list of oldest universities in continuous operation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 This is a list of the oldest existing universities in continuous operation in the world.
Inclusion in this list is determined by the date at which the educational institute first met the traditional definition of a
This is a list of the oldest existing universities in continuous operation in the world.
Inclusion in this list is determined by the date at which the educational institute first met the traditional definition of a
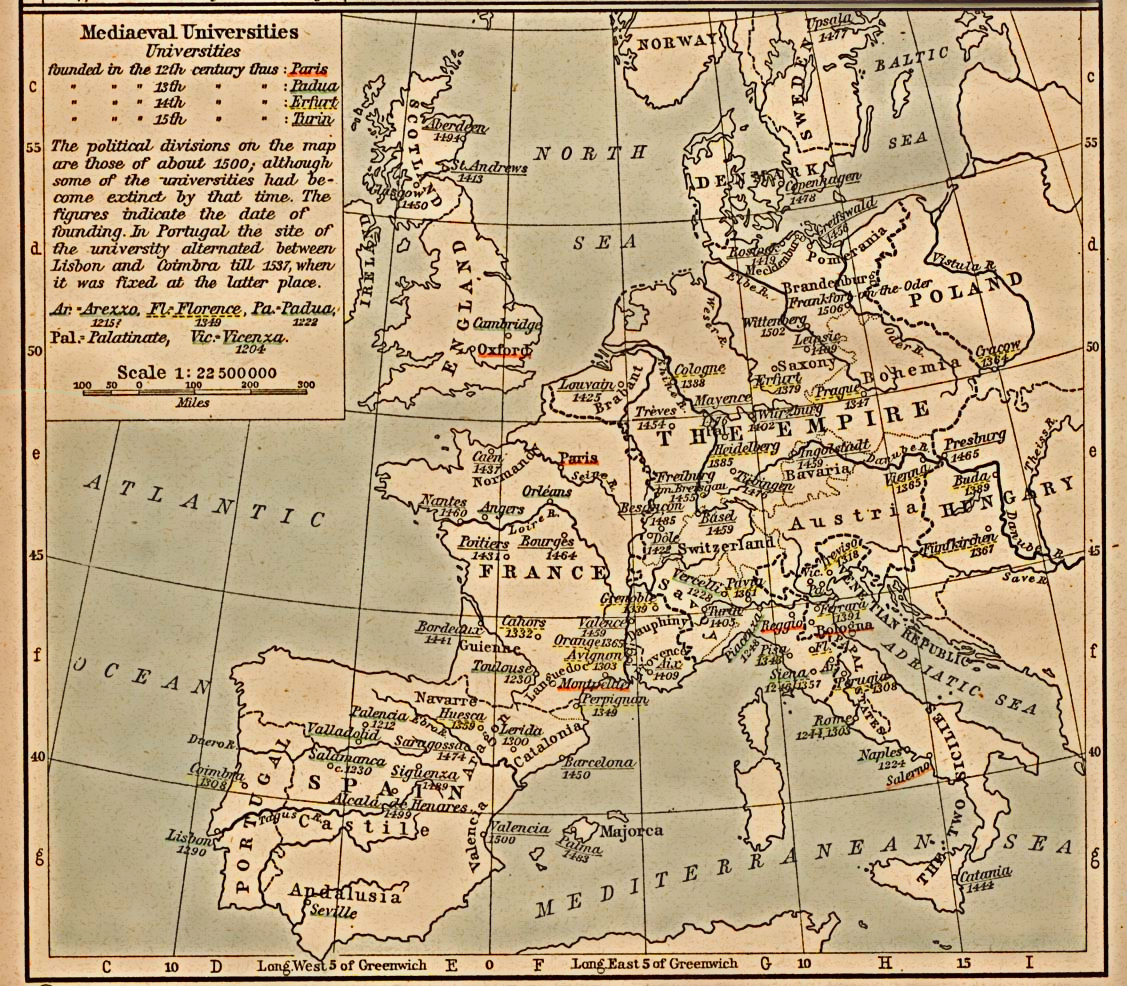 This list includes medieval universities that were founded before 1500 and which have retained institutional continuity since then (excluding not only those that ceased to exist, but also those that merged into or split away to an institution which is regarded as newly established). Several of these have been closed for brief periods: for example the University of Siena was closed 18051815 during
This list includes medieval universities that were founded before 1500 and which have retained institutional continuity since then (excluding not only those that ceased to exist, but also those that merged into or split away to an institution which is regarded as newly established). Several of these have been closed for brief periods: for example the University of Siena was closed 18051815 during


 This is a list of the oldest existing universities in continuous operation in the world.
Inclusion in this list is determined by the date at which the educational institute first met the traditional definition of a
This is a list of the oldest existing universities in continuous operation in the world.
