest volcanic eruption in recorded history when the volcano Mount Tambora erupted in 1815—turning 1816 into the Year Without A Summer due to the levels of global dimming sulfate aerosols and ash expelled—it exploded with a force of roughly 33 billion tons of TNT or 33,000 megatons of TNT this is about 2.2 million Little Boy, Hiroshima Bombs, and ejected of mostly rock/tephra, that included 120 million tonnes of sulfur dioxide as Mount Tambora#Global effects, an upper estimate. A larger eruption, approximately 74,000 years ago, in Mount Toba produced of tephra, forming lake Toba, and produced an estimated of sulfur dioxide. The explosive energy of the eruption may have been as high as equivalent to 20,000,000 megatons (Mt) of TNT, while the asteroid created Chicxulub impact, that is connected with the extinction of the dinosaurs corresponds to at least 70,000,000 Mt of energy, which is roughly 7000 times the maximum arsenal of the US and Soviet Union.
However, comparisons with supervolcanos, supervolcanoes are more misleading than helpful due to the different aerosols released, the likely air burst fuzing height of nuclear weapons and the globally scattered location of these potential nuclear detonations all being in contrast to the singular and subterranean nature of a Supervolcano, supervolcanic eruption. Moreover, assuming the entire world stockpile of weapons were grouped together, it would be difficult, due to the nuclear fratricide effect, to ensure the individual weapons would go off all at once. Nonetheless, many people believe that a full-scale nuclear war would result, through the nuclear winter effect, in the human extinction, extinction of the human species, though not all analysts agree on the assumptions that underpin these nuclear winter models.
On 26 September 1983, a Soviet early warning station under the command of Stanislav Petrov falsely detected 5 inbound intercontinental ballistic missiles from the US. Petrov correctly assessed the situation as a false alarm, and hence did not report his finding to his superiors. It is quite possible that his actions prevented "World War III", as the Soviet policy at that time was Launch on warning, immediate nuclear response upon discovering inbound ballistic missiles.
The world came unusually close to nuclear war in November 1983 when the Soviet Union thought that the NATO military exercise Able Archer 83 was a ruse or "cover-up" to begin a nuclear first strike. The Soviets responded by raising readiness and preparing their nuclear arsenal for High-alert nuclear weapon, immediate use. Soviet fears of an attack ceased once the exercise concluded without incident.
Post–Cold War
Although thedissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
ended the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
and greatly reduced tensions between the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
and the Russia, Russian Federation, the Soviet Union's formal successor state, both countries remained in a "nuclear stand-off" due to the continuing presence of a very large number of deliverable nuclear warheads on both sides. Additionally, the end of the Cold War led the United States to become increasingly concerned with the development of nuclear technology by other nations outside of the former Soviet Union. In 1995, a branch of the U.S. Strategic Command produced an outline of forward-thinking strategies in the document "Essentials of Post–Cold War Deterrence".
In 1995, a Black Brant (rocket), Black Brant sounding rocket launched from the Andøya Space Center caused a high alert in Russia, known as the Norwegian rocket incident, Norwegian Rocket Incident. The Russians thought it might be a nuclear missile launched from an American submarine.
In 1996, a Russian Continuity of government#Soviet Union and Russia, continuity of government facility, Kosvinsky Mountain, which is believed to be a counterpart to the US Cheyenne Mountain Complex, was completed. It was designed to resist US nuclear bunker buster, earth-penetrating nuclear warheads, and is believed to host the Russian Strategic Rocket Forces alternate command post, a post for the general staff built to compensate for the vulnerability of older Soviet era command posts in the Moscow region. In spite of this, the primary command posts for the Strategic Rocket Forces remains Kuntsevo in Moscow and the secondary is the Kosvinsky Mountain in the Ural Mountains. The timing of the Kosvinsky facilities completion date is regarded as one explanation for U.S. interest in a new nuclear "bunker buster" Earth-penetrating warhead and the declaration of the deployment of the B61 nuclear bomb, B-61 mod 11 in 1997; Kosvinsky is protected by about 1000 feet of granite.
