Musica universalis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The ''musica universalis'' (literally universal music), also called music of the spheres or harmony of the spheres, is a philosophical concept that regards proportions in the movements of
The ''musica universalis'' (literally universal music), also called music of the spheres or harmony of the spheres, is a philosophical concept that regards proportions in the movements of
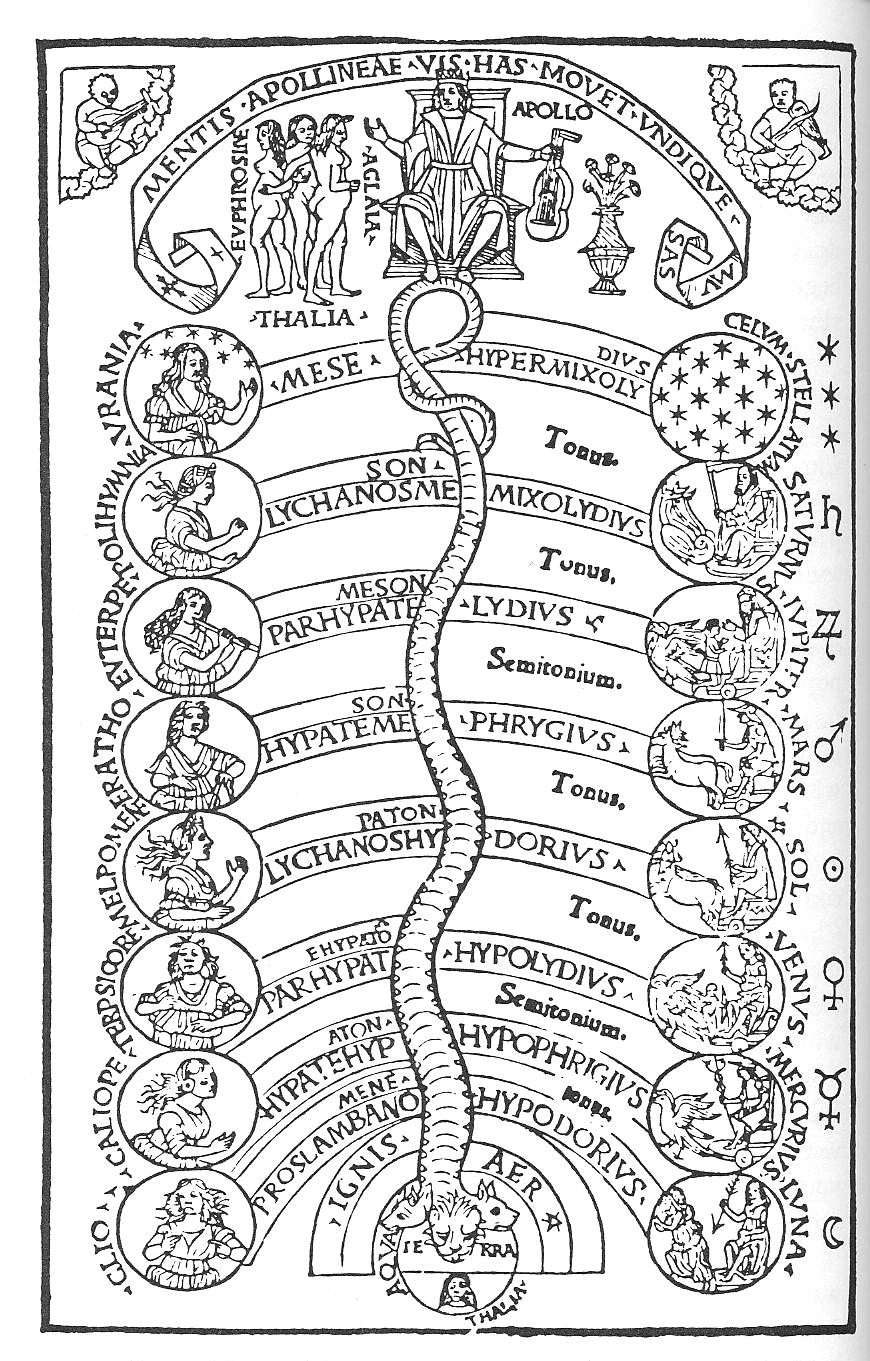 The concept of the "music of the spheres" incorporates the metaphysical principle that mathematical relationships express qualities or "tones" of energy which manifest in numbers, visual angles, shapes and sounds – all connected within a pattern of proportion. Pythagoras first identified that the pitch of a musical note is in inverse proportion to the length of the string that produces it, and that intervals between harmonious sound frequencies form simple numerical ratios. Pythagoras proposed that the Sun, Moon and planets all emit their own unique hum based on their orbital revolution, and that the quality of life on Earth reflects the tenor of celestial sounds which are physically imperceptible to the human ear. Subsequently, Plato described astronomy and music as "twinned" studies of sensual recognition: astronomy for the eyes, music for the ears, and both requiring knowledge of numerical proportions.
