neutrophils on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in different animals.
They are formed from
 When adhered to a surface, neutrophil granulocytes have an average diameter of 12–15 micrometers (µm) in peripheral blood smears. In suspension, human neutrophils have an average diameter of 8.85 µm.
With the eosinophil and the basophil, they form the class of ''polymorphonuclear cells'', named for the
When adhered to a surface, neutrophil granulocytes have an average diameter of 12–15 micrometers (µm) in peripheral blood smears. In suspension, human neutrophils have an average diameter of 8.85 µm.
With the eosinophil and the basophil, they form the class of ''polymorphonuclear cells'', named for the 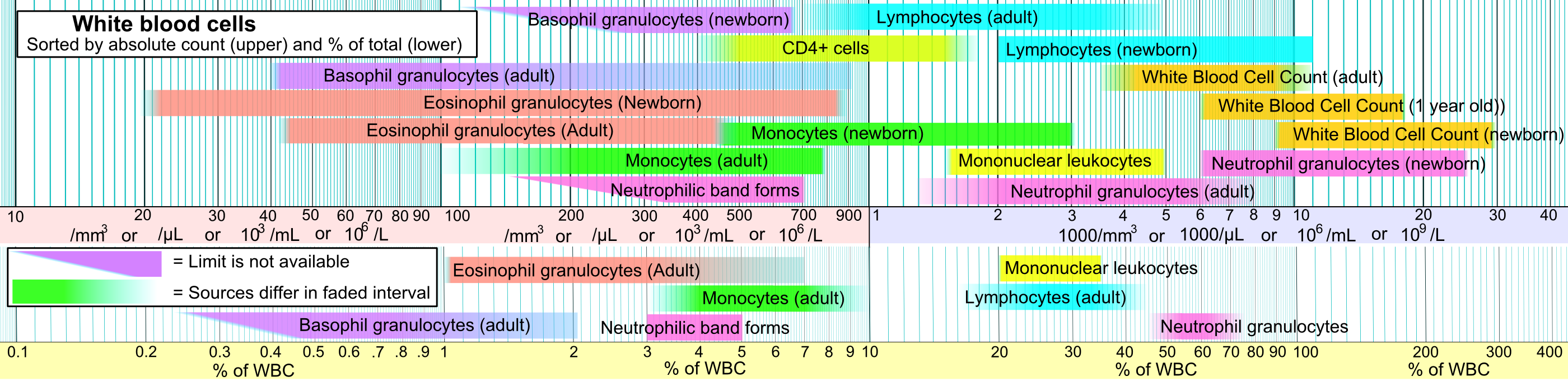 Neutrophils are the most abundant white blood cells in humans (approximately 1011 are produced daily); they account for approximately 50–70% of all white blood cells (leukocytes). The stated normal range for human blood counts varies between laboratories, but a neutrophil count of 2.5–7.5 × 109/L is a standard normal range. People of
Neutrophils are the most abundant white blood cells in humans (approximately 1011 are produced daily); they account for approximately 50–70% of all white blood cells (leukocytes). The stated normal range for human blood counts varies between laboratories, but a neutrophil count of 2.5–7.5 × 109/L is a standard normal range. People of
 The average lifespan of inactivated human neutrophils in the circulation has been reported by different approaches to be between 5 and 135 hours.
Upon activation, they marginate (position themselves adjacent to the blood vessel endothelium) and undergo selectin-dependent capture followed by
The average lifespan of inactivated human neutrophils in the circulation has been reported by different approaches to be between 5 and 135 hours.