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
Nuclear disarmament, disarmament committee stated that there are more than 16,000 strategic and tactical nuclear weapons ready for deployment and another 14,000 in storage, with the U.S. having nearly 7,000 ready for use and 3,000 in storage, and Russia having about 8,500 ready for use and 11,000 in storage. In addition, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
is thought to possess about 400 nuclear weapons, United Kingdom, Britain about 200, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
about 350, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
about 80–100, and Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
100–110. North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and T ...
is confirmed as having nuclear weapons, though it is not known how many, with most estimates between 1 and 10. Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
is also widely believed to Nuclear weapons and Israel, possess usable nuclear weapons. NATO has Nuclear sharing, stationed about 480 American nuclear weapons in Belgium, Netherlands, the Netherlands, Italy, Germany, and Turkey, and several other nations are thought to be in pursuit of an arsenal of their own.
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
's nuclear policy was significantly affected by the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965, 1965 war with India. The 1971 war and India's nuclear program played a role in Pakistan's decision to go nuclear. India and Pakistan both decided not to participate in the NPT. Pakistan's nuclear policy became fixated on India because India refused to join the NPT and remained open to nuclear weapons. Impetus by Indian actions spurred Pakistan's nuclear research. After nuclear weapons construction was started by President Zulfikar Ali Bhutto's command, the chair of Pakistan Atomic Energy Commission Usmani quit in objection. The Kargil War, 1999 war between Pakistan and India occurred after both acquired nuclear weapons. It is believed by some that nuclear weapons are the reason a big war has not broken out in the subcontinent. India and Pakistan still have a risk of nuclear conflict on the issue of war over Kashmir. Nuclear capability deliverable by sea were claimed by Pakistan in 2012. The aim was to achieve a "minimum credible deterrence". Pakistan's nuclear program culminated in the tests at Chagai-I, Chagai. One of the aims of Pakistan's programs is fending off potential annexation and maintaining independence.
A key development in nuclear warfare throughout the 2000s and early 2010s is the nuclear proliferation, proliferation of nuclear weapons to the Developing country, developing world, with India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
and Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
both publicly testing several nuclear devices, and North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and T ...
conducting an underground nuclear test on October 9, 2006. The United States Geological Survey, U.S. Geological Survey measured a 4.2 magnitude earthquake in the area where the North Korean test is said to have occurred. A further test was announced by the North Korean government on May 25, 2009. Iran, meanwhile, has embarked on a nuclear program which, while officially for civilian purposes, has come under close scrutiny by the United Nations and many individual states.
Recent studies undertaken by the Central Intelligence Agency, CIA cite the enduring Indo-Pakistani wars and conflicts, India-Pakistan conflict as the one "flash point" most likely to escalate into a nuclear war. During the Kargil War in 1999, Pakistan came close to using its nuclear weapons in case the conventional military situation underwent further deterioration. Pakistan's foreign minister had even warned that it would "use any weapon in our arsenal", hinting at a nuclear strike against India. The statement was condemned by the international community, with Pakistan denying it later on. This conflict remains the only war (of any sort) between two declared nuclear powers. The 2001-2002 India-Pakistan standoff again stoked fears of nuclear war between the two countries. Despite these very serious and relatively recent threats, relations between India and Pakistan have been improving somewhat over the last few years. However, with the 2008 Mumbai attacks, November 26, 2008 Mumbai terror attacks, tensions again worsened.
 Another potential geopolitical issue that is considered particularly worrisome by military analysts is a possible conflict between the
Another potential geopolitical issue that is considered particularly worrisome by military analysts is a possible conflict between the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
and the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
over Taiwan. Although economic forces are thought to have reduced the possibility of a military conflict, there remains concern about the increasing military buildup of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
(China is rapidly increasing its naval capacity), and that any move toward Taiwan independence could potentially spin out of control.
