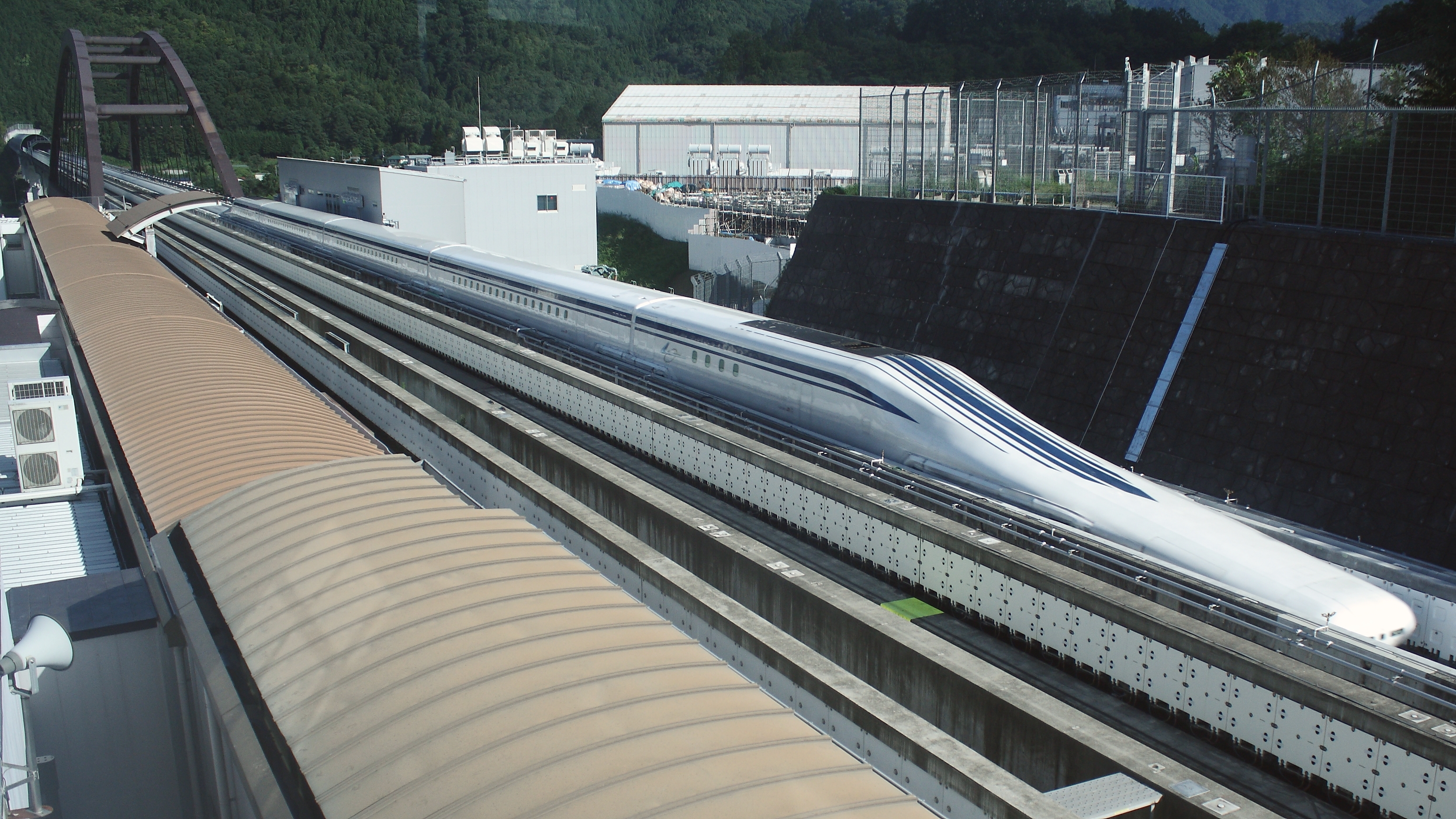


Maglev (derived from ''
magnetic levitation''), is a system of
train
In rail transport, a train (from Old French , from Latin , "to pull, to draw") is a series of connected vehicles that run along a railway track and transport people or freight. Trains are typically pulled or pushed by locomotives (often ...
transportation that uses two sets of
electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire wound into a coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated in ...
s: one set to repel and push the train up off the
track
Track or Tracks may refer to:
Routes or imprints
* Ancient trackway, any track or trail whose origin is lost in antiquity
* Animal track, imprints left on surfaces that an animal walks across
* Desire path, a line worn by people taking the shorte ...
, and another set to move the elevated train ahead, taking advantage of the lack of
friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:
*Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of ...
. Such trains rise approximately off the track. There are both high speed, intercity maglev systems (over ), and low speed, urban maglev systems ( to ) being built and under construction and development.
With maglev technology, the train travels along a guideway of electromagnets which control the train's stability and speed. While the propulsion and levitation require no moving parts, the
bogie
A bogie ( ) (in some senses called a truck in North American English) is a chassis or framework that carries a wheelset, attached to a vehicle—a modular subassembly of wheels and axles. Bogies take various forms in various modes of transp ...
s can move in relation to the main body of the vehicle and some technologies require support by retractable wheels at low speeds under . This compares with
electric multiple unit
An electric multiple unit or EMU is a multiple-unit train consisting of self-propelled carriages using electricity as the motive power. An EMU requires no separate locomotive, as electric traction motors are incorporated within one or a number ...
s that may have several dozen parts per bogie. Maglev trains can therefore in some cases be quieter and smoother than conventional trains and have the potential for much higher speeds.
Maglev vehicles have set
several speed records, and maglev trains can accelerate and decelerate much faster than conventional trains; the only practical limitation is the safety and comfort of the passengers, although
wind resistance
In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) is a force acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding flu ...
at very high speeds can cause running costs that are four to five times that of conventional high-speed rail (such as the
Tokaido Shinkansen). The power needed for levitation is typically not a large percentage of the overall energy consumption of a high-speed maglev system. Overcoming drag, which makes all open-air land transport more
energy intensive at higher speeds, takes the most energy.
Vactrain technology has been proposed as a means to overcome this limitation. Maglev systems have been much more expensive to construct than conventional train systems, although the simpler construction of maglev vehicles makes them cheaper to manufacture and maintain.
The
Shanghai maglev train, also known as the Shanghai Transrapid, has a top speed of . The line is the fastest operational high-speed maglev train, designed to connect
Shanghai Pudong International Airport
Shanghai Pudong International Airport is one of two international airports serving Shanghai and a major aviation hub of East Asia. Pudong Airport serves both international flights and a smaller number of domestic fights, while the city's oth ...
and the outskirts of central
Pudong
Pudong is a district of Shanghai located east of the Huangpu, the river which flows through central Shanghai. The name ''Pudong'' was originally applied to the Huangpu's east bank, directly across from the west bank or Puxi, the historic city ...
,
Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Chinese, Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four Direct-administered municipalities of China, direct-administered municipalities of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the ...
. It covers a distance of in just over 8minutes. For the first time, the launch generated wide public interest and media attention, propelling the popularity of the mode of transportation.
Despite over a century of research and development, maglev transport systems are now operational in just three countries (Japan, South Korea and China). The incremental benefits of maglev technology have often been considered hard to justify against cost and risk, especially where there is an existing or proposed conventional high-speed train line with spare passenger carrying capacity, such as
high-speed rail in Europe.
Development
In the late 1940s, the British electrical engineer
Eric Laithwaite, a professor at
Imperial College London
Imperial College London (legally Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine) is a public research university in London, United Kingdom. Its history began with Prince Albert, consort of Queen Victoria, who developed his vision for a cu ...
, developed the first full-size working model of the
linear induction motor. He became professor of heavy electrical engineering at Imperial College in 1964, where he continued his successful development of the linear motor. Since linear motors do not require physical contact between the vehicle and guideway, they became a common fixture on advanced transportation systems in the 1960s and 1970s. Laithwaite joined one such project, the
Tracked Hovercraft
Tracked Hovercraft was an experimental high speed train developed in the United Kingdom during the 1960s. It combined two British inventions, the hovercraft and linear induction motor, in an effort to produce a train system that would provide ...
, although the project was cancelled in 1973.
The linear motor was naturally suited to use with maglev systems as well. In the early 1970s, Laithwaite discovered a new arrangement of magnets, the
magnetic river, that allowed a single linear motor to produce both lift and forward thrust, allowing a maglev system to be built with a single set of magnets. Working at the
British Rail Research Division in
Derby
Derby ( ) is a city and unitary authority area in Derbyshire, England. It lies on the banks of the River Derwent in the south of Derbyshire, which is in the East Midlands Region. It was traditionally the county town of Derbyshire. Derby g ...
, along with teams at several civil engineering firms, the "transverse-flux" system was developed into a working system.
The first commercial maglev
people mover
A people mover or automated people mover (APM) is a type of small scale automated guideway transit system. The term is generally used only to describe systems serving relatively small areas such as airports, downtown districts or theme parks. ...
was simply called "
MAGLEV" and officially opened in 1984 near
Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the We ...
, England. It operated on an elevated section of monorail track between
Birmingham Airport
Birmingham Airport , formerly ''Birmingham International Airport'', is an international airport located east-southeast of Birmingham city centre, west-northwest of Coventry slightly north of Bickenhill village, in the Metropolitan Borou ...
and
Birmingham International railway station, running at speeds up to . The system was closed in 1995 due to reliability problems.
History
First maglev patent
High-speed transportation patents were granted to various inventors throughout the world.
[, 21 January 1972. Page 10 Column 1 Line 15 to Page 10 Column 2 Line 25.] The first relevant patent, (2 December 1902), issued to Albert C. Albertson, used magnetic levitation to take part of the weight off of the wheels while using conventional propulsion.
Early United States patents for a
linear motor
A linear motor is an electric motor that has had its stator and rotor "unrolled", thus, instead of producing a torque (rotation), it produces a linear force along its length. However, linear motors are not necessarily straight. Characteristica ...
propelled train were awarded to German inventor
Alfred Zehden. The inventor was awarded (14 February 1905) and (21 August 1907). In 1907, another early electromagnetic transportation system was developed by F. S. Smith.
[, 2 July 1907.] In 1908,
Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the United States, U.S. U.S. state, state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County, Ohio, Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along ...
mayor
Tom L. Johnson
Tom Loftin Johnson (July 18, 1854 – April 10, 1911) was an American industrialist, Georgist politician, and important figure of the Progressive Era and a pioneer in urban political and social reform. He was a U.S. Representative from 1891 to ...
filed a patent for a wheel-less "high-speed railway" levitated by an induced magnetic field.
[, 17 March 1914] Jokingly known as "Greased Lightning," the suspended car operated on a 90-foot test track in Johnson's basement "absolutely noiseless
yand without the least vibration." A series of German patents for magnetic levitation trains propelled by linear motors were awarded to
Hermann Kemper between 1937 and 1941. An early maglev train was described in , "Magnetic system of transportation", by G. R. Polgreen on 25 August 1959. The first use of "maglev" in a United States patent was in "Magnetic levitation guidance system"
[; 26 March 1973.] by Canadian Patents and Development Limited.