Aristotle characterised the theory as follows: Hosted at the Internet Classics Archive.
Aristotle rejected the idea, however, as incompatible with his own cosmological model, and on the grounds that "excessive noises ... shatter the solid bodies even of inanimate things", and therefore any sounds made by the planets would necessarily exert a tremendous physical force upon the body.
The concept of the "music of the spheres" incorporates the metaphysical principle that mathematical relationships express qualities or "tones" of energy which manifest in numbers, visual angles, shapes and sounds – all connected within a pattern of proportion. Pythagoras first identified that the pitch of a musical note is in inverse proportion to the length of the string that produces it, and that intervals between harmonious sound frequencies form simple numerical ratios. Pythagoras proposed that the Sun, Moon and planets all emit their own unique hum based on their orbital revolution, and that the quality of life on Earth reflects the tenor of celestial sounds which are physically imperceptible to the human ear. Subsequently, Plato described astronomy and music as "twinned" studies of sensual recognition: astronomy for the eyes, music for the ears, and both requiring knowledge of numerical proportions.
Aristotle characterised the theory as follows: Hosted at the Internet Classics Archive.
Aristotle rejected the idea, however, as incompatible with his own cosmological model, and on the grounds that "excessive noises ... shatter the solid bodies even of inanimate things", and therefore any sounds made by the planets would necessarily exert a tremendous physical force upon the body.
 ''Harmonices'' is split into five books, or chapters. The first and second books give a brief discussion on
''Harmonices'' is split into five books, or chapters. The first and second books give a brief discussion on
"The Music of the Spheres"
''In Our Time''. BBC Radio 4. June 19, 2008.
"The Harmony of the Spheres"
AudioCipher. December 31, 2021. {{DEFAULTSORT:Musica Universalis Acoustics Ancient astronomy Concepts in aesthetics Concepts in logic Concepts in metaphysics Concepts in the philosophy of science Early scientific cosmologies Esoteric cosmology History of education History of logic History of mathematics History of philosophy History of science Metaphysical theories Numerology Philosophical concepts Philosophical theories Philosophy of music Pythagorean philosophy
 The ''musica universalis'' (literally universal music), also called music of the spheres or harmony of the spheres, is a philosophical concept that regards proportions in the movements of
The ''musica universalis'' (literally universal music), also called music of the spheres or harmony of the spheres, is a philosophical concept that regards proportions in the movements of celestial bodies
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are often u ...
– the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
, Moon, and planets – as a form of music. The theory, originating in ancient Greece, was a tenet of Pythagoreanism, and was later developed by 16th-century astronomer Johannes Kepler. Kepler did not believe this "music" to be audible, but felt that it could nevertheless be heard by the soul. The idea continued to appeal to scholars until the end of the Renaissance, influencing many schools of thought, including humanism.
History
 The concept of the "music of the spheres" incorporates the metaphysical principle that mathematical relationships express qualities or "tones" of energy which manifest in numbers, visual angles, shapes and sounds – all connected within a pattern of proportion. Pythagoras first identified that the pitch of a musical note is in inverse proportion to the length of the string that produces it, and that intervals between harmonious sound frequencies form simple numerical ratios. Pythagoras proposed that the Sun, Moon and planets all emit their own unique hum based on their orbital revolution, and that the quality of life on Earth reflects the tenor of celestial sounds which are physically imperceptible to the human ear. Subsequently, Plato described astronomy and music as "twinned" studies of sensual recognition: astronomy for the eyes, music for the ears, and both requiring knowledge of numerical proportions.
Aristotle characterised the theory as follows: Hosted at the Internet Classics Archive.
Aristotle rejected the idea, however, as incompatible with his own cosmological model, and on the grounds that "excessive noises ... shatter the solid bodies even of inanimate things", and therefore any sounds made by the planets would necessarily exert a tremendous physical force upon the body.