Upon activation, they marginate (position themselves adjacent to the blood vessel endothelium) and undergo selectin-dependent capture followed by
 Neutrophils are phagocytes, capable of ingesting microorganisms or particles. For targets to be recognized, they must be coated in opsoninsa process known as antibody opsonization. They can internalize and kill many
Neutrophils are phagocytes, capable of ingesting microorganisms or particles. For targets to be recognized, they must be coated in opsoninsa process known as antibody opsonization. They can internalize and kill many  Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
 Low neutrophil counts are termed '' neutropenia''. This can be congenital (developed at or before birth) or it can develop later, as in the case of aplastic anemia or some kinds of
Low neutrophil counts are termed '' neutropenia''. This can be congenital (developed at or before birth) or it can develop later, as in the case of aplastic anemia or some kinds of
File:Histopathology of neutrophil infiltration in myocardial infarction.jpg, Neutrophils are seen in a
"This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ )" as seen in this
 Two functionally unequal subpopulations of neutrophils were identified on the basis of different levels of their reactive oxygen metabolite generation, membrane permeability, activity of enzyme system, and ability to be inactivated. The cells of one subpopulation with high membrane permeability (neutrophil-killers) intensively generate reactive oxygen metabolites and are inactivated in consequence of interaction with the substrate, whereas cells of another subpopulation (neutrophil-cagers) produce reactive oxygen species less intensively, don't adhere to substrate and preserve their activity. Additional studies have shown that lung tumors can be infiltrated by various populations of neutrophils.
Two functionally unequal subpopulations of neutrophils were identified on the basis of different levels of their reactive oxygen metabolite generation, membrane permeability, activity of enzyme system, and ability to be inactivated. The cells of one subpopulation with high membrane permeability (neutrophil-killers) intensively generate reactive oxygen metabolites and are inactivated in consequence of interaction with the substrate, whereas cells of another subpopulation (neutrophil-cagers) produce reactive oxygen species less intensively, don't adhere to substrate and preserve their activity. Additional studies have shown that lung tumors can be infiltrated by various populations of neutrophils.
File:S1-Polymorphonuclear Cells with Conidia in Liquid Media.ogv, A rapidly moving neutrophil can be seen taking up several conidia over an imaging time of 2 hours with one frame every 30 seconds.
File:S15-Competitive Phagocytosis Assay in Collagen.ogg, A neutrophil can be seen here selectively taking up several ''Candida'' yeasts ( fluorescently labeled in green) despite several contacts with '' Aspergillus fumigatus'' conidia (unlabeled, white/clear) in a 3-D collagen matrix. Imaging time was 2 hours with one frame every 30 seconds.
Neutrophils display highly directional amoeboid motility in infected footpad and phalanges. Intravital imaging was performed in the footpad path of LysM-eGFP mice 20 minutes after infection with '' Listeria monocytogenes''.
File:Illu blood cell lineage.jpg, Blood cell lineage
File:Hematopoiesis (human) diagram en.svg, More complete lineages
Neutropenia InformationAbsolute Neutrophil Count CalculatorNeutrophil Trace Element Content and Distribution
{{DEFAULTSORT:Neutrophil Granulocyte Cell biology Granulocytes Phagocytes Human cells Articles containing video clips
stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of ...
s in the bone marrow and differentiated into subpopulations of neutrophil-killers and neutrophil-cagers. They are short-lived and highly mobile, as they can enter parts of tissue where other cells/molecules cannot. Neutrophils may be subdivided into segmented neutrophils and banded neutrophils (or bands). They form part of the polymorphonuclear cells family (PMNs) together with basophils and eosinophils.
The name ''neutrophil'' derives from staining characteristics on hematoxylin
Haematoxylin or hematoxylin (), also called natural black 1 or C.I. 75290, is a compound extracted from heartwood of the logwood tree ('' Haematoxylum campechianum'') with a chemical formula of . This naturally derived dye has been used as ...
and eosin ( H&E) histological or cytological preparations. Whereas basophilic white blood cells stain dark blue and eosinophilic white blood cells stain bright red, neutrophils stain a neutral pink. Normally, neutrophils contain a nucleus divided into 2–5 lobes.
Neutrophils are a type of phagocyte and are normally found in the blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
stream. During the beginning (acute
Acute may refer to:
Science and technology
* Acute angle
** Acute triangle
** Acute, a leaf shape in the glossary of leaf morphology
* Acute (medicine), a disease that it is of short duration and of recent onset.
** Acute toxicity, the adverse ef ...
) phase of inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
, particularly as a result of bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
l infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
, environmental exposure, and some cancers,
neutrophils are one of the first responders of inflammatory cells to migrate toward the site of inflammation. They migrate through the blood vessels and then through interstitial space, following chemical signals such as interleukin-8 (IL-8), C5a, fMLP, Leukotriene B4, and H2O2 in a process called chemotaxis. They are the predominant cells in pus, accounting for its whitish/yellowish appearance.