New York, United States, 1968
In 1959, while delayed in traffic on the
Throgs Neck Bridge
The Throgs Neck Bridge is a suspension bridge in New York City, carrying six lanes of Interstate 295 (I-295) over the East River where it meets the Long Island Sound. The bridge connects the Throggs Neck section of the Bronx with the Bay Ter ...
,
James Powell, a researcher at
Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL), thought of using magnetically levitated transportation.
Powell and BNL colleague
Gordon Danby
Gordon Thompson Danby (November 8, 1929 – August 2, 2016) was a Canadian-American physicist notable (together with Dr. James R. Powell) for his work on superconducting Maglev, for which he shared the Franklin Institute 'Medal 2000 for Engineer ...
worked out a maglev concept using static magnets mounted on a moving vehicle to induce electrodynamic lifting and stabilizing forces in specially shaped loops, such as
figure-of-8 coils on a guideway. These were patented in 1968–1969.
Japan, 1969–present
Japan operates two independently developed maglev trains. One is
HSST (and its descendant, the
Linimo
, formally the is a magnetic levitation train line in Aichi Prefecture, Japan, near the city of Nagoya
is the largest city in the Chūbu region, the fourth-most populous city and third most populous urban area in Japan, with a populatio ...
line) by
Japan Airlines and the other, which is more well known, is
SCMaglev
The SCMaglev (superconducting maglev, formerly called the MLU) is a magnetic levitation ( maglev) railway system developed by Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central) and the Railway Technical Research Institute.
On 21 April 2015, a manned s ...
by the
Central Japan Railway Company
is the main railway company operating in the Chūbu (Nagoya) region of central Japan. It is officially abbreviated in English as JR Central and in Japanese as JR Tōkai ( ja, JR東海, links=no). ''Tōkai'' is a reference to the geographical ...
.
The development of the latter started in 1969. Maglev trains on the
Miyazaki test track regularly hit by 1979. After an accident which destroyed the train, a new design was selected. In
Okazaki, Japan (1987), the SCMaglev was used for test rides at the Okazaki exhibition. Tests in Miyazaki continued throughout the 1980s, before transferring to a far longer test track, long, in Yamanashi in 1997. The track has since been extended to almost . The current world speed record for crewed trains was set there in 2015.
Development of
HSST started in 1974. In
Tsukuba
is a city located in Ibaraki Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 244,528 in 108,669 households and a population density of 862 persons per km². The percentage of the population aged over 65 was 20.3%. The total ar ...
, Japan (1985), the HSST-03 (
Linimo
, formally the is a magnetic levitation train line in Aichi Prefecture, Japan, near the city of Nagoya
is the largest city in the Chūbu region, the fourth-most populous city and third most populous urban area in Japan, with a populatio ...
) became popular at the
Tsukuba World Exposition, in spite of its low top speed. In
Saitama, Japan (1988), the HSST-04-1 was revealed at the Saitama exhibition in
Kumagaya
is a city located in Saitama Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 195,277 in 87,827 households and a population density of 1200 persons per km². The total area of the city is .
Geography
Kumagaya is one of the large ...
. Its fastest recorded speed was .
Construction of a new high-speed maglev line, the
Chuo Shinkansen, started in 2014. It is being built by extending the SCMaglev test track in Yamanashi in both directions. The completion date is currently unknown, with the most recent estimate of 2027 no longer possible following a local governmental rejection of a construction permit.
Hamburg, Germany, 1979
Transrapid 05 was the first maglev train with longstator propulsion licensed for passenger transportation. In 1979, a track was opened in
Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
for the first
International Transportation Exhibition (IVA 79). Interest was sufficient that operations were extended three months after the exhibition finished, having carried more than 50,000 passengers. It was reassembled in
Kassel
Kassel (; in Germany, spelled Cassel until 1926) is a city on the Fulda River in northern Hesse, Germany. It is the administrative seat of the Regierungsbezirk Kassel and the district of the same name and had 201,048 inhabitants in December 2020 ...
in 1980.
Ramenskoye, Moscow, USSR, 1979

In 1979 the
USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nati ...
town of
Ramenskoye (
Moscow oblast
Moscow Oblast ( rus, Моско́вская о́бласть, r=Moskovskaya oblast', p=mɐˈskofskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ), or Podmoskovye ( rus, Подмоско́вье, p=pədmɐˈskovʲjə, literally " under Moscow"), is a federal subject of R ...
) built an experimental test site for running experiments with cars on magnetic suspension. The test site consisted of a 60-metre ramp which was later extended to 980 metres. From the late 1970s to the 1980s five prototypes of cars were built that received designations from TP-01 (ТП-01) to TP-05 (ТП-05).
The early cars were supposed to reach the speed up to 100 km/h.
The construction of a maglev track using the technology from Ramenskoye started in
Armenian SSR
The Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic,; russian: Армянская Советская Социалистическая Республика, translit=Armyanskaya Sovetskaya Sotsialisticheskaya Respublika) also commonly referred to as Soviet A ...
in 1987 and was planned to be completed in 1991. The track was supposed to connect the cities of
Yerevan
Yerevan ( , , hy, Երևան , sometimes spelled Erevan) is the capital and largest city of Armenia and one of the world's oldest continuously inhabited cities. Situated along the Hrazdan River, Yerevan is the administrative, cultural, and i ...
and
Sevan via the city of
Abovyan. The original design speed was 250 km/h which was later lowered to 180 km/h. However, the
Spitak earthquake in 1988 and the
First Nagorno-Karabakh War
The First Nagorno-Karabakh War, referred to in Armenia as the Artsakh Liberation War ( hy, Արցախյան ազատամարտ, Artsakhyan azatamart) was an ethnic conflict, ethnic and territorial conflict that took place from February 1988 t ...
caused the project to freeze. In the end the overpass was only partially constructed.
In the early 1990s, the maglev theme was continued by the Engineering Research Center "TEMP" (ИНЦ "ТЭМП") this time by the order from the
Moscow government. The project was named V250 (В250). The idea was to build a high-speed maglev train to connect
Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
to the
Sheremetyevo airport. The train would consist of 64-seater cars and run at speeds up to 250 km/h.
[ In 1993, due to the ]financial crisis
A financial crisis is any of a broad variety of situations in which some financial assets suddenly lose a large part of their nominal value. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, many financial crises were associated with banking panics, and man ...
, the project was abandoned. However, from 1999 the "TEMP" research center had been participating as a co-developer in the creation of the linear motors for the Moscow Monorail
The Moscow Monorail (russian: Московский монорельс) is a monorail line located in the North-Eastern Administrative Okrug of Moscow, Russia. It runs from the Timiryazevskaya via Fonvisinskaya and VDNHa metro stations to Serge ...
system.
Birmingham, United Kingdom, 1984–1995
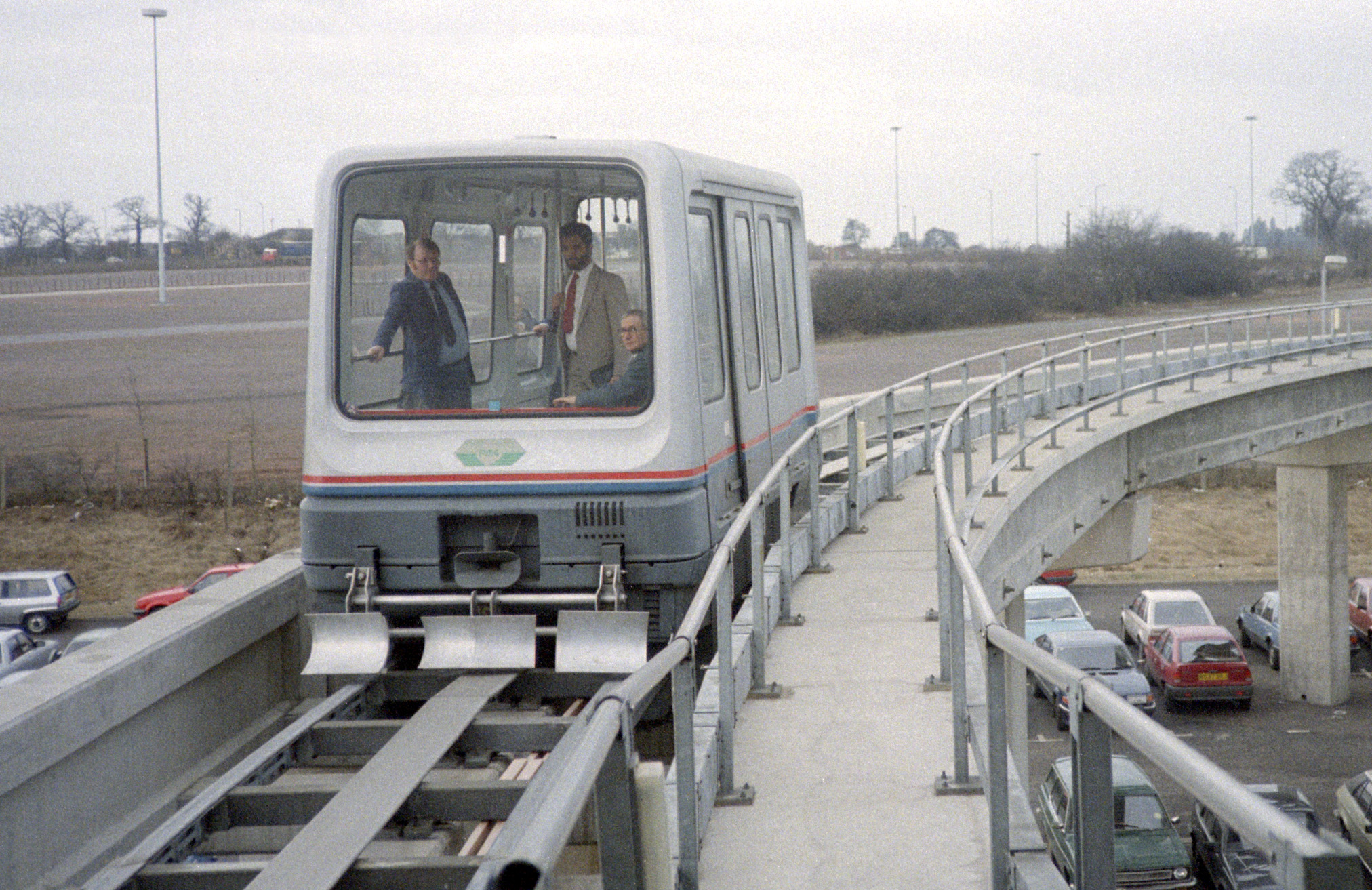 The world's first commercial maglev system was a low-speed maglev shuttle that ran between the airport terminal of Birmingham International Airport and the nearby Birmingham International railway station between 1984 and 1995. Its track length was , and trains levitated at an altitude of , levitated by electromagnets, and propelled with linear induction motors. It operated for 11 years and was initially very popular with passengers, but obsolescence problems with the electronic systems made it progressively unreliable as years passed, leading to its closure in 1995. One of the original cars is now on display at
The world's first commercial maglev system was a low-speed maglev shuttle that ran between the airport terminal of Birmingham International Airport and the nearby Birmingham International railway station between 1984 and 1995. Its track length was , and trains levitated at an altitude of , levitated by electromagnets, and propelled with linear induction motors. It operated for 11 years and was initially very popular with passengers, but obsolescence problems with the electronic systems made it progressively unreliable as years passed, leading to its closure in 1995. One of the original cars is now on display at Railworld
Railworld Wildlife Haven is a charity in Peterborough which has a nature haven, a model railway and other exhibits. It is located on a landscaped former coal storage yard which once served Peterborough Power Station.