The concept of the "music of the spheres" incorporates the metaphysical principle that mathematical relationships express qualities or "tones" of energy which manifest in numbers, visual angles, shapes and sounds – all connected within a pattern of proportion. Pythagoras first identified that the pitch of a musical note is in inverse proportion to the length of the string that produces it, and that intervals between harmonious sound frequencies form simple numerical ratios. Pythagoras proposed that the Sun, Moon and planets all emit their own unique hum based on their orbital revolution, and that the quality of life on Earth reflects the tenor of celestial sounds which are physically imperceptible to the human ear. Subsequently, Plato described astronomy and music as "twinned" studies of sensual recognition: astronomy for the eyes, music for the ears, and both requiring knowledge of numerical proportions.
Aristotle characterised the theory as follows: Hosted at the Internet Classics Archive.
Aristotle rejected the idea, however, as incompatible with his own cosmological model, and on the grounds that "excessive noises ... shatter the solid bodies even of inanimate things", and therefore any sounds made by the planets would necessarily exert a tremendous physical force upon the body.
Boethius
Anicius Manlius Severinus Boethius, commonly known as Boethius (; Latin: ''Boetius''; 480 – 524 AD), was a Roman senator, consul, ''magister officiorum'', historian, and philosopher of the Early Middle Ages. He was a central figure in the tra ...
, in his influential work ''De Musica'', described three categories of music:Boethius. ''De Institutione Musica'', I. 2.
* ''musica mundana'' (sometimes referred to as ''musica universalis'')
* ''musica humana'' (the internal music of the human body)
* ''musica quae in quibusdam constituta est instrumentis'' (sounds made by singers and instrumentalists)
Boethius believed that ''musica mundana'' could only be discovered through the intellect, but that the order found within it was the same as that found in audible music, and that both reflect the beauty of God.
''Harmonices Mundi''
' ''Musica universalis'' — which had existed as a metaphysical concept since the time of the Greeks — was often taught inquadrivium
From the time of Plato through the Middle Ages, the ''quadrivium'' (plural: quadrivia) was a grouping of four subjects or arts—arithmetic, geometry, music, and astronomy—that formed a second curricular stage following preparatory work in the ...
, and this intriguing connection between music and astronomy stimulated the imagination of Johannes Kepler as he devoted much of his time after publishing the ''Mysterium'' ''Cosmographicum'' (Mystery of the Cosmos), looking over tables and trying to fit the data to what he believed to be the true nature of the cosmos as it relates to musical sound. In 1619, Kepler published ''Harmonices Mundi'' (literally Harmony of the Worlds), expanding on the concepts he introduced in ''Mysterium'' and positing that musical intervals
In music theory, an interval is a difference in pitch between two sounds.
An interval may be described as horizontal, linear, or melodic if it refers to successively sounding tones, such as two adjacent pitches in a melody, and vertical or ha ...
and harmonies
In music, harmony is the process by which individual sounds are joined together or composed into whole units or compositions. Often, the term harmony refers to simultaneously occurring frequencies, pitches ( tones, notes), or chords. Howev ...
describe the motions of the six known planets of the time. He believed that this harmony — while inaudible — could be heard by the soul, and that it gave a "very agreeable feeling of bliss, afforded him by this music in the imitation of God." In ''Harmonices'', Kepler — who took issue with Pythagorean observations — laid out an argument for a Christian-centric creator who had made an explicit connection between geometry, astronomy, and music, and that the planets were arranged intelligently.
 ''Harmonices'' is split into five books, or chapters. The first and second books give a brief discussion on
''Harmonices'' is split into five books, or chapters. The first and second books give a brief discussion on regular polyhedron
A regular polyhedron is a polyhedron whose symmetry group acts transitively on its flags. A regular polyhedron is highly symmetrical, being all of edge-transitive, vertex-transitive and face-transitive. In classical contexts, many different equival ...
and their congruences
In abstract algebra, a congruence relation (or simply congruence) is an equivalence relation on an algebraic structure (such as a group, ring, or vector space) that is compatible with the structure in the sense that algebraic operations done wit ...
, reiterating the idea he introduced in ''Mysterium'' that the five regular solids known about since antiquity define the orbits of the planets and their distances from the sun. Book three focuses on defining musical harmonies, including consonance and dissonance
In music, consonance and dissonance are categorizations of simultaneous or successive sounds. Within the Western tradition, some listeners associate consonance with sweetness, pleasantness, and acceptability, and dissonance with harshness, unpl ...