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
is thought to possess somewhere between one hundred and four hundred nuclear warheads. It has been asserted that the Dolphin-class submarines which Israel received from Germany have been adapted to carry nuclear-armed Popeye (missile), Popeye cruise missiles, so as to give Israel a second strike capability. Israel has been involved in wars with its neighbors in the Middle East (and with other "non-state actors" in Lebanon and Palestine (region), Palestine) on numerous prior occasions, and its small geographic size and population could mean that, in the event of future wars, the Israel Defense Forces might have very little time to react to an invasion or other major threat. Such a situation could escalate to nuclear warfare very quickly in some scenarios.
On March 7, 2013, North Korea threatened the United States with a pre-emptive nuclear strike. On April 9, North Korea urged foreigners to leave South Korea, stating that both countries were on the verge of nuclear war. On April 12, North Korea stated that a nuclear war was unavoidable. The country declared Japan as its first target.
In 2014, when Russia–United States relations, Russia-United States and Russia–NATO relations, Russia-NATO relations worsened over the Russo-Ukrainian War, the Russian state-owned television channel Russia 1 stated that "Russia is the only country in the world that is really capable of turning the USA into radioactive ash." U.S. Secretary of Defense Ash Carter considered proposing deployment of ground-launched cruise missiles in Europe that could pre-emptively destroy Russian weapons.
In August 2017, North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and T ...
warned that it might launch mid-range ballistic missiles into waters within of Guam, following an North Korea–United States relations#Trump administration (2017–2021), exchange of threats between the governments of North Korea and the United States. 2017–18 North Korea crisis, Escalating tensions between North Korea and the United States, including threats by both countries that they could use nuclear weapons against one another, prompted a heightened state of readiness in Hawaii. The perceived ballistic missile threat broadcast all over Hawaii on 13 January 2018 was a 2018 Hawaii false missile alert, false missile alarm.
In October 2018, the former Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev commented that U.S. withdrawal from the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty is "not the work of a great mind" and that "a new arms race has been announced".
In early 2019, more than 90% of world's 13,865 nuclear weapons were owned by Russia and the United States.
In 2019, Vladimir Putin warned that Russia would deploy Nuclear weapon, nuclear missiles in Europe if the United States deployed Intermediate-range ballistic missile, intermediate-range nuclear missiles there. Journalist Dmitry Kiselyov listed the targets in the United States, which includes The Pentagon, Camp David, Fort Ritchie, McClellan Air Force Base, and Jim Creek Naval Radio Station. Kremlin Press Secretary, Kremlin spokesperson Dmitry Peskov denies the existence of the target list.
On February 24, 2022, in a televised address preceding the start of Russia's 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, full-scale invasion of Ukraine, Russian President Vladimir Putin stated that Russia "is today one of the most powerful nuclear powers in the world... No one should have any doubts that a direct attack on our country will lead to defeat and dire consequences for any potential aggressor." Later in the same speech, Putin stated: "Now a few important, very important words for those who may be tempted to intervene in ongoing events. Whoever tries to hinder us, and even more so to create threats for our country, for our people, should know that Russia's response will be immediate and will lead you to such consequences that you have never experienced in your history." On February 27, 2022, Putin publicly put his nuclear forces on alert, stating that NATO powers had made "aggressive statements". On April 14, ''The New York Times'' reported comments by CIA director William J. Burns (diplomat), William Burns, who said "potential desperation" could lead President Putin to order the use of tactical nuclear weapon
A tactical nuclear weapon (TNW) or non-strategic nuclear weapon (NSNW) is a nuclear weapon that is designed to be used on a battlefield in military situations, mostly with friendly forces in proximity and perhaps even on contested friendly territo ...
s. On September 21, 2022, days before declaring the annexation of additional parts of Ukraine, Putin claimed in a national television address that high NATO officials had made statements about the possibility of "using nuclear weapons of mass destruction against Russia", and stated "if the territorial integrity of our country is threatened, we will certainly use all the means at our disposal to protect Russia and our people... It's not a bluff." NBC News characterized Putin's statements as a "thinly veiled" threat that Putin was willing to risk nuclear conflict if necessary to win the war with Ukraine. Hans M. Kristensen, director of the Nuclear Information Project at the Federation of American Scientists, stated that "if you start detonating nuclear weapons in the [battlefield] you potentially get Nuclear fallout, radioactive fallout that you can't control — it could rain over your own troops as well, so it might not be an advantage to do that in the field."