It was founded by Rev. R ...
in Peterborough, together with the RTV31 hover train vehicle. Another is on display at the National Railway Museum in York.
Several favourable conditions existed when the link was built:
* The British Rail Research vehicle was 3 tonnes and extension to the 8-tonne vehicle was easy.
* Electrical power was available.
* The airport and rail buildings were suitable for terminal platforms.
* Only one crossing over a public road was required and no steep gradients were involved.
* Land was owned by the railway or airport.
* Local industries and councils were supportive.
* Some government finance was provided and because of sharing work, the cost per organization was low.
After the system closed in 1995, the original guideway lay dormant until 2003, when a replacement cable-hauled system, the AirRail Link Cable Liner people mover, was opened.
Emsland, Germany, 1984–2012
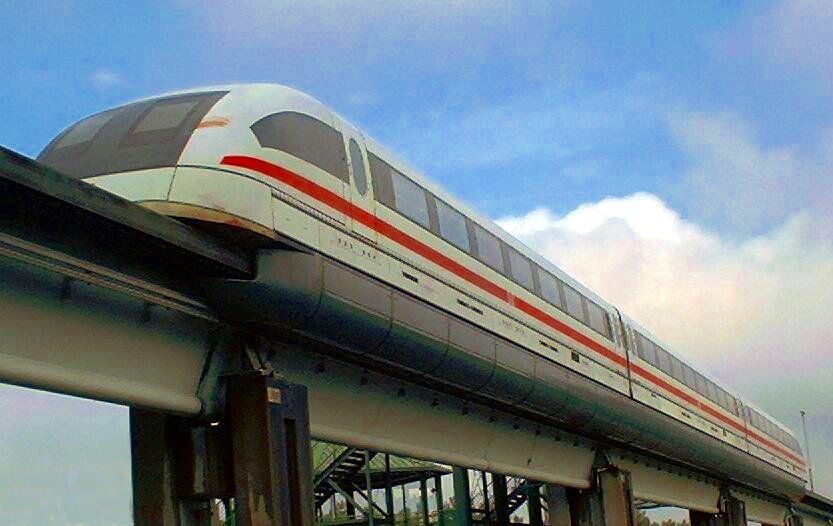 Transrapid, a German maglev company, had a test track in
Transrapid, a German maglev company, had a test track in Emsland
Landkreis Emsland () is a district in Lower Saxony, Germany named after the river Ems. It is bounded by (from the north and clockwise) the districts of Leer, Cloppenburg and Osnabrück, the state of North Rhine-Westphalia (district of Steinf ...
with a total length of . The single-track line ran between Dörpen and Lathen
Lathen is a municipality in the Emsland district, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is the location of the Emsland Transrapid Test facility, a testing site for Transrapid maglev trains.
See also
*2006 Lathen maglev train accident
On 22 September ...
with turning loops at each end. The trains regularly ran at up to . Paying passengers were carried as part of the testing process. The construction of the test facility began in 1980 and finished in 1984.
In 2006, the Lathen maglev train accident occurred, killing 23 people. It was found to have been caused by human error in implementing safety checks. From 2006 no passengers were carried. At the end of 2011 the operation licence expired and was not renewed, and in early 2012 demolition permission was given for its facilities, including the track and factory.
In March 2021 it was reported the CRRC was investigating reviving the Emsland test track. In May 2019 CRRC had unveiled its 'CRRC 600' prototype which is designed to reach .
Vancouver, Canada and Hamburg, Germany, 1986–88
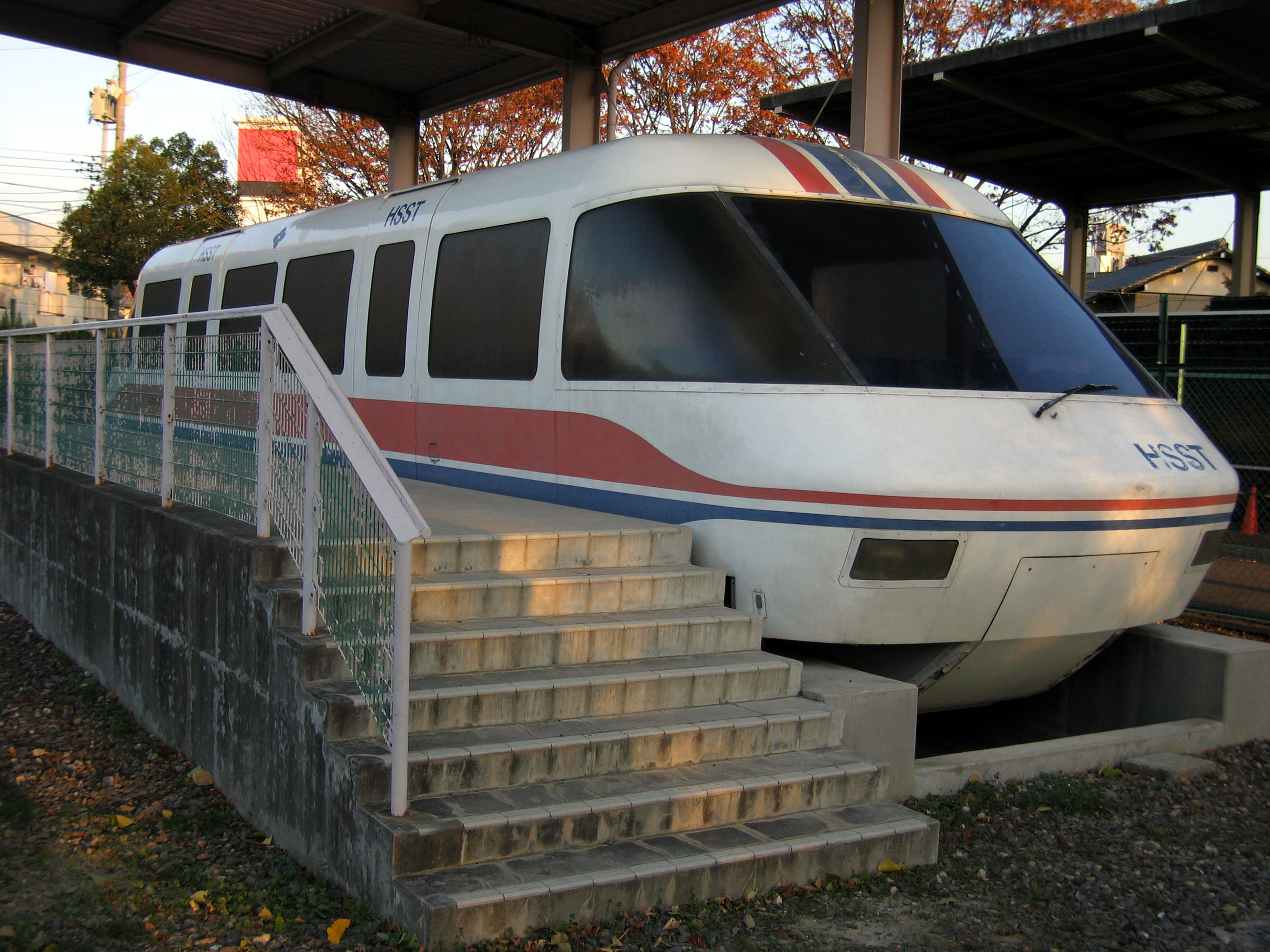 In Vancouver, Canada, the HSST-03 by HSST Development Corporation ( Japan Airlines and
In Vancouver, Canada, the HSST-03 by HSST Development Corporation ( Japan Airlines and Sumitomo Corporation
is one of the largest worldwide ''sogo shosha'' general trading companies, and is a diversified corporation. The company was incorporated in 1919 and is a member company of the Sumitomo Group.
It is listed on three Japanese stock exchanges ...
) was exhibited at Expo 86
The 1986 World Exposition on Transportation and Communication, or simply Expo 86, was a World's Fair held in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada from May 2 until October 13, 1986. The fair, the theme of which was "Transportation and Communicat ...
, and ran on a test track that provided guests with a ride in a single car along a short section of track at the fairgrounds. It was removed after the fair. It was shown at the Aoi Expo in 1987 and is now on static display at Okazaki Minami Park.
Berlin, Germany, 1984–1992
In West Berlin
West Berlin (german: Berlin (West) or , ) was a political enclave which comprised the western part of Berlin during the years of the Cold War. Although West Berlin was de jure not part of West Germany, lacked any sovereignty, and was under mi ...
, the M-Bahn was built in 1984. It was a driverless maglev system with a track connecting three stations. Testing with passenger traffic started in August 1989, and regular operation started in July 1991. Although the line largely followed a new elevated alignment, it terminated at Gleisdreieck U-Bahn station, where it took over an unused platform for a line that formerly ran to East Berlin
East Berlin was the ''de facto'' capital city of East Germany from 1949 to 1990. Formally, it was the Soviet sector of Berlin, established in 1945. The American, British, and French sectors were known as West Berlin. From 13 August 1961 u ...
. After the fall of the Berlin Wall
The Berlin Wall (german: Berliner Mauer, ) was a guarded concrete barrier that encircled West Berlin from 1961 to 1989, separating it from East Berlin and East Germany (GDR). Construction of the Berlin Wall was commenced by the gover ...
, plans were set in motion to reconnect this line (today's U2). Deconstruction of the M-Bahn line began only two months after regular service began and was completed during February 1992.
South Korea, 1993–present
 In 1993, South Korea completed the development of its own maglev train, shown off at the
In 1993, South Korea completed the development of its own maglev train, shown off at the Taejŏn Expo '93
Taejon Expo '93 was a three-month international exposition held between Saturday, August 7, 1993 and Sunday, November 7, 1993 in the central South Korean city of Daejeon (at the time spelled "Taejŏn").
Theme
The theme of the exposition was " ...
, which was developed further into a full-fledged maglev capable of travelling up to in 2006. This final model was incorporated in the Incheon Airport Maglev which opened on 3 February 2016, making South Korea the world's fourth country to operate its own self-developed maglev after the United Kingdom's Birmingham International Airport, Germany's Berlin M-Bahn, and Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
's Linimo
, formally the is a magnetic levitation train line in Aichi Prefecture, Japan, near the city of Nagoya
is the largest city in the Chūbu region, the fourth-most populous city and third most populous urban area in Japan, with a populatio ...
. It links Incheon International Airport to the Yongyu Station and Leisure Complex on Yeongjong island. It offers a transfer to the Seoul Metropolitan Subway
The Seoul Metropolitan Subway is a metropolitan railway system consisting of 23 rapid transit, light metro, commuter rail and people mover lines located in northwest South Korea. The system serves most of the Seoul Metropolitan Area inc ...
at AREX
AREX (Airport Railroad Express) is a South Korean commuter rail line that links Incheon International Airport with Seoul Station via Gimpo International Airport. The section between the two airports opened on March 23, 2007, and line was exten ...