Neutrophils are recruited to the site of injury within minutes following trauma and are the hallmark of acute inflammation; however, due to some pathogens being indigestible, they might not be able to resolve certain infections without the assistance of other types of immune cells.
Structure
nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
* Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
' multilobulated shape (as compared to lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic a ...
s and monocyte
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and conventional dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also ...
s, the other types of white cells). The nucleus has a characteristic lobed appearance, the separate lobes connected by chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important ...
. The nucleolus disappears as the neutrophil matures, which is something that happens in only a few other types of nucleated cells. Up to 17% of female human neutrophil nuclei have a drumstick-shaped appendage which contains the inactivated X chromosome. In the cytoplasm, the Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles i ...
is small, mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used ...
and ribosomes are sparse, and the rough endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum ...
is absent. The cytoplasm also contains about 200 granules, of which a third are azurophilic.
Neutrophils will show increasing segmentation (many segments of the nucleus) as they mature. A normal neutrophil should have 3–5 segments. Hypersegmentation is not normal but occurs in some disorders, most notably vitamin B12 deficiency. This is noted in a manual review of the blood smear and is positive when most or all of the neutrophils have 5 or more segments.
 Neutrophils are the most abundant white blood cells in humans (approximately 1011 are produced daily); they account for approximately 50–70% of all white blood cells (leukocytes). The stated normal range for human blood counts varies between laboratories, but a neutrophil count of 2.5–7.5 × 109/L is a standard normal range. People of
Neutrophils are the most abundant white blood cells in humans (approximately 1011 are produced daily); they account for approximately 50–70% of all white blood cells (leukocytes). The stated normal range for human blood counts varies between laboratories, but a neutrophil count of 2.5–7.5 × 109/L is a standard normal range. People of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
n and Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
ern descent may have lower counts, which are still normal. A report may divide neutrophils into segmented neutrophils and bands.
When circulating in the bloodstream and inactivated, neutrophils are spherical. Once activated, they change shape and become more amorphous or amoeba-like and can extend pseudopods
A pseudopod or pseudopodium (plural: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a eukaryotic cell membrane that is emerged in the direction of movement. Filled with cytoplasm, pseudopodia primarily consist of actin filame ...
as they hunt for antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respon ...
s.
In 1973, Sanchez et al. found that the capacity of neutrophils to engulf bacteria is reduced when simple sugars like glucose, fructose as well as sucrose, honey and orange juice were ingested, while the ingestion of starches had no effect. Fasting, on the other hand, strengthened the neutrophils' phagocytic capacity to engulf bacteria. It was concluded that the function, and not the number, of phagocytes in engulfing bacteria was altered by the ingestion of sugars. In 2007 researchers at the Whitehead Institute of Biomedical Research found that given a selection of sugars on microbial surfaces, the neutrophils reacted to some types of sugars preferentially. The neutrophils preferentially engulfed and killed beta-1,6-glucan targets compared to beta-1,3-glucan targets.
Development
Life span
integrin
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle ...
-dependent adhesion in most cases, after which they migrate into tissues, where they survive for 1–2 days. Neutrophils have also been demonstrated to be released into the blood from a splenic reserve following myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which ma ...
.
Neutrophils are much more numerous than the longer-lived monocyte
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and conventional dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also ...
/ macrophage phagocytes. A pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a g ...
(disease-causing microorganism or virus) is likely to first encounter a neutrophil. Some experts hypothesize that the short lifetime of neutrophils is an evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
ary adaptation. The short lifetime of neutrophils minimizes propagation of those pathogens that parasitize phagocytes because the more time such parasites spend outside a host cell, the more likely they will be destroyed by some component of the body's defenses. Also, because neutrophil antimicrobial products can also damage host tissues, their short life limits damage to the host during inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
.
Neutrophils will be removed after phagocytosis of pathogens by macrophages. PECAM-1 and phosphatidylserine on the cell surface are involved in this process.
Function
Chemotaxis
Neutrophils undergo a process called chemotaxis via amoeboid movement, which allows them to migrate toward sites of infection or inflammation. Cell surface receptors allow neutrophils to detect chemical gradients of molecules such as interleukin-8 (IL-8),interferon gamma
Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. The existence of this interferon, which early in its history was known as immune interferon, was described by E. F. Wheelock ...