According to a peer-reviewed study published in the journal ''Nature Food'' in August 2022, a full-scale nuclear war between the U.S. and Russia would kill 360 million people directly, with a further 5 billion people dying from starvation. More than 2 billion people would die from a smaller-scale nuclear war between India and Pakistan.
Sub-strategic use
The above examples envisage nuclear warfare at a strategic level, i.e.,total war
Total war is a type of warfare that includes any and all civilian-associated resources and infrastructure as legitimate military targets, mobilizes all of the resources of society to fight the war, and gives priority to warfare over non-com ...
. However, nuclear powers have the ability to undertake more limited engagements.
"Sub-strategic use" includes the use of either "low-yield" tactical nuclear weapons, or of variable yield strategic nuclear weapons in a very limited role, as compared to battlefield exchanges of larger-yield strategic nuclear weapons. This was described by the UK Parliamentary Defence Select Committee as "the launch of one or a limited number of missiles against an adversary as a means of conveying a political message, warning or demonstration of resolve". It is believed that all current nuclear weapons states possess tactical nuclear weapons, with the exception of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, which decommissioned its tactical warheads in 1998. However, the UK does possess scalable-yield strategic warheads, and this technology tends to blur the difference between "strategic", "sub-strategic", and "tactical" use or weapons. American, French and British nuclear submarines are believed to carry at least ''some'' missiles with dial-a-yield warheads for this purpose, potentially allowing a strike as low as one kiloton (or less) against a single target. Only the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
and the Republic of India have declarative, unqualified, unconditional "no first use" nuclear weapons policies. India and Pakistan maintain only a credible minimum deterrence.
Commodore Tim Hare, former Director of Nuclear Policy at the British Ministry of Defence, has described "sub-strategic use" as offering the Government "an extra option in the escalatory process before it goes for an all-out strategic strike which would deliver unacceptable damage". However, this sub-strategic capacity has been criticized as potentially increasing the "acceptability" of using nuclear weapons. Combined with the trend in the reduction in the worldwide nuclear arsenal as of 2007 is the warhead miniaturization and modernization of the remaining strategic weapons that is presently occurring in all the declared nuclear weapon states, into more "usable" configurations. The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute suggests that this is creating a culture where use of these weapons is more acceptable and therefore is increasing the risk of war, as these modern weapons do not possess the same psychological deterrent value as the large Cold-War era, multi-megaton warheads.
In many ways, this present change in the balance of terror can be seen as the complete embracement of the switch from the 1950s Eisenhower, Eisenhower doctrine of "massive retaliation" to one of "flexible response", which has been growing in importance in the US nuclear war fighting plan/Single Integrated Operational Plan, SIOP every decade since.
For example, the United States adopted a policy in 1996 of allowing the targeting of its nuclear weapons at non-state actors ("terrorists") armed with weapons of mass destruction
A weapon of mass destruction (WMD) is a chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear, or any other weapon that can kill and bring significant harm to numerous individuals or cause great damage to artificial structures (e.g., buildings), natu ...
.
Another dimension to the tactical use of nuclear weapons is that of such weapons deployed at sea for use against surface and submarine vessels. Until 1992, vessels of the United States Navy (and their aircraft) deployed various such weapons as bombs, rockets (guided and unguided), torpedoes, and depth charges. Such tactical naval nuclear weapons were considered more acceptable to use early in a conflict because there would be few civilian casualties. It was feared by many planners that such use would probably quickly have escalated into a large-scale nuclear war. This situation was particularly exacerbated by the fact that such weapons at sea were not constrained by the safeguards provided by the Permissive Action Link attached to U.S. Air Force and Army nuclear weapons. It is unknown if the navies of the other nuclear powers yet today deploy tactical nuclear weapons at sea.