's Incheon International Airport Station
Incheon International Airport Terminal 1 Station is a railway station on AREX and Incheon Airport Maglev. It is in Incheon International Airport's transport center near Terminal 1.
Both commuter("All-stop") and express services stop at this stati ...
and is offered free of charge to anyone to ride, operating between 9am and 6pm with 15-minute intervals.
The maglev system was co-developed by the South Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM) and Hyundai Rotem
Hyundai Rotem (founded in 1977) is a South Korean company that manufactures rolling stock, defense products and plant equipment. It is a part of the Hyundai Motor Group. Its name was changed from Rotem to Hyundai Rotem in December 2007 to refl ...
. It is long, with six stations and a operating speed.
Two more stages are planned of and . Once completed it will become a circular line.
Germany/China, 2010–present
Transport System Bögl
Transport System Bögl (TSB) is a maglev system for driverless trains developed by the German construction company Max Bögl since 2010. Its primary intended use is for short to medium distances (up to 30 km) and speeds up to 150 km/h for uses s ...
(TSB) is a driverless maglev system developed by the German construction company Max Bögl
Max Bögl is a German multinational major construction company based in Sengenthal, Germany.__NOTOC__
Projects
The company has carried out several major projects in transport infrastructure, civil engineering and sport venues. It has also pat ...
since 2010. Its primary intended use is for short to medium distances (up to 30 km) and speeds up to 150 km/h for uses such as airport shuttle
An airport bus, or airport shuttle bus or airport shuttle is a bus used to transport people to and from, or within airports. These vehicles will usually be equipped with larger luggage space, and incorporate special branding. They are also com ...
s. The company has been doing test runs on an 820-meter-long test track at their headquarters in Sengenthal
Sengenthal is a municipality in the district of Neumarkt in Bavaria in Germany. Local economy
Sengenthal is the headquarters of the construction company Max Bögl the developer of Transport System Bögl who also have a testing site in Sengentha ...
, Upper Palatinate
The Upper Palatinate (german: Oberpfalz, , ) is one of the seven administrative districts of Bavaria, Germany, and is located in the east of Bavaria.
Geography
The Upper Palatinate is a landscape with low mountains and numerous ponds and lak ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, since 2012 clocking over 100,000 tests covering a distance of over 65,000 km as of 2018.
In 2018 Max Bögl signed a joint venture with the Chinese company Chengdu Xinzhu Road & Bridge Machinery Co. with the Chinese partner given exclusive rights of production and marketing for the system in China. The joint venture constructed a demonstration line near Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), alternatively romanized as Chengtu, is a sub-provincial city which serves as the capital of the Chinese provin ...
, China, and two vehicles were airlifted there in June, 2020.
China, 2000-present
According to the International Maglev Board there are at least four maglev research programmes underway in China at the following institutions: Southwest Jiaotong University
Southwest Jiaotong University () is located in national central city Chengdu, Sichuan Province, affiliated to the Ministry of Education of the People's Republic of China. It's a national key university co-supported by the Ministry of Educatio ...
(Chengdu), Tongji University (Shanghai), CRRC Tangshan-Changchun Railway Vehicle Co. and Chengdu Aircraft Industry Group. The latest high speed prototype, unveiled in July 2021, was manufactured by CRRC Qingdao Sifang
CRRC Qingdao Sifang Co., Ltd. () is a Chinese rolling stock manufacturer based in Qingdao, Shandong province. Founded in 1900 during the German occupation, Qingdao Sifang is one of the oldest rolling stock manufacturers in China.
History
Qi ...
.
Low-to-medium speed
Development of the low-to-medium speed systems, that is, , by the CRRC has led to opening of operational lines such as the Changsha Maglev Express
The Changsha Maglev Express () is a medium-low speed magnetic levitation, or '' maglev'' line in Changsha, China. This is China's second maglev line, after Shanghai Maglev, and the first domestically built maglev line that uses indigenous tech ...
in 2016 and the Line S1 in Beijing in 2017.
In April 2020 a new model capable of and compatible with the Changsha line completed testing. The vehicle, under development since 2018, has a 30 percent increase in traction efficiency and a 60 percent increase in speed over the stock in use on the line since.
High speed
 There are currently two competing efforts into high-speed maglev systems, i.e., .
* The first is based on the Transrapid technology used in the Shanghai maglev train and is developed by the CRRC under license from Thyssen-Krupp.
There are currently two competing efforts into high-speed maglev systems, i.e., .
* The first is based on the Transrapid technology used in the Shanghai maglev train and is developed by the CRRC under license from Thyssen-Krupp.Southwest Jiaotong University
Southwest Jiaotong University () is located in national central city Chengdu, Sichuan Province, affiliated to the Ministry of Education of the People's Republic of China. It's a national key university co-supported by the Ministry of Educatio ...
in Chengdu, the design uses high-temperature superconducting magnets, is designed for and was demonstrated on a test track.
Technology
In the public imagination, "maglev" often evokes the concept of an elevated monorail
A monorail (from "mono", meaning "one", and " rail") is a railway in which the track consists of a single rail or a beam.
Colloquially, the term "monorail" is often used to describe any form of elevated rail or people mover. More accurat ...
track with a linear motor
A linear motor is an electric motor that has had its stator and rotor "unrolled", thus, instead of producing a torque (rotation), it produces a linear force along its length. However, linear motors are not necessarily straight. Characteristica ...
. Maglev systems may be monorail or dual rail—the SCMaglev
The SCMaglev (superconducting maglev, formerly called the MLU) is a magnetic levitation ( maglev) railway system developed by Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central) and the Railway Technical Research Institute.
On 21 April 2015, a manned s ...
MLX01 for instance uses a trench-like track—and not all monorail trains are maglevs. Some railway transport systems incorporate linear motors but use electromagnetism only for propulsion
Propulsion is the generation of force by any combination of pushing or pulling to modify the translational motion of an object, which is typically a rigid body (or an articulated rigid body) but may also concern a fluid. The term is derived f ...
, without levitating the vehicle. Such trains have wheels and are not maglevs. Maglev tracks, monorail or not, can also be constructed at grade or underground in tunnels. Conversely, non-maglev tracks, monorail or not, can be elevated or underground too. Some maglev trains do incorporate wheels and function like linear motor-propelled wheeled vehicles at slower speeds but levitate at higher speeds. This is typically the case with electrodynamic suspension
Electrodynamic suspension (EDS) is a form of magnetic levitation in which there are conductors which are exposed to time-varying magnetic fields. This induces eddy currents in the conductors that creates a repulsive magnetic field which holds the ...
maglev trains. Aerodynamic
Aerodynamics, from grc, ἀήρ ''aero'' (air) + grc, δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dyn ...
factors may also play a role in the levitation of such trains.
 The two main types of maglev technology are:
* Electromagnetic suspension (EMS), electronically controlled electromagnets in the train attract it to a magnetically conductive (usually steel) track.
*
The two main types of maglev technology are:
* Electromagnetic suspension (EMS), electronically controlled electromagnets in the train attract it to a magnetically conductive (usually steel) track.
* Electrodynamic suspension
Electrodynamic suspension (EDS) is a form of magnetic levitation in which there are conductors which are exposed to time-varying magnetic fields. This induces eddy currents in the conductors that creates a repulsive magnetic field which holds the ...
(EDS) uses superconducting electromagnets or strong permanent magnets that create a magnetic field, which induces currents in nearby metallic conductors when there is relative movement, which pushes and pulls the train towards the designed levitation position on the guide way.
Electromagnetic suspension (EMS)
 In electromagnetic suspension (EMS) systems, the train levitates above a steel rail while
In electromagnetic suspension (EMS) systems, the train levitates above a steel rail while electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire wound into a coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated in ...
s, attached to the train, are oriented toward the rail from below. The system is typically arranged on a series of C-shaped arms, with the upper portion of the arm attached to the vehicle, and the lower inside edge containing the magnets. The rail is situated inside the C, between the upper and lower edges.
Magnetic attraction varies inversely with the square of distance, so minor changes in distance between the magnets and the rail produce greatly varying forces. These changes in force are dynamically unstable—a slight divergence from the optimum position tends to grow, requiring sophisticated feedback systems to maintain a constant distance from the track, (approximately ).
The major advantage to suspended maglev systems is that they work at all speeds, unlike electrodynamic systems, which only work at a minimum speed of about . This eliminates the need for a separate low-speed suspension system, and can simplify track layout. On the downside, the dynamic instability demands fine track tolerances, which can offset this advantage. Eric Laithwaite was concerned that to meet required tolerances, the gap between magnets and rail would have to be increased to the point where the magnets would be unreasonably large.[ In practice, this problem was addressed through improved feedback systems, which support the required tolerances.
]
Electrodynamic suspension (EDS)
 In electrodynamic suspension (EDS), both the guideway and the train exert a magnetic field, and the train is levitated by the repulsive and attractive force between these magnetic fields.
In electrodynamic suspension (EDS), both the guideway and the train exert a magnetic field, and the train is levitated by the repulsive and attractive force between these magnetic fields.[ In addition, the attractive force varies in the opposite manner, providing the same adjustment effects. No active feedback control is needed.
However, at slow speeds, the current induced in these coils and the resultant magnetic flux is not large enough to levitate the train. For this reason, the train must have wheels or some other form of landing gear to support the train until it reaches take-off speed. Since a train may stop at any location, due to equipment problems for instance, the entire track must be able to support both low- and high-speed operation.
Another downside is that the EDS system naturally creates a field in the track in front and to the rear of the lift magnets, which acts against the magnets and creates magnetic drag. This is generally only a concern at low speeds, and is one of the reasons why JR abandoned a purely repulsive system and adopted the sidewall levitation system.][ Alternatively, propulsion coils on the guideway are used to exert a force on the magnets in the train and make the train move forward. The propulsion coils that exert a force on the train are effectively a linear motor: an alternating current through the coils generates a continuously varying magnetic field that moves forward along the track. The frequency of the alternating current is synchronized to match the speed of the train. The offset between the field exerted by magnets on the train and the applied field creates a force moving the train forward.
]
Tracks
The term "maglev" refers not only to the vehicles, but to the railway system as well, specifically designed for magnetic levitation and propulsion. All operational implementations of maglev technology make minimal use of wheeled train technology and are not compatible with conventional rail track
A railway track (British English and UIC terminology) or railroad track (American English), also known as permanent way or simply track, is the structure on a railway or railroad consisting of the rails, fasteners, railroad ties (sleeper ...
s. Because they cannot share existing infrastructure, maglev systems must be designed as standalone systems. The SPM maglev system is inter-operable with steel rail tracks and would permit maglev vehicles and conventional trains to operate on the same tracks.["Maglev: How they're Getting Trains off the Ground"](_blank)
''Popular Science'', December 1973 p. 135.
MAN
A man is an adult male human. Prior to adulthood, a male human is referred to as a boy (a male child or adolescent). Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chromo ...
in Germany also designed a maglev system that worked with conventional rails, but it was never fully developed.
Evaluation
Each implementation of the magnetic levitation principle for train-type travel involves advantages and disadvantages.
Neither Inductrack nor the Superconducting EDS are able to levitate vehicles at a standstill, although Inductrack provides levitation at much lower speed; wheels are required for these systems. EMS systems are wheel-free.