Inclusion in this list is determined by the date at which the educational institute first met the traditional definition of a university
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
used by academic historians although it may have existed as a different kind of institution before that time. This definition limits the term "university" to institutions with distinctive structural and legal features that developed in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, and which make the university form different from other institutions of higher learning in the pre-modern world, even though these may sometimes now be referred to popularly as universities.
To be included in the list, the university must have been founded prior to 1500 in Europe or be the oldest university derived from the medieval European model in a country or region. It must also still be in operation, with institutional continuity retained throughout its history. So some early universities, including the University of Paris
The University of Paris (), known Metonymy, metonymically as the Sorbonne (), was the leading university in Paris, France, from 1150 to 1970, except for 1793–1806 during the French Revolution. Emerging around 1150 as a corporation associated wit ...
, founded around the beginning of the 13th century but abolished by the French Revolution in 1793, are excluded. Some institutions reemerge, but with new foundations, such as the modern University of Paris, which came into existence in 1896 after the ''Louis Liard law'' disbanded Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
's University of France system.
The word "university" is derived from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
, which approximately means "community of teachers and scholars." The University of Bologna
The University of Bologna (, abbreviated Unibo) is a Public university, public research university in Bologna, Italy. Teaching began around 1088, with the university becoming organised as guilds of students () by the late 12th century. It is the ...
in Bologna
Bologna ( , , ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Emilia-Romagna region in northern Italy. It is the List of cities in Italy, seventh most populous city in Italy, with about 400,000 inhabitants and 150 different nationalities. Its M ...
, Italy, where teaching began around 1088 and which was organised into a university in the late 12th century, is the world's oldest university in continuous operation, and the first university in the sense of a higher-learning and degree-awarding institute.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f. The origin of many medieval universities can be traced back to the Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
cathedral school
Cathedral schools began in the Early Middle Ages as centers of advanced education, some of them ultimately evolving into medieval universities. Throughout the Middle Ages and beyond, they were complemented by the monastic schools. Some of these ...
s or monastic school
Monastic schools () were, along with cathedral schools, the most important institutions of higher learning in the Latin West#Use with regard to Christianity, Latin West from the early Middle Ages until the 12th century. Since Cassiodorus's educatio ...
s, which appeared as early as the 6th century and were run for hundreds of years prior to their formal establishment as universities in the high medieval period.
Ancient higher-learning institutions
A variety of ancient higher-learning institutions were developed in many cultures to provide institutional frameworks for scholarly activities. These ancient centres were sponsored and overseen by courts; by religious institutions, which sponso ...
, such as those of ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically r ...
, Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
, ancient Persia
The history of Iran (also known as Persia) is intertwined with Greater Iran, which is a socio-cultural region encompassing all of the areas that have witnessed significant settlement or influence exerted by the Iranian peoples and the Iranian ...
, ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Em ...
, Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion () was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' continued to be used as a n ...
, ancient China
The history of China spans several millennia across a wide geographical area. Each region now considered part of the Chinese world has experienced periods of unity, fracture, prosperity, and strife. Chinese civilization first emerged in the Y ...
, ancient India
Anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. The earliest known human remains in South Asia date to 30,000 years ago. Sedentism, Sedentariness began in South Asia around 7000 BCE; ...
and the Islamic world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
, are not included in this list owing to their cultural, historical, structural and legal differences from the medieval European university from which the modern university evolved.Rüegg, Walter: "Foreword. The University as a European Institution", in: ''A History of the University in Europe. Vol. 1: Universities in the Middle Ages'', Cambridge University Press, 1992, , pp. XIX–XX. These include the University of al-Qarawiyyin
The University of al-Qarawiyyin (), also written Al-Karaouine or Al Quaraouiyine, is a university located in Fez, Morocco. It was founded as a mosque by Fatima al-Fihri in 857–859 and subsequently became one of the leading spiritual and educ ...
, University of Ez-Zitouna
Ez-Zitouna University (, ) is an Ancient higher-learning institutions, ancient public university in Tunis, Tunisia. The university originated in the Al-Zaytuna Mosque, founded at the end of the 7th or in the early 8th century, which developed into ...
and Al-Azhar University
The Al-Azhar University ( ; , , ) is a public university in Cairo, Egypt. Associated with Al-Azhar Al-Sharif in Islamic Cairo, it is Egypt's oldest degree-granting university and is known as one of the most prestigious universities for Islamic ...
, which were founded as mosque
A mosque ( ), also called a masjid ( ), is a place of worship for Muslims. The term usually refers to a covered building, but can be any place where Salah, Islamic prayers are performed; such as an outdoor courtyard.
