minimum deviation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In a prism, the angle of deviation () decreases with increase in the angle of incidence () up to a particular angle. This angle of incidence where the angle of deviation in a prism is minimum is called the minimum deviation position of the prism and that very deviation angle is known as the minimum angle of deviation (denoted by , , or ).


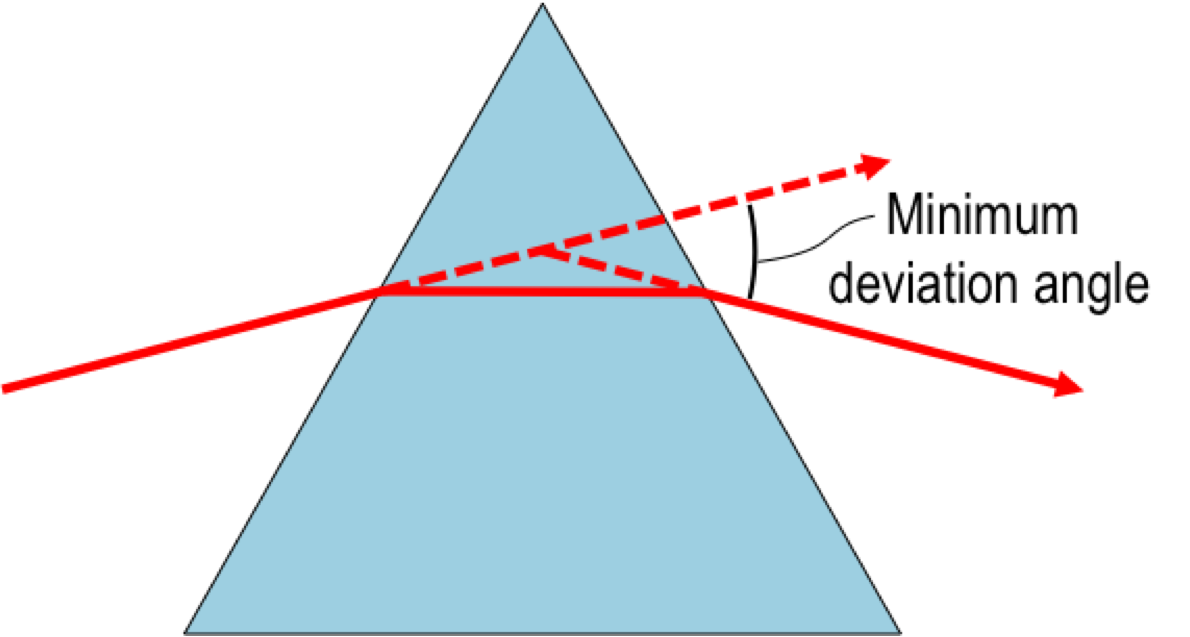 The angle of minimum deviation is related with the
The angle of minimum deviation is related with the
Part 1
an
Part 2
at
Refraction through a Prism
in NCERT Tectbook
Minimum Deviation by Prism
by Mark A Peterson,


 The angle of minimum deviation is related with the
The angle of minimum deviation is related with the refractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, ...
as:
This is useful to calculate the refractive index of a material. Rainbow and halo occur at minimum deviation. Also, a thin prism is always set at minimum deviation.
Formula
In minimum deviation, the refracted ray in the prism is parallel to its base. In other words, the light ray is symmetrical about the axis of symmetry of the prism. Also, the angles of refractions are equal i.e. . And, the angle of incidence and angle of emergence equal each other (). This is clearly visible in the graph below. The formula for minimum deviation can be derived by exploiting the geometry in the prism. The approach involves replacing the variables in theSnell's law
Snell's law (also known as Snell–Descartes law and ibn-Sahl law and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing throug ...
in terms of the Deviation and Prism Angles by making the use of the above properties.
From the angle sum of ,
Using the exterior angle theorem in ,
This can also be derived by putting in the prism formula:
From Snell's law
Snell's law (also known as Snell–Descartes law and ibn-Sahl law and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing throug ...
,
(where is the refractive index, is the Angle of Prism and is the Minimum Angle of Deviation.)
This is a convenient way used to measure the refractive index of a material(liquid or gas) by directing a light ray through a prism of negligible thickness at minimum deviation filled with the material or in a glass prism dipped in it.
Worked out examples:
Answer: 37°, 49°
Solution:
Here, ,
Plugging them in the above formula,
Also,
This is also apparent in the graph below.
Answer: 60°
Solution:
Here,
Using the above formula,
Also, the variation of the angle of deviation with an arbitrary angle of incidence can be encapsulated into a single equation by expressing in terms of in the prism formula using Snell's law:
Finding the minima of this equation will also give the same relation for minimum deviation as above.
For thin prism
In a thin or small angle prism, as the angles become very small, thesine
In mathematics, sine and cosine are trigonometric functions of an angle. The sine and cosine of an acute angle are defined in the context of a right triangle: for the specified angle, its sine is the ratio of the length of the side that is opp ...
of the angle nearly equals the angle itself and this yields many useful results.
Because and are very small,
Interestingly, using a similar approach with the Snell's law
Snell's law (also known as Snell–Descartes law and ibn-Sahl law and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing throug ...
and the prism formula for an in general thin-prism ends up in the very same result for the deviation angle.
Because , and are small,
From the prism formula,
Thus, it can be said that a thin prism is always in minimum deviation.
Experimental determination
Minimum deviation can be found manually or with spectrometer. Either the prism is kept fixed and the incidence angle is adjusted or the prism is rotated keeping the light source fixed.Minimum angle of dispersion
''The minimum angle of dispersion'' for white light is the difference in minimum deviation angle between red and violet rays of a light ray through a prism. For a thin prism, the deviation of violet light, is and that of red light, is . The difference in the deviation between red and violet light, is called the ''Angular Dispersion'' produced by the prism.Applications
One of the factors that causes a rainbow is the bunching of light rays at the minimum deviation angle that is close to the rainbow angle (42°). It is also responsible for phenomena like halos and sundogs, produced by the deviation of sunlight in mini prisms of hexagonal ice crystals in the air bending light with a minimum deviation of 22°.See also
{{Portal, physics * Prism *Refraction
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenomen ...
* Geometrical optics
Geometrical optics, or ray optics, is a model of optics that describes light propagation in terms of '' rays''. The ray in geometrical optics is an abstraction useful for approximating the paths along which light propagates under certain circumstan ...
References
External links
* Minimum DeviatioPart 1
an
Part 2
at
Khan Academy
Khan Academy is an American non-profit educational organization created in 2008 by Sal Khan. Its goal is creating a set of online tools that help educate students. The organization produces short lessons in the form of videos. Its website also i ...
Refraction through a Prism
in NCERT Tectbook
Minimum Deviation by Prism
by Mark A Peterson,
Mount Holyoke College
Mount Holyoke College is a private liberal arts women's college in South Hadley, Massachusetts. It is the oldest member of the historic Seven Sisters colleges, a group of elite historically women's colleges in the Northeastern United States. ...
Geometrical optics
Light