, intervals (including the problems of just tuning), their relations to string length which was a discovery made by Pythagoras, and what makes music pleasurable to listen to in his opinion. In the fourth book, Kepler presents a metaphysical basis for this system, along with arguments as to why the harmony of the worlds appeals to the intellectual soul in the same manner that the harmony of music appeals to the human soul. Here, he also uses the naturalness of this harmony as an argument for heliocentrism. In book five, Kepler describes in detail the orbital motion of the planets and how this motion nearly perfectly matches musical harmonies. Finally, after a discussion on astrology
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Dif ...
in book five, Kepler ends ''Harmonices'' by describing his third law, which states that — for any planet — the cube of the semi-major axis of its elliptical orbit is proportional to the square of its orbital period.
In the final book of ''Harmonices'', Kepler explains how the ratio of the maximum and minimum angular speeds of each planet (i.e., its speeds at the perihelion and aphelion) is very nearly equivalent to a consonant musical interval. Furthermore, the ratios between these extreme speeds of the planets compared against each other create even more mathematical harmonies. These speeds explain the eccentricity of the orbits of the planets in a natural way that appealed to Kepler's religious beliefs in a heavenly creator.
While Kepler did believe that the harmony of the worlds was inaudible, he related the motions of the planets to musical concepts in book four of ''Harmonices''. He makes an analogy between comparing the extreme speeds of one planet and the extreme speeds of multiple planets with the difference between monophonic and polyphonic
Polyphony ( ) is a type of musical texture consisting of two or more simultaneous lines of independent melody, as opposed to a musical texture with just one voice, monophony, or a texture with one dominant melodic voice accompanied by chords, ...
music. Because planets with larger eccentricities have a greater variation in speed they produce more "notes." Earth's maximum and minimum speeds, for example, are in a ratio of roughly 16 to 15, or that of a semitone, whereas Venus' orbit is nearly circular, and therefore only produces a singular note. Mercury, which has the largest eccentricity, has the largest interval, a minor tenth, or a ratio of 12 to 5. This range, as well as the relative speeds between the planets, led Kepler to conclude that the Solar System was composed of two basses ( Saturn and Jupiter), a tenor ( Mars), two altos ( Venus and Earth), and a soprano ( Mercury), which had sung in "perfect concord," at the beginning of time, and could potentially arrange themselves to do so again. He was certain of the link between musical harmonies and the harmonies of the heavens and believed that "man, the imitator of the Creator," had emulated the polyphony of the heavens so as to enjoy "the continuous duration of the time of the world in a fraction of an hour."
Kepler was so convinced of a creator that he was convinced of the existence of this harmony despite a number of inaccuracies present in ''Harmonices''. Many of the ratios differed by an error greater than simple measurement error from the true value for the interval, and the ratio between Mars' and Jupiter's angular velocities does not create a consonant interval, though every other combination of planets does. Kepler brushed aside this problem by making the argument, with the math to support it, that because these elliptical paths had to fit into the regular solids described in ''Mysterium'' the values for both the dimensions of the solids and the angular speeds would have to differ from the ideal values to compensate. This change also had the benefit of helping Kepler retroactively explain why the regular solids encompassing each planet were slightly imperfect. Philosophers posited that the Creator liked variation in the celestial music.
Kepler's books are well-represented in the Library of Sir Thomas Browne, who also expressed a belief in the music of the spheres:
"For there is a musicke where-ever there is a harmony, order or proportion; and thus farre we may maintain the musick of the spheres; for those well ordered motions, and regular paces, though they give no sound unto the eare, yet to the understanding they strike a note most full of harmony. Whatsoever is harmonically composed, delights in harmony."
Orbital resonance
In celestial mechanics,orbital resonance
In celestial mechanics, orbital resonance occurs when orbiting bodies exert regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually because their orbital periods are related by a ratio of small integers. Most commonly, this relations ...
occurs when orbiting bodies exert regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually because their orbital periods are related by a ratio of small integers. This has been referred to as a "modern take" on the theory of ''musica universalis''. This idea has been further explored in a musical animation, created by an artist at the European Southern Observatory, of the planetary system TOI-178, which has five planets locked in a chain of orbital resonances.
Cultural influence
William Shakespeare makes reference to the music of the spheres in ''The Merchant of Venice
''The Merchant of Venice'' is a play by William Shakespeare, believed to have been written between 1596 and 1598. A merchant in Venice named Antonio defaults on a large loan provided by a Jewish moneylender, Shylock.