Originally, mosques were si ...
s in 859, 698 or 734, and 972 respectively. These developed associated madrasa
Madrasa (, also , ; Arabic: مدرسة , ), sometimes Romanization of Arabic, romanized as madrasah or madrassa, is the Arabic word for any Educational institution, type of educational institution, secular or religious (of any religion), whet ...
s; the dates when organised teaching began are uncertain, but by 1129 for al-Qarawiyyin in the 13th century for Ez-Zitouna, and Al-Azhar. They became universities in 1963, 1956 and 1961 respectively.
Medieval origins
The university as aninstitution
An institution is a humanly devised structure of rules and norms that shape and constrain social behavior. All definitions of institutions generally entail that there is a level of persistence and continuity. Laws, rules, social conventions and ...
was historically rooted in medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
society, which it in turn influenced and shaped. Academic historian Walter Rüegg asserts that:
Modern spread
From theearly modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
onwards, the university spread from the medieval Latin West across the globe, eventually replacing all other higher-learning institutions and becoming the preeminent institution for higher education everywhere. The process occurred in the following chronological order:
* Southern and Western Europe (from the 11th or 12th century)
* Central and Northern Europe (from the 14th or 15th century)
* Americas (from the 16th century)
* Australia (from the 19th century)
* Asia and Africa (from the 19th or 20th century), with the exception of the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, where the University of Santo Tomas
The University of Santo Tomas (UST; ), officially the Pontifical and Royal University of Santo Tomas, The Catholic University of the Philippines or colloquially as ''Ustê'' (), is a Private university, private Catholic school, Catholic researc ...
was established in the 17th century.
Founded as universities before 1500
 This list includes medieval universities that were founded before 1500 and which have retained institutional continuity since then (excluding not only those that ceased to exist, but also those that merged into or split away to an institution which is regarded as newly established). Several of these have been closed for brief periods: for example the University of Siena was closed 18051815 during
This list includes medieval universities that were founded before 1500 and which have retained institutional continuity since then (excluding not only those that ceased to exist, but also those that merged into or split away to an institution which is regarded as newly established). Several of these have been closed for brief periods: for example the University of Siena was closed 18051815 during the Napoleonic wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
, and universities in the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the south ...
and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
were closed during Nazi occupation, 1938–1945.
Universities are dated from when, according to scholars, they first met the definition of a university. In cases such as the universities of Bologna
Bologna ( , , ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Emilia-Romagna region in northern Italy. It is the List of cities in Italy, seventh most populous city in Italy, with about 400,000 inhabitants and 150 different nationalities. Its M ...
and Oxford
Oxford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and non-metropolitan district in Oxfordshire, England, of which it is the county town.
The city is home to the University of Oxford, the List of oldest universities in continuou ...
which trace their history back to teaching in individual schools prior to their formation into a university, or which existed in another form prior to being a university, the date in the list below is thus later than the date given by the institutions for their foundation.
Oldest universities by country or region after 1500 still in operation
The majority of European countries had universities by 1500. Many universities were established at institutes of learning such as schools and colleges that may have been founded significantly earlier but were not classed as universities upon their foundation; this is normally described in the notes for that institution. In some countries (particularly the US and those influenced by its culture), degree-granting higher education institutions that would normally be called universities are instead called colleges. In this case, both the oldest institution that would normally be regarded as a university and the oldest institution (if different) to actually be called a university are given. In many parts of the world, the first university to have a presence was an institution based elsewhere (often theUniversity of London
The University of London (UoL; abbreviated as Lond or more rarely Londin in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a collegiate university, federal Public university, public research university located in London, England, United Kingdom. The ...
via the affiliation of a local college); where this is different from the first locally established university, both are given.
Africa
Asia
Europe
While Europe had 143 universities in 1789, theFrench Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
The French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars (sometimes called the Great French War or the Wars of the Revolution and the Empire) were a series of conflicts between the French and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompas ...
took a heavy toll, reducing the number to 83 by 1815. The universities of France were abolished and over half of the universities in both Germany and Spain were destroyed. By the mid 19th century, Europe had recovered to 98 universities.
Latin America and the Caribbean
North America
In the United States, the colonial colleges awarded degrees from their foundation, but none were formally named as universities prior to theAmerican Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
, leading to various claims to be the first university in the United States. The earliest Canadian institutions were founded as colleges, without degree awarding powers, and gained degree granting authority and university status later.
Oceania
See also
* *List of medieval universities
The list of Medieval university, medieval universities comprises University, universities (more precisely, ''studium generale, studia generalia'') which existed in Europe during the Middle Ages.Rüegg 1992, pp. XIX–XX It also includes ...
* List of oldest institutions in continuous operation
Notes
References
{{Lists of European universities and colleges by era Oldest universities in continuous operation Oldest in continuous operation