(IFN-γ), C3a, C5a, and Leukotriene B4, which these cells use to direct the path of their migration.
Neutrophils have a variety of specific receptors, including ones for complement, cytokines like interleukins and IFN-γ, chemokine
Chemokines (), or chemotactic cytokines, are a family of small cytokines or signaling proteins secreted by cells that induce directional movement of leukocytes, as well as other cell types, including endothelial and epithelial cells. In additi ...
s, lectins, and other proteins. They also express receptors to detect and adhere to endothelium
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the ve ...
and Fc receptors for opsonin.
In leukocytes responding to a chemoattractant
Chemotaxis (from '' chemo-'' + ''taxis'') is the movement of an organism or entity in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemica ...
, the cellular polarity is regulated by activities of small Rho
Rho (uppercase Ρ, lowercase ρ or ; el, ρο or el, ρω, label=none) is the 17th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 100. It is derived from Phoenician letter res . Its uppercase form uses the sa ...
guanosine triphosphatase
GTPases are a large family of hydrolase enzymes that bind to the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and hydrolyze it to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The GTP binding and hydrolysis takes place in the highly conserved P-loop "G domain", a pro ...
s ( Rho GTPases) and the phosphoinositide 3-kinases ( PI3Ks). In neutrophils, lipid products of PI3Ks regulate activation of Rac1, hematopoietic Rac2, and RhoG GTPases of the Rho family and are required for cell motility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy.
Definitions
Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms th ...
. Rac-GTPases regulate cytoskeletal dynamics and facilitate neutrophils adhesion, migration, and spreading. They accumulate asymmetrically to the plasma membrane at the leading edge of polarized cells. Spatially regulating Rho GTPases and organizing the leading edge of the cell, PI3Ks and their lipid products could play pivotal roles in establishing leukocyte polarity, as compass molecules that tell the cell where to crawl.
It has been shown in mice that in certain conditions neutrophils have a specific type of migration behaviour referred to as neutrophil swarming during which they migrate in a highly coordinated manner and accumulate and cluster to sites of inflammation.
Anti-microbial function
Being highly motile, neutrophils quickly congregate at a focus ofinfection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
, attracted by cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in au ...
s expressed by activated endothelium
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the ve ...
, mast cells, and macrophages. Neutrophils express and release cytokines, which in turn amplify inflammatory reactions by several other cell types.
In addition to recruiting and activating other cells of the immune system, neutrophils play a key role in the front-line defense against invading pathogens. Neutrophils have three methods for directly attacking micro-organisms: phagocytosis (ingestion), degranulation
Degranulation is a cellular process that releases antimicrobial cytotoxic or other molecules from secretory vesicles called granules found inside some cells. It is used by several different cells involved in the immune system, including gra ...
(release of soluble anti-microbials), and generation of neutrophil extracellular traps
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are networks of extracellular fibers, primarily composed of DNA from neutrophils, which bind pathogens. Neutrophils are the immune system's first line of defense against infection and have conventionally ...
(NETs).
Phagocytosis
 Neutrophils are phagocytes, capable of ingesting microorganisms or particles. For targets to be recognized, they must be coated in opsoninsa process known as antibody opsonization. They can internalize and kill many
Neutrophils are phagocytes, capable of ingesting microorganisms or particles. For targets to be recognized, they must be coated in opsoninsa process known as antibody opsonization. They can internalize and kill many microbe
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s, each phagocytic event resulting in the formation of a phagosome into which reactive oxygen species and hydrolytic enzymes are secreted. The consumption of oxygen during the generation of reactive oxygen species has been termed the " respiratory burst", although unrelated to respiration or energy production.
The respiratory burst involves the activation of the enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
NADPH oxidase, which produces large quantities of superoxide, a reactive oxygen species. Superoxide decays spontaneously or is broken down via enzymes known as superoxide dismutase
Superoxide dismutase (SOD, ) is an enzyme that alternately catalyzes the dismutation (or partitioning) of the superoxide () radical into ordinary molecular oxygen (O2) and hydrogen peroxide (). Superoxide is produced as a by-product of oxygen ...
s (Cu/ZnSOD and MnSOD), to hydrogen peroxide, which is then converted to hypochlorous acid (HClO), by the green heme enzyme myeloperoxidase. It is thought that the bactericidal properties of HClO are enough to kill bacteria phagocytosed by the neutrophil, but this may instead be a step necessary for the activation of proteases.