The Nuclear Posture Review, 2018 US Nuclear Posture Review emphasised the need for the US to have sub-strategic nuclear weapons as additional layers for its nuclear deterrence.
Nuclear terrorism
Nuclear terrorism by non-state organizations or actors (even individuals) is a largely unknown and understudied factor in nuclear deterrence thinking, as states possessing nuclear weapons are susceptible to retaliation in kind, while sub- or trans-state actors may be less so. The collapse of the Soviet Union has given rise to the possibility that former Soviet nuclear weapons might become available on the black market (so-called 'loose nukes'). A number of other concerns have been expressed about the security of nuclear weapons in newer nuclear powers with relatively less stable governments, such asPakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
, but in each case, the fears have been addressed to some extent by statements and evidence provided by those nations, as well as cooperative programs between nations. Worry remains, however, in many circles that a relative decrease in the security of nuclear weapons has emerged in recent years, and that terrorists or others may attempt to exert control over (or use) nuclear weapons, militarily applicable technology, or nuclear materials and fuel.
Another possible nuclear terrorism threat are devices designed to disperse radioactive materials over a large area using conventional explosives, called dirty bombs. The detonation of a "dirty bomb" would not cause a nuclear explosion, nor would it release enough radiation to kill or injure a large number of people. However, it could cause severe disruption and require potentially very costly decontamination procedures and increased spending on security measures.
Radioactive materials can also be used for targeted assassinations. For example, the Alexander Litvinenko poisoning, poisoning of Alexander Litvinenko was described by medical professionals, as "an ominous landmark: the beginning of an era of nuclear terrorism
Nuclear terrorism refers to any person or persons detonating a nuclear weapon as an act of terrorism (i.e., illegal or immoral use of violence for a political or religious cause). Some definitions of nuclear terrorism include the sabotage of a ...
."Radiological Terrorism: “Soft Killers”by Morten Bremer Mærli, Bellona Foundation
Survival
The predictions of the effects of a major countervalue nuclear exchange include millions of city dweller deaths within a short period of time. Some 1980s predictions had gone further and argued that a full-scale nuclear war could eventually bring about the extinction of the human race. Such predictions, sometimes but not always based on total war with nuclear arsenals atCold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
highs, received contemporary criticism. On the other hand, some 1980s governmental predictions, such as FEMA's CRP-2B and NATO's Carte Blanche (war game), Carte Blanche, have received criticism from groups such as the Federation of American Scientists for being overly optimistic. CRP-2B, for instance, infamously predicted that 80% of Americans would survive a nuclear exchange with the Soviet Union, a figure that neglected nuclear war's impacts on healthcare infrastructure, the food supply, and the ecosystem and assumed that all major cities could be successfully evacuated within 3–5 days. A number of Cold War publications advocated preparations that could purportedly enable a large proportion of civilians to survive even a total nuclear war. Among the most famous of these is ''Nuclear War Survival Skills''.
To avoid injury and death from a nuclear weapon's heat flash and blast effects, the two most far ranging prompt effects of nuclear weapons, schoolchildren were taught to duck and cover by the early Cold War Duck and Cover (film), film of the same name. Such advice is once again being given in case of nuclear terrorism, nuclear terrorist attacks.
Prussian blue, or "Radiogardase", is stockpiled in the US, along with potassium iodide and DPTA as pharmaceuticals useful in treating internal exposure to harmful radioisotopes in fallout.
Publications on adapting to a changing diet and supplying nutritional food sources following a nuclear war, with particular focus on agricultural radioecology, include ''Nutrition in the postattack environment'' by the RAND corporation.
The British government developed a public alert system for use during a nuclear attack with the expectation of a four-minute warning before detonation. The United States expected a warning time of anywhere from half an hour (for land-based missiles) to less than three minutes (for submarine-based weapons). Many countries maintain plans for continuity of government following a nuclear attack or similar disasters. These range from a designated survivor, intended to ensure the survival of some form of government leadership, to the Soviet Dead Hand (nuclear war), Dead Hand system, which allows for retaliation even if all Soviet leadership were destroyed. Nuclear submarines are given letters of last resort: orders on what action to take in the event that an enemy nuclear strike has destroyed the government.