Although classified as a ...
:''
In the 1910s, Danish composer Rued Langgaard
Rued Langgaard (; born Rud Immanuel Langgaard; 28 July 1893 – 10 July 1952) was a late-Romantic Danish composer and organist. His then-unconventional music was at odds with that of his Danish contemporaries but was recognized 16 years afte ...
composed a pioneering orchestral work titled '' Music of the Spheres''.
Paul Hindemith
Paul Hindemith (; 16 November 189528 December 1963) was a German composer, music theorist, teacher, violist and conductor. He founded the Amar Quartet in 1921, touring extensively in Europe. As a composer, he became a major advocate of the '' ...
also made use of the concept in his 1957 opera, ''Die Harmonie der Welt
''Die Harmonie der Welt'' (''The Harmony of the World'') is an opera in five acts by Paul Hindemith. The German libretto was by the composer.
The title of the opera is taken from ''Harmonices Mundi'' by the astronomer Johannes Kepler (1571–1630 ...
'' ("The Harmony of the World"), based upon the life of Johannes Kepler.
A number of other modern compositions have been inspired by the concept of ''musica universalis''. Among these are ''Harmony of the Spheres'' by Neil Ardley
Neil Richard Ardley (26 May 1937 – 23 February 2004) was a prominent English jazz pianist and composer, who also made his name as the author of more than 100 popular books on science and technology, and on music.
Early years
Neil Ardle ...
, '' Music of the Spheres'' by Mike Oldfield
Mike may refer to:
Animals
* Mike (cat), cat and guardian of the British Museum
* Mike the Headless Chicken, chicken that lived for 18 months after his head had been cut off
* Mike (chimpanzee), a chimpanzee featured in several books and documen ...
, '' The Earth Sings Mi Fa Mi'' by The Receiving End of Sirens
The Receiving End of Sirens was an American rock band from Belchertown, Massachusetts, United States. Formed in 2003, the band broke up in 2008 then briefly reunited in 2010. On February 18, 2020, the band announced a brief reunion tour.
Over ...
, '' Music of the Spheres'' by Ian Brown, "Cosmogony
Cosmogony is any model concerning the origin of the cosmos or the universe.
Overview
Scientific theories
In astronomy, cosmogony refers to the study of the origin of particular astrophysical objects or systems, and is most commonly used i ...
" by Björk
Björk Guðmundsdóttir ( , ; born 21 November 1965), known mononymously as Björk, is an Icelandic singer, songwriter, composer, record producer, and actress. Noted for her distinct three-octave vocal range and eccentric persona, she has de ...
, and the Coldplay
Coldplay are a British Rock music, rock band formed in London in 1997. They consist of vocalist and pianist Chris Martin, guitarist Jonny Buckland, bassist Guy Berryman, drummer Will Champion and creative director Phil Harvey (manager), Phil H ...
album '' Music of the Spheres''.
'' Music of the Spheres'' was also the title of a companion piece to the video game '' Destiny'', composed by Martin O'Donnell, Michael Salvatori, and Paul McCartney.
See also
*Asteroseismology
Asteroseismology or astroseismology is the study of oscillations in stars. Stars have many resonant modes and frequencies, and the path of sound waves passing through a star depends on the speed of sound, which in turn depends on local temperature ...
* Plato's ''Timaeus''
* This Is My Father's World
* Titius–Bode law
The Titius–Bode law (sometimes termed just Bode's law) is a formulaic prediction of spacing between planets in any given solar system. The formula suggests that, extending outward, each planet should be approximately twice as far from the Sun as ...
* Sacred geometry
* Shabd
Notes
Sources
* * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Martineau, John (2002). ''A Little Book of Coincidence in the Solar System''. Gardener's Books. * * * *External links
"The Music of the Spheres"
''In Our Time''. BBC Radio 4. June 19, 2008.
"The Harmony of the Spheres"
AudioCipher. December 31, 2021. {{DEFAULTSORT:Musica Universalis Acoustics Ancient astronomy Concepts in aesthetics Concepts in logic Concepts in metaphysics Concepts in the philosophy of science Early scientific cosmologies Esoteric cosmology History of education History of logic History of mathematics History of philosophy History of science Metaphysical theories Numerology Philosophical concepts Philosophical theories Philosophy of music Pythagorean philosophy