Though neutrophils can kill many microbes, the interaction of neutrophils with microbes and molecules produced by microbes often alters neutrophil turnover. The ability of microbes to alter the fate of neutrophils is highly varied, can be microbe-specific, and ranges from prolonging the neutrophil lifespan to causing rapid neutrophil lysis
Lysis ( ) is the breaking down of the membrane of a cell, often by viral, enzymic, or osmotic (that is, "lytic" ) mechanisms that compromise its integrity. A fluid containing the contents of lysed cells is called a ''lysate''. In molecular b ...
after phagocytosis. '' Chlamydia pneumoniae'' and '' Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' have been reported to delay neutrophil apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes in ...
.
Thus, some bacteriaand those that are predominantly intracellular pathogenscan extend the neutrophil lifespan by disrupting the normal process of spontaneous apoptosis and/or PICD (phagocytosis-induced cell death). On the other end of the spectrum, some pathogens such as '' Streptococcus pyogenes'' are capable of altering neutrophil fate after phagocytosis by promoting rapid cell lysis and/or accelerating apoptosis to the point of secondary necrosis. Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
Degranulation
Neutrophils also release an assortment of proteins in three types of granules by a process calleddegranulation
Degranulation is a cellular process that releases antimicrobial cytotoxic or other molecules from secretory vesicles called granules found inside some cells. It is used by several different cells involved in the immune system, including gra ...
. The contents of these granules have antimicrobial properties, and help combat infection. Glitter cell Glitter cells (also called Sternheimer-Malbin positive cells) are polymorphonuclear leukocyte neutrophils with granules that show a Brownian movement and that are found in the urine, most commonly associated with urinary tract infections or pyelon ...
s are polymorphonuclear leukocyte neutrophils with granules.
Neutrophil extracellular traps
In 2004, Brinkmann and colleagues described a striking observation that activation of neutrophils causes the release of web-like structures of DNA; this represents a third mechanism for killing bacteria. Theseneutrophil extracellular traps
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are networks of extracellular fibers, primarily composed of DNA from neutrophils, which bind pathogens. Neutrophils are the immune system's first line of defense against infection and have conventionally ...
(NETs) comprise a web of fibers composed of chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important ...
and serine proteases that trap and kill extracellular microbes. It is suggested that NETs provide a high local concentration of antimicrobial components and bind, disarm, and kill microbes independent of phagocytic uptake. In addition to their possible antimicrobial properties, NETs may serve as a physical barrier that prevents further spread of pathogens. Trapping of bacteria may be a particularly important role for NETs in sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
, where NETs are formed within blood vessels. Finally, NET formation has been demonstrated to augment macrophage bactericidal activity during infection. Recently, NETs have been shown to play a role in inflammatory diseases, as NETs could be detected in preeclampsia
Pre-eclampsia is a disorder of pregnancy characterized by the onset of high blood pressure and often a significant amount of protein in the urine. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In severe cases of the disease ...
, a pregnancy-related inflammatory disorder in which neutrophils are known to be activated. Neutrophil NET formation may also impact cardiovascular disease, as NETs may influence thrombus
A thrombus (plural thrombi), colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of ...
formation in coronary arteries
The coronary arteries are the arterial blood vessels of coronary circulation, which transport oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. The heart requires a continuous supply of oxygen to function and survive, much like any other tissue or organ ...
.
NETs are now known to exhibit pro- thrombotic effects both ''in vitro'' and ''in vivo''. More recently, in 2020 NETs were implicated in the formation of blood clots in cases of severe COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quick ...
.
Clinical significance
 Low neutrophil counts are termed '' neutropenia''. This can be congenital (developed at or before birth) or it can develop later, as in the case of aplastic anemia or some kinds of
Low neutrophil counts are termed '' neutropenia''. This can be congenital (developed at or before birth) or it can develop later, as in the case of aplastic anemia or some kinds of leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ...
. It can also be a side-effect of medication
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and ...
, most prominently chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemother ...
. Neutropenia makes an individual highly susceptible to infections. It can also be the result of colonization by intracellular neutrophilic parasites.
In alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (A1AD or AATD) is a genetic disorder that may result in lung disease or liver disease. Onset of lung problems is typically between 20 and 50 years of age. This may result in shortness of breath, wheezing, or an ...
, the important neutrophil elastase is not adequately inhibited by alpha 1-antitrypsin
Alpha-1 antitrypsin or α1-antitrypsin (A1AT, α1AT, A1A, or AAT) is a protein belonging to the serpin superfamily. It is encoded in humans by the ''SERPINA1'' gene. A protease inhibitor, it is also known as alpha1–proteinase inhibitor (A1PI) ...
, leading to excessive tissue damage in the presence of inflammation – the most prominent one being emphysema. Negative effects of elastase have also been shown in cases when the neutrophils are excessively activated (in otherwise healthy individuals) and release the enzyme in extracellular space. Unregulated activity of neutrophil elastase can lead to disruption of pulmonary barrier showing symptoms corresponding with acute lung injury. The enzyme also influences activity of macrophages by cleaving their toll-like receptors (TLRs) and downregulating cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in au ...
expression by inhibiting nuclear translocation of NF-κB.
In Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF), a mutation in the ''pyrin'' (or ''marenostrin
''MEFV'' (Mediterranean fever) is a human gene that provides instructions for making a protein called pyrin (also known as marenostrin). Pyrin is produced in certain white blood cells (neutrophils, eosinophils and monocytes) that play a role in i ...
'') gene, which is expressed mainly in neutrophil granulocytes, leads to a constitutively active acute-phase response and causes attacks of fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
, arthralgia, peritonitis, and – eventually – amyloidosis
Amyloidosis is a group of diseases in which abnormal proteins, known as amyloid fibrils, build up in tissue. There are several non-specific and vague signs and symptoms associated with amyloidosis. These include fatigue, peripheral edema, weig ...
.
Hyperglycemia can lead to neutrophil dysfunction. Dysfunction in the neutrophil biochemical pathway myeloperoxidase as well as reduced degranulation are associated with hyperglycemia.
The Absolute neutrophil count Absolute neutrophil count (ANC) is a measure of the number of neutrophil granulocytes (also known as polymorphonuclear cells, PMN's, polys, granulocytes, segmented neutrophils or segs) present in the blood. Neutrophils are a type of white blood ce ...
(ANC) is also used in diagnosis and prognosis. ANC is the gold standard for determining severity of neutropenia, and thus neutropenic fever. Any ANC < 1500 cells / mm3 is considered neutropenia, but <500 cells / mm3 is considered severe. There is also new research tying ANC to myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which ma ...
as an aid in early diagnosis. Neutrophils promote ventricular tachycardia in acute myocardial infarction.
In autopsy, the presence of neutrophils in the heart or brain is one of the first signs of infarction, and is therefore useful the diagnosis of myocardial infarction and stroke
A stroke is a disease, medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemorr ...
, and the timing thereof.
myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which ma ...
at approximately 12–24 hours,"This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ )" as seen in this
micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a m ...
.
File:Histopathology of thalamus infarction at approximately 24 hours, high magnification, annotated.jpg, In stroke
A stroke is a disease, medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemorr ...
, they are beginning to infiltrate the infarcted brain after 6 to 8 hours.
Neutrophil antigens
There are five (HNA 1–5) sets of neutrophil antigens recognized. The three HNA-1 antigens (a-c) are located on the low affinity Fc-γ receptor IIIb (FCGR3B : CD16b) The single known HNA-2a antigen is located on CD177. The HNA-3 antigen system has two antigens (3a and 3b) which are located on the seventh exon of the CLT2 gene ( SLC44A2). The HNA-4 and HNA-5 antigen systems each have two known antigens (a and b) and are located in the β2integrin
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle ...
. HNA-4 is located on the αM chain ( CD11b) and HNA-5 is located on the αL integrin unit (CD11a
Integrin, alpha L (antigen CD11A (p180), lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1; alpha polypeptide), also known as ITGAL, is a protein that in human is encoded by ''ITGAL'' gene. CD11a functions in the immune system. It is involved in cellular a ...
).
Subpopulations
Video
Additional images
References
External links
Neutropenia Information
{{DEFAULTSORT:Neutrophil Granulocyte Cell biology Granulocytes Phagocytes Human cells Articles containing video clips