A number of other countries around the world have taken significant efforts to maximize their survival prospects in the event of large calamities, both natural and manmade. For example, metro stations in Pyongyang Metro, Pyongyang, North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and T ...
, were constructed below ground, and were designed to serve as nuclear shelters in the event of war, with each station entrance built with thick steel blast doors. An example of privately funded fallout shelters is the Ark Two Shelter in Ontario, Canada, and Autonomous building, autonomous shelters have been constructed with an emphasis on post-war networking and reconstruction.
In Switzerland, the majority of homes have an underground blast shelter, blast and fallout shelter. The country has an overcapacity of such shelters and can accommodate slightly more than the nation's population size.
While the nuclear fallout shelters described above are the ideal long-term protection methods against dangerous radiation exposure in the event of a nuclear catastrophe, it is also necessary to have Radiation protection#Externally Penetrating Radiation Protective Equipment, mobile protection equipment for medical and security personnel to safely assist in containment, evacuation, and many other necessary public safety objectives which ensue as a result of nuclear detonation. There are many basic shielding strategies used to protect against the deposition of radioactive material from external radiation environments. Respirators that protect against internal deposition are used to prevent the inhalation and ingestion of radioactive material and dermal protective equipment which is used to protect against the deposition of material on external structures like skin, hair, and clothing. While these protection strategies do slightly reduce the exposure, they provide almost no protection from externally penetrating Gamma ray, gamma radiation, which is the cause of acute radiation syndrome and can be extremely lethal in high dosages. Naturally, shielding the entire body from high-energy gamma radiation is optimal, but the required mass to provide adequate attenuation makes functional movement nearly impossible.
Recent scientific studies have shown the feasibility of partial body shielding as a viable protection strategy against externally penetrating gamma radiation. The concept is based in providing sufficient attenuation to only the most radio-sensitive organs and tissues in efforts to defer the onset of acute radiation syndrome, the most immediate threat to humans from high doses of gamma radiation. Acute radiation syndrome is a result of irreversible bone marrow damage from high-energy radiation exposure. Due to the regenerative property of hematopoietic stem cells found in bone marrow, it is only necessary to protect enough bone marrow to repopulate the exposed areas of the body with the shielded supply. Because 50% of the body's supply of bone marrow is stored in the pelvic region which is also in close proximity to other radio-sensitive organs in the abdomen, the lower torso is a logical choice as the primary target for protection.Waterman, Gideon; Kase, Kenneth; Orion, Itzhak; Broisman, Andrey; Milstein, Oren (2017-09). "Selective Shielding of Bone Marrow". ''Health Physics''. 113 (3): 195–208. . International Standard Serial Number, ISSN 0017-9078.
In fiction
Nuclear warfare and weapons are staple elements of speculative fiction.See also
* Air Force Global Strike Command * Basic Encyclopedia * Broken-backed war theory * Cuban Missile Crisis *Doomsday Clock
The Doomsday Clock is a symbol that represents the likelihood of a man-made global catastrophe, in the opinion of the members of the ''Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists''. Maintained since 1947, the clock is a metaphor for threats to humanity ...
* Global catastrophic risk
* Human extinction
* International Luxembourg Forum on Preventing Nuclear Catastrophe
* List of CBRN warfare forces
* List of nuclear close calls
* List of states with nuclear weapons
* Mount Yamantau
* Nuclear arms race
* Nuclear blackout
* Nuclear briefcase
* Nuclear famine
* Nuclear holocaust
* Nuclear terrorism
* Nuclear weapon
* Nuclear weapons and the United States
* Nuclear weapons debate
* Nuclear winter
* People's Liberation Army Rocket Force
* Permissive Action Link
* Prevention of nuclear catastrophe
* Transition to war
* World War III
* ''''
References
Further reading
* Laura Grego and David Wright, "Broken Shield: Missiles designed to destroy incoming nuclear warheads fail frequently in tests and could increase global risk of mass destruction", ''Scientific American'', vol. 320, no. no. 6 (June 2019), pp. 62–67. "Nuclear-armed missiles are a political problem that technology cannot solve.... Current U.S. missile defense plans are being driven largely by technology, politics and fear. Missile defenses will not allow us to escape our vulnerability tonuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb ...