The German Transrapid, Japanese HSST (Linimo), and Korean Rotem EMS maglevs levitate at a standstill, with electricity extracted from guideway using power rails for the latter two, and wirelessly for Transrapid. If guideway power is lost on the move, the Transrapid is still able to generate levitation down to speed, using the power from onboard batteries. This is not the case with the HSST and Rotem systems.
Propulsion
EMS systems such as HSST/Linimo
, formally the is a magnetic levitation train line in Aichi Prefecture, Japan, near the city of Nagoya
is the largest city in the Chūbu region, the fourth-most populous city and third most populous urban area in Japan, with a populatio ...
can provide both levitation and propulsion
Propulsion is the generation of force by any combination of pushing or pulling to modify the translational motion of an object, which is typically a rigid body (or an articulated rigid body) but may also concern a fluid. The term is derived f ...
using an onboard linear motor. But EDS systems and some EMS systems such as Transrapid levitate but do not propel. Such systems need some other technology for propulsion. A linear motor (propulsion coils) mounted in the track is one solution. Over long distances coil costs could be prohibitive.
Stability
Earnshaw's theorem shows that no combination of static magnets can be in a stable equilibrium. Therefore a dynamic (time varying) magnetic field is required to achieve stabilization. EMS systems rely on active electronic stabilization that constantly measures the bearing distance and adjusts the electromagnet current accordingly. EDS systems rely on changing magnetic fields to create currents, which can give passive stability.
Because maglev vehicles essentially fly, stabilisation of pitch, roll and yaw is required. In addition to rotation, surge (forward and backward motions), sway (sideways motion) or heave (up and down motions) can be problematic.
Superconducting magnets on a train above a track made out of a permanent magnet lock the train into its lateral position. It can move linearly along the track, but not off the track. This is due to the Meissner effect and flux pinning
Flux pinning is a phenomenon that occurs when flux vortices in a type-II superconductor are prevented from moving within the bulk of the superconductor, so that the magnetic field lines are "pinned" to those locations. The superconductor must be a ...
.
Guidance system
Some systems use Null Current systems (also sometimes called Null Flux systems).[ These use a coil that is wound so that it enters two opposing, alternating fields, so that the average flux in the loop is zero. When the vehicle is in the straight ahead position, no current flows, but any moves off-line create flux that generates a field that naturally pushes/pulls it back into line.
]
Proposed technology enhancements
Evacuated tubes
Some systems (notably the Swissmetro
''Swissmetro'' is a proposed Swiss transportation system based on vacuum-train (also known as vactrain) technology. It was invented by Swiss engineer Rodolphe Nieth in 1974 and it is presently being promoted and developed as SwissMetro-NG ("NG" fo ...
system and the Hyperloop) propose the use of vactrains—maglev train technology used in evacuated (airless) tubes, which removes air drag. This has the potential to increase speed and efficiency greatly, as most of the energy for conventional maglev trains is lost to aerodynamic drag.
Rail-maglev hybrid
The Polish startup Hyperloop#Nevomo (previously Hyper Poland), Nevomo (previously ''Hyper Poland'') is developing a system for modifying existing railway tracks into a maglev system, on which conventional wheel-rail trains, as well maglev vehicles can travel. Vehicles on this so-called ‘magrail’ system will be able to reach speeds of up to 300 km/h at significantly lower infrastructure costs than stand-alone maglev lines. Similar to proposed #Evacuated tubes, Vactrain systems, magrail is designed to allow a later-stage upgrade with a vacuum cover which will enable vehicles to reach speeds of up to 600 km/h due to reduced air pressure, making the system similar to a hyperloop, but without the necessity for dedicated infrastructure corridors.
Energy use
Energy for maglev trains is used to accelerate the train. Energy may be regained when the train slows down via regenerative braking. It also levitates and stabilises the train's movement. Most of the energy is needed to overcome air drag. Some energy is used for air conditioning, heating, lighting and other miscellany.
At low speeds the percentage of power used for levitation can be significant, consuming up to 15% more power than a subway or light rail service. For short distances the energy used for acceleration might be considerable.
The force used to overcome air drag increases with the square of the velocity and hence dominates at high speed. The energy needed per unit distance increases by the square of the velocity and the time decreases linearly. However power increases by the cube of the velocity. For example, 2.37 times as much power is needed to travel at than , while drag increases by 1.77 times the original force.
Aircraft take advantage of lower air pressure and lower temperatures by cruising at altitude to reduce energy consumption but unlike trains need to aviation fuel, carry fuel on board. This has led to the suggestion of vactrain, conveying maglev vehicles through partially evacuated tubes.
High-speed maglev comparison with conventional high speed trains
Maglev transport is non-contact and electric powered. It relies less or not at all on the wheels, bearings and axles common to wheeled rail systems.Central Japan Railway Company
is the main railway company operating in the Chūbu (Nagoya) region of central Japan. It is officially abbreviated in English as JR Central and in Japanese as JR Tōkai ( ja, JR東海, links=no). ''Tōkai'' is a reference to the geographical ...
SCMaglev
The SCMaglev (superconducting maglev, formerly called the MLU) is a magnetic levitation ( maglev) railway system developed by Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central) and the Railway Technical Research Institute.
On 21 April 2015, a manned s ...
use rubber tires at low speeds, reducing efficiency gains.
* Weight: The electromagnets in many EMS and EDS designs require between 1 and 2 kilowatts per ton. The use of superconductor magnets can reduce the electromagnets' energy consumption. A 50-ton Transrapid maglev vehicle can lift an additional 20 tons, for a total of 70 tons, which consumes . Most energy use for the TRI is for propulsion and overcoming air resistance at speeds over .
* Weight loading: High-speed rail requires more support and construction for its concentrated wheel loading. Maglev cars are lighter and distribute weight more evenly.
* Noise: Because the major source of noise of a maglev train comes from displaced air rather than from wheels touching rails, maglev trains produce less noise than a conventional train at equivalent speeds. However, the psychoacoustic profile of the maglev may reduce this benefit: a study concluded that maglev noise should be rated like road traffic, while conventional trains experience a 5–10 dB "bonus", as they are found less annoying at the same loudness level.
High-speed maglev comparison with aircraft
Differences between airplane and maglev travel:
* Efficiency: For maglev systems the lift-to-drag ratio can exceed that of aircraft (for example Inductrack can approach 200:1 at high speed, far higher than any aircraft). This can make maglevs more efficient per kilometer. However, at high cruising speeds, aerodynamic drag is much larger than lift-induced drag. Jet-powered aircraft take advantage of low air density at high altitudes to significantly reduce air drag. Hence despite their lift-to-drag ratio disadvantage, they can travel more efficiently at high speeds than maglev trains that operate at sea level.
* Routing: Maglevs offer competitive journey times for distances of or less. Additionally, maglevs can easily serve intermediate destinations.
* Availability: Maglevs are little affected by weather.
* Travel time: Maglevs do not face the extended security protocols faced by air travelers nor is time consumed for taxiing, or for queuing for take-off and landing.
Economics
As more maglev systems are deployed, experts expect construction costs to drop by employing new construction methods and from economies of scale.
High speed systems
The Shanghai maglev demonstration line cost US$1.2 billion to build in 2004.
Low speed systems
The Japanese Linimo
, formally the is a magnetic levitation train line in Aichi Prefecture, Japan, near the city of Nagoya
is the largest city in the Chūbu region, the fourth-most populous city and third most populous urban area in Japan, with a populatio ...
HSST, cost approximately US$100 million/km to build.
Nagoya builds Maglev Metro
'', International Railway Journal, May 2004.
Records
The highest-recorded maglev speed is , achieved in Japan by JR Central's L0 superconducting maglev on 21 April 2015,
History of maglev speed records
Systems
Operational systems
High speed
= Shanghai Maglev (2003)
=
The Shanghai Maglev Train, also known as the Transrapid, has a top speed of . The line is the fastest, first commercially successful, operational Maglev train designed to connect Shanghai Pudong International Airport
Shanghai Pudong International Airport is one of two international airports serving Shanghai and a major aviation hub of East Asia. Pudong Airport serves both international flights and a smaller number of domestic fights, while the city's oth ...
and the outskirts of central Pudong
Pudong is a district of Shanghai located east of the Huangpu, the river which flows through central Shanghai. The name ''Pudong'' was originally applied to the Huangpu's east bank, directly across from the west bank or Puxi, the historic city ...
, Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Chinese, Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four Direct-administered municipalities of China, direct-administered municipalities of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the ...
. It covers a distance of in 7 or 8 minutes.
Low speed
= Linimo (Tobu Kyuryo Line, Japan) (2005)
=
 The commercial automation, automated "Urban Maglev" system commenced operation in March 2005 in Aichi, Japan. The Tobu Kyuryo Line, otherwise known as the
The commercial automation, automated "Urban Maglev" system commenced operation in March 2005 in Aichi, Japan. The Tobu Kyuryo Line, otherwise known as the Linimo
, formally the is a magnetic levitation train line in Aichi Prefecture, Japan, near the city of Nagoya
is the largest city in the Chūbu region, the fourth-most populous city and third most populous urban area in Japan, with a populatio ...
line, covers . It has a minimum operating radius of and a maximum gradient of 6%. The linear-motor magnetically levitated train has a top speed of . More than 10 million passengers used this "urban maglev" line in its first three months of operation. At 100 km/h, it is sufficiently fast for frequent stops, has little or no noise impact on surrounding communities, can navigate short radius rights of way, and operates during inclement weather. The trains were designed by the Chubu HSST Development Corporation, which also operates a test track in Nagoya.
= Daejeon Expo Maglev (2008)
=
The first maglev test trials using electromagnetic suspension opened to public was HML-03, made by Hyundai Heavy Industries for the Taejŏn Expo '93, Daejeon Expo in 1993, after five years of research and manufacturing two prototypes, HML-01 and HML-02.
= Incheon Airport Maglev (2016)
=
The Incheon Airport Maglev began commercial operation on 3 February 2016.Linimo
, formally the is a magnetic levitation train line in Aichi Prefecture, Japan, near the city of Nagoya
is the largest city in the Chūbu region, the fourth-most populous city and third most populous urban area in Japan, with a populatio ...
, it has a more futuristic design thanks to it being lighter with construction costs cut to half.