s. Instead large-scale developments will create barriers to taking real steps toward Nuclear disarmament, reducing nuclear risks—by blocking further cuts in nuclear arsenals and potentially spurring new deployments." (p. 67.)
* Jessica T. Mathews, "The New Nuclear Threat", ''The New York Review of Books'', vol. LXVII, no. 13 (20 August 2020), pp. 19–21. "[P]owerful reasons to doubt that there could be a limited nuclear war [include] those that emerge from any study of history, a knowledge of how humans act under pressure, or experience of government." (p. 20.)
"Possibility of Nuclear War in Asia: An Indian Perspective"
a project of United Service Institution of India, USI, Discusses the possibility of a nuclear war in Asia from the
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
n point of view.
* Thomas Powers, "The Nuclear Worrier" (review of Daniel Ellsberg, ''The Doomsday Machine: Confessions of a Nuclear War Planner'', New York, Bloomsbury, 2017, , 420 pp.), ''The New York Review of Books'', vol. LXV, no. 1 (18 January 2018), pp. 13–15.
"Presidency in the Nuclear Age"
conference and forum at the John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum, JFK Library, Boston, October 12, 2009. Four panels: "The Race to Build the Bomb and the Decision to Use It", "Cuban Missile Crisis and the First Nuclear Test Ban Treaty", "The Cold War and the Nuclear Arms Race", and "Nuclear Weapons, Terrorism, and the Presidency". * Tom Stevenson, "A Tiny Sun" (review of Fred Kaplan (journalist), Fred Kaplan, ''The Bomb: Presidents, Generals, and the Secret History of Nuclear War'', Simon and Schuster, 2021, 384 pp.; and Keir A. Lieber and Daryl G. Press, ''The Myth of the Nuclear Revolution: Power Politics in the Atomic Age'', Cornell, 2020, 180 pp.), ''London Review of Books'', vol. 44, no. 4 (24 February 2022), pp. 29–32. "Nuclear strategists systematically underestimate the chances of nuclear accident... [T]here have been too many close calls for accidental use to be discounted." (p. 32.)
External links
Fallout: After a Nuclear Attack
– slideshow by ''Life magazine'' *
The Effects of Nuclear War
'' (1979) — handbook produced by the United States Office of Technology Assessment (hosted by the Federation of American Scientists) *
Nuclear Attack Planning Base – 1990
' (1987) — assessment of the effects of a major Soviet attack on the United States produced by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (hosted by the Federation of American Scientists) *
Nuclear War Survival Skills
' (1979/1987) — handbook produced by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (use menu at left to navigate)
Ground Zero: A Javascript simulation of the effects of a nuclear explosion in a city
British RAF manual on the effects of nuclear explosions dated 1955
by Alan F. Philips, M.D.
Interactive Timeline of the Nuclear Age
Annotated bibliography on nuclear warfare from the Alsos Digital Library for Nuclear Issues
* DeVolpi, Alexander, Vladimir E. Minkov, Vadim A. Simonenko, and George S. Stanford. 2004. ''Nuclear Shadowboxing: Contemporary Threats from Cold War Weaponry'', Vols. 1 and 2. Fidlar Doubleday.
An in depth history of American air weapons and nuclear bombs from the reference book ''American Combat Planes of the 20th Century'' by Ray Wagner
NUKEMAP3D
– a 3D nuclear weapons effects simulator powered by Google Maps. {{DEFAULTSORT:Nuclear Warfare Nuclear warfare, Nuclear weapons, Warfare