= Changsha Maglev (2016)
=
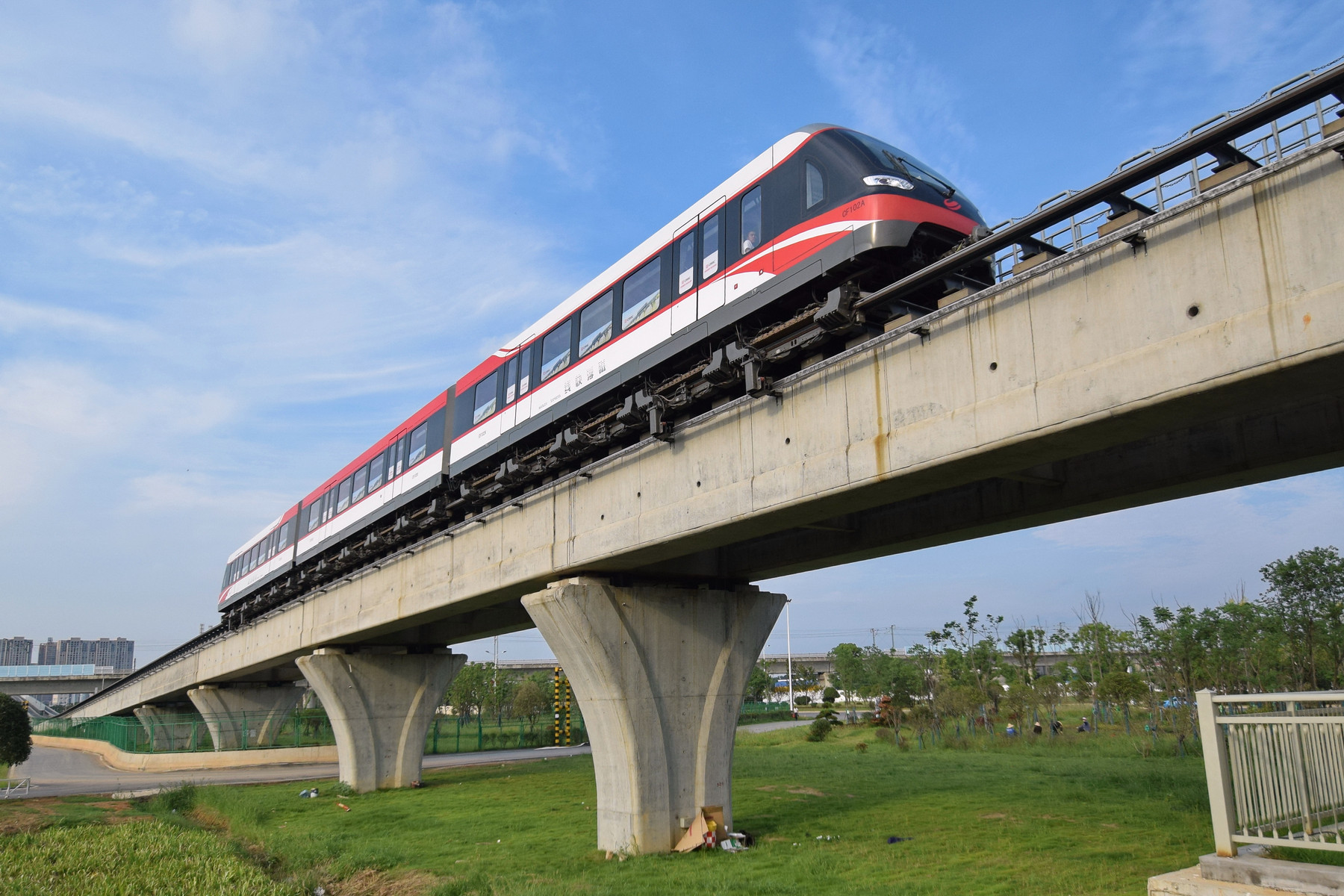 The Hunan provincial government launched the construction of a maglev line between Changsha Huanghua International Airport and Changsha South Railway Station, covering a distance of 18.55 km. Construction started in May 2014 and was completed by the end of 2015. Trial runs began on 26 December 2015 and trial operations started on 6 May 2016. As of 13 June 2018 the Changsha maglev had covered a distance of 1.7 million km and carried nearly 6 million passengers. A second generation of these vehicles has been produced which have a top speed of . In July 2021 the new model entered service operating at a top speed of , which reduced the travel time by 3 minutes.
The Hunan provincial government launched the construction of a maglev line between Changsha Huanghua International Airport and Changsha South Railway Station, covering a distance of 18.55 km. Construction started in May 2014 and was completed by the end of 2015. Trial runs began on 26 December 2015 and trial operations started on 6 May 2016. As of 13 June 2018 the Changsha maglev had covered a distance of 1.7 million km and carried nearly 6 million passengers. A second generation of these vehicles has been produced which have a top speed of . In July 2021 the new model entered service operating at a top speed of , which reduced the travel time by 3 minutes.
= Beijing S1 Line (2017)
=
Beijing has built China's second low-speed maglev line, S1 Line, Beijing Subway, using technology developed by National University of Defense Technology. The line was opened on 30 December 2017.
The line operates at speeds up to 100 km/h.
Fenghuang Maglev (2022)
Fenghuang Maglev (凤凰磁浮) is a medium- to low-speed maglev line in Fenghuang County, Xiangxi Tujia and Miao Autonomous Prefecture, Xiangxi, Hunan province, China. The line operates at speeds up to 100 km/h. The first phase is 9.12 km with 4 stations (and 2 more future infill stations). The first phase opened on 30 July 2022 and connects the Fenghuang railway station on the Zhangjiajie–Jishou–Huaihua high-speed railway with the Fenghuang Folklore Garden.
Maglevs under construction
Chūō Shinkansen (Japan)
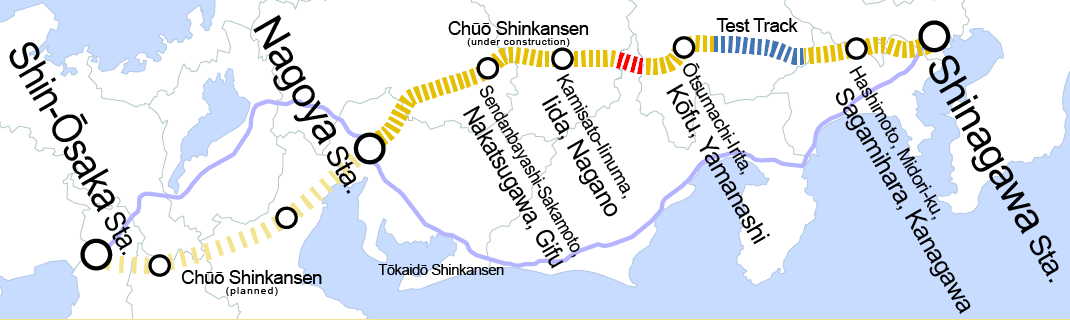 The Chuo Shinkansen is a high-speed maglev line in Japan. Construction began in 2014, commercial operations was expected to start by 2027. The 2027 target was given up in July 2020. The Linear Chuo Shinkansen Project aims to connect Tokyo and Osaka by way of Nagoya, the capital city of Aichi Prefecture, Aichi, in approximately one hour, less than half the travel time of the fastest existing bullet trains connecting the three metropolises. The full track between Tokyo and Osaka was originally expected to be completed in 2045, but the operator is now aiming for 2037.
The L0 Series train type is undergoing testing by the
The Chuo Shinkansen is a high-speed maglev line in Japan. Construction began in 2014, commercial operations was expected to start by 2027. The 2027 target was given up in July 2020. The Linear Chuo Shinkansen Project aims to connect Tokyo and Osaka by way of Nagoya, the capital city of Aichi Prefecture, Aichi, in approximately one hour, less than half the travel time of the fastest existing bullet trains connecting the three metropolises. The full track between Tokyo and Osaka was originally expected to be completed in 2045, but the operator is now aiming for 2037.
The L0 Series train type is undergoing testing by the Central Japan Railway Company
is the main railway company operating in the Chūbu (Nagoya) region of central Japan. It is officially abbreviated in English as JR Central and in Japanese as JR Tōkai ( ja, JR東海, links=no). ''Tōkai'' is a reference to the geographical ...
(JR Central) for eventual use on the Chūō Shinkansen line. It set a crewed Land speed record for rail vehicles, world speed record of on 21 April 2015.
Qingyuan Maglev (China)
Qingyuan Maglev (清远磁浮旅游专线) is a medium- to low-speed maglev line in Qingyuan, Guangdong province, China. The line will operate at speeds up to 100 km/h.[ The first phase is 8.1 km with 3 stations (and 1 more future infill station).]
Test tracks
AMT test track – Powder Springs, Georgia, USA
A second prototype system in Powder Springs, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, USA, was built by American Maglev Technology, Inc. The test track is long with a curve. Vehicles are operated up to , below the proposed operational maximum of . A June 2013 review of the technology called for an extensive testing program to be carried out to ensure the system complies with various regulatory requirements including the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) People Mover Standard. The review noted that the test track is too short to assess the vehicles' dynamics at the maximum proposed speeds.
FTA's UMTD program, USA
In the US, the Federal Transit Administration (FTA) Urban Maglev Technology Demonstration program funded the design of several low-speed urban maglev demonstration projects. It assessed HSST for the Maryland Department of Transportation and maglev technology for the Colorado Department of Transportation. The FTA also funded work by General Atomics at California University of Pennsylvania to evaluate the MagneMotion M3 and of the Maglev2000 of Florida superconducting EDS system. Other US urban maglev demonstration projects of note are the LEVX in Washington State and the Massachusetts-based Magplane.
San Diego, California USA
General Atomics has a test facility in San Diego, that is used to test Union Pacific's freight shuttle in Los Angeles. The technology is "passive" (or "permanent"), using permanent magnets in a Halbach array for lift and requiring no electromagnets for either levitation or propulsion. General Atomics received US$90 million in research funding from the federal government. They are also considering their technology for high-speed passenger services.
SCMaglev, Yamanashi Japan
Japan has a demonstration line in Yamanashi prefecture where test train SCMaglev L0 Series Shinkansen reached , faster than any wheeled trains.[ In comparison, Transrapid uses conventional electromagnets and attractive (force), attractive-type electromagnetic suspension (EMS).]
Sengenthal, Germany and Chengdu, China
Transport System Bögl
Transport System Bögl (TSB) is a maglev system for driverless trains developed by the German construction company Max Bögl since 2010. Its primary intended use is for short to medium distances (up to 30 km) and speeds up to 150 km/h for uses s ...
, a division of German construction company Max Bögl, has built a test track in Sengenthal
Sengenthal is a municipality in the district of Neumarkt in Bavaria in Germany. Local economy
Sengenthal is the headquarters of the construction company Max Bögl the developer of Transport System Bögl who also have a testing site in Sengentha ...
, Bavaria, Germany. In appearance, it's more like the German M-Bahn than the Transrapid system.
The vehicle tested on the track is patented in the US by Max Bögl. The company is also in a Transport System Bögl#Chinese joint venture, joint venture with a Chinese firm. A demonstration line has been built near Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), alternatively romanized as Chengtu, is a sub-provincial city which serves as the capital of the Chinese provin ...
, China and two vehicles were airlifted there in June, 2000.
Southwest Jiaotong University, China
On 31 December 2000, the first crewed high-temperature superconducting maglev was tested successfully at Southwest Jiaotong University
Southwest Jiaotong University () is located in national central city Chengdu, Sichuan Province, affiliated to the Ministry of Education of the People's Republic of China. It's a national key university co-supported by the Ministry of Educatio ...
, Chengdu, China. This system is based on the principle that bulk high-temperature superconductors can be levitated stably above or below a permanent magnet. The load was over and the levitation gap over . The system uses liquid nitrogen to cool the superconductor.
Jiading Campus of Tongji University, China
A maglev :de:CM1 Dolphin#test track, test track has been operating since 2006 at the Jiading Campus of Tongji University, northwest of Shanghai. The track uses the same design as the operating Shanghai Maglev. Top speed is restricted to due to the length of track and its topology.
Proposed maglev systems
Many maglev systems have been proposed in North America, Asia and Europe. Many are in the early planning stages or were explicitly rejected.
Australia
;Sydney-Illawarra
A maglev route was proposed between Sydney and Wollongong. The proposal came to prominence in the mid-1990s. The Sydney–Wollongong commuter corridor is the largest in Australia, with upwards of 20,000 people commuting each day. Current trains use the Eastern Suburbs & Illawarra railway line, Illawarra line, between the cliff face of the Illawarra escarpment and the Pacific Ocean, with travel times about 2 hours. The proposal would cut travel times to 20 minutes.
;Melbourne
 In late 2008, a proposal was put forward to the Government of Victoria to build a privately funded and operated maglev line to service the Greater Melbourne metropolitan area in response to the Eddington Transport Report, Victoria, Eddington Transport Report that did not investigate above-ground transport options. The maglev would service a population of over 4 million and the proposal was costed at A$8 billion.
However, despite road congestion and Australia's highest roadspace per capita, the government dismissed the proposal in favour of road expansion including an A$8.5 billion road tunnel, $6 billion extension of the EastLink (Melbourne), Eastlink to the Western Ring Road and a $700 million Frankston Bypass.
In late 2008, a proposal was put forward to the Government of Victoria to build a privately funded and operated maglev line to service the Greater Melbourne metropolitan area in response to the Eddington Transport Report, Victoria, Eddington Transport Report that did not investigate above-ground transport options. The maglev would service a population of over 4 million and the proposal was costed at A$8 billion.
However, despite road congestion and Australia's highest roadspace per capita, the government dismissed the proposal in favour of road expansion including an A$8.5 billion road tunnel, $6 billion extension of the EastLink (Melbourne), Eastlink to the Western Ring Road and a $700 million Frankston Bypass.
Canada
Toronto Zoo: Edmonton-based Magnovate has proposed a new ride and transportation system at the Toronto Zoo reviving the Toronto Zoo Domain Ride system, which was closed following two severe accidents in 1994. The Zoo's board unanimously approved the proposal on 29 November 2018.
The company will construct and operate the $25 million system on the former route of the Domain Ride (known locally as the Monorail, despite not being considered one) at zero cost to the Zoo and operate it for 15 years, splitting the profits with the Zoo. The ride will serve a single-directional loop around Zoo grounds, serving five stations and likely replacing the current Zoomobile tour tram service. Planned to be operational by 2022 at the earliest, this will become the first commercially operating maglev system in North America should it be approved.
China
Beijing – Guangzhou line
A maglev test line linking Xianning in Hubei Province and Changsha in Hunan Province will start construction in 2020. The test line is about in length and might be part of Beijing – Guangzhou maglev in long-term planning. In 2021, the Guangdong government proposed a Maglev line between Hong Kong and Guangzhou via Shenzhen and beyond to Beijing.
Other proposed lines
;Shanghai – Hangzhou
China planned to extend the existing Shanghai Maglev Train, initially by around to Shanghai Hongqiao Airport and then to the city of Hangzhou (Shanghai-Hangzhou Maglev Train). If built, this would be the first Inter-city rail, inter-city maglev rail line in commercial service.
The project was controversial and repeatedly delayed. In May 2007 the project was suspended by officials, reportedly due to public concerns about radiation from the system. In January and February 2008 hundreds of residents demonstrated in downtown Shanghai that the line route came too close to their homes, citing concerns about electromagnetic pollution, sickness due to exposure to the strong magnetic field, noise, pollution and devaluation of property near to the lines. Final approval to build the line was granted on 18 August 2008. Originally scheduled to be ready by Expo 2010, plans called for completion by 2014. The Shanghai municipal government considered multiple options, including building the line underground to allay public fears. This same report stated that the final decision had to be approved by the National Development and Reform Commission.
In 2007 the Shanghai municipal government was considering building a factory in Nanhui district to produce low-speed maglev trains for urban use.
;Shanghai – Beijing
A proposed line would have connected Shanghai to Beijing, over a distance of , at an estimated cost of £15.5 billion.
Germany
On 25 September 2007, Bavaria announced a high-speed maglev-rail service from Munich to its Munich International Airport, airport. The Bavarian government signed contracts with Deutsche Bahn and Transrapid with Siemens and ThyssenKrupp for the €1.85 billion project.
On 27 March 2008, the Federal Ministry of Transport, Building and Urban Affairs (Germany), German Transport minister announced the project had been cancelled due to rising costs associated with constructing the track. A new estimate put the project between €3.2–3.4 billion.
Hong Kong
In March 2021 a government official said Hong Kong would be included in a planned maglev network across China, planned to operate at and begin opening by 2030.
Hong Kong is already connected to the Chinese high speed rail network by the Guangzhou–Shenzhen–Hong Kong Express Rail Link, which opened on Sunday 23 September 2018.
India
Mumbai – Delhi: A project was presented to then Indian railway minister (Mamata Banerjee) by an American company to connect Mumbai and Delhi. Then Prime Minister Manmohan Singh said that if the line project was successful the Indian government would build lines between other cities and also between Mumbai Central and Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport.
Mumbai – Nagpur: The State of Maharashtra approved a feasibility study for a maglev train between Mumbai and Nagpur, some apart.
Chennai – Bangalore – Mysore: A detailed report was to be prepared and submitted by December 2012 for a line to connect Chennai to Mysore via Bangalore at a cost $26 million per kilometre, reaching speeds of 350 km/h.
Iran
In May 2009, Iran and a German company signed an agreement to use maglev to link Tehran and Mashhad. The agreement was signed at the Mashhad International Fair site between Iranian Ministry of Roads and Transportation and the German company. The line possibly could reduce travel time between Tehran and Mashhad to about 2.5 hours. Munich-based Schlegel Consulting Engineers said they had signed the contract with the Iranian ministry of transport and the governor of Mashad. "We have been mandated to lead a German consortium in this project," a spokesman said. "We are in a preparatory phase." The project could be worth between €10 billion and €12 billion, the Schlegel spokesman said.
Italy
A first proposal was formalized in April 2008, in Brescia, by journalist Andrew Spannaus who recommended a high-speed connection between Malpensa airport to the cities of Milan, Bergamo and Brescia.
In March 2011, Nicola Oliva proposed a maglev connection between Pisa airport and the cities of Prato and Florence (Santa Maria Novella train station and Florence Airport). The travelling time would be reduced from the typical 1 hour 15 minutes to around 20 minutes. The second part of the line would be a connection to Livorno, to integrate maritime, aerial and terrestrial transport systems.
Malaysia/Singapore
A Consortium led by UEM Group Bhd and ARA Group, proposed maglev technology to link Malaysian cities to Singapore. The idea was first mooted by YTL Group. Its technology partner then was said to be Siemens. High costs sank the proposal. The concept of a high-speed rail link from Kuala Lumpur to Singapore resurfaced. It was cited as a proposed "high impact" project in the Economic Transformation Programme (ETP) that was unveiled in 2010. Approval has been given for the Kuala Lumpur–Singapore high-speed rail project, but not using maglev technology.
Philippines
Udenna Corporation, Philtram Consortium's Cebu Monorail project will be initially built as a monorail
A monorail (from "mono", meaning "one", and " rail") is a railway in which the track consists of a single rail or a beam.
Colloquially, the term "monorail" is often used to describe any form of elevated rail or people mover. More accurat ...
system. In the future, it will be upgraded to a patented maglev technology named Spin-Induced Lenz's Law Magnetic Levitation Train.
Switzerland
SwissRapide: The SwissRapide AG together with the SwissRapide Consortium was planning and developing the first maglev monorail system for intercity traffic between the country's major cities. SwissRapide was to be financed by private investors. In the long-term, the SwissRapide Express was to connect the major cities north of the Alps between Geneva and St. Gallen, including Lucerne and Basel. The first projects were Bern – Zurich, Lausanne – Geneva as well as Zurich – Winterthur. The first line (Lausanne – Geneva or Zurich – Winterthur) could go into service as early as 2020.
Swissmetro
''Swissmetro'' is a proposed Swiss transportation system based on vacuum-train (also known as vactrain) technology. It was invented by Swiss engineer Rodolphe Nieth in 1974 and it is presently being promoted and developed as SwissMetro-NG ("NG" fo ...
: An earlier project, Swissmetro AG envisioned a partially evacuated underground maglev (a vactrain). As with SwissRapide, Swissmetro envisioned connecting the major cities in Switzerland with one another. In 2011, Swissmetro AG was dissolved and the IPRs from the organisation were passed onto the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, EPFL in Lausanne.
United Kingdom
London – Glasgow: A line was proposed in the United Kingdom from London to Glasgow with several route options through the Midlands, Northwest and Northeast of England. It was reported to be under favourable consideration by the government. The approach was rejected in the Government White paper#In government, White Paper ''Delivering a Sustainable Railway'' published on 24 July 2007. Another high-speed link was planned between Glasgow and Edinburgh but the technology remained unsettled.
United States
Washington, D.C. to New York City: Using SCMaglev, Superconducting Maglev (SCMAGLEV) technology developed by the Central Japan Railway Company
is the main railway company operating in the Chūbu (Nagoya) region of central Japan. It is officially abbreviated in English as JR Central and in Japanese as JR Tōkai ( ja, JR東海, links=no). ''Tōkai'' is a reference to the geographical ...
, the Northeast Maglev would ultimately connect major Northeast metropolitan hubs and airports traveling more than , with a goal of one-hour service between Washington, D.C. and New York City. The Federal Railroad Administration and Maryland Department of Transportation are currently preparing an Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) to evaluate the potential impacts of constructing and operating the system's first leg between Washington, DC and Baltimore, Baltimore, Maryland with an intermediate stop at Baltimore/Washington International Airport, BWI Airport.
Union Pacific freight conveyor: Plans are under way by American railroad operator Union Pacific to build a container shuttle between the Ports of Port of Los Angeles, Los Angeles and Port of Long Beach, Long Beach, with UP's intermodal container transfer facility. The system would be based on "passive" technology, especially well-suited to freight transfer as no power is needed on board. The vehicle is a chassis that glides to its destination. The system is being designed by General Atomics.
Incidents
Two incidents involved fires. A Japanese test train in Miyazaki, MLU002, was completely consumed by a fire in 1991.
On 11 August 2006, a fire broke out on the commercial Shanghai Transrapid shortly after arriving at the Longyang terminal. People were evacuated without incident before the vehicle was moved about 1 kilometre to keep smoke from filling the station. NAMTI officials toured the SMT maintenance facility in November 2010 and learned that the cause of the fire was "thermal runaway" in a battery tray. As a result, SMT secured a new battery vendor, installed new temperature sensors and insulators and redesigned the trays.
On 22 September 2006, a Lathen train collision, Transrapid train collided with a maintenance vehicle on a test/publicity run in Lathen (Lower Saxony / north-western Germany). Twenty-three people were killed and ten were injured; these were the first maglev crash fatalities. The accident was caused by human error. Charges were brought against three Transrapid employees after a year-long investigation.
See also
* Bombardier Advanced Rapid Transit – Transit systems using Linear induction motors
* Electromagnetic suspension
* Ground effect train
* Hyperloop
* Land speed record for rail vehicles
* Launch loop would be a maglev system for launching to orbit or escape velocity
* Mass driver
* Nagahori Tsurumi-ryokuchi Line
*Oleg Tozoni worked on a published non-linearly stabilised maglev design
* StarTram – a maglev launch system
* Transfer table
Notes
References
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
*
*
United States Federal Railroad AdministrationUS MagneticGlideThe International Maglev Board
Maglev professionals' info platform for all maglev transport systems and related technologies.
Maglev Net – Maglev News and Information
*
{{Authority control
Maglev,
Electrodynamics
Emerging technologies
Experimental and prototype high-speed trains
Magnetic propulsion devices
 Maglev (derived from '' magnetic levitation''), is a system of
Maglev (derived from '' magnetic levitation''), is a system of  In 1979 the
In 1979 the  The world's first commercial maglev system was a low-speed maglev shuttle that ran between the airport terminal of Birmingham International Airport and the nearby Birmingham International railway station between 1984 and 1995. Its track length was , and trains levitated at an altitude of , levitated by electromagnets, and propelled with linear induction motors. It operated for 11 years and was initially very popular with passengers, but obsolescence problems with the electronic systems made it progressively unreliable as years passed, leading to its closure in 1995. One of the original cars is now on display at
The world's first commercial maglev system was a low-speed maglev shuttle that ran between the airport terminal of Birmingham International Airport and the nearby Birmingham International railway station between 1984 and 1995. Its track length was , and trains levitated at an altitude of , levitated by electromagnets, and propelled with linear induction motors. It operated for 11 years and was initially very popular with passengers, but obsolescence problems with the electronic systems made it progressively unreliable as years passed, leading to its closure in 1995. One of the original cars is now on display at  Transrapid, a German maglev company, had a test track in
Transrapid, a German maglev company, had a test track in  In Vancouver, Canada, the HSST-03 by HSST Development Corporation ( Japan Airlines and
In Vancouver, Canada, the HSST-03 by HSST Development Corporation ( Japan Airlines and  In 1993, South Korea completed the development of its own maglev train, shown off at the
In 1993, South Korea completed the development of its own maglev train, shown off at the  There are currently two competing efforts into high-speed maglev systems, i.e., .
* The first is based on the Transrapid technology used in the Shanghai maglev train and is developed by the CRRC under license from Thyssen-Krupp.
** In 2006 the CM1 Dolphin prototype was unveiled and began testing on a new test track at Tongji University, northwest of Shanghai.
** A prototype vehicle of the CRRC 600 was developed in 2019 and tested from June 2020.
** In March 2021 a model began trials.
** In July 2021, the CRRC 600 maglev, capable of travelling up to , was unveiled in Qingdao. It was reported to be the world's fastest ground vehicle.
** A high speed test track is under development in China and also, in April 2021, there was consideration given to re-opening the Emsland test facility in Germany.
* A second, incompatible high-speed prototype was unveiled in January 2021. Developed at
There are currently two competing efforts into high-speed maglev systems, i.e., .
* The first is based on the Transrapid technology used in the Shanghai maglev train and is developed by the CRRC under license from Thyssen-Krupp.
** In 2006 the CM1 Dolphin prototype was unveiled and began testing on a new test track at Tongji University, northwest of Shanghai.
** A prototype vehicle of the CRRC 600 was developed in 2019 and tested from June 2020.
** In March 2021 a model began trials.
** In July 2021, the CRRC 600 maglev, capable of travelling up to , was unveiled in Qingdao. It was reported to be the world's fastest ground vehicle.
** A high speed test track is under development in China and also, in April 2021, there was consideration given to re-opening the Emsland test facility in Germany.
* A second, incompatible high-speed prototype was unveiled in January 2021. Developed at  In electrodynamic suspension (EDS), both the guideway and the train exert a magnetic field, and the train is levitated by the repulsive and attractive force between these magnetic fields. In some configurations, the train can be levitated only by repulsive force. In the early stages of maglev development at the Miyazaki test track, a purely repulsive system was used instead of the later repulsive and attractive EDS system. The magnetic field is produced either by superconducting magnets (as in JR–Maglev) or by an array of permanent magnets (as in Inductrack). The repulsive and attractive force in the track is created by an induced magnetic field in wires or other conducting strips in the track.
A major advantage of EDS maglev systems is that they are dynamically stable—changes in distance between the track and the magnets creates strong forces to return the system to its original position. In addition, the attractive force varies in the opposite manner, providing the same adjustment effects. No active feedback control is needed.
However, at slow speeds, the current induced in these coils and the resultant magnetic flux is not large enough to levitate the train. For this reason, the train must have wheels or some other form of landing gear to support the train until it reaches take-off speed. Since a train may stop at any location, due to equipment problems for instance, the entire track must be able to support both low- and high-speed operation.
Another downside is that the EDS system naturally creates a field in the track in front and to the rear of the lift magnets, which acts against the magnets and creates magnetic drag. This is generally only a concern at low speeds, and is one of the reasons why JR abandoned a purely repulsive system and adopted the sidewall levitation system. At higher speeds other modes of drag dominate.
The drag force can be used to the electrodynamic system's advantage, however, as it creates a varying force in the rails that can be used as a reactionary system to drive the train, without the need for a separate reaction plate, as in most linear motor systems. Laithwaite led development of such "traverse-flux" systems at his Imperial College laboratory. Alternatively, propulsion coils on the guideway are used to exert a force on the magnets in the train and make the train move forward. The propulsion coils that exert a force on the train are effectively a linear motor: an alternating current through the coils generates a continuously varying magnetic field that moves forward along the track. The frequency of the alternating current is synchronized to match the speed of the train. The offset between the field exerted by magnets on the train and the applied field creates a force moving the train forward.
In electrodynamic suspension (EDS), both the guideway and the train exert a magnetic field, and the train is levitated by the repulsive and attractive force between these magnetic fields. In some configurations, the train can be levitated only by repulsive force. In the early stages of maglev development at the Miyazaki test track, a purely repulsive system was used instead of the later repulsive and attractive EDS system. The magnetic field is produced either by superconducting magnets (as in JR–Maglev) or by an array of permanent magnets (as in Inductrack). The repulsive and attractive force in the track is created by an induced magnetic field in wires or other conducting strips in the track.
A major advantage of EDS maglev systems is that they are dynamically stable—changes in distance between the track and the magnets creates strong forces to return the system to its original position. In addition, the attractive force varies in the opposite manner, providing the same adjustment effects. No active feedback control is needed.
However, at slow speeds, the current induced in these coils and the resultant magnetic flux is not large enough to levitate the train. For this reason, the train must have wheels or some other form of landing gear to support the train until it reaches take-off speed. Since a train may stop at any location, due to equipment problems for instance, the entire track must be able to support both low- and high-speed operation.
Another downside is that the EDS system naturally creates a field in the track in front and to the rear of the lift magnets, which acts against the magnets and creates magnetic drag. This is generally only a concern at low speeds, and is one of the reasons why JR abandoned a purely repulsive system and adopted the sidewall levitation system. At higher speeds other modes of drag dominate.
The drag force can be used to the electrodynamic system's advantage, however, as it creates a varying force in the rails that can be used as a reactionary system to drive the train, without the need for a separate reaction plate, as in most linear motor systems. Laithwaite led development of such "traverse-flux" systems at his Imperial College laboratory. Alternatively, propulsion coils on the guideway are used to exert a force on the magnets in the train and make the train move forward. The propulsion coils that exert a force on the train are effectively a linear motor: an alternating current through the coils generates a continuously varying magnetic field that moves forward along the track. The frequency of the alternating current is synchronized to match the speed of the train. The offset between the field exerted by magnets on the train and the applied field creates a force moving the train forward.
 The commercial automation, automated "Urban Maglev" system commenced operation in March 2005 in Aichi, Japan. The Tobu Kyuryo Line, otherwise known as the
The commercial automation, automated "Urban Maglev" system commenced operation in March 2005 in Aichi, Japan. The Tobu Kyuryo Line, otherwise known as the  The Hunan provincial government launched the construction of a maglev line between Changsha Huanghua International Airport and Changsha South Railway Station, covering a distance of 18.55 km. Construction started in May 2014 and was completed by the end of 2015. Trial runs began on 26 December 2015 and trial operations started on 6 May 2016. As of 13 June 2018 the Changsha maglev had covered a distance of 1.7 million km and carried nearly 6 million passengers. A second generation of these vehicles has been produced which have a top speed of . In July 2021 the new model entered service operating at a top speed of , which reduced the travel time by 3 minutes.
The Hunan provincial government launched the construction of a maglev line between Changsha Huanghua International Airport and Changsha South Railway Station, covering a distance of 18.55 km. Construction started in May 2014 and was completed by the end of 2015. Trial runs began on 26 December 2015 and trial operations started on 6 May 2016. As of 13 June 2018 the Changsha maglev had covered a distance of 1.7 million km and carried nearly 6 million passengers. A second generation of these vehicles has been produced which have a top speed of . In July 2021 the new model entered service operating at a top speed of , which reduced the travel time by 3 minutes.
 The Chuo Shinkansen is a high-speed maglev line in Japan. Construction began in 2014, commercial operations was expected to start by 2027. The 2027 target was given up in July 2020. The Linear Chuo Shinkansen Project aims to connect Tokyo and Osaka by way of Nagoya, the capital city of Aichi Prefecture, Aichi, in approximately one hour, less than half the travel time of the fastest existing bullet trains connecting the three metropolises. The full track between Tokyo and Osaka was originally expected to be completed in 2045, but the operator is now aiming for 2037.
The L0 Series train type is undergoing testing by the
The Chuo Shinkansen is a high-speed maglev line in Japan. Construction began in 2014, commercial operations was expected to start by 2027. The 2027 target was given up in July 2020. The Linear Chuo Shinkansen Project aims to connect Tokyo and Osaka by way of Nagoya, the capital city of Aichi Prefecture, Aichi, in approximately one hour, less than half the travel time of the fastest existing bullet trains connecting the three metropolises. The full track between Tokyo and Osaka was originally expected to be completed in 2045, but the operator is now aiming for 2037.
The L0 Series train type is undergoing testing by the  In late 2008, a proposal was put forward to the Government of Victoria to build a privately funded and operated maglev line to service the Greater Melbourne metropolitan area in response to the Eddington Transport Report, Victoria, Eddington Transport Report that did not investigate above-ground transport options. The maglev would service a population of over 4 million and the proposal was costed at A$8 billion.
However, despite road congestion and Australia's highest roadspace per capita, the government dismissed the proposal in favour of road expansion including an A$8.5 billion road tunnel, $6 billion extension of the EastLink (Melbourne), Eastlink to the Western Ring Road and a $700 million Frankston Bypass.
In late 2008, a proposal was put forward to the Government of Victoria to build a privately funded and operated maglev line to service the Greater Melbourne metropolitan area in response to the Eddington Transport Report, Victoria, Eddington Transport Report that did not investigate above-ground transport options. The maglev would service a population of over 4 million and the proposal was costed at A$8 billion.
However, despite road congestion and Australia's highest roadspace per capita, the government dismissed the proposal in favour of road expansion including an A$8.5 billion road tunnel, $6 billion extension of the EastLink (Melbourne), Eastlink to the Western Ring Road and a $700 million Frankston